合成生物学 ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (5): 1145-1166.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-082
农业合成生物学驱动动物营养创新:进展与展望
李一塍, 罗会颖, 姚斌, 涂涛
- 中国农业科学院北京畜牧兽医研究所,畜禽营养与饲养全国重点实验室,北京 100193
-
收稿日期:2025-08-01修回日期:2025-08-29出版日期:2025-10-31发布日期:2025-11-05 -
通讯作者:涂涛 -
作者简介:李一塍 (1999—), 男,博士研究生。研究方向为动物营养与饲料。E-mail:li_yi_c@163.com涂涛 (1988—),男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为饲料用酶工程,在饲用酶解决养殖业供需平衡、缓解养殖环境污染、保障动物产品安全等方面取得了一系列原创性成果。E-mail:tutao@caas.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(L2324219)
Agricultural synthetic biology driving innovation in animal nutrition: advances and prospects
LI Yicheng, LUO Huiying, YAO Bin, TU Tao
- State Key Laboratory of Animal Nutrition and Feeding,Institute of Animal Sciences,Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Beijing 100193,China
-
Received:2025-08-01Revised:2025-08-29Online:2025-10-31Published:2025-11-05 -
Contact:TU Tao
摘要:
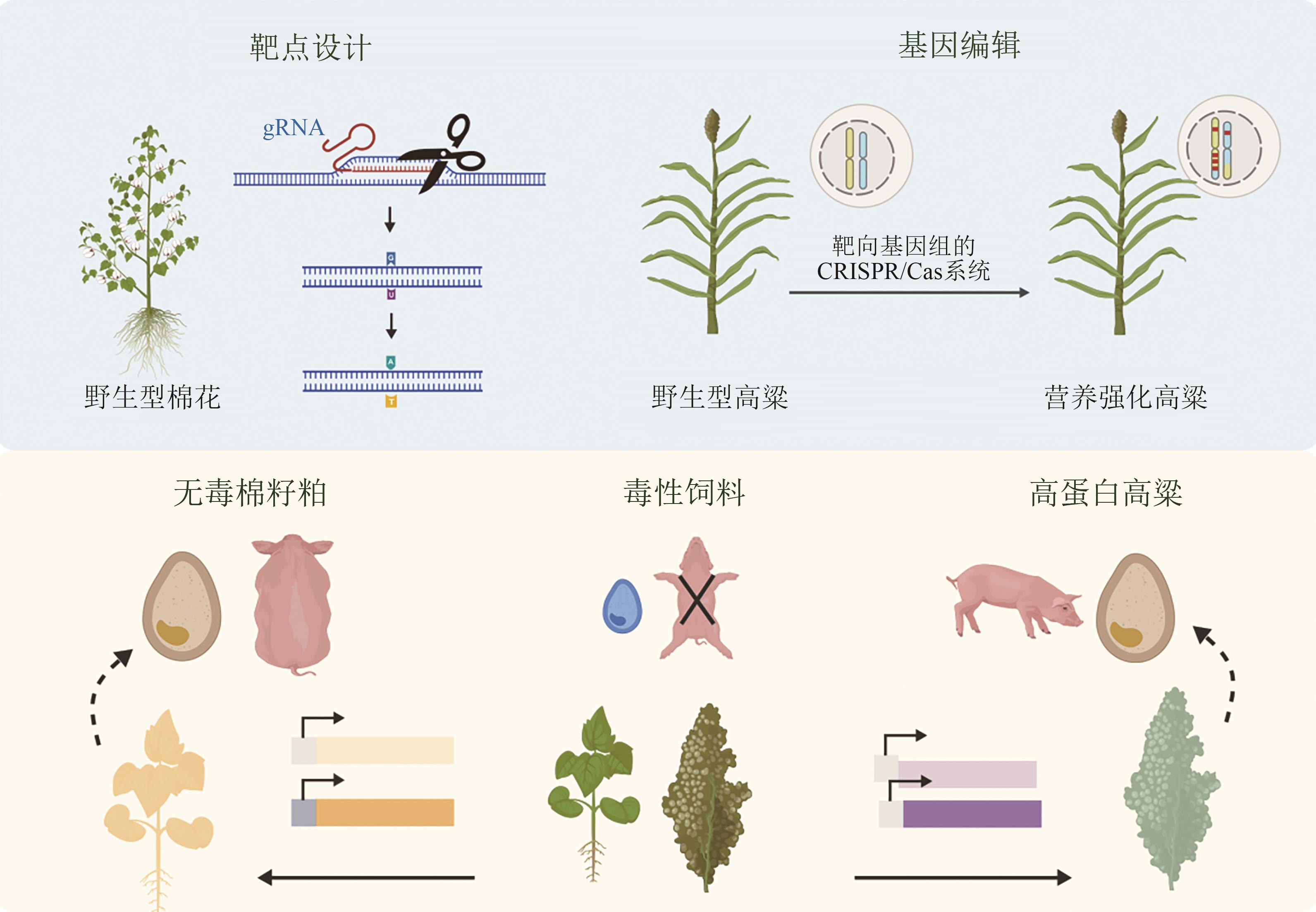
动物营养是保障畜牧业可持续发展的关键环节,动物营养过程的效率直接关系到资源利用效率、环境承载能力与粮食安全。随着农业合成生物技术的快速发展,研究者正积极应用工程化策略革新动物营养利用体系,主要涵盖饲料原料开发、饲料添加剂合成及胃肠道高效营养转化等方向。本文系统综述了该领域的最新进展,重点聚焦于基因编辑作物、微生物蛋白、饲料添加剂、胃肠道工程微生物等方向的关键使能技术与工程化策略,阐释了农业合成生物学在提升饲料利用效率、保障动物健康及促进畜牧业绿色转型中的巨大潜力。探讨了当前农业合成生物学在动物营养领域所面临的挑战与未来发展趋势,包括多基因系统设计与AI设计驱动生物育种进入4.0时代,动态调控系统开发与机器学习强化细胞工厂全局调控,多维度设计与学科交叉用于解析与调控动物消化系统。强调了其理念与技术对于突破现有技术瓶颈的关键作用。未来,农业合成生物学将通过深度融合多组学、机器学习与自动化平台技术,突破基因编辑与菌群调控难题,驱动动物营养创新发展。
中图分类号:
引用本文
李一塍, 罗会颖, 姚斌, 涂涛. 农业合成生物学驱动动物营养创新:进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(5): 1145-1166.
LI Yicheng, LUO Huiying, YAO Bin, TU Tao. Agricultural synthetic biology driving innovation in animal nutrition: advances and prospects[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 1145-1166.
