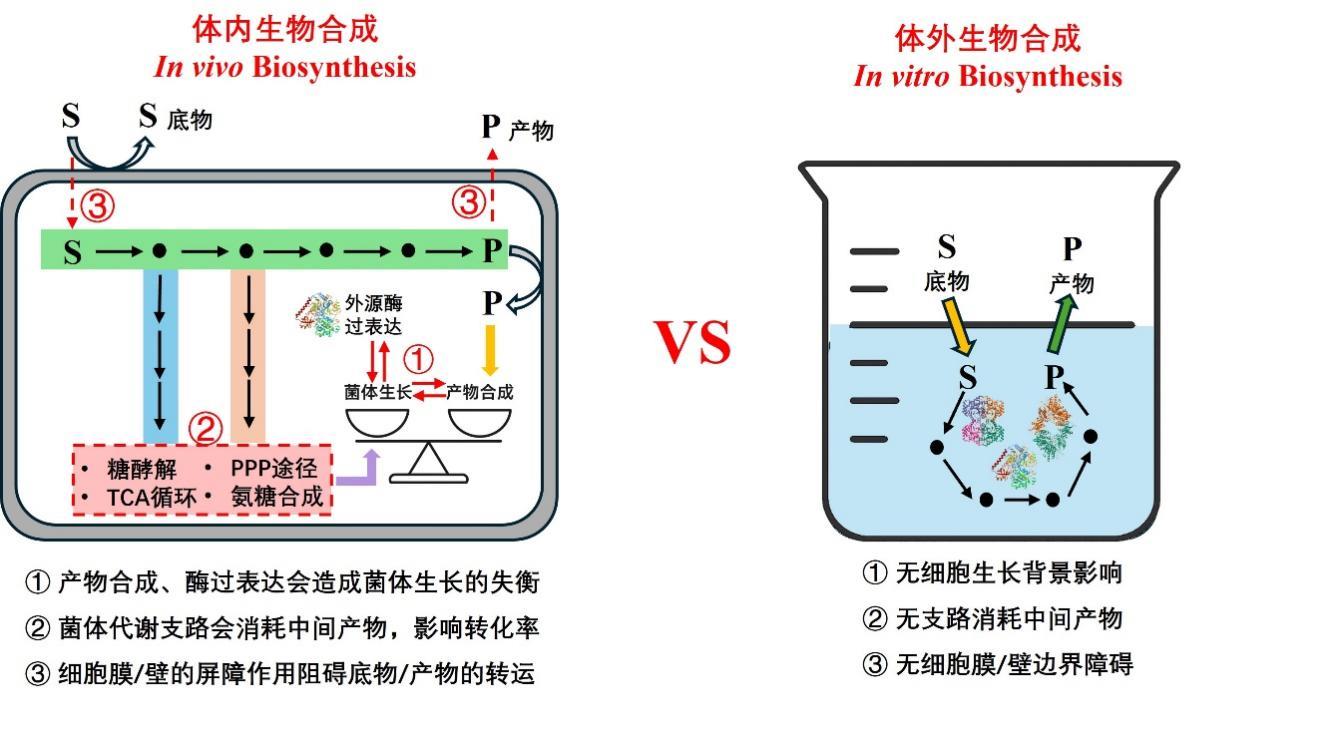
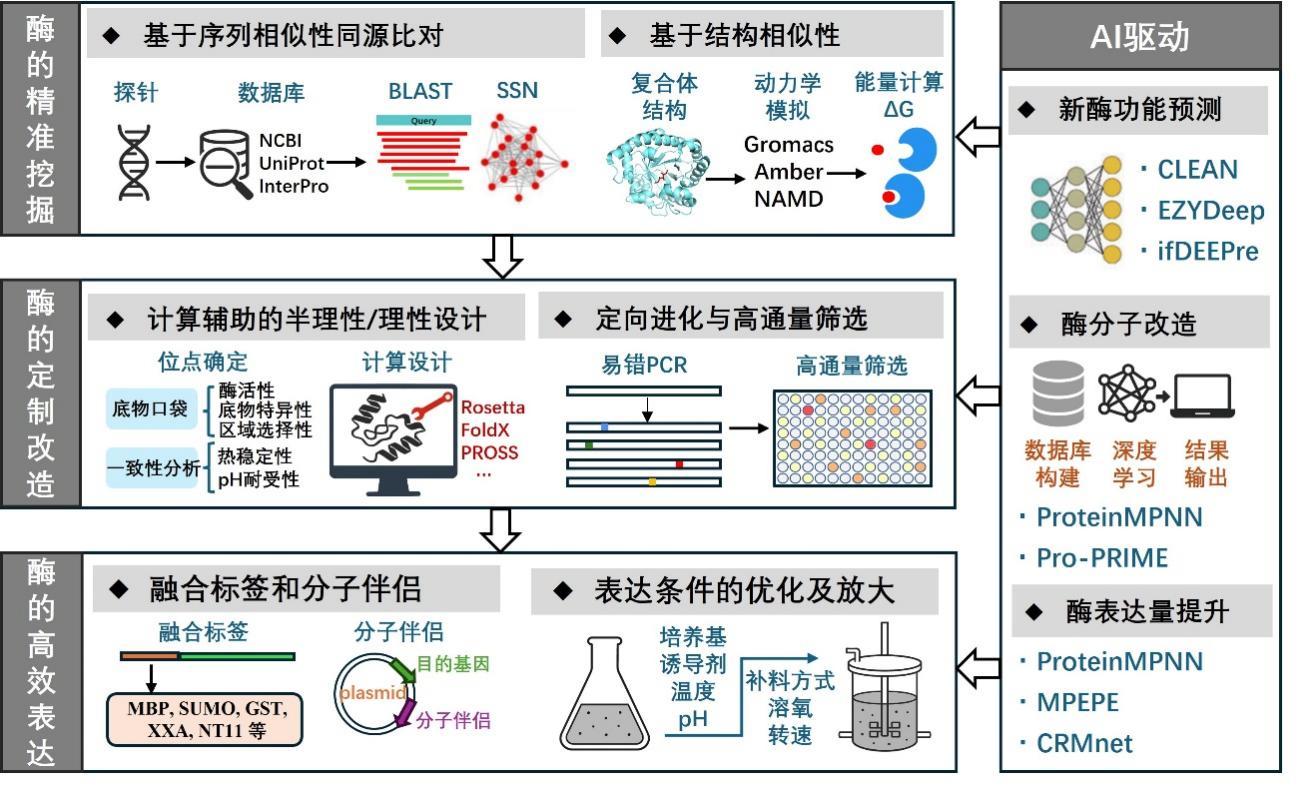
Advances and applications of in vitro biosynthesis of carbohydrates
ZHU Yueming1,3, YANG Jiangang1,3,4, ZENG Yan1,3, DONG Qianzhen2, SUN Yuanxia1,3,4
- 1.Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Tianjin 300308,China
2.Haihe Laboratory of Synthetic Biology,Tianjin 300308,China
3.National Center of Technology Innovation for Synthetic Biology,Tianjin 300308,China
4.Key Laboratory of Engineering Biology for Low-carbon Manufacturing,Tianjin 300308,China
-
Received:2025-05-28Revised:2025-07-08Published:2025-07-09 -
Contact:SUN Yuanxia
糖质的体外生物合成技术及应用进展
朱玥明1,3, 杨建刚1,3,4, 曾艳1,3, 董乾震2, 孙媛霞1,3,4
- 1.中国科学院天津工业生物技术研究所,天津 300308
2.合成生物学海河实验室,天津 300308
3.国家合成生物技术创新中心,天津 300308
4.低碳合成工程生物学全国重点实验室,天津 300308
-
通讯作者:孙媛霞 -
作者简介:朱玥明 (1982—),男,博士,副研究员。研究方向为酶工程、微生物代谢工程。E-mail:zhu_ym@tib.cas.cn孙媛霞 (1963—),女,博士,研究员。研究方向为糖生物学、糖工程与酶工程,建立了功能糖类及其衍生物的绿色生物制造技术。E-mail:sun_yx@tib.cas.cn -
基金资助:中国科学院关键核心技术攻坚先导专项(XDC0120203);合成生物学海河实验室颠覆性创新项目(22HHSWSS00016);合成生物学海河实验室攻关项目(22HHSWSS00003);天津合成生物技术创新能力提升行动(TSBICIP-KJGG-028);山东省重点研发计划项目(2023CXGC010714)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHU Yueming, YANG Jiangang, ZENG Yan, DONG Qianzhen, SUN Yuanxia. Advances and applications of in vitro biosynthesis of carbohydrates[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-050.
