Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (4): 824-839.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-077
• Research Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Development of CRISPRa for metabolic engineering applications in cyanobacteria
WANG Tiantian1,2, ZHU Hong1, YANG Chen1
- 1.CAS Key Laboratory of Synthetic Biology,CAS Center for Excellence in Molecular Plant Sciences,Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS),Shanghai 200032,China
2.University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
-
Received:2022-12-30Revised:2023-02-20Online:2023-09-14Published:2023-08-31 -
Contact:YANG Chen
蓝细菌CRISPRa系统的开发及其代谢工程应用
王甜甜1,2, 朱虹1, 杨琛1
- 1.中国科学院合成生物学重点实验室,中国科学院分子植物科学卓越创新中心,上海 200032
2.中国科学院大学,北京 100049
-
通讯作者:杨琛 -
作者简介:王甜甜 (1992—),女,博士研究生。研究方向为蓝细菌基因组编辑及萜类化合物代谢工程。E-mail:wangtiantian@cemps.ac.cn朱虹 (1983—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为微生物代谢工程。E-mail:zhuhong@cemps.ac.cn杨琛 (1974—),女,研究员,博士,博士生导师。研究方向为:①开发代谢流量分析与代谢组分析技术;②研究重要模式及工业微生物代谢网络调控的分子机制,揭示各种调节机制对代谢流量的调控机理,为合理改造细胞代谢、优化微生物生产提供理论依据;③开展光合微生物的代谢工程与合成生物学研究,建立萜类化合物的光合自养细胞工厂。E-mail:cyang@cemps.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2021YFA0909702);国家自然科学基金(31925001);中国科学院战略性先导科技专项(XDB27020000)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WANG Tiantian, ZHU Hong, YANG Chen. Development of CRISPRa for metabolic engineering applications in cyanobacteria[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(4): 824-839.
王甜甜, 朱虹, 杨琛. 蓝细菌CRISPRa系统的开发及其代谢工程应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(4): 824-839.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2022-077
引物 Primer | 5′-3′序列 Sequences 5′-3′ |
|---|---|
| Pendo-F | GAGACACAACGTGGCTTTCCCGCGGCCGCTTACGAAATCATCCTGTGGAGCTTAGTAG |
| Pendo-R | CTATTGAGTATTTCTTATCCATTTTTGCCTCCTAAAATAAAAAGTTTAAATTAAATC |
| dCas9-F | ATGGATAAGAAATACTCAATAGGCTTAG |
| dCas9-R | AATGATTTTCTGGTGGCTCATGGAACCGCCACCGCCGGAACCGCCACCGCCTGCGCAGTCACCTCCTAGCTGACTCAA |
| nudⅠ-F | ATGCGACAACGGACTATTGTATG |
| nudⅠ-R | GATGGGTAATTTCGCTGAGATGCATGGTATATCTCCTTCTTACTAGTCTCTCTCTTGTACATTACAGAAGACCTTTCAAACGTAAC |
| dxs-F | ATGCATCTCAGCGAAATTACCCATC |
| dxs-R | AGCCGGATTAATAATCTGGCTTTTTATATTCTCTTTAAGCCGAAGCAGCACCAAT |
| P18082-F | TTAATTAACCTGCCGAG |
| P18082-R | AGCTCTTCGCCCTTGCTCATGGTACCTTTCTCCTCTTTAATGAATTCGCCTG |
| P18082 upstream-F | ACCGTTTCAGCTGGTGATTTGGATCCGCATGCCCGATCAACGTCTC |
| P18082 upstream -R | ACCTCGGCAGGTTAATTAAGACCGGTATGCCTAATGTA |
| sfgfp -F | ATGAGCAAGGGCGAAGAG |
| sfgfp-R | AGCCAAGCTGGAGACCGTTTAAACTCACTACTTGTACAGTTCATCCATGCCA |
| qPCR-nudI-F | ATGGTGCTTATTTGCT |
| qPCR-nudI-R | TGTTCTCCCAGTTCTT |
| qPCR-dxs-F | ACCCATCCCAACCAGC |
| qPCR-dxs-R | TTCCACCACGCCCAAG |
| qPCR-gpps-F | GCGGGTGGAACGGCTG |
| qPCR-gpps-R | CCTTGTGATTGGTGGG |
| NSⅡ-up-F验证 | ACCTTGCGTCGGTGCTGAGTC |
| dxs-R验证 | TTGCTCAAGCTGAGCAACCGAC |
| NSⅢ-up-F验证 | GATGCACGAGCGTAATGCTCAC |
| NSⅢ-del-R验证 | TCTCGCTAATTGTGGGAGAGGAG |
Table 3 Primers used in this study
引物 Primer | 5′-3′序列 Sequences 5′-3′ |
|---|---|
| Pendo-F | GAGACACAACGTGGCTTTCCCGCGGCCGCTTACGAAATCATCCTGTGGAGCTTAGTAG |
| Pendo-R | CTATTGAGTATTTCTTATCCATTTTTGCCTCCTAAAATAAAAAGTTTAAATTAAATC |
| dCas9-F | ATGGATAAGAAATACTCAATAGGCTTAG |
| dCas9-R | AATGATTTTCTGGTGGCTCATGGAACCGCCACCGCCGGAACCGCCACCGCCTGCGCAGTCACCTCCTAGCTGACTCAA |
| nudⅠ-F | ATGCGACAACGGACTATTGTATG |
| nudⅠ-R | GATGGGTAATTTCGCTGAGATGCATGGTATATCTCCTTCTTACTAGTCTCTCTCTTGTACATTACAGAAGACCTTTCAAACGTAAC |
| dxs-F | ATGCATCTCAGCGAAATTACCCATC |
| dxs-R | AGCCGGATTAATAATCTGGCTTTTTATATTCTCTTTAAGCCGAAGCAGCACCAAT |
| P18082-F | TTAATTAACCTGCCGAG |
| P18082-R | AGCTCTTCGCCCTTGCTCATGGTACCTTTCTCCTCTTTAATGAATTCGCCTG |
| P18082 upstream-F | ACCGTTTCAGCTGGTGATTTGGATCCGCATGCCCGATCAACGTCTC |
| P18082 upstream -R | ACCTCGGCAGGTTAATTAAGACCGGTATGCCTAATGTA |
| sfgfp -F | ATGAGCAAGGGCGAAGAG |
| sfgfp-R | AGCCAAGCTGGAGACCGTTTAAACTCACTACTTGTACAGTTCATCCATGCCA |
| qPCR-nudI-F | ATGGTGCTTATTTGCT |
| qPCR-nudI-R | TGTTCTCCCAGTTCTT |
| qPCR-dxs-F | ACCCATCCCAACCAGC |
| qPCR-dxs-R | TTCCACCACGCCCAAG |
| qPCR-gpps-F | GCGGGTGGAACGGCTG |
| qPCR-gpps-R | CCTTGTGATTGGTGGG |
| NSⅡ-up-F验证 | ACCTTGCGTCGGTGCTGAGTC |
| dxs-R验证 | TTGCTCAAGCTGAGCAACCGAC |
| NSⅢ-up-F验证 | GATGCACGAGCGTAATGCTCAC |
| NSⅢ-del-R验证 | TCTCGCTAATTGTGGGAGAGGAG |
菌株 Strain | 基因型 Genotype | 来源 Source |
|---|---|---|
| Synechococcus elongatus PCC7942 | Wild type | ATCC |
