合成生物学 ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (5): 892-903.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-024
生物设施平台及其工业应用
赵国淼1,2, 杨鑫1,2, 张媛1,2, 王靖1,2, 谭剑1,2, 魏超1,2, 周娜娜1,2, 李凡1,2, 王小艳1,2
- 1.中粮营养健康研究院有限公司,北京 102209
2.营养健康与食品安全北京市重点实验室,北京 102209
-
收稿日期:2023-03-17修回日期:2023-05-08出版日期:2023-10-31发布日期:2023-11-15 -
通讯作者:王小艳 -
作者简介:赵国淼 (1989—),男,博士,工程师。研究方向为工业微生物改造与高通量筛选、计算生物学与生物信息学。E-mail:zhaoguomiao@cofco.com王小艳 (1980—),女,博士,正高级工程师。研究方向围绕淀粉质原料生物加工过程工业菌株和酶制剂的开发,主要聚焦生物燃料乙醇、生物基材料、功能糖等领域。E-mail:wangxiaoyan@cofco.com -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划“合成生物学”重点专项,合成生物学自动化铸造平台关键技术研发(2018YFA0902900)
Biofoundry and its industrial application
ZHAO Guomiao1,2, YANG Xin1,2, ZHANG Yuan1,2, WANG Jing1,2, TAN Jian1,2, WEI Chao1,2, ZHOU Nana1,2, LI Fan1,2, WANG Xiaoyan1,2
- 1.Nutrition & Health Research Institute,COFCO Corporation,Beijing 102209,China
2.Beijing Key Laboratory of Nutrition,Health and Food Safety,Beijing 102209,China
-
Received:2023-03-17Revised:2023-05-08Online:2023-10-31Published:2023-11-15 -
Contact:WANG Xiaoyan
摘要:
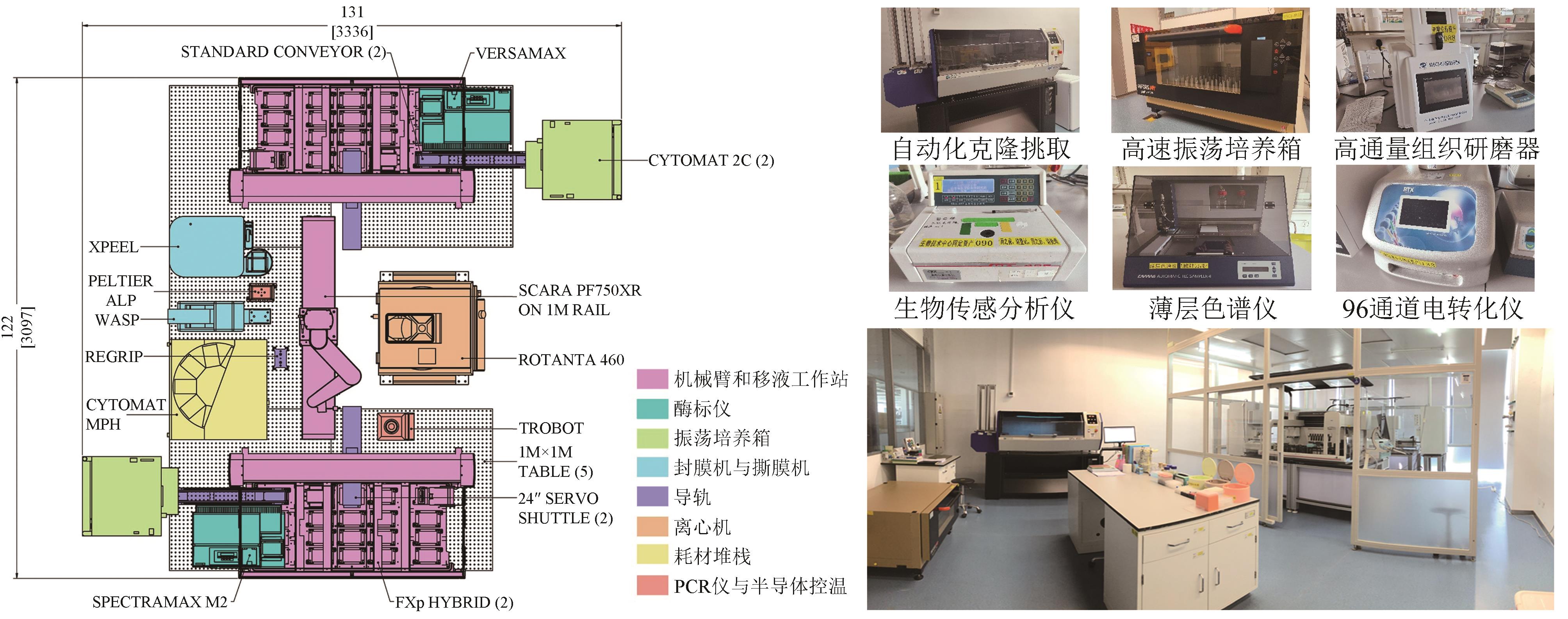
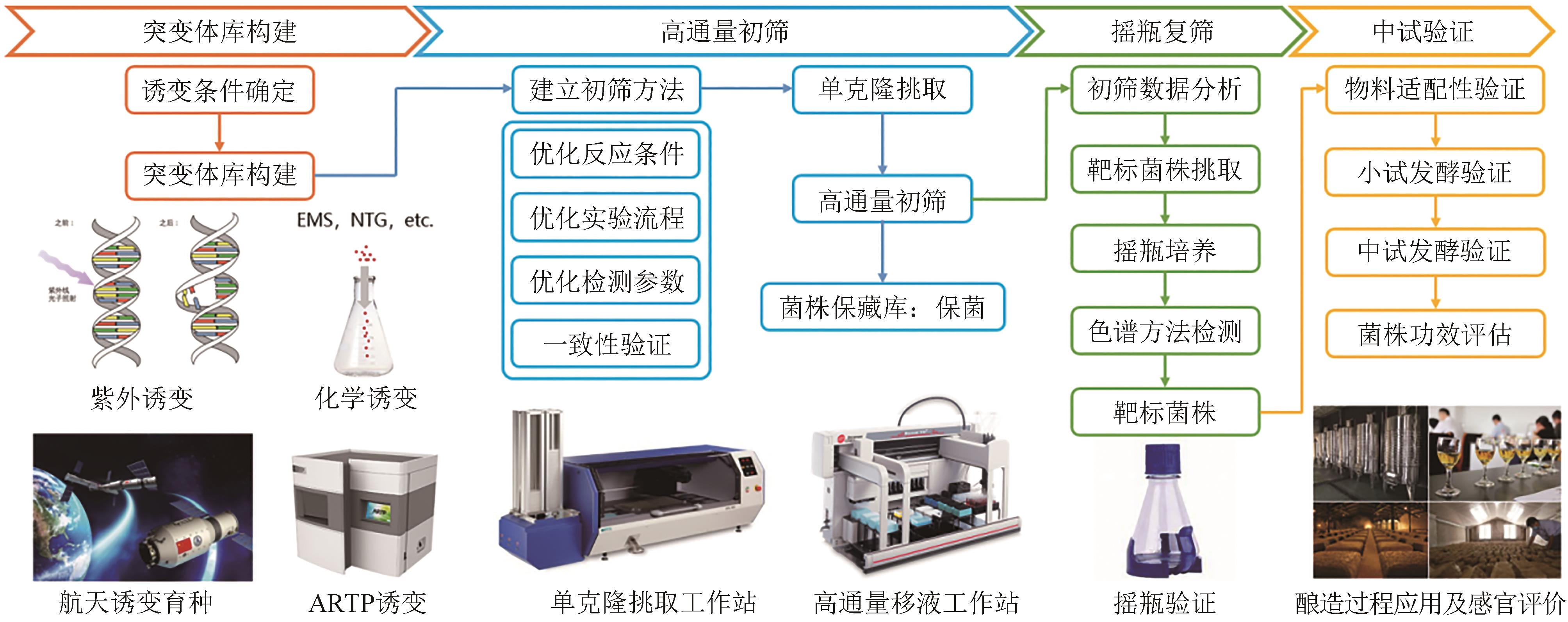
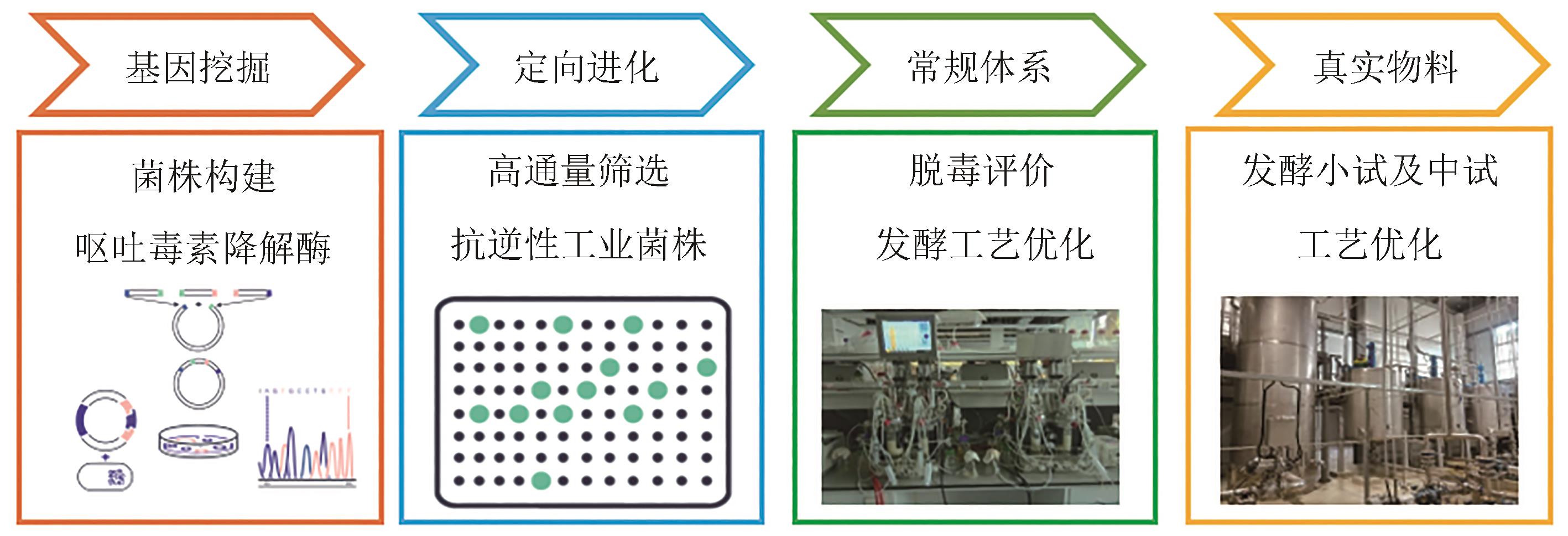
传统菌株改造和筛选实验存在操作烦琐、耗时、易错、难以规模化等问题,生物设施平台将自动化、机器人技术、数据分析与生物研究相结合,通过导轨和机械手臂实现自动化操作,提高了实验操作的稳定性,通过缩小培养体积(微孔板或微液滴),提高了培养和筛选通量,解决了上述问题,大大提高了研发效率。本文简单介绍了自动化设施平台的发展和常见的高通量检测方法,重点介绍了中粮营养健康研究院的自动化设施平台,并结合开展的项目叙述了平台在生物燃料菌株开发、传统酿造菌株筛选、酶的定向进化和筛选等领域的应用,可以预见自动化和高通量化在菌株改造和筛选方向巨大的应用价值。实验室自动化是涉及机械工程、自动化、计算机和生命科学等学科的交叉领域,需要各方面共同努力,才能推动实验室向更高程度的自动化和智能化方向发展。
中图分类号:
引用本文
赵国淼, 杨鑫, 张媛, 王靖, 谭剑, 魏超, 周娜娜, 李凡, 王小艳. 生物设施平台及其工业应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 892-903.
ZHAO Guomiao, YANG Xin, ZHANG Yuan, WANG Jing, TAN Jian, WEI Chao, ZHOU Nana, LI Fan, WANG Xiaoyan. Biofoundry and its industrial application[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(5): 892-903.
| 筛选方法 | 检测信号 | 灵敏度 | 通量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MTP[ | 吸光度和荧光强度 | 一般 | 106个/天 |
| FACS[ | 荧光强度 | 高 | 108个/时 |
| DMF[ | 荧光强度、拉曼光谱、吸光度、质谱 | 高 | 108个/天 |
表1 三种筛选方法对比
Table 1 Comparison of three screening methods
| 筛选方法 | 检测信号 | 灵敏度 | 通量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MTP[ | 吸光度和荧光强度 | 一般 | 106个/天 |
| FACS[ | 荧光强度 | 高 | 108个/时 |
| DMF[ | 荧光强度、拉曼光谱、吸光度、质谱 | 高 | 108个/天 |
| 1 | LEE S Y, KIM H U, CHAE T U, et al. A comprehensive metabolic map for production of bio-based chemicals[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2019, 2(1): 18-33. |
