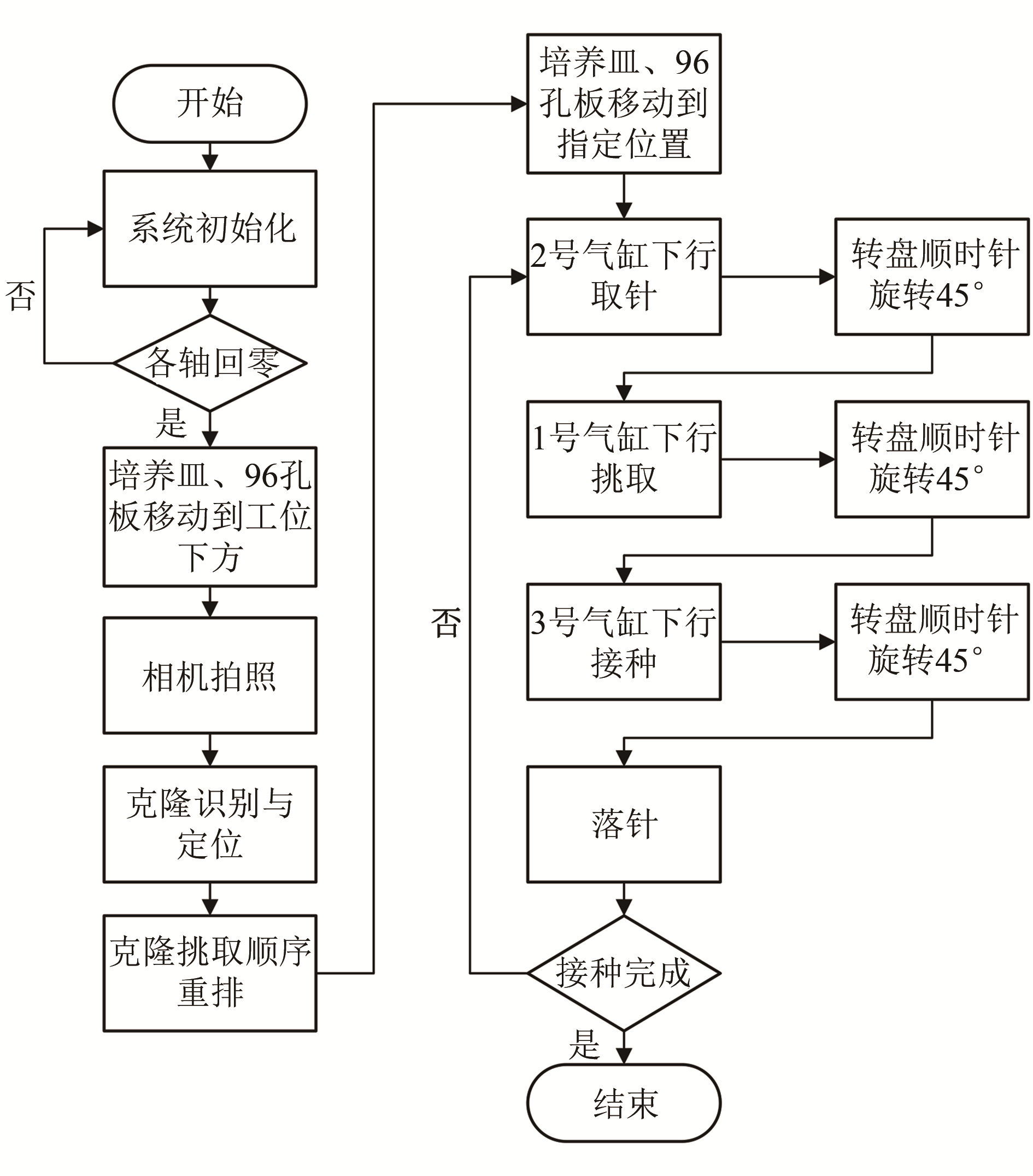
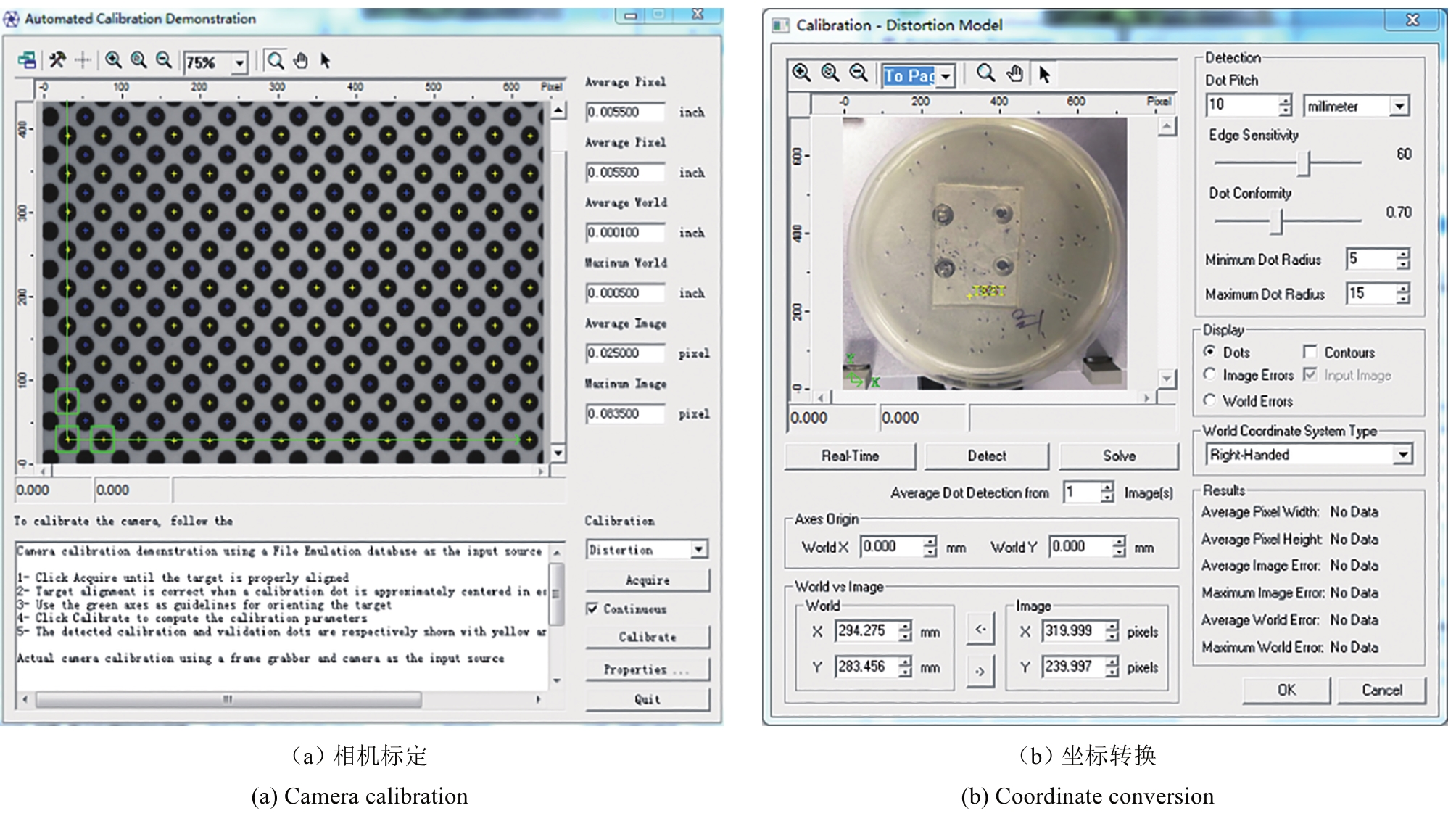
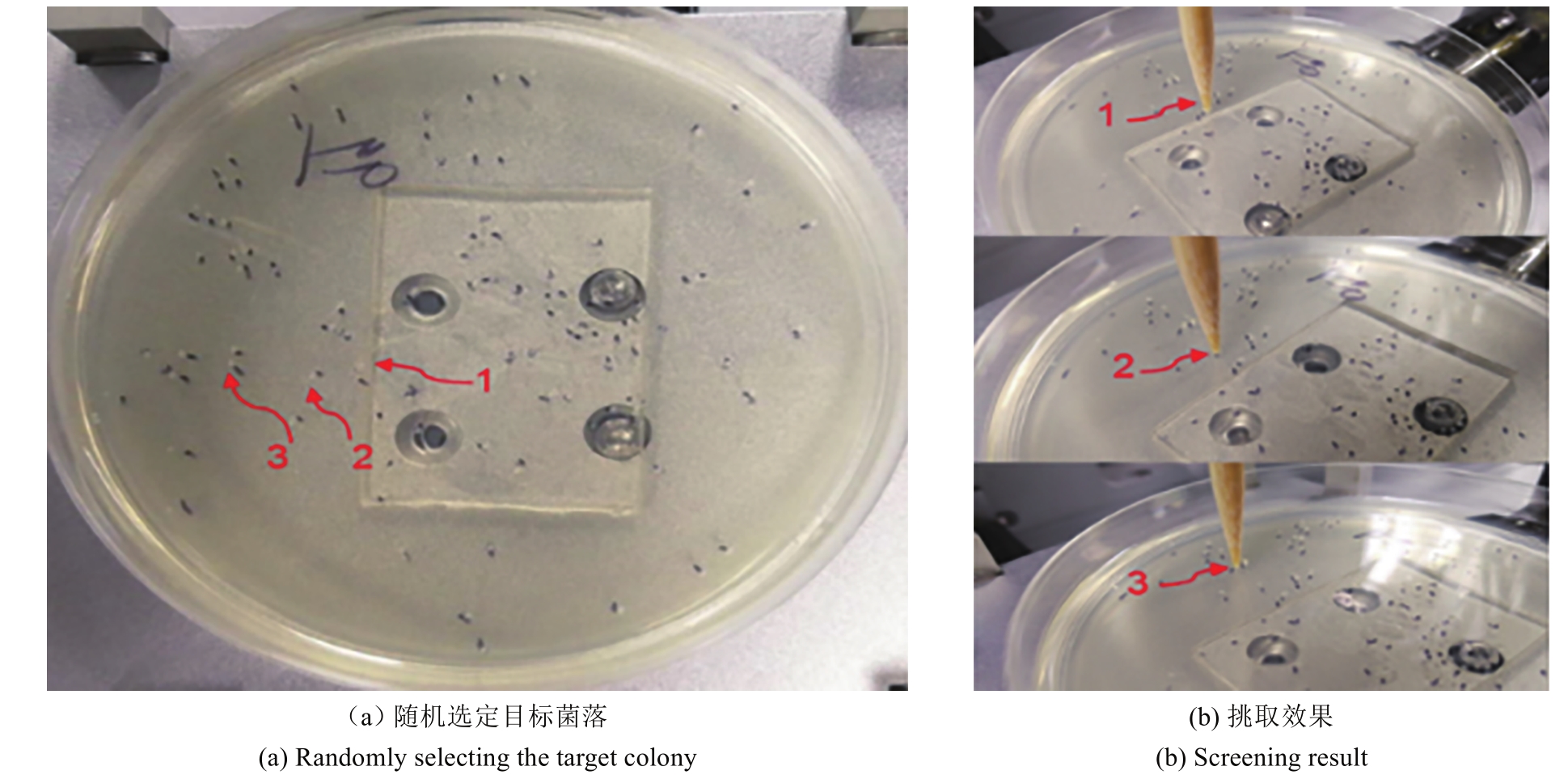
Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (1): 134-144.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-059
• Invited Review • Previous Articles
Design and experimental research of new robot for clone selection
ZHU Wei1,2, ZHAO Wenling1,2, HE Kai1,2
- 1.Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Precision Engineering,Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenzhen 518055,Guangdong,China
2.Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Joint Laboratory of Human-Machine Intelligence-Synergy Systems,Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenzhen 518055,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2020-04-04Revised:2020-11-17Online:2021-03-12Published:2021-02-28 -
Contact:HE Kai
新型克隆挑取机器人设计与实验研究
朱伟1,2, 赵文亮1,2, 何凯1,2
- 1.中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院,深圳市精密工程重点实验室,广东 深圳 518055
2.中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院,粤港澳人机智能协同系统联合实验室 广东 深圳 518055
-
通讯作者:何凯 -
作者简介:朱伟(1991-),男,硕士,助理工程师,主要研究方向为机械结构设计、运动控制、机器视觉。E-mail:wei.zhu@siat.ac.cn
何凯(1972-),男,博士,教授级高级工程师,主要研究方向为精密制造及自动化技术、工业机器人、金属成形技术及装备、生物制造自动化技术等。E-mail:kai.he@siat.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0902900)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHU Wei, ZHAO Wenling, HE Kai. Design and experimental research of new robot for clone selection[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(1): 134-144.