朱玥明, 杨建刚, 曾艳, 董乾震, 孙媛霞. 糖质的体外生物合成技术及应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-050.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2025-050
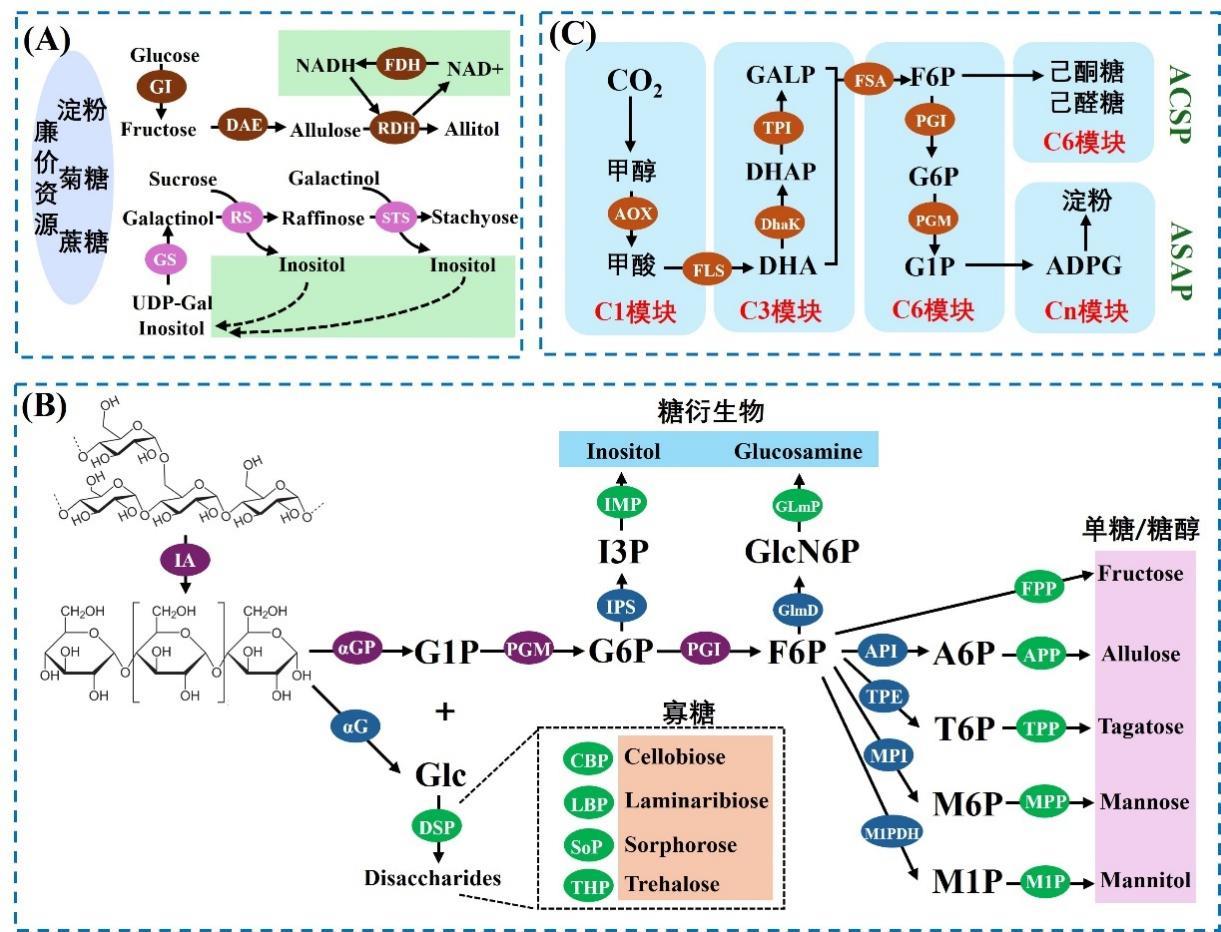
Fig. 3 Application of in vitro biosynthesis in carbohydrate production(A) Application of coenzyme recycling in the in vitro biosynthesis. GI, glucose isomerase; DAE, D-allulose 3-epimerase; RDH, ribitol dehydrogenase; FDH, formate dehydrogenase; GS, galactinol synthase; RS, raffinose synthase, STS, stachyose synthase. (B) Application of thermodynamic driving in the in vitro biosynthesis. IA, isoamylase; αGP, α-glucan phosphorylase; PGM, phosphoglucomutase; PGI, phosphoglucose isomerase; API, allulose 6-phosphate isomerase; TPE, tagatose 6-phosphate 4-epimerase; MPI, mannose 6-phosphate isomerase; M1PDH, mannitol 1-phosphate 5-dehyrogenase; FPP, fructose 6-phosphatase; APP, allulose 6-phosphatase; TPP, tagatose 6-phosphatase; MPP, mannose 6-phosphatase; M1P, mannitol 1-phosphatase; αG, α-glucosidase; DSP, disaccharide phosphorylase; CBP, cellobiose phosphorylase; LBP, laminaribiose phosphorylase; SoP, 1,2-β-oligoglucan phosphorylase; THP, trehalose phosphorylase; IPS, inositol 1-phosphate synthase; IMP, inositol monophosphatase; GlmD, glucosamine 6-phosphate deaminase; GlmP, glucosamine 6-phosphate phosphatase. (C) In vitro biosynthetic pathways for sugar and starch production from carbon dioxide. AOX, alcohol oxidase; FLS, formolase; DhaK, dihydroxyacetonekinase; TPI, triosephosphateisomerase; FSA, fructose 6-phosphate aldolase; PGI, phosphoglucose isomerase; PGM, phosphoglucomutase.