| 2 | CHEN X L, GAO C, GUO L, et al. DCEO biotechnology: tools to design, construct, evaluate, and optimize the metabolic pathway for biosynthesis of chemicals[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(1): 4-72. |
| 3 | RUGBJERG P, SOMMER M O A. Overcoming genetic heterogeneity in industrial fermentations[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2019, 37(8): 869-876. |
| 4 | WEHRS M, TANJORE D, ENG T, et al. Engineering robust production microbes for large-scale cultivation[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 2019, 27(6): 524-537. |
| 5 | LEE S Y, KIM H U. Systems strategies for developing industrial microbial strains[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2015, 33(10): 1061-1072. |
| 6 | ZHANG X, ZHANG X M, XU G Q, et al. Integration of ARTP mutagenesis with biosensor-mediated high-throughput screening to improve L-serine yield in Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(14): 5939-5951. |
| 7 | GU Y, XU X H, WU Y K, et al. Advances and prospects of Bacillus subtilis cellular factories: from rational design to industrial applications[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 50: 109-121. |
| 8 | CARBONELL P, JERVIS A J, ROBINSON C J, et al. An automated Design-Build-Test-Learn pipeline for enhanced microbial production of fine chemicals[J]. Communications Biology, 2018, 1: 66. |
| 9 | ZENG W Z, GUO L K, XU S, et al. High-throughput screening technology in industrial biotechnology[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2020, 38(8): 888-906. |
| 10 | QUAGLIA D, EBERT M C C J C, MUGFORD P F, et al. Enzyme engineering: a synthetic biology approach for more effective library generation and automated high-throughput screening[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(2): e0171741. |
| 11 | ZHANG Y V, ROCKWOOD A. Impact of automation on mass spectrometry[J]. Clinica Chimica Acta, 2015, 450: 298-303. |
| 12 | LONGWELL C K, LABANIEH L, COCHRAN J R. High-throughput screening technologies for enzyme engineering[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2017, 48: 196-202. |
| 13 | RAN C, MISHRA S, TONG S, et al. Engineering biological systems using automated biofoundries[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 42: 98-108. |
| 14 | ZHANG J Z, CHEN Y C, FU L H, et al. Accelerating strain engineering in biofuel research via build and test automation of synthetic biology[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2021, 67: 88-98. |
