合成生物学 ›› 2020, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (2): 121-140.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-016
植物合成生物学研究进展
张博1, 马永硕2,3, 尚轶1, 黄三文2
- 1.云南师范大学马铃薯科学研究院, 云南省马铃薯生物学重点实验室,云南 昆明 650500
2.中国农业科学院农业基因组研究所,农业部基因组分析重点实验室,广东省岭南现代农业实验室,广东 深圳 518120
3.麻省理工学院化学工程系,马萨诸塞州 剑桥市,02139
-
收稿日期:2020-03-04修回日期:2020-04-09出版日期:2020-04-30发布日期:2020-08-04 -
通讯作者:黄三文 -
作者简介:张博(1992—),女,博士研究生,研究方向为作物营养与风味品质。E-mail:zhangbo_solab@163.com
尚轶(1982—),男,研究员,研究方向为植物次生代谢。E-mail:shangyi@ynnu.edu.cn
黄三文(1971—),男,研究员,研究方向为功能基因组。E-mail:huangsanwen@caas.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划“合成生物学”重点专项;合成植物天然产物的微生物细胞工厂构建及其应用示范项目(2018YFA0901800);云南师范大学研究生科研创新基金项目(ysdyjs2019170)
Recent advances in plant synthetic biology
ZHANG Bo1, MA Yongshuo2,3, SHANG Yi1, HUANG Sanwen2
- 1.Key Laboratory for Potato Biology of Yunnan Province, The CAAS-YNNU-YINMORE Joint Academy of Potato Science, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming 650500,Yunnan,China
2.Shenzhen Branch, Guangdong Laboratory for Lingnan Modern Agriculture, Genome Analysis Laboratory of the Ministry of Agriculture, Agricultural Genomics Institute at Shenzhen, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Shenzhen 518120, Guangdong,China
3.Chemical Engineering, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 02139, USA
-
Received:2020-03-04Revised:2020-04-09Online:2020-04-30Published:2020-08-04 -
Contact:HUANG Sanwen
摘要:
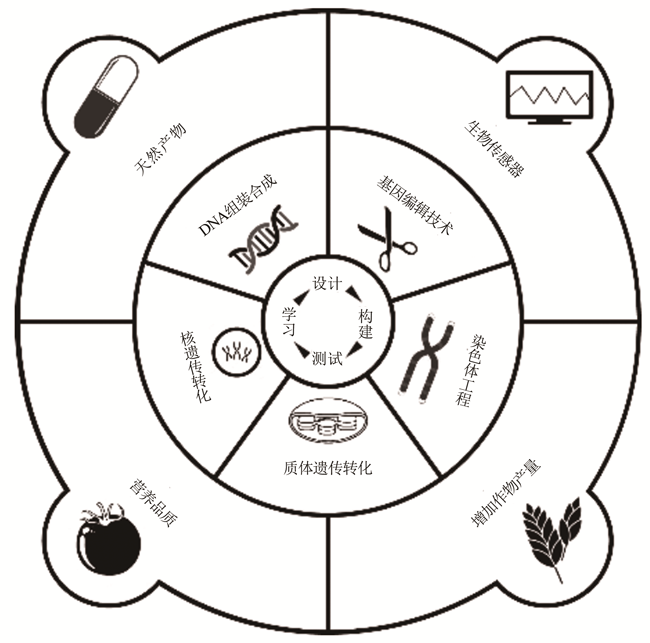
合成生物学是汇聚了工程学和生物学的新兴交叉学科,近年来逐步在植物研究领域中显现其重要作用。利用合成生物学技术不仅可以对作物的产量及营养品质性状进行精准的改良和优化,还有望将植物改造成高价值的植物天然产物生产工厂满足人们更多的需求。本文从DNA合成与组装、植物基因编辑技术、核和质体遗传转化体系以及染色体工程等方面介绍了在植物中广泛应用的合成生物学技术。阐述了利用合成生物学开展多样化生物传感器设计、作物产量优化、营养品质强化、植物天然产物与蛋白高效合成等方面的最新研究进展。最后讨论了目前植物合成生物学所面临的问题以及今后的发展趋势。相信经过新一轮的快速发展,植物合成生物学将在未来农作物育种中发挥越来越重要的作用。
中图分类号:
引用本文
张博, 马永硕, 尚轶, 黄三文. 植物合成生物学研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(2): 121-140.
ZHANG Bo, MA Yongshuo, SHANG Yi, HUANG Sanwen. Recent advances in plant synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(2): 121-140.
