• 特约评述 •
工程菌的生物安全防控策略
甘牡丹, 左静蕊, 曹友志
- 苏州大学,功能纳米与软物质研究院,江苏 苏州 215123
-
收稿日期:2025-02-14修回日期:2025-04-27出版日期:2025-05-06 -
通讯作者:甘牡丹 -
作者简介:甘牡丹 (1987—),女,硕士,实验师。研究方向为基因工程改造病毒、工程菌和病原微生物的生物安全评价和实验室管理。E-mail:gmd@suda.edu.cn
Biocontainment strategies of engineered bacteria
GAN Mudan, ZUO Jingrui, CAO Youzhi
- Functional Nano and Soft Materials (FUNSOM),Soochow University,Suzhou 215123,Jiangsui,China
-
Received:2025-02-14Revised:2025-04-27Online:2025-05-06 -
Contact:GAN Mudan
摘要:
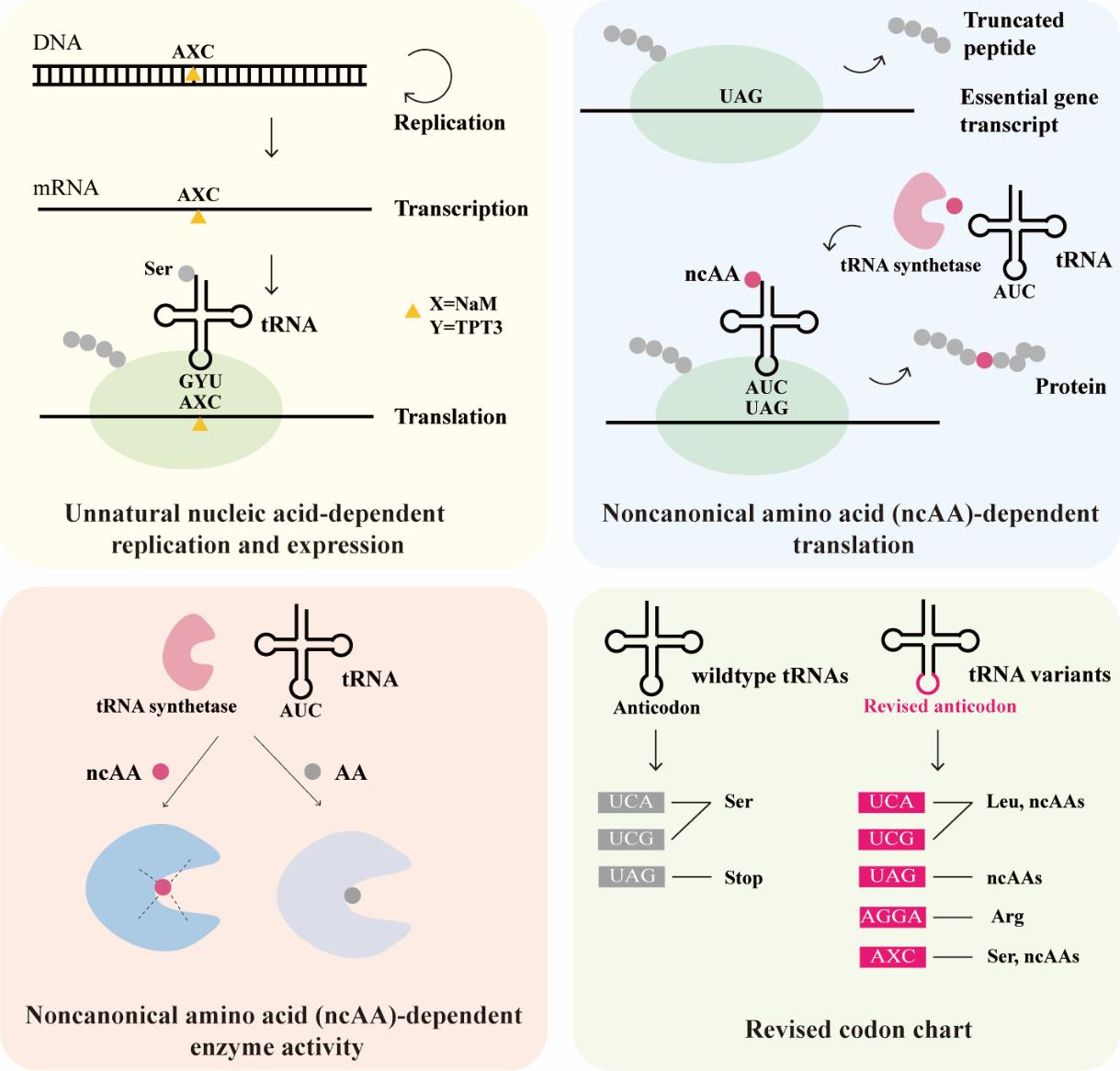
随着人工设计的基因元件和工程菌应用于医学诊断和疾病治疗领域的增加,由此产生的生物安全风险也越来越受到重视。本文主要回顾了合成生物学的生物安全防控策略,特别介绍了近几年医学诊疗工程菌的生物安全防控研究。工程菌的生物安全防控可以防止宿主菌和基因元件脱离病灶区域向环境泄漏。基于营养缺陷或自杀基因的调控系统广泛用于限制工程菌的逃逸,基因元件拆分和靶向降解策略则可以防止基因元件扩散到环境中被其他细胞利用。环境中的代谢物和基因片段可能转移进入工程菌,这是导致生物安全防控机制失效的重要因素。非天然核苷酸和非天然氨基酸等非天然复制翻译系统的正交性好,可以大幅减少环境和工程菌间的相互影响。综合不同合成生物学原理设计的多层生物安全防控系统对于未来解决生物安全问题具有极大潜力。
中图分类号:
引用本文
甘牡丹, 左静蕊, 曹友志. 工程菌的生物安全防控策略[J]. 合成生物学, DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-010.
GAN Mudan, ZUO Jingrui, CAO Youzhi. Biocontainment strategies of engineered bacteria[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-010.
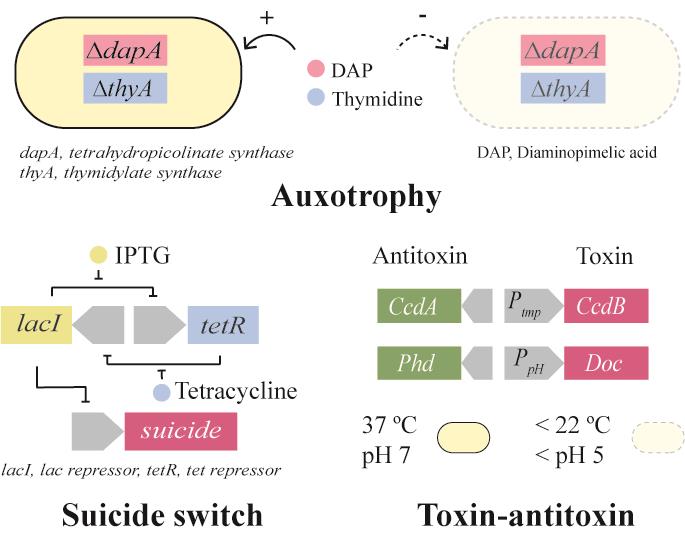
| 生物安全防控策略 | 实例 |
|---|---|
| 营养缺陷 | dapA基因敲除的营养缺陷[ |
| 自杀基因调控开关 | ATc调控的Deadman自杀基因开关;LacI-GalR融合转录因子的Passcode自杀基因开关[ |
| 毒素-抗毒素 | 温度响应的CcdB-CcdA毒素-抗毒素分子对[ |
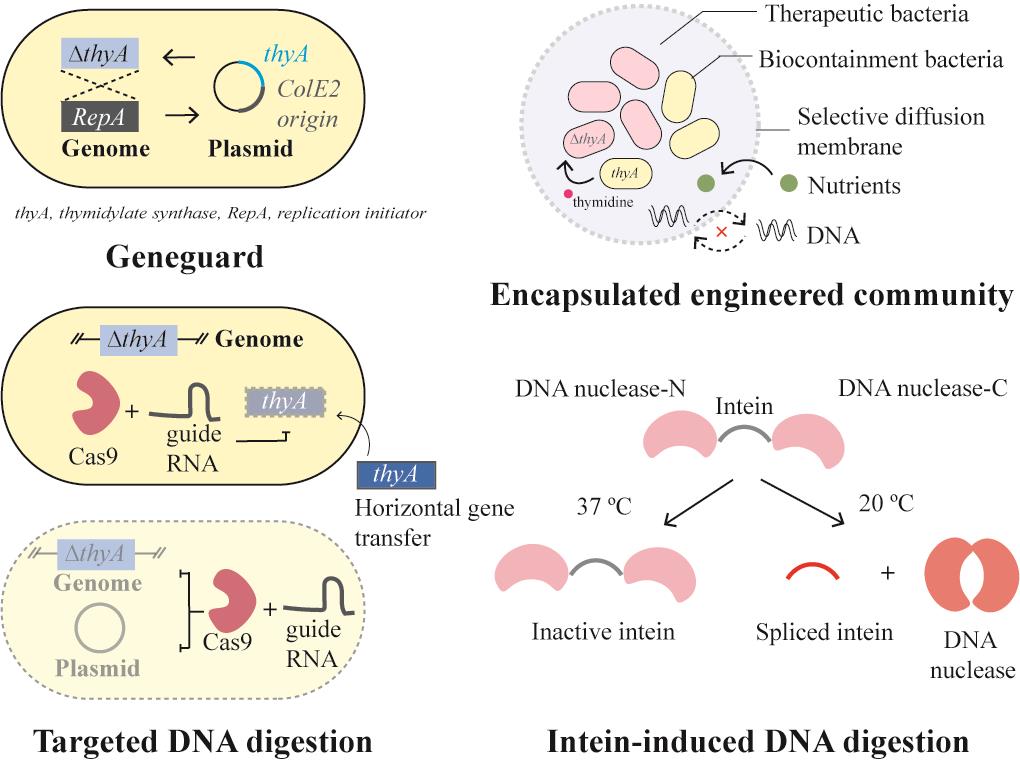
| 基因元件拆分 | Geneguard质粒宿主依赖系统[ |
| DNA降解 | 靶向外源基因的Cas9系统[ |
| 降低突变 | 基因组插入序列元件IS敲除[ |
| 物理隔离 | GelMA包裹的工程菌[ |
表1 生物安全防控策略实例
Table 1 Examples of biocontainment strategies
| 生物安全防控策略 | 实例 |
|---|---|
| 营养缺陷 | dapA基因敲除的营养缺陷[ |
| 自杀基因调控开关 | ATc调控的Deadman自杀基因开关;LacI-GalR融合转录因子的Passcode自杀基因开关[ |
| 毒素-抗毒素 | 温度响应的CcdB-CcdA毒素-抗毒素分子对[ |
| 基因元件拆分 | Geneguard质粒宿主依赖系统[ |
| DNA降解 | 靶向外源基因的Cas9系统[ |
| 降低突变 | 基因组插入序列元件IS敲除[ |
| 物理隔离 | GelMA包裹的工程菌[ |
| 1 | GURBATRI C R, ARPAIA N, DANINO T. Engineering bacteria as interactive cancer therapies[J]. Science, 2022, 378(6622): 858-864. |
| 2 | KIM K, KANG M, CHO B K. Systems and synthetic biology-driven engineering of live bacterial therapeutics[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2023, 11: 1267378. |
| 3 | RAMAN V, DESHPANDE C P, KHANDUJA S, et al. Build-a-bug workshop: using microbial-host interactions and synthetic biology tools to create cancer therapies[J]. Cell Host & Microbe, 2023, 31(10): 1574-1592. |
| 4 | CIOCAN D, ELINAV E. Engineering bacteria to modulate host metabolism[J]. Acta Physiologica, 2023, 238(3): e14001. |
| 5 | ZHAI L, FU L Y, WEI W, et al. Advances of bacterial biomaterials for disease therapy[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2024, 13(5): 1400-1411. |
| 6 | YAN S Z, GAN Y, XU H Z, et al. Bacterial carrier-mediated drug delivery systems: a promising strategy in cancer therapy[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2025, 12: 1526612. |
| 7 | DEY S, SANKARAN S. Engineered bacterial therapeutics with material solutions[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2024, 42(12): 1663-1676. |
| 8 | LEE J W, CHAN C T Y, SLOMOVIC S, et al. Next-generation biocontainment systems for engineered organisms[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2018, 14(6): 530-537. |