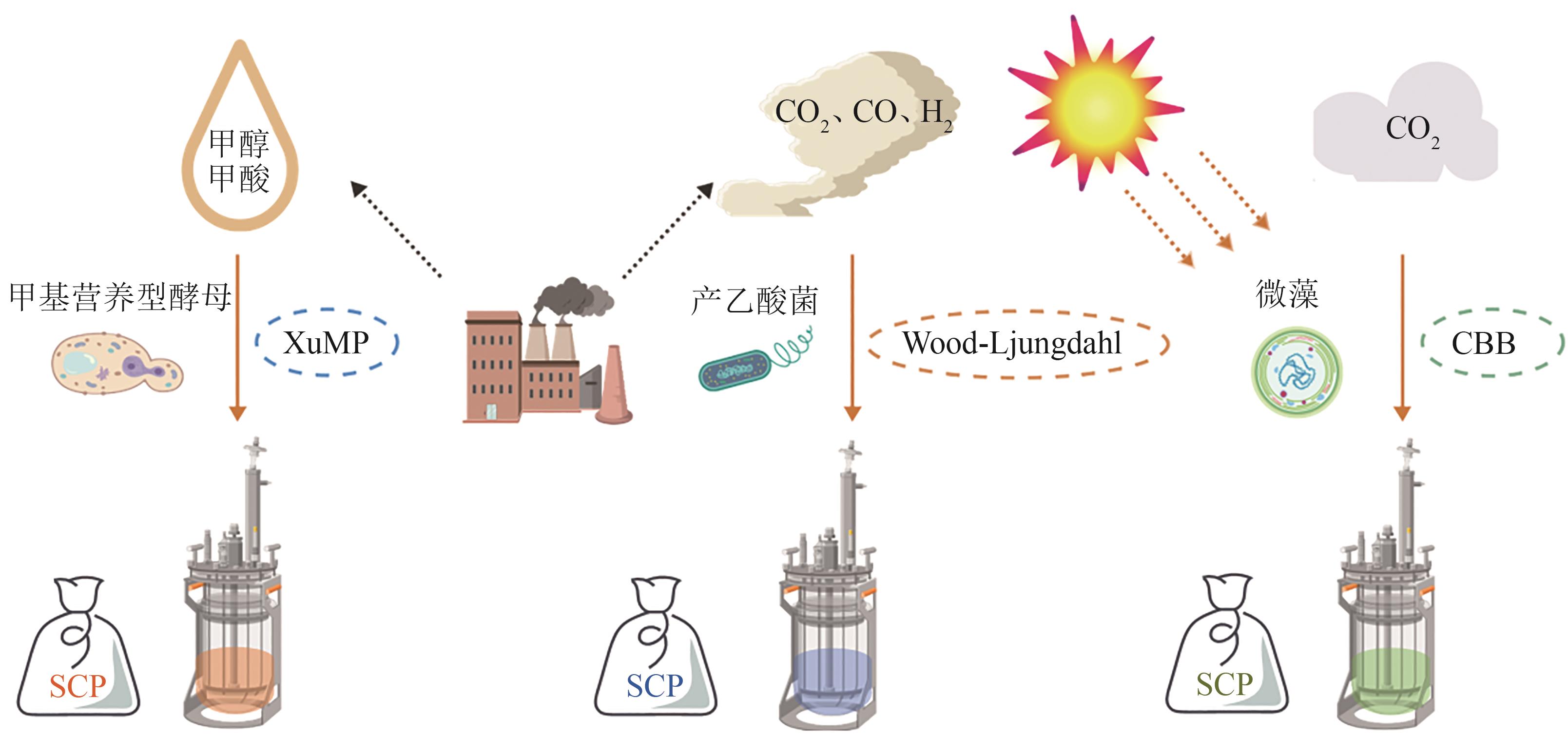
| 微生物类型 | 菌种 | 底物 | 代谢途径 | 改造方法 | 产量/产率 | 产物 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甲基营养型酵母 | P. pastoris | 甲醇 | 氮代谢和细胞壁代谢 | 适应性实验室进化,过表达GDH1或GLN1 | 0.506 g/g DCW | 单细胞蛋白 | [ |
| 非天然甲基酵母 | Y. lipolytica | 甲醇 | RuMP和XuMP途径 | 引入RuMP和XuMP途径基因,敲除内源甲醛脱氢酶 | 1.1 g/L 72 h | 单细胞蛋白 | [ |
| 产乙酸菌 | A. woodii | 甲基、CO | 氢气利用途径 | 双敲除氢化酶hydBA/hdcr | — | 乳酸、单细胞蛋白 | [ |
| 天然甲酸利用菌 | P. communis | CO2 | — | 偶联电催化CO2还原模块与副球菌同化利用甲酸过程 | 2.6 g/L | 单细胞蛋白 | [ |
| 产乙酸菌 | Acetobacterium | CO2 | Wood-Ljungdahl途径 | 集成产乙酸菌利用CO2和产碱菌利用乙酸过程 | 1.5 g/(L·d) | 单细胞蛋白 | [ |
| 酵母 | S. cerevisiae | 玉米 秸秆 | — | 表面展示CBP和PGP | 3.23 g/L | 单细胞蛋白 | [ |
| R. toruloides | 玉米 秸秆 | — | 全过程设计预处理 | 蛋白208 g/kg 靛蓝素72 g/kg | 单细胞蛋白、靛蓝素 | [ | |
| C. utilisACCC 20060 | 棉花 秸秆 | — | 木糖利用微生物筛选 | 5.74 g/L | 单细胞蛋白 | [ |
表1 部分可合成单细胞蛋白的微生物
Table 1 Microorganisms capable to synthesize single-cell proteins
| 微生物类型 | 菌种 | 底物 | 代谢途径 | 改造方法 | 产量/产率 | 产物 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甲基营养型酵母 | P. pastoris | 甲醇 | 氮代谢和细胞壁代谢 | 适应性实验室进化,过表达GDH1或GLN1 | 0.506 g/g DCW | 单细胞蛋白 | [ |
| 非天然甲基酵母 | Y. lipolytica | 甲醇 | RuMP和XuMP途径 | 引入RuMP和XuMP途径基因,敲除内源甲醛脱氢酶 | 1.1 g/L 72 h | 单细胞蛋白 | [ |
| 产乙酸菌 | A. woodii | 甲基、CO | 氢气利用途径 | 双敲除氢化酶hydBA/hdcr | — | 乳酸、单细胞蛋白 | [ |
| 天然甲酸利用菌 | P. communis | CO2 | — | 偶联电催化CO2还原模块与副球菌同化利用甲酸过程 | 2.6 g/L | 单细胞蛋白 | [ |
| 产乙酸菌 | Acetobacterium | CO2 | Wood-Ljungdahl途径 | 集成产乙酸菌利用CO2和产碱菌利用乙酸过程 | 1.5 g/(L·d) | 单细胞蛋白 | [ |
| 酵母 | S. cerevisiae | 玉米 秸秆 | — | 表面展示CBP和PGP | 3.23 g/L | 单细胞蛋白 | [ |
| R. toruloides | 玉米 秸秆 | — | 全过程设计预处理 | 蛋白208 g/kg 靛蓝素72 g/kg | 单细胞蛋白、靛蓝素 | [ | |
| C. utilisACCC 20060 | 棉花 秸秆 | — | 木糖利用微生物筛选 | 5.74 g/L | 单细胞蛋白 | [ |
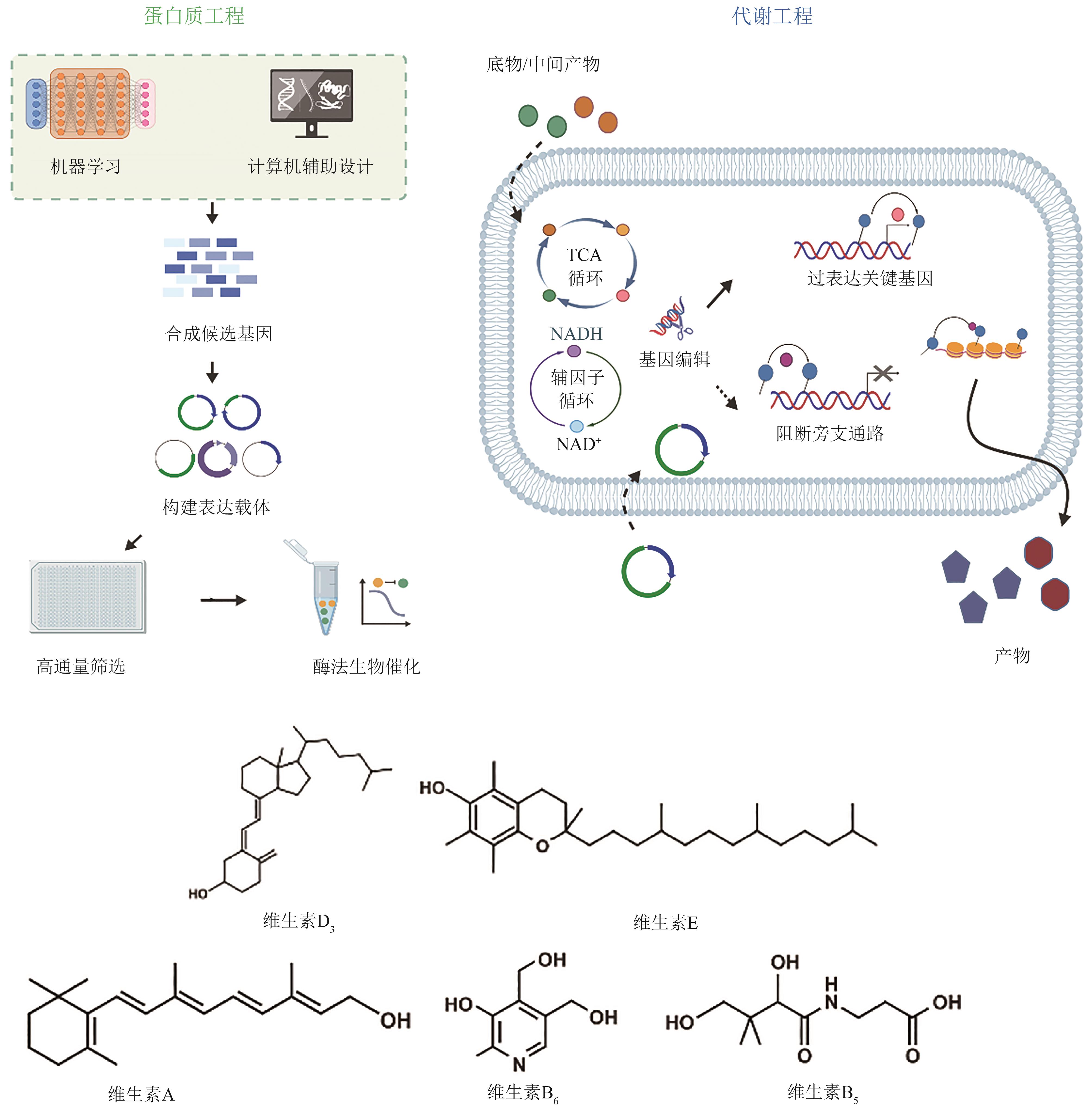
| 维生素 | 种类 | 改造方法 | 产量 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25(OH)VD3 | P450酶 | 嵌合型P450酶,全细胞催化 | 1.96 g/L | [ |
| VA | S. cerevisiae | 组合表达两种β-胡萝卜素裂解酶,引入视黄醇脱氢酶RDH12 | 5.21 g/L | [ |
| α-Tocotrienol | S. cerevisiae | 截短N端转运肽,解除限速步骤、增强前体供应,设计了冷休克触发温度控制系统 | 320 mg/L | [ |
| VB6 | E. coli | 解耦生长途径与生产途径,上游模块强化前体供应,下游模块改造限速酶 | 1409 mg/L | [ |
| VB5 | E. coli | 设计温度敏感开关动态调控细胞,精准分配碳通量,对关键酶进行理性改造 | 97.2 g/L | [ |
表2 代表性维生素及其衍生物的生物合成
Table 2 Biosynthesis of representative vitamins and their derivatives
| 维生素 | 种类 | 改造方法 | 产量 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25(OH)VD3 | P450酶 | 嵌合型P450酶,全细胞催化 | 1.96 g/L | [ |
| VA | S. cerevisiae | 组合表达两种β-胡萝卜素裂解酶,引入视黄醇脱氢酶RDH12 | 5.21 g/L | [ |
| α-Tocotrienol | S. cerevisiae | 截短N端转运肽,解除限速步骤、增强前体供应,设计了冷休克触发温度控制系统 | 320 mg/L | [ |
| VB6 | E. coli | 解耦生长途径与生产途径,上游模块强化前体供应,下游模块改造限速酶 | 1409 mg/L | [ |
| VB5 | E. coli | 设计温度敏感开关动态调控细胞,精准分配碳通量,对关键酶进行理性改造 | 97.2 g/L | [ |
| 氨基酸 | 菌株 | 改造策略 | 产量 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-赖氨酸 | C. glutamicum | 代谢工程重定向碳通量,并利用动态启动子库调控NADPH供应 | 223.4 g/L | [ |
| C. glutamicum | 关键酶改造、增加草酰乙酸和NADPH的供应及异源表达果糖激酶基因gmuE,提高生长速率 | 196.58 g/L | [ | |
| L-蛋氨酸 | E. coli | 增强琥珀酰辅酶A供应,引入直接硫磺酸化途径和削弱L-苏氨酸支链途径 | 20.39 g/L | [ |
| L-色氨酸 | E. coli | 优化了抗反馈酶AroG、TrpE和SerA的组合;敲入yddG和prsL135I,敲除poxB基因 | 43.0 g/L | [ |
| L-缬氨酸 | C. necator | 强化缬氨酸输出蛋白,敲除PHB合成途径,并筛选高效内源AHAS酶 | 972 mg/L | [ |
| L-异亮氨酸 | E. coli | 使用柠檬酸途径替代苏氨酸途径,同时强化DcuD转运蛋白并重构非氧化糖酵解途径 | 56.6 g/L | [ |
表3 代表性氨基酸的生物合成
Table 3 Biosynthesis of representative amino acids
| 氨基酸 | 菌株 | 改造策略 | 产量 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-赖氨酸 | C. glutamicum | 代谢工程重定向碳通量,并利用动态启动子库调控NADPH供应 | 223.4 g/L | [ |
| C. glutamicum | 关键酶改造、增加草酰乙酸和NADPH的供应及异源表达果糖激酶基因gmuE,提高生长速率 | 196.58 g/L | [ | |
| L-蛋氨酸 | E. coli | 增强琥珀酰辅酶A供应,引入直接硫磺酸化途径和削弱L-苏氨酸支链途径 | 20.39 g/L | [ |
| L-色氨酸 | E. coli | 优化了抗反馈酶AroG、TrpE和SerA的组合;敲入yddG和prsL135I,敲除poxB基因 | 43.0 g/L | [ |
| L-缬氨酸 | C. necator | 强化缬氨酸输出蛋白,敲除PHB合成途径,并筛选高效内源AHAS酶 | 972 mg/L | [ |
| L-异亮氨酸 | E. coli | 使用柠檬酸途径替代苏氨酸途径,同时强化DcuD转运蛋白并重构非氧化糖酵解途径 | 56.6 g/L | [ |
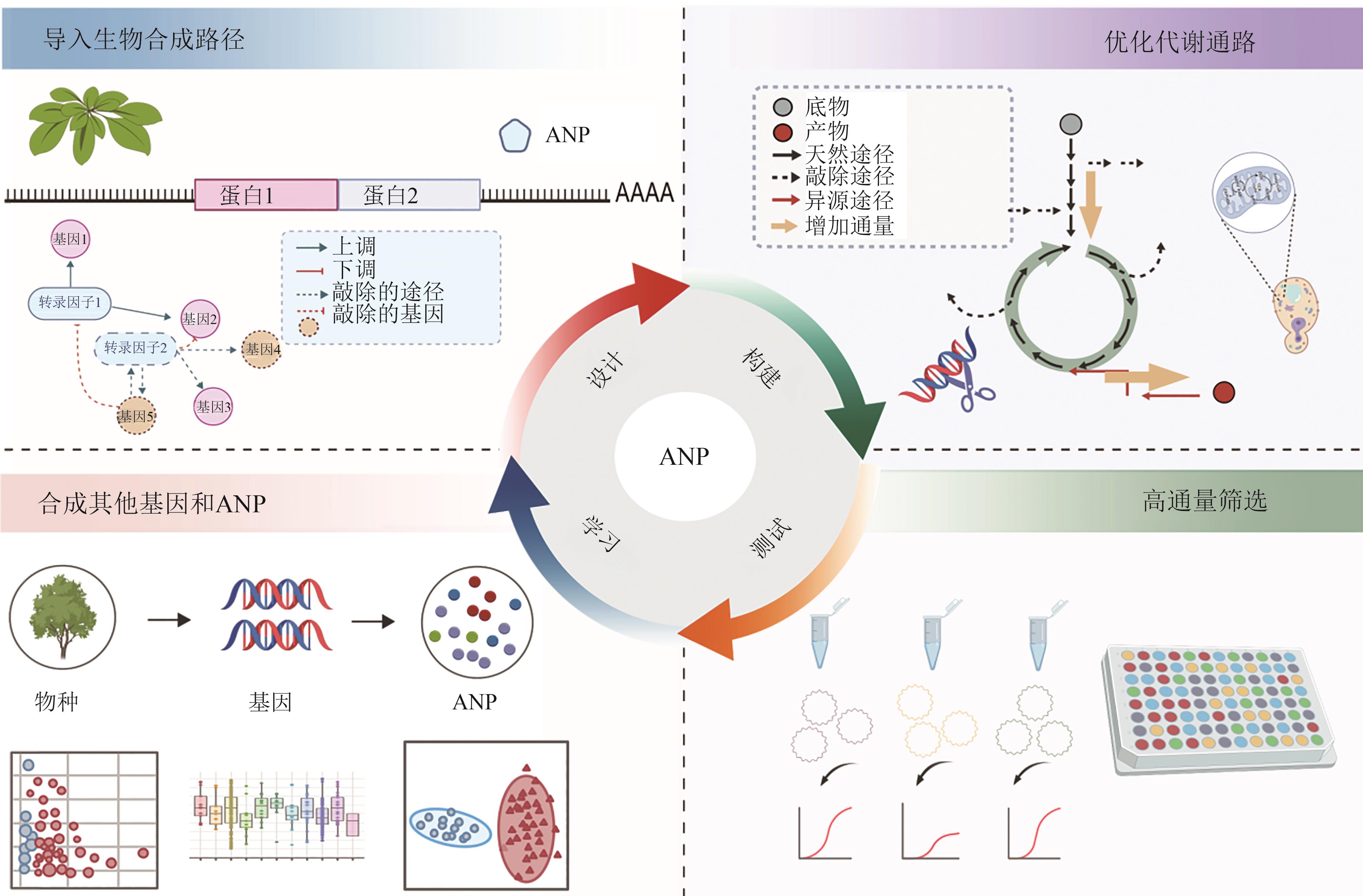
图5 农业合成生物学引导活性植物天然产物合成 [15](图5使用BioGDP.com制作)
Fig. 5 Agricultural synthetic biology drives active plant natural product synthesis [15](Fig. 5 was created with BioGDP.com)
| [1] | 马玉琪, 任新平. 基于合成生物学技术缓解大豆蛋白短缺的探讨[J]. 中国农业综合开发, 2025(3): 48-53. |
| MA Y Q, REN X P. Exploration of synthetic biology-based technology to alleviate the shortage of soy protein [J]. Agricultural Comprehensive Development in China, 2025(3): 48-53. | |
| [2] | 朱丽慧, 肖长峰, 杨长锁. 饲料酶制剂的作用机制及其在家禽饲料中的应用[J]. 上海畜牧兽医通讯, 2024(3): 1-7, 85. |