| PCC 7942-G01 | P18082 sfgfp integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G02 | P18082 sfgfp pcpc sgRNA 106 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G03 | P18082 sfgfp pcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G09 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at NSⅢ P18082 sfgfpPcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G10 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoA integrated at NSⅢ P18082 sfgfpPcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G11 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoD integrated at NSⅡ P18082 sfgfpPcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G12 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoA NTD integrated at NSⅢ P18082 sfgfpPcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G13 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-soxS integrated at NSⅢ P18082 sfgfpPcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G14 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at NSⅢ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H1 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G15 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at NSⅢ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H2 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G16 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at NSⅢ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H3 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G17 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at NSⅢ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H5 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G18 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G19 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G27 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H1 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G28 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H2 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G29 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H3 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G30 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H5 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G31 | Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9 integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H1 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G32 | Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9 integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H2 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G33 | Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9 integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H3 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G34 | Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9 integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G35 | Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9 integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H5 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G36 | Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H1 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G37 | Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H2 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G38 | Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H3 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G39 | Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G40 | Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H5 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G45 | PJ23108 dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ | This work |
| PCC 7942-S01 | P18082 nudⅠ Pcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-S02 | P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-S03 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at NSⅢ P18082 nudⅠ Pcpc sgRNA-H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-S04 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 nudⅠ Pcpc sgRNA-H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-S05 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at NSⅢ P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc sgRNA-H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-S06 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc sgRNA-H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-S07 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc sgRNA-106 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-S12 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc sgRNA-H4 Ptrc crRNA-g1 PJ23119 tracrRNA integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-S13 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc sgRNA-H4 Ptrc crRNA-g2 PJ23119 tracrRNA integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-S14 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc sgRNA-H4 Ptrc crRNA-106 PJ23119 tracrRNA integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
Table 1 Strains used in this study
菌株 Strain | 基因型 Genotype | 来源 Source |
|---|---|---|
| Synechococcus elongatus PCC7942 | Wild type | ATCC |
