合成生物学 ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (4): 764-788.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-048
非生物元件增强的合成生物杂合体系研究进展
黄瑜晴1, 吴涵1, 李晓彬1, 刘君禹1, 马少华1,2, 戈钧2,3, 邢新会1,2,3, 张灿阳1,2
- 1.清华大学深圳国际研究生院生物医药与健康工程研究院,广东 深圳 518005
2.工业生物催化教育部重点实验室(清华大学),北京 100084
3.清华大学化学工程系,北京 100084
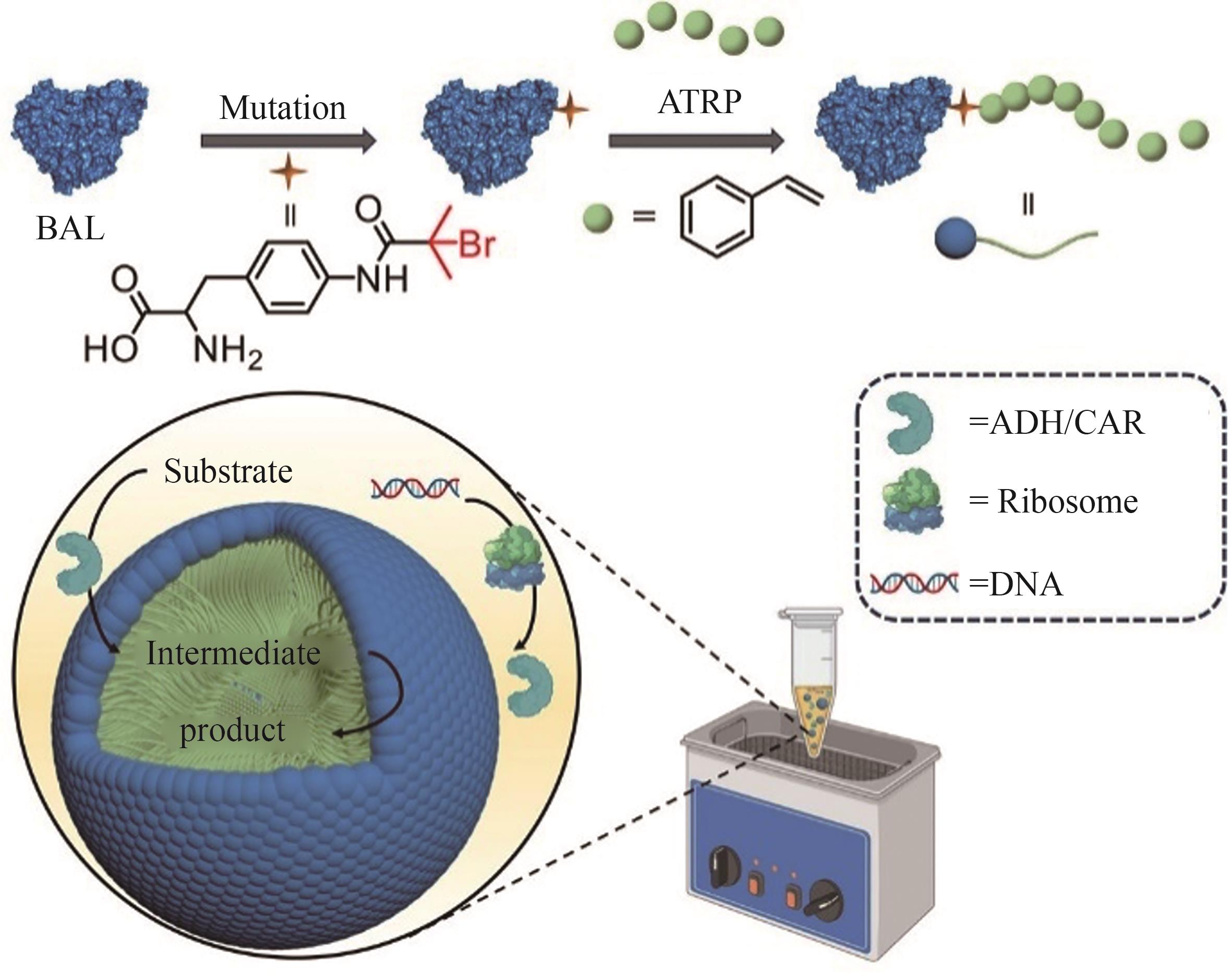
-
收稿日期:2025-05-23修回日期:2025-07-13出版日期:2025-08-31发布日期:2025-09-03 -
通讯作者:张灿阳 -
作者简介:黄瑜晴 (2001—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为口服递送大分子-工程菌杂合体系设计与创制。E-mail:huangyq23@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn吴涵 (2000—),男,硕士研究生。研究方向为中性粒细胞介导的PAE纳米颗粒靶向药物递送体系设计与开发。E-mail:wuhan23@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn张灿阳 (1985—),男,副教授,博士生导师。