| [1] | CAMERON D E, BASHOR C J, COLLINS J J. A brief history of synthetic biology [J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2014, 12(5): 381-390. |
| [2] | FOLDI J, CONNOLLY J A, TAKANO E, et al. Synthetic biology of natural products engineering: recent advances across the discover-design-build-test-learn cycle [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2024, 13(9): 2684-2692. |
| [3] | MENG F, ELLIS T. The second decade of synthetic biology: 2010-2020 [J]. Nature Communication, 2020,11(1): 5174. |
| [4] | VOIGT C A. Synthetic biology 2020-2030: six commercially-available products that are changing our world [J]. Nature Communication, 2020, 11(1): 6379. |
| [5] | CLAASSENS N J, BURGENER S, VOGELI B, et al. A critical comparison of cellular and cell-free bioproduction systems [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2019, 60: 221-229. |
| [6] | WU G, YAN Q, JONES J A, et al. Metabolic burden: cornerstones in synthetic biology and metabolic engineering applications [J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2016, 34(8): 652-664. |
| [7] | JUNG S W, YEOM J, PARK J S, et al. Recent advances in tuning the expression and regulation of genes for constructing microbial cell factories [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2021, 50: 107767. |
| [8] | RADDE N, MORTENSEN G A, BHAT D, et al. Measuring the burden of hundreds of BioBricks defines an evolutionary limit on constructability in synthetic biology [J]. Nature Communication, 2024, 15(1): 6242. |
| [9] | MAO J, ZHANG H, CHEN Y, et al. Relieving metabolic burden to improve robustness and bioproduction by industrial microorganisms [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2024, 74: 108401. |
| [10] | CHUBUKOV V, MUKHOPADHYAY A, PETZOLD C J, et al. Synthetic and systems biology for microbial production of commodity chemicals [J]. NPJ Systems Biology and Applications, 2016, 2: 16009. |
| [11] | CORREA G G, LINS MRDCR, SILVA B F, et al. A modular autoinduction device for control of gene expression in Bacillus subtilis [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 61: 326-334. |
| [12] | BADRI A, WILLIAMS A, AWOFIRANYE A, et al. Complete biosynthesis of a sulfated chondroitin in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature Communication, 2021, 12(1): 1389. |
| [13] | ZHANG Y-HP, ZHU Z, YOU C, et al. In vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): definitions, opportunities, and challenges [J]. Synthetic Biology and Engineering, 2023, 1(2): 10013. |
| [14] | WEI X, YANG X, HU C, et al. ATP-free in vitro biotransformation of starch-derived maltodextrin into poly-3-hydroxybutyrate via acetyl-CoA [J]. Nature Communication, 2024, 15(1): 3267. |
| [15] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 等. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| SHI T, SONG Z, SONG S, et al. In vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): a new frontier of industrial biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. | |
| [16] | ZHANG Y H. Production of biocommodities and bioelectricity by cell-free synthetic enzymatic pathway biotransformations: challenges and opportunities [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2010, 105(4): 663-677. |
| [17] | QIN Y, LI Q, FAN L, et al. Biomanufacturing by in vitro Biotransformation (ivBT) using purified cascade multi-enzymes [J]. Advances in Biochemical Engineering-Biotechnology, 2023, 186: 1-27. |
| [18] | ZHANG P, WANG J, DING X, et al. Exploration of the tolerance ability of a cell-free biosynthesis system to toxic substances [J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2019, 189(4): 1096-1107. |
| [19] | YOU C, CHEN H, MYUNG S, et al. Enzymatic transformation of nonfood biomass to starch [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(18): 7182-7187. |
| [20] | DESVAUX M, GUEDON E, PETITDEMANGE H. Cellulose catabolism by Clostridium cellulolyticum growing in batch culture on defined medium [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2000, 66(6): 2461-2470. |
| [21] | PERSSON O, VALADI A, NYSTROM T, et al. Metabolic control of the Escherichia coli universal stress protein response through fructose-6-phosphate [J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2007, 65(4): 968-978. |
| [22] | RICHARDS G R, PATEL M V, LLOYD C R, et al. Depletion of glycolytic intermediates plays a key role in glucose-phosphate stress in Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2013, 195(21): 4816-4825. |
| [23] | XING M N, ZHANG X Z, HUANG H. Application of metagenomic techniques in mining enzymes from microbial communities for biofuel synthesis [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2012, 30(4): 920-929. |
| [24] | HON J, BORKO S, STOURAC J, et al. EnzymeMiner: automated mining of soluble enzymes with diverse structures, catalytic properties and stabilities [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 48(W1): W104-W109. |