| 1 | WATSON J D, CRICK F H C. Molecular structure of nucleic acids; a structure for deoxyribose nucleic acid[J]. Nature, 1953, 171(4356):737-738 |
| 2 | BENNER S A, SISMOUR A M. Synthetic biology[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2005, 6(7): 533-543. |
| 3 | 赵国屏. 合成生物学:开启生命科学“会聚”研究新时代[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2018,33(11): 1135-1149. |
| ZHAO G P. Synthetic biology: unsealing the convergence era of life science research [J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 33(11): 1135-1149 | |
| 4 | KEASLING J D. Synthetic biology and the development of tools for metabolic engineering [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2012, 14(3): 189-195. |
| 5 | KHALIL A S, COLLINS J J. Synthetic biology: applications come of age [J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2010, 11(5): 367-379. |
| 6 | 张先恩. 中国合成生物学发展回顾与展望[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2019,49(12): 1543-1572. |
| ZHANG X E. Synthetic biology in China: review and prospects (in Chinese) [J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Vitae, 2019, 49(12):1543-1572 | |
| 7 | SLUSARCZYK A L, LIN A, WEISS R. Foundations for the design and implementation of synthetic genetic circuits [J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2012, 13(6): 406-420. |
| 8 | GARDNER T S, CANTOR C R, COLLINS J J. Construction of a genetic toggle switch in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6767): 339-342. |
| 9 | ELOWITZ M B, LIEBLER S. A synthetic oscillatory network of transcriptional regulators [J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6767):335-338. |
| 10 | PURNICK P E M, WEISS R. The second wave of synthetic biology: from modules to systems [J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2009, 10(6): 410-422. |
| 11 | CELLO J, PAUL A V, WIMMER E. Chemical synthesis of poliovirus cDNA: generation of infectious virus in the absence of natural template [J]. Science, 2002, 297(5583): 1016-1018. |
| 12 | SMITH H O, HUTCHISON C R, PFANNKOCH C, et al. Generating a synthetic genome by whole genome assembly: phiX174 bacteriophage from synthetic oligonucleotides [J]. PNAS, 2003, 100(26): 15440-15445. |
| 13 | GIBSON D G, GLASS J I, LARTIGUE C, et al. Creation of a bacterial cell controlled by a chemically synthesized genome[J]. Science, 2010, 329(5987):52-56. |
| 14 | DYMOND J S, RICHARDSON S M, COOMBES C E, et al. Synthetic chromosome arms function in yeast and generate phenotypic diversity by design[J]. Nature, 2011, 477(7365): 471-476. |
| 15 | BOEKE J D, CHURCH G, HESSEL A, et al. The genome project-write [J]. Science, 2016, 353(6295):126-127. |
| 16 | ANDERSON J C, CLARKE E J, ARKIN A P, et al. Environmentally controlled invasion of cancer cells by engineered bacteria [J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2006, 355(4): 619-627. |
| 17 | THALLINGER B, PRASETYO E N, NYANHONGO G S, et al. Antimicrobial enzymes: an emerging strategy to fight microbes and microbial biofilms [J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2013, 8(1): 97-109. |
| 18 | CHAN C T Y, LEE J W, CAMERON D E, et al. 'Deadman' and 'Passcode' microbial kill switches for bacterial containment [J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2016, 12(2): 82-86. |
| 19 | STEEN E J, KANG Y, BOKINSKY G, et al. Microbial production of fatty-acid-derived fuels and chemicals from plant biomass[J]. Nature, 2010, 463(7280): 559-562. |
| 20 | GONG Y, WAN X, JIANG M, et al. Metabolic engineering of microorganisms to produce omega-3 very long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids[J]. Progress in Lipid Research, 2014, 56: 19-35. |
| 21 | LEONG Y K, SHOW P L, OOI C W, et al. Current trends in polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) biosynthesis insights from the recombinant Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2014, 180(06): 52-65. |
| 22 | ARENDT P, POLLIER J, CALLEWAERT N, et al. Synthetic biology for production of natural and new-to-nature terpenoids in photosynthetic organisms[J]. The Plant Journal, 2016, 87(1): 16-37. |
| 23 | JIANG Z, KEMPINSKI C, BUSH C J, et al. Engineering triterpene and methylated triterpene production in plants provides biochemical and physiological insights into terpene metabolism [J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 170(2): 702-716. |
| 24 | MALHOTRA K, SUBRAMANIYAN M, RAWAT K, et al. Compartmentalized metabolic engineering for artemisinin biosynthesis and effective malaria treatment by oral delivery of plant cells [J]. Molecular Plant, 2016, 9(11): 1464-1477. |
| 25 | FREEMONT P S. Synthetic biology industry: data-driven design is creating new opportunities in biotechnology [J]. Emerging Topics in Life Sciences, 2019, 3(5): 651-657. |
| 26 | BALTES N J, VOYTAS D F. Enabling plant synthetic biology through genome engineering [J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2015, 33(2): 120-131. |
| 27 | KÜKEN A, NIKOLOSKI Z. Computational approaches to design and test plant synthetic metabolic pathways [J]. Plant Physiology, 2019, 179(3): 894-906. |
| 28 | POUVREAU B, VANHERCKE T, SINGH S. From plant metabolic engineering to plant synthetic biology: The evolution of the design/build/test/learn cycle [J]. Plant Science, 2018, 273: 3-12. |
| 29 | LIU W, STEWART C N. Plant synthetic biology [J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2015, 20(5): 309-317. |
| 30 | BOCK R. Strategies for metabolic pathway engineering with multiple transgenes [J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2013, 83(1/2): 21-31. |
| 31 | YU W, YAU Y, BIRCHLER J A. Plant artificial chromosome technology and its potential application in genetic engineering [J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2016, 14(5): 1175-1182. |
