合成生物学 ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (5): 837-849.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-024
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
利用异源表达挖掘纤维堆囊菌So0157-2的新型天然产物
周海波, 申琪瑶, 陈汉娜, 王宗杰, 李越中, 张友明, 卞小莹
- 山东大学,微生物技术国家重点实验室,山东 青岛 266237
-
收稿日期:2021-02-20修回日期:2021-04-06出版日期:2021-10-31发布日期:2021-11-19 -
通讯作者:张友明,卞小莹 -
作者简介:周海波 (1987—),男,博士,助理研究员。研究方向为微生物次级代谢产物的发现及其生物合成途径解析。E-mail:haibozhou@sdu.edu.cn张友明 (1964—),男,博士生导师,教授。研究方向为基因组编辑与合成生物学等。E-mail:zhangyouminng@sdu.edu.cn卞小莹 (1983—),男,博士生导师,教授。研究方向为微生物天然产物合成生物学等。E-mail:bianxiaoying@sdu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2019YFA0905700);国家自然科学基金(32070060);山东省自然科学基金(ZR2020QH345)
Genome mining for novel natural products in Sorangium cellulosum So0157-2 by heterologous expression
ZHOU Haibo, SHEN Qiyao, CHEN Hanna, WANG Zongjie, LI Yuezhong, ZHANG Youming, BIAN Xiaoying
- State Key Laboratory of Microbial Technology,Shandong University,Qingdao 266237,Shandong,China
-
Received:2021-02-20Revised:2021-04-06Online:2021-10-31Published:2021-11-19 -
Contact:ZHANG Youming, BIAN Xiaoying