| 9 | ASIN-GARCIA E, KALLERGI A, LANDEWEERD L, et al. Genetic safeguards for safety-by-design: so close yet so far[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2020, 38(12): 1308-1312. |
| 10 | PARKER M T, KUNJAPUR A M. Deployment of engineered microbes: contributions to the bioeconomy and considerations for biosecurity[J]. Health Security, 2020, 18(4): 278-296. |
| 11 | ARNOLDS K L, DAHLIN L R, DING L, et al. Biotechnology for secure biocontainment designs in an emerging bioeconomy[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2021, 71: 25-31. |
| 12 | OU Y K, GUO S J. Safety risks and ethical governance of biomedical applications of synthetic biology[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2023, 11: 1292029. |
| 13 | HALAWA E M, FADEL M, AL-RABIA M W, et al. Antibiotic action and resistance: updated review of mechanisms, spread, influencing factors, and alternative approaches for combating resistance[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2024, 14: 1305294. |
| 14 | PANTOJA ANGLES A, VALLE-PÉREZ A U, HAUSER C, et al. Microbial biocontainment systems for clinical, agricultural, and industrial applications[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2022, 10: 830200. |
| 15 | HUANG Y, LIN X J, YU S Y, et al. Intestinal engineered probiotics as living therapeutics: chassis selection, colonization enhancement, gene circuit design, and biocontainment[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2022, 11(10): 3134-3153. |
| 16 | ARBOLEDA-GARCÍA A, ALARCON-RUIZ I, BOADA-ACOSTA L, et al. Advancements in synthetic biology-based bacterial cancer therapy: a modular design approach[J]. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology, 2023, 190: 104088. |
| 17 | MOE-BEHRENS G H G, DAVIS R, HAYNES K A. Preparing synthetic biology for the world[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2013, 4: 5. |
| 18 | WILSON D J. NIH guidelines for research involving recombinant DNA molecules[J]. Accountability in Research, 1993, 3(2-3): 177-185. |
| 19 | FENG G Q, HUANG H N, CHEN Y G. Effects of emerging pollutants on the occurrence and transfer of antibiotic resistance genes: a review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 420: 126602. |
| 20 | WANG S M, LI W, XI B D, et al. Mechanisms and influencing factors of horizontal gene transfer in composting system: a review[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2024, 955: 177017. |
| 21 | 中华人民共和国科学技术部. 基因工程安全管理办法[EB/OL]. [2025-02-12]. . |
| 22 | NELSON M T, CHARBONNEAU M R, COIA H G, et al. Characterization of an engineered live bacterial therapeutic for the treatment of phenylketonuria in a human gut-on-a-chip[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 2805. |
| 23 | LEVENTHAL D S, SOKOLOVSKA A, LI N, et al. Immunotherapy with engineered bacteria by targeting the STING pathway for anti-tumor immunity[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 2739. |
| 24 | CHAN C T Y, LEE J W, CAMERON D E, et al. 'Deadman' and 'Passcode' microbial kill switches for bacterial containment[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2016, 12(2): 82-86. |