朱伟, 赵文亮, 何凯. 新型克隆挑取机器人设计与实验研究[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(1): 134-144.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2020-059
| 引脚 | 信号 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | EXO 0 | 一号气爪输出 |
| 2 | EXO 1 | 二号气爪输出 |
| 3 | EXO 2 | 三号气爪输出 |
| 4 | EXO 3 | 四号气爪输出 |
| 5 | EXO 4 | 五号气爪输出 |
| 6 | EXO 5 | 六号气爪输出 |
| 7 | EXO 6 | 七号气爪输出 |
| 8 | EXO 7 | 八号气爪输出 |
| 9 | EXO 8 | 一号气缸输出 |
| 10 | EXO 9 | 二号气缸输出 |
| 11 | EXO 10 | 三号气缸输出 |
Tab. 2 Address allocation and function of the output ports
| 引脚 | 信号 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | EXO 0 | 一号气爪输出 |
| 2 | EXO 1 | 二号气爪输出 |
| 3 | EXO 2 | 三号气爪输出 |
| 4 | EXO 3 | 四号气爪输出 |
| 5 | EXO 4 | 五号气爪输出 |
| 6 | EXO 5 | 六号气爪输出 |
| 7 | EXO 6 | 七号气爪输出 |
| 8 | EXO 7 | 八号气爪输出 |
| 9 | EXO 8 | 一号气缸输出 |
| 10 | EXO 9 | 二号气缸输出 |
| 11 | EXO 10 | 三号气缸输出 |
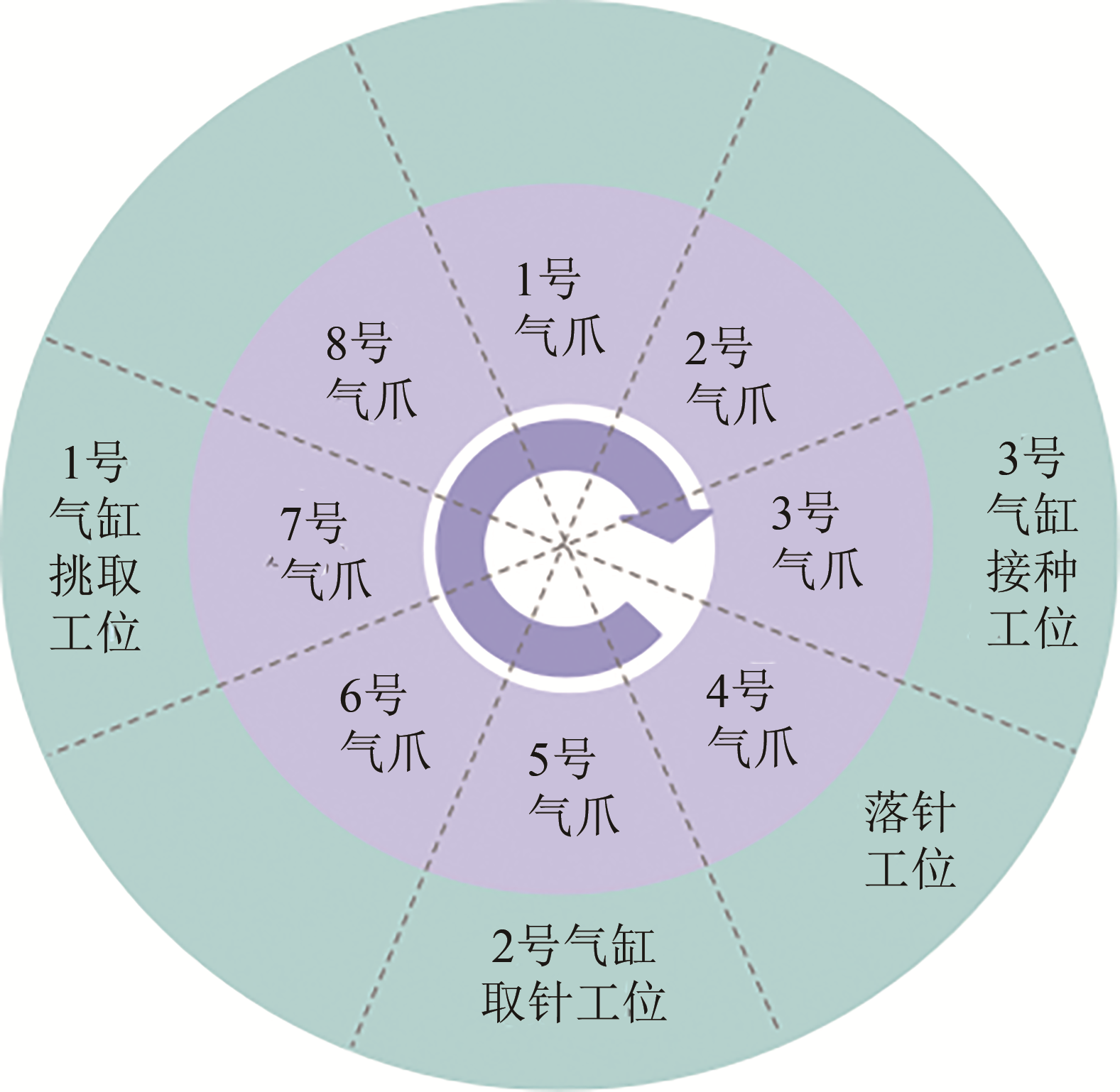
| 循环次数 | 气爪编号 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 取针 | 挑取 | 接种 | 落针 | |
| 1 | 5 | 7 | 3 | 4 |
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 3 |
| 3 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 2 |
| 4 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 1 |
| 5 | 1 | 3 | 7 | 8 |
| 6 | 8 | 2 | 6 | 7 |
| 7 | 7 | 1 | 5 | 6 |
| 8 | 6 | 8 | 4 | 5 |
Tab. 3 Picking function of the needles on each pneumatic gripper in a full-load working cycle
| 循环次数 | 气爪编号 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 取针 | 挑取 | 接种 | 落针 | |
| 1 | 5 | 7 | 3 | 4 |
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 3 |
| 3 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 2 |
| 4 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 1 |
| 5 | 1 | 3 | 7 | 8 |
| 6 | 8 | 2 | 6 | 7 |
| 7 | 7 | 1 | 5 | 6 |
| 8 | 6 | 8 | 4 | 5 |
| 引脚 | 信号 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | HOME 0 | 一轴原点输入 |
| 2 | HOME 1 | 二轴原点输入 |
| 3 | HOME 2 | 三轴原点输入 |
| 4 | HOME 3 | 四轴原点输入 |
| 5 | LIMIT 0+ | 一轴正向限位 |
| 6 | LIMIT 0- | 一轴负向限位 |
| 7 | LIMIT 1+ | 二轴正向限位 |
| 8 | LIMIT 1- | 二轴负向限位 |
| 9 | LIMIT 2+ | 三轴正向限位 |
| 10 | LIMIT 2- | 三轴负向限位 |
| 11 | LIMIT 3+ | 四轴正向限位 |
| 12 | LIMIT 3- | 四轴负向限位 |
| 13 | EXI 0 | 转盘零点输入 |
| 14 | EXI 1 | 转块零点输入 |
| 15 | EXI 2 | 转块一孔有无输入 |
| 16 | EXI 3 | 转块二孔有无输入 |
Tab. 1 Address allocation and function of the input ports
| 引脚 | 信号 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | HOME 0 | 一轴原点输入 |
| 2 | HOME 1 | 二轴原点输入 |
| 3 | HOME 2 | 三轴原点输入 |
| 4 | HOME 3 | 四轴原点输入 |
| 5 | LIMIT 0+ | 一轴正向限位 |
| 6 | LIMIT 0- | 一轴负向限位 |
| 7 | LIMIT 1+ | 二轴正向限位 |
| 8 | LIMIT 1- | 二轴负向限位 |
| 9 | LIMIT 2+ | 三轴正向限位 |
| 10 | LIMIT 2- | 三轴负向限位 |
| 11 | LIMIT 3+ | 四轴正向限位 |
| 12 | LIMIT 3- | 四轴负向限位 |