摘要:
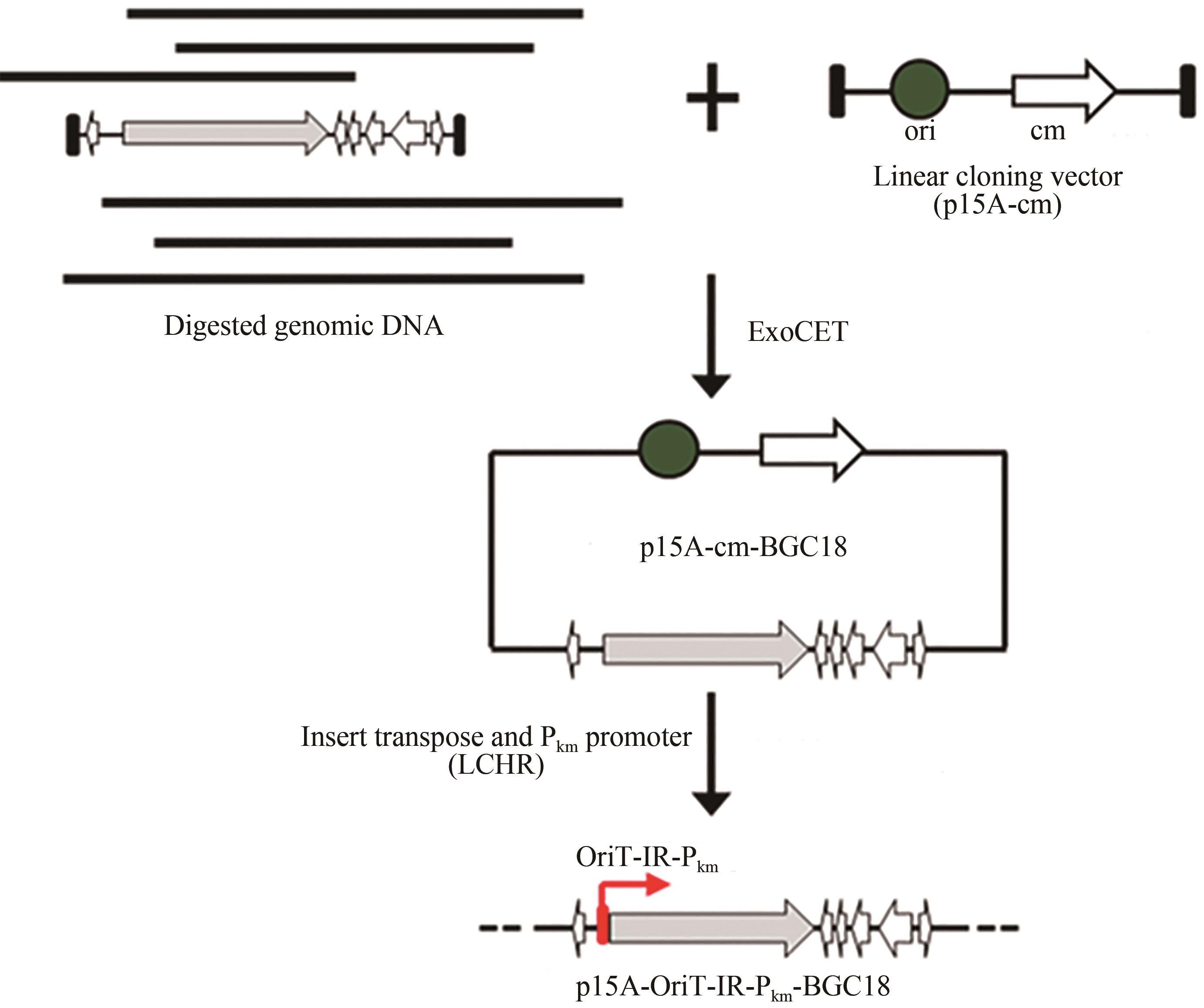
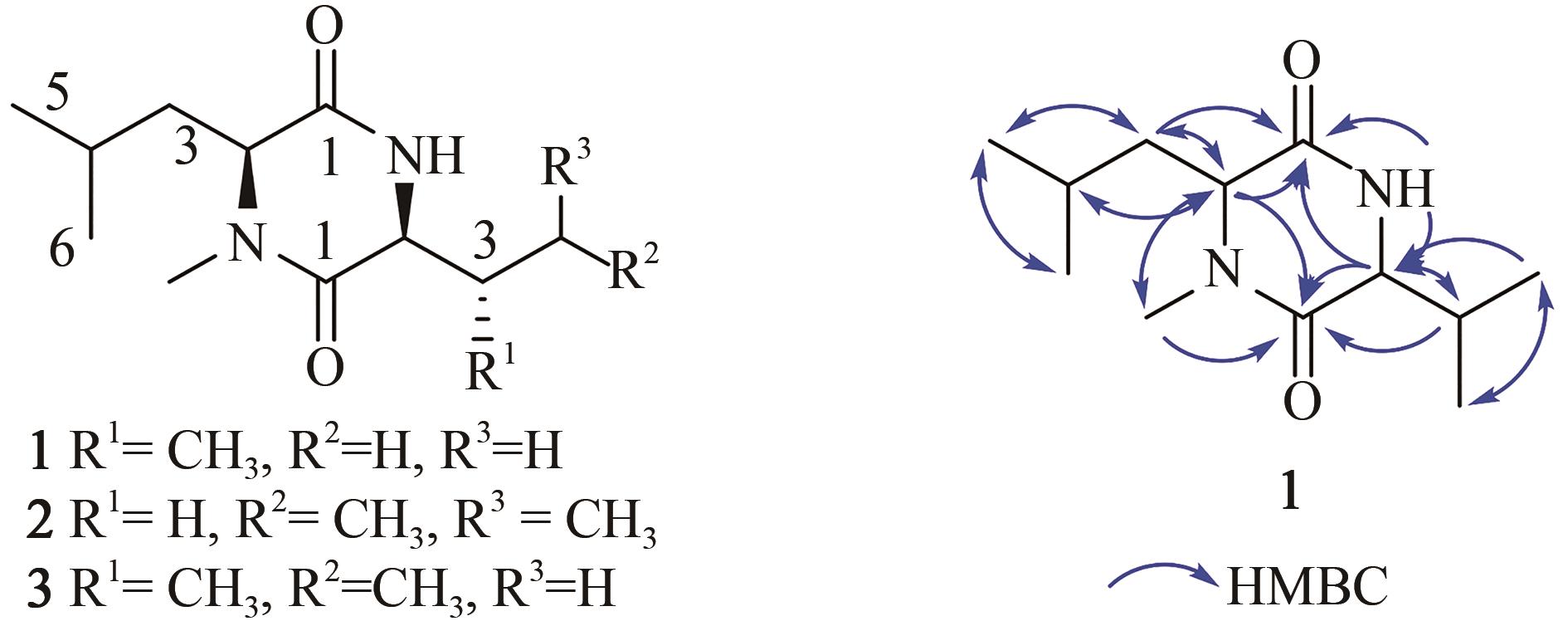
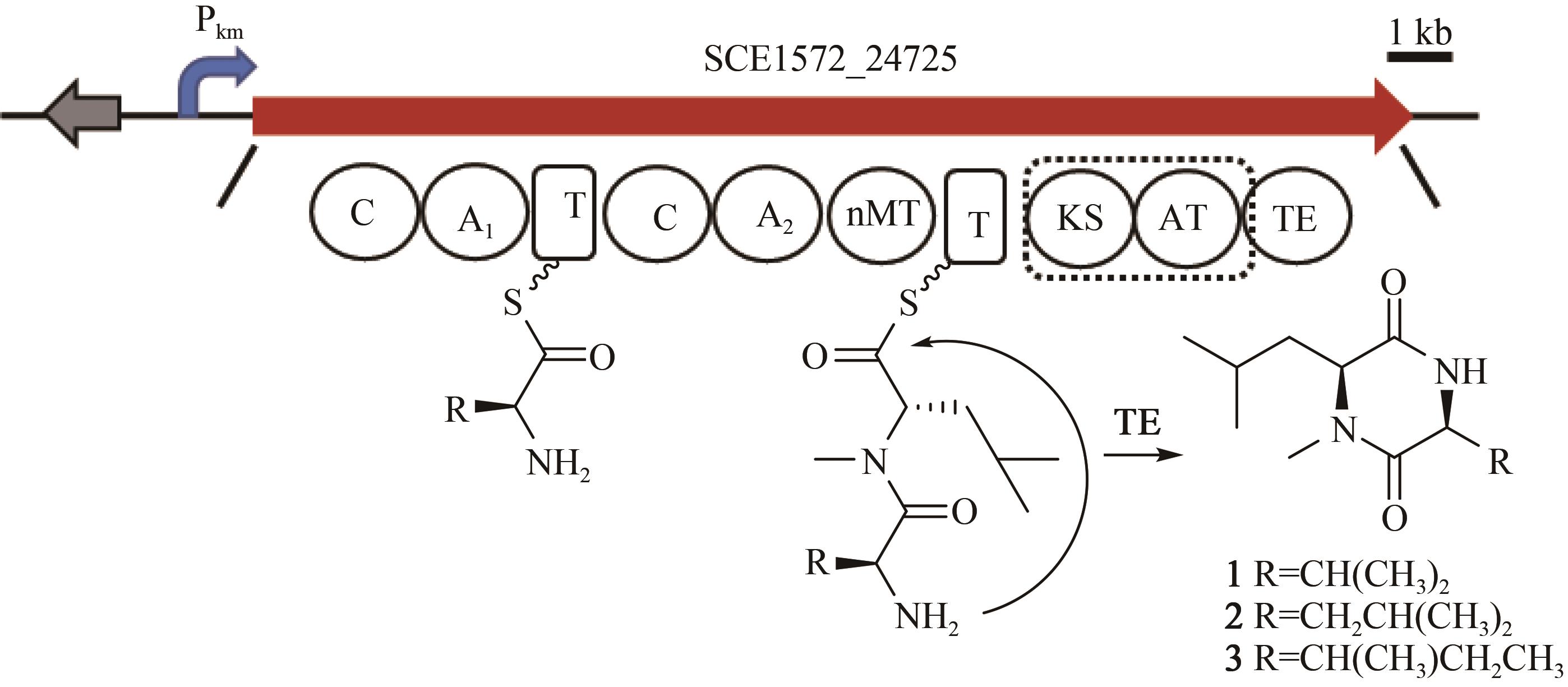
黏细菌是天然产物的重要来源。纤维堆囊菌So0157-2是抗癌药物埃博霉素的产生菌,并且是已知基因组最大的原核生物。生物信息学分析发现该菌一共含有35个次级代谢产物生物合成基因簇,除了已知的埃博霉素基因簇和其他两个萜类化合物生物合成基因簇与已知基因簇的相似度为100%之外,其他基因簇与已知化合物基因簇相似度均较低,其中包括17个聚酮合酶(polyketide synthase,PKS)、非核糖体肽合成酶(nonribosomal peptide synthetase,NRPS)及其杂合的基因簇。由于纤维堆囊菌So0157-2生长缓慢、培养困难且难以在本源菌中进行遗传改造。因此,将其生物合成基因簇转移到简单宿主中,利用异源表达策略是挖掘该菌中新颖天然产物的一个有效途径。本文利用直接克隆技术从纤维堆囊菌So0157-2基因组DNA中克隆了1个包含NRPS和PKS结构域的基因簇BGC18,将其转移至伯克氏菌DSM 7029中进行异源表达。通过液质联用分析,色谱柱靶向分离纯化,进而通过NMR结构鉴定和Marfey反应确定了3个化合物分别为Cyclo(N-Me-L-Leu-L-Val)(1)、Cyclo(N-Me-L-Leu-L-Leu)(2)、Cyclo(N-Me-L-Leu-L-Ile)(3)。化合物结构的多样性来源于第1个腺苷化结构域对底物识别的宽泛性(Val/Leu/Ile)。生物合成途径分析推测由于缺少硫醇化结构域导致PKS模块被跳过,从而只获得了NRPS指导合成的环二肽产物1~3,这可能是细菌中一种实现化合物多样性的方式。本论文以基因簇直接克隆与异源表达相结合的策略,成功实现了一个来源于纤维堆囊菌So0157-2中的NRPS-PKS杂合基因簇的异源表达,分离并鉴定了3个该基因簇对应的表达产物。本研究为后续从该菌株中挖掘更多活性天然产物奠定了技术基础,也为其他难培养菌株的次级代谢产物的挖掘提供了思路。
中图分类号:
引用本文
周海波, 申琪瑶, 陈汉娜, 王宗杰, 李越中, 张友明, 卞小莹. 利用异源表达挖掘纤维堆囊菌So0157-2的新型天然产物[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(5): 837-849.