| ZHU L H, XIAO C F, YANG C S. The functionality of feed enzyme preparations and their application in poultry feed[J]. Shanghai Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2024(3): 1-7, 85. | |
| [3] | 杨全中, 张玉国, 申绯翡, 等. 维生素D3和维生素A调控动物脂质代谢机制的研究进展[J]. 中国饲料, 2025(10): 1-4. |
| YANG Q Z, ZHANG Y G, SHEN F F, et al. Research progress on the mechanisms of vitamin D3 and vitamin A in regulating animal lipid metabolism[J]. China Feed, 2025(10): 1-4. | |
| [4] | 张法玲, 徐群, 张桂凤, 等. 低蛋白氨基酸平衡日粮技术在猪生产中的应用研究进展[J]. 山东畜牧兽医, 2025, 46(5): 107-112. |
| ZHANG F L, XU Q, ZHANG G F, et al. Research progress on the application of low protein amino acid balanced diet technology in swine production [J]. Shandong Journal of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2025, 46(5): 107-112. | |
| [5] | ROSS F C, PATANGIA D, GRIMAUD G, et al. The interplay between diet and the gut microbiome: implications for health and disease[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2024, 22(11): 671-686. |
| [6] | 吴杰, 赵乔. 合成生物学在现代农业中的应用与前景[J]. 植物生理学报, 2020, 56(11): 2308-2316. |
| WU J, ZHAO Q. The application and prospect of synthetic biology in future agriculture[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2020, 56(11): 2308-2316. | |
| [7] | 毛瑞超, 王宝俊. 合成生物元件与线路的智能设计[J]. 生物工程学报, 2025, 41(3): 1023-1051. |
| MAO R C, WANG B J. Machine learning-aided design of synthetic biological parts and circuits[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2025, 41(3): 1023-1051. | |
| [8] | SINGH N, LANE S, YU T H, et al. A generalized platform for artificial intelligence-powered autonomous enzyme engineering[J]. Nature Communications, 2025, 16: 5648. |
| [9] | ZHANG Y, HUANG G M, ZHAO Y X, et al. Revolutionizing crop breeding: next-generation artificial intelligence and big data-driven intelligent design[J]. Engineering, 2025, 44: 245-255. |
| [10] | 李百慧, 拜彬强, 赵国君, 等. 四类非常规饲料研究现状及展望[J]. 饲料工业, 2024, 45(22): 140-144. |
| LI B H, BAI B Q, ZHAO G J, et al. Research status and prospect of four kinds of unconventional feed province[J]. Feed Industry, 2024, 45(22): 140-144. | |
| [11] | 浦华, 杨静, 王永伟, 等. 保障国家粮食安全的蛋白替代战略构想[J]. 中国工程科学, 2023, 25(4): 149-157. |
| PU H, YANG J, WANG Y W, et al. Protein substitution strategy for ensuring national food security in China[J]. Strategic Study of Chinese Academy of Engineering, 2023, 25(4): 149-157. | |
| [12] | 张寒, 韩梅, 郑竟成, 等. 硫苷降解菌筛选及改良菜籽粕营养特性的研究[J]. 中国油脂, 2025, 50(3): 22-28, 43. |
| ZHANG H, HAN M, ZHENG J C, et al. Screening of glucosinolates-degrading bacteria and their role in improving the nutrition characteristics of rapeseed meal[J]. China Oils and Fats, 2025, 50(3): 22-28, 43. | |
| [13] | 张璐瑶, 范志勇, 王永伟, 等. 棉籽粕和菜籽粕内源抗营养因子脱除技术研究进展[J]. 饲料研究, 2024, 47(2): 133-138. |
| ZHANG L Y, FAN Z Y, WANG Y W, et al. Research progress on removal technology of endogenous anti-nutritional factors in cottonseed meal and rapeseed meal[J]. Feed Research, 2024, 47(2): 133-138. | |
| [14] | 印遇龙, 杨哲. 非常规饲料的开发与高效利用[J]. 饲料工业, 2025, 46(1): 2-10. |
| YIN Y L, YANG Z. Development and efficient utilization of unconventional feed[J]. Feed Industry, 2025, 46(1): 2-10. | |
| [15] | JIANG S, LI H Q, ZHANG L, et al. Generic Diagramming Platform (GDP): a comprehensive database of high-quality biomedical graphics[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2025, 53(D1): D1670-D1676. |
| [16] | ZHANG L, YANG X L, NIE C X, et al. Combined transcriptomics and cellular analyses reveal the molecular mechanism by which Candida tropicalis ZD-3 adapts to and degrades gossypol[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 279: 135294. |
| [17] | WANG W K, ZHANG F, CHEN H W, et al. Integrative omics and gene knockout analyses suggest a possible gossypol detoxification mechanism and potential key regulatory genes of a ruminal Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2025, 73(2): 1619-1629. |
| [18] | LI B, LIANG S J, ALARIQI M, et al. The application of temperature sensitivity CRISPR/LbCpf1 (LbCas12a) mediated genome editing in allotetraploid cotton (G. hirsutum) and creation of nontransgenic, gossypol-free cotton[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2021, 19(2): 221-223. |
| [19] | LIN J L, FANG X, LI J X, et al. Dirigent gene editing of gossypol enantiomers for toxicity-depleted cotton seeds[J]. Nature Plants, 2023, 9(4): 605-615. |