| 25 | FERRY Q R V, LYUTOVA R, FULGA T A. Rational design of inducible CRISPR guide RNAs for de novo assembly of transcriptional programs[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 14633. |
| 26 | STIRLING F, NAYDICH A, BRAMANTE J, et al. Synthetic cassettes for pH-mediated sensing, counting, and containment[J]. Cell Reports, 2020, 30(9): 3139-3148.e4. |
| 27 | WRIGHT O, DELMANS M, STAN G B, et al. GeneGuard: a modular plasmid system designed for biosafety[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2015, 4(3): 307-316. |
| 28 | HUANG S Q, LEE A J, TSOI R, et al. Coupling spatial segregation with synthetic circuits to control bacterial survival[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2016, 12(2): 859. |
| 29 | HAYASHI N, LAI Y, FUERTE-STONE J, et al. Cas9-assisted biological containment of a genetically engineered human commensal bacterium and genetic elements[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15: 2096. |
| 30 | FOO G W, LEICHTHAMMER C D, SAITA I M, et al. Intein-based thermoregulated meganucleases for containment of genetic material[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2024, 52(4): 2066-2077. |
| 31 | CAI Y Z, AGMON N, CHOI W J, et al. Intrinsic biocontainment: multiplex genome safeguards combine transcriptional and recombinational control of essential yeast genes[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(6): 1803-1808. |
| 32 | CALLAWAY E. 'Minimal' cell raises stakes in race to harness synthetic life[J]. Nature, 2016, 531(7596): 557-558. |
| 33 | WU F, LIN S S, LUO H L, et al. Noncontact microbiota transplantation by core-shell microgel-enabled nonleakage envelopment[J]. Science Advances, 2025, 11(6): eadr7373. |
| 34 | ZOU Z P, CAI Z H, ZHANG X P, et al. Delivery of encapsulated intelligent engineered probiotic for inflammatory bowel disease therapy[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2025, 14(3): 2403704. |
| 35 | INDA-WEBB M E, JIMENEZ M, LIU Q, et al. Sub-1.4 Cm3 capsule for detecting labile inflammatory biomarkers in situ [J]. Nature, 2023, 620(7973): 386-392. |
| 36 | HIROTA R, ABE K, KATSUURA Z I, et al. A novel biocontainment strategy makes bacterial growth and survival dependent on phosphite[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 44748. |
| 37 | AGMON N, TANG Z J, YANG K, et al. Low escape-rate genome safeguards with minimal molecular perturbation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(8): E1470-E1479. |
| 38 | ASIN-GARCIA E, BATIANIS C, LI Y S, et al. Phosphite synthetic auxotrophy as an effective biocontainment strategy for the industrial chassis Pseudomonas putida [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2022, 21(1): 156. |
| 39 | SEBESTA J, XIONG W, GUARNIERI M T, et al. Biocontainment of genetically engineered algae[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 839446. |
| 40 | BONGAERTS N, EDOO Z, ABUKAR A A, et al. Low-cost anti-mycobacterial drug discovery using engineered E. coli [J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 3905. |
| 41 | HEDIN K A, KRUSE V, VAZQUEZ-URIBE R, et al. Biocontainment strategies for in vivo applications of Saccharomyces boulardii [J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2023, 11: 1136095. |