ZHOU Haibo, SHEN Qiyao, CHEN Hanna, WANG Zongjie, LI Yuezhong, ZHANG Youming, BIAN Xiaoying. Genome mining for novel natural products in Sorangium cellulosum So0157-2 by heterologous expression[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(5): 837-849.
| Strains/Plasmids | Description | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Strains | [ | |
| Escherichia coli GB05-dir | GB2005, araC-PBAD-ETgA; recE, recT, redγ, and recA regulated by arabinose-induced promoter are inserted at ybcC locus | |
| E. coli GB05-red | GB2005, araC-PBAD-αβγA; redα, redβ, redγ, and recA regulated by arabinose-induced promoter are integrated at ybcC locus | [ |
| S. cellulosum So0157-2 | wild type harboring BGC18 | [ |
| S. brevitalea DSM 7029 | Burkholderiales strain DSM 7029, [Polyangium] brachysporum DSM 7029 (K481-B101; ATCC 53080) | [ |
| DSM7029:Pkm-BGC18 | Pkm-BGC18 was inserted into genome of Schlegelella brevitalea DSM 7029, kmR | This work |
| Plasmids | ||
| p15A-cm-tetR-tetO-hyg-ccdB | direct cloning vector, p15A replicon, containing a tetracycline inducible promoter PtetO, cmR/hygR | [ |
| pR6K-oriT-TnpA-IR-km | R6K replicon, containing MycoMar transposase gene (tnpA) and conjugation element oriT, kmR | [ |
| p15A-cm-BGC18 | BGC18 was cloned into cloning vector, cmR | This work |
| p15A-oriT-IR-Pkm-BGC18 | Expression vector of BGC18 with Pkm was inserted into upstream of the first core gene of BGC18, containing transposon elements oriT-tnpA-IR, kmR | This work |
表1 本研究所用的菌株和质粒
Tab. 1 Strains and plasmids used in this study
| Strains/Plasmids | Description | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Strains | [ | |
| Escherichia coli GB05-dir | GB2005, araC-PBAD-ETgA; recE, recT, redγ, and recA regulated by arabinose-induced promoter are inserted at ybcC locus | |
| E. coli GB05-red | GB2005, araC-PBAD-αβγA; redα, redβ, redγ, and recA regulated by arabinose-induced promoter are integrated at ybcC locus | [ |
| S. cellulosum So0157-2 | wild type harboring BGC18 | [ |
| S. brevitalea DSM 7029 | Burkholderiales strain DSM 7029, [Polyangium] brachysporum DSM 7029 (K481-B101; ATCC 53080) | [ |
| DSM7029:Pkm-BGC18 | Pkm-BGC18 was inserted into genome of Schlegelella brevitalea DSM 7029, kmR | This work |
| Plasmids | ||
| p15A-cm-tetR-tetO-hyg-ccdB | direct cloning vector, p15A replicon, containing a tetracycline inducible promoter PtetO, cmR/hygR | [ |
| pR6K-oriT-TnpA-IR-km | R6K replicon, containing MycoMar transposase gene (tnpA) and conjugation element oriT, kmR | [ |
| p15A-cm-BGC18 | BGC18 was cloned into cloning vector, cmR | This work |
| p15A-oriT-IR-Pkm-BGC18 | Expression vector of BGC18 with Pkm was inserted into upstream of the first core gene of BGC18, containing transposon elements oriT-tnpA-IR, kmR | This work |
| Primers | Sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| BGC18-HAF | cagtatggccgatcggggtgtcagcggtcaacacgcgagctcgctcgctctgtggcggcgctctcatggtgcAACGCTCTCTACTAGAGTCA |
| BGC18-HAR | gacgtgaccgggtatcgctaggtccacccaccaggagtccggccagggatccggagagtgagagttcaacgcGGGTCTTAAGACGTCGATATCT |
| IR-Pkm-C18-HAF1 | gcctgcgatcgtaccattacgtatttttgcgcgagcggaacggtatgcagGCTGATCTTCAGATCCTCTAC |
| IR-Pkm-C18-HAR1 | tcgagccgcaaggcgcattcttgctccagagagagcggcatagtacccaacctcctTCAGAAGAACTCGTCAAGAAG |
| detect-C18 in 7029-F1 | GATGGGTTATCAGGACTACGC |
| detect-C18 in 7029-R1 | CGAGGAGCCTGTAGAACGCGT |
| detect-C18 in 7029-F2 | TCGACGATCAGGTGAAGATCCA |
| detect-C18 in 7029-R2 | AGCTCTCCATAGGTGAGCGAA |
| detect-C18 in 7029-F3 | TGAAGATCCGCGGCTATCGCA |