研究方向为面向生物医药与生命健康领域重大需求与问题,设计和开发多功能工程化生物材料载体和递送(剂型)策略,用于疾病诊断与治疗,如癌症、感染、自身免疫性疾病,具体包括:刺激-响应型(聚β-氨基酯)材料库的设计(计算机辅助和模拟)与建立;细胞介导的免疫调控靶向系统的开发;基于产品工程与制剂工程的生物医药与健康工程研究;微针相关技术与产品开发。 E-mail:zhang.cy@sz.tsinghua.edu.cn
第一联系人:共同第一作者 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2023YFA0913600);国家重点研发计划(2023YFA0913602)
Recent advancements in non-biological component-augmented synthetic bio-hybrid systems
HUANG Yuqing1, WU Han1, LI Xiaobin1, LIU Junyu1, MA Shaohua1,2, GE Jun2,3, XING Xinhui1,2,3, ZHANG Canyang1,2
- 1.Institute of Biopharmaceutical and Health Engineering,Tsinghua Shenzhen International Graduate School,Shenzhen 518005,Guangdong,China
2.Key Laboratory of Industrial Biocatalysis,Ministry of Education,Tsinghua University,Beijing 100084,China
3.Department of Chemical Engineering,Tsinghua University,Beijing 100084,China
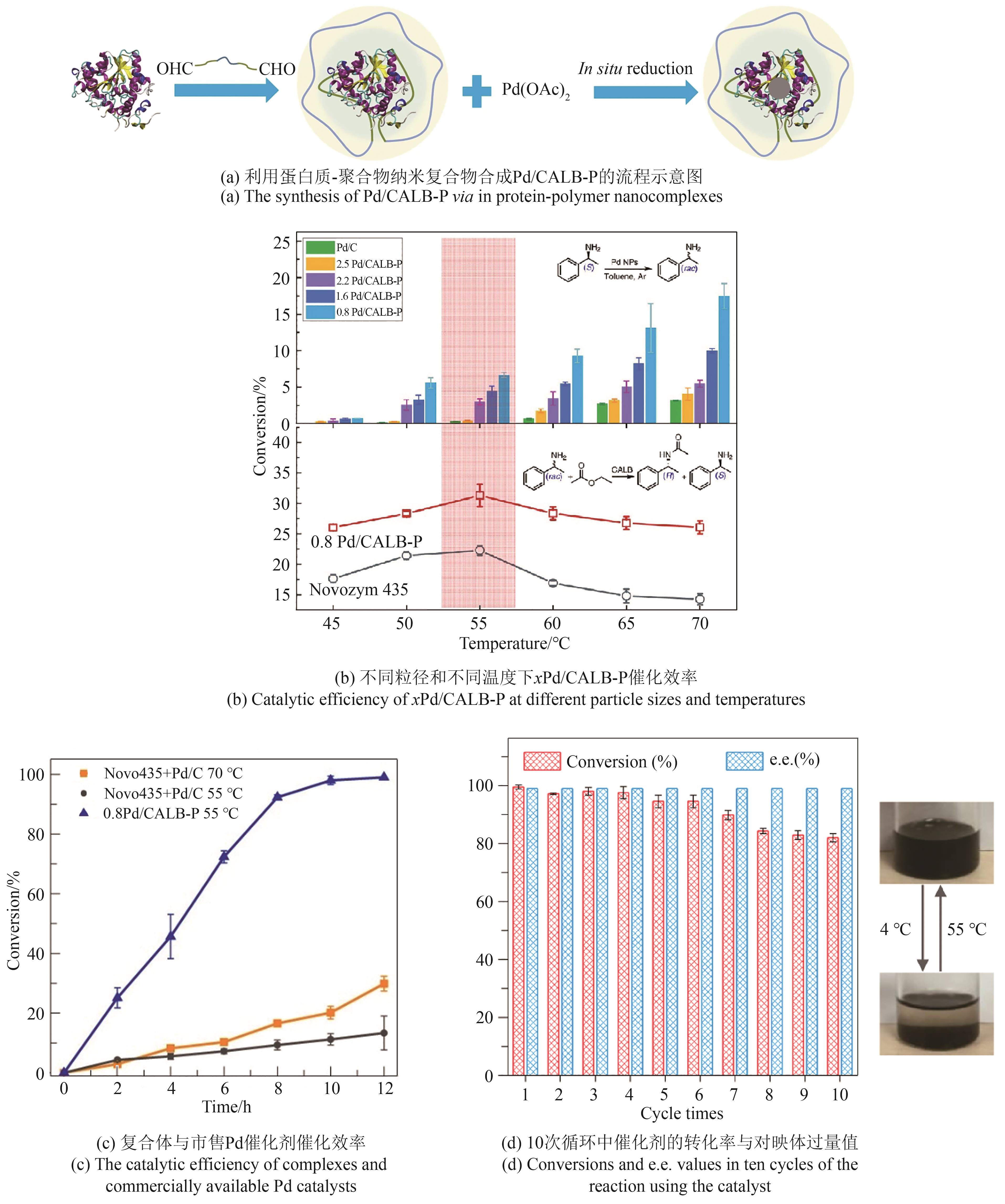
-
Received:2025-05-23Revised:2025-07-13Online:2025-08-31Published:2025-09-03 -
Contact:ZHANG Canyang
摘要:
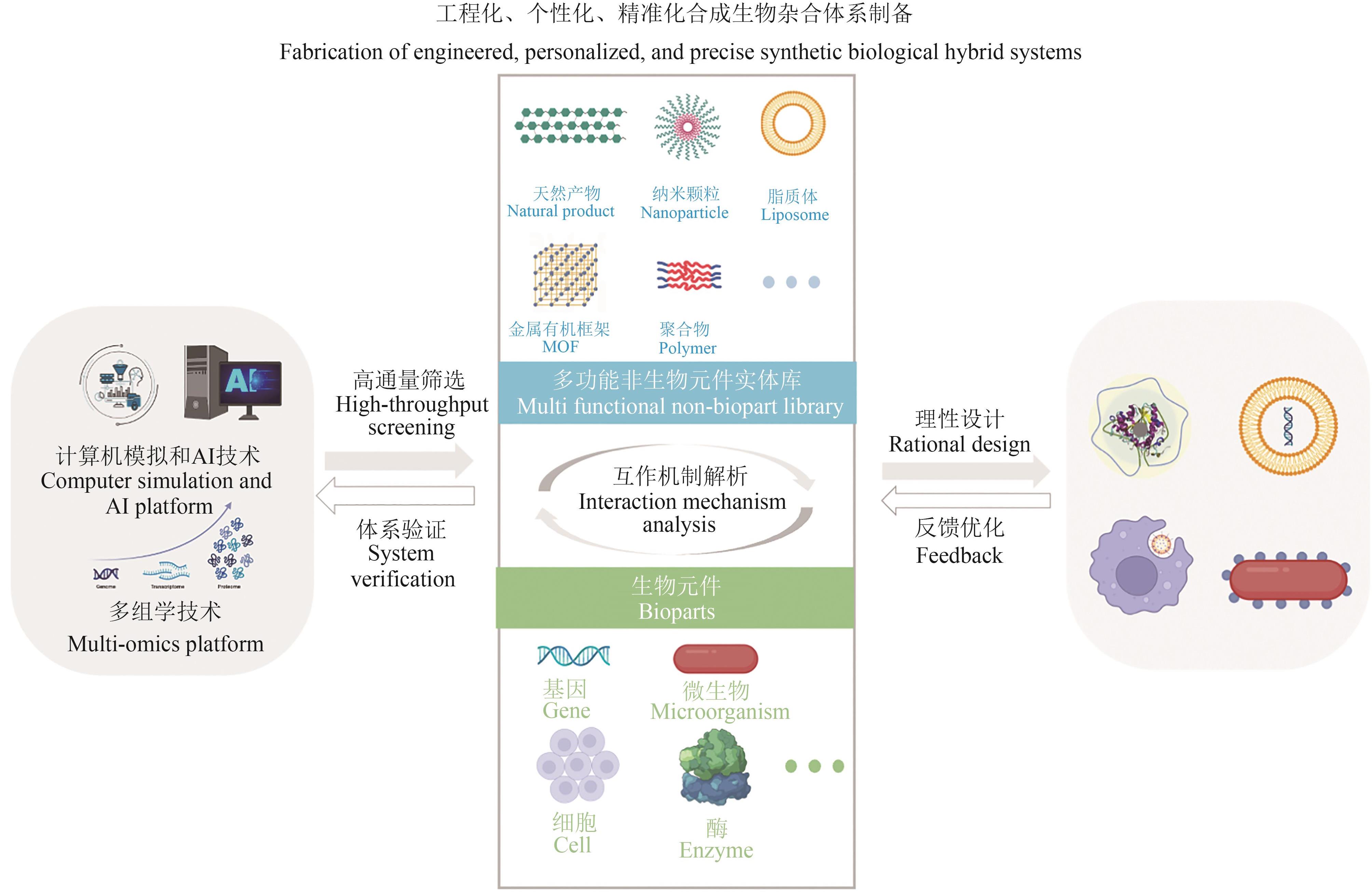
利用人工非生物元件对生命体进行设计与改造是合成生物学的一大机遇。开发非生物元件-生物元件合成生物杂合体系,可以突破天然生化反应的局限,实现生物元件与非生物元件的协同增效和功能超越,在生物制造和生物医药新应用领域前景广阔,已成为合成生物学研究中备受关注的前沿方向。然而,相比于类型繁多和功能丰富的非生物元件,现有杂合体系的功能还较为单一。针对这一问题,本文系统综述了近年来非生物元件-生物元件合成生物杂合体系的研究进展,依据体系类型进行分类总结,通过对典型研究的深入分析,在归纳其功能实现途径的基础上,进一步揭示了现有体系在功能扩展和机制解析方面的局限性,并展望了该领域在多平台联用、工程化设计和精准调控等方面的发展前景。
中图分类号:
引用本文
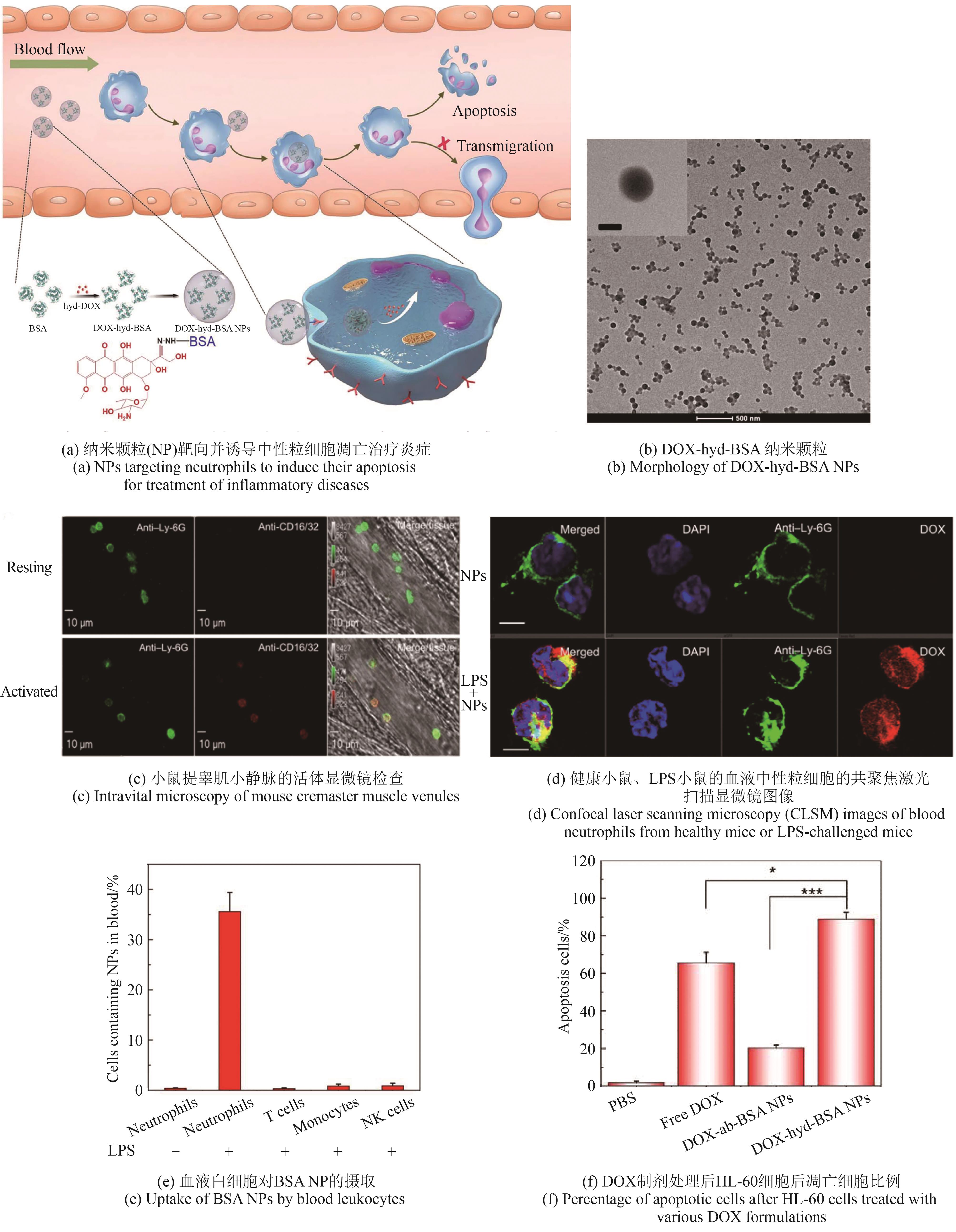
黄瑜晴, 吴涵, 李晓彬, 刘君禹, 马少华, 戈钧, 邢新会, 张灿阳. 非生物元件增强的合成生物杂合体系研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(4): 764-788.