| [20] | LIU G Q, GILDING E K, KERR E D, et al. Increasing protein content and digestibility in sorghum grain with a synthetic biology approach[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2019, 85: 27-34. |
| [21] | LI A X, JIA S G, YOBI A, et al. Editing of an alpha-kafirin gene family increases, digestibility and protein quality in sorghum[J]. Plant Physiology, 2018, 177(4): 1425-1438. |
| [22] | ELKONIN L A, GERASHCHENKOV G A, BORISENKO N V, et al. Development of sorghum mutants with improved in vitro protein digestibility by CRISPR/Cas9 editing of kafirin genes[J]. The Crop Journal, 2023, 11(5): 1411-1418. |
| [23] | NYYSSÖLÄ A, SUHONEN A, RITALA A, et al. The role of single cell protein in cellular agriculture[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2022, 75: 102686. |
| [24] | BALAGURUNATHAN B, LING H, CHOI W J, et al. Potential use of microbial engineering in single-cell protein production[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2022, 76: 102740. |
| [25] | MENG J, LIU S F, GAO L, et al. Economical production of Pichia pastoris single cell protein from methanol at industrial pilot scale[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2023, 22(1): 198. |
| [26] | WANG G K, OLOFSSON-DOLK M, HANSSON F G, et al. Engineering yeast Yarrowia lipolytica for methanol assimilation[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2021, 10(12): 3537-3550. |
| [27] | MOON J, WASCHINGER L M, MÜLLER V. Lactate formation from fructose or C1 compounds in the acetogen Acetobacterium woodii by metabolic engineering[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2023, 107(17): 5491-5502. |
| [28] | CUI H J, LIU W S, MA C L, et al. Converting CO2 to single-cell protein via an integrated electrocatalytic-biosynthetic system[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environment and Energy, 2024, 350: 123946. |
| [29] | PAN Z Y, GUO Y H, RONG W H, et al. Single-cell protein production from CO2 and electricity with a recirculating anaerobic-aerobic bioprocess[J]. Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, 2025, 24: 100525. |
| [30] | XU X X, ZHANG W, YOU C, et al. Biosynthesis of artificial starch and microbial protein from agricultural residue[J]. Science Bulletin, 2023, 68(2): 214-223. |
| [31] | MU J J, WANG L, WANG F, et al. Low-carbon bioconversion of corn stover through whole process design[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2025, 508: 160911. |
| [32] | ZHONG P X, CHEN P Y, HUO P J, et al. Characterization of cotton stalk as a lignocellulosic feedstock for single-cell protein production[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2025, 417: 131797. |
| [33] | GAO L, KHOO S C, ZHANG Z K, et al. Trends in sustainable single-cell protein from non-grain feedstocks[J/OL]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2025. (2025-06-03)[2025-08-01]. . |
| [34] | DUAN X P, GAO J Q, ZHOU Y J. Advances in engineering methylotrophic yeast for biosynthesis of valuable chemicals from methanol[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2018, 29(5): 681-686. |
| [35] | ZHU P, ZHANG Z Q, LI Y F. Converting heterotrophic Saccharomyces cerevisiae to a synthetic methylotroph[J]. Trends in Chemistry, 2024, 6(2): 55-57. |
| [36] | KREMP F, MÜLLER V. Methanol and methyl group conversion in acetogenic bacteria: biochemistry, physiology and application[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2021, 45(2): fuaa040. |
| [37] | 王永伟, 施晶晶, 段涛, 等. 生物技术在粮油饲料资源增值转化中的应用研究进展[J]. 粮油食品科技, 2023, 31(5): 152-159. |
| WANG Y W, SHI J J, DUAN T, et al. Research progress on the application of biotechnology in value-added conversion of grain, oil and feed resources[J]. Science and Technology of Cereals, Oils and Foods, 2023, 31(5): 152-159. | |
| [38] | ZHANG Q L, LIANG H L, LONGSHAW M, et al. Effects of replacing fishmeal with methanotroph (Methylococcus capsulatus, Bath) bacteria meal (FeedKind®) on growth and intestinal health status of juvenile largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides)[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2022, 122: 298-305. |
| [39] | ØVERLAND M, TAUSON A H, SHEARER K, et al. Evaluation of methane-utilising bacteria products as feed ingredients for monogastric animals[J]. Archives of Animal Nutrition, 2010, 64(3): 171-189. |
| [40] | LONG B, ZHANG F Z, DAI S Y, et al. Engineering strategies to optimize lignocellulosic biorefineries[J]. Nature Reviews Bioengineering, 2025, 3(3): 230-244. |