| [25] | JIA B, HAN X, KIM K H, et al. Discovery and mining of enzymes from the human gut microbiome [J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2022, 40(2): 240-254. |
| [26] | JOHNSON M, ZARETSKAYA I, RAYTSELIS Y, et al. NCBI BLAST: a better web interface [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2008, 36(Web Server issue): W5-9. |
| [27] | Consortium UniProt. UniProt: a worldwide hub of protein knowledge [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47(D1): D506-D515. |
| [28] | BLUM M, CHANG H Y, CHUGURANSKY S, et al. The InterPro protein families and domains database: 20 years on [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2021, 49(D1): D344-D354. |
| [29] | DUMORNE K, CORDOVA D C, ASTORGA-ELO M, et al. Extremozymes: a potential source for industrial applications [J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 27(4): 649-659. |
| [30] | LI L, LIU X, BAI Y, et al. High-throughput screening techniques for the selection of thermostable enzymes [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024, 72(8): 3833-3845. |
| [31] | WANG Y, LI W, WANG D, et al. Screening and characterization of thermostable xylose isomerase from Rhodothermus marinus for erythrose production from one-carbon source [J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2025, 186: 110607. |
| [32] | GERLT J A, BOUVIER J T, DAVIDSON D B, et al. Enzyme Function Initiative-Enzyme Similarity Tool (EFI-EST): A web tool for generating protein sequence similarity networks [J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2015, 1854(8): 1019-1037. |
| [33] | BURROUGHS A M, ALLEN K N, DUNAWAY-MARIANO D, et al. Evolutionary genomics of the HAD superfamily: understanding the structural adaptations and catalytic diversity in a superfamily of phosphoesterases and allied enzymes [J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2006, 361(5): 1003-1034. |
| [34] | LI Y, SHI T, HAN P, et al. Thermodynamics-driven production of value-added D-allulose from inexpensive starch by an in vitro enzymatic synthetic biosystem [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2021, 11(9): 5088–5099. |
| [35] | MAK W S, TRAN S, MARCHESCHI R, et al. Integrative genomic mining for enzyme function to enable engineering of a non-natural biosynthetic pathway [J]. Nature Communication, 2015, 6: 10005. |
| [36] | SONG Y, DIMAIO F, WANG R Y, et al. High-resolution comparative modeling with RosettaCM [J]. Structure, 2013, 21(10): 1735-1742. |
| [37] | MILLER B R III, MCGEE T D, SWAILS J M, et al. MMPBSA.py: an efficient program for end-state free energy calculations [J]. Journal of chemical theory and computation, 2012, 8(9): 3314-3321. |
| [38] | BONETTA R, VALENTINO G. Machine learning techniques for protein function prediction [J]. Proteins, 2020, 88(3): 397-413. |
| [39] | WANG Y, HAN S, WANG Y, et al. Artificial intelligence technology assists enzyme prediction and rational design [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2025, 73(12): 7065-7073. |
| [40] | YU T, CUI H, LI J C, et al. Enzyme function prediction using contrastive learning [J]. Science, 2023, 379(6639): 1358-1363. |
| [41] | BOULAHROUF K, ALIOUANE S E, CHEHILI H, et al. EZYDeep: a deep learning tool for enzyme function prediction based on sequence information [J]. The Open Bioinformatics Journal, 2023, 16(1): 1-8. |
| [42] | TAN Q, XIAO J, CHEN J, et al. ifDEEPre: large protein language-based deep learning enables interpretable and fast predictions of enzyme commission numbers [J]. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2024, 25(4): bbae225. |
| [43] | REETZ M T, SUN Z, QU G. Enzyme engineering: selective catalysts for applications in biotechnology, organic chemistry, and life science [M]. John Wiley & Sons, 2023. |
| [44] | VICTORINO I, GONSALES N, ANTONIO F, et al. Enzyme engineering and its industrial applications [J]. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 2022, 69(2): 389-409. |
| [45] | MAZURENKO S, PROKOP Z, DAMBORSKY J. Machine learning in enzyme engineering [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(2): 1210-1223. |
| [46] | SONG Z, ZHANG Q, WU W, et al. Rational design of enzyme activity and enantioselectivity [J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2023, 11:1129149. |
| [47] | CHICA R A, DOUCET N, PELLETIER J N. Semi-rational approaches to engineering enzyme activity: combining the benefits of directed evolution and rational design [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2005, 16(4): 378-384. |
| [48] | WATERHOUSE A, BERTONI M, BIENERT S, et al. SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 46(W1): W296-W303. |
| [49] | ABRAMSON J, ADLER J, DUNGER J, et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3 [J]. Nature, 2024, 630(8016): 493-500. |
| [50] | SOUSA S F, FERNANDES P A, RAMOS M J. Protein-ligand docking: current status and future challenges [J]. Proteins, 2006, 65(1):15-26. |
