合成生物学 ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (6): 1126-1149.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-007
米曲霉异源表达天然产物研究进展
董佳钰1, 李敏1, 肖宗华1, 胡明1, 松田侑大2, 汪伟光1
- 1.云南民族大学,国家民委民族药内生菌天然产物合成生物学重点实验室,教育部国家民委民族药资源化学重点实验室,云南,昆明 650031
2.香港城市大学化学系,香港 999077
-
收稿日期:2022-01-22修回日期:2022-02-16出版日期:2022-12-31发布日期:2023-01-17 -
通讯作者:松田侑大,汪伟光 -
作者简介:董佳钰 (1997—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为真菌来源天然产物生物合成。E-mail:785661452@qq.com松田侑大 (1988—),男,助理教授,博士生导师。研究方向为天然产物生物合成和合成生物学。E-mail:ymatsuda@cityu.edu.hk汪伟光 (1984—),男,研究员,硕士生导师。研究方向为天然药物化学。E-mail:wwg@live.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(31960095);云南省应用基础项目(202101AS070022)
Recent advances in heterologous production of natural products using Aspergillus oryzae
DONG Jiayu1, LI Min1, XIAO Zonghua1, HU Ming1, MATSUDA Yudai2, WANG Weiguang1
- 1.Key Laboratory of Natural Products Synthetic Biology of Ethnic Medicinal Endophytes,State Ethnic Affairs Commission,and Key Laboratory of Chemistry in Ethnic Medicinal Resources,State Ethnic Affairs Commission and Ministry of Education,Yunnan Minzu University,Kunming 650031,Yunnan,China
2.Department of Chemistry,City University of Hong Kong,Kowloon,Hong Kong SAR 999077,China
-
Received:2022-01-22Revised:2022-02-16Online:2022-12-31Published:2023-01-17 -
Contact:MATSUDA Yudai, WANG Weiguang
摘要:
天然产物是创新药物和生物农药研发的重要源泉。阐明天然产物生物合成关键基因的功能、解析其生物合成通路和酶催化机制对于促进功能天然产物的应用和开发至关重要。异源表达是研究天然产物生物合成和合成生物学的重要手段之一。近年来,米曲霉异源宿主得到了广泛的应用。通过基因工程技术,将目的天然产物生物合成基因和基因簇在米曲霉中异源表达,不仅能够有效地激活沉默的生物合成基因和基因簇,挖掘全新活性天然产物,而且可以快速高效地鉴定天然产物生物合成基因功能,解析和重构其生物合成途径。米曲霉异源表达宿主已经成为天然产物合成生物学研究的强有力工具。本文对米曲霉遗传转化系统在天然产物研究中的应用进行了系统综述。首先,概述了异源表达的应用和意义,介绍了米曲霉遗传转化系统的发展过程、应用基础和优势以及遗传转化方法的实践和优化。其次,根据不同天然产物的结构类型和与之相对应的合成酶特点,着重介绍了该体系表达各类天然产物的成功案例。最后,对米曲霉异源表达宿主在天然产物化学领域的研究和应用前景进行了总结和展望。随着基因编辑、定向进化、合成生物学、生物信息学技术以及人工智能技术的发展和应用,米曲霉异源表达宿主的发展和完善将会极大地促进更多天然产物化学研究技术的发展和革新,以期为天然产物合成生物学的研究和创新药物研发提供借鉴。
中图分类号:
引用本文
董佳钰, 李敏, 肖宗华, 胡明, 松田侑大, 汪伟光. 米曲霉异源表达天然产物研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(6): 1126-1149.
DONG Jiayu, LI Min, XIAO Zonghua, HU Ming, MATSUDA Yudai, WANG Weiguang. Recent advances in heterologous production of natural products using Aspergillus oryzae[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(6): 1126-1149.
| 化合物名称和编号 | 基因来源 | 表达宿主 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
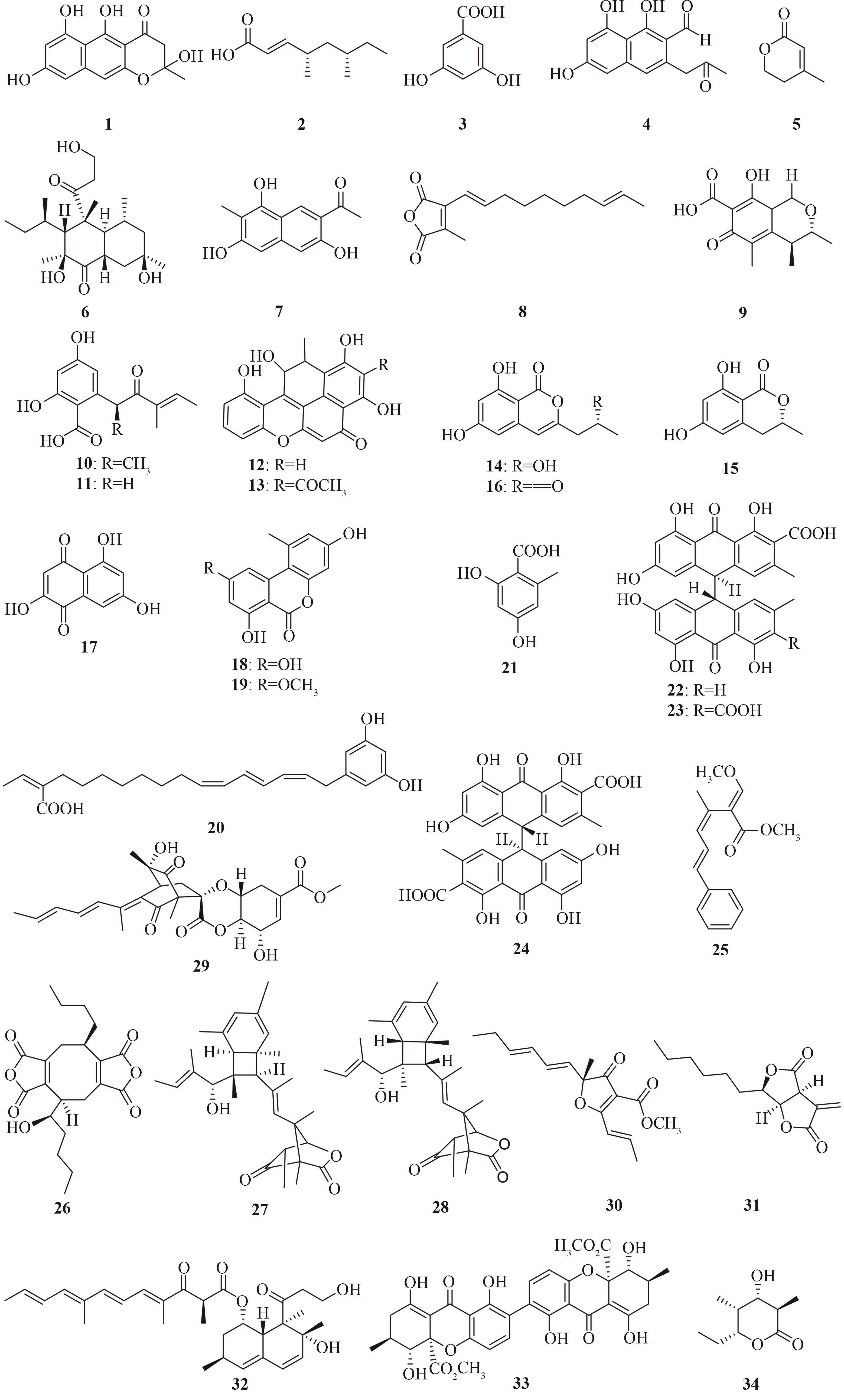
| YWA1 (1) | Aspergillus fumigatus | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ |
| 2 | Phoma sp. C2932 | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ |
| 3,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid (3) | Aspergillus oryzae RIB40 | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ |
| 4 | Nectria haematococca mpVI 77-13-4 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| anhydromevalonolactone (5) | Xylaria sp. BCC 1067 | A. oryzae U1638 | [ |
| betaenone B (6) | Phoma betae Fr. | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| 2-acetyl-7-methyl-3,6,8-trihydroxynaphthalene (7) | Talaromyces stipitatus ATCC 10500 | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ |
| 8 | unidentified fungus ATCC 74256 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| citrinin (9) | Monascus ruber M7 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| 10和11 | Arthrinium sp. NF2194 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
dalmanol A (12) acetodalmanol A (13) | Daldinia eschscholzii | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
(-)-orthosporin (14) (-)-6-hydroxymellein (15) | Menisporopsis theobromae BCC 4162 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
benzopyran (16) flaviolin (17) | Cladosporium fulvum | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ |
alternariol (18) alternariol monomethyl ether (19) | Alternaria alternata ATCC 66981 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| soppiline C (20) | Penicillium soppi Okera-1 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| orsellinic acid (21) | Fusarium sp. NBRC100844 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| 22-24 | Aspergillus terreus | A. oryzae ∆snfA∆SCAP | [ |
| strobilurin A (25) | Strobilurus tenacellus | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| zopfiellin (26) | Zopfiella curvata No. 37-3 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| shimalactone A (27)、shimalactone B (28) | Emericella variecolor GF10 | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ |
| spirosorbicillinol B (29) | Trichoderma reesei QM6a | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| gregatin A (30) | Penicillium sp. sh18 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| sporothriolide (31) | Hypomontagnella monticulosa MUCL 54604 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| 32 | Emericella variecolor NBRC 32302 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| secalonic acid D (33) | Aspergillus aculeatus CBS 172.66 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| TKL (34) | Saccharopolyspora erythraea | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
表1 米曲霉异源表达的代表性聚酮类化合物来源基因以及宿主信息
Tab. 1 Representative polyketides heterologously produced in Aspergillus oryzae, origins of the biosynthetic genes, and hosts used for the heterologous expression
| 化合物名称和编号 | 基因来源 | 表达宿主 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| YWA1 (1) | Aspergillus fumigatus | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ |
| 2 | Phoma sp. C2932 | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ |
| 3,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid (3) | Aspergillus oryzae RIB40 | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ |
| 4 | Nectria haematococca mpVI 77-13-4 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| anhydromevalonolactone (5) | Xylaria sp. BCC 1067 | A. oryzae U1638 | [ |
| betaenone B (6) | Phoma betae Fr. | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| 2-acetyl-7-methyl-3,6,8-trihydroxynaphthalene (7) | Talaromyces stipitatus ATCC 10500 | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ |
| 8 | unidentified fungus ATCC 74256 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| citrinin (9) | Monascus ruber M7 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| 10和11 | Arthrinium sp. NF2194 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
dalmanol A (12) acetodalmanol A (13) | Daldinia eschscholzii | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
(-)-orthosporin (14) (-)-6-hydroxymellein (15) | Menisporopsis theobromae BCC 4162 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
benzopyran (16) flaviolin (17) | Cladosporium fulvum | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ |
alternariol (18) alternariol monomethyl ether (19) | Alternaria alternata ATCC 66981 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| soppiline C (20) | Penicillium soppi Okera-1 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| orsellinic acid (21) | Fusarium sp. NBRC100844 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| 22-24 | Aspergillus terreus | A. oryzae ∆snfA∆SCAP | [ |
| strobilurin A (25) | Strobilurus tenacellus | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| zopfiellin (26) | Zopfiella curvata No. 37-3 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| shimalactone A (27)、shimalactone B (28) | Emericella variecolor GF10 | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ |
| spirosorbicillinol B (29) | Trichoderma reesei QM6a | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| gregatin A (30) | Penicillium sp. sh18 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| sporothriolide (31) | Hypomontagnella monticulosa MUCL 54604 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| 32 | Emericella variecolor NBRC 32302 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| secalonic acid D (33) | Aspergillus aculeatus CBS 172.66 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| TKL (34) | Saccharopolyspora erythraea | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
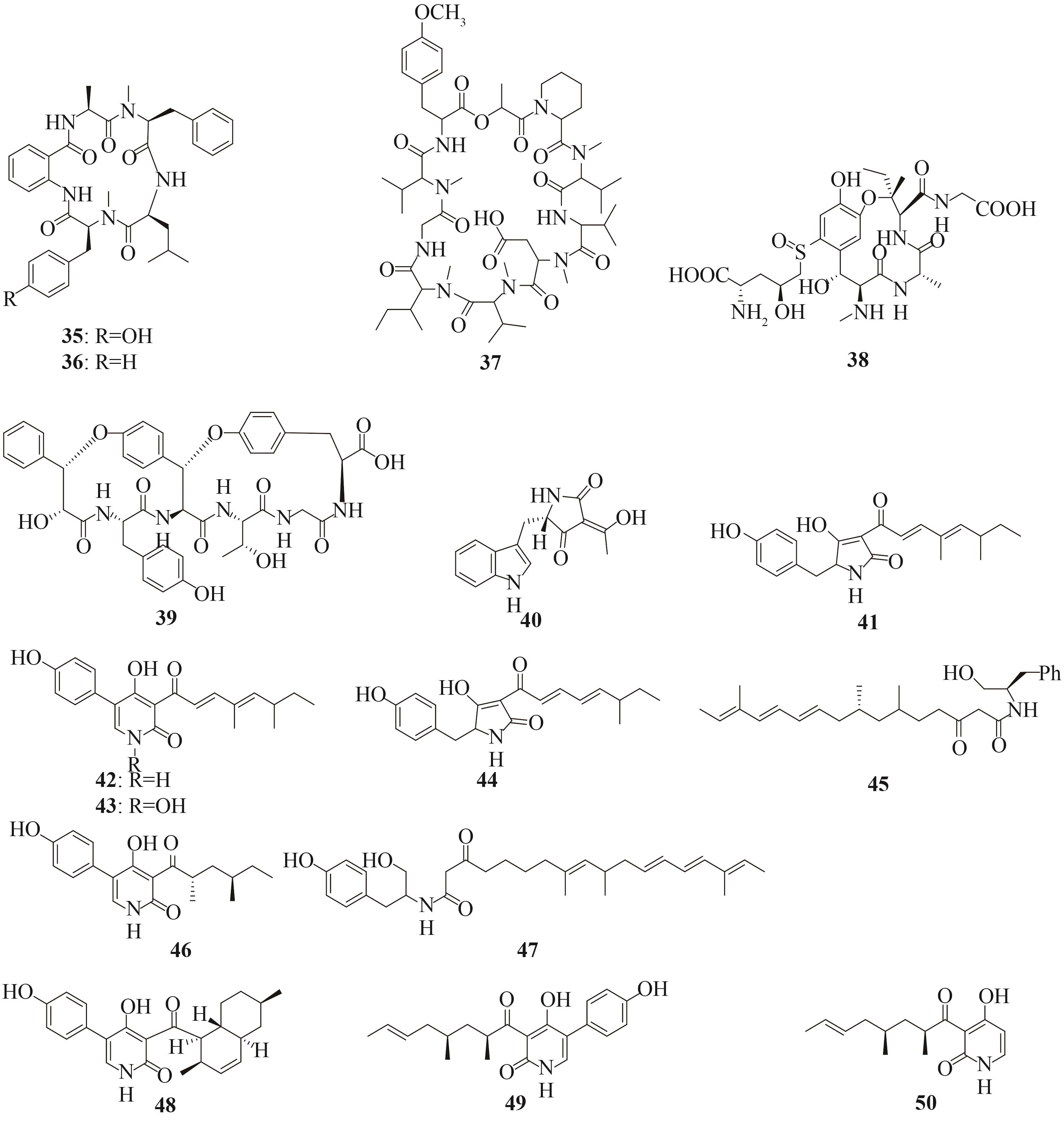
| 化合物分类 | 化合物名称和编号 | 基因来源 | 表达宿主 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非核糖体多肽 | cycloaspeptide A (35) cycloaspeptide E (36) | Penicillium soppii CBS 869.70 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| KK-1 (37) | Curvularia clavata | A. oryzae CNT | [ | |
| 核糖体多肽 | ustiloxin B (38) | Aspergillus flavus CA14 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| asperipin-2a (39) | Aspergillus flavus CA14 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| 聚酮和非核糖体多肽杂合化合物 | cAATrp (40) | Aspergillus flavus NRRL 3357 | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ |
pretenellin A (41)、pretenellin B (42) tenellin (43) | Beauveria bassiana 110.25 | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ | |
pretenellin A (41) desmethyl-pretenellin A (44) | Beauveria bassiana 992.05 | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ | |
| 45 | Aspergillus clavatus NRRL1 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| aspyridone A (46) | Aspergillus nidulans SB4.1 | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ | |
| 47 | Magnaporthe oryzae | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ | |
| didymellamide B (48) | Alternaria solani A-17 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| tolypyridone C (49)、tolypyridone D (50) | Tolypocladium sp. 49Y | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
表2 米曲霉异源表达的代表性肽类化合物来源基因以及宿主信息
Tab. 2 Representative peptide natural products heterologously produced in Aspergillus oryzae, origins of the biosynthetic genes, and hosts used for the heterologous expression
| 化合物分类 | 化合物名称和编号 | 基因来源 | 表达宿主 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非核糖体多肽 | cycloaspeptide A (35) cycloaspeptide E (36) | Penicillium soppii CBS 869.70 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| KK-1 (37) | Curvularia clavata | A. oryzae CNT | [ | |
| 核糖体多肽 | ustiloxin B (38) | Aspergillus flavus CA14 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| asperipin-2a (39) | Aspergillus flavus CA14 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| 聚酮和非核糖体多肽杂合化合物 | cAATrp (40) | Aspergillus flavus NRRL 3357 | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ |
pretenellin A (41)、pretenellin B (42) tenellin (43) | Beauveria bassiana 110.25 | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ | |
pretenellin A (41) desmethyl-pretenellin A (44) | Beauveria bassiana 992.05 | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ | |
| 45 | Aspergillus clavatus NRRL1 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| aspyridone A (46) | Aspergillus nidulans SB4.1 | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ | |
| 47 | Magnaporthe oryzae | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ | |
| didymellamide B (48) | Alternaria solani A-17 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| tolypyridone C (49)、tolypyridone D (50) | Tolypocladium sp. 49Y | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
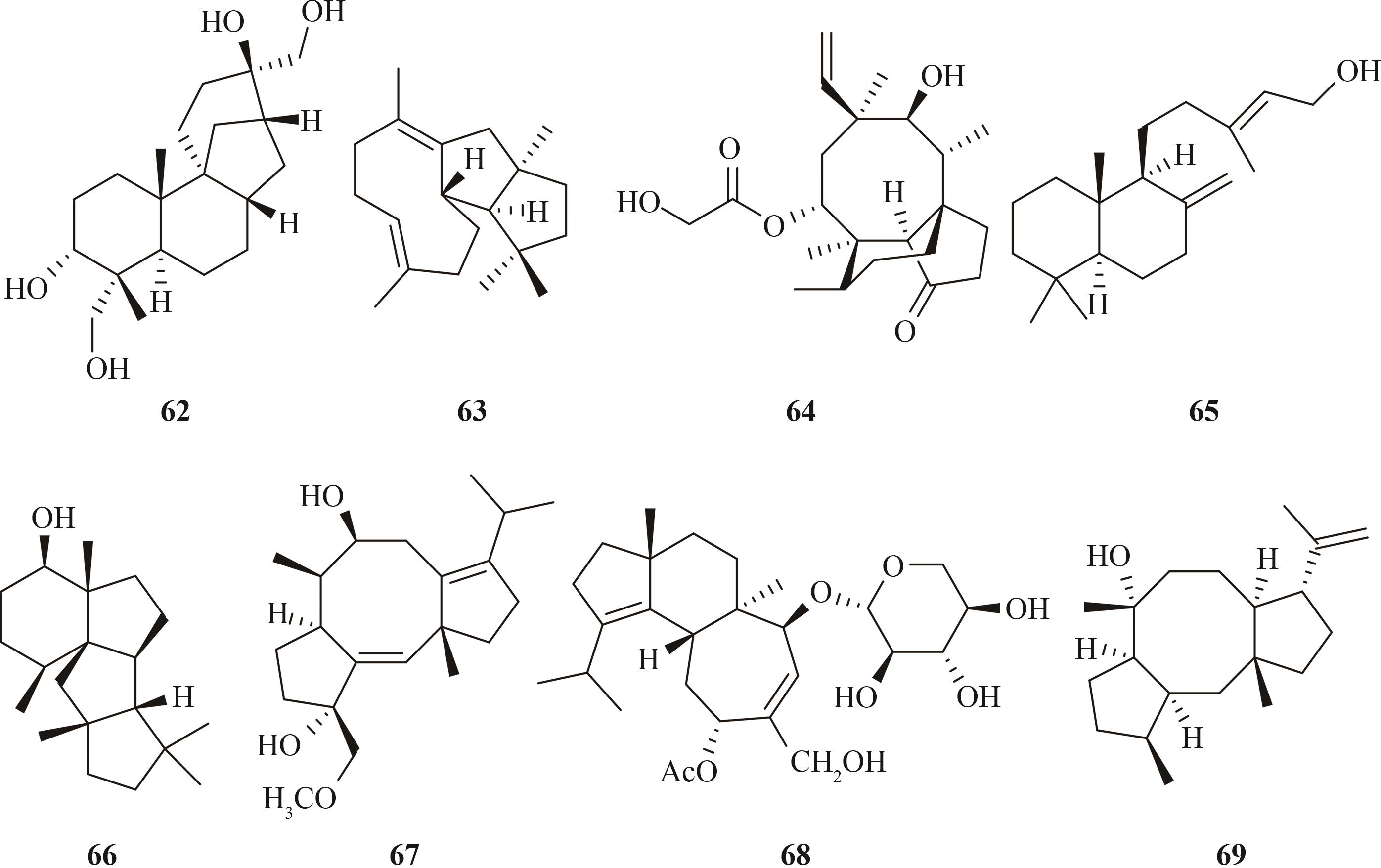
| 结构分类 | 化合物名称和编号 | 基因来源 | 表达宿主 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 倍半萜 | abscisic acid (51) | Botrytis cinerea SAS56 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| trichobrasilenol (52) | T. atroviride FKI-3849 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| aculene D (53)、asperaculane C(54)、asperaculane D(55)、asperaculane E(56)、asperaculane F(57)、asperaculane G (58) | A. aculeatus ATCC16872 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
brasilane A (59)、brasilane D (60) brasilane E (61) | Annulohypoxylon truncatum CBS 140778 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| 二萜 | aphidicolin (62) | Phoma betae PS-13 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| variediene (63) | Emericella variecolor NBRC 32302 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| pleuromutilin (64) | Clitopilus passeckerianus ATCC 34646 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| Clitopillus pseudo-pinsitus ATCC20527 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | ||
| Clitopilus passeckerianus ATCC 34646 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | ||
| (+)-copalol (65) | Penicillium verruculosum TPU1311和Penicillium fellutanum ATCC 48694 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| 66 | Penicillium chrysogenum MT-12 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| brassicicene Ⅰ (67) | Pseudocercospora fijiensis 10CR-1-24 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| erinacine Q (68) | Hericium erinaceus yamabushitake Y2 | A. oryzae NSPlD1 | [ | |
| myrothec-15(17)-en-7-ol (69) | Myrothecium graminearum ZLW0801-19 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
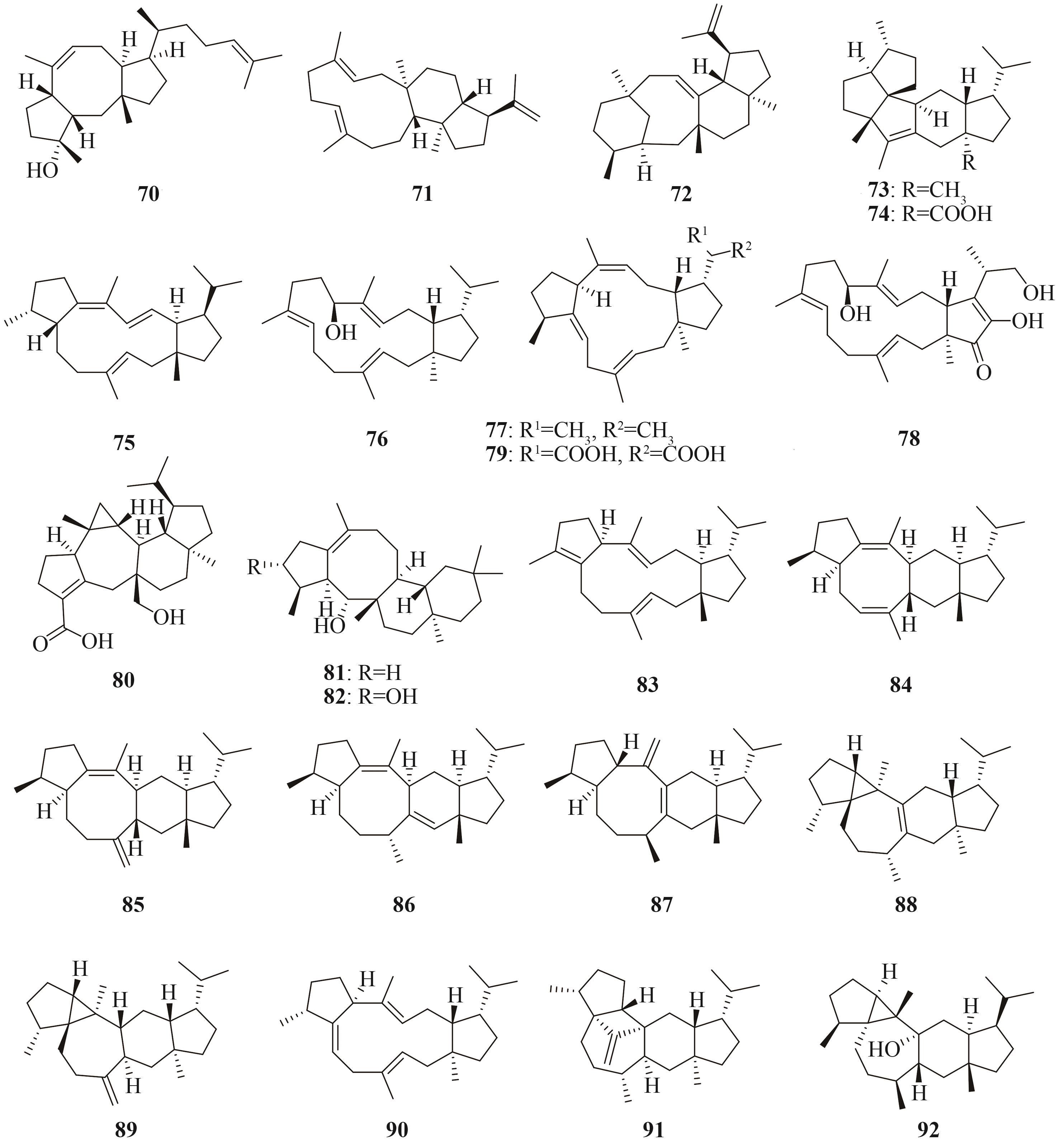
| 二倍半萜 | ophiobolin F (70) | Aspergillus clavatus NRRL1 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| Aspergillus calidoustus CBS121601 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | ||
| stellata-2,6,19-triene (71) | Emericella variecolor NBRC32302 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| astellifadiene (72) | Emericella variecolor NBRC32302 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
quiannulatene (73) quiannulatic acid (74) | Emericella variecolor NBRC32302 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| Bm1 (75)、 Bm3 (76) | Bipolaris maydis ATCC48331 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| Pb1 (77) | Phoma betae PS-13 | |||
| (-)-terpestacin (78) | Bipolaris maydis C5 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| betaestacin Ⅱ (79) | Phoma betae PS-13 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| asperterpenoid A (80) | Talaromyces wortmannii ATCC 26942 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| asperterpenol A(81)、 asperterpenol B (82) | Aspergillus calidoustus CBS121601 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
aspergiltriene A (83) aspergildiene A(84)、aspergildiene B(85)、aspergildiene C(86)、aspergildiene D (87) | Aspergillus ustus 094102 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
fusoxypene A(88)、fusoxypene B(89)、fusoxypene C (90) (-)-astellatene (91) | Fusarium oxysporum FO14005 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| preaspterpenacid I (92) | Aspergillus terreus NIH 2624 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | ||
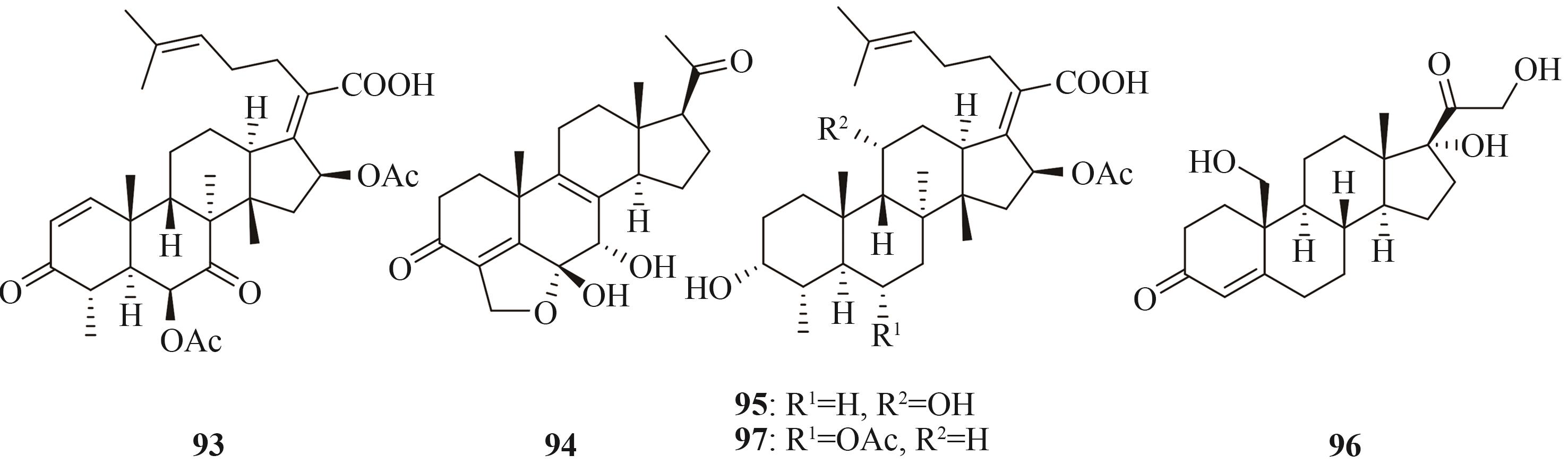
| 三萜和甾体 | helvolic acid (93) | Aspergillus fumigatus Af293 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| 94 | Nodulisporium sp. (no. 65-17-2-1) | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| fusidic acid (95) | Acremonium fusidioides ATCC 14700 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| 96 | Thanatephorus cucumeris NBRC 6298 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| cephalosporin P1 (97) | Acremonium chrysogenum ATCC 11550 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
