|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Application and prospect of live cell DNA-based molecular recorders in cell lineage tracing
Synthetic Biology Journal
2025, 6 (3):
651-668.
DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-082
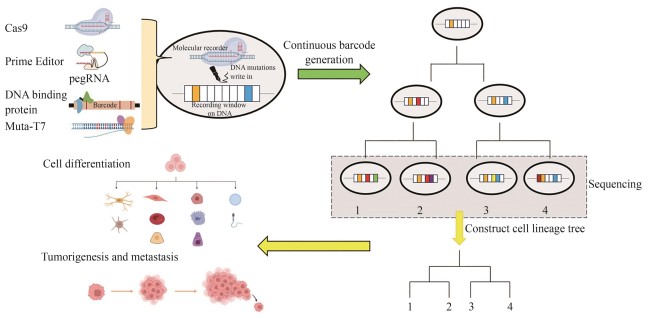
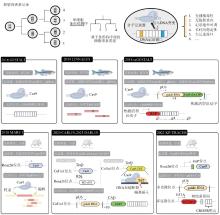
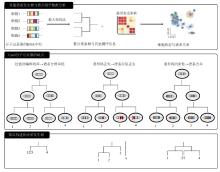
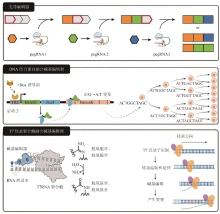
Tracing the division and differentiation history of cells is a critical issue in organismal development and cancer research. Live cell DNA-based molecular recorders, a synthetic system that induces heritable DNA variations, offers an innovative approach for reconstructing cell lineage histories. As a representative for the new generation of cell lineage tracing method, this system can be integrated with high-throughput single-cell sequencing and multi-omics analysis, enabling the reconstruction of developmental differentiation pathways of cells and the phylogenetic trees of tumorigenesis as well. Live cell DNA-based molecular recorders serve as an effective platform for exploring these core biological processes. This review systematically analyzes the technological evolution of Cas9-based molecular recorders in lineage tracing since 2016 and its applications, while also analyzing the research trends of some novel molecular recorders and evaluating their advantages and limitations. Since 2016, molecular recorders based on the CRISPR-Cas9 system have made significant progress and gradually become the mainstream technology in this field. However, Cas9-based molecular recorders still suffer from several inherent limitations, such as the low lineage resolution due to insufficient editing efficiencies, the loss of recorded information caused by DNA double-strand breaks, and potential lineage merging due to barcode homoplasy. These limitations pose challenges for researchers to explore and develop new types of molecular recorders as more efficient and precise tools for cell lineage tracing. Novel molecular recorders based on new principles, such as prime editors, DNA-binding protein-fused base editors, and T7 RNA polymerase-fused base editors, can avoid DNA double-strand breaks and record information through base substitutions rather than deletions. Compared to the Cas9 system, they exhibit unique advantages but also come with potential risks and challenges. Prime editors can record information in a temporal sequential manner, but off-target effects remain a concern. DNA-binding protein-fused base editors offer high editing efficiencies and specificities, but their effectiveness across different cell types requires further exploration. T7 RNA polymerase-fused base editors have achieved success in in vivo directed evolution systems, but their application in mammalian systems is still limited. In the future, the research of DNA-based molecular recorders should focus on optimizing editing efficiency, reducing information loss, improving lineage recovery efficiency, and exploring their application potentials in complicated biological systems.
Table 1
Summary of the characteristics of Cas9-based molecular recorders
Extracts from the Article
2016年,CRISPR-Cas9系统被引入细胞谱系追踪领域,推动了这一领域的迅速发展。本节中,我们将对近年来的代表性研究进行系统性的介绍(图1、表1),重点关注Cas9分子记录器的技术发展和遇到的问题,同时,也对每项研究的体系和结论进行简单的介绍。
Other Images/Table from this Article
|