Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (2): 247-255.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8208.2020-051
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Genome design and synthesis: from replication to rational design
WANG Junyi, WU Xiaole, CAO Yueyang, LI Bingzhi
- Frontiers Science Center for Synthetic Biology and Key Laboratory of Systems Bioengineering (Ministry of Education),School of Chemical Engineering and Technology,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China
-
Received:2020-06-17Revised:2020-12-25Online:2021-04-30Published:2021-04-30 -
Contact:LI Bingzhi
基因组设计与合成:从复写到理性设计
汪君仪, 武晓乐, 曹月阳, 李炳志
- 教育部合成生物学前沿科学中心,系统生物工程教育部重点实验室,天津大学化工学院,天津 300072
-
通讯作者:李炳志 -
作者简介:汪君仪 (1996—),女,博士研究生,研究方向为酿酒酵母基因组设计合成。E-mail:13821492269@163.com
李炳志(1981—),男,博士,教授,研究方向为合成生物学与生物质生物转化。E-mail:bzli@tju.edu.cn -
基金资助:真核微生物基因组的人工设计与合成(2018YFA0900100)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WANG Junyi, WU Xiaole, CAO Yueyang, LI Bingzhi. Genome design and synthesis: from replication to rational design[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(2): 247-255.
汪君仪, 武晓乐, 曹月阳, 李炳志. 基因组设计与合成:从复写到理性设计[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(2): 247-255.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8208.2020-051
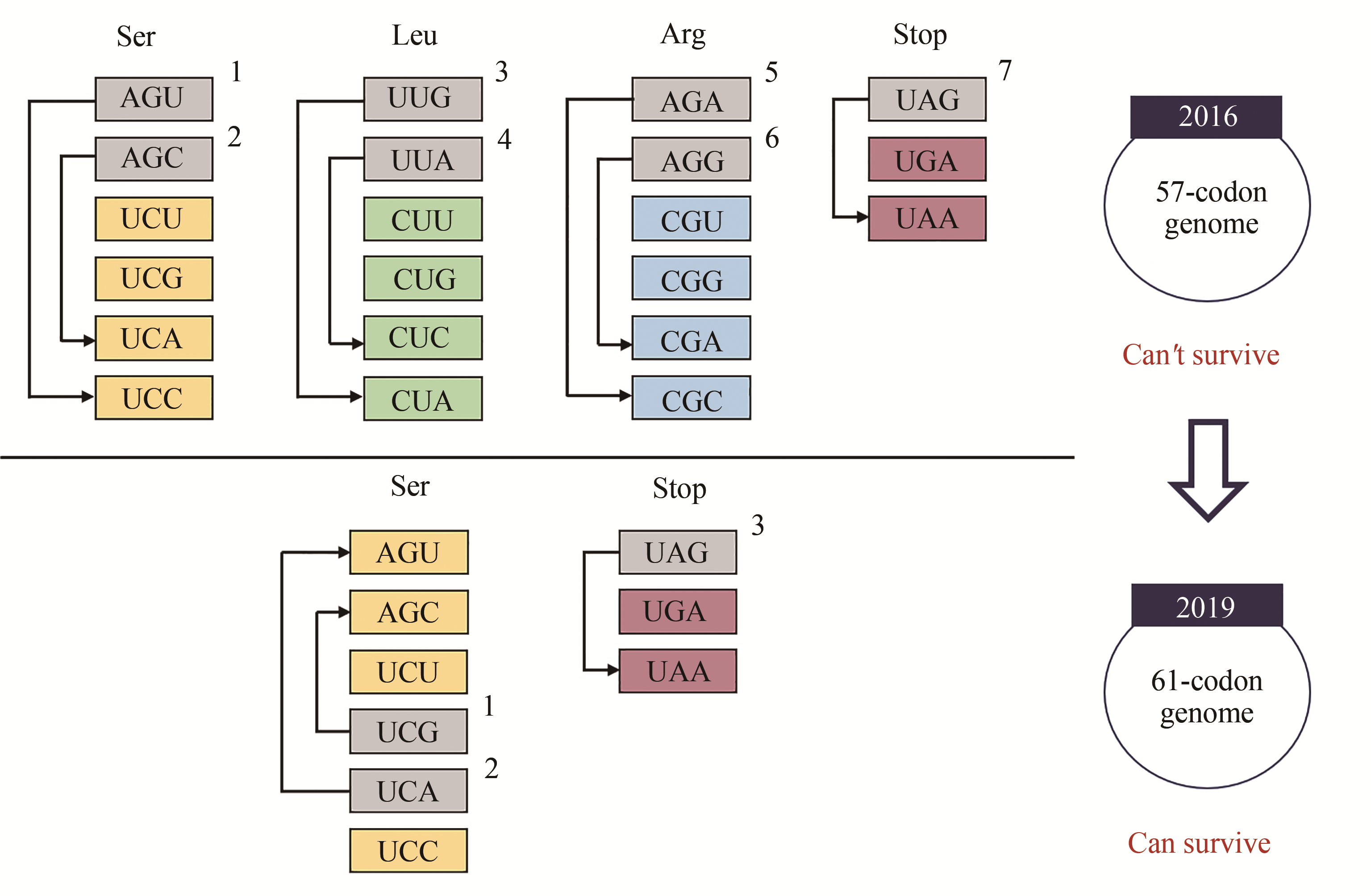
Fig. 1 Research progress on codons deletion[16,18](In 2016, seven codons were replaced with synonymous alternatives the entire genome of E. coli by Church's group, more than 90% of the genes retained functionality[16]; In 2019, Chin's group recoded 18 214 codons to create a strain with a 61-codon genome [18])
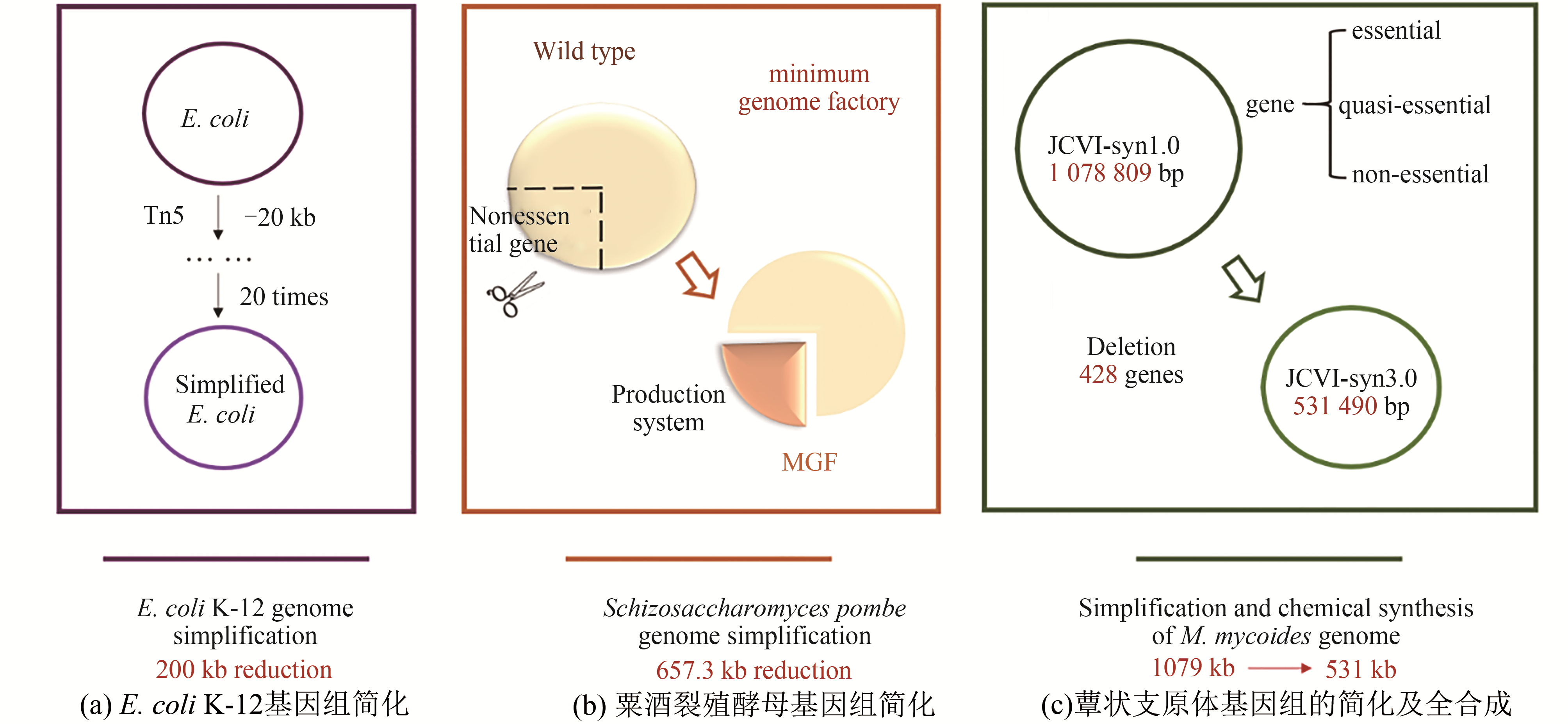
Fig. 2 Advances in genome simplification[19,50-51][(a) Simplification of the E. coli K-12 genome. The deletion procedure has reduced the genome at an average of 200 kb by using specialized transposons (Tn5 derivatives) to create deletions in the E. coli K-12 chromosome[50]. (b) Simplification of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe genome. Researchers have reduced the genome of S. pombe by 657.3 kb using a large-scale gene deletion method called LATOUR[51]. (c) Simplification and chemical synthesis of M. mycoides genome. Using whole-genome design and complete chemical synthesis, researchers have minimized the 1079-kilobase pair synthetic genome of M. mycoides JCVI-syn1.0. Three cycles of design, synthesis, and testing, with the retention of essential and quasi-essential genes, produced JCVI-syn3.0 (531 kilobase pairs, 473 genes)[19]]