| detect-C18 in 7029-R3 | CGGGAACTGGAACAGGTCCAT |
| detect-C18 in 7029-F4 | TTCTTCGTCAACGCCGCGCC |
| detect-C18 in 7029-R4 | GCGATAGGCGTGCACCGTGC |
| detect-C18 in 7029-F5 | TCACGCTGCCGCAAGCACTC |
| detect-C18 in 7029-R5 | GCTCTGCGAAGGACGTCCTC |
表2 本研究所用的引物
Tab. 2 Primers used in this study
| Primers | Sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| BGC18-HAF | cagtatggccgatcggggtgtcagcggtcaacacgcgagctcgctcgctctgtggcggcgctctcatggtgcAACGCTCTCTACTAGAGTCA |
| BGC18-HAR | gacgtgaccgggtatcgctaggtccacccaccaggagtccggccagggatccggagagtgagagttcaacgcGGGTCTTAAGACGTCGATATCT |
| IR-Pkm-C18-HAF1 | gcctgcgatcgtaccattacgtatttttgcgcgagcggaacggtatgcagGCTGATCTTCAGATCCTCTAC |
| IR-Pkm-C18-HAR1 | tcgagccgcaaggcgcattcttgctccagagagagcggcatagtacccaacctcctTCAGAAGAACTCGTCAAGAAG |
| detect-C18 in 7029-F1 | GATGGGTTATCAGGACTACGC |
| detect-C18 in 7029-R1 | CGAGGAGCCTGTAGAACGCGT |
| detect-C18 in 7029-F2 | TCGACGATCAGGTGAAGATCCA |
| detect-C18 in 7029-R2 | AGCTCTCCATAGGTGAGCGAA |
| detect-C18 in 7029-F3 | TGAAGATCCGCGGCTATCGCA |
| detect-C18 in 7029-R3 | CGGGAACTGGAACAGGTCCAT |
| detect-C18 in 7029-F4 | TTCTTCGTCAACGCCGCGCC |
| detect-C18 in 7029-R4 | GCGATAGGCGTGCACCGTGC |
| detect-C18 in 7029-F5 | TCACGCTGCCGCAAGCACTC |
| detect-C18 in 7029-R5 | GCTCTGCGAAGGACGTCCTC |
| Gene Clusters | Type | Similar known cluster | Similarity |
|---|---|---|---|
BGC1 BGC2 BGC3 BGC4 BGC5 BGC6 BGC7 BGC8 BGC9 BGC10 BGC11 BGC12 BGC13 BGC14 BGC15 BGC16 BGC17 BGC18 BGC19 BGC20 BGC21 BGC22 BGC23 BGC24 BGC25 BGC26 BGC27 BGC28 BGC29 BGC30 BGC31 BGC32 BGC33 BGC34 BGC35 | RiPP-like NRPS Thioamitides NRPS-PKS NRPS-PKS hglE-KS RiPP-like RiPP-like Indole T3PKS NRPS-T1PKS Terpene T1PKS NRPS RiPP-like thioamitides NRPS NRPS-T1PKS NRPS-T1PKS hglE-KS NRPS-T1PKS NRPS-T1PKS arylpolyene LAP, RRE-containing RiPP-like RiPP-like T1PKS T1PKS microbiridin phosphonate NRPS RiPP-like NRPS-T1PKS terpene NRPS | — — — pyxipyrrolone A/B kirromycin — — — — alkylpyrone-407/393 disorazol A geosmin pallasoren — — — myxochelin A/B — Epothilone — — Hapalosin N-tetradecanoyl tyrosine — — — — — microviridin J — coelibactin — crochelin A eremophikene — | — — — 11% 5% — — — — 6% 23% 100% 50% — — — 50% — 100% — — 40% 6% — — — — — 66% — 45% — 26% 100% — |
表3 antiSMASH 预测So0157-2基因组编码的生物合成基因簇
Tab. 3 Biosynthetic gene clusters in the genome of so0157-2 predicted by antiSMASH
| Gene Clusters | Type | Similar known cluster | Similarity |
|---|---|---|---|
BGC1 BGC2 BGC3 BGC4 BGC5 BGC6 BGC7 BGC8 BGC9 BGC10 BGC11 BGC12 BGC13 BGC14 BGC15 BGC16 BGC17 BGC18 BGC19 BGC20 BGC21 BGC22 BGC23 BGC24 BGC25 BGC26 BGC27 BGC28 BGC29 BGC30 BGC31 BGC32 BGC33 BGC34 BGC35 | RiPP-like NRPS Thioamitides NRPS-PKS NRPS-PKS hglE-KS RiPP-like RiPP-like Indole T3PKS NRPS-T1PKS Terpene T1PKS NRPS RiPP-like thioamitides NRPS NRPS-T1PKS NRPS-T1PKS hglE-KS NRPS-T1PKS NRPS-T1PKS arylpolyene LAP, RRE-containing RiPP-like RiPP-like T1PKS T1PKS microbiridin phosphonate NRPS RiPP-like NRPS-T1PKS terpene NRPS | — — — pyxipyrrolone A/B kirromycin — — — — alkylpyrone-407/393 disorazol A geosmin pallasoren — — — myxochelin A/B — Epothilone — — Hapalosin N-tetradecanoyl tyrosine — — — — — microviridin J — coelibactin — crochelin A eremophikene — | — — — 11% 5% — — — — 6% 23% 100% 50% — — — 50% — 100% — — 40% 6% — — — — — 66% — 45% — 26% 100% — |
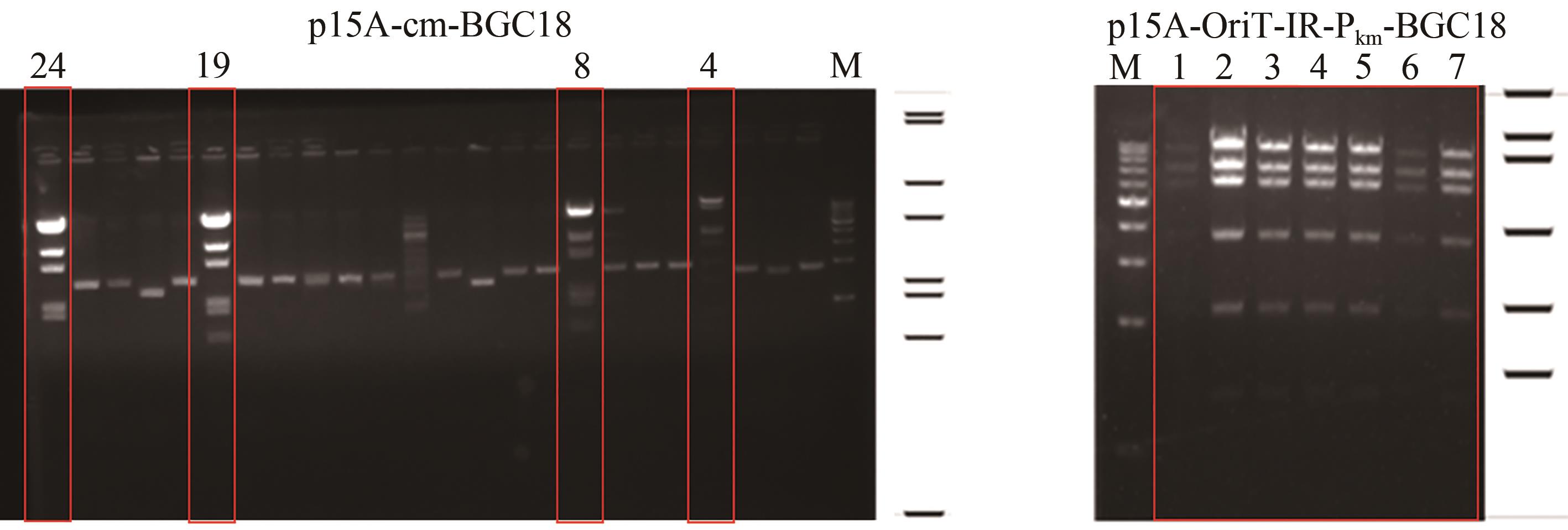
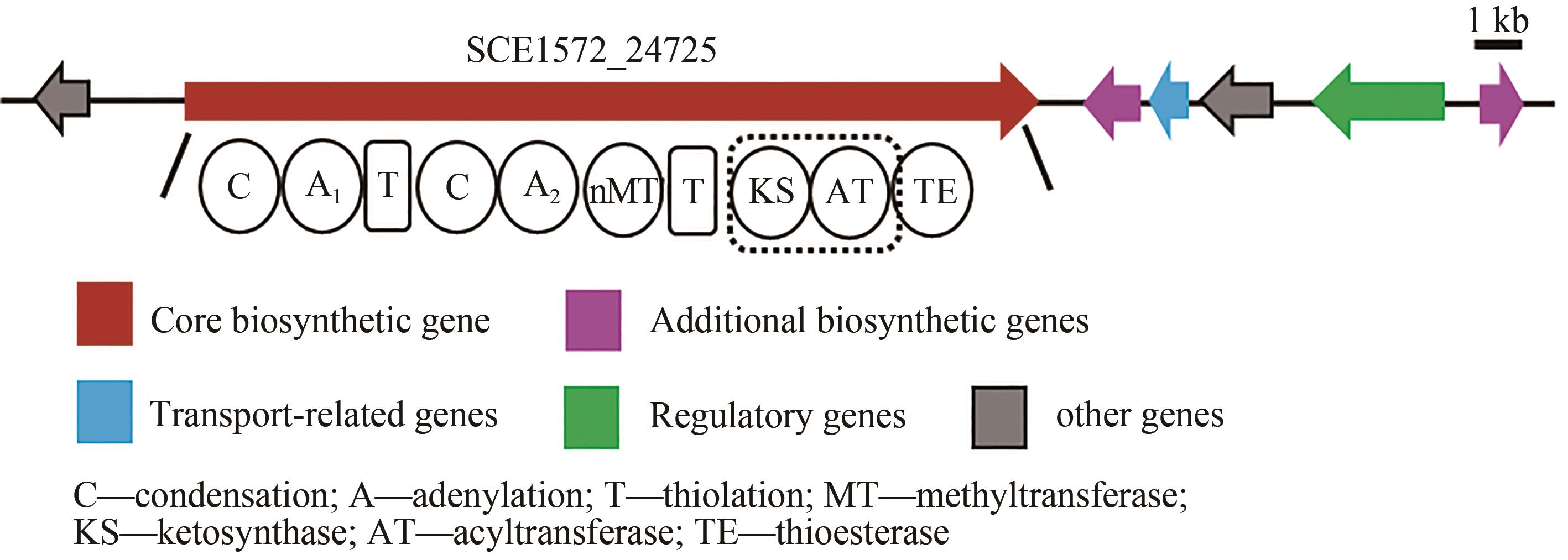
图3 重组质粒p15A-cm-BGC18(a)和p15A-OriT-IR-Pkm-BGC18(b)分别以MscⅠ和ApaLⅠ酶切鉴定(红色方框代表酶切条带正确)
Fig. 3 a: Restriction analysis of the recombinant plasmids p15A-cm-BGC18 by MscⅠ(a) and p15A-OriT-IR-Pkm-BGC18 by ApaLⅠ(b)(Red box indicates right recombinant plasmids)