HUANG Yuqing, WU Han, LI Xiaobin, LIU Junyu, MA Shaohua, GE Jun, XING Xinhui, ZHANG Canyang. Recent advancements in non-biological component-augmented synthetic bio-hybrid systems[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 764-788.
| [1] | BYRNE G, DIMITROV D, MONOSTORI L, et al. Biologicalisation: biological transformation in manufacturing[J]. CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology, 2018, 21: 1-32. |
| [2] | BERGS T, SCHWANEBERG U, BARTH S, et al. Application cases of biological transformation in manufacturing technology[J]. CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology, 2020, 31: 68-77. |
| [3] | VIJAYARAM S, RAZAFINDRALAMBO H, SUN Y Z, et al. Applications of green synthesized metal nanoparticles: a review[J]. Biological Trace Element Research, 2024, 202(1): 360-386. |
| [4] | 张晓龙, 王晨芸, 刘延峰, 等. 基于合成生物技术构建高效生物制造系统的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(6): 863-875. |
| ZHANG X L, WANG C Y, LIU Y F, et al. Research progress of constructing efficient biomanufacturing system based on synthetic biotechnology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(6): 863-875. | |
| [5] | LI X Y, CAO Y F, LUO K, et al. Highly active enzyme-metal nanohybrids synthesized in protein-polymer conjugates[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2019, 2(8): 718-725. |
| [6] | LU H F, OUYANG J P, LIU W Q, et al. Enzyme-polymer-conjugate-based pickering emulsions for cell-free expression and cascade biotransformation[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(52): e202312906. |
| [7] | WEBER E W, MAUS M V, MACKALL C L. The emerging landscape of immune cell therapies[J]. Cell, 2020, 181(1): 46-62. |
| [8] | UDDIN F, RUDIN C M, SEN T. CRISPR gene therapy: applications, limitations, and implications for the future[J]. Frontiers in Oncology, 2020, 10: 1387. |
| [9] | UDDIN M N, RONI M A. Challenges of storage and stability of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines[J]. Vaccines, 2021, 9(9): 1033. |
| [10] | YIN Y, TANG W, MA X Y, et al. Biomimetic neutrophil and macrophage dual membrane-coated nanoplatform with orchestrated tumor-microenvironment responsive capability promotes therapeutic efficacy against glioma[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 433: 133848. |
| [11] | XIE B B, ZHAO H C, DING Y F, et al. Supramolecularly engineered conjugate of bacteria and cell membrane-coated magnetic nanoparticles for enhanced ferroptosis and immunotherapy of tumors[J]. Advanced Science, 2023, 10(34): 2304407. |
| [12] | WANG G H, XIE L S, LI B, et al. A nanounit strategy reverses immune suppression of exosomal PD-L1 and is associated with enhanced ferroptosis[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 5733. |