| [41] | WANG G K, WU X, YIN Y L. Synthetic biology-driven customization of functional feed resources[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2022, 40(7): 777-780. |
| [42] | 郭怡廷, 吴本刚, 刘丹丹, 等. 维生素的生理功能及其在动物健康与营养中的应用[J]. 当代畜牧, 2023(8): 17-24. |
| GUO Y T, WU B G, LIU D D, et al. Physiological functions of vitamins and their applications in animal health and nutrition [J]. Contemporary Animal Husbandry, 2023(8): 17-24. | |
| [43] | 张博, 廖宇哲, 余浩楠, 等. 水溶性维生素的生物合成[J]. 生物工程学报, 2024, 40(8): 2528-2551. |
| ZHANG B, LIAO Y Z, YU H N, et al. Biosynthesis of water-soluble vitamins[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2024, 40(8): 2528-2551. | |
| [44] | 张博, 余浩楠, 朱丽丹, 等. 脂溶性维生素的生物合成[J]. 生物工程学报, 2024, 40(8): 2552-2569. |
| ZHANG B, YU H N, ZHU L D, et al. Biosynthesis of fat-soluble vitamins[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2024, 40(8): 2552-2569. | |
| [45] | LIANG Z Q, ZHOU Q, LI Y C, et al. Efficient C25-hydroxylation of vitamin D3 utilizing an artificial self-sufficient whole-cell cytochrome P450 biocatalyst[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2025, 73(17): 10378-10388. |
| [46] | SHI Y, LU S H, ZHOU X, et al. Systematic metabolic engineering enables highly efficient production of vitamin A in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2025, 10(1): 58-67. |
| [47] | SHEN B, ZHOU P P, JIAO X, et al. Fermentative production of vitamin E tocotrienols in Saccharomyces cerevisiae under cold-shock-triggered temperature control[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 5155. |
| [48] | LIU L X, LI J L, GAI Y M, et al. Protein engineering and iterative multimodule optimization for vitamin B6 production in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 5304. |
| [49] | WANG Y H, ZHOU J P, ZHANG Z, et al. Efficient carbon flux allocation towards D-pantothenic acid production via growth-decoupled strategy in Escherichia coli [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2024, 411: 131325. |
| [50] | ZHANG L H, PIAO X S. Use of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 in diets for sows: a review[J]. Animal Nutrition, 2021, 7(3): 728-736. |
| [51] | 郭亮, 高聪, 柳亚迪, 等. 大肠杆菌生产饲用氨基酸的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(6): 964-981. |
| GUO L, GAO C, LIU Y D, et al. Advances in bioproduction of feed amino acid by Escherichia coli [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(6): 964-981. | |
| [52] | 刘佳, 盛琦, 刘开放, 等. 微生物制造饲用氨基酸助力豆粕减量替代[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2025, 40(1): 25-35. |
| LIU J, SHENG Q, LIU K F, et al. Microbial production of feed amino acids promotes reduction and replacement of soybean meal[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2025, 40(1): 25-35. | |
| [53] | 姚斌, 徐欣欣, 张杰, 等. 饲用氨基酸的生物合成与产业化应用[J]. 动物营养学报, 2025, 37(1): 1-14. |
| YAO B, XU X X, ZHANG J, et al. Biosynthesis and industrial application of feed amino acids[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2025, 37(1): 1-14. | |
| [54] | LIU J, OU Y, XU J Z, et al. L-lysine production by systems metabolic engineering of an NADPH auto-regulated Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 387: 129701. |
| [55] | LIU Z Y, LIU J, ZHANG F, et al. Modifying Corynebacterium glutamicum by metabolic engineering for efficient synthesis of L-lysine[J]. Systems Microbiology and Biomanufacturing, 2025, 5(1): 288-299. |
| [56] | WANG L J, GUO Y Y, LI M Y, et al. Antibiotic-free high-level L-methionine production in engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024, 72(46): 25791-25800. |
| [57] | HOU M L, GAO S Q, WU J, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli to enhance L-tryptophan biosynthesis[J]. Systems Microbiology and Biomanufacturing, 2025, 5(2): 622-634. |
| [58] | WANG L, YAO J H, TU T, et al. Heterotrophic and autotrophic production of L-isoleucine and L-valine by engineered Cupriavidus necator H16[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2024, 398: 130538. |
| [59] | ZHANG Q Q, WANG Y H, WANG X L, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for efficient L-isoleucine production based on the citramalate pathway[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2025, 73(19): 11900-11911. |
| [60] | 梁洪慧, 谭会泽, 赵江涛, 等. 饲料原料中抗营养因子的研究进展[J]. 粮食与饲料工业, 2022(1): 49-53, 59. |