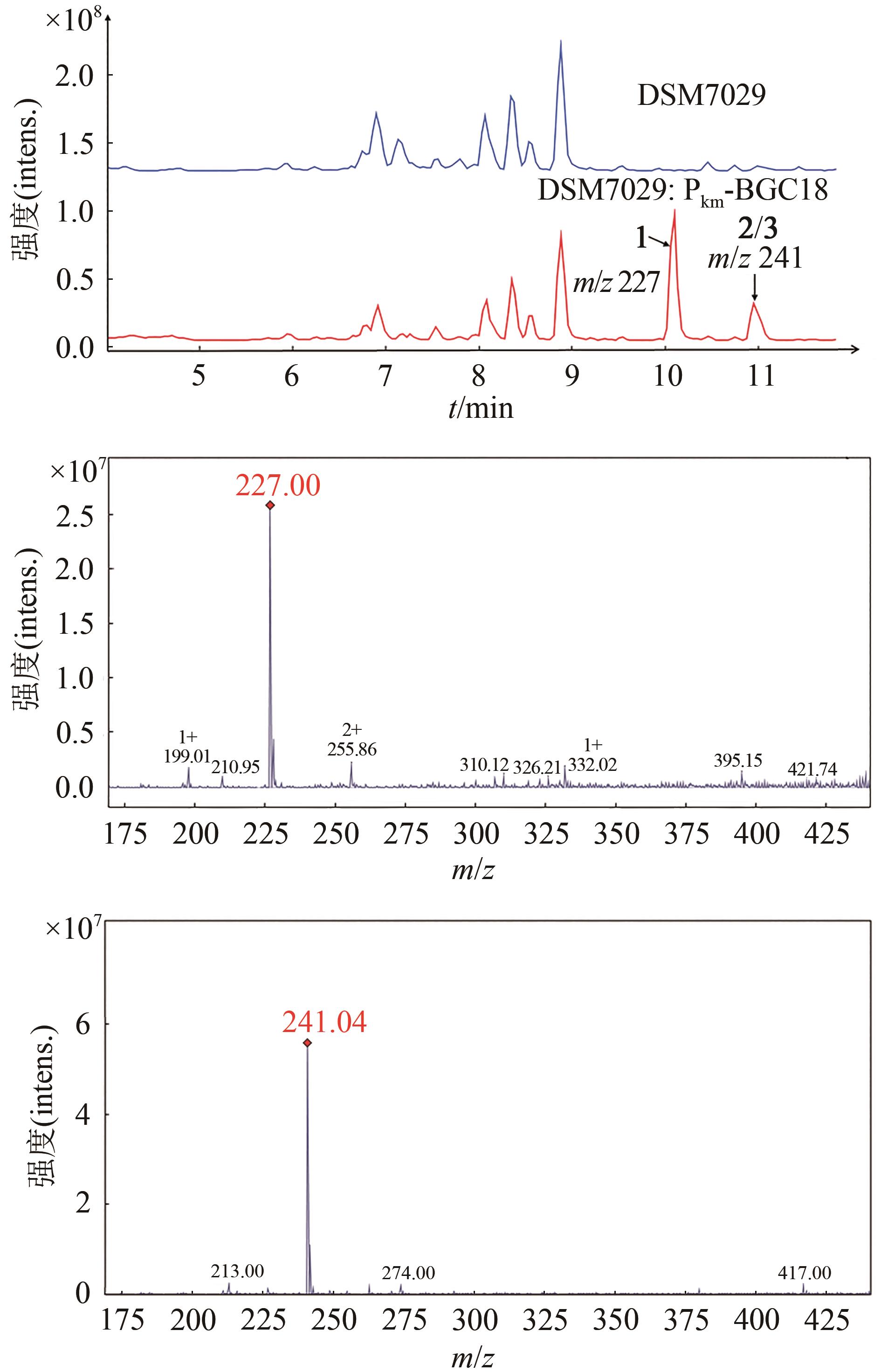
图4 BGC18在S. brevitalea DSM 7029中的异源表达产物LC-MS分析(BPC+:m/z 200~300)
Fig. 4 LC-MS analysis for the heterologous products of BGC18 expressed in S. brevitalea DSM 7029
| No | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC | δH (J in Hz) | δH (J in Hz) | δH (J in Hz) | ||
| N-Me-Leu | 1 2 3 4 5 6 N-Me | 167.6, C 59.2, CH 42.7, CH2 25.1, CH 23.1, CH3 21.8, CH3 32.1, CH3 | 3.78, dd (4.5, 8.2) 1.58, m 1.87, m 0.89, d (6.7) 0.93, d (6.7) 2.82, s | 3.79, t (6.7) 1.59, t (7.0) 1.79, m 0.90, d (6.5) 0.93, d (6.5) 2.82, s | 3.78, dd (4.5, 8.1) 1.58, m 1.87, m 0.89, d (6.5) 0.93, d (6.5) 2.82, s |
| Val/Leu/Ile | 1 2 3 4 5 6 NH | 165.1, C 60.1, CH 32.6, CH 19.2, CH3 18.1, CH3 | 3.55, dd (3.6, 5.2) 2.01, m 0.92, d (6.8) 0.84, d (6.8) 8.24, d (2.4) | 3.73, dt (3.9, 8.7) 1.52, m 1.45, m 1.79, m 0.86, d (6.5) 0.90, d (6.5) 8.39, d (2.6) | 3.61, dd (3.8, 4.8) 1.73, m 1.43, m 1.11, m 0.84, t (6.5) 0.89, d (6.5) 8.23, d (1.6) |
表4 化合物1~3的NMR核磁数据
Tab. 4 1H (500 MHz) and 13C (125 MHz) data of 1~3 in DMSO-d6
| No | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC | δH (J in Hz) | δH (J in Hz) | δH (J in Hz) | ||
| N-Me-Leu | 1 2 3 4 5 6 N-Me | 167.6, C 59.2, CH 42.7, CH2 25.1, CH 23.1, CH3 21.8, CH3 32.1, CH3 | 3.78, dd (4.5, 8.2) 1.58, m 1.87, m 0.89, d (6.7) 0.93, d (6.7) 2.82, s | 3.79, t (6.7) 1.59, t (7.0) 1.79, m 0.90, d (6.5) 0.93, d (6.5) 2.82, s | 3.78, dd (4.5, 8.1) 1.58, m 1.87, m 0.89, d (6.5) 0.93, d (6.5) 2.82, s |
| Val/Leu/Ile | 1 2 3 4 5 6 NH | 165.1, C 60.1, CH 32.6, CH 19.2, CH3 18.1, CH3 | 3.55, dd (3.6, 5.2) 2.01, m 0.92, d (6.8) 0.84, d (6.8) 8.24, d (2.4) | 3.73, dt (3.9, 8.7) 1.52, m 1.45, m 1.79, m 0.86, d (6.5) 0.90, d (6.5) 8.39, d (2.6) | 3.61, dd (3.8, 4.8) 1.73, m 1.43, m 1.11, m 0.84, t (6.5) 0.89, d (6.5) 8.23, d (1.6) |
| Amino acid | Configuration | Retention time | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| N-Me-L-Leu | L | 12.9 | 12.9 | 12.9 | 12.9 |
| D | 13.2 | ||||
| Val | L | 11.6 | 11.6 | ||
| D | 12.5 | ||||
| Leu | L | 29.7 | 29.7 | ||
| D | 33.1 | ||||
| Ile | L | 29.1 | 29.1 | ||
| D | 32.5 | ||||
| allo-Ile | L | 29.2 | |||
| D | 32.6 | ||||
表5 化合物1~3氨基酸与marfey试剂衍生产物的保留时间
Tab. 5 Retention time of amino acids derivatized with Marfey′s reagent
| Amino acid | Configuration | Retention time | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| N-Me-L-Leu | L | 12.9 | 12.9 | 12.9 | 12.9 |
| D | 13.2 | ||||
| Val | L | 11.6 | 11.6 | ||
| D | 12.5 | ||||
| Leu | L | 29.7 | 29.7 | ||
| D | 33.1 | ||||
| Ile | L | 29.1 | 29.1 | ||
| D | 32.5 | ||||
| allo-Ile | L | 29.2 | |||
| D | 32.6 | ||||
| 1 | HERRMANN J, FAYAD A A, MÜLLER R. Natural products from myxobacteria: novel metabolites and bioactivities[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2017, 34(2): 135-160. |
| 2 | WEISSMAN K J, MÜLLER R. Myxobacterial secondary metabolites: bioactivities and modes-of-action[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2010, 27(9): 1276-1295. |
| 3 | WENZEL S C, MÜLLER R. Myxobacteria—'microbial factories' for the production of bioactive secondary metabolites[J]. Molecular Biosystems, 2009, 5(6): 567-574. |
| 4 | SCHÄBERLE T F, LOHR F, SCHMITZ A, et al. Antibiotics from myxobacteria[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2014, 31(7): 953-972. |
| 5 | 刘冰花. 黏细菌生物活性物质的研究[J]. 成都大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 30(2): 108-113. |
| LIU B H. Study of myxobacterial bioactive substances[J]. Journal of Chengdu University (Natural Science), 2011, 30(2): 108-113. | |