表3 米曲霉异源表达的代表性萜类化合物来源基因以及宿主信息
Tab. 3 Representative terpenoids heterologously produced in Aspergillus oryzae, origins of the biosynthetic genes, and hosts used for the heterologous expression
| 结构分类 | 化合物名称和编号 | 基因来源 | 表达宿主 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 倍半萜 | abscisic acid (51) | Botrytis cinerea SAS56 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| trichobrasilenol (52) | T. atroviride FKI-3849 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| aculene D (53)、asperaculane C(54)、asperaculane D(55)、asperaculane E(56)、asperaculane F(57)、asperaculane G (58) | A. aculeatus ATCC16872 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
brasilane A (59)、brasilane D (60) brasilane E (61) | Annulohypoxylon truncatum CBS 140778 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| 二萜 | aphidicolin (62) | Phoma betae PS-13 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| variediene (63) | Emericella variecolor NBRC 32302 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| pleuromutilin (64) | Clitopilus passeckerianus ATCC 34646 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| Clitopillus pseudo-pinsitus ATCC20527 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | ||
| Clitopilus passeckerianus ATCC 34646 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | ||
| (+)-copalol (65) | Penicillium verruculosum TPU1311和Penicillium fellutanum ATCC 48694 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| 66 | Penicillium chrysogenum MT-12 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| brassicicene Ⅰ (67) | Pseudocercospora fijiensis 10CR-1-24 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| erinacine Q (68) | Hericium erinaceus yamabushitake Y2 | A. oryzae NSPlD1 | [ | |
| myrothec-15(17)-en-7-ol (69) | Myrothecium graminearum ZLW0801-19 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| 二倍半萜 | ophiobolin F (70) | Aspergillus clavatus NRRL1 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| Aspergillus calidoustus CBS121601 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | ||
| stellata-2,6,19-triene (71) | Emericella variecolor NBRC32302 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| astellifadiene (72) | Emericella variecolor NBRC32302 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
quiannulatene (73) quiannulatic acid (74) | Emericella variecolor NBRC32302 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| Bm1 (75)、 Bm3 (76) | Bipolaris maydis ATCC48331 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| Pb1 (77) | Phoma betae PS-13 | |||
| (-)-terpestacin (78) | Bipolaris maydis C5 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| betaestacin Ⅱ (79) | Phoma betae PS-13 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| asperterpenoid A (80) | Talaromyces wortmannii ATCC 26942 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| asperterpenol A(81)、 asperterpenol B (82) | Aspergillus calidoustus CBS121601 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
aspergiltriene A (83) aspergildiene A(84)、aspergildiene B(85)、aspergildiene C(86)、aspergildiene D (87) | Aspergillus ustus 094102 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
fusoxypene A(88)、fusoxypene B(89)、fusoxypene C (90) (-)-astellatene (91) | Fusarium oxysporum FO14005 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| preaspterpenacid I (92) | Aspergillus terreus NIH 2624 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | ||
| 三萜和甾体 | helvolic acid (93) | Aspergillus fumigatus Af293 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| 94 | Nodulisporium sp. (no. 65-17-2-1) | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| fusidic acid (95) | Acremonium fusidioides ATCC 14700 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| 96 | Thanatephorus cucumeris NBRC 6298 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| cephalosporin P1 (97) | Acremonium chrysogenum ATCC 11550 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
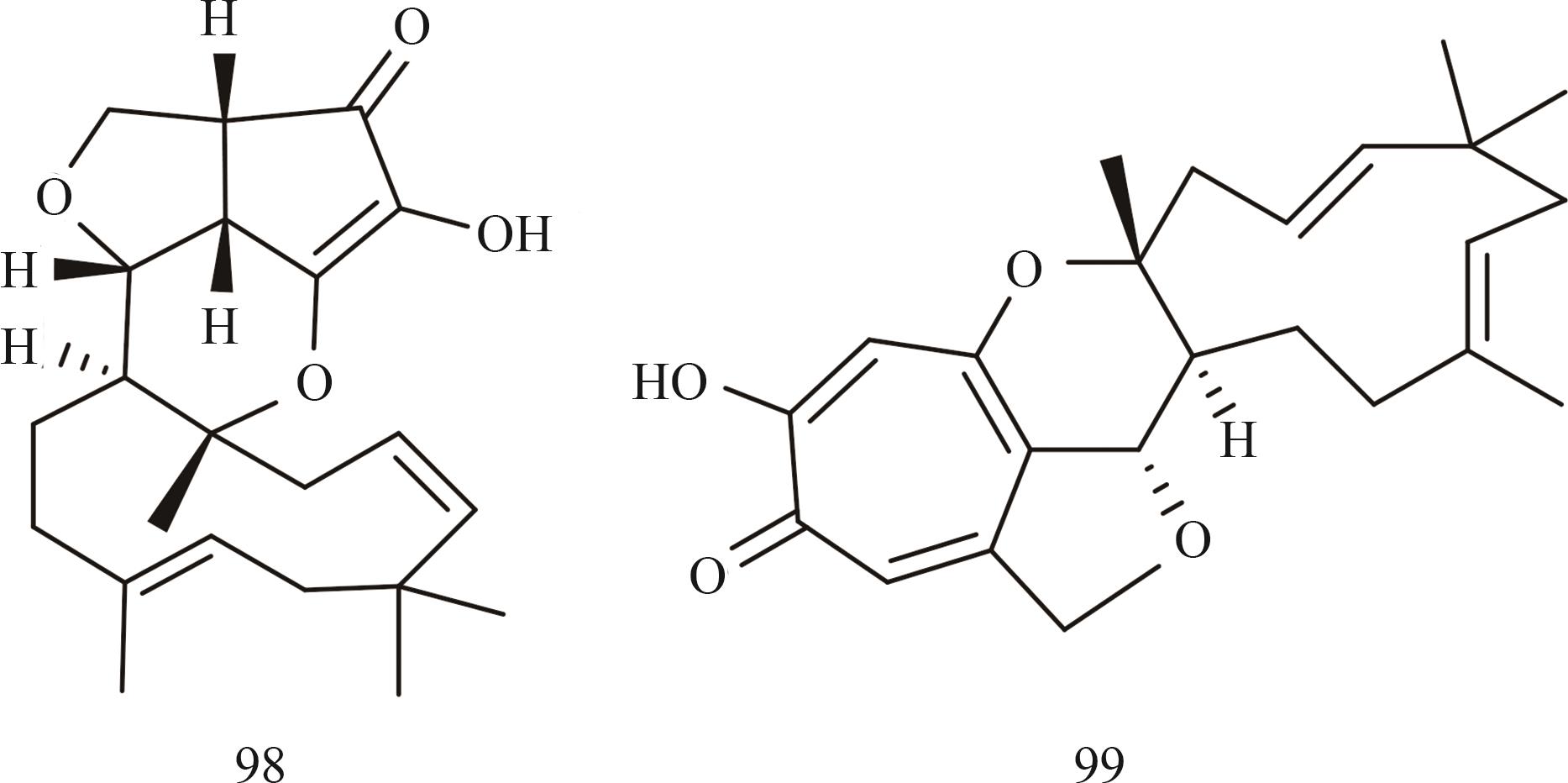
图7 经由米曲霉系统异源表达的代表性I型萜烯环化酶聚酮杂萜化合物结构
Fig. 7 Structures of polyketide-terpenoid hybrids (synthesized using a class Ⅰ terpene cyclase) heterologously produced in the Aspergillus oryzae system
| 化合物分类 | 化合物名称和编号 | 基因来源 | 表达宿主 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Ⅰ型萜烯环化酶 (聚酮杂萜) | xenovulene A (98) | Acremonium strictum IMI 501407 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| xenovulene B (99) | Acremonium strictum IMI 501407 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
Ⅱ型萜烯环化酶 (聚酮杂萜) | deacetyl-pyripyropene E (100) | Aspergillus fumigatus FO-1289 | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ |
11-deacetyl-pyripyropene O (101) deacetyl-pyripyropene A (102) | Penicillium coprobium PF1169 | A. oryzae HL-1105 | [ | |
| pyripyropene A (103) | Penicillium coprobium PF1169 | A. oryzae HL-1105 | [ | |
| andrastin A (104) | Penicillium chrysogenum NBRC 32030 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| preaustinoid A3 (105) | Aspergillus nidulans FGSC A4 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| anditomin (106) | Emericella variecolor NBRC 32302 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| terretonin (107) | Aspergillus terreus NIH 2624 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| citreohybridonol (108) | Emericella variecolor NBRC 32302 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| berkeleydione (109) | Penicillium brasilianum NBRC 6234 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| novofumigatonin (110) | Aspergillus novofumigatus IBT 16806 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| chrodrimanin B (111) | Penicillium verruculosum TPU1311 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
chevalone E (112) sartorypyrone D (113) | Aspergillus versicolor 0312 Aspergillus felis 0260 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| 114 | Fusarium graminearum PH-1 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
andiconin B (115) andiconin D (116) | Aspergillus sp. TJ23 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| funiculolide A、funiculolide B、 funiculolide C、funiculolide D (117~120) | Aspergillus funiculosus CBS 116.56 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| setosusin (121) | Aspergillus duricaulis CBS 481.65 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
Ⅱ型萜烯环化酶 (吲哚类杂萜) | paxilline (122) | Penicillium paxilli | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
aflatrem (123) β-aflatrem (124) | Aspergillus flavus NBRC 4295 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| penitrem A (125) | Penicillium simplicissimum AK-40 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| shearinine D (126) | Penicillium janthinellum PN2408 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| sespendole (127) | Pseudobotrytis terrestris FKA-25 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| lolitrem B (128) | Epichloë festucae var. loll | A. oryzae NSPlD1 | [ | |
| 其他类型杂萜 | LL-Z1272β (129) | Stachybotrys bisbyi PYH05-7 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| daurichromenic acid (130) | Rhododendron dauricum | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| 5-chlorodaurichromenic acid (131) | Fusarium sp. NBRC100844 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | ||