| 42 | RUEDA-MEJIA M P, BÜHLMANN A, ORTIZ-MERINO R A, et al. Pantothenate auxotrophy in a naturally occurring biocontrol yeast[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2023, 89(7): e00884-23. |
| 43 | LINDNER S N, RAMIREZ L C, KRÜSEMANN J L, et al. NADPH-auxotrophic E. coli: a sensor strain for testing in vivo regeneration of NADPH[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(12): 2742-2749. |
| 44 | ISABELLA V M, HA B N, CASTILLO M J, et al. Development of a synthetic live bacterial therapeutic for the human metabolic disease phenylketonuria[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(9): 857-864. |
| 45 | KURTZ C B, MILLET Y A, PUURUNEN M K, et al. An engineered E. coli Nissle improves hyperammonemia and survival in mice and shows dose-dependent exposure in healthy humans[J]. Science Translational Medicine, 2019, 11(475): eaau7975. |
| 46 | LUKE J J, PIHA-PAUL S A, MEDINA T, et al. Phase I study of SYNB1891, an engineered E. coli nissle strain expressing STING agonist, with and without atezolizumab in advanced malignancies[J]. Clinical Cancer Research, 2023, 29(13): 2435-2444. |
| 47 | ATA Ö, MATTANOVICH D. Into the metabolic wild: Unveiling hidden pathways of microbial metabolism[J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 2024, 17(8): e14548. |
| 48 | JONES B S, LAMB L S, GOLDMAN F, et al. Improving the safety of cell therapy products by suicide gene transfer[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2014, 5: 254. |
| 49 | ČELEŠNIK H, TANŠEK A, TAHIROVIĆ A, et al. Biosafety of biotechnologically important microalgae: intrinsic suicide switch implementation in Cyanobacterium synechocystis sp. PCC 6803[J]. Biology Open, 2016, 5(4): 519-528. |
| 50 | ZHOU Y Q, SUN T, CHEN Z X, et al. Development of a new biocontainment strategy in model Cyanobacterium Synechococcus strains[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(11): 2576-2584. |
| 51 | HOFFMANN S A, CAI Y Z. Engineering stringent genetic biocontainment of yeast with a protein stability switch[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15: 1060. |
| 52 | VARMA S, GULATI K A, SRIRAMAKRISHNAN J, et al. Environment signal dependent biocontainment systems for engineered organisms: Leveraging triggered responses and combinatorial systems[J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2025, 10(2): 356-364. |
| 53 | MU Z P, ZOU Z N, YANG Y, et al. A genetically engineered Escherichia coli that senses and degrades tetracycline antibiotic residue[J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2018, 3(3): 196-203. |
| 54 | HALVORSEN T M, RICCI D P, PARK D M, et al. Comparison of kill switch toxins in plant-beneficial Pseudomonas fluorescens reveals drivers of lethality, stability, and escape[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2022, 11(11): 3785-3796. |
| 55 | JURĖNAS D, FRAIKIN N, GOORMAGHTIGH F, et al. Biology and evolution of bacterial toxin–antitoxin systems[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2022, 20(6): 335-350. |