| 6 | 赵婷峰, 龚国利. 黏细菌: 天然的制药厂[J]. 生物技术通报, 2014(12): 40-46. |
| ZHAO T F, GONG G L. Myxobacteria: natural pharmaceutical factories[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2014(12): 40-46. | |
| 7 | HAN K, LI Z F, PENG R, et al. Extraordinary expansion of a Sorangium cellulosum genome from an alkaline milieu[J]. Scientific Reports, 2013, 3: 2101. |
| 8 | LI Z F, ZHU L P, GU J Y, et al. Isolation and characterisation of the epothilone gene cluster with flanks from high alkalotolerant strain Sorangium cellulosum (So0157-2)[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 33(7): 137. |
| 9 | 龚国利, 黄宇莹. 黏细菌纤维堆囊菌的基因组学研究现状[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2014, 33(5): 1133-1138. |
| GONG G L, HUANG Y Y. Research status of genomics of myxobacteria Sorangium cellulosum [J]. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2014, 33(5): 1133-1138. | |
| 10 | ZHAO L, LI P F, LU C H, et al. Glycosylation and production characteristics of epothilones in alkali-tolerant Sorangium cellulosum strain So0157-2[J]. The Journal of Microbiology, 2010, 48(4): 438-444. |
| 11 | WANG J, ZHANG H, YING L, et al. Five new epothilone metabolites from Sorangium cellulosum strain So0157-2[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 2009, 62: 483-487. |
| 12 | ZHAO L, ZHAO B B, LU C H, et al. Two epothilones from Sorangium cellulosum strain So0157-2[J]. Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines, 2010, 8: 298-300. |
| 13 | WANG J D, JIANG N, ZHANG H, et al. New epothilone congeners from Sorangium cellulosum strain So0157-2[J]. Natural Product Research, 2011, 25(18): 1707-1712. |
| 14 | LU C, ZHAO L, LI Y, et al. Four natural epothilone derivatives isolated from Sorangium cellulosum strain So0157-2[J]. Journal of Chinese Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2013, 22(1): 28-31. |
| 15 | ZHANG Y J, DENG A W, ZHANG H, et al. Epothilone O, a new member of this family from Sorangium cellulosum strain So0157-2[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 2013, 66(5): 285-286. |
| 16 | HUO L, HUG J J, FU C, et al. Heterologous expression of bacterial natural product biosynthetic pathways[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2019, 36(10): 1412-1436. |
| 17 | ONGLEY S E, BIAN X, NEILAN B A, et al. Recent advances in the heterologous expression of microbial natural product biosynthetic pathways[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2013, 30: 1121-1138. |
| 18 | ZHANG J J, TANG X Y, MOORE B S. Genetic platforms for heterologous expression of microbial natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2019, 36(9): 1313-1332. |
| 19 | LUO Y, ENGHIAD B, ZHAO H. New tools for reconstruction and heterologous expression of natural product biosynthetic gene clusters[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2016, 33(2): 174-182. |
| 20 | LUO Y, LI B Z, LIU D, et al. Engineered biosynthesis of natural products in heterologous hosts[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(15): 5265-5290. |
| 21 | FU J, BIAN X Y, HU S B, et al. Full-length RecE enhances linear-linear homologous recombination and facilitates direct cloning for bioprospecting[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2012, 30(5): 440-446. |
| 22 | WANG H L, LI Z, JIA R N, et al. ExoCET: exonuclease in vitro assembly combined with RecET recombination for highly efficient direct DNA cloning from complex genomes[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 46(5): e28. |