| ilicicolin A、 ilicicolin B (132和133) | Acremonium egyptiacum F-1392 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| biscognienyne B (134) | Biscogniauxia sp. (71-10-1-1) | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
表4 米曲霉异源表达的代表性杂萜类化合物来源基因以及宿主信息
Tab. 4 Representative meroterpenoids heterologously produced in Aspergillus oryzae, origins of the biosynthetic genes, and hosts used for the heterologous expression
| 化合物分类 | 化合物名称和编号 | 基因来源 | 表达宿主 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Ⅰ型萜烯环化酶 (聚酮杂萜) | xenovulene A (98) | Acremonium strictum IMI 501407 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| xenovulene B (99) | Acremonium strictum IMI 501407 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
Ⅱ型萜烯环化酶 (聚酮杂萜) | deacetyl-pyripyropene E (100) | Aspergillus fumigatus FO-1289 | A. oryzae M-2-3 | [ |
11-deacetyl-pyripyropene O (101) deacetyl-pyripyropene A (102) | Penicillium coprobium PF1169 | A. oryzae HL-1105 | [ | |
| pyripyropene A (103) | Penicillium coprobium PF1169 | A. oryzae HL-1105 | [ | |
| andrastin A (104) | Penicillium chrysogenum NBRC 32030 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| preaustinoid A3 (105) | Aspergillus nidulans FGSC A4 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| anditomin (106) | Emericella variecolor NBRC 32302 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| terretonin (107) | Aspergillus terreus NIH 2624 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| citreohybridonol (108) | Emericella variecolor NBRC 32302 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| berkeleydione (109) | Penicillium brasilianum NBRC 6234 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| novofumigatonin (110) | Aspergillus novofumigatus IBT 16806 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| chrodrimanin B (111) | Penicillium verruculosum TPU1311 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
chevalone E (112) sartorypyrone D (113) | Aspergillus versicolor 0312 Aspergillus felis 0260 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| 114 | Fusarium graminearum PH-1 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
andiconin B (115) andiconin D (116) | Aspergillus sp. TJ23 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| funiculolide A、funiculolide B、 funiculolide C、funiculolide D (117~120) | Aspergillus funiculosus CBS 116.56 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| setosusin (121) | Aspergillus duricaulis CBS 481.65 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
Ⅱ型萜烯环化酶 (吲哚类杂萜) | paxilline (122) | Penicillium paxilli | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
aflatrem (123) β-aflatrem (124) | Aspergillus flavus NBRC 4295 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| penitrem A (125) | Penicillium simplicissimum AK-40 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| shearinine D (126) | Penicillium janthinellum PN2408 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| sespendole (127) | Pseudobotrytis terrestris FKA-25 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| lolitrem B (128) | Epichloë festucae var. loll | A. oryzae NSPlD1 | [ | |
| 其他类型杂萜 | LL-Z1272β (129) | Stachybotrys bisbyi PYH05-7 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |
| daurichromenic acid (130) | Rhododendron dauricum | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| 5-chlorodaurichromenic acid (131) | Fusarium sp. NBRC100844 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | ||
| ilicicolin A、 ilicicolin B (132和133) | Acremonium egyptiacum F-1392 | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ | |
| biscognienyne B (134) | Biscogniauxia sp. (71-10-1-1) | A. oryzae NSAR1 | [ |

图8 经由米曲霉系统异源表达的代表性Ⅱ型萜烯环化酶聚酮杂萜化合物结构
Fig. 8 Structures of polyketide-terpenoid hybrids (synthesized using a class Ⅱ terpene cyclase) heterologously produced in the Aspergillus oryzae system
| 1 | FROMMER W B, NINNEMANN O. Heterologous expression of genes in bacterial, fungal, animal, and plant cells[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 1995, 46(1): 419-444. |
| 2 | GOMES A R, BYREGOWDA S M, VEEREGOWDA B M, et al. An overview of heterologous expression host systems for the production of recombinant proteins[J]. Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 2016, 4(7): 346-356. |
| 3 | VALERO F. Heterologous expression systems for lipases: A review[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2012, 861: 161-178. |
| 4 | KEASLING J D. Synthetic biology for synthetic chemistry[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2008, 3(1): 64-76. |
| 5 | BREITLING R, TAKANO E. Synthetic biology advances for pharmaceutical production[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2015, 35: 46-51. |
| 6 | SMANSKI M J, ZHOU H, CLAESEN J, et al. Synthetic biology to access and expand nature's chemical diversity[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2016, 14(3): 135-149. |
| 7 | LAZARUS C M, WILLIAMS K, BAILEY A M. Reconstructing fungal natural product biosynthetic pathways[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2014, 31(10): 1339-1347. |
| 8 | ZHANG J J, TANG X Y, MOORE B S. Genetic platforms for heterologous expression of microbial natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2019, 36(9): 1313-1332. |
| 9 | 马紫卉, 李伟, 尹文兵. 真菌天然产物异源生产研究进展[J]. 微生物学报, 2016, 56(3): 429-440. |
| MA Z H, LI W, YIN W B. Progress in heterologous expression of fungal natural products[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2016, 56(3): 429-440. | |
| 10 | ICHISHIMA E. Development of enzyme technology for Aspergillus oryzae, A. sojae, and A. luchuensis, the national microorganisms of Japan[J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2016, 80(9): 1681-1692. |
| 11 | FRISVAD J C, MØLLER L L H, LARSEN T O, et al. Safety of the fungal workhorses of industrial biotechnology: update on the mycotoxin and secondary metabolite potential of Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus oryzae, and Trichoderma reesei [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(22): 9481-9515. |
| 12 | TANAKA M, GOMI K. Induction and repression of hydrolase genes in Aspergillus oryzae [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2021, 12: 677603. |
| 13 | JIN F J, HU S, WANG B T, et al. Advances in genetic engineering technology and its application in the industrial fungus Aspergillus oryzae [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2021, 12(353): 644404. |
| 14 | ZHAO G Z, YAO Y P, QI W, et al. Draft genome sequence of Aspergillus oryzae strain 3.042[J]. Eukaryotic Cell, 2012, 11(9): 1178. |
| 15 | MACHIDA M, ASAI K, SANO M, et al. Genome sequencing and analysis of Aspergillus oryzae [J]. Nature, 2005, 438(7071): 1157-1161. |
| 16 | AWAKAWA T, ABE I. Reconstitution of polyketide-derived meroterpenoid biosynthetic pathway in Aspergillus oryzae [J]. Journal of Fungi, 2021, 7(6): 486. |
| 17 | OIKAWA H. Reconstitution of biosynthetic machinery of fungal natural products in heterologous hosts[J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2020, 84(3): 433-444. |
| 18 | PARK H S, JUN S C, HAN K H, et al. Diversity, application, and synthetic biology of industrially important Aspergillus fungi[J]. Advances in Applied Microbiology, 2017, 100: 161-202. |
| 19 | OIKAWA H. Heterologous production of fungal natural products: Reconstitution of biosynthetic gene clusters in model host Aspergillus oryzae [J]. Proceedings of the Japan Academy Series B-Physical and Biological Sciences, 2020, 96(9): 420-430. |