| 56 | SOUCY S M, HUANG J L, GOGARTEN J P. Horizontal gene transfer: building the web of life[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2015, 16(8): 472-482. |
| 57 | WOLFF J H, MIKKELSEN J G. Delivering genes with human immunodeficiency virus-derived vehicles: still state-of-the-art after 25 years[J]. Journal of Biomedical Science, 2022, 29(1): 79. |
| 58 | ENG A, BORENSTEIN E. Microbial community design: methods, applications, and opportunities[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2019, 58: 117-128. |
| 59 | IBRAHIM M, RAAJARAAM L, RAMAN K. Modelling microbial communities: Harnessing consortia for biotechnological applications[J]. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 2021, 19: 3892-3907. |
| 60 | MIMEE M, CITORIK R J, LU T K. Microbiome therapeutics- advances and challenges[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2016, 105(Pt A): 44-54. |
| 61 | KE J, WANG B, YOSHIKUNI Y. Microbiome engineering: synthetic biology of plant-associated microbiomes in sustainable agriculture[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2021, 39(3): 244-261. |
| 62 | RAPP K M, JENKINS J P, BETENBAUGH M J. Partners for life: building microbial consortia for the future[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2020, 66: 292-300. |
| 63 | OZDEMIR T, FEDOREC A J H, DANINO T, et al. Synthetic biology and engineered live biotherapeutics: toward increasing system complexity[J]. Cell Systems, 2018, 7(1): 5-16. |
| 64 | DOU J, BENNETT M R. Synthetic biology and the gut microbiome[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2018, 13(5): 1700159. |
| 65 | NEVOT G, SANTOS-MORENO J, CAMPAMÀ-SANZ N, et al. Synthetically programmed antioxidant delivery by a domesticated skin commensal[J]. Cell Systems, 2025, 16(2): 101169. |
| 66 | VANARSDALE E, NAVID A, CHU M J, et al. Electrogenetic signaling and information propagation for controlling microbial consortia via programmed lysis[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2023, 120(5): 1366-1381. |
| 67 | CALIANDO B J, VOIGT C A. Targeted DNA degradation using a CRISPR device stably carried in the host genome[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 6989. |
| 68 | ROTTINGHAUS A G, FERREIRO A, FISHBEIN S R S, et al. Genetically stable CRISPR-based kill switches for engineered microbes[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 672. |
| 69 | ASIN-GARCIA E, MARTIN-PASCUAL M, GARCIA-MORALES L, et al. ReScribe: an unrestrained tool combining multiplex recombineering and minimal-PAM ScCas9 for genome recoding Pseudomonas putida [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2021, 10(10): 2672-2688. |
| 70 | HARTIG A M, DAI W T, ZHANG K, et al. Influence of environmental conditions on the escape rates of biocontained genetically engineered microbes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2024, 58(51): 22657-22667. |
| 71 | ASIN-GARCIA E, MARTIN-PASCUAL M, DE BUCK C, et al. GenoMine: a CRISPR-Cas9-based kill switch for biocontainment of Pseudomonas putida [J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2024, 12: 1426107. |