| 32 | PATRON N J. Blueprints for green biotech: development and application of standards for plant synthetic biology [J]. Biochemical Society Transactions, 2016, 44(3): 702-708. |
| 33 | PATRON N J, ORZAEZ D, MARILLONNET S, et al. Standards for plant synthetic biology: a common syntax for exchange of DNA parts [J]. New Phytol., 2015, 208(1): 13-19. |
| 34 | SCHAUMBERG K A, ANTUNES M S, KASSAW T K, et al. Quantitative characterization of genetic parts and circuits for plant synthetic biology[J]. Nature Methods, 2016, 13(1): 94-100. |
| 35 | KITAOKA N, LU X, YANG B, et al. The application of synthetic biology to elucidation of plant mono-, sesqui-, and diterpenoid metabolism [J]. Molecular Plant, 2015, 8(1): 6-16. |
| 36 | SAINSBURY F, LOMONOSSOFF G P. Transient expressions of synthetic biology in plants [J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2014, 19: 1-7 |
| 37 | AGAPAKIS C M. Designing synthetic biology [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2014, 3(3): 121-128. |
| 38 | CHEE M, YANG R, HUBBELL E, et al. Accessing genetic information with high-density DNA arrays [J]. Science, 1996, 274(5287): 610-614. |
| 39 | CARUTHERS M H. A brief review of DNA and RNA chemical synthesis [J]. Biochemical Society Transactions, 2011, 39(2): 575-580. |
| 40 | HUGHES R A, ELLINGTON A D. Synthetic DNA synthesis and assembly: putting the synthetic in synthetic biology [J]. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 2017, 9(1): A23812. |
| 41 | PALLUK S, ARLOW D H, DE ROND T, et al. De novo DNA synthesis using polymerase-nucleotide conjugates [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(7): 645-650. |
| 42 | TANG L. An enzymatic oligonucleotide synthesizer [J]. Nature Methods, 2018, 15(8): 568. |
| 43 | SLEIGHT S C, BARTLEY B A, LIEVIANT J A, et al. In-Fusion BioBrick assembly and re-engineering[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, 38(8): 2624-2636. |
| 44 | HARTLEY J L, TEMPLE G F, BRASCH M A. DNA cloning using in vitro site-specific recombination[J]. Genome Research, 2000, 10(11): 1788-1795. |
| 45 | ANDERSON J C, DUEBER J E, LEGUIA M, et al. BglBricks: a flexible standard for biological part assembly [J]. Journal of Biological Engineering, 2010, 4(1): 1-12. |
| 46 | ENGLER C, GRUETZNER R, KANDZIA R, et al. Golden gate shuffling: a one-pot DNA shuffling method based on type IIs restriction enzymes [J]. PLoS One, 2009, 4(5): E5553. |
| 47 | WEBER E, ENGLER C, GRUETZNER R, et al. A modular cloning system for standardized assembly of multigene constructs [J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(2): E16765. |
| 48 | SARRION-PERDIGONES A, FALCONI E E, ZANDALINAS S I, et al. GoldenBraid: an iterative cloning system for standardized assembly of reusable genetic modules [J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(7): E21622. |
| 49 | PÜLLMANN P, ULPINNIS C, MARILLONNET S, et al. Golden Mutagenesis: an efficient multi-site-saturation mutagenesis approach by Golden Gate cloning with automated primer design [J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1):10932-10942. |
| 50 | CHIASSON D, GIMÉNEZ-OYA V, BIRCHENEDER M, et al. A unified multi-kingdom Golden Gate cloning platform [J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1):10131-10142. |
| 51 | LEE D J, BINGLE L E H, HEURLIER K, et al. Gene doctoring: a method for recombineering in laboratory and pathogenic Escherichia coli strains [J]. BMC Microbiology, 2009, 9(1): 252-265. |
| 52 | LI Z, XING A, MOON B P, et al. A Cre/loxP-mediated self-activating gene excision system to produce marker gene free transgenic soybean plants [J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2007, 65(3): 329-341. |
| 53 | LLOYD A M, DAVIS R W. Functional expression of the yeast FLP/FRT site-specific recombination system in Nicotiana tabacum [J]. Mol. Gen. Genet., 1994, 242(6): 653-657. |
| 54 | ZHU Q, ZENG D, YU S, et al. From golden rice to aSTARice: bioengineering astaxanthin biosynthesis in rice endosperm [J]. Molecular Plant, 2018, 11(12): 1440-1448. |
| 55 | SHEN B R, WANG L M, LIN X L, et al. Engineering a new chloroplastic photorespiratory bypass to increase photosynthetic efficiency and productivity in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2019, 2(12): 199-214. |
| 56 | CHEN Q J, XIE M, MA X X, et al. MISSA is a highly efficient in vivo DNA assembly method for plant multiple-gene transformation [J]. Plant Physiology, 2010, 153(1):41-51. |
| 57 | ZHANG H, WANG X, DONG L, et al. MISSA 2.0: an updated synthetic biology toolbox for assembly of orthogonal CRISPR/Cas systems [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(41993):1-12. |
| 58 | TANG L, MAO B, LI Y, et al. Knockout of OsNramp5 using the CRISPR/Cas9 system produces low Cd-accumulating indica rice without compromising yield [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017,7(14438):1-12. |
| 59 | LAN S, YUFENG H, YAPING F, et al. Rapid generation of genetic diversity by multiplex CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing in rice [J]. Science China, 2017, 60(5): 506-515. |
| 60 | MA X L. A Robust CRISPR/Cas9 system for convenient, high-efficiency multiplex genome editing in monocot and dicot plants [J]. Molecular Plant, 2015, 8(8):1274-1284. |
| 61 | XING H L, DONG L, WANG Z P, et al. A CRISPR/Cas9 toolkit for multiplex genome editing in plants [J]. BMC Plant Biol., 2014, 14(327):1-12. |
| 62 | ORDON J, GANTNER J, KEMNA J, et al. Generation of chromosomal deletions in dicotyledonous plants employing a user-friendly genome editing toolkit[J]. The Plant Journal, 2017, 89(1): 155-168. |
| 63 | XIE K, MINKENBERG B, YANG Y. Boosting CRISPR/Cas9 multiplex editing capability with the endogenous tRNA-processing system [J]. PNAS, 2015, 112(11): 3570-3575. |