| 15 | LE FEUVRE R A, SCRUTTON N S. A living foundry for Synthetic Biological Materials: a synthetic biology roadmap to new advanced materials[J]. Synthetic & Systems Biotechnology, 2018, 3(2): 105-112. |
| 16 | HILLSON N, CADDICK M, CAI Y Z, et al. Building a global alliance of biofoundries[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 2040. |
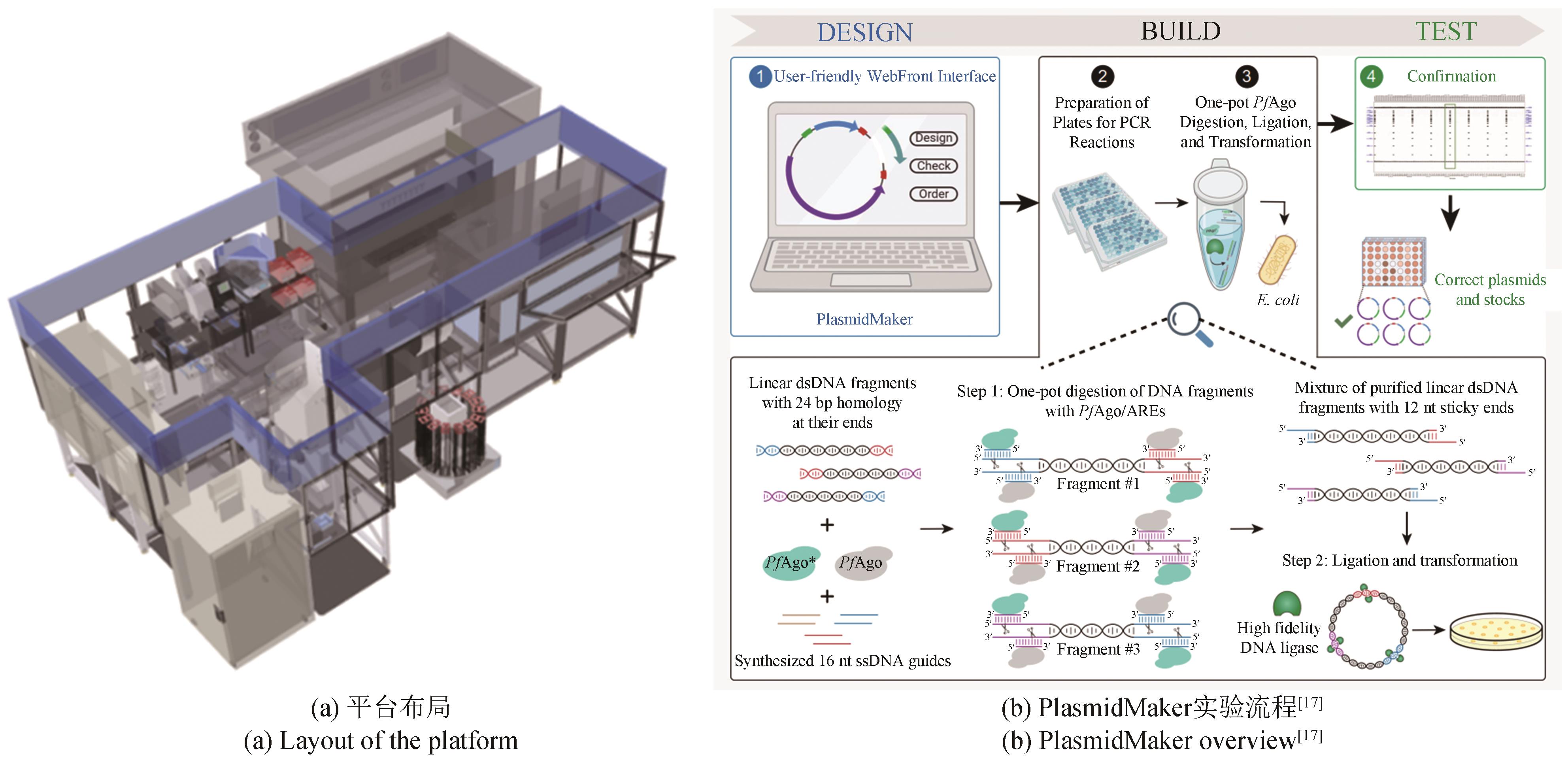
| 17 | ENGHIAD B, XUE P, SINGH N, et al. PlasmidMaker is a versatile, automated, and high throughput end-to-end platform for plasmid construction[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 2697. |
| 18 | ZHAO H M. Illinois biological foundry for advanced biomanufacturing (iBioFAB)[C/OL]. Synthetic Biology: Engineering, Evolution, and Design Conference 2015, SEED 2015, 2015, 2: 784-785[2023-03-01]. . |
| 19 | HAMEDIRAD M, CHAO R, WEISBERG S, et al. Towards a fully automated algorithm driven platform for biosystems design[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 5150. |
| 20 | XU K, QIN L, BAI W X, et al. Multilevel defense system (MDS) relieves multiple stresses for economically boosting ethanol production of industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2020, 5(2): 572-582. |
| 21 | LIU W S, JIANG R R. Combinatorial and high-throughput screening approaches for strain engineering[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 99(5): 2093-2104. |
| 22 | ALPER H, MIYAOKU K, STEPHANOPOULOS G. Construction of lycopene-overproducing E. coli strains by combining systematic and combinatorial gene knockout targets[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2005, 23(5): 612-616. |
| 23 | ÖZAYDIN B, BURD H, LEE T S, et al. Carotenoid-based phenotypic screen of the yeast deletion collection reveals new genes with roles in isoprenoid production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2013, 15: 174-183. |
| 24 | ZELCBUCH L, ANTONOVSKY N, BAR-EVEN A, et al. Spanning high-dimensional expression space using ribosome-binding site combinatorics[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2013, 41(9): e98. |
| 25 | LEE J H, LEE S H, YIM S S, et al. Quantified high-throughput screening of Escherichia coli producing poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) based on FACS[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2013, 170(7): 1767-1779. |