| 20 | JIN F J, MARUYAMA J I, JUVVADI P R, et al. Development of a novel quadruple auxotrophic host transformation system by argB gene disruption using adeA gene and exploiting adenine auxotrophy in Aspergillus oryzae [J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2004, 239(1): 79-85. |
| 21 | FUJII T, YAMAOKA H, GOMI K, et al. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the ribonuclease T1 gene (rntA) from Aspergillus oryzae and its expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Aspergillus oryzae [J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 1995, 59(10): 1869-1874. |
| 22 | JIN F J, MARUYAMA J I, JUVVADI P R, et al. Adenine auxotrophic mutants of Aspergillus oryzae: development of a novel transformation system with triple auxotrophic hosts[J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2004, 68(3): 656-662. |
| 23 | YAMADA O, LEE B R, GOMI K, et al. Cloning and functional analysis of the Aspergillus oryzae conidiation regulator gene brlA by its disruption and misscheduled expression[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 1999, 87(4): 424-429. |
| 24 | YAMADA O, NAN S N, AKAO T, et al. dffA gene from Aspergillus oryzae encodes L-ornithine N5 -oxygenase and is indispensable for deferriferrichrysin biosynthesis[J]. Journal of Bioscience & Bioengineering, 2003, 95(1): 82-88. |
| 25 | KUBODERA T, YAMASHITA N, NISHIMURA A. Pyrithiamine resistance gene (ptrA) of Aspergillus oryzae: cloning, characterization and application as a dominant selectable marker for transformation[J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2000, 64(7): 1416-1421. |
| 26 | MATSUDA Y, WAKIMOTO T, MORI T, et al. Complete biosynthetic pathway of anditomin: nature's sophisticated synthetic route to a complex fungal meroterpenoid[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(43): 15326-15336. |
| 27 | GALLAGHER R R, PATEL J R, INTERIANO A L, et al. Multilayered genetic safeguards limit growth of microorganisms to defined environments[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2015, 43(3): 1945-1954. |
| 28 | TAGAMI K, MINAMI A, FUJII R, et al. Rapid reconstitution of biosynthetic machinery for fungal metabolites in Aspergillus oryzae: total biosynthesis of aflatrem[J]. ChemBioChem, 2014, 15(14): 2076-2080. |
| 29 | YAMANE M, MINAMI A, LIU C W, et al. Biosynthetic machinery of diterpene pleuromutilin isolated from basidiomycete fungi[J]. ChemBioChem, 2017, 18(23): 2317-2322. |
| 30 | LIU C W, MINAMI A, OZAKI T, et al. Efficient reconstitution of basidiomycota diterpene erinacine gene cluster in ascomycota host Aspergillus oryzae based on genomic DNA sequences[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(39): 15519-15523. |
| 31 | LEBE K E, COX R J. O-Methylation steps during strobilurin and bolineol biosynthesis[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(54): 31527-31531. |
| 32 | SAKAI K, KINOSHITA H, NIHIRA T. Heterologous expression system in Aspergillus oryzae for fungal biosynthetic gene clusters of secondary metabolites[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2012, 93(5): 2011-2022. |
| 33 | WEI X X, CHEN X X, CHEN L, et al. Heterologous biosynthesis of tetrahydroxanthone dimers: determination of key factors for selective or divergent synthesis[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2021, 84(5): 1544-1549. |
| 34 | BAILEY A M, ALBERTI F, KILARU S, et al. Identification and manipulation of the pleuromutilin gene cluster from Clitopilus passeckerianus for increased rapid antibiotic production[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 25202. |
| 35 | WEI X X, MATSUYAMA T, SATO H, et al. Molecular and computational bases for spirofuranone formation in setosusin biosynthesis[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2021, 143(42): 17708-17715. |
| 36 | HERTWECK C. The biosynthetic logic of polyketide diversity[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2009, 48(26): 4688-4716. |
| 37 | MA S M, LI J W H, CHOI J W, et al. Complete reconstitution of a highly reducing iterative polyketide synthase[J]. Science, 2009, 326(5952): 589-592. |
| 38 | GOMES E S, SCHUCH V, DE MACEDO LEMOS E G. Biotechnology of polyketides: new breath of life for the novel antibiotic genetic pathways discovery through metagenomics[J]. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 2013, 44(4): 1007-1034. |
| 39 | WATANABE A, FUJII I, TSAI H, et al. Aspergillus fumigatus alb1 encodes naphthopyrone synthase when expressed in Aspergillus oryzae [J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2000, 192(1): 39-44. |
| 40 | COX R J, GLOD F, HURLEY D, et al. Rapid cloning and expression of a fungal polyketide synthase gene involved in squalestatin biosynthesis[J]. Chemical Communications, 2004, (20): 2260-2261. |
| 41 | SESHIME Y, JUVVADI P R, KITAMOTO K, et al. Aspergillus oryzae type Ⅲ polyketide synthase CsyA is involved in the biosynthesis of 3,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2010, 20(16): 4785-4788. |
| 42 | AWAKAWA T, KAJI T, WAKIMOTO T, et al. A heptaketide naphthaldehyde produced by a polyketide synthase from Nectria haematococca [J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2012, 22(13): 4338-4340. |
| 43 | WATTANACHAISAEREEKUL S, TACHALEAT A, PUNYA J, et al. Assessing medium constituents for optimal heterologous production of anhydromevalonolactone in recombinant Aspergillus oryzae [J]. AMB Express, 2014, 4: 52. |
| 44 | PUNYA J, TACHALEAT A, WATTANACHAISAEREEKUL S, et al. Functional expression of a foreign gene in Aspergillus oryzae producing new pyrone compounds[J]. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 2013, 50: 55-62. |
| 45 | UGAI T, MINAMI A, FUJII R, et al. Heterologous expression of highly reducing polyketide synthase involved in betaenone biosynthesis[J]. Chemical Communications, 2015, 51(10): 1878-1881. |
| 46 | HASHIMOTO M, WAKANA D, UEDA M, et al. Product identification of non-reducing polyketide synthases with C-terminus methyltransferase domain from Talaromyces stipitatus using Aspergillus oryzae heterologous expression[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2015, 25(7): 1381-1384. |
| 47 | FUJII R, MATSU Y, MINAMI A, et al. Biosynthetic study on antihypercholesterolemic agent phomoidride: general biogenesis of fungal dimeric anhydrides[J]. Organic Letters, 2015, 17(22): 5658-5661. |
| 48 | HE Y, COX R J. The molecular steps of citrinin biosynthesis in fungi[J]. Chemical Science, 2016, 7(3): 2119-2127. |
| 49 | ZHANG X, WANG T T, XU Q L, et al. Genome mining and comparative biosynthesis of meroterpenoids from two phylogenetically distinct fungi[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(27): 8184-8188. |
| 50 | ZHOU Z Z, ZHU H J, LIN L P, et al. Dalmanol biosyntheses require coupling of two separate polyketide gene clusters[J]. Chemical Science, 2019, 10(1): 73-82. |
| 51 | BUNNAK W, WONNAPINIJ P, SRIBOONLERT A, et al. Heterologous biosynthesis of a fungal macrocyclic polylactone requires only two iterative polyketide synthases[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2019, 17(2): 374-379. |
| 52 | GRIFFITHS S A, COX R J, OVERDIJK E J R, et al. Assignment of a dubious gene cluster to melanin biosynthesis in the tomato fungal pathogen Cladosporium fulvum [J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(12): e0209600. |