| 13 | EXI 0 | 转盘零点输入 |
| 14 | EXI 1 | 转块零点输入 |
| 15 | EXI 2 | 转块一孔有无输入 |
| 16 | EXI 3 | 转块二孔有无输入 |
| 选取点 | 实际坐标(mm) | 定位坐标(mm) | (ΔX,ΔY) | 误差 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (-10.000,10.000) | (-10.031,10.005) | (-0.031,0.005) | 0.031 |
| 2 | (-20.000,20.000) | (-20.034,20.006) | (-0.034,0.006) | 0.035 |
| 3 | (-30.000,30.000) | (-30.013,30.006) | (-0.013,0.006) | 0.014 |
| 4 | (-30.000,10.000) | (-30.008,10.027) | (-0.008,0.027) | 0.028 |
| 5 | (-10.000,30.000) | (-10.021,29.985) | (-0.021,-0.015) | 0.026 |
| 6 | (10.000,10.000) | (9.994,10.009) | (-0.006,0.009) | 0.011 |
| 7 | (20.000,20.000) | (20.008,20.003) | (0.008,0.003) | 0.009 |
| 8 | (30.000,30.000) | (30.057,30.001) | (0.057,0.001) | 0.057 |
| 9 | (30.000,10.000) | (29.980,10.015) | (-0.020,0.015) | 0.025 |
| 10 | (10.000,30.000) | (10.044,29.996) | (0.044,-0.004) | 0.044 |
| 11 | (10.000,-10.000) | (9.998,-10.001) | (-0.002,-0.001) | 0.002 |
| 12 | (20.000,-20.000) | (20.005,-20.037) | (0.005,-0.037) | 0.037 |
| 13 | (30.000,-30.000) | (30.035,-30.065) | (0.035,-0.065) | 0.074 |
| 14 | (30.000,-10.000) | (29.994,-10.009) | (-0.006,-0.009) | 0.011 |
| 15 | (10.000,-30.000) | (10.027,-30.037) | (0.027,-0.037) | 0.046 |
| 16 | (-10.000,-10.000) | (-10.018,-10.001) | (-0.018,-0.001) | 0.018 |
| 17 | (-20.000,-20.000) | (-20.002,-20.004) | (-0.002,-0.004) | 0.004 |
| 18 | (-30.000,-30.000) | (-29.988,-30.017) | (0.012,-0.017) | 0.021 |
| 19 | (-10.000,-30.000) | (-10.007,-30.023) | (-0.007,-0.023) | 0.024 |
| 20 | (-30.000,-10.000) | (-29.994,-9.992) | (0.006,0.008) | 0.010 |
Tab. 4 Experimental results
| 选取点 | 实际坐标(mm) | 定位坐标(mm) | (ΔX,ΔY) | 误差 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (-10.000,10.000) | (-10.031,10.005) | (-0.031,0.005) | 0.031 |
| 2 | (-20.000,20.000) | (-20.034,20.006) | (-0.034,0.006) | 0.035 |
| 3 | (-30.000,30.000) | (-30.013,30.006) | (-0.013,0.006) | 0.014 |
| 4 | (-30.000,10.000) | (-30.008,10.027) | (-0.008,0.027) | 0.028 |
| 5 | (-10.000,30.000) | (-10.021,29.985) | (-0.021,-0.015) | 0.026 |
| 6 | (10.000,10.000) | (9.994,10.009) | (-0.006,0.009) | 0.011 |
| 7 | (20.000,20.000) | (20.008,20.003) | (0.008,0.003) | 0.009 |
| 8 | (30.000,30.000) | (30.057,30.001) | (0.057,0.001) | 0.057 |
| 9 | (30.000,10.000) | (29.980,10.015) | (-0.020,0.015) | 0.025 |
| 10 | (10.000,30.000) | (10.044,29.996) | (0.044,-0.004) | 0.044 |
| 11 | (10.000,-10.000) | (9.998,-10.001) | (-0.002,-0.001) | 0.002 |
| 12 | (20.000,-20.000) | (20.005,-20.037) | (0.005,-0.037) | 0.037 |
| 13 | (30.000,-30.000) | (30.035,-30.065) | (0.035,-0.065) | 0.074 |
| 14 | (30.000,-10.000) | (29.994,-10.009) | (-0.006,-0.009) | 0.011 |