| LIANG H H, TAN H Z, ZHAO J T, et al. The research progress of antinutritional factors in feedstuff[J]. Cereal & Feed Industry, 2022(1): 49-53, 59. | |
| [61] | 庞业惠, 字向东. 饲用酶制剂的功能及其在畜牧业中的应用[J]. 现代畜牧兽医, 2020(9): 61-64. |
| PANG Y H, ZI X D. Function of feed enzyme preparation and its application in animal husbandry[J]. Modern Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2020(9): 61-64. | |
| [62] | SU X Y, YAO B. Exploiting enzymes as a powerful tool to modulate the gut microbiota[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 2022, 30(4): 314-317. |
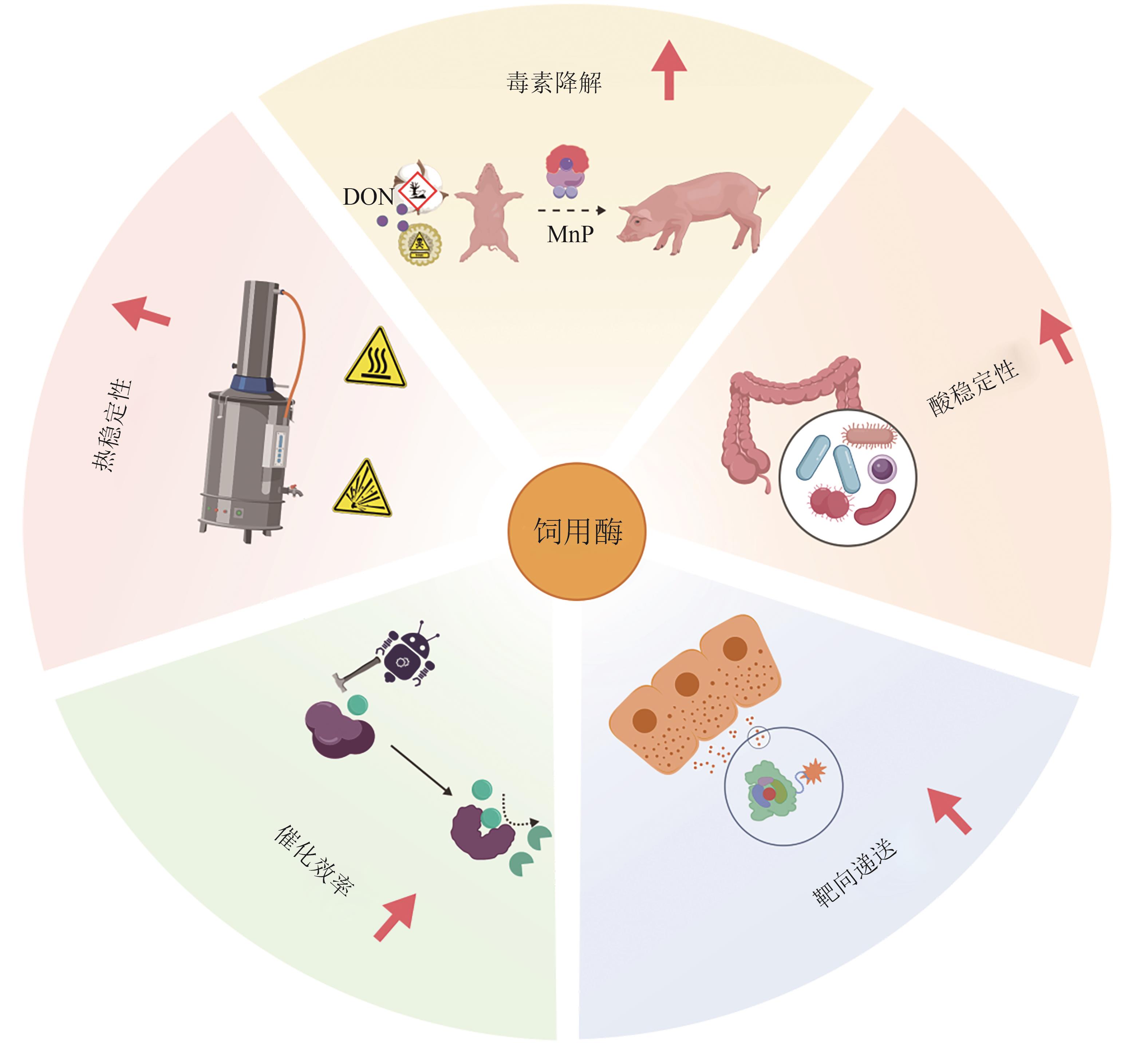
| [63] | ZHOU Y W, ANOOPKUMAR A N, TARAFDAR A, et al. Microbial engineering for the production and application of phytases to the treatment of the toxic pollutants: a review[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 308: 119703. |
| [64] | TU T, WANG Q, DONG R Y, et al. Achieving thermostability of a phytase with resistance up to 100 ℃[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2024, 300(12): 107992. |
| [65] | ASHOK P P, DASGUPTA D, RAY A, et al. Challenges and prospects of microbial α-amylases for industrial application: a review[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2023, 40(2): 44. |
| [66] | LIAO M, DONG R Y, LI L X, et al. High production of maltooligosaccharides in the starch liquefaction process: a study on the hyperthermophilic mechanism of α-amylase[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2023, 71(16): 6480-6489. |
| [67] | LIAO M, FENG S H, LIU X Q, et al. Novel insights into enzymatic thermostability: the “Short Board” theory and Zero-Shot Hamiltonian model[J]. Advanced Science, 2024, 11(45): 2470274. |
| [68] | WANG T, ZHOU N N, DING F F, et al. Xylanase enhances gut microbiota-derived butyrate to exert immune-protective effects in a histone deacetylase-dependent manner[J]. Microbiome, 2024, 12(1): 212. |
| [69] | SÜRMELI Y, ŞANLI-MOHAMED G. Engineering of xylanases for the development of biotechnologically important characteristics[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2023, 120(5): 1171-1188. |
| [70] | DONG R Y, LIAO M, LIU X Q, et al. Effectiveness of ruminal xylanase with an extra proline-rich C-terminus on lignocellulosic biomass degradation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 372: 128695. |
| [71] | HAO Z Z, ZHANG W J, WANG X L, et al. Identification of WxL and S-layer proteins from Lactobacillus brevis with the ability to bind cellulose and xylan[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(8): 4136. |
| [72] | SINGH A K, IQBAL H M N, CARDULLO N, et al. Structural insights, biocatalytic characteristics, and application prospects of lignin-modifying enzymes for sustainable biotechnology[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2023, 242: 124968. |
| [73] | SU X Y, WANG S, WANG X L, et al. Targeting deoxynivalenol for degradation by a chimeric manganese peroxidase/glutathione system[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2024, 273: 116130. |
| [74] | LIU X Q, DING S J, GAO F, et al. Exploring the cellulolytic and hemicellulolytic activities of manganese peroxidase for lignocellulose deconstruction[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels and Bioproducts, 2023, 16(1): 139. |
| [75] | YAN Y R, LIU X Q, JIANG X, et al. Surface charge modifications modulate glucose oxidase pH-activity profiles for efficient gluconic acid production[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 372: 133817. |
| [76] | LI L X, LIU M Y, YAN Y R, et al. Chemoenzymatic two-step synthesis of tartaric acid employing glucose oxidase in combination with bimetallic AuPt/TiO2 catalyst[J]. Green Synthesis and Catalysis, 2025. (2025-01-10)[2025-08-01]. . |
| [77] | PATRA A K, AMASHEH S, ASCHENBACH J R. Modulation of gastrointestinal barrier and nutrient transport function in farm animals by natural plant bioactive compounds - a comprehensive review[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2019, 59(20): 3237-3266. |
| [78] | LIN J J, YIN X, ZENG Y R, et al. Progress and prospect: biosynthesis of plant natural products based on plant chassis[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2023, 69: 108266. |
| [79] | LAN H J, WANG H, CHEN C, et al. Flavonoids and gastrointestinal health: single molecule for multiple roles[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2024, 64(30): 10987-11005. |