| 53 | WENDEROTH M, GARGANESE F, SCHMIDT-HEYDT M, et al. Alternariol as virulence and colonization factor of Alternaria alternata during plant infection[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2019, 112(1): 131-146. |
| 54 | KANEKO A, MORISHITA Y, TSUKADA K, et al. Post-genomic approach based discovery of alkylresorcinols from a cricket-associated fungus, Penicillium soppi [J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2019, 17(21): 5239-5243. |
| 55 | BERTRAND R L, SORENSEN J L. Lost in translation: challenges with heterologous expression of lichen polyketide synthases[J]. Chemistry Select, 2019, 4(21): 6473-6483. |
| 56 | KAN E, KATSUYAMA Y, MARUYAMA J I, et al. Efficient heterologous production of atrochrysone carboxylic acid-related polyketides in an Aspergillus oryzae host with enhanced malonyl-coenzyme A supply[J]. The Journal of General and Applied Microbiology, 2020, 66(3): 195-199. |
| 57 | SHIINA T, OZAKI T, MATSU Y, et al. Oxidative ring contraction by a multifunctional dioxygenase generates the core cycloocatadiene in the biosynthesis of fungal dimeric anhydride zopfiellin[J]. Organic Letters, 2020, 22(5): 1997-2001. |
| 58 | FUJII I, HASHIMOTO M, KONISHI K, et al. Functional analysis of a biosynthetic gene cluster demonstrates role of spontaneous double bicyclo‐ring formation including 8π-6π electrocyclization in shimalactone biosynthesis[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(22): 8464-8470. |
| 59 | KAHLERT L, BASSIONY E F, COX R J, et al. Diels-Alder reactions during the biosynthesis of sorbicillinoids[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(14): 5816-5822. |
| 60 | WANG W G, WANG H, DU L Q, et al. Molecular basis for the biosynthesis of an unusual chain-fused polyketide, gregatin A[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(18): 8464-8472. |
| 61 | TIAN D S, KUHNERT E, OUAZZANI J, et al. The sporothriolides. a new biosynthetic family of fungal secondary metabolites[J]. Chemical Science, 2020, 11(46): 12477-12484. |
| 62 | TAO H, MORI T, WEI X X, et al. One polyketide synthase, two distinct products: trans-acting enzyme-controlled product divergence in calbistrin biosynthesis[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(16): 8851-8858. |
| 63 | FENG J, HAUSER M, COX R J, et al. Engineering Aspergillus oryzae for the heterologous expression of a bacterial modular polyketide synthase[J]. Journal of Fungi, 2021, 7(12): 1085. |
| 64 | MOOTZ H D, MARAHIEL M A. Biosynthetic systems for nonribosomal peptide antibiotic assembly[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 1997, 1(4): 543-551. |
| 65 | SCHWARZER D, FINKING R, MARAHIEL M A. Nonribosomal peptides: from genes to products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2003, 20(3): 275-287. |
| 66 | DE MATTOS-SHIPLEY K M J, GRECO C, HEARD D M, et al. The cycloaspeptides: uncovering a new model for methylated nonribosomal peptide biosynthesis[J]. Chemical Science, 2018, 9(17): 4109-4117. |
| 67 | YOSHIMI A, YAMAGUCHI S, FUJIOKA T, et al. Heterologous production of a novel cyclic peptide compound, KK-1, in Aspergillus oryzae [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9: 690. |
| 68 | KESSLER S C, CHOOI Y H. Out for a RiPP: Challenges and advances in genome mining of ribosomal peptides from fungi[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2022, 39(2): 222-230. |
| 69 | YE Y, MINAMI A, IGARASHI Y, et al. Unveiling the biosynthetic pathway of the ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide ustiloxin B in filamentous fungi[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(28): 8072-8075. |
| 70 | YE Y, OZAKI T, UMEMURA M, et al. Heterologous production of asperipin-2a: proposal for sequential oxidative macrocyclization by a fungi-specific DUF3328 oxidase[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2019, 17(1): 39-43. |
| 71 | BOETTGER D, HERTWECK C. Molecular diversity sculpted by fungal PKS-NRPS hybrids[J]. ChemBioChem, 2013, 14(1): 28-42. |
| 72 | FISCH K M. Biosynthesis of natural products by microbial iterative hybrid PKS-NRPS[J]. RSC Advances, 2013, 3(40): 18228-18247. |
| 73 | SESHIME Y, JUVVADI P R, TOKUOKA M, et al. Functional expression of the Aspergillus flavus PKS-NRPS hybrid CpaA involved in the biosynthesis of cyclopiazonic acid[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2009, 19(12): 3288-3292. |
| 74 | HENEGHAN M N, YAKASAI A A, HALO L M, et al. First heterologous reconstruction of a complete functional fungal biosynthetic multigene cluster[J]. ChemBioChem, 2010, 11(11): 1508-1512. |
| 75 | FISCH K M, BAKEER W, YAKASAI A A, et al. Rational domain swaps decipher programming in fungal highly reducing polyketide synthases and resurrect an extinct metabolite[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(41): 16635-16641. |
| 76 | FUJII R, MINAMI A, GOMI K, et al. Biosynthetic assembly of cytochalasin backbone[J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 2013, 54(23): 2999-3002. |
| 77 | WASIL Z, PAHIRULZAMAN K A K, BUTTS C, et al. One pathway, many compounds: Heterologous expression of a fungal biosynthetic pathway reveals its intrinsic potential for diversity[J]. Chemical Science, 2013, 4(10): 3845-3856. |
| 78 | SONG Z S, BAKEER W, MARSHALL J W, et al. Heterologous expression of the avirulence gene ACE1 from the fungal rice pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae [J]. Chemical Science, 2015, 6(8): 4837-4845. |
| 79 | UGAI T, MINAMI A, GOMI K, et al. Genome mining approach for harnessing the cryptic gene cluster in Alternaria solani: production of PKS-NRPS hybrid metabolite, didymellamide B[J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 2016, 57(25): 2793-2796. |
| 80 | ZHANG W Y, ZHONG Y, YU Y, et al. 4-Hydroxy pyridones from heterologous expression and cultivation of the native host[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2020, 83(11): 3338-3346. |
| 81 | GAO Y, HONZATKO R B, PETERS R J. Terpenoid synthase structures: a so far incomplete view of complex catalysis[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2012, 29(10): 1153-1175. |
| 82 | QUIN M B, FLYNN C M, SCHMIDT-DANNERT C. Traversing the fungal terpenome[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2014, 31(10): 1449-1473. |
| 83 | RUDOLF J D, CHANG C Y. Terpene synthases in disguise: enzymology, structure, and opportunities of non-canonical terpene synthases[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2020, 37(3): 425-463. |
| 84 | AVALOS M, GARBEVA P, VADER L, et al. Biosynthesis, evolution and ecology of microbial terpenoids[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2022, 39(2): 249-272. |
| 85 | CHRISTIANSON D W. Structural and chemical biology of terpenoid cyclases[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(17): 11570-11648. |
| 86 | JACKSON B E, HART-WELLS E A, MATSUDA S P T. Metabolic engineering to produce sesquiterpenes in yeast[J]. Organic Letters, 2003, 5(10): 1629-1632. |
| 87 | SONG A A L, ABDULLAH J O, ABDULLAH M P, et al. Overexpressing 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (HMGR) in the lactococcal mevalonate pathway for heterologous plant sesquiterpene production[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(12): e52444. |
| 88 | SONG A A, ABDULLAH J ONG, ABDULLAH M P, et al. Engineering the lactococcal mevalonate pathway for increased sesquiterpene production[J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2014, 355(2): 177-184. |
