Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (1): 77-87.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-001
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Synthetic biology based on dynamical analysis
WANG Ruiqi1, CHEN Luonan2,3
- 1.Department of Mathematics,Shanghai University,Shanghai 200444,China
2.Key Laboratory of Systems Biology,Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology,Center for Excellence in Molecular Cell Science,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shanghai 200031,China
3.Key Laboratory of Systems Health Science of Zhejiang Province,Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study,University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Hangzhou 310024,Zhejiang,China
-
Received:2022-12-31Revised:2023-07-04Online:2024-03-20Published:2024-02-29 -
Contact:CHEN Luonan
基于动力学分析的合成生物学研究
王瑞琦1, 陈洛南2,3
- 1.上海大学数学系,上海 200444
2.中国科学院分子细胞科学卓越创新中心,上海生物化学与细胞生物学研究所系统生物学重点实验室,上海 200031
3.浙江省系统健康科学重点实验室,中国科学院中国科学院大学杭州高等研究院,浙江 杭州 310024
-
通讯作者:陈洛南 -
作者简介:王瑞琦 (1974—), 男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为计算生物学与非线性动力学中稳定性、摄动、与分支理论等。 E-mail:rqwang@shu.edu.cn陈洛南 (1962—), 男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为网络生物学、计算生物学、机器学习与人工智能等。 E-mail:lnchen@sibcb.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(12371497);国家重点研发计划(2017YFA0505500);中国科学院战略优先研究计划(XDB38040400);华大基因深圳开放项目(BGIRSZ20210010)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WANG Ruiqi, CHEN Luonan. Synthetic biology based on dynamical analysis[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(1): 77-87.
王瑞琦, 陈洛南. 基于动力学分析的合成生物学研究[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 77-87.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2023-001
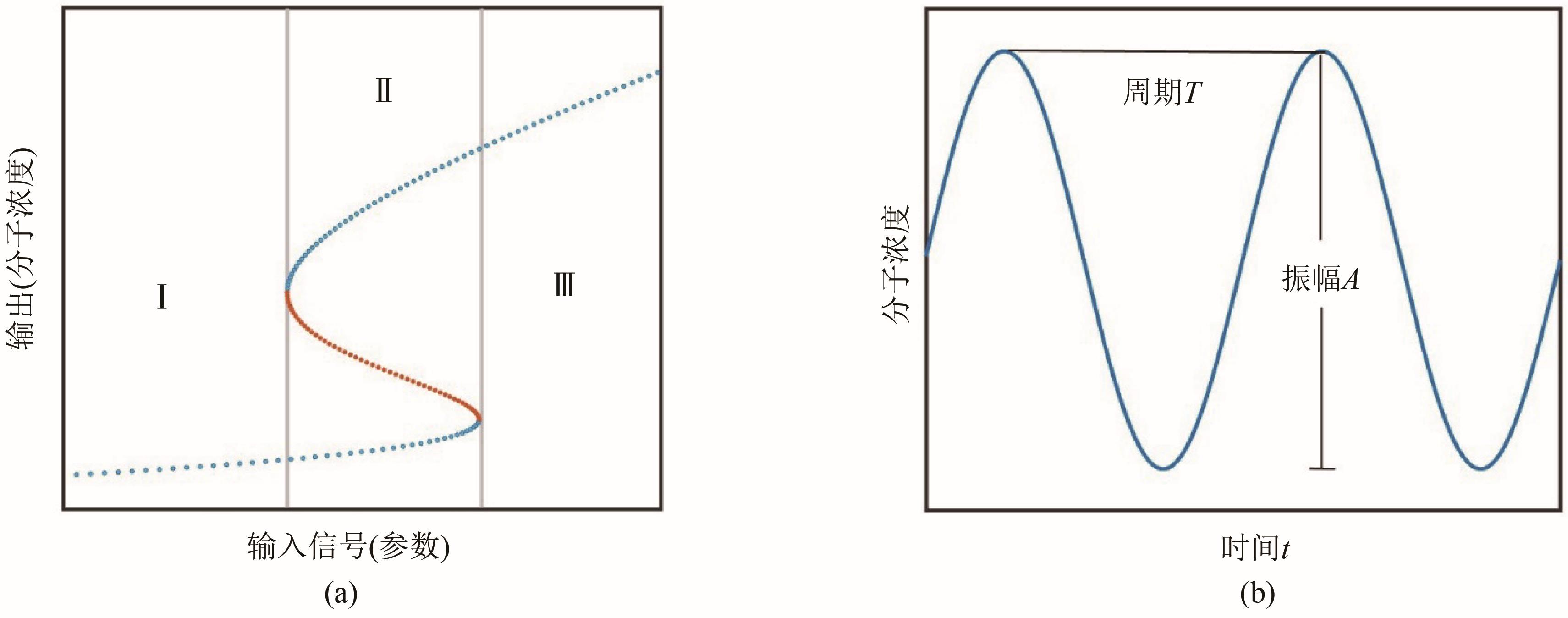
Fig. 1 Common switching dynamics for the intervals Ⅰ and Ⅲ, the system is monostable, but for the interval Ⅱ, the system is bistable (a), and periodic oscillations (b)
| 1 | GARDNER T S, CANTOR C R, COLLINS J J. Construction of a genetic toggle switch in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6767): 339-342. |
| 2 | ELOWITZ M B, LEIBLER S. A synthetic oscillatory network of transcriptional regulators[J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6767): 335-338. |
| 3 | SLUSARCZYK A L, LIN A, WEISS R. Foundations for the design and implementation of synthetic genetic circuits[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2012, 13(6): 406-420. |
| 4 | KOBAYASHI T, CHEN L N, AIHARA K. Modeling genetic switches with positive feedback loops[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2003, 221(3): 379-399. |
| 5 | WANG R Q, JING Z J, CHEN L N. Modelling periodic oscillation in gene regulatory networks by cyclic feedback systems[J]. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 2005, 67(2): 339-367. |
| 6 | GOLDBETER A. A model for circadian oscillations in the Drosophila period protein (PER)[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences, 1995, 261(1362): 319-324. |
| 7 | SMOLEN P, BAXTER D A, BYRNE J H. Frequency selectivity, multistability, and oscillations emerge from models of genetic regulatory systems[J]. The American Journal of Physiology, 1998, 274(2): C531-C542. |
| 8 | WOLF D M, EECKMAN F H. On the relationship between genomic regulatory element organization and gene regulatory dynamics[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 1998, 195(2): 167-186. |
| 9 | LIPSHTAT A, LOINGER A, BALABAN N Q, et al. Genetic toggle switch without cooperative binding[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2006, 96(18): 188101. |