| 1 | SANGER F, NICKLEN S, COULSON A R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1977, 74(12): 5463-5467. |
| 2 | STEUERNAGEL B, TAUDIEN S, GUNDLACH H, et al. De novo 454 sequencing of barcoded BAC pools for comprehensive gene survey and genome analysis in the complex genome of barley[J]. BMC Genomics, 2009, 10(1): 547. |
| 3 | ROTHBERG J M, HINZ W, REARICK T M, et al. An integrated semiconductor device enabling non-optical genome sequencing[J]. Nature, 2011, 475(7356): 348-352. |
| 4 | CELLO J, PAUL A V, WIMMER E. Chemical synthesis of poliovirus cDNA: generation of infectious virus in the absence of natural template[J]. Science, 2002, 297(5583): 1016-1018. |
| 5 | SMITH H O, HUTCHISON C A, PFANNKOCH C, et al. Generating a synthetic genome by whole genome assembly: φX174 bacteriophage from synthetic oligonucleotides[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2003, 100(26): 15440-15445. |
| 6 | THAO T T N, LABROUSSAA F, EBERT N, et al. Rapid reconstruction of SARS-CoV-2 using a synthetic genomics platform[J]. Nature, 2020. |
| 7 | GIBSON D G, BENDERS G A, ANDREWS-PFANNKOCH C, et al. Complete chemical synthesis, assembly, and cloning of a Mycoplasma genitalium genome[J]. Science, 2008, 319(5867): 1215-1220. |
| 8 | GIBSON D G, GLASS J I, LARTIGUE C, et al. Creation of a bacterial cell controlled by a chemically synthesized genome[J]. Science, 2010, 329(5987): 52-56. |
| 9 | ZIMMER R, GIBBINS A M. Construction and characterization of a large-fragment chicken bacterial artificial chromosome library[J]. Genomics, 1997, 42(2): 217-226. |
| 10 | DE LISE A M, TUAN R S. Electroporation-mediated DNA transfection of embryonic chick limb mesenchymal cells[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2000: 377-382. |
| 11 | CO D O, BOROWSKI A H, LEUNG J D, et al. Generation of transgenic mice and germline transmission of a mammalian artificial chromosome introduced into embryos by pronuclear microinjection[J]. Chromosome Research, 2000, 8(3):183-191. |
| 12 | PAULIS M. Chromosome transfer via cell fusion[J]. Methods of Molecular Biology, 2011,738: 57-67. |
| 13 | BROWN D M, CHAN Y A, DESAI P J, et al. Efficient size-independent chromosome delivery from yeast to cultured cell lines[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2016(7):e50. |