| 89 | ASADOLLAHI M A, MAURY J, MØLLER K, et al. Production of plant sesquiterpenes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: effect of ERG9 repression on sesquiterpene biosynthesis[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2008, 99(3): 666-677. |
| 90 | KUSUMA H S, MAHFUD M. Box-Behnken design for investigation of microwave-assisted extraction of patchouli oil[C]//AIP Conference Proceedings. Semarang: AIP Publishing LLC, 2015, 1699: 050014. |
| 91 | ALBERTSEN L, CHEN Y, BACH L S, et al. Diversion of flux toward sesquiterpene production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by fusion of host and heterologous enzymes[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 77(3): 1033-1040. |
| 92 | TAKINO J, KOZAKI T, SATO Y, et al. Unveiling biosynthesis of the phytohormone abscisic acid in fungi: unprecedented mechanism of core scaffold formation catalyzed by an unusual sesquiterpene synthase[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(39): 12392-12395. |
| 93 | MURAI K, LAUTERBACH L, TERAMOTO K, et al. An unusual skeletal rearrangement in the biosynthesis of the sesquiterpene trichobrasilenol from Trichoderma [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(42): 15046-15050. |
| 94 | LEE C F, CHEN L X, CHIANG C Y, et al. The biosynthesis of norsesquiterpene aculenes requires three cytochrome P450 enzymes to catalyze a stepwise demethylation process[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(51): 18414-18418. |
| 95 | FENG J, SURUP F, HAUSER M, et al. Biosynthesis of oxygenated brasilane terpene glycosides involves a promiscuous N-acetylglucosamine transferase[J]. Chemical Communications, 2020, 56(82): 12419-12422. |
| 96 | RICO-MARTÍNEZ M, MEDINA F G, MARRERO J G, et al. Biotransformation of diterpenes[J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(21): 10627-10647. |
| 97 | FUJII R, MINAMI A, TSUKAGOSHI T, et al. Total biosynthesis of diterpene aphidicolin, a specific inhibitor of DNA polymerase α: heterologous expression of four biosynthetic genes in Aspergillus oryzae [J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2011, 75(9): 1813-1817. |
| 98 | QIN B, MATSUDA Y, MORI T, et al. An unusual chimeric diterpene synthase from Emericella variecolor and its functional conversion into a sesterterpene synthase by domain swapping[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(5): 1658-1661. |
| 99 | ALBERTI F, KHAIRUDIN K, VENEGAS E R, et al. Heterologous expression reveals the biosynthesis of the antibiotic pleuromutilin and generates bioactive semi-synthetic derivatives[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 1831. |
| 100 | MITSUHASHI T, OKADA M, ABE I. Identification of chimeric αβγ diterpene synthases possessing both Type II terpene cyclase and prenyltransferase activities[J]. ChemBioChem, 2017, 18(21): 2104-2109. |
| 101 | MITSUHASHI T, KIKUCHI T, HOSHINO S, et al. Crystalline sponge method enabled the investigation of a prenyltransferase-terpene synthase chimeric enzyme, whose product exhibits broadened NMR signals[J]. Organic Letters, 2018, 20(18): 5606-5609. |
| 102 | TAZAWA A, YE Y, OZAKI T, et al. Total biosynthesis of brassicicenes: identification of a key enzyme for skeletal diversification[J]. Organic Letters, 2018, 20(19): 6178-6182. |
| 103 | LIN F L, LAUTERBACH L, ZOU J, et al. Mechanistic characterization of the fusicoccane-type diterpene synthase for myrothec-15(17)-en-7-ol[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(7): 4306-4312. |
| 104 | LI K K, GUSTAFSON K R. Sesterterpenoids: chemistry, biology, and biosynthesis[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2021, 38(7): 1251-1281. |
| 105 | GUO K, LIU Y, LI S H. The untapped potential of plant sesterterpenoids: chemistry, biological activities and biosynthesis[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2021, 38(12): 2293-2314. |
| 106 | CHIBA R, MINAMI A, GOMI K, et al. Identification of ophiobolin F synthase by a genome mining approach: A sesterterpene synthase from Aspergillus clavatus [J]. Organic Letters, 2013, 15(3): 594-597. |
| 107 | QUAN Z Y, DICKSCHAT J S. On the mechanism of ophiobolin F synthase and the absolute configuration of its product by isotopic labelling experiments[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2020, 18(31): 6072-6076. |
| 108 | MATSUDA Y, MITSUHASHI T, QUAN Z Y, et al. Molecular basis for stellatic acid biosynthesis: a genome mining approach for discovery of sesterterpene synthases[J]. Organic Letters, 2015, 17(18): 4644-4647. |
| 109 | MATSUDA Y, MITSUHASHI T, LEE S K, et al. Astellifadiene: structure determination by NMR spectroscopy and crystalline sponge method, and elucidation of its biosynthesis[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(19): 5785-5788. |
| 110 | OKADA M, MATSUDA Y, MITSUHASHI T, et al. Genome-based discovery of an unprecedented cyclization mode in fungal sesterterpenoid biosynthesis[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(31): 10011-10018. |
| 121 | CAO Z Q, LI S Y, LV J M, et al. Biosynthesis of clinically used antibiotic fusidic acid and identification of two short-chain dehydrogenase/reductases with converse stereoselectivity[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2019, 9(2): 433-442. |
| 122 | WANG J L, ZHANG Y N, LIU H H, et al. A biocatalytic hydroxylation-enabled unified approach to C19-hydroxylated steroids[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 3378. |
| 123 | CAO Z Q, LV J M, LIU Q, et al. Biosynthetic study of cephalosporin P1 reveals a multifunctional P450 enzyme and a site-selective acetyltransferase[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2020, 15(1): 44-51. |
| 124 | GERIS R, SIMPSON T J. Meroterpenoids produced by fungi[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2009, 26(8): 1063-1094. |
| 125 | SCHOR R, SCHOTTE C, WIBBERG D, et al. Three previously unrecognised classes of biosynthetic enzymes revealed during the production of xenovulene A[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 1963. |
| 126 | SCHOTTE C, LI L, WIBBERG D, et al. Synthetic biology driven biosynthesis of unnatural tropolone sesquiterpenoids[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(52): 23870-23878. |
| 127 | ITOH T, TOKUNAGA K, MATSUDA Y, et al. Reconstitution of a fungal meroterpenoid biosynthesis reveals the involvement of a novel family of terpene cyclases[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2010, 2(10): 858-864. |
| 128 | HU J, OKAWA H, YAMAMOTO K, et al. Characterization of two cytochrome P450 monooxygenase genes of the pyripyropene biosynthetic gene cluster from Penicillium coprobium[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 2011, 64(3): 221-227. |
| 129 | HU J, FURUTANI A, YAMAMOTO K, et al. Characterization of two acetyltransferase genes in the pyripyropene biosynthetic gene cluster from Penicillium coprobium [J]. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment, 2014, 28(5): 818-826. |
| 130 | MATSUDA Y, AWAKAWA T, ABE I. Reconstituted biosynthesis of fungal meroterpenoid andrastin A[J]. Tetrahedron, 2013, 69(38): 8199-8204. |
| 131 | MATSUDA Y, AWAKAWA T, WAKIMOTO T, et al. Spiro-ring formation is catalyzed by a multifunctional dioxygenase in austinol biosynthesis[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(30): 10962-10965. |