| 64 | LI J, MENG X, ZONG Y, et al. Gene replacements and insertions in rice by intron targeting using CRISPR-Cas9 [J]. Nature Plants, 2016, 2(10):1-6. |
| 65 | QIN L, LI J, WANG Q, et al. High‐efficient and precise base editing of C•G to T•A in the allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) genome using a modified CRISPR /Cas9 system[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 18(1): 45-56. |
| 66 | HUA K, TAO X, YUAN F, et al. Precise A•T to G•C base editing in the rice genome [J]. Molecular Plant, 2018, 11(4): 627-630. |
| 67 | ZONG Y, SONG Q, LI C, et al. Efficient C-to-T base editing in plants using a fusion of nCas9 and human APOBEC3A[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(10): 950-953. |
| 68 | KUANG Y, LI S, REN B, et al. Base-editing-mediated artificial evolution of OsALS1 In Planta to develop novel herbicide-tolerant rice germplasms [J]. Molecular Plant, 2020. |
| 69 | LI C, ZHANG R, MENG X, et al. Targeted, random mutagenesis of plant genes with dual cytosine and adenine base editors [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j: molp.2020.01.010 . |
| 70 | SI X, ZHANG H, WANG Y, et al. Manipulating gene translation in plants by CRISPR-Cas9-mediated genome editing of upstream open reading frames [J]. Nature Protocols, 2020, 15(2): 338-363. |
| 71 | LI X, XIE Y, ZHU Q, et al. Targeted genome editing in genes and cis-regulatory regions improves qualitative and quantitative traits in crops [J]. Molecular Plant, 2017, 10(11): 1368-1370. |
| 72 | ZHANG H, SI X, JI X, et al. Genome editing of upstream open reading frames enables translational control in plants [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(9): 894-898. |
| 73 | WANG J W, GRANDIO E G, NEWKIRK G M, et al. Nanoparticle-mediated genetic engineering of plants [J]. Molecular Plant, 2019, 12(8): 1037-1040. |
| 74 | LIU Q, CHEN B, WANG Q, et al. Carbon nanotubes as molecular transporters for walled plant cells [J]. Nano Letters, 2009, 9(3): 1007-1010. |
| 75 | HUSSAIN H I, YI Z, ROOKES J E, et al. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a biomolecule delivery vehicle in plants [J]. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2013, 15(6): 1-15. |
| 76 | ZHAO X, MENG Z, WANG Y, et al. Pollen magnetofection for genetic modification with magnetic nanoparticles as gene carriers[J]. Nature Plants, 2017, 3(12): 956-964. |
| 77 | RAN Y, LIANG Z, GAO C. Current and future editing reagent delivery systems for plant genome editing [J]. Science China Life Sciences, 2017, 60(5): 490-505. |
| 78 | WOO J W, KIM J, KWON S I, et al. DNA-free genome editing in plants with preassembled CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoproteins [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2015, 33(11): 1162-1164. |
| 79 | LIANG Z, CHEN K, LI T, et al. Efficient DNA-free genome editing of bread wheat using CRISPR/Cas9 ribonucleoprotein complexes[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1):14261-14265. |
| 80 | ALTPETER F, SPRINGER N M, BARTLEY L E, et al. Advancing crop transformation in the era of genome editing [J]. The Plant Cell, 2016: 196-2016. |
| 81 | MAHER M F, NASTI R A, VOLLBRECHT M, et al. Plant gene editing through de novo induction of meristems[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(1): 84-89. |
| 82 | REED J, OSBOURN A. Engineering terpenoid production through transient expression in Nicotiana benthamiana [J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2018, 37(10): 1431-1441. |
| 83 | VERMA D, DANIELL H. Chloroplast vector systems for biotechnology applications [J]. Plant Physiology, 2007, 145(4): 1129-1143. |
| 84 | FUENTES P, ZHOU F, ERBAN A, et al. A new synthetic biology approach allows transfer of an entire metabolic pathway from a medicinal plant to a biomass crop [J]. eLife, 2016,5. |
| 85 | OEY M, LOHSE M, KREIKEMEYER B, et al. Exhaustion of the chloroplast protein synthesis capacity by massive expression of a highly stable protein antibiotic [J]. The Plant Journal, 2009, 57(3): 436-445. |
| 86 | BOCK R. Engineering plastid genomes: methods, tools, and applications in basic research and biotechnology [J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2015, 66: 211-241. |
| 87 | KWAK S, LEW T T S, SWEENEY C J, et al. Chloroplast-selective gene delivery and expression in planta using chitosan-complexed single-walled carbon nanotube carriers[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2019, 14(5): 447-455. |
| 88 | GORANTALA J, GROVER S, RAHI A, et al. Generation of protective immune response against anthrax by oral immunization with protective antigen plant-based vaccine[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2014, 176: 1-10. |
| 89 | HASSAN S W, WAHEED M T, MULLER M, et al. Expression of HPV-16 L1 capsomeres with glutathione-S-transferase as a fusion protein in tobacco plastids: an approach for a capsomere-based HPV vaccine[J]. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother., 2014, 10(10): 2975-2982. |
| 90 | LEE S, LI B, JIN S, et al. Expression and characterization of antimicrobial peptides Retrocyclin-101 and Protegrin-1 in chloroplasts to control viral and bacterial infections[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2011, 9(1): 100-115. |
| 91 | STEGEMANN S, BOCK R. Exchange of genetic material between cells in plant tissue grafts [J]. Science, 2009, 324(5927): 649-651. |
| 92 | STEGEMANN S, KEUTHE M, GREINER S, et al. Horizontal transfer of chloroplast genomes between plant species[J]. PNAS, 2012, 109(7): 2434-2438. |
| 93 | YU W, YAU Y, BIRCHLER J A. Plant artificial chromosome technology and its potential application in genetic engineering [J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2016, 14 (5): 1175-1182. |