| PCC 7942-G01 | P18082 sfgfp integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G02 | P18082 sfgfp pcpc sgRNA 106 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G03 | P18082 sfgfp pcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G09 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at NSⅢ P18082 sfgfpPcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G10 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoA integrated at NSⅢ P18082 sfgfpPcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G11 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoD integrated at NSⅡ P18082 sfgfpPcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G12 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoA NTD integrated at NSⅢ P18082 sfgfpPcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G13 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-soxS integrated at NSⅢ P18082 sfgfpPcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G14 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at NSⅢ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H1 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G15 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at NSⅢ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H2 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G16 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at NSⅢ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H3 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G17 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at NSⅢ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H5 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G18 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G19 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G27 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H1 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G28 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H2 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G29 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H3 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G30 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H5 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G31 | Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9 integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H1 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G32 | Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9 integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H2 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G33 | Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9 integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H3 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G34 | Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9 integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G35 | Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9 integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H5 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G36 | Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H1 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G37 | Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H2 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G38 | Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H3 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G39 | Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G40 | Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H5 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-G45 | PJ23108 dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ | This work |
| PCC 7942-S01 | P18082 nudⅠ Pcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-S02 | P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc sgRNA H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-S03 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at NSⅢ P18082 nudⅠ Pcpc sgRNA-H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-S04 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 nudⅠ Pcpc sgRNA-H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-S05 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at NSⅢ P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc sgRNA-H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-S06 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc sgRNA-H4 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-S07 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc sgRNA-106 integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-S12 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc sgRNA-H4 Ptrc crRNA-g1 PJ23119 tracrRNA integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-S13 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc sgRNA-H4 Ptrc crRNA-g2 PJ23119 tracrRNA integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
| PCC 7942-S14 | Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ integrated at rpoZ P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc sgRNA-H4 Ptrc crRNA-106 PJ23119 tracrRNA integrated at NSⅡ | This work |
质粒 Plasmid | 描述 Description | 来源 Source |
|---|---|---|
| P01 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 sfgfp | This work |
| P02 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H1 | This work |
| P03 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H2 | This work |
| P04 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H3 | This work |
| P05 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H4 | This work |