| 15 | (10.000,-30.000) | (10.027,-30.037) | (0.027,-0.037) | 0.046 |
| 16 | (-10.000,-10.000) | (-10.018,-10.001) | (-0.018,-0.001) | 0.018 |
| 17 | (-20.000,-20.000) | (-20.002,-20.004) | (-0.002,-0.004) | 0.004 |
| 18 | (-30.000,-30.000) | (-29.988,-30.017) | (0.012,-0.017) | 0.021 |
| 19 | (-10.000,-30.000) | (-10.007,-30.023) | (-0.007,-0.023) | 0.024 |
| 20 | (-30.000,-10.000) | (-29.994,-9.992) | (0.006,0.008) | 0.010 |
| 1 | HUGHES S R, BUTT R, BARTULETT S, et al. Design and construction of a first-generation high-throughput integrated robotic molecular biology platform for bioenergy applications[J]. Journal of Laboratory Automation, 2011, 16(4):292-307. |
| 2 | ALYSSA M R, TANVEER S B, ROSSANA C, et al. Targeted proteomics for metabolic pathway optimization: application to terpene production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2015, 13(2):194-203. |
| 3 | 田良玉. 乳酸菌高密度规模发酵工艺优化[D]. 扬州:扬州大学,2018. |
| TIAN Liangyu. Optimization of high-density fermentation process of lactic acid bacteria[D]. Yangzhou :Yangzhou University, 2018. | |
| 4 | 杨书香,刘群. 基因检测技术的应用及国内行业发展现状[J]. 绿色科技,2015,12:281-283. |
| YANG Shuxiang, LIU Qun. Application of gene detection technology and development status of domestic industry[J]. Green Technology,2015,12:281-283. | |
| 5 | 何青梅.生物技术在农业作物病虫害防治上的使用[J].农民致富之友,2018(16):59. |
| HE Qingmei. The application of biotechnology in the control of agricultural crop diseases and insect pests[J]. Friends of Farmers Getting Rich,2018(16):59. | |
| 6 | 冯薇. 现代生物技术的知识产权保护及企业的相关策略研究[D].成都:电子科技大学,2011. |
| FENG Wei. Research on intellectual property protection of modern biotechnology and related strategies of enterprises[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology, 2011. | |
| 7 | 王会, 戴俊彪, 罗周卿. 基因组的"读-改-写"技术[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(5): 503-515. |
| WANG Hui, DAI Junbiao, LUO Zhouqing. The "read-modify-write" technology of genome[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(5): 503-515. | |
| 8 | 袁盛建, 马迎飞. 噬菌体合成生物学研究进展和应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(6): 635-655. |
| YUAN Shengjian, MA Yingfei.Research progress and application of phage synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(6): 635-655. | |
| 9 | 齐永. LRIG3基因在三种膀胱癌细胞系中的表达及对其细胞周期、侵袭性和凋亡的影响[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2012. |
| QI Yong. LRIG3 gene expression in three bladder cancer cell lines and its effect on cell cycle, invasiveness and apoptosis[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology,2012. | |
| 10 | 张钰. rhAm原核/真核表达系统的构建及其生物学活性研究[D].广州:暨南大学,2018. |