| 14 | SUZUKI T, KAZUKI Y, HARA T, et al. Current advances in microcell-mediated chromosome transfer technology and its applications[J]. Experimental Cell Research, 2020, 390(1):111915. |
| 15 | LAJOIE M J, ROVNER A J, GOODMAN D B, et al. Genomically recoded organisms expand biological functions[J]. Science, 2013, 342(6156): 357-360. |
| 16 | OSTROV N, LANDON M, GUELL M, et al. Design, synthesis, and testing toward a 57-codon genome[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6301): 819-822. |
| 17 | WANG K, FREDENS J, BRUNNER S F, et al. Defining synonymous codon compression schemes by genome recoding[J]. Nature, 2016, 539(7627): 59-64. |
| 18 | FREDENS J, WANG K, DE LA TORRE D, et al. Total synthesis of Escherichia coli with a recoded genome[J]. Nature, 2019, 569(7757): 514-518. |
| 19 | HUTCHISON C A, CHUANG R Y, NOSKOV V N, et al. Design and synthesis of a minimal bacterial genome[J]. Science, 2016, 351(6280). |
| 20 | DYMOND J S, RICHARDSON S M, COOMBES C E, et al. Synthetic chromosome arms function in yeast and generate phenotypic diversity by design[J]. Nature, 2011, 477(7365): 471-476. |
| 21 | ANNALURU N, MULLER H, MITCHELL L A, et al. Total synthesis of a functional d esigner eukaryotic chromosome[J]. Science, 2014, 344(6179): 55-58. |
| 22 | SHEN Y, WANG Y, CHEN T, et al. Deep functional analysis of synII, a 770-kilobase synthetic yeast chromosome[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6329): eaaf4791. |
| 23 | XIE Z X, LI B Z, MITCHELL L A, et al. "Perfect" designer chromosome V and behavior of a ring derivative[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6329): eaaf4704. |
| 24 | MITCHELL L A, WANG A, STRACQUADANIO G, et al. Synthesis, debugging, and effects of synthetic chromosome consolidation: synVI and beyond[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6329): eaaf4831. |
| 25 | WU Y, LI B Z, ZHAO M, et al. Bug mapping and fitness testing of chemically synthesized chromosome X[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6329): eaaf4706. |
| 26 | ZHANG W, ZHAO G, LUO Z, et al. Engineering the ribosomal DNA in a megabase synthetic chromosome[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6329): eaaf3981. |
| 27 | SHAO Y, LU N, WU Z, et al. Creating a functional single-chromosome yeast[J]. Nature, 2018, 560(7718): 331-335. |
| 28 | SHAO Y, LU N, CAI C, et al. A single circular chromosome yeast[J]. Cell Research, 2019, 29(1): 87-89. |
| 29 | OSTROV N, BEAL J, ELLIS T, et al. Technological challenges and milestones for writing genomes[J]. Science, 2019, 366(6463): 310-312. |