| P06 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H5 | This work |
| P07 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA 106 | This work |
| P08 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 nudⅠ Pcpc sgRNA H4 | This work |
| P09 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc sgRNA H4 | This work |
| P10 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc sgRNA 106 | This work |
| P11 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc crRNA g1 PJ23119 tracrRNA | This work |
| P12 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc crRNA g2 PJ23119 tracrRNA | This work |
| P13 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc crRNA 106 PJ23119 tracrRNA | This work |
| P14 | PCL1920; Kanr ; NSⅢ targeting; Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-soxS | This work |
| P15 | PCL1920; Kanr; NSⅢ targeting; Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ | This work |
| P16 | PCL1920; Kanr; NSⅢ targeting; Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoD | This work |
| P17 | PCL1920; Kanr; NSⅢ targeting; Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoA | This work |
| P18 | PCL1920; Kanr; NSⅢ targeting; Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoA NTD | This work |
| P19 | PCL1920; Kanr; RpoZ targeting; Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ | This work |
| P20 | PCL1920; Kanr;RpoZ targeting; Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ | This work |
| P21 | PCL1920; Kanr; RpoZ targeting; Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9 | This work |
| P22 | PCL1920; Kanr; RpoZ targeting; PJ23108 dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ | This work |
| P23 | PCL1920; Kanr; RpoZ targeting; Pcpc dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ | This work |
| P24 | PCL1920; Kanr; RpoZ targeting; Pcpc dCas9 | This work |
| P25 | PCL1920; Kanr; NSⅢ targeting; Pcpc dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ | This work |
Table 2 Plasmids used in this study
质粒 Plasmid | 描述 Description | 来源 Source |
|---|---|---|
| P01 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 sfgfp | This work |
| P02 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H1 | This work |
| P03 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H2 | This work |
| P04 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H3 | This work |
| P05 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H4 | This work |
| P06 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA H5 | This work |
| P07 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 sfgfp Pcpc sgRNA 106 | This work |
| P08 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 nudⅠ Pcpc sgRNA H4 | This work |
| P09 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc sgRNA H4 | This work |
| P10 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc sgRNA 106 | This work |
| P11 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc crRNA g1 PJ23119 tracrRNA | This work |
| P12 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc crRNA g2 PJ23119 tracrRNA | This work |
| P13 | PCL1920; Specr; NSⅡ targeting; P18082 nudⅠ dxs Pcpc crRNA 106 PJ23119 tracrRNA | This work |
| P14 | PCL1920; Kanr ; NSⅢ targeting; Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-soxS | This work |
| P15 | PCL1920; Kanr; NSⅢ targeting; Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ | This work |
| P16 | PCL1920; Kanr; NSⅢ targeting; Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoD | This work |
| P17 | PCL1920; Kanr; NSⅢ targeting; Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoA | This work |
| P18 | PCL1920; Kanr; NSⅢ targeting; Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoA NTD | This work |
| P19 | PCL1920; Kanr; RpoZ targeting; Pendo dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ | This work |
| P20 | PCL1920; Kanr;RpoZ targeting; Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ | This work |
| P21 | PCL1920; Kanr; RpoZ targeting; Pendo rpoZ-CAGGGGSGGGGS-dCas9 | This work |
| P22 | PCL1920; Kanr; RpoZ targeting; PJ23108 dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ | This work |
| P23 | PCL1920; Kanr; RpoZ targeting; Pcpc dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ | This work |
| P24 | PCL1920; Kanr; RpoZ targeting; Pcpc dCas9 | This work |
| P25 | PCL1920; Kanr; NSⅢ targeting; Pcpc dCas9-CAGGGGSGGGGS-rpoZ | This work |
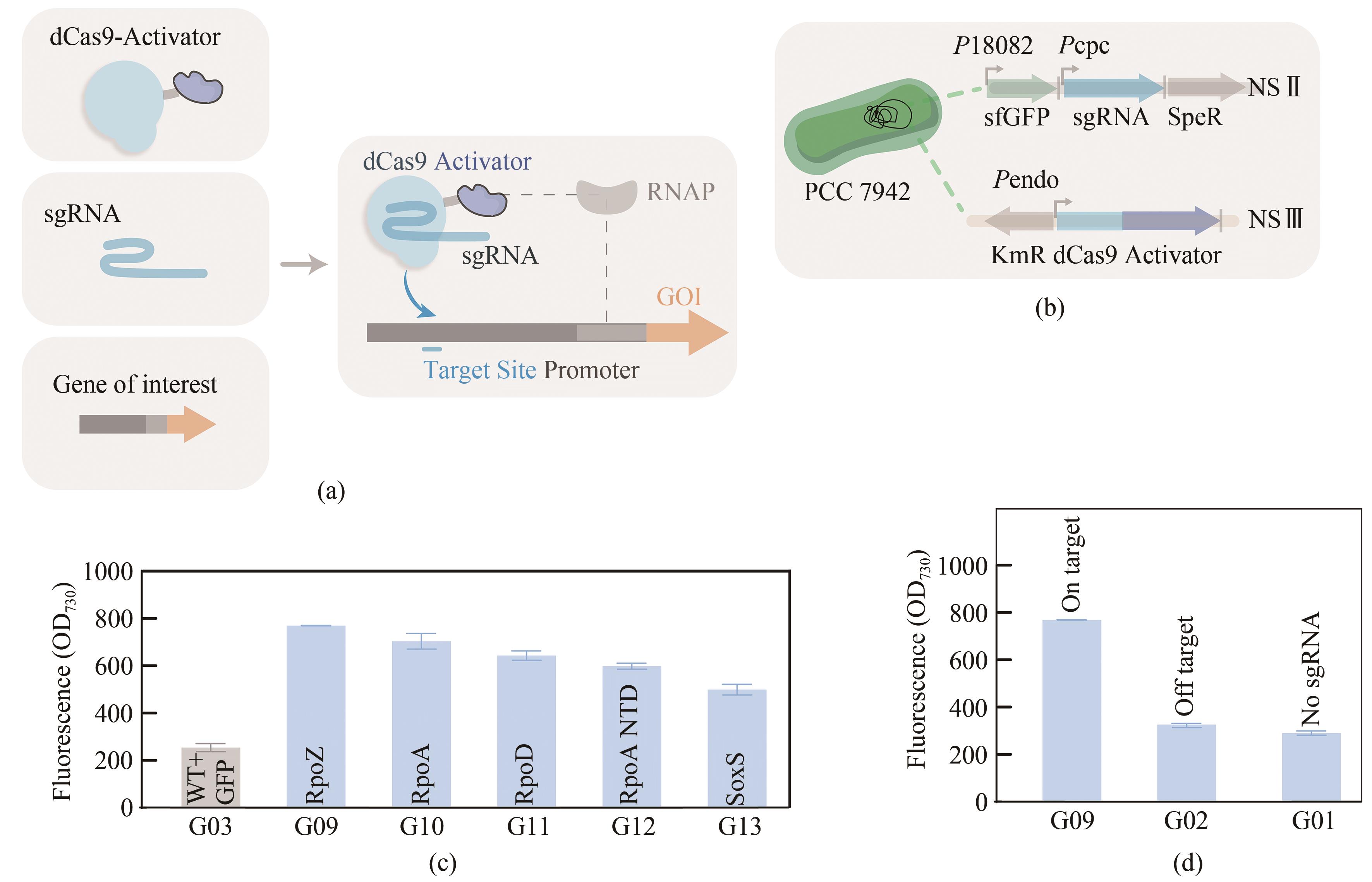
Fig. 1 Configuration of CRISPRa in PCC7942(a) Components of the CRISPRa system. (b) The expression cassette encoding dCas9 anda transcriptional activator fusion protein was inserted into the NSⅢ site of PCC7942, and the report genes sfgfp and sgRNA were integrated into the NSⅡ site of PCC7942. (c) The fluorescence intensities of strains G03, G09, G10, G11, G12, and G13 with different transcriptional activators. (d) The fluorescence signal level of G01(control strain without sgRNA) and G02(control strain with an off target sgRNA 106).