| [80] | LIU Q L, LIU Y, LI G, et al. De novo biosynthesis of bioactive isoflavonoids by engineered yeast cell factories[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 6085. |
| [81] | XIE J L, TIAN J Y, KHAN S, et al. Glyceollin biosynthesis in a plant chassis engineered for isoflavone production[J/OL]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2025. (2025-05-28)[2025-08-01]. . |
| [82] | WANG C, MA W, XU L W, et al. Integrative metabolic and cellular organelle engineering for improving biosynthesis of flavonoid compounds in saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Food Bioscience, 2024, 60: 103996. |
| [83] | LIU M S, WANG C, REN X F, et al. Remodelling metabolism for high-level resveratrol production in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 365: 128178. |
| [84] | ZANG Y, SUN R N, FENG R Q, et al. Recent advances of terpenoids with intriguing chemical skeletons and biological activities[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemistry, 2025, 43(4): 443-469. |
| [85] | YU B X, MA T Y, NAWAZ M, et al. Advances in metabolic engineering for the accumulation of astaxanthin biosynthesis[J/OL]. Molecular Biotechnology, 2024. (2024-10-07)[2025-06-01]. |
| [86] | KANG W, MA T, LIU M, et al. Modular enzyme assembly for enhanced cascade biocatalysis and metabolic flux[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 4248. |
| [87] | LI M, ZHOU P P, CHEN M K, et al. Spatiotemporal regulation of astaxanthin synthesis in S. cerevisiae [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2022, 11(8): 2636-2649. |
| [88] | LI J, ZHAO J R, WANG X H, et al. Ginsenoside - a promising natural active ingredient with steroidal hormone activity[J]. Food & Function, 2024, 15(4): 1825-1839. |
| [89] | ZHOU C, CHEN T J, GU A D, et al. Combining protein and metabolic engineering to achieve green biosynthesis of 12β-O-Glc-PPD in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Green Chemistry, 2023, 25(4): 1356-1367. |
| [90] | KIM J E, JANG I S, SON S H, et al. Tailoring the Saccharomyces cerevisiae endoplasmic reticulum for functional assembly of terpene synthesis pathway[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 56: 50-59. |
| [91] | LI C L, ZHOU Z Y, WANG W T, et al. Development of antibacterial peptides with membrane disruption and folate pathway inhibitory activities against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2024, 67(2): 1044-1060. |
| [92] | SILVEIRA R F, ROQUE-BORDA C A, VICENTE E F. Antimicrobial peptides as a feed additive alternative to animal production, food safety and public health implications: an overview[J]. Animal Nutrition, 2021, 7(3): 896-904. |
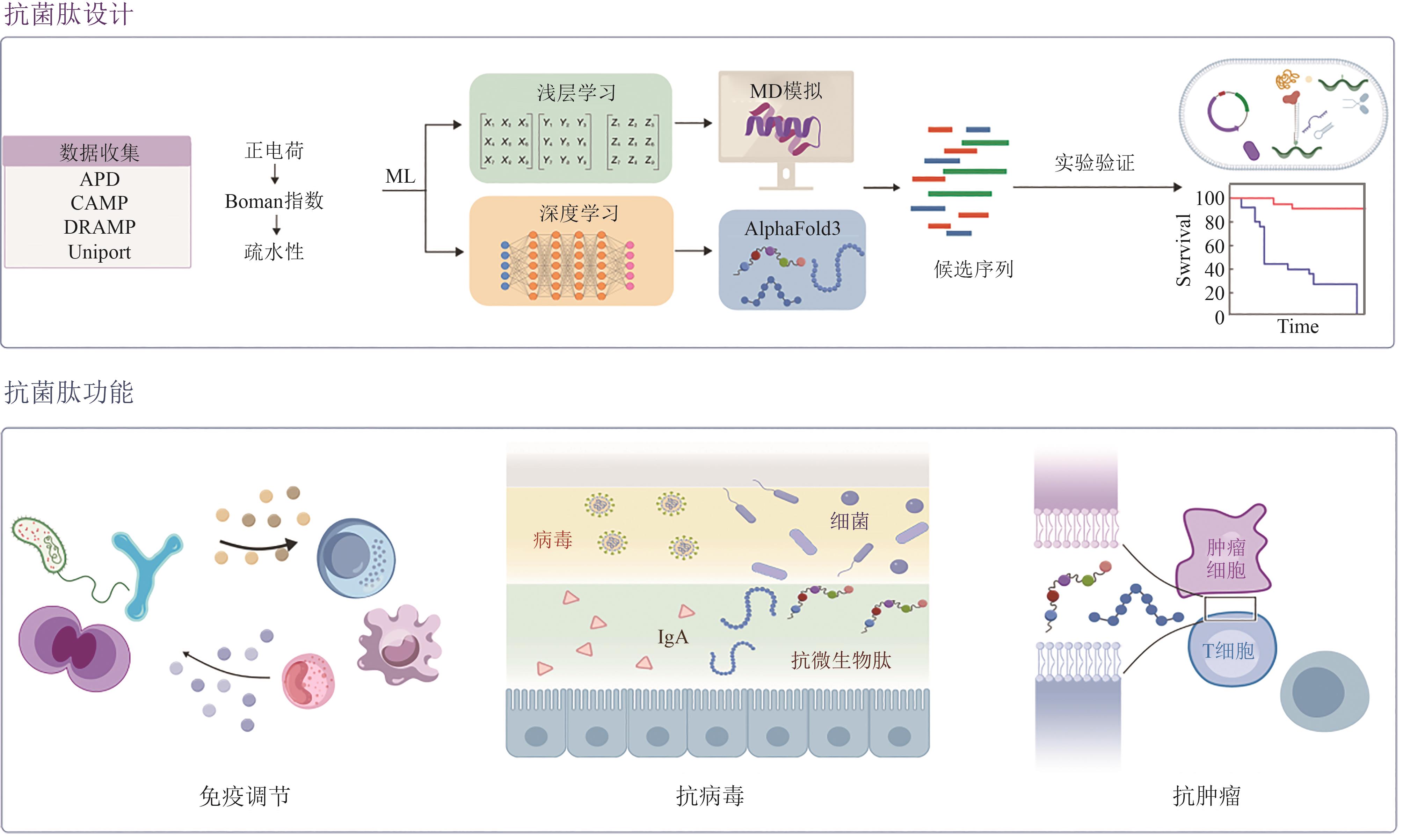
| [93] | BOTELHO SAMPAIO DE OLIVEIRA K, LOPES LEITE M, ALBUQUERQUE CUNHA V, et al. Challenges and advances in antimicrobial peptide development[J]. Drug Discovery Today, 2023, 28(8): 103629. |
| [94] | TORRES M D T, BROOKS E F, CESARO A, et al. Mining human microbiomes reveals an untapped source of peptide antibiotics[J]. Cell, 2024, 187(19): 5453-5467.e15. |
| [95] | WANG X F, TANG J Y, SUN J, et al. ProT-diff: a modularized and efficient strategy for de novo generation of antimicrobial peptide sequences by integrating protein language and diffusion models[J]. Advanced Science, 2024, 11(43): 2406305. |
| [96] | CAPECCHI A, CAI X G, PERSONNE H, et al. Machine learning designs non-hemolytic antimicrobial peptides[J]. Chemical Science, 2021, 12(26): 9221-9232. |
| [97] | TAN P, WU C C, TANG Q, et al. pH-triggered size-transformable and bioactivity-switchable self-assembling chimeric peptide nanoassemblies for combating drug-resistant bacteria and biofilms[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(29): 2210766. |
| [98] | JENNINGS S A V, CLAVEL T. Synthetic communities of gut microbes for basic research and translational approaches in animal health and nutrition[J]. Annual Review of Animal Biosciences, 2024, 12: 283-300. |
| [99] | NAGARAJA T G. 388 Nutrition and the ruminal microbiome: emerging frontiers from an old friend[J]. Journal of Animal Science, 2020, 98(S4): 171. |
| [100] | 慕春龙, 李轩, 吴海琴, 等. 微生物群系与动物消化道营养[J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2023, 53(5): 626-636. |
| MU C L, LI X, WU H Q, et al. Gut microbiome and gastrointestinal nutrition in animals[J]. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 2023, 53(5): 626-636. | |