| [51] | YANG C, CHEN E A, ZHANG Y. Protein-ligand docking in the machine-learning era [J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(14): 4568. |
| [52] | VAN DER SPOEL D, LINDAHL E, HESS B, et al. GROMACS: fast, flexible, and free [J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2005, 26(16):1701-1718. |
| [53] | LEE T S, ALLEN B K, GIESE T J, et al. Alchemical binding free energy calculations in AMBER20: advances and best practices for drug discovery [J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2020, 60(11): 5595-5623. |
| [54] | TIAN C, YANG J, LIU C, et al. Engineering substrate specificity of HAD phosphatases and multienzyme systems development for the thermodynamic-driven manufacturing sugars [J]. Nature Communication, 2022, 13(1): 3582. |
| [55] | ZHANG T, LIU P, WEI H, et al. Protein engineering of glucosylglycerol phosphorylase facilitating efficient and highly regio- and stereoselective glycosylation of polyols in a synthetic system [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2022, 12(24): 15715-15727. |
| [56] | ROMERO P A, ARNOLD F H. Exploring protein fitness landscapes by directed evolution [J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2009, 10(12): 866-876. |
| [57] | COPP J N, HANSON-MANFUL P, ACKERLEY D F, et al. Error-prone PCR and effective generation of gene variant libraries for directed evolution [J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2014, 1179: 3-22. |
| [58] | HUANG R, CHEN H, ZHONG C, et al. High-throughput screening of coenzyme preference change of thermophilic 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase from NADP(+) to NAD(.) [J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 32644. |
| [59] | MA C, LIU M, YOU C, et al. Engineering a diaphorase via directed evolution for enzymatic biofuel cell application [J]. Bioresources and Bioprocessing, 2020, 7: 23. |
| [60] | ZHOU W, HUANG R, ZHU Z, et al. Coevolution of both thermostability and activity of polyphosphate glucokinase from Thermobifida fusca YX [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2018, 84(16): e01224-18. |
| [61] | ZHU Y, CHEN P, DONG Q, et al. Protein engineering of transaminase facilitating enzyme cascade reaction for the biosynthesis of azasugars [J]. iScience, 2024, 27(3): 109034. |
| [62] | YANG K K, WU Z, ARNOLD F H. Machine-learning-guided directed evolution for protein engineering [J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(8): 687-694. |
| [63] | SUMIDA K H, NUNEZ-FRANCO R, KALVET I, et al. Improving protein expression, stability, and function with ProteinMPNN [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2024, 146(3): 2054-2061. |
| [64] | BIAN J, TAN P, NIE T, et al. Optimizing enzyme thermostability by combining multiple mutations using protein language model [J]. mLife, 2024, 3(4): 492-504. |
| [65] | REUTEN R, NIKODEMUS D, OLIVEIRA M B, et al. Maltose-Binding Protein (MBP), a secretion-enhancing tag for mammalian protein expression systems [J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(3): e0152386. |
| [66] | GUERRERO F, CIRAGAN A, IWAI H. Tandem SUMO fusion vectors for improving soluble protein expression and purification [J]. Protein Expression and Purification, 2015, 116: 42-49. |
| [67] | REBAY I, FEHON R G. Preparation of soluble GST fusion proteins [J]. Cold Spring Harb Protocols, 2009, 2009(11): pdb.prot4996. |
| [68] | XIE X, WU P, HUANG X, et al. Retro-protein XXA is a remarkable solubilizing fusion tag for inclusion bodies [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2022, 1(1):51. |
| [69] | NGUYEN T K M, KI M R, SON R G, et al. The NT11, a novel fusion tag for enhancing protein expression in Escherichia coli [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 103(5): 2205-2216. |
| [70] | DE MARCO A. Protocol for preparing proteins with improved solubility by co-expressing with molecular chaperones in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature Protocols, 2007, 2(10): 2632-2639. |
| [71] | DING Z, GUAN F, XU G, et al. MPEPE, a predictive approach to improve protein expression in E. coli based on deep learning [J]. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 2022, 20: 1142-1153. |
| [72] | KHADYE V S, SAWANT S, SHAIKH K, et al. Optimal secretion of thermostable β-glucosidase in Bacillus subtilis by signal peptide optimization [J]. Protein Expression and Purification, 2021, 182: 105843. |
| [73] | PAN Y, YANG J, WU J, et al. Current advances of Pichia pastoris as cell factories for production of recombinant proteins [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2022, 13: 1059777. |
| [74] | INAN M, ARYASOMAYAJULA D, SINHA J, et al. Enhancement of protein secretion in Pichia pastoris by overexpression of protein disulfide isomerase [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2006, 93(4): 771-778. |