靶点 TargetSites | DNA序列(5′→3′) DNA Sequences(5′→3′) | Target Strand | Distance toTSS/bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | ATGTAACACCGTGCGTGTTG | NT | -216 |
| H2 | GAAGATCCGGCCTGCAGCCA | NT | -236 |
| H3 | GGCTCGAGTCGACAGTTCAT | NT | -273 |
| H4 | CTACGGAACTCTTGTGCGTA | T | -327 |
| H5 | GCAAAAGCTCATTTCTGAAG | T | -397 |
| g1 | CACTCAAAGGATAGACGGGA | NT | +48 |
| g2 | TCCCATTGCGCTAAGCCCTA | NT | +960 |
Table 4 Targeting sequences for the CRISPRa system used in this study
靶点 TargetSites | DNA序列(5′→3′) DNA Sequences(5′→3′) | Target Strand | Distance toTSS/bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | ATGTAACACCGTGCGTGTTG | NT | -216 |
| H2 | GAAGATCCGGCCTGCAGCCA | NT | -236 |
| H3 | GGCTCGAGTCGACAGTTCAT | NT | -273 |
| H4 | CTACGGAACTCTTGTGCGTA | T | -327 |
| H5 | GCAAAAGCTCATTTCTGAAG | T | -397 |
| g1 | CACTCAAAGGATAGACGGGA | NT | +48 |
| g2 | TCCCATTGCGCTAAGCCCTA | NT | +960 |
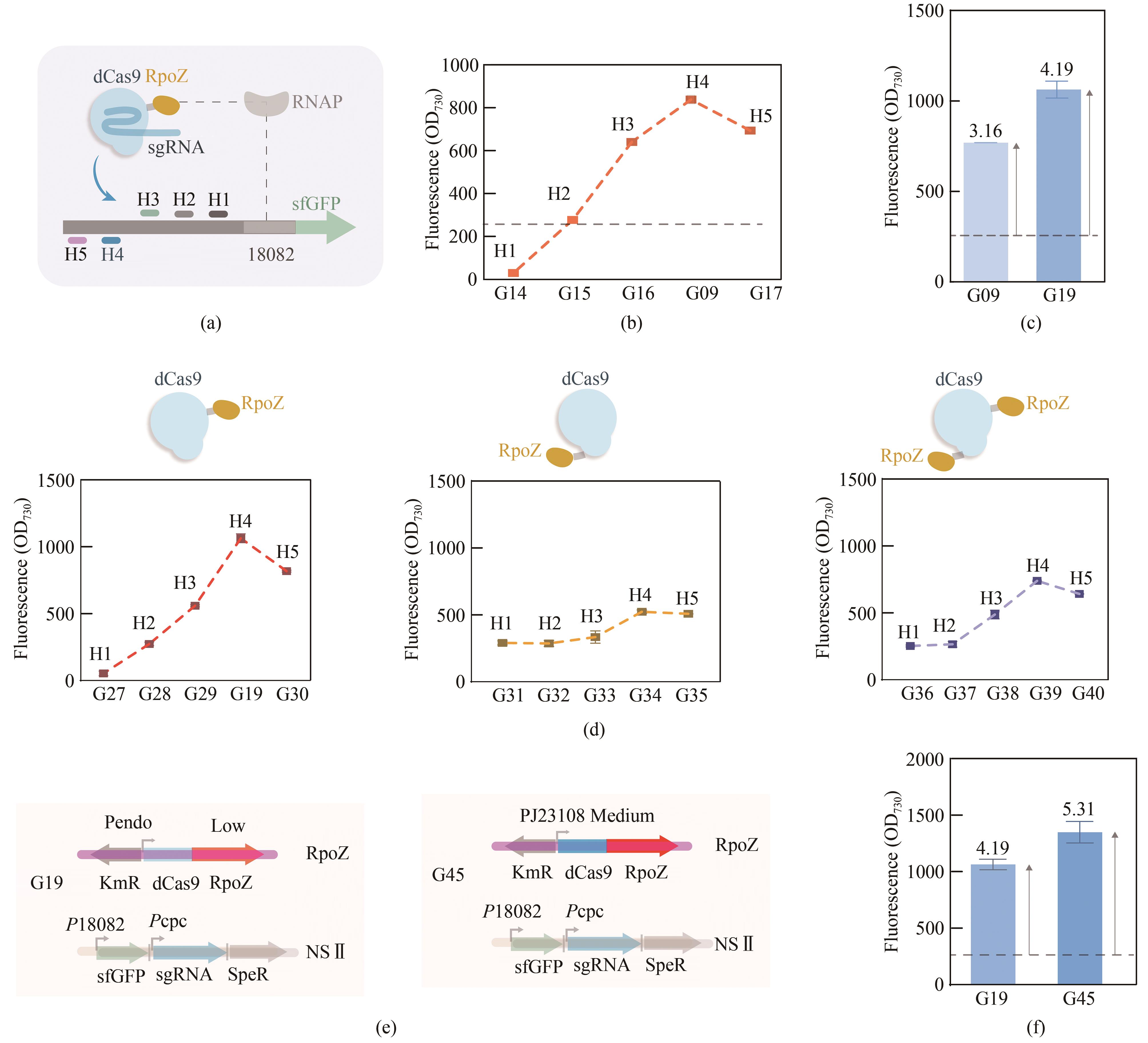
Fig. 2 Optimization of the CRISPRa system(a)Scheme of different targeting sites for CRISPRa. (b) The fluorescence intensities of strains G09, G14, G15,G16, and G17 with different targeting sites. (c) The fluorescence intensity of G19 strain with genetic knockout of endogenous rpoZ. (d) Effect of different orientations of the dCas9 and RpoZ fusion on CRISPRa performance. (e) Expression of dCas9-RpoZ was increased in G45 strain by replacing the promoter Pendo with PJ23108. (f) The fluorescence intensity of G45 strain.