| 23 | 郑文韬, 张友明, 卞小莹. Red/ET同源重组技术及其在微生物基因组挖掘中的应用进展[J]. 微生物学报, 2017, 57(11): 1735-1746. |
| ZHENG W T, ZHANG Y M, BIAN X Y. Advances in Red/ET recombineering and its application for microbial genome mining[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2017, 57(11): 1735-1746. | |
| 24 | WANG H, BIAN X, XIA L, et al. Improved seamless mutagenesis by recombineering using ccdB for counterselection[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2014, 42(5): e37. |
| 25 | BIAN X, PLAZA A, YAN F, et al. Rational and efficient site-directed mutagenesis of adenylation domain alters relative yields of luminmide derivatives in vivo [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2015, 112(7): 1343-1353. |
| 26 | WANG H L, LI Z, JIA R N, et al. RecET direct cloning and Redαβ recombineering of biosynthetic gene clusters, large operons or single genes for heterologous expression[J]. Nature Protocols. 2016, 11(7): 1175-1190. |
| 27 | ABBASI M N, FU J, BIAN X, et al. Recombineering for genetic engineering of natural product biosynthetic pathways[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2020, 38(7): 715-728. |
| 28 | ZHONG L, DIAO X, ZHANG N, et al. Engineering and elucidation of the lipoinitiation process in nonribosomal peptide biosynthesis[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 296. |
| 29 | WATANABE K, OIKAWA H. Robust platform for de novo production of heterologous polyketides and nonribosomal peptides in Escherichia coli [J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2007, 5(4): 593-602. |
| 30 | 马紫卉, 李伟, 尹文兵. 真菌天然产物异源生产研究进展[J]. 微生物学报, 2016, 56(3): 429-440. |
| MA Z H, LI W, YIN W B. Progress in heterologous expression of fungal natural products-a review[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2016, 56(3): 429-440. | |
| 31 | TSUNEMATSU Y, ISHIUCHI K, HOTTA K, et al. Yeast-based genome mining, production and mechanistic studies of the biosynthesis of fungal polyketide and peptide natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2013, 30(8): 1139-1149. |
| 32 | MYRONOVSKYI M, LUZHETSKYY A. Heterologous production of small molecules in the optimized Streptomyces hosts[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2019, 36(9): 1281-1294. |
| 33 | 王素英, 蒋雪, 张宏宇. 放线菌次级代谢产物合成基因簇异源表达体系的研究进展[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(34): 9-16. |
| WANG S Y, JIANG X, ZHANG H Y. Advances in heterologous expression system of secondary metabolite synthesis gene clusters of actinomycetes[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(34): 9-16. | |
| 34 | YU Y C, WANG H M, TANG B, et al. Reassembly of the biosynthetic gene cluster enables high epothilone yield in engineered Schlegelella brevitalea [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(8): 2009-2022. |
| 35 | WANG X, ZHOU H B, CHEN H N, et al. Discovery of recombinases enables genome mining of cryptic biosynthetic gene clusters in Burkholderiales species[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(18): E4255-E4263. |
| 36 | BIAN X Y, TANG B, YU Y C, et al. Heterologous production and yield improvement of epothilones in Burkholderiales strain DSM 7029[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2017, 12(7): 1805-1812. |
| 37 | OUYANG Q, WANG X, ZHANG N, et al. Promoter screening facilitates heterologous production of complex secondary metabolites in Burkholderiales strains[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(2): 457-460. |