| [75] | 张以恒, 陈雪梅, 石婷. 生物制造的市本率(PC值):定义与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 8-17. |
| ZHANG Y H, CHEN X, SHI T. Price to Cost-of-raw-materials Ratio (PC) of biomanufacturing: definition and application [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 8-17. | |
| [76] | BEBER M E, GOLLUB M G, MOZAFFARI D, et al. eQuilibrator 3.0: a database solution for thermodynamic constant estimation [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2022, 50(D1): D603-D609. |
| [77] | GAO J, MA S, MAJOR D T, et al. Mechanisms and free energies of enzymatic reactions [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2006, 106(8): 3188-3209. |
| [78] | YANG J, ZHANG T, TIAN C, et al. Multi-enzyme systems and recombinant cells for synthesis of valuable saccharides: advances and perspectives [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2019, 37(7): 107406. |
| [79] | WEN L, HUANG K, WEI M, et al. Facile enzymatic synthesis of ketoses [J]. Angewandte Chemie-international Edition, 2015, 54(43):12654-12658. |
| [80] | ANDEXER J N, RICHTER M. Emerging enzymes for ATP regeneration in biocatalytic processes [J]. Chembiochem, 2015, 16(3): 380-386. |
| [81] | RESNICK S M, ZEHNDER A J. In vitro ATP regeneration from polyphosphate and AMP by polyphosphate: AMP phosphotransferase and adenylate kinase from Acinetobacter johnsonii 210A [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2000, 66(5): 2045-2051. |
| [82] | MYUNG S, ROLLIN J, YOU C, et al. In vitro metabolic engineering of hydrogen production at theoretical yield from sucrose [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2014, 24: 70-77. |
| [83] | YOU C, SHI T, LI Y, et al. An in vitro synthetic biology platform for the industrial biomanufacturing of myo-inositol from starch [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2017, 114(8): 1855-1864. |
| [84] | ZHONG C, YOU C, WEI P, et al. Thermal cycling cascade biocatalysis of myo-inositol synthesis from sucrose [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(9): 5992-5999. |
| [85] | WANG W, LIU M, YOU C, et al. ATP-free biosynthesis of a high-energy phosphate metabolite fructose 1,6-diphosphate by in vitro metabolic engineering [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 42: 168-174. |
| [86] | ZHU Y, LI H, LIU P, et al. Construction of allitol synthesis pathway by multi-enzyme coexpression in Escherichia coli and its application in allitol production [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2015, 42(5): 661-669. |
| [87] | SATOH Y, TAJIMA K, TANNAI H, et al. Enzyme-catalyzed poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) synthesis from acetate with CoA recycling and NADPH regeneration in Vitro [J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2003, 95(4): 335-341. |
| [88] | RELYEA H A, VAN DER DONK W A. Mechanism and applications of phosphite dehydrogenase [J]. Bioorganic Chemistry, 2005, 33(3): 171-189. |
| [89] | ZHAO H, VAN DER DONK W A. Regeneration of cofactors for use in biocatalysis [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2003, 14(6): 583-589. |
| [90] | LI J, MU S, YANG J, et al. Glycosyltransferase engineering and multi-glycosylation routes development facilitating synthesis of high-intensity sweetener mogrosides [J]. iScience, 2022, 25(10): 105222. |
| [91] | BAULER P, HUBER G, LEYH T, et al. Channeling by proximity: the catalytic advantages of active site colocalization using brownian dynamics [J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2010, 1(9): 1332-1335. |
| [92] | FAN L, WANG Y, TUYISHIME P, et al. Engineering artificial fusion proteins for enhanced methanol bioconversion [J]. Chembiochem, 2018, 19(23): 2465-2471. |
| [93] | TIAN J, JIA R, WENGE D, et al. One-step purification and immobilization of recombinant proteins using SpyTag/SpyCatcher chemistry [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2021, 43(5): 1075-1087. |
| [94] | STAHL S W, NASH M A, FRIED D B, et al. Single-molecule dissection of the high-affinity cohesin-dockerin complex [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(50): 20431-20436. |
| [95] | SUN X, ZHANG T, LIU Y, et al. Self-assembled multienzyme complex facilitates synthesis of glucosylglycerol from maltodextrin and glycerol [J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2024, 104(1): 266-272. |
| [96] | HAN P, ZHOU X, YOU C. Efficient multi-enzymes immobilized on porous microspheres for producing inositol from starch [J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2020, 8: 380. |
| [97] | HAN P, YOU C, LI Y, et al. High-titer production of myo-inositol by a co-immobilized four-enzyme cocktail in biomimetic mineralized microcapsules [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 461: 141946. |
| [98] | YANG J, SONG W, CAI T, et al. De novo artificial synthesis of hexoses from carbon dioxide [J]. Science Bulletin (Beijing), 2023, 68(20): 2370-2381. |