| 72 | PANTOJA ANGLES A, ALI Z, MAHFOUZ M. CS-cells: a CRISPR-Cas12 DNA device to generate chromosome-shredded cells for efficient and safe molecular biomanufacturing[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2022, 11(1): 430-440. |
| 73 | YANG B, WU C, TENG Y X, et al. Tailoring microbial fitness through computational steering and CRISPRi-driven robustness regulation[J]. Cell Systems, 2024, 15(12): 1133-1147.e4. |
| 74 | YANG Z K, LUO H, ZHANG Y M, et al. Pan-genomic analysis provides novel insights into the association of E.coli with human host and its minimal genome[J]. Bioinformatics, 2019, 35(12): 1987-1991. |
| 75 | TANG T C, THAM E, LIU X Y, et al. Hydrogel-based biocontainment of bacteria for continuous sensing and computation[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2021, 17(6): 724-731. |
| 76 | DATTA D, WEISS E L, WANGPRASEURT D, et al. Phenotypically complex living materials containing engineered cyanobacteria[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 4742. |
| 77 | CHE H C, WANG Z Y, LI Y, et al. A stable and sensitive engineering bacterial sensor via physical biocontainment and two-stage signal amplification[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2024, 96(21): 8807-8813. |
| 78 | ROMESBERG F E. Creation, optimization, and use of semi-synthetic organisms that store and retrieve increased genetic information[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2022, 434(8): 167331. |
| 79 | KIMOTO M, HIRAO I. Genetic alphabet expansion technology by creating unnatural base pairs[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(21): 7602-7626. |
| 80 | KIMOTO M, HIRAO I. Genetic code engineering by natural and unnatural base pair systems for the site-specific incorporation of non-standard amino acids into proteins[J]. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, 2022, 9: 851646. |
| 81 | GERECHT K, FREUND N, LIU W, et al. The expanded central dogma: genome resynthesis, orthogonal biosystems, synthetic genetics[J]. Annual Review of Biophysics, 2023, 52: 413-432. |
| 82 | DÖRRENHAUS R, WAGNER P K, KATH-SCHORR S. Two are not enough: synthetic strategies and applications of unnatural base pairs[J]. Biological Chemistry, 2023, 404(10): 883-896. |
| 83 | AWAWDEH A, RADECKI A A, VARGAS-RODRIGUEZ O. Suppressor tRNAs at the interface of genetic code expansion and medicine[J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 2024, 15: 1420331. |
| 84 | COSTELLO A, PETERSON A A, CHEN P H, et al. Genetic code expansion history and modern innovations[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2024, 124(21): 11962-12005. |
| 85 | YI H B, LEE S, SEO K, et al. Cellular and biophysical applications of genetic code expansion[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2024, 124(11): 7465-7530. |
| 86 | KIM Y J, CHO S H, KIM J C, et al. tRNA engineering strategies for genetic code expansion[J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 2024, 15: 1373250. |
| 87 | GÓMEZ-TATAY L, HERNÁNDEZ-ANDREU J M. Xenobiology for the biocontainment of synthetic organisms: opportunities and challenges[J]. Life, 2024, 14(8): 996. |
| 88 | MARLIÈRE P, PATROUIX J, DÖRING V, et al. Chemical evolution of a bacterium’s genome[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2011, 50(31): 7109-7114. |