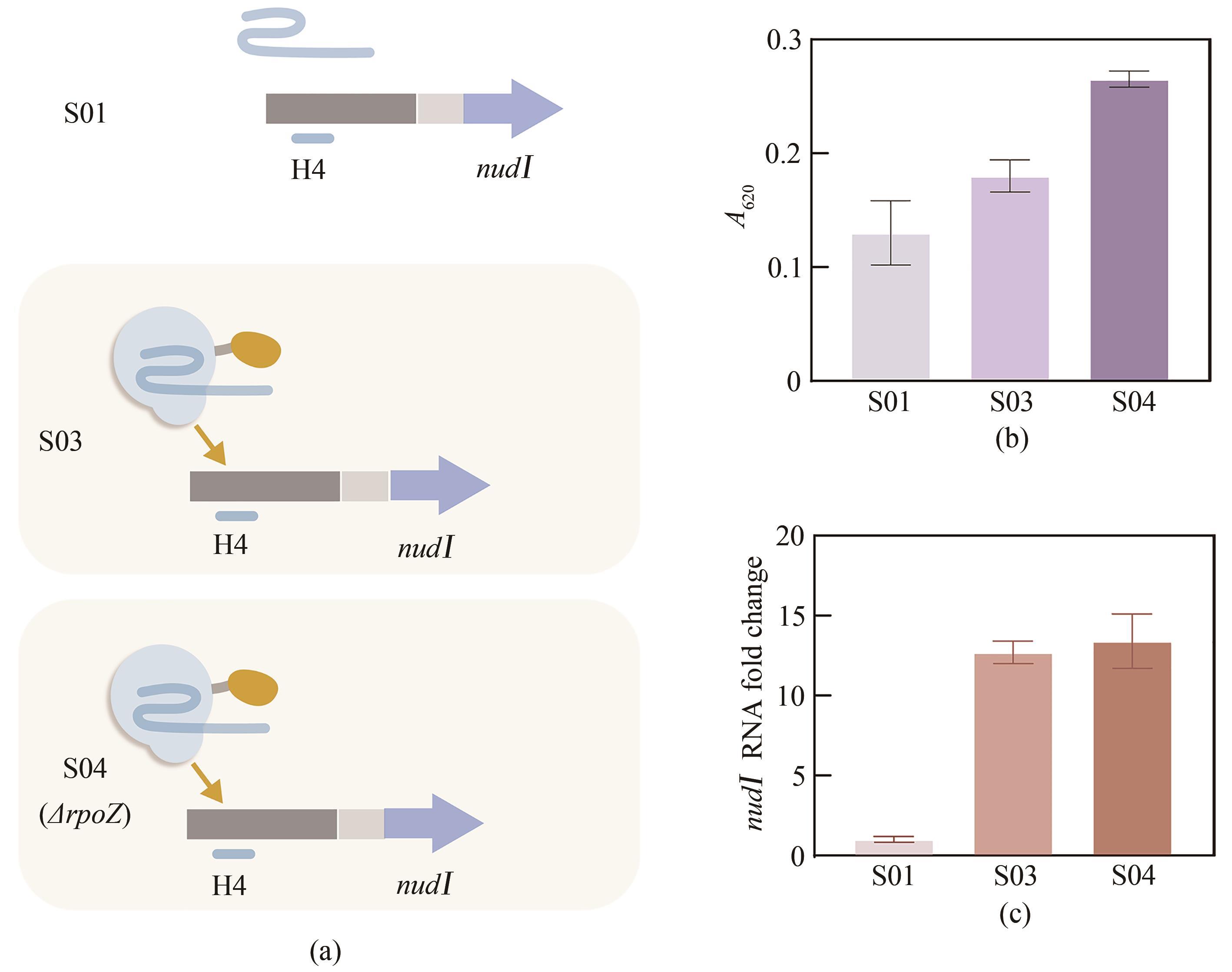
Fig. 3 Activation of nudⅠ by CRISPRa(a) Scheme of nudⅠ activation by CRISPRa. The sgRNA H4 and nudⅠ were inserted into the NSⅡ site. The DNA fragment encoding dCas9-RpoZ was inserted into the NSⅢ site or to replace endogenous rpoZ, generating strains S03 and S04, respectively. The control strain S01 lacked dCas9-RpoZ. (b) Isopentenol production by strains S01, S03, and S04. Cells were cultivated for 96 h, and isopentenol in the culture supernatant was detected by a colorimetric assay. (c) Transcriptional level of nudⅠ in strains S01, S03, and S04. RNA was isolated from cellscultivated for 72 h.

Fig. 4 Simultaneous activation of nudⅠ and dxs by CRISPRa(a) 1-Deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase encoded by dxs catalyzes the first reaction of the MEP pathway. (b)Scheme of nudⅠ and dxs activation by CRISPRa. The sgRNA H4, nudⅠ, and dxs were inserted into the NSⅡ site. The DNA fragment encoding dCas9-RpoZ was inserted into the NSⅢ site or to replace endogenous rpoZ, generating strains S05 and S06, respectively. S02 (without dCas9-RpoZ) and S07 (with an off target sgRNA 106) are the control strains. (c) Isopentenol production by strains S02, S05, S06, and S07.Cells were cultivated for 96 h, and isopentenol in the culture supernatant was detected by a colorimetric assay. (f) Transcriptional levels of nudI and dxs in strains S02, S05, S06, and S07. RNA was isolated from cells cultivated for 72 h.