| [99] | WANG L, DASH S, NG C Y, et al. A review of computational tools for design and reconstruction of metabolic pathways [J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2017, 2(4): 243-252. |
| [100] | JANG W D, KIM G B, KIM Y, et al. Applications of artificial intelligence to enzyme and pathway design for metabolic engineering [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2022, 73: 101-107. |
| [101] | WEI F, CAI J, MAO Y, et al. Unveiling metabolic engineering strategies by quantitative heterologous pathway design [J]. Advanced Science, 2024, 11(45): e2404632. |
| [102] | IZUMORI K. Izumoring: a strategy for bioproduction of all hexoses [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2006, 124(4): 717-722. |
| [103] | MEN Y, ZHU P, ZHU Y, et al. The development of low-calorie sugar and functional jujube food using biological transformation and fermentation coupling technology [J]. Food Science & Nutrition, 2019, 7(4): 1302-1310. |
| [104] | MEN Y, ZHU Y, ZENG Y, et al. Co-expression of D-glucose isomerase and D-psicose 3-epimerase: development of an efficient one-step production of D-psicose [J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2014, 64-65: 1-5. |
| [105] | ZHU P, ZENG Y, CHEN P, et al. A one-pot two-enzyme system on the production of high value-added D-allulose from Jerusalem artichoke tubers [J]. Process Biochemistry, 2020, 88: 90-96. |
| [106] | WEI X, LI Q, HU C, et al. An ATP-free in vitro synthetic enzymatic biosystem facilitating one-pot stoichiometric conversion of starch to mannitol [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2021, 105(5):1913-1924. |
| [107] | YAN J, CHEN P, ZENG Y, et al. Production of neoagarobiose from agar through a dual-enzyme and two-stage hydrolysis strategy [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2020, 160: 288-295. |
| [108] | ALI M Y, LIAQAT F, KHAZI M I, et al. Utilization of glycosyltransferases as a seamless tool for synthesis and modification of the oligosaccharides-A review [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2023, 249: 125916. |
| [109] | TIAN C, YANG J, ZENG Y, et al. Biosynthesis of raffinose and stachyose from sucrose via an in vitro multienzyme system [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2019, 85(2): e02306-18. |
| [110] | SUN S, WEI X, ZHOU X, et al. Construction of an artificial in vitro synthetic enzymatic platform for upgrading low-cost starch to value-added disaccharides [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2021, 69(1): 302-314. |
| [111] | SUN S, YOU C. Disaccharide phosphorylases: Structure, catalytic mechanisms and directed evolution [J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2021, 6(1): 23-31. |
| [112] | CAI T, SUN H, QIAO J, et al. Cell-free chemoenzymatic starch synthesis from carbon dioxide [J]. Science, 2021, 373(6562): 1523-1527. |
| [113] | XU X, ZHANG W, YOU C, et al. Biosynthesis of artificial starch and microbial protein from agricultural residue [J]. Science Bulletin, 2023, 68(2): 214-223. |
| [114] | LI Y, YOU C, ZHANG YH. In vitro biotransformation of high-titer D-glucarate by stepwise-added enzyme cocktails [J]. Organic Process Research & Development, 2024, 28(2): 478-486. |
| [115] | MENG D, WEI X, BAI X, et al. Artificial in vitro synthetic enzymatic biosystem for the one-pot sustainable biomanufacturing of glucosamine from starch and inorganic ammonia [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(23): 13809-13819. |
| [1] | ZHANG Jun, JIN Shixue, YUN Qian, QU Xudong. Biosynthesis of the unnatural extender units with polyketides and their structural modifications for applications in medicines [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 561-570. |
| [2] | KANG Liqi, TAN Pan, HONG Liang. Enzyme engineering in the age of artificial intelligence [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(3): 524-534. |
| [3] | CUI Xinyu, WU Ranran, WANG Yuanming, ZHU Zhiguang. Construction and enhancement of enzymatic bioelectrocatalytic systems [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(5): 1006-1030. |
| [4] | GAO Hutao, WANG Jia, SUN Xinxiao, SHEN Xiaolin, YUAN Qipeng. De novo biosynthesis of 3-phenylpropanol in E. coli [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(6): 1046-1060. |
| [5] | WAN Yichen, XU Kongliang, ZHENG Renchao, ZHENG Yuguo. In vitro biosynthesis of chemicals: pathway design, component assembly and applications-a review [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(6): 886-901. |
| [6] | ZHANG Yi-Heng. Remembering Professor Daniel I.C. Wang’s contribution to biorefining and my perspective on the progress [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(4): 497-508. |
| [7] | SHI Ran, JIANG Zhengqiang. Enzymatic synthesis of 2'-fucosyllactose: advances and perspectives [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(4): 481-494. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||