| [101] | RONDA C, CHEN S P, CABRAL V, et al. Metagenomic engineering of the mammalian gut microbiome in situ [J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(2): 167-170. |
| [102] | AUFFRET M D, STEWART R D, DEWHURST R J, et al. Identification of microbial genetic capacities and potential mechanisms within the rumen microbiome explaining differences in beef cattle feed efficiency[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, 11: 1229. |
| [103] | MCGOVERN E, MCGEE M, BYRNE C J, et al. Investigation into the effect of divergent feed efficiency phenotype on the bovine rumen microbiota across diet and breed[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 15317. |
| [104] | XUE M Y, XIE Y Y, ZANG X W, et al. Deciphering functional groups of rumen microbiome and their underlying potentially causal relationships in shaping host traits[J]. iMeta, 2024, 3(4): e225. |
| [105] | HU J, CHEN J W, MA L B, et al. Characterizing core microbiota and regulatory functions of the pig gut microbiome[J]. The ISME Journal, 2024, 18(1): wrad037. |
| [106] | QUAN J H, HUANG R, WANG Z, et al. P2X7 receptor mediates NLRP3-dependent IL-1β secretion and parasite proliferation in Toxoplasma gondii -infected-infected human small intestinal epithelial cells[J]. Parasites & Vectors, 2018, 11(1): 1. |
| [107] | WANG H Y, XU R Y, ZHANG H, et al. Swine gut microbiota and its interaction with host nutrient metabolism[J]. Animal Nutrition, 2020, 6(4): 410-420. |
| [108] | THAISS C A, LEVY M, KOREM T, et al. Microbiota diurnal rhythmicity programs host transcriptome oscillations[J]. Cell, 2016, 167(6): 1495-1510.e12. |
| [109] | MOON T S. Probiotic and microbiota engineering for practical applications[J]. Current Opinion in Food Science, 2024, 56: 101130. |
| [110] | INDA-WEBB M E, JIMENEZ M, LIU Q, et al. Sub-1.4 cm3 capsule for detecting labile inflammatory biomarkers in situ [J]. Nature, 2023, 620(7973): 386-392. |
| [111] | JIN W B, LI T T, HUO D, et al. Genetic manipulation of gut microbes enables single-gene interrogation in a complex microbiome[J]. Cell, 2022, 185(3): 547-562.e22. |
| [112] | JIN W B, GUO C J. Genetic manipulations of nonmodel gut microbes[J]. iMeta, 2024, 3(4): e216. |
| [113] | LI H R, ZHANG S S, YIN J Y, et al. Minimal logic gates for probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 sensing and treatment of dual-bacteria intestinal infection[J]. Gut Microbes, 2025, 17(1): 2530156. |
| [114] | YANG Q, XIANG W, KHAN A, et al. Programmable probiotic consortium employ an oleic acid-inducible system to sense and degrade cholesterol in high-fat diet mice[J]. Gut Microbes, 2025, 17(1): 2531198. |
| [115] | HUANG Y C, WANG H H, ZHU Y D, et al. THP9 enhances seed protein content and nitrogen-use efficiency in maize[J]. Nature, 2022, 612(7939): 292-300. |
| [116] | LI G T, AN L N, YANG W N, et al. Integrated biotechnological and AI innovations for crop improvement[J]. Nature, 2025, 643(8073): 925-937. |
| [117] | DOMAN J L, PANDEY S, NEUGEBAUER M E, et al. Phage-assisted evolution and protein engineering yield compact, efficient prime editors[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(18): 3983-4002.e26. |
| [118] | GELSINGER D R, VO P L H, KLOMPE S E, et al. Bacterial genome engineering using CRISPR-associated transposases[J]. Nature Protocols, 2024, 19(3): 752-790. |
| [119] | ZHENG N, CAI Y C, ZHANG Z H, et al. Tailoring industrial enzymes for thermostability and activity evolution by the machine learning-based iCASE strategy[J]. Nature Communications, 2025, 16: 604. |
| [120] | DOMENZAIN I, LU Y, WANG H Y, et al. Computational biology predicts metabolic engineering targets for increased production of 103 valuable chemicals in yeast[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2025, 122(9): e2417322122. |
| [121] | BRIZUELA C A, LIU G, STOKES J M, et al. AI methods for antimicrobial peptides: progress and challenges[J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 2025, 18(1): e70072. |
| [122] | LIU H Y, SONG Z L, ZHANG Y, et al. De novo design of self-assembling peptides with antimicrobial activity guided by deep learning[J]. Nature Materials, 2025, 24(8): 1295-1306. |
| [1] | 曲泽鹏, 陈沫先, 曹朝辉, 左文龙, 陈业, 戴磊. 合成微生物群落研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(6): 621-634. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||