| 132 | MATSUDA Y, IWABUCHI T, WAKIMOTO T, et al. Uncovering the unusual D-ring construction in terretonin biosynthesis by collaboration of a multifunctional cytochrome P450 and a unique isomerase[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(9): 3393-3401. |
| 133 | MATSUDA Y, QUAN Z Y, MITSUHASHI T, et al. Cytochrome P450 for citreohybridonol synthesis: oxidative derivatization of the andrastin scaffold[J]. Organic Letters, 2016, 18(2): 296-299. |
| 134 | MATSUDA Y, IWABUCHI T, FUJIMOTO T, et al. Discovery of key dioxygenases that diverged the paraherquonin and acetoxydehydroaustin pathways in Penicillium brasilianum [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(38): 12671-12677. |
| 135 | MATSUDA Y, BAI T X, PHIPPEN C B W, et al. Novofumigatonin biosynthesis involves a non-heme iron-dependent endoperoxide isomerase for orthoester formation[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 2587. |
| 136 | BAI T X, QUAN Z Y, ZHAI R, et al. Elucidation and heterologous reconstitution of chrodrimanin B biosynthesis[J]. Organic Letters, 2018, 20(23): 7504-7508. |
| 137 | WANG W G, DU L Q, SHENG S L, et al. Genome mining for fungal polyketide-diterpenoid hybrids: discovery of key terpene cyclases and multifunctional P450s for structural diversification[J]. Organic Chemistry Frontiers, 2019, 6(5): 571-578. |
| 138 | XIAO Z H, DONG J Y, LI A, et al. Biocatalytic and chemical derivatization of the fungal meroditerpenoid chevalone E[J]. Organic Chemistry Frontiers, 2022, 9(7): 1837-1843. |
| 139 | TSUKADA K, SHINKI S, KANEKO A, et al. Synthetic biology based construction of biological activity-related library of fungal decalin-containing diterpenoid pyrones[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 1830. |
| 140 | BAI T X, MATSUDA Y, TAO H, et al. Structural diversification of andiconin-derived natural products by α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases[J]. Organic Letters, 2020, 22(11): 4311-4315. |
| 141 | YAN D X, MATSUDA Y. Genome mining-driven discovery of 5-methylorsellinate-derived meroterpenoids from Aspergillus funiculosus [J]. Organic Letters, 2021, 23(8): 3211-3215. |
| 142 | TAGAMI K, LIU C W, MINAMI A, et al. Reconstitution of biosynthetic machinery for indole-diterpene paxilline in Aspergillus oryzae [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(4): 1260-1263. |
| 143 | LIU C W, TAGAMI K, MINAMI A, et al. Reconstitution of biosynthetic machinery for the synthesis of the highly elaborated indole diterpene penitrem[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(19): 5748-5752. |
| 144 | LIU C W, MINAMI A, DAIRI T, et al. Biosynthesis of shearinine: Diversification of a tandem prenyl moiety of fungal indole diterpenes[J]. Organic Letters, 2016, 18(19): 5026-5029. |
| 111 | NARITA K, SATO H, MINAMI A, et al. Focused genome mining of structurally related sesterterpenes: enzymatic formation of enantiomeric and diastereomeric products[J]. Organic Letters, 2017, 19(24): 6696-6699. |
| 112 | NARITA K, MINAMI A, OZAKI T, et al. Total biosynthesis of antiangiogenic agent (–)-terpestacin by artificial reconstitution of the biosynthetic machinery in Aspergillus oryzae [J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2018, 83(13): 7042-7048. |
| 113 | GAO L, NARITA K, OZAKI T, et al. Identification of novel sesterterpenes by genome mining of phytopathogenic fungi Phoma and Colletotrichum sp.[J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 2018, 59(12): 1136-1139. |
| 114 | HUANG J H, LV J M, WANG Q Z, et al. Biosynthesis of an anti-tuberculosis sesterterpenoid asperterpenoid A[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2019, 17(2): 248-251. |
| 115 | QUAN Z Y, DICKSCHAT J S. Biosynthetic gene cluster for asperterpenols A and B and the cyclization mechanism of asperterpenol A synthase[J]. Organic Letters, 2020, 22(19): 7552-7555. |
| 116 | GUO J J, CAI Y S, CHENG F C, et al. Genome mining reveals a multiproduct sesterterpenoid biosynthetic gene cluster in Aspergillus ustus [J]. Organic Letters, 2021, 23(5): 1525-1529. |
| 117 | JIANG L, ZHANG X, SATO Y, et al. Genome-based discovery of enantiomeric pentacyclic sesterterpenes catalyzed by fungal bifunctional terpene synthases[J]. Organic Letters, 2021, 23(12): 4645-4650. |
| 118 | HARRISON D M. The biosynthesis of triterpenoids and steroids[J]. Natural Product Reports, 1985, 2(6): 525-560. |
| 119 | LV J M, HU D, GAO H, et al. Biosynthesis of helvolic acid and identification of an unusual C-4-demethylation process distinct from sterol biosynthesis[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 1644. |
| 120 | WANG G Q, CHEN G D, QIN S Y, et al. Biosynthetic pathway for furanosteroid demethoxyviridin and identification of an unusual pregnane side-chain cleavage[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 1838. |
| 145 | KUDO K, LIU C W, MATSUMOTO T, et al. Heterologous biosynthesis of fungal indole sesquiterpene sespendole[J]. ChemBioChem, 2018, 19(14): 1492-1497. |
| 146 | JIANG Y L, OZAKI T, HARADA M, et al. Biosynthesis of indole diterpene lolitrems: Radical-induced cyclization of an epoxyalcohol affording a characteristic lolitremane skeleton[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(41): 17996-18002. |
| 147 | LI C, MATSUDA Y, GAO H, et al. Biosynthesis of LL-Z1272β: Discovery of a new member of NRPS-like enzymes for aryl-aldehyde formation[J]. ChemBioChem, 2016, 17(10): 904-907. |
| 148 | OKADA M, SAITO K, WONG C P, et al. Combinatorial biosynthesis of (+)-daurichromenic acid and its halogenated analogue[J]. Organic Letters, 2017, 19(12): 3183-3186. |
| 149 | ARAKI Y, AWAKAWA T, MATSUZAKI M, et al. Complete biosynthetic pathways of ascofuranone and ascochlorin in Acremonium egyptiacum [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(17): 8269-8274. |
| 150 | LV J M, GAO Y H, ZHAO H, et al. Biosynthesis of biscognienyne B involving a cytochrome P450-dependent alkynylation[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(32): 13531-13536. |
| 151 | TAKUSAGAWA S, SATOH Y, OHTSU I, et al. Ergothioneine production with Aspergillus oryzae [J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2019, 83(1): 181-184. |
| 152 | NEWMAN D J, CRAGG G M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2020, 83(3): 770-803. |
| 153 | ATANASOV A G, ZOTCHEV S B, DIRSCH V M, et al. Natural products in drug discovery: advances and opportunities[J]. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2021, 20(3): 200-216. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | 仲泉周, 单依怡, 裴清云, 金艳芸, 王艺涵, 孟璐远, 王歆韵, 张雨鑫, 刘坤媛, 王慧中, 冯尚国. 生物合成法生产α-熊果苷的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 118-135. |
| [7] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [8] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [9] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [10] | 竺方欢, 岑雪聪, 陈振. 微生物合成二元醇研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1367-1385. |
| [11] | 刘益宁, 蒲伟, 杨金星, 王钰. ω-氨基酸与内酰胺的生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1350-1366. |
| [12] | 李庚, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 王佳, 袁其朋. 过氧化物酶的重组表达和应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1498-1517. |
| [13] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [14] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [15] | 程晓雷, 刘天罡, 陶慧. 萜类化合物的非常规生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1050-1071. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||