Fig. 5 Simultaneous activation of nudⅠ and dxs and repression of gpps by CRISPRa(a) gpps catalyzes a key competing reaction for isopentenol biosynthesis; (b) Location of the gpps gene and the targeting sites g1 and g2 on the PCC 7942 genome; (c) The g1 and g2 sites of gpps in strain S06 were targeted, generating strains S12 and S13, respectively. S14 (with an off target sgRNA 106) is a control strain. (d) Transcriptional levels of gpps, nudⅠ and dxs in strains S02, S06, S12, S13, and S14. RNA was isolated from cells grown to OD730 of about 0.7. (e) Isopentenol production by strains S02, S06, S13, and S14. Isopentenol in the culture supernatant was detected by a colorimetric assay. (f) Isopentenol production by strains S02, S06, and S13. Culture supernatants were collected at OD730 of about 2.0, and isopentenol was detected by gas chromatography.
| 1 | GAO X, GAO F, LIU D, et al. Engineering the methylerythritol phosphate pathway in cyanobacteria for photosynthetic isoprene production from CO2 [J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2016, 9(4): 1400-1411. |
| 2 | NI J, TAO F, XU P, et al. Engineering cyanobacteria for photosynthetic production of C3 platform chemicals and terpenoids from CO2 [J]. Advancesin Experimental Medicine and Biology, 2018, 1080: 239-259. |
| 3 | ROUSSOU S, ALBERGATI A, LIANG F Y, et al. Engineered cyanobacteria with additional overexpression of selected Calvin-Benson-Bassham enzymes show further increased ethanol production[J]. Metabolic Engineering Communications, 2021, 12: e00161. |
| 4 | KOBAYASHI S, ATSUMI S, IKEBUKURO K, et al. Light-induced production of isobutanol and 3-methyl-1-butanol by metabolically engineered cyanobacteria[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2022, 21(1): 7. |
| 5 | WANG B, ECKERT C, MANESS P C, et al. A genetic toolbox for modulating the expression of heterologous genes in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(1): 276-286. |
| 6 | CHI X T, ZHANG S S, SUN H L, et al. Adopting a theophylline-responsive riboswitch for flexible regulation and understanding of glycogen metabolism in Synechococcus elongatusPCC 7942[J]. Frontiersin Microbiology, 2019, 10: 551. |
| 7 | CAICEDO-BURBANO P, SMIT T, PINEDA HERNÁNDEZ H, et al. Construction of fully segregated genomic libraries in polyploid organisms such as Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(10): 2632-2638. |
| 8 | BEHLE A, SAAKE P, GERMANN A T, et al. Comparative dose-response analysis of inducible promoters in cyanobacteria[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(4): 843-855. |
| 9 | YUNUS I S, ANFELT J, SPORRE E, et al. Synthetic metabolic pathways for conversion of CO2 into secreted short-to medium-chain hydrocarbons using cyanobacteria[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2022, 72: 14-23. |
| 10 | WENDT K E, UNGERER J, COBB R E, et al. CRISPR/Cas9 mediated targeted mutagenesis of the fast growing cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus UTEX 2973[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2016, 15(1): 115. |
| 11 | SENGUPTA A, PRITAM P, JAISWAL D, et al. Photosynthetic co-production of succinate and ethylene in a fast-growing cyanobacterium, Synechococcus elongatus PCC 11801[J]. Metabolites, 2020, 10(6): 250. |
| 12 | LI H, SHEN C R, HUANG C H, et al. CRISPR-Cas9 for the genome engineering of cyanobacteria and succinate production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2016, 38: 293-302. |
| 13 | YAO L, SHABESTARY K, BJÖRK S M, et al. Pooled CRISPRi screening of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 for enhanced industrial phenotypes[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1666. |
| 14 | CHOI S Y, WOO H M. CRISPRi-dCas12a: A dCas12a-mediated CRISPR interference for repression of multiple genes and metabolic engineering in cyanobacteria[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(9): 2351-2361. |
| 15 | HU J H, MILLER S M, GEURTS M H, et al. Evolved Cas9 variants with broad PAM compatibility and high DNA specificity[J]. Nature, 2018, 556(7699): 57-63. |
| 16 | LU Z H, YANG S H, YUAN X, et al. CRISPR-assisted multi-dimensional regulation for fine-tuning gene expression in Bacillus subtilis [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47(7): e40. |
| 17 | LIU Y, WAN X Y, WANG B J. Engineered CRISPRa enables programmable eukaryote-like gene activation in bacteria[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 3693. |
| 18 | BIKARD D, JIANG W Y, SAMAI P, et al. Programmable repression and activation of bacterial gene expression using an engineered CRISPR-Cas system[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2013, 41(15): 7429-7437. |
| 19 | YU L J, SU W, FEY P D, et al. Yield improvement of the anti-MRSA antibiotics WAP-8294A by CRISPR/dCas9 combined with refactoring self-protection genes in Lysobacter enzymogenes OH11[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(1): 258-266. |