| 38 | FU J, TEUCHER M., ANASTASSIADIS K, et al. Chapter eight-a recombineering pipeline to make conditional targeting constructs [J]. Methods in Enzymology, 2010, 477: 125-144. |
| 39 | TANG B, YU Y, LIANG J, et al. Reclassification of 'Polyangium brachysporum' DSM 7029 as Schlegelella brevitalea sp. nov[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2019, 69(9): 2877-2883. |
| 40 | GIGLIO S, JIANG J Y, SAINT C P, et al. Isolation and characterization of the gene associated with Geosmin production in cyanobacteria[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(21): 8027-8032. |
| 41 | SCHIFRIN A, LY T T, GÜNNEWICH N, et al. Characterization of the gene cluster CYP264B1-geoA from Sorangium cellulosum So ce56: Biosynthesis of (+)-eremophilene and its hydroxylation[J]. Chembiochem, 2015, 16(2): 337-344. |
| 42 | MIYANAGA A, KUDO F, EGUCHI T. Protein-protein interactions in polyketide synthase-nonribosomal peptide synthetase hybrid assembly lines[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2018, 35(11): 1185-1209. |
| 43 | WEN S J, HU T S, YAO Z J. Macrocyclization studies and total synthesis of cyclomarin C, an anti-inflammatory marine cyclopeptide[J]. Tetrahedron, 2005, 61(21): 4931-4938. |
| 44 | KATSUTA R, TOYODA M, YAJIMA A, et al. Synthesis and stereochemistry of JBIR-81, a peptide enamide derived from aspergilli [J]. Tetrahedron Letters. 2018, 59: 1010-1013. |
| 45 | CRYLE M J, BELL S G, SCHLICHTING I. Structural and biochemical characterization of the cytochrome P450 CypX (CYP134A1) from Bacillus subtilis: A cyclo-L-leucyl-L-leucyl dipeptide oxidase[J]. Biochemistry, 2010, 49(34): 7282-7296. |
| 46 | CHEN H N, ZHOU H B, SUN T, et al. Identification of holrhizins E-Q reveals the diversity of nonribosomal lipopeptides in Paraburkholderia rhizoxinica [J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2020, 83(2): 537-541. |
| 47 | CHEN H N, SUN T, BAI X P, et al. Genomics-driven activation of silent biosynthetic gene clusters in Burkholderia gladioli by screening recombineering system[J]. Molecules, 2021, 26: 700. |
| [1] | 惠真, 唐啸宇. CRISPR/Cas9编辑系统在微生物天然产物研究中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 658-671. |
| [2] | 宋永相, 张秀凤, 李艳芹, 肖华, 闫岩. 自抗性基因导向的活性天然产物挖掘[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 474-491. |
| [3] | 施鑫杰, 杜艺岭. 双嵌入家族抗肿瘤非核糖体肽的生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 593-611. |
| [4] | 雷茹, 陶慧, 刘天罡. 基因组深度挖掘驱动微生物萜类化合物高效发现[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 507-526. |
| [5] | 奚萌宇, 胡逸灵, 顾玉诚, 戈惠明. 基因组挖掘指导天然药物分子的发现[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 447-473. |
| [6] | 虞旭昶, 吴辉, 李雷. 文库构建与基因簇靶向筛选驱动的微生物天然产物高效发现[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 492-506. |
| [7] | 陈锡玮, 张华然, 邹懿. 真菌源非核糖体肽类药物生物合成及代谢工程[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 571-592. |
| [8] | 林继聪, 邹根, 刘宏民, 魏勇军. CRISPR/Cas基因组编辑技术在丝状真菌次级代谢产物合成中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(4): 738-755. |
| [9] | 赖铭元, 韦健, 许建和, 郁惠蕾. 非特异性过加氧酶(UPO)的研究综述[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(6): 1235-1249. |
| [10] | 董佳钰, 李敏, 肖宗华, 胡明, 松田侑大, 汪伟光. 米曲霉异源表达天然产物研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(6): 1126-1149. |
| [11] | 杨谦, 程伯涛, 汤志军, 刘文. 基因组挖掘在天然产物发现中的应用和前景[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(5): 697-715. |
| [12] | 王凤姣, 徐海洋, 闫建斌, 李伟. 植物天然农药除虫菊酯的生物合成和应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(5): 751-763. |
| [13] | 侯正杰, 孙慧中, 白松, 陈新月, 曹春阳, 程景胜. 环脂肽生物合成的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(4): 577-597. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||