| 10 | WIGGINS S. Introduction to applied nonlinear dynamical systems and chaos[M/OL]. New York, NY: Springer New York, 1990[2022-12-30]. . |
| 11 | CHEN L N, WANG R Q, LI C G, et al. Modeling biomolecular networks in cells: structures and dynamics[M/OL]. London: Springer, 2010[2022-12-30]. . |
| 12 | SNOUSSI H EL, THOMAS R. Logical identification of all steady states: the concept of feedback loop characteristic states[J]. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 1993, 55(5): 973-991. |
| 13 | THOMAS R. The role of feedback circuits: positive feedback circuits are a necessary condition for positive real eigenvalues of the Jacobian matrix[J]. Berichte der Bunsengesellschaft Für Physikalische Chemie, 1994, 98(9): 1148-1151. |
| 14 | ANGELI D, FERRELL J E JR, SONTAG E D. Detection of multistability, bifurcations, and hysteresis in a large class of biological positive-feedback systems[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101(7): 1822-1827. |
| 15 | GOSSEN M, BUJARD H. Tight control of gene expression in mammalian cells by tetracycline-responsive promoters[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1992, 89(12): 5547-5551. |
| 16 | LOU C B, LIU X L, NI M, et al. Synthesizing a novel genetic sequential logic circuit: a push-on push-off switch[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2010, 6: 350. |
| 17 | CHEN S B, ZHANG H Q, SHI H D, et al. Automated design of genetic toggle switches with predetermined bistability[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2012, 1(7): 284-290. |
| 18 | ZHU R J, DEL RIO-SALGADO J M, GARCIA-OJALVO J, et al. Synthetic multistability in mammalian cells[J]. Science, 2022, 375(6578): eabg9765. |
| 19 | DEANS T L, CANTOR C R, COLLINS J J. A tunable genetic switch based on RNAi and repressor proteins for regulating gene expression in mammalian cells[J]. Cell, 2007, 130(2): 363-372. |
| 20 | FRANKO N, TEIXEIRA A P, XUE S, et al. Design of modular autoproteolytic gene switches responsive to anti-coronavirus drug candidates[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 6786. |
| 21 | 娄春波, 杜沛, 孟凡康, 等. 人工基因线路的研究进展和未来挑战[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2018, 33(11): 1158-1165. |
| LOU C B, DU P, MENG F K, et al. Development and challenges of synthetic genetic circuits[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 33(11): 1158-1165. | |
| 22 | STRICKER J, COOKSON S, BENNETT M R, et al. A fast, robust and tunable synthetic gene oscillator[J]. Nature, 2008, 456(7221): 516-519. |
| 23 | THOMAS R, THIEFFRY D, KAUFMAN M. Dynamical behaviour of biological regulatory networks—Ⅰ. Biological role of feedback loops and practical use of the concept of the loop-characteristic state[J]. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 1995, 57(2): 247-276. |
| 24 | MACDONALD N. Biological delay systems: linear stability theory[M/OL]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1989[2022-12-30]. . |
| 25 | WANG R Q, CHEN L N, AIHARA K. Construction of genetic oscillators with interlocked feedback networks[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2006, 242(2): 454-463. |
| 26 | GONZE D, RUOFF P. The Goodwin oscillator and its legacy[J]. Acta Biotheoretica, 2021, 69(4): 857-874. |
| 27 | O'BRIEN E L, VAN ITALLIE E, BENNETT M R. Modeling synthetic gene oscillators[J]. Mathematical Biosciences, 2012, 236(1): 1-15. |
| 28 | NOVÁK B, TYSON J J. Design principles of biochemical oscillators[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2008, 9(12): 981-991. |