| ZHANG Yu. Construction of rhAm prokaryotic / eukaryotic expression system and its biological activity[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University, 2018. | |
| 11 | 孙成信.国产自动化实验室流水线产品未来发展和技术预测[J].临床检验杂志(电子版),2020,9(1):249-251. |
| SHUN Chengxin. The future development and technology prediction of domestic automated laboratory assembly line products [J]. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Medicine (Electronic Version), 2020, 9(1):249-251. | |
| 12 | Uber D C, Jaklevic J M, Theil E H,et al.Application of robotics and image processing to automated colony picking and arraying[J]. Biotechniques, 1991, 11(5):642-647. |
| 13 | Jones P, Watson A, Davies M,et al.Integration of image analysis and robotics into a fully automated colony picking and plate handling system[J].Nucleic Acids Research, 1992, 20(17):4599-4606. |
| 14 | Briner D R, Sardhara A D, Sugar T G.A multi-pin end-effector for a robotic colony picker[C]//2009 ASME Early Career Technical Conference,Alabama:ASME Early Career Technical Journal, 2009:222-228. |
| 15 | Hughes S R, Butt T R, Bartolett S, et al. Design and construction of a first-generation high-throughput integrated robotic molecular biology platform for bioenergy applications[J]. Journal of Laboratory Automation, 2011, 16(4):292-307. |
| 16 | Heins R A, Cheng X, Nath S, et al. Phylogenomically guided identification of industrially relevant gh1 β-glucosidases through DNA synthesis and nanostructure-initiator mass spectrometry[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2014, 9(9):2082-2091. |
| 17 | Robotics Hudson. Rapid pick-brochure [EB/OL].[2021-02-26]. . |
| 18 | 于哲.克隆的图像识别及挑取移液机器人运动控制系统[D].广州:机械科学研究院, 2005. |
| YU Zhe. Clone image recognition and picking pipette robot motion control system [D]. Guangzhou: Institute of Mechanical Science, 2005. | |
| 19 | 张国忠.克隆挑取及微量液体提取机器人控制系统[D].广州:机械科学研究院, 2004. |
| ZHANG Guozhong. Cloning picking and micro liquid extraction robot control system [D]. Guangzhou: Institute of Mechanical Science, 2004. | |
| 20 | 曾祥忠. 机器视觉及其应用(系列讲座)第二讲图像采集技术—机器视觉的基础[J]. 应用光学, 2006(6):5-9. |
| ZENG Xiangzhong. Machine vision and its applications (series lectures) lecture 2: image acquisition technology—the foundation of machine vision [J]. Applied Optics, 2006 (6): 5-9. | |
| 21 | 雷文华. 机器视觉及其应用(系列讲座)第一讲机器视觉发展概述[J]. 应用光学, 2006(5):1-4. |
| LEI Wenhua. Machine vision and its applications (series lectures) lecture 1: overview of machine vision development [J]. Applied Optics, 2006 (5): 1-4 | |
| 22 | 朱虹. 机器视觉及其应用(系列讲座)第三讲图像处理与分析—机器视觉的核心[J]. 应用光学, 2007(1):10-13. |
| ZHU Hong. Machine vision and its applications (lecture series) lecture 3 image processing and analysis—the core of machine vision [J]. Applied Optics, 2007 (1): 10-13. | |