| 30 | 柴梦哲, 贾斌, 李炳志,等. 人工基因组合成与重排研究进展[J]. 生命科学, 2019, 31(4):46-53. |
| CHAI M Z, JIA B, LI B Z, et al. Progress in research on artificial gene assembly and rearrangement [J]. Chinese Bulletin Life Science, 2019, 31(4): 46-53. | |
| 31 | 罗周卿, 戴俊彪. 合成基因组学:设计与合成的艺术[J]. 生物工程学报, 2017, 33(3): 331-342. |
| LUO Z Q, DAI J B. Synthetic genomics: the art of design and synthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2017, 33(3): 331-342. | |
| 32 | GUSTAFSSON C, GOVINDARAJAN S, MINSHULL J. Codon bias and heterologous protein expression[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2004, 22(7): 346-353. |
| 33 | CHIN J X, CHUNG B K S, Lee D Y. Codon Optimization OnLine (COOL): a web-based multi-objective optimization platform for synthetic gene design[J]. Bioinformatics, 2014, 30(15): 2210-2212. |
| 34 | CANNAROZZI G, SCHRAUDOLPH N N, FATY M, et al. A role for codon order in translation dynamics[J]. Cell, 2010, 141(2): 355-367. |
| 35 | RICHARDSON S M, MITCHELL L A, STRACQUADANIO G, et al. Design of a synthetic yeast genome[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6329): 1040-1044. |
| 36 | LUO Z, WANG L, WANG Y, et al. Identifying and characterizing SCRaMbLEd synthetic yeast using ReSCuES[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1-10. |
| 37 | MA L, LI Y, CHEN X, et al. SCRaMbLE generates evolved yeasts with increased alkali tolerance[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2019, 18(1): 52. |
| 38 | HOESS R H, WIERZBICKI A, ABREMSKI K. The role of the loxP spacer region in PI site-specific recombination[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1986, 14(5): 2287-2300. |
| 39 | SHEN Y, STRACQUADANIO G, WANG Y, et al. SCRaMbLE generates designed combinatorial stochastic diversity in synthetic chromosomes[J]. Genome Research, 2016, 26(1): 36-49. |
| 40 | JIA B, WU Y, LI B Z, et al. Precise control of SCRaMbLE in synthetic haploid and diploid yeast[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1-13. |
| 41 | LIN Q, QI H, WU Y, et al. Robust orthogonal recombination system for versatile genomic elements rearrangement in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 15249. |
| 42 | HOCHREIN L, MITCHELL L A, SCHULZ K, et al. L-SCRaMbLE as a tool for light-controlled Cre-mediated recombination in yeast[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1-10. |