| 29 | TSAI T Y C, CHOI Y S, MA W Z, et al. Robust, tunable biological oscillations from interlinked positive and negative feedback loops[J]. Science, 2008, 321(5885): 126-129. |
| 30 | MAEDA K, KURATA H. Long negative feedback loop enhances period tunability of biological oscillators[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2018, 440: 21-31. |
| 31 | WANG R Q, CHEN L N, AIHARA K. Detection of cellular rhythms and global stability within interlocked feedback systems[J]. Mathematical Biosciences, 2007, 209(1): 171-189. |
| 32 | HASTY J, ISAACS F, DOLNIK M, et al. Designer gene networks: towards fundamental cellular control[J]. Chaos, 2001, 11(1): 207-220. |
| 33 | CHEN L N, AIHARA K. A model of periodic oscillation for genetic regulatory systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅰ: Fundamental Theory and Applications, 2002, 49(10): 1429-1436. |
| 34 | WANG R, ZHOU T, JING Z, et al. Modelling periodic oscillation of biological systems with multiple timescale networks[J]. Systems Biology, 2004, 1(1): 71-84. |
| 35 | CILIBERTO A, CAPUANI F, TYSON J J. Modeling networks of coupled enzymatic reactions using the total quasi-steady state approximation[J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2007, 3(3): e45. |
| 36 | TURANYI T, TOMLIN A S, PILLING M J. On the error of the quasi-steady-state approximation[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1993, 97(1): 163-172. |
| 37 | STELLING J, SAUER U, SZALLASI Z, et al. Robustness of cellular functions[J]. Cell, 2004, 118(6): 675-685. |
| 38 | PURCELL O, SAVERY N J, GRIERSON C S, et al. A comparative analysis of synthetic genetic oscillators[J]. Journal of the Royal Society, Interface, 2010, 7(52): 1503-1524. |
| 39 | LI Z D, LIU S X, YANG Q. Incoherent inputs enhance the robustness of biological oscillators[J]. Cell Systems, 2017, 5(1): 72-81.e4. |
| 40 | STELLING J, GILLES E D, F J Ⅲ DOYLE. Robustness properties of circadian clock architectures[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101(36): 13210-13215. |
| 41 | BAUM K, POLITI A Z, KOFAHL B, et al. Feedback, mass conservation and reaction kinetics impact the robustness of cellular oscillations[J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2016, 12(12): e1005298. |
| 42 | HU C Y, MURRAY R M. Layered feedback control overcomes performance trade-off in synthetic biomolecular networks[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 5393. |
| 43 | KUZNETSOV Y A. Elements of applied bifurcation theory[M/OL]. New York, NY: Springer New York, 1995[2022-12-30]. . |
| 44 | MILLER M B, BASSLER B L. Quorum sensing in bacteria[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 2001, 55: 165-199. |
| 45 | WANG R Q, LI C G, CHEN L N, et al. Modeling and analyzing biological oscillations in molecular networks[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2008, 96(8): 1361-1385. |
| 46 | YOU L C, COX R S, WEISS R, et al. Programmed population control by cell–cell communication and regulated killing[J]. Nature, 2004, 428(6985): 868-871. |
| 47 | WINFREE A T. Biological rhythms and the behavior of populations of coupled oscillators[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 1967, 16(1): 15-42. |
| 48 | PIKOVSKY A, ROSENBLUM M, KURTHS J. Synchronization: a universal concept in nonlinear sciences[M/OL]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2001[2022-12-30]. . |
| 49 | ZHOU T S, CHEN L N, AIHARA K. Molecular communication through stochastic synchronization induced by extracellular fluctuations[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2005, 95(17): 178103. |