| 94 | BIRCHLER J A, GRAHAM N D, SWYERS N C, et al. Plant minichromosomes[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2016, 37(4): 135-142. |
| 95 | BIRCHLER J A, SWYERS N C. Engineered minichromosomes in plants [J]. Experimental Cell Research, 2020, 388(2): 111852. |
| 96 | YU W, HAN F, BIRCHLER J A. Engineered minichromosomes in plants [J]. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 2007, 18(5): 425-431. |
| 97 | GAETA R T, MASONBRINK R E, KRISHNASWAMY L, et al. Synthetic chromosome platforms in plants [J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2012, 63(1): 307-330. |
| 98 | ANANIEV E V, ANANIEV E V, WU C, et al. Artificial chromosome formation in maize (Zea mays L.)[J]. Chromosoma, 2009, 118(2): 157-177. |
| 99 | DAWE R K. Charting the path to fully synthetic plant chromosomes [J]. Exp. Cell Res., 2020,390(1): 111951. |
| 100 | FENG C, YUAN J, BAI H, et al. The deposition of CENH3 in maize is stringently regulated [J]. The Plant Journal, 2019.DOI: 10.1111/tpj.14606 . |
| 101 | BIRCHLER J A. Engineered minichromosomes in plants [J]. Chromosome Research, 2015, 23(1): 77-85. |
| 102 | BIRCHLER J A. Promises and pitfalls of synthetic chromosomes in plants [J]. Trends Biotechnol, 2015, 33(3): 189-194. |
| 103 | WALIA A, WAADT R, JONES A M. Genetically encoded biosensors in plants: pathways to discovery [J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2018, 69: 497-524. |
| 104 | NAKAI J, OHKURA M. Probing calcium ions with biosensors [J]. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev., 2003, 20: 3-21. |
| 105 | LIAO C, SMET W, BRUNOUD G, et al. Reporters for sensitive and quantitative measurement of auxin response [J]. Nature Methods, 2015, 12(3): 207-210. |
| 106 | BENCIVENGA S, SIMONINI S, BENKOVA E, et al. The transcription factors BEL1 and SPL are required for cytokinin and auxin signaling during ovule development in Arabidopsis [J]. The Plant Cell, 2012, 7(24): 2886-2897. |
| 107 | STEPANOVA A N, YUN J, LIKHACHEVA A V, et al. Multilevel Interactions between Ethylene and Auxin in Arabidopsis Roots [J]. The Plant Cell, 2007, 19(7): 2169-2185. |
| 108 | KIM T, HAUSER F, HA T, et al. Chemical genetics reveals negative regulation of abscisic acid signaling by a plant immune response pathway [J]. Current Biology, 2011, 21(11): 990-997. |
| 109 | SADANANDOM A, NAPIER R M. Biosensors in plants [J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2010, 13(6): 736-743. |
| 110 | JONES A M, Å DANIELSON J, MANOJKUMAR S N, et al. Abscisic acid dynamics in roots detected with genetically encoded FRET sensors[J]. eLife, 2014,3:E01741. |
| 111 | MUKHERJEE P, BANERJEE S, WHEELER A, et al. Live imaging of inorganic phosphate in plants with cellular and subcellular resolution [J]. Plant Physiol., 2015, 167(3): 628-638. |
| 112 | LEGRIS M, KLOSE C, BURGIE E S, et al. Phytochrome B integrates light and temperature signals in Arabidopsis [J]. Science, 2016, 354(6314): 897-900. |
| 113 | WONG M H, GIRALDO J P, KWAK S, et al. Nitroaromatic detection and infrared communication from wild-type plants using plant nanobionics [J]. Nature Materials, 2017, 16(2): 264-272. |
| 114 | CHIDA H, NAKAZAWA A, AKAZAKI H, et al. Expression of the algal cytochrome c6 gene in Arabidopsis enhances photosynthesis and growth [J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2007, 48(7): 948-957. |
| 115 | WILLCOX D, CHAPPELL B G N, HOGG K F, et al. A general catalytic β-C—H carbonylation of aliphatic amines to β-lactams[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6314): 851-857. |
| 116 | LIEMAN-HURWITZ J, RACHMILEVITCH S, MITTLER R, et al. Enhanced photosynthesis and growth of transgenic plants that express ictB, a gene involved in HCO3 - accumulation in cyanobacteria [J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2003, 1(1): 43-50. |
| 117 | GONG H Y, LI Y, FANG G, et al. Transgenic rice expressing Ictb and FBP/Sbpase derived from cyanobacteria exhibits enhanced photosynthesis and mesophyll conductance to CO2 [J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(10): E140928. |
| 118 | LIN M T, OCCHIALINI A, ANDRALOJC P J, et al. A faster Rubisco with potential to increase photosynthesis in crops [J]. Nature, 2014, 513(7519): 547-550. |
| 119 | WANG H, YAN X, AIGNER H, et al. Rubisco condensate formation by CcmM in β-carboxysome biogenesis[J]. Nature, 2019, 566(7742): 131-135. |
| 120 | SCHWANDER T, SCHADA VON BORZYSKOWSKI L, BURGENER S, et al. A synthetic pathway for the fixation of carbon dioxide in vitro [J]. Science, 2016, 354(6314): 900-904. |
| 121 | BETTI M, BAUWE H, BUSCH F A, et al. Manipulating photorespiration to increase plant productivity: recent advances and perspectives for crop improvement [J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(10): 2977-2988. |
| 122 | SOUTH P F, CAVANAGH A P, LIU H W, et al. Synthetic glycolate metabolism pathways stimulate crop growth and productivity in the field[J]. Science, 2019, 363(6422): T9077. |
| 123 | SAVKA M A, DESSAUX Y, GARDEENER M S, et al. The “Biased Rhizosphere” concept and advances in the omics era to study bacterial competitiveness and persistence in the phytosphere[M] Hoboken: Wiley-Blackwell, 2013. |
| 124 | GEDDES B A, PARAMASIVAN P, JOFFRIN A, et al. Engineering transkingdom signalling in plants to control gene expression in rhizosphere bacteria[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1):3430-3440. |
| 125 | ROGERS C, OLDROYD G E D. Synthetic biology approaches to engineering the nitrogen symbiosis in cereals [J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2014, 65(8): 1939-1946. |
| 126 | ALTÚZAR-MOLINA A, LOZANO L, ORTÍZ-BERROCAL M, et al. Expression of the legume-specific nod factor receptor proteins alters developmental and immune responses in rice[J]. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 2020. DOI: 10.1007/s11105-019-01188-9 . |