| 89 | MALYSHEV D A, DHAMI K, LAVERGNE T, et al. A semi-synthetic organism with an expanded genetic alphabet[J]. Nature, 2014, 509(7500): 385-388. |
| 90 | ZHANG Y, PTACIN J L, FISCHER E C, et al. A semi-synthetic organism that stores and retrieves increased genetic information[J]. Nature, 2017, 551(7682): 644-647. |
| 91 | MUKAI T, LAJOIE M J, ENGLERT M, et al. Rewriting the genetic code[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 2017, 71: 557-577. |
| 92 | WANG L, BROCK A, HERBERICH B, et al. Expanding the genetic code of Escherichia coli [J]. Science, 2001, 292(5516): 498-500. |
| 93 | KATO Y. Translational control using an expanded genetic code[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(4): 887. |
| 94 | CHANG T T, DING W C, YAN S R, et al. A robust yeast biocontainment system with two-layered regulation switch dependent on unnatural amino acid[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 6487. |
| 95 | KATO Y. An engineered bacterium auxotrophic for an unnatural amino acid: a novel biological containment system[J]. PeerJ, 2015, 3: e1247. |
| 96 | KATO Y. Extremely low leakage expression systems using dual transcriptional-translational control for toxic protein production[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(3): 705. |
| 97 | KURU E, MÄÄTTÄLÄ R M, NOGUERA K, et al. Release factor inhibiting antimicrobial peptides improve nonstandard amino acid incorporation in wild-type bacterial cells[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2020, 15(7): 1852-1861. |
| 98 | GAO X W, SUN Y J, YANG Y H, et al. Directed evolution of hydroxylase XcP4H for enhanced 5-HTP production in engineered probiotics to treat depression[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2025, 307: 142250. |
| 99 | ROVNER A J, HAIMOVICH A D, KATZ S R, et al. Recoded organisms engineered to depend on synthetic amino acids[J]. Nature, 2015, 518(7537): 89-93. |
| 100 | XUAN W M, SCHULTZ P G. A strategy for creating organisms dependent on noncanonical amino acids[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(31): 9170-9173. |
| 101 | TACK D S, ELLEFSON J W, THYER R, et al. Addicting diverse bacteria to a noncanonical amino acid[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2016, 12(3): 138-140. |
| 102 | MANDELL D J, LAJOIE M J, MEE M T, et al. Biocontainment of genetically modified organisms by synthetic protein design[J]. Nature, 2015, 518(7537): 55-60. |
| 103 | KOH M, NASERTORABI F, HAN G W, et al. Generation of an orthogonal protein-protein interface with a noncanonical amino acid[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(16): 5728-5731. |
| 104 | GAN F, LIU R H, WANG F, et al. Functional replacement of histidine in proteins to generate noncanonical amino acid dependent organisms[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(11): 3829-3832. |
| 105 | LAJOIE M J, ROVNER A J, GOODMAN D B, et al. Genomically recoded organisms expand biological functions[J]. Science, 2013, 342(6156): 357-360. |
| 106 | FREDENS J, WANG K H, DE LA TORRE D, et al. Total synthesis of Escherichia coli with a recoded genome[J]. Nature, 2019, 569(7757): 514-518. |