| 50 | CHEN L N, WANG R Q, ZHOU T S, et al. Noise-induced cooperative behavior in a multicell system[J]. Bioinformatics, 2005, 21(11): 2722-2729. |
| 51 | WANG R Q, CHEN L N. Synchronizing genetic oscillators by signaling molecules[J]. Journal of Biological Rhythms, 2005, 20(3): 257-269. |
| 52 | WANG R Q, CHEN L N, AIHARA K. Synchronizing a multicellular system by external input: an artificial control strategy[J]. Bioinformatics, 2006, 22(14): 1775-1781. |
| 53 | DANINO T, MONDRAGÓN-PALOMINO O, TSIMRING L, et al. A synchronized quorum of genetic clocks[J]. Nature, 2010, 463(7279): 326-330. |
| 54 | MCMILLEN D, KOPELL N, HASTY J, et al. Synchronizing genetic relaxation oscillators by intercell signaling[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2002, 99(2): 679-684. |
| 55 | GARCIA-OJALVO J, ELOWITZ M B, STROGATZ S H. Modeling a synthetic multicellular clock: repressilators coupled by quorum sensing[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101(30): 10955-10960. |
| 56 | WAGEMAKERS A, BULDÚ J M, GARCÍA-OJALVO J, et al. Synchronization of electronic genetic networks[J]. Chaos, 2006, 16(1): 013127. |
| 57 | BASU S, GERCHMAN Y, COLLINS C H, et al. A synthetic multicellular system for programmed pattern formation[J]. Nature, 2005, 434(7037): 1130-1134. |
| 58 | MILO R, SHEN-ORR S, ITZKOVITZ S, et al. Network motifs: simple building blocks of complex networks[J]. Science, 2002, 298(5594): 824-827. |
| 59 | ALON U. Network motifs: theory and experimental approaches[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2007, 8(6): 450-461. |
| 60 | MA W Z, TRUSINA A, EL-SAMAD H, et al. Defining network topologies that can achieve biochemical adaptation[J]. Cell, 2009, 138(4): 760-773. |
| 61 | ZHANG X P, LIU F, CHENG Z, et al. Cell fate decision mediated by p53 pulses[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(30): 12245-12250. |
| 62 | NASERI G, KOFFAS M A G. Application of combinatorial optimization strategies in synthetic biology[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 2446. |
| 63 | RADIVOJEVIĆ T, COSTELLO Z, WORKMAN K, et al. A machine learning Automated Recommendation Tool for synthetic biology[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 4879. |
| 64 | KARKARIA B D, Manhart A, FEDOREC A J H, et al. Chaos in synthetic microbial communities[J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2022, 18(10): e1010548. |
| [1] | MENG Qian, YIN Cong, HUANG Weiren. Tumor organoids and their research progress in synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(1): 191-201. |
| [2] | Qingyun RUAN, Xin HUANG, Zijun MENG, Shu QUAN. Computational design and directed evolution strategies for optimizing protein stability [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 5-29. |
| [3] | Jianming LIU, Anping ZENG. Cell-free multi-enzyme machines for CO2 capture, utilization and its associated challenges [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(5): 825-832. |
| [4] | Tao TU, Huiying LUO, Bin YAO. Progress in the application of protein engineering in the developing of feed enzymes [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(3): 487-499. |
| [5] | Yuqi TANG, Songtao YE, Jia LIU, Xin ZHANG. Molecular chaperones promote protein stability and evolution [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(3): 445-464. |
| [6] | Byuri SIM, Yilei ZHAO. Assessment on the pre-reaction state of enzyme: could we understand catalytic activity with near transition-state molecular dynamic simulation?-a review [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(3): 567-586. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||