| 127 | GEDDES B A, RYU M, MUS F, et al. Use of plant colonizing bacteria as chassis for transfer of N2-fixation to cereals[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2015, 32(4): 216-222. |
| 128 | BAGESHWAR U K, SRIVASTAVA M, PARDHA-SARADHI P, et al. An environment friendly engineered Azotobacter can replace substantial amount of urea fertilizer and yet sustain same wheat yield [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2017(5): 517-590. |
| 129 | OLDROYD G E, DIXON R. Biotechnological solutions to the nitrogen problem [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2014, 26:19-24. |
| 130 | ZHU Q, RILEY W J, TANG J, et al. Multiple soil nutrient competition between plants, microbes, and mineral surfaces: model development, parameterization, and example applications in several tropical forests [J]. Biogeosciences, 2016, 13(1): 341-363. |
| 131 | RICHARDSON A E, SIMPSON R J. Soil Microorganisms mediating phosphorus availability [J]. Plant Physiology, 2011, 156(3): 989-996. |
| 132 | RAGHOTHAMA K G, KARTHIKEYAN A S. Phosphate acquisition [J]. Plant and Soil, 2005, 274(1/2): 37-49. |
| 133 | LIU P, CAI Z, CHEN Z, et al. A root-associated purple acid phosphatase, SgPAP23, mediates extracellular phytate-P utilization in Stylosanthes guianensis [J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2018, 41(12): 2821-2834. |
| 134 | MA X, WRIGHT E, GE Y, et al. Improving phosphorus acquisition of white clover (Trifolium repens L.) by transgenic expression of plant-derived phytase and acid phosphatase genes[J]. Plant Science, 2009, 176(4): 479-488. |
| 135 | LÓPEZ-BUCIO J, de la VEGA O M, GUEVARA-GARCÍA A, et al. Enhanced phosphorus uptake in transgenic tobacco plants that overproduce citrate[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2000, 18(4): 450-453. |
| 136 | SHAHZAD Z, AMTMANN A. Food for thought: how nutrients regulate root system architecture [J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2017, 39: 80-87. |
| 137 | CASTRILLO G, TEIXEIRA P J P L, PAREDES S H, et al. Root microbiota drive direct integration of phosphate stress and immunity[J]. Nature, 2017, 543(7646): 513-518. |
| 138 | ZHU J K. Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants [J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2002, 53(1): 247-273. |
| 139 | RODRIGUEZ P L, MÁRQUEZ J A, DUPEUX F, et al. The abscisic acid receptor PYR1 in complex with abscisic acid [J]. Nature, 2009, 462(7273): 665-668. |
| 140 | PARK S, PETERSON F C, MOSQUNA A, et al. Agrochemical control of plant water use using engineered abscisic acid receptors[J]. Nature, 2015, 520(7548): 545-548. |
| 141 | NEMHAUSER J L, TORII K U. Plant synthetic biology for molecular engineering of signalling and development [J]. Nature Plants, 2016, 2(3):16010. |
| 142 | PARK S Y, FUNG P, NISHIMURA N, et al. Abscisic acid inhibits type 2C protein phosphatases via the PYR/PYL family of START proteins[J]. Science, 2009, 324(5930): 1068-1071. |
| 143 | CAO M, LIU X, ZHANG Y, et al. An ABA-mimicking ligand that reduces water loss and promotes drought resistance in plants [J]. Cell Research, 2013, 23(8): 1043-1054. |
| 144 | OKAMOTO M, PETERSON F C, DEFRIES A, et al. Activation of dimeric ABA receptors elicits guard cell closure, ABA-regulated gene expression, and drought tolerance[J]. PNAS, 2013, 110(29): 12132-12137. |
| 145 | CAO M, ZHANG Y, LIU X, et al. Combining chemical and genetic approaches to increase drought resistance in plants[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1):1183. |
| 146 | VAIDYA A S, HELANDER J D M, PETERSON F C, et al. Dynamic control of plant water use using designed ABA receptor agonists [J]. Science, 2019, 3 66(6464): W8848. |
| 147 | OGO Y, OZAWA K, ISHIMARU T, et al. Transgenic rice seed synthesizing diverse flavonoids at high levels: a new platform for flavonoid production with associated health benefits [J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2013, 11(6): 734-746. |
| 148 | YAN S, CHEN N, HUANG Z, et al. Anthocyanin Fruit encodes an R2R3‐MYB transcription factor, SlAN2-like, activating the transcription of SlMYBATV to fine‐tune anthocyanin content in tomato fruit[J]. New Phytologist, 2019, 225(5): 2048-2063. |
| 149 | ZHANG Y, BUTELLI E, ALSEEKH S, et al. Multi-level engineering facilitates the production of phenylpropanoid compounds in tomato [J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6(1). DOI: 10.1038/ncomms9635 . |
| 150 | JIAN W, CAO H, YUAN S, et al. SlMYB75, an MYB-type transcription factor, promotes anthocyanin accumulation and enhances volatile aroma production in tomato fruits[J]. Horticulture Research, 2019, 6(1). DOI:10.1038/S41438-018-0098-y . |
| 151 | FITZPATRICK T B, BASSET G J C, BOREL P, et al. Vitamin deficiencies in humans: can plant science help? [J]. The Plant Cell, 2012, 24(2): 395-414. |
| 152 | YE X, AL-BABILI S, KLOTI A, et al. Engineering the provitamin A (beta-carotene) biosynthetic pathway into (carotenoid-free) rice endosperm [J]. Science, 2000, 287(5451): 303-305. |
| 153 | CHE P, ZHAO Z, GLASSMAN K, et al. Elevated vitamin E content improves all-trans β-carotene accumulation and stability in biofortified sorghum [J]. PNAS, 2016, 113(39): 11040-11045. |
| 154 | QINLONG Z S Y D. Development of "purple endosperm rice" by engineering anthocyanin biosynthesis in the endosperm with a high-efficiency transgene stacking System [J]. Molecular Plant, 10(7):918-929. |
| 155 | LIU X, LI S, YANG W, et al. Synthesis of seed-specific bidirectional promoters for metabolic engineering of anthocyanin-rich maize [J]. Plant Cell Physiol., 2018, 59(10): 1942-1955. |
| 156 | MILLER B D D, WELCH R M. Food system strategies for preventing micronutrient malnutrition [J]. Food Policy, 2013, 42: 115-128. |