| [13] | TANG T C, AN B L, HUANG Y Y, et al. Materials design by synthetic biology[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2021, 6(4): 332-350. |
| [14] | PATRA P, DAS M, KUNDU P, et al. Recent advances in systems and synthetic biology approaches for developing novel cell-factories in non-conventional yeasts[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2021, 47: 107695. |
| [15] | BARWINSKA-SENDRA A, GARCIA Y M, SENDRA K M, et al. An evolutionary path to altered cofactor specificity in a metalloenzyme[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 2738. |
| [16] | CAO Y F, LI X Y, GE J. Enzyme catalyst engineering toward the integration of biocatalysis and chemocatalysis[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2021, 39(11): 1173-1183. |
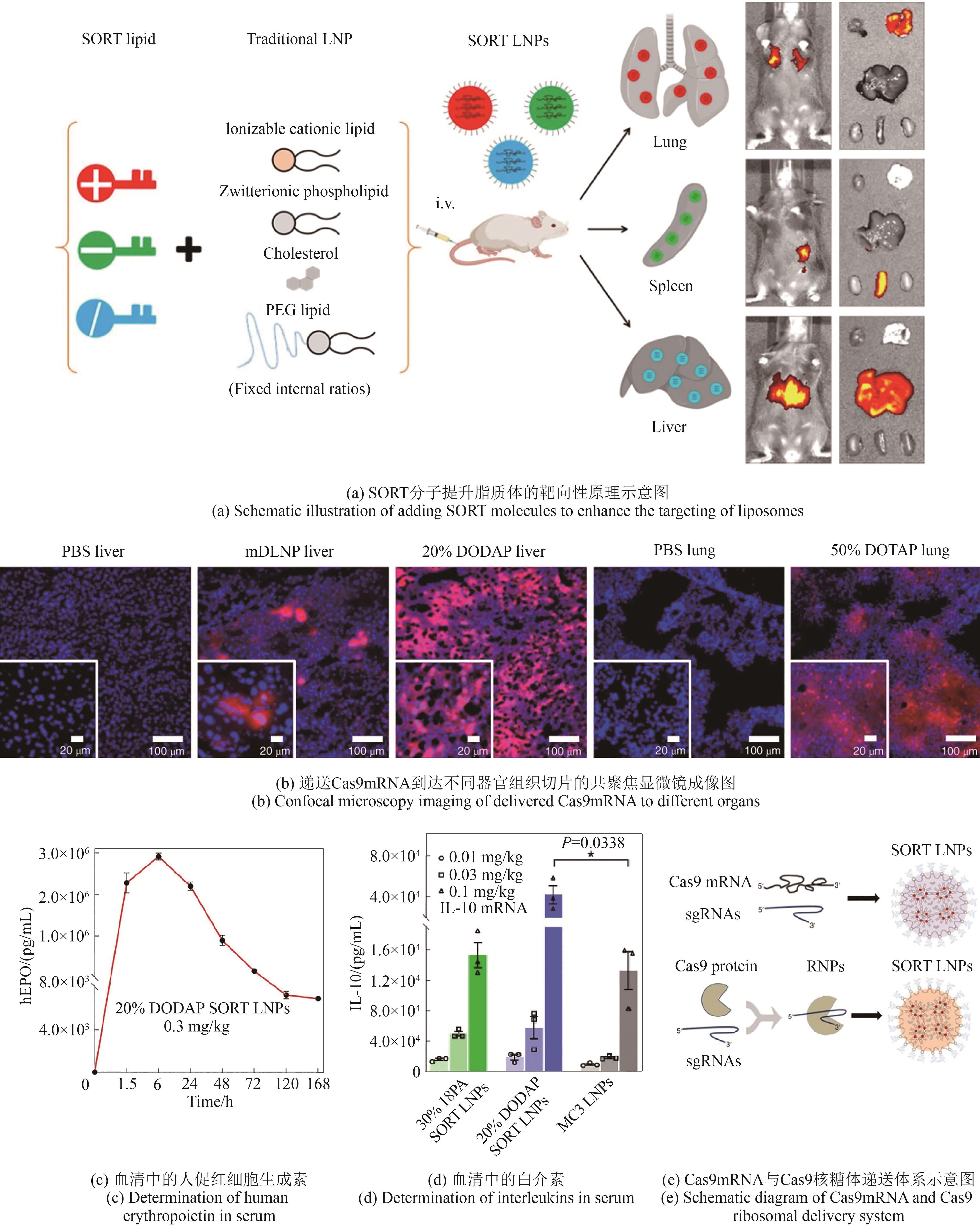
| [17] | LI X Y, FAN Y K, LIAO Q S, et al. Efficient enzyme-metal hybrid catalysts constructed with polymer[J]. ChemCatChem, 2023, 15(1): e202201319. |
| [18] | XIONG J R, CAI X Y, GE J. Enzyme-metal nanocomposites for antibacterial applications[J]. Particuology, 2022, 64: 134-139. |
| [19] | LI X Y, FU C C, LUO L Q, et al. Design of enzyme-metal hybrid catalysts for organic synthesis[J]. Cell Reports Physical Science, 2022, 3(3): 100742. |
| [20] | LIU W Q, ZHANG L K, CHEN M Z, et al. Cell-free protein synthesis: recent advances in bacterial extract sources and expanded applications[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 141: 182-189. |
| [21] | YANG J, SUN Y, SHI H, et al. Small ligand-involved pickering droplet interface controls reaction selectivity of metal catalysts[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2025, 147(7): 5984-5995. |
| [22] | QIAO J, SONG Y Y, CHEN C F, et al. In situ determination of sialic acid on cell surface with a pH-regulated polymer enzyme nanoreactor[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 93(19): 7317-7322. |
| [23] | HONG S Y, CHOI D W, KIM H N, et al. Protein-based nanoparticles as drug delivery systems[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2020, 12(7): 604. |
| [24] | ZHANG C Y, DONG X Y, GAO J, et al. Nanoparticle-induced neutrophil apoptosis increases survival in sepsis and alleviates neurological damage in stroke[J]. Science Advances, 2019, 5(11): eaax7964. |
| [25] | WENG Y L, CHEN R, HUI Y, et al. Boosting enzyme activity in enzyme metal-organic framework composites[J]. Chem & Bio Engineering, 2024, 1(2): 99-112. |
| [26] | VAIDYA L B, NADAR S S, RATHOD V K. Entrapment of surfactant modified lipase within zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF)-8[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2020, 146: 678-686. |