| 26 | TYO K E J, JIN Y S, ESPINOZA F A, et al. Identification of gene disruptions for increased poly-3-hydroxybutyrate accumulation in Synechocystis PCC 6803[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2009, 25(5): 1236-1243. |
| 27 | KLEIN-MARCUSCHAMER D, SANTOS C N S, YU H M, et al. Mutagenesis of the bacterial RNA polymerase alpha subunit for improvement of complex phenotypes[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2009, 75(9): 2705-2711. |
| 28 | ALPER H, MOXLEY J, NEVOIGT E, et al. Engineering yeast transcription machinery for improved ethanol tolerance and production[J]. Science, 2006, 314(5805): 1565-1568. |
| 29 | BASAK S, GENG H F, JIANG R R. Rewiring global regulator cAMP receptor protein (CRP) to improve E. coli tolerance towards low pH[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2014, 173: 68-75. |
| 30 | LIU H M, YAN M, LAI C G, et al. gTME for improved xylose fermentation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J].Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2010, 160(2): 574-582. |
| 31 | CHONG H Q, HUANG L, YEOW J, et al. Improving ethanol tolerance of Escherichia coli by rewiring its global regulator cAMP receptor protein (CRP)[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(2): e57628. |
| 32 | HENNING H, LEGGEWIE C, POHL M, et al. Identification of novel benzoylformate decarboxylases by growth selection[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2006, 72(12): 7510-7517. |
| 33 | PFLEGER B F, PITERA D J, SMOLKE C D, et al. Combinatorial engineering of intergenic regions in operons tunes expression of multiple genes[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2006, 24(8): 1027-1032. |
| 34 | BOERSMA Y L, DRÖGE M J, VAN DER SLOOT A M, et al. A novel genetic selection system for improved enantioselectivity ofBacillus subtilis lipase A[J]. ChemBioChem, 2008, 9(7): 1110-1115. |
| 35 | BOLES E, OREB M. A growth-based screening system for hexose transporters in yeast[M/OL]//Methods in Molecular Biology. New York, NY: Springer New York, 2018, 1713: 123-135 [2023-03-01]. . |
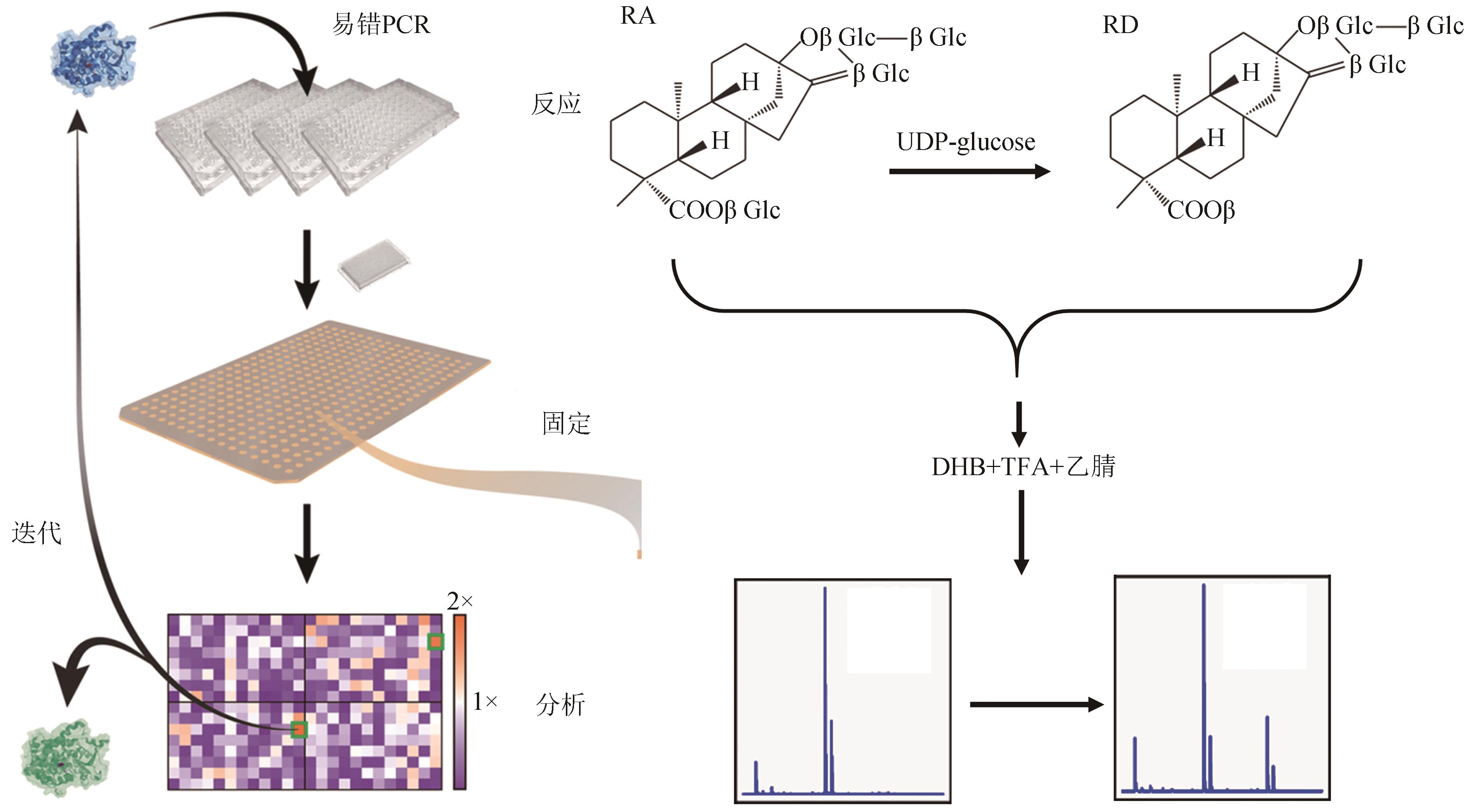
| 36 | DIETRICH J A, MCKEE A E, KEASLING J D. High-throughput metabolic engineering: advances in small-molecule screening and selection[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2010, 79: 563-590. |
| 37 | LATCHMAN D S. Transcription factors: an overview[J]. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 1997, 29(12): 1305-1312. |