| 23 | ZHAO H. Illinois biological foundry for advanced biomanufacturing (iBioFAB)[C]// In Synthetic Biology: Engineering, Evolution, and Design Conference 2015, 2015:784-785. |
| 24 | 张静静,张雯佳,曾磊,等. 迈瑞 BS480 全自动生化分析仪性能评价[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2015, 31(11):1852-1854. |
| ZHANG Jingjing, ZHANG Wenjia, ZENG Lei, et al. Performance evaluation of Mindray BS480 automatic biochemical analyzer[J]. Journal of Practical Medicine, 2015, 31(11):1852-1854. | |
| 25 | 贠远,徐青松,李杨民. 并联微操作机器人技术及应用进展[J]. 机械工程学报, 2008, 44(12):12-23. |
| YUN Yuan, Qingsong XV, LI Yangming. Technology and application progress of parallel micro-operation robot [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2008, 44(12):12-23. | |
| 26 | TILLICH U M, WOLTER N, SCHULZE K, et al. High-throughput cultivation and screening platform for unicellular phototrophs[J]. BMC Microbiology, 2014, 14(1):239. |
| 27 | JAVIDPOUR P, DEUTSCH S, MUTALIK V K, et al. Investigation of proposed ladderane biosynthetic genes from anammox bacteria by heterologous expression in E. coli [J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(3):0151087. |
| 28 | HEINS R A, CHENG X, NATH S, et al. Phylogenomically guided identification of industrially relevant gh1 β-glucosidases through DNA synthesis and nanostructure-initiator mass spectrometry[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2014, 9(9):2082-2091. |
| 29 | HUDSON Robotics. Rapid pick-brochure [EB/OL].[2021-02-26]. . |
| 30 | BING W C, XING C, HING P S. Research of BP neural network algorithm testing platform based on OPC communication[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 21(5): 15-44. |
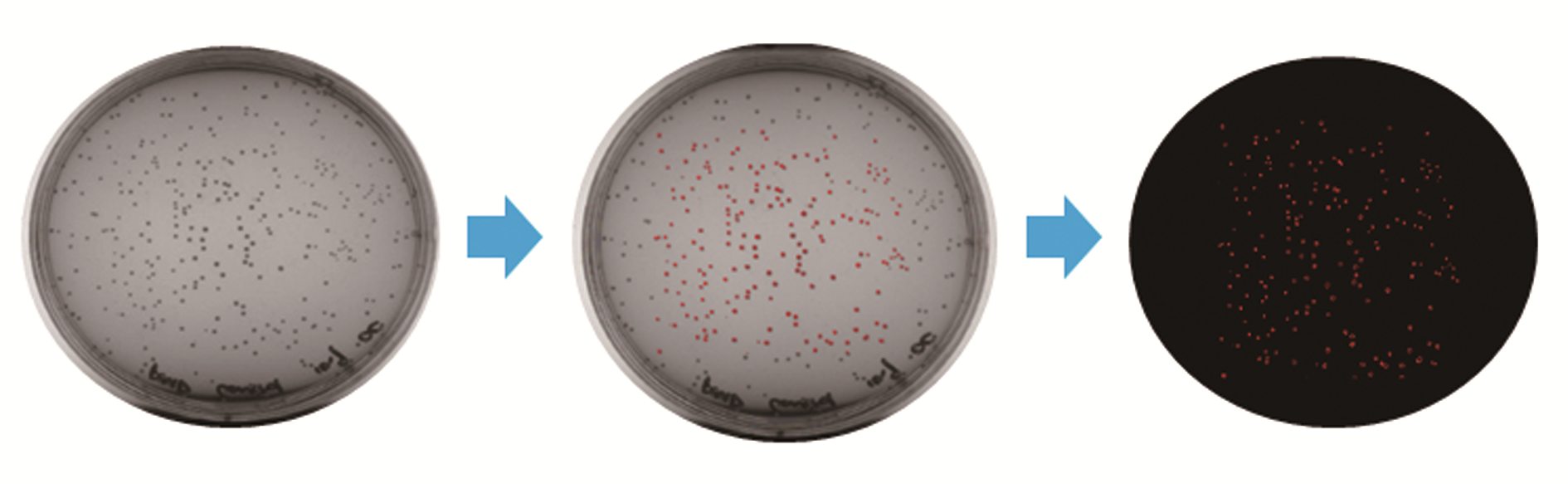
| 31 | 谢非, 汪璠, 杨继全, 等. 一种目标菌落自动定位与识别方法: 201910211847.7[P]. 2019-06-28. |
| XIE Fei, WANG Pan, YANG Jiquan. A method for automatic positioning and identification of target colonies: CN 201910211847.7 [P]. 2019-06-28. |
| [1] | LIU Renmei, LI Leshi, YANG Xiaoyan, CHEN Xianjun, YANG Yi. Technologies for precise spatiotemporal control of post-transcriptional RNA metabolism [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 141-164. |
| [2] | YU Yuanhuan, ZHOU Yang, WANG Xinyi, KONG Deqiang, YE Haifeng. Advances in optogenetics for biomedical research [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 102-140. |
| [3] | LIN Zhi, HU Zhiwei, QU Xudong, LIN Shuangjun. Advances and challenges in microbial production of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(5): 716-733. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||