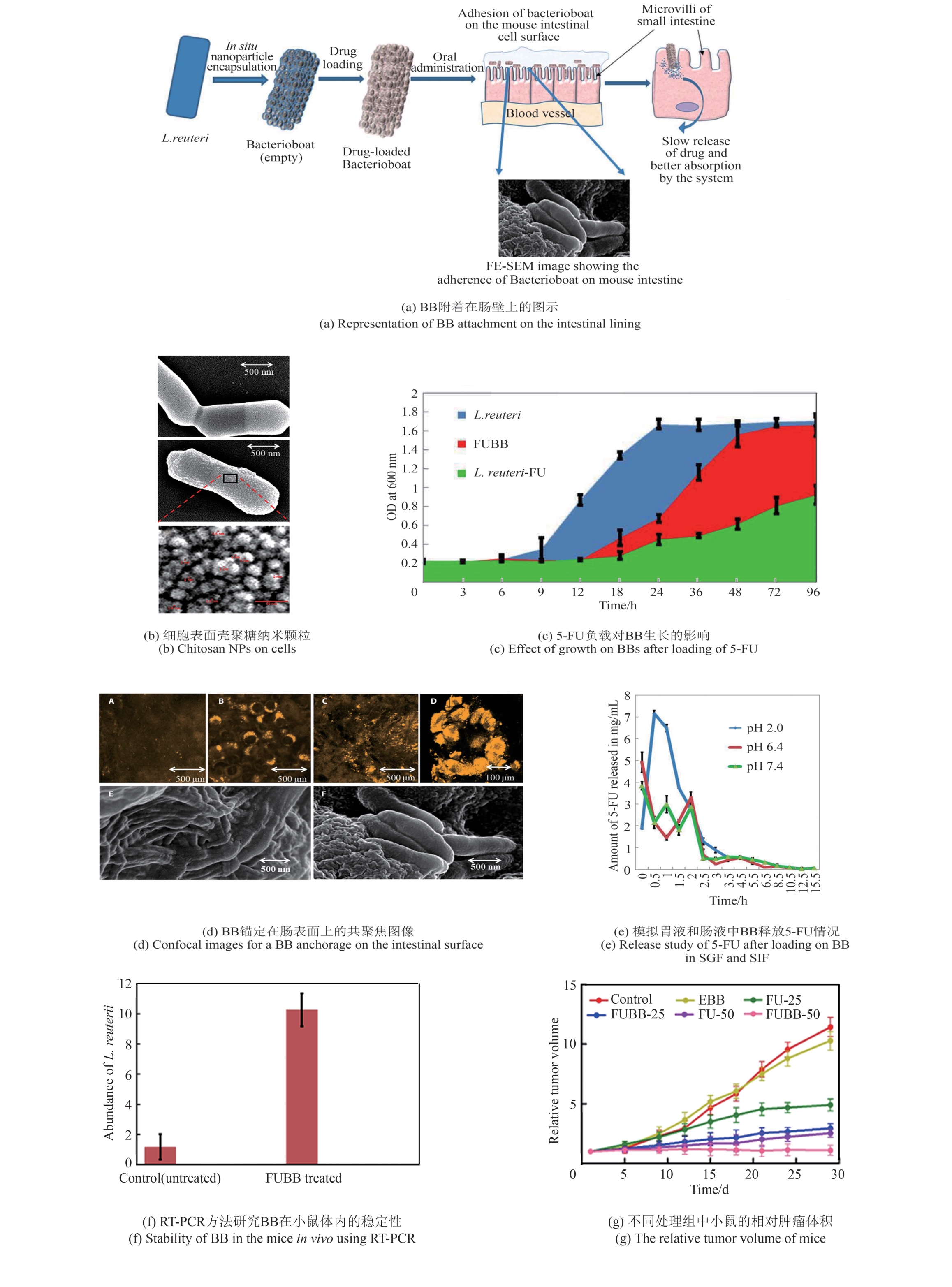
| [27] | NADAR S S, RATHOD V K. Immobilization of proline activated lipase within metal organic framework (MOF)[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2020, 152: 1108-1112. |
| [28] | BELL D J, WIESE M, SCHÖNBERGER A A, et al. Catalytically active hollow fiber membranes with enzyme-embedded metal-organic framework coating[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(37): 16047-16053. |
| [29] | XU Y Z, LIU S Y, LIU J L, et al. In situ enzyme immobilization with oxygen-sensitive luminescent metal-organic frameworks to realize “all-in-one” multifunctions[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2019, 25(21): 5463-5471. |
| [30] | WANG Y F, TIAN G F, HUANG J, et al. Mussel-inspired protein-based nanoparticles for curcumin encapsulation and promoting antitumor efficiency[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 273: 132965. |
| [31] | ORTEGA-NIETO C, LOSADA-GARCIA N, PESSELA B C, et al. Design and synthesis of copper nanobiomaterials with antimicrobial properties[J]. ACS Bio & Med Chem Au, 2023, 3(4): 349-358. |
| [32] | TONG P F, ASIF M, AJMAL M, et al. A multicomponent polymer-metal-enzyme system as electrochemical biosensor for H2O2 detection[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2022, 10: 874965. |
| [33] | DUAN L, OUYANG K, XU X, et al. Nanoparticle delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 for genome editing[J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 2021, 12: 673286. |
| [34] | EREL-AKBABA G, CARVALHO L A, TIAN T, et al. Radiation-induced targeted nanoparticle-based gene delivery for brain tumor therapy[J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(4): 4028-4040. |
| [35] | MADKHALI O, MEKHAIL G, WETTIG S D. Modified gelatin nanoparticles for gene delivery[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2019, 554: 224-234. |
| [36] | WU J Y, CHEN J, FENG Y J, et al. An immune cocktail therapy to realize multiple boosting of the cancer-immunity cycle by combination of drug/gene delivery nanoparticles[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(40): eabc7828. |
| [37] | YANG Q, ZHOU Y H, CHEN J, et al. Gene therapy for drug-resistant glioblastoma via lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles combined with focused ultrasound[J]. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 2021, 16: 185-199. |
| [38] | EYGERIS Y, GUPTA M, KIM J, et al. Chemistry of lipid nanoparticles for RNA delivery[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2022, 55(1): 2-12. |
| [39] | EYGERIS Y, PATEL S, JOZIC A, et al. Deconvoluting lipid nanoparticle structure for messenger RNA delivery[J]. Nano Letters, 2020, 20(6): 4543-4549. |