| 38 | BINDER S, SCHENDZIELORZ G, STÄBLER N, et al. A high-throughput approach to identify genomic variants of bacterial metabolite producers at the single-cell level[J]. Genome Biology, 2012, 13(5): R40. |
| 39 | MAHR R, GÄTGENS C, GÄTGENS J, et al. Biosensor-driven adaptive laboratory evolution of l-valine production in Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2015, 32: 184-194. |
| 40 | BASTET L, TURCOTTE P, WADE J T, et al. Maestro of regulation: riboswitches orchestrate gene expression at the levels of translation, transcription and mRNA decay[J]. RNA Biology, 2018: 15(6): 679-682. |
| 41 | ECKDAHL T T, CAMPBELL A M, HEYER L J, et al. Programmed evolution for optimization of orthogonal metabolic output in bacteria[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(2): e0118322. |
| 42 | DIXON N, DUNCAN J N, GEERLINGS T, et al. Reengineering orthogonally selective riboswitches[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(7): 2830-2835. |
| 43 | WANG J L, WEI J H, SU S H, et al. Novel fluorescence resonance energy transfer optical sensors for vitamin B12 detection using thermally reduced carbon dots[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2015, 39(1): 501-507. |
| 44 | NGUYEN T T T, HUY B T, TAWFIK S M, et al. Highly selective and sensitive optosensing of glutathione based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer of upconversion nanoparticles coated with a Rhodamine B derivative[J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 13(1): 2671-2679. |
| 45 | DING Y D, LI J, ENTERINA J R, et al. Ratiometric biosensors based on dimerization-dependent fluorescent protein exchange[J]. Nature Methods, 2015, 12(3): 195-198. |
| 46 | FU X Z, ZHANG Y Y, XU Q, et al. Recent advances on sorting methods of high-throughput droplet-based microfluidics in enzyme directed evolution[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2021, 9: 666867. |
| 47 | ZHANG Z D, GUO Q, WANG Y T, et al. High-throughput screening of microbial strains in large-scale microfluidic droplets[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2023, 11: 1105277. |
| 48 | UTHARALA R, GRAB A, VAFAIZADEH V, et al. A microfluidic Braille valve platform for on-demand production, combinatorial screening and sorting of chemically distinct droplets[J]. Nature Protocols, 2022, 17(12): 2920-2965. |
| 49 | KÖRFER G, PITZLER C, VOJCIC L, et al. In vitro flow cytometry-based screening platform for cellulase engineering[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 26128. |