| 107 | NYERGES A, VINKE S, FLYNN R, et al. A swapped genetic code prevents viral infections and gene transfer[J]. Nature, 2023, 615(7953): 720-727. |
| 108 | CHOI Y N, KIM D, LEE S, et al. Quadruplet Codon decoding-based versatile genetic biocontainment system[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2025, 53(1): gkae1292. |
| 109 | LAWSON C E, MARTÍ J M, RADIVOJEVIC T, et al. Machine learning for metabolic engineering: a review[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2021, 63: 34-60. |
| 110 | DIANAWATI D, MISHRA V, SHAH N P. Survival of microencapsulated probiotic bacteria after processing and during storage: a review[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2016, 56(10): 1685-1716. |
| 111 | NGUYEN T T, NGUYEN P T, PHAM M N, et al. Synbiotics: a new route of self-production and applications to human and animal health[J]. Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins, 2022, 14(5): 980-993. |
| 112 | HASSANISAADI M, VATANKHAH M, KENNEDY J F, et al. Advancements in xanthan gum: a macromolecule for encapsulating plant probiotic bacteria with enhanced properties[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2025, 348: 122801. |
| 113 | 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 中华人民共和国生物安全法[EB/OL]. [2025-02-12]. . |
| [1] | 陈盈盈, 刘扬, 史俊杰, 马俊英, 鞠建华. CRISPR/Cas基因编辑及其新兴技术在丝状真菌研究中的系统应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 672-693. |
| [2] | 许志锰, 谢震. 引导编辑研究进展及其应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 1-15. |
| [3] | 陈雅如, 曹英秀, 宋浩. 电活性微生物基因编辑与转录调控技术进展与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(6): 1281-1299. |
| [4] | 柳柯, 林桂虹, 刘坤, 周伟, 王风清, 魏东芝. CRISPR/Cas系统的挖掘、改造与功能拓展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 47-66. |
| [5] | 梁丽亚, 刘嵘明. 靶向DNA的Ⅱ类CRISPR/Cas系统的蛋白工程化改造[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 86-101. |
| [6] | 刘佳昕, 程驰, 李欣启, 汪超俊, 张颖, 薛闯. 梭菌分子遗传改造工具研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(6): 1201-1217. |
| [7] | 毕嘉成, 田志刚. 合成免疫学与未来NK细胞免疫治疗[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(1): 22-34. |
| [8] | 汪庆卓, 宋萍, 黄和. 合成生物技术驱动天然的真核油脂细胞工厂开发[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(6): 920-941. |
| [9] | 肖晗, 刘宜欣. CRISPR-Cas系统编辑丝状真菌的进展与挑战[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(2): 274-286. |
| [10] | 李洋, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 袁其朋, 闫亚军, 王佳. CRISPR基因编辑技术在微生物合成生物学领域的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(1): 106-120. |
| [11] | 杨永富, 耿碧男, 宋皓月, 何桥宁, 何明雄, 鲍杰, 白凤武, 杨世辉. 运动发酵单胞菌底盘细胞研究现状及展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(1): 59-90. |
| [12] | 袁飞燕, 于洋, 李春. 基于非天然结构组件的人工酶设计与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(6): 685-696. |
| [13] | 曹中正, 张心怡, 徐艺源, 周卓, 魏文胜. 基因组编辑技术及其在合成生物学中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(4): 413-426. |
| [14] | 林璐, 吕雪芹, 刘延峰, 堵国成, 陈坚, 刘龙. 枯草芽孢杆菌底盘细胞的设计、构建与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(2): 247-265. |
| [15] | 张博, 马永硕, 尚轶, 黄三文. 植物合成生物学研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(2): 121-140. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||