| 20 | PENG R, WANG Y, FENG W W, et al. CRISPR/dCas9-mediated transcriptional improvement of the biosynthetic gene cluster for the epothilone production in Myxococcus xanthus [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2018, 17(1): 15. |
| 21 | DONG C, FONTANA J, PATEL A, et al. Synthetic CRISPR-Cas gene activators for transcriptional reprogramming in bacteria[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 2489. |
| 22 | NIU F X, HUANG Y B, JI L N, et al. Genomic and transcriptional changes in response to pinene tolerance and overproduction in evolved Escherichia coli [J]. Syntheticand Systems Biotechnology, 2019, 4(3): 113-119. |
| 23 | FONTANA J, DONG C, KIATTISEWEE C, et al. Effective CRISPRa-mediated control of gene expression in bacteria must overcome strict target site requirements[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1618. |
| 24 | HO H I, FANG J R, CHEUNG J, et al. Programmable CRISPR-Cas transcriptional activation in bacteria[J]. MolecularSystemsBiology, 2020, 16(7): e9427. |
| 25 | WITHERS S T, GOTTLIEB S S, LIEU B, et al. Identification of isopentenol biosynthetic genes from Bacillus subtilisby a screening method based on isoprenoid precursor toxicity[J]. Appliedand Environmental Microbiology, 2007, 73(19): 6277-6283. |
| 26 | FOO J L, JENSEN H M, DAHL R H, et al. Improving microbial biogasoline production in Escherichia coli using tolerance engineering[J]. mBio, 2014, 5(6): e01932. |
| 27 | GEORGE K W, THOMPSON M G, KANG A, et al. Metabolic engineering for the high-yield production of isoprenoid-based C5 alcohols in E. coli [J]. ScientificReports, 2015, 5: 11128. |
| 28 | KANG A, GEORGE K W, WANG G, et al. Isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP)-bypass mevalonate pathways for isopentenol production[J]. MetabolicEngineering, 2016, 34: 25-35. |
| 29 | TIAN T, KANG J W, KANG A, et al. Redirecting metabolic flux via combinatorial multiplex CRISPRi-mediated repression for isopentenol production in Escherichia coli [J]. ACS SyntheticBiology, 2019, 8(2): 391-402. |
| 30 | CHOU H H, KEASLING J D. Synthetic pathway for production of five-carbon alcohols from isopentenyl diphosphate[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2012, 78(22): 7849-7855. |
| 31 | RIPPKA R, DERUELLES J, WATERBURY J B, etal. Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria[J]. Microbiology, 1979, 111(1): 1-61. |
| 32 | PÉDELACQ J D, CABANTOUS S, TRAN T, et al. Engineering and characterization of a superfolder green fluorescent protein[J]. NatureBiotechnology, 2006, 24(1): 79-88. |
| 33 | LINSHIZ G, JENSEN E, STAWSKI N, et al. End-to-end automated microfluidic platform for synthetic biology: from design to functional analysis[J]. Journal of Biological Engineering, 2016, 10: 3. |
| 34 | ORLOVA I, NAGEGOWDA D A, KISH C M, et al. The small subunit of snapdragon geranyl diphosphate synthase modifies the chain length specificity of tobacco geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase in planta[J]. The Plant Cell, 2009, 21(12): 4002-4017. |
| 35 | GILBERT L A, HORLBECK M A, ADAMSON B, et al. Genome-scale CRISPR-mediated control of gene repression and activation[J]. Cell, 2014, 159(3): 647-661. |
| 36 | KONERMANN S, BRIGHAM M D, TREVINO A E, et al. Genome-scale transcriptional activation by an engineered CRISPR-Cas9 complex[J]. Nature, 2015, 517(7536): 583-588. |
| 37 | JOUNG J, KONERMANN S, GOOTENBERG J S, et al. Genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 knockout and transcriptional activation screening[J]. NatureProtocols, 2017, 12(4): 828-863. |
| 38 | HORLBECK M A, GILBERT L A, VILLALTA J E, et al. Compact and highly active next-generation libraries for CRISPR-mediated gene repression and activation[J]. eLife, 2016, 5: e19760. |
| 39 | WANG G C, CHOW R D, BAI Z G, et al. Multiplexed activation of endogenous genes by CRISPRa elicits potent antitumor immunity[J]. Nature Immunology, 2019, 20(11): 1494-1505. |
| 40 | VAN DER WEYDEN L, OFFORD V, TURNER G, et al. Membrane protein regulators of melanoma pulmonary colonization identified using a CRISPRa screen and spontaneous metastasis assay in mice[J]. G3 Genes Genomes Genetics, 2021, 11(7): jkab157. |
| 41 | SIEPE D H, HENNEBERG L T, WILSON S C, et al. Identification of orphan ligand-receptor relationships using a cell-based CRISPRa enrichment screening platform[J]. eLife, 2022, 11: e81398. |
| [1] | SUN Huili, CUI Jinyu, LUAN Guodong, LYU Xuefeng. Progress of cyanobacterial synthetic biotechnology for efficient light-driven carbon fixation and ethanol production [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(6): 1161-1177. |
| [2] | Zhengxin DONG, Tao SUN, Lei CHEN, Weiwen ZHANG. Applications of regulatory engineering in photosynthetic cyanobacteria [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(5): 966-984. |
| [3] | Fei TAO, Tao SUN, Yu WANG, Ting WEI, Jun NI, Ping XU. Challenges and opportunities in the research of Synechococcus chassis under the context of carbon peak and neutrality [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(5): 932-952. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||