| 50 | WANG Y T, ZHANG X X, SHANG L R, et al. Thriving microfluidic technology[J]. Science Bulletin, 2021, 66(1): 9-12. |
| 51 | 涂然, 李世新, 李昊霓, 等. 液滴微流控技术在微生物工程菌株选育中的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023(1): 165-184. |
| TU R, LI S X, LI H N, et al. Advances and applications of droplet-based microfluidics in evolution and screening of engineered microbial strains[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023(1): 165-184. | |
| 52 | LEAMON J H, LINK D R, EGHOLM M, et al. Overview: methods and applications for droplet compartmentalization of biology[J]. Nature Methods, 2006, 3(7): 541-543. |
| 53 | GIELEN F, HOURS R, EMOND S, et al. Ultrahigh-throughput-directed enzyme evolution by absorbance-activated droplet sorting (AADS)[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(47): E7383-E7389. |
| 54 | BARET J C, MILLER O J, TALY V, et al. Fluorescence-activated droplet sorting (FADS): efficient microfluidic cell sorting based on enzymatic activity[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2009, 9(13): 1850-1858. |
| 55 | GOTO H, KANAI Y, YOTSUI A, et al. Microfluidic screening system based on boron-doped diamond electrodes and dielectrophoretic sorting for directed evolution of NAD(P)-dependent oxidoreductases[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2020, 20(4): 852-861. |
| 56 | WANG X X, REN L H, SU Y T, et al. Raman-activated droplet sorting (RADS) for label-free high-throughput screening of microalgal single-cells[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 89(22): 12569-12577. |
| 57 | SESEN M, WHYTE G. Image-based single cell sorting automation in droplet microfluidics[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 8736. |
| 58 | HOLLAND-MORITZ D A, WISMER M K, MANN B F, et al. Mass activated droplet sorting (MADS) enables high-throughput screening of enzymatic reactions at nanoliter scale[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(11): 4470-4477. |
| 59 | 王小艳, 秦磊, 刘辉, 等. 淀粉质燃料乙醇发酵胁迫及菌株耐受性改造[J]. 精细化工, 2019, 36(4): 568-574. |
| WANG X Y, QIN L, LIU H, et al. Research progress of starchy fuel ethanol fermentation and the tolerance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Fine Chemicals, 2019, 36(4): 568-574. | |
| 60 | PHAN A P H, NGO T T, LENHOFF H M. Spectrophotometric assay for lysine decarylase[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 1982, 120(1): 193-197. |