| [40] | FRANCIA V, SCHIFFELERS R M, CULLIS P R, et al. The biomolecular corona of lipid nanoparticles for gene therapy[J]. Bioconjugate Chemistry, 2020, 31(9): 2046-2059. |
| [41] | KROHN-GRIMBERGHE M, MITCHELL M J, SCHLOSS M J, et al. Nanoparticle-encapsulated siRNAs for gene silencing in the haematopoietic stem-cell niche[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2020, 4(11): 1076-1089. |
| [42] | MIRZA Z, KARIM S. Nanoparticles-based drug delivery and gene therapy for breast cancer: recent advancements and future challenges[J]. Seminars in Cancer Biology, 2021, 69: 226-237. |
| [43] | CHENG Q, WEI T, FARBIAK L, et al. Selective organ targeting (SORT) nanoparticles for tissue-specific mRNA delivery and CRISPR-Cas gene editing[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2020, 15(4): 313-320. |
| [44] | WANG Z C, WANG R R, GENG Z X, et al. Enzyme hybrid nanoflowers and enzyme@metal-organic frameworks composites: fascinating hybrid nanobiocatalysts[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2024, 44(4): 674-697. |
| [45] | ZHUANG J, GONG H, ZHOU J R, et al. Targeted gene silencing in vivo by platelet membrane-coated metal-organic framework nanoparticles[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(13): eaaz6108. |
| [46] | POSTLER T S, GHOSH S. Understanding the holobiont: how microbial metabolites affect human health and shape the immune system[J]. Cell Metabolism, 2017, 26(1): 110-130. |
| [47] | SUN J B, LI Y, LIANG X J, et al. Bacterial magnetosome: a novel biogenetic magnetic targeted drug carrier with potential multifunctions[J]. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2011, 2011(1): 469031. |
| [48] | CAO Z P, LIU J Y. Bacteria and bacterial derivatives as drug carriers for cancer therapy[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2020, 326: 396-407. |
| [49] | SHIVALKAR S, CHOWDHARY P, AFSHAN T, et al. Nanoengineering of biohybrid micro/nanobots for programmed biomedical applications[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2023, 222: 113054. |
| [50] | AKOLPOGLU M B, ALAPAN Y, DOGAN N O, et al. Magnetically steerable bacterial microrobots moving in 3D biological matrices for stimuli-responsive cargo delivery[J]. Science Advances, 2022, 8(28): eabo6163. |
| [51] | ALAPAN Y, YASA O, YIGIT B, et al. Microrobotics and microorganisms: biohybrid autonomous cellular robots[J]. Annual Review of Control, Robotics, and Autonomous Systems, 2019, 2: 205-230. |
| [52] | AKIN D, STURGIS J, RAGHEB K, et al. Bacteria-mediated delivery of nanoparticles and cargo into cells[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2007, 2(7): 441-449. |