| 43 | SHEN M J, WU Y, YANG K, et al. Heterozygous diploid and interspecies SCRaMbLEing[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1-8. |
| 44 | WU Y, ZHU R Y, Mitchell L A, et al. In vitro DNA SCRaMbLE[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1-9. |
| 45 | LIU W, LUO Z, WANG Y, et al. Rapid pathway prototyping and engineering using in vitro and in vivo synthetic genome SCRaMbLE-in methods[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1-12. |
| 46 | BLOUNT B A, GOWERS G O F, HO J C H, et al. Rapid host strain improvement by in vivo rearrangement of a synthetic yeast chromosome[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1-10. |
| 47 | WANG J, JIA B, XIE Z, et al. Improving prodeoxyviolacein production via multiplex SCRaMbLE iterative cycles[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2018, 12(4): 806-814. |
| 48 | WANG P X, XU H, LI H, et al. SCRaMbLEing of a synthetic yeast chromosome with clustered essential genes reveals synthetic lethal interactions[J].ACS Synthetic Biology,2020,9(5):1181-1189. |
| 49 | LUO Z Q, YU K, XIE S Q, et al. Compacting a synthetic yeast chromosome arm[J]. Genome Biology, 2021, 22. DOI: 10.1186/s 13059-020-02232-8 . |
| 50 | GORYSHIN I Y, NAUMANN T A, APODACA J, et al. Chromosomal deletion formation system based on Tn5 double transposition: use for making minimal genomes and essential gene analysis[J]. Genome Research, 2003, 13(4): 644-653. |
| 51 | KUMAGAI H, SASAKI M, IDIRIS A, et al. Minimum genome factories in Schizosaccharomyces pombe [M]//Microbial production, Tokyo: Springer, 2014: 17-24. |
| 52 | BOEKE J D, CHURCH G, HESSEL A, et al. The genome project-write[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6295): 126-127. |
| 53 | MEINKE G, BOHM A, HAUBER J, et al. Cre recombinase and other tyrosine recombinases[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2016, 116(20): 12785-12820. |
| [1] | HE Bo, FU Zongheng, WU Yi, ZHAO Guangrong. Research progress of synthetic mammalian genomics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(1): 78-97. |
| [2] | Hui WANG, Junbiao DAI, Zhouqing LUO. Reading, editing, and writing techniques for genome research [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(5): 503-515. |
| [3] | Mingzhu DING, Bingzhi LI, Ying WANG, Zexiong XIE, Duo LIU, Yingjin YUAN. Significant research progress in synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(1): 7-28. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||