| 157 | MINHAS A P, TULI R, PURI S. Pathway editing targets for thiamine biofortification in rice grains [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9:975-982. |
| 158 | DONG W, THOMAS N, RONALD P C, et al. Overexpression of thiamin biosynthesis genes in rice increases leaf and unpolished grain thiamin content but not resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 616-626. |
| 159 | CHEN H, XIONG L. Enhancement of vitamin B6 levels in seeds through metabolic engineering [J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2009, 7(7): 673-681. |
| 160 | BAGRI D S, UPADHYAYA D C, KUMAR A, et al. Overexpression of PDX-II gene in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) leads to the enhanced accumulation of vitamin B6 in tuber tissues and tolerance to abiotic stresses[J]. Plant Science, 2018, 272: 267-275. |
| 161 | LI R, WANG Q, MCHUGHEN A. Chinese government reaffirms backing for GM products [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2015, 33(10): 1029. |
| 162 | NAQVI S, ZHU C, FARRE G, et al. Transgenic multivitamin corn through biofortification of endosperm with three vitamins representing three distinct metabolic pathways[J]. PNAS, 2009, 106(19): 7762-7767. |
| 163 | NUNES A C S, KALKMANN D C, ARAGÃO F J L. Folate biofortification of lettuce by expression of a codon optimized chicken GTP cyclohydrolase I gene[J]. Transgenic Research, 2009, 18(5): 661-667. |
| 164 | BLANCQUAERT D, STOROZHENKO S, DAELE J VAN, et al. Enhancing pterin and para-aminobenzoate content is not sufficient to successfully biofortify potato tubers and Arabidopsis thaliana plants with folate[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2013, 64(12): 3899-3909. |
| 165 | DIAZ D L G R, GREGORY J R, HANSON A D. Folate biofortification of tomato fruit [J]. PNAS, 2007, 104(10): 4218-4222. |
| 166 | BLANCQUAERT D, DAELE J VAN, STROBBE S, et al. Improving folate (vitamin B9) stability in biofortified rice through metabolic engineering[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2015, 33(10): 1076-1078. |
| 167 | DE LEPELEIRE J, STROBBE S, VERSTRAETE J, et al. Folate biofortification of potato by tuber-specific expression of four folate biosynthesis genes[J]. Molecular Plant, 2018, 11(1): 175-188. |
| 168 | BULLEY S, WRIGHT M, ROMMENS C, et al. Enhancing ascorbate in fruits and tubers through over-expression of the l-galactose pathway gene GDP-l-galactose phosphorylase[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2012, 10(4): 390-397. |
| 169 | GEST N, GARCHERY C, GAUTIER H, et al. Light‐dependent regulation of ascorbate in tomato by a monodehydroascorbate reductase localized in peroxisomes and the cytosol[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2013, 11(3): 344-354. |
| 170 | LAING W A, MARTÍNEZ-SÁNCHEZ M, WRIGHT M A, et al. An upstream open reading frame is essential for feedback regulation of ascorbate biosynthesis in Arabidopsis [J]. The Plant Cell, 2015, 27(3): 772-786. |
| 171 | ZHANG H, SI X, JI X, et al. Genome editing of upstream open reading frames enables translational control in plants[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 3 6(9): 894-898. |
| 172 | LI T, YANG X, YU Y, et al. Domestication of wild tomato is accelerated by genome editing [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(12): 1160-1163. |
| 173 | ZHANG L, LUO Y, LIU B, et al. Overexpression of the maize γ-tocopherol methyltransferase gene (ZmTMT) increases α-tocopherol content in transgenic Arabidopsis and maize seeds[J]. Transgenic Research, 2020, 29(1): 95-104. |
| 174 | KONDA A R, NAZARENUS T J, NGUYEN H, et al. Metabolic engineering of soybean seeds for enhanced vitamin E tocochromanol content and effects on oil antioxidant properties in polyunsaturated fatty acid-rich germplasm[J]. Metab. Eng., 2020, 57: 63-73. |
| 175 | LIU D J, WANG Y B, GUO C H, et al. Enhanced iron and zinc accumulation in genetically engineered wheat plants using sickle alfalfa (Medicago falcata L.) ferritin gene[J]. Cereal Research Communications, 2016, 44(1): 24-34. |
| 176 | MASUDA H, USUDA K, KOBAYASHI T, et al. Overexpression of the barley nicotianamine synthase gene HvNAS1 increases iron and zinc concentrations in rice grains[J]. Rice, 2009, 2(4): 155-166. |
| 177 | NOZOYE T. The Nicotianamine synthase gene is a useful candidate for improving the nutritional qualities and Fe-deficiency tolerance of various crops [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00340 . |
| 178 | NARAYANAN N, BEYENE G, CHAUHAN R D, et al. Biofortification of field-grown cassava by engineering expression of an iron transporter and ferritin[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2019, 37(2): 144-151. |
| 179 | BANAKAR R, ALVAREZ FERNÁNDEZ Á, ABADÍA J, et al. The expression of heterologous Fe (III) phytosiderophore transporter HvYS1 in rice increases Fe uptake, translocation and seed loading and excludes heavy metals by selective Fe transport [J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 15(4): 423-432. |
| 180 | LI S, LIU X, ZHOU X, et al. Improving zinc and iron accumulation in maize grains using the zinc and iron transporter ZmZIP5 [J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2019, 60(9): 2077-2085. |
| 181 | ALURU M R, RODERMEL S R, REDDY M B. Genetic modification of low phytic acid 1-1 maize to enhance iron content and bioavailability[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2011, 59(24): 12954-12962. |
| 182 | BOONYAVES K, WU T, GRUISSEM W, et al. Enhanced grain iron levels in rice expressing an IRON-REGULATED METAL TRANSPORTER, NICOTIANAMINE SYNTHASE, and FERRITIN gene cassette [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8:130-140. |