| [53] | KAUR P, GHOSH S, BHOWMICK A, et al. Bacterioboat—a novel tool to increase the half-life period of the orally administered drug[J]. Science Advances, 2022, 8(10): eabh1419. |
| [54] | ZOU Z P, DU Y, FANG T T, et al. Biomarker-responsive engineered probiotic diagnoses, records, and ameliorates inflammatory bowel disease in mice[J]. Cell Host & Microbe, 2023, 31(2): 199-212.e5. |
| [55] | WANG X Y, CAO Z P, ZHANG M M, et al. Bioinspired oral delivery of gut microbiota by self-coating with biofilms[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(26): eabb1952. |
| [56] | CAO Z P, WANG X Y, PANG Y, et al. Biointerfacial self-assembly generates lipid membrane coated bacteria for enhanced oral delivery and treatment[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 5783. |
| [57] | LIN S S, MUKHERJEE S, LI J J, et al. Mucosal immunity-mediated modulation of the gut microbiome by oral delivery of probiotics into Peyer’s patches[J]. Science Advances, 2021, 7(20): eabf0677. |
| [58] | LIU J, WANG Y X, HEELAN W J, et al. Mucoadhesive probiotic backpacks with ROS nanoscavengers enhance the bacteriotherapy for inflammatory bowel diseases[J]. Science Advances, 2022, 8(45): eabp8798. |
| [59] | DE WOUTERS T, JANS C, NIEDERBERGER T, et al. Adhesion potential of intestinal microbes predicted by physico-chemical characterization methods[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(8): e0136437. |
| [60] | CHENG Z H, ZHENG Y Y, YANG W, et al. Pathogenic bacteria exploit transferrin receptor transcytosis to penetrate the blood-brain barrier[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2023, 120(39): e2307899120. |
| [61] | SUN R, LIU M Z, LU J P, et al. Bacteria loaded with glucose polymer and photosensitive ICG silicon-nanoparticles for glioblastoma photothermal immunotherapy[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 5127. |
| [62] | KARMAKAR R. State of the art of bacterial chemotaxis[J]. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 2021, 61(5): 366-379. |
| [63] | LI J H, DEKANOVSKY L, KHEZRI B, et al. Biohybrid micro- and nanorobots for intelligent drug delivery[J]. Cyborg and Bionic Systems, 2022, 2022: 9824057. |
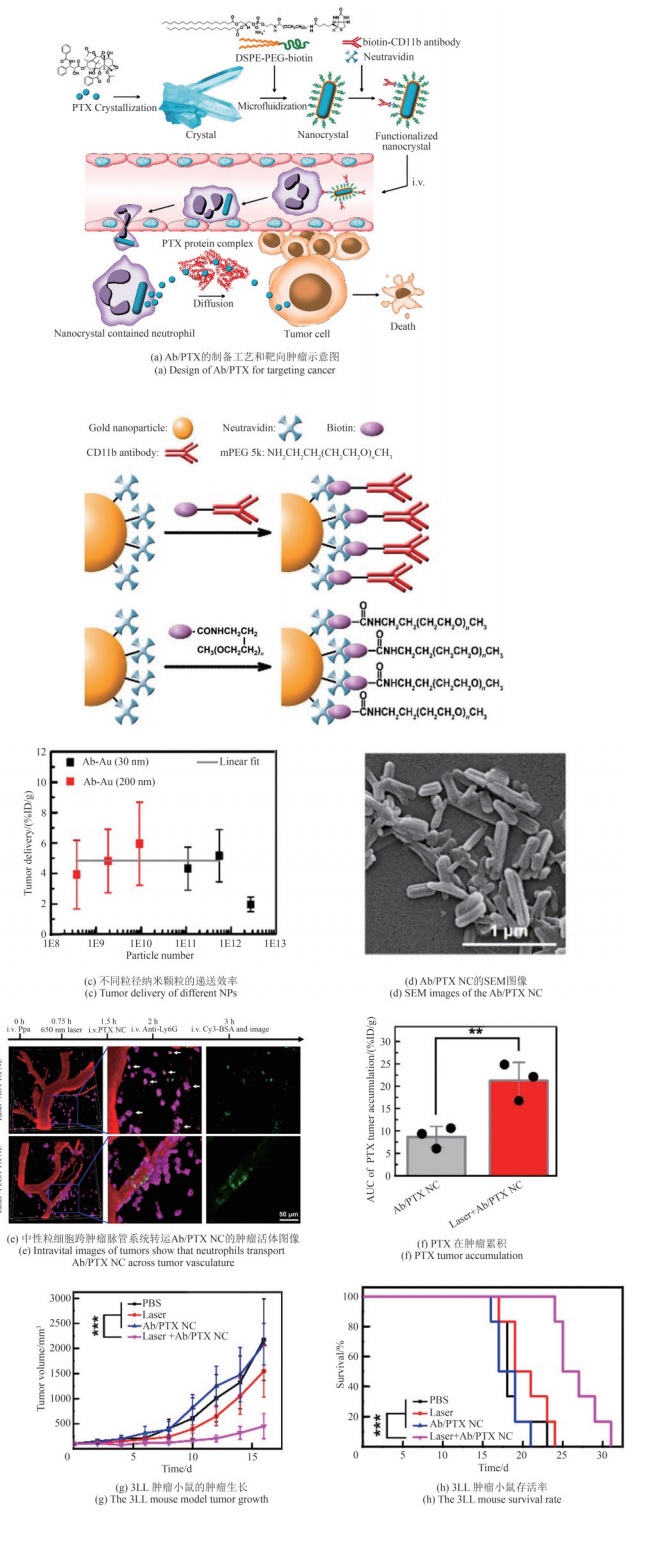
| [64] | LI M, LI S Y, ZHOU H, et al. Chemotaxis-driven delivery of nano-pathogenoids for complete eradication of tumors post-phototherapy[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 1126. |
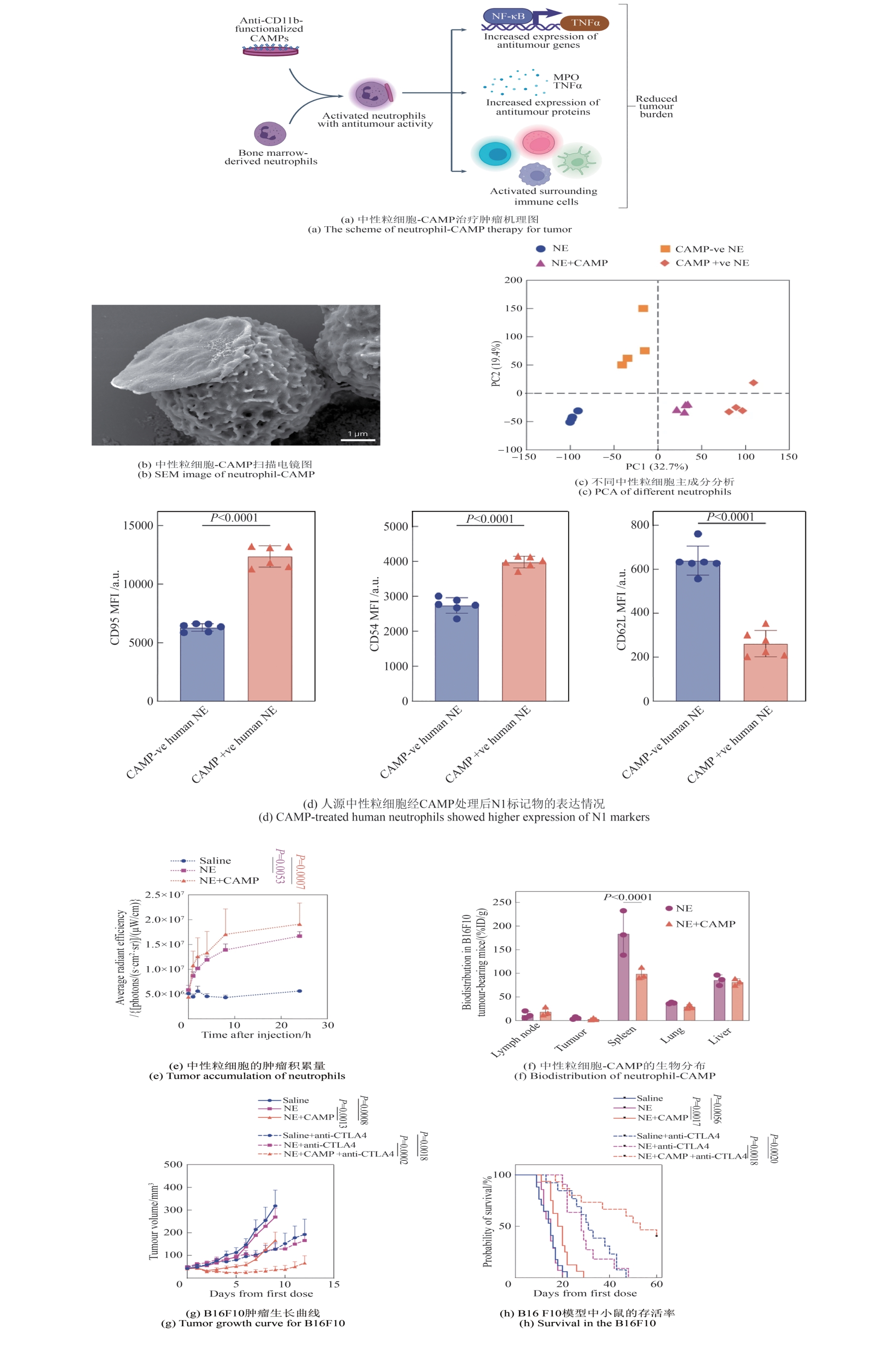
| [65] | LV X Y, WANG L C, MEI A Q, et al. Recent nanotechnologies to overcome the bacterial biofilm matrix barriers[J]. Small, 2023, 19(6): 2206220. |
| [66] | HAHN J S, DING S W, IM J W, et al. Bacterial therapies at the interface of synthetic biology and nanomedicine[J]. Nature Reviews Bioengineering, 2024, 2(2): 120-135. |