| 61 | 夏冰, 丁子元, 郑晓卫, 等. 植物乳杆菌和菌剂及其在生物胺降解、黄酒生产中的应用: CN111254101B[P]. 2020-07-28. |
| XIA B, DING Z Y, ZHENG X W, et al. Lactobacillus plantarum, microbial inoculum and application of Lactobacillus plantarum and microbial inoculum in biogenic amine degradation and yellow rice wine production: CN111254101B[P]. 2020-07-28. | |
| 62 | 王德昌, 明明, 周维广. 分光光度法测定高级醇[J]. 啤酒科技, 2005(3): 37-38. |
| WANG D C, MING M, ZHOU W G. Spectrophotometric determination of higher alcohols[J]. Beer Science and Technology, 2005(3): 37-38. | |
| 63 | 杨鑫, 孙浩轩, 何伟, 等. 一步法制备四甲基吡嗪用反应装置: CN218077901U[P]. 2022-12-20. |
| YANG X, SUN H X, HE W, et al. Reaction device for preparing tetramethylpyrazine by one-step method: CN218077901U[P]. 2022-12-20. | |
| 64 | 丁子元, 杨鑫, 靳喜庆, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌、菌剂、应用及制备四甲基吡嗪的方法: CN115386525B[P]. 2023-01-31. |
| DING Z Y, YANG X, JIN X Q, et al. Bacillus subtilis, fungicide, application and method for preparing tetramethylpyrazine: CN115386525B[P]. 2023-01-31. | |
| 65 | KONG C L, LI A H, SU J, et al. Flavor modification of dry red wine from Chinese spine grape by mixed fermentation with Pichia fermentans and S. cerevisiae [J]. LWT, 2019, 109: 83-92. |
| 66 | 刘沛通, 丁子元, 于庆泉, 等. 优良本土酿酒酵母的酿造特性研究[J]. 中国食品学报, 2023, 23(1), 204-215. |
| LIU P T, DING Z Y, YU Q Q, et al. Studies on oenological characteristics of high-quality Chinese indigenous Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2023, 23(1), 204-215. | |
| 67 | 刘沛通, 丁子元, 郑晓卫, 等. 酿酒酵母和菌剂以及它们在制备发酵产品特别是怀涿盆地葡萄酒酿造中的应用: CN111961603B[P]. 2021-01-01. |
| LIU P T, DING Z Y, ZHENG X W, et al. Saccharomyces cerevisiae and microbial agent as well as application thereof to preparation of fermented product and particularly brewing of wine in Huazhuo Basin: CN111961603B[P]. 2021-01-01. | |
| 68 | 郑晓卫, 刘沛通, 李泽福, 等. 抗逆性优良的空间育种酿酒酵母及其应用: CN115651852B[P]. 2023-04-11. |
| ZHENG X W, LIU P T, LI Z F, et al. Spatial breeding Saccharomyces cerevisiae with excellent stress resistance and application thereof: CN115651852B[P]. 2023-04-11. | |
| 69 | 王千, 白杰, 江会锋. 合成生物学酶改造设计技术的研究进展[J]. 生命科学, 2021, 33(12): 1493-1501. |
| WANG Q, BAI J, JIANG H F. Research progress on technologies of enzyme engineering and design in synthetic biology[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2021, 33(12): 1493-1501. | |
| 70 | 赵聪敏. 甜菊糖苷单体分离、甜味特性及应用研究[D]. 邯郸: 河北工程大学, 2021. |
| ZHAO C M. Isolation of stevia glycoside, sweetness characteristics and application[D]. Handan: Hebei University of Engineering, 2021. | |