| 183 | KRAEMER U. The dilemma of controlling heavy metal accumulation in plants [J]. New Phytologist, 2009, 181(1): 3-5. |
| 184 | UENO D, YAMAJI N, KONO I, et al. Gene limiting cadmium accumulation in rice [J]. PNAS, 2010, 107(38): 16500-16505. |
| 185 | MIETTINEN K, DONG L, NAVROT N, et al. The seco-iridoid pathway from Catharanthus roseus [J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5(1): 3606. |
| 186 | LAU W, SATTELY E S. Six enzymes from mayapple that complete the biosynthetic pathway to the etoposide aglycone [J]. Science, 2015, 349(6253): 1224-1228. |
| 187 | POLTURAK G, BREITEL D, GROSSMAN N, et al. Elucidation of the first committed step in betalain biosynthesis enables the heterologous engineering of betalain pigments in plants[J]. New Phytologist, 2016, 210(1): 269-283. |
| 188 | TORRENS-SPENCE M P, PLUSKAL T, LI F S, et al. Complete pathway elucidation and heterologous reconstitution of Rhodiola salidroside biosynthesis[J]. Molecular Plant, 2018, 11(1): 205-217. |
| 189 | WANG B, KASHKOOLI A B, SALLETS A, et al. Transient production of artemisinin in Nicotiana benthamiana is boosted by a specific lipid transfer protein from A. annua [J]. Metab. Eng., 2016, 38: 159-169. |
| 190 | LI J, MUTANDA I, WANG K, et al. Chloroplastic metabolic engineering coupled with isoprenoid pool enhancement for committed taxanes biosynthesis in Nicotiana benthamiana [J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 4850. |
| 191 | LI Y, WANG H, ZHANG Y, et al. Can the world’s favorite fruit, tomato, provide an effective biosynthetic chassis for high-value metabolites?[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2018, 37(10): 1443-1450. |
| 192 | POLTURAK G, GROSSMAN N, VELA-CORCIA D, et al. Engineered gray mold resistance, antioxidant capacity, and pigmentation in betalain-producing crops and ornamentals[J]. PNAS, 2017, 114(34): 9062-9067. |
| 193 | NOGUEIRA M, ENFISSI E M A, MARTÍNEZ VALENZUELA M E, et al. Engineering of tomato for the sustainable production of ketocarotenoids and its evaluation in aquaculture feed[J]. PNAS, 2017, 114(41): 10876-10881. |
| 194 | SONAWANE P D, POLLIER J, PANDA S, et al. Plant cholesterol biosynthetic pathway overlaps with phytosterol metabolism[J]. Nature Plants, 2017, 3(1): 16205. DOI: 10.1038/nplants. 2016. 205 . |
| 195 | XIAO H, ZHANG Y, WANG M. Discovery and engineering of cytochrome P450s for terpenoid biosynthesis [J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2019, 37(6): 618-631. |
| 196 | LI D W, MA Y S, ZHOU Y, et al. A structural and data-driven approach to engineering a plant cytochrome P450 enzyme [J]. Science China Life Sciences, 2019, 62(7): 873-882. |
| 197 | CHOI K R, JANG W D, YANG D, et al. Systems metabolic engineering strategies: integrating systems and synthetic biology with metabolic engineering [J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2019, 37(8): 817-837. |
| 198 | NANDY D, MAITY A, MITRA A K. Target-specific gene delivery in plant systems and their expression: insights into recent developments [J]. Journal of Biosciences, 2020, 45(1). DOI: 10.1007/s12038-020-0008-y . |
| 199 | ZUO E, SUN Y, WEI W, et al. Cytosine base editor generates substantial off-target single-nucleotide variants in mouse embryos [J]. Science, 2019, 364(6437): 289. |
| 200 | SCHIEMANN J, DIETZ-PFEILSTETTER A, HARTUNG F, et al. Risk assessment and regulation of plants modified by modern biotechniques: current status and future challenges [J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2019, 70(1): 699-726. |
| 201 | WANG F, ZHANG W. Synthetic biology: recent progress, biosafety and biosecurity concerns, and possible solutions [J]. Journal of Biosafety and Biosecurity, 2019, 1(1): 22-30. |
| 202 | WARNER A. Against the grain [J]. New Scientist, 2017, 235(3144): 24-25. |
| 203 | GÓMEZ-TATAY L, GÓMEZ-TATAY L, HERNÁNDEZ-ANDREU J M. Biosafety and biosecurity in synthetic biology: a review [J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2019, 49(17): 1587-1621. |
| 204 | LI Q, HAN X. Self-assembled "breathing" grana-like cisternae stacks [J]. Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(25): E1707482. |
| [1] | 郭姝媛, 张倩楠, 姑丽克孜·买买提热夏提, 杨一群, 于涛. 液体生物燃料合成与炼制的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 18-44. |
| [2] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [3] | 赵亮, 李振帅, 付丽平, 吕明, 王士安, 张全, 刘立成, 李福利, 刘自勇. 生物转化一碳化合物原料产油脂与单细胞蛋白研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1300-1318. |
| [4] | 竺方欢, 岑雪聪, 陈振. 微生物合成二元醇研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1367-1385. |
| [5] | 禹伟, 高教琪, 周雍进. 一碳生物转化合成有机酸的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1169-1188. |
| [6] | 陈锡玮, 张华然, 邹懿. 真菌源非核糖体肽类药物生物合成及代谢工程[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 571-592. |
| [7] | 谢皇, 郑义蕾, 苏依婷, 阮静怡, 李永泉. 放线菌聚酮类化合物生物合成体系重构研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| [8] | 陈盈盈, 刘扬, 史俊杰, 马俊英, 鞠建华. CRISPR/Cas基因编辑及其新兴技术在丝状真菌研究中的系统应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 672-693. |
| [9] | 惠真, 唐啸宇. CRISPR/Cas9编辑系统在微生物天然产物研究中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 658-671. |
| [10] | 赵静宇, 张健, 祁庆生, 王倩. 基于细菌双组分系统的生物传感器的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 38-52. |
| [11] | 许志锰, 谢震. 引导编辑研究进展及其应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 1-15. |
| [12] | 孙绘梨, 崔金玉, 栾国栋, 吕雪峰. 面向高效光驱固碳产醇的蓝细菌合成生物技术研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(6): 1161-1177. |
| [13] | 晏雄鹰, 王振, 娄吉芸, 张皓瑜, 黄星宇, 王霞, 杨世辉. 生物燃料高效生产微生物细胞工厂构建研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(6): 1082-1121. |
| [14] | 陈雅如, 曹英秀, 宋浩. 电活性微生物基因编辑与转录调控技术进展与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(6): 1281-1299. |
| [15] | 程真真, 张健, 高聪, 刘立明, 陈修来. 代谢工程改造微生物利用甲酸研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(4): 756-778. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||