| 71 | 祁飞, 刘瑞敏, 张真真. 一种通过易错PCR技术及高通量筛选提高葡萄糖基转移酶EUGT11酶活方法: CN113584016A[P]. 2021-11-02. |
| QI F, LIU R M, ZHANG Z Z. Method for improving enzyme activity of glucosyltransferase EUGT11 through error-prone PCR technology and high-throughput screening: CN113584016A[P]. 2021-11-02. | |
| 72 | 谭剑, 佟毅, 赵国淼, 等. 玉米赤霉烯酮浓度及其降解酶酶活力的测定方法以及玉米赤霉烯酮降解菌的筛选方法: CN112577930A[P]. 2021-03-30. |
| TAN J, TONG Y, ZHAO G M, et al. Zearalenone concentration and zearalenone degrading enzyme activity determination method and zearalenone degrading bacterium screening method: CN112577930A[P]. 2021-03-30. | |
| 73 | 赵国淼, 佟毅, 谭剑, 等. 测定呕吐毒素浓度的方法及其应用: CN114813895A[P]. 2022-07-29. |
| ZHAO G M, TONG Y, TAN J, et al. Method for determining vomitoxin concentration and application thereof: CN114813895A[P]. 2022-07-29. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 雷茹, 陶慧, 刘天罡. 基因组深度挖掘驱动微生物萜类化合物高效发现[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 507-526. |
| [3] | 郭肖杰, 剪兴金, 王立言, 张翀, 邢新会. 合成生物学表型测试生物反应器及其装备化研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 16-37. |
| [4] | 陈永灿, 司同, 张建志. 自动化合成生物技术在DNA组装与微生物底盘操作中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 857-876. |
| [5] | 刘欢, 崔球. 原位电离质谱技术在微生物菌株筛选中的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 980-999. |
| [6] | 张志强, 张扬, 邱维宝, 郑海荣. 超声移液及微量移液技术进展和展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 916-931. |
| [7] | 胡哲辉, 徐娟, 卞光凯. 自动化高通量技术在天然产物生物合成中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 932-946. |
| [8] | 马翠, 杨凡, 张君泰, 何凯. 面向自动化铸造平台的多功能微孔板检测系统[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 1036-1049. |
| [9] | 吴玉洁, 刘欣欣, 刘健慧, 杨开广, 随志刚, 张丽华, 张玉奎. 基于高通量液相色谱质谱技术的菌株筛选与关键分子定量分析研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 1000-1019. |
| [10] | 秦伟彤, 杨广宇. 微液滴高通量筛选方法的研究与应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 966-979. |
| [11] | 卢挥, 张芳丽, 黄磊. 合成生物学自动化装置iBioFoundry的构建与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 877-891. |
| [12] | 涂然, 李世新, 李昊霓, 王猛. 液滴微流控技术在微生物工程菌株选育中的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 165-184. |
| [13] | 张亭, 冷梦甜, 金帆, 袁海. 合成生物研究重大科技基础设施概述[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(1): 184-194. |
| [14] | 褚亚东, 赵宗保. 小型集成化自动移液工作站系统及应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(1): 195-208. |
| [15] | 李祎, 林振泉, 刘子鹤. 酿酒酵母适应性实验室进化工具的最新进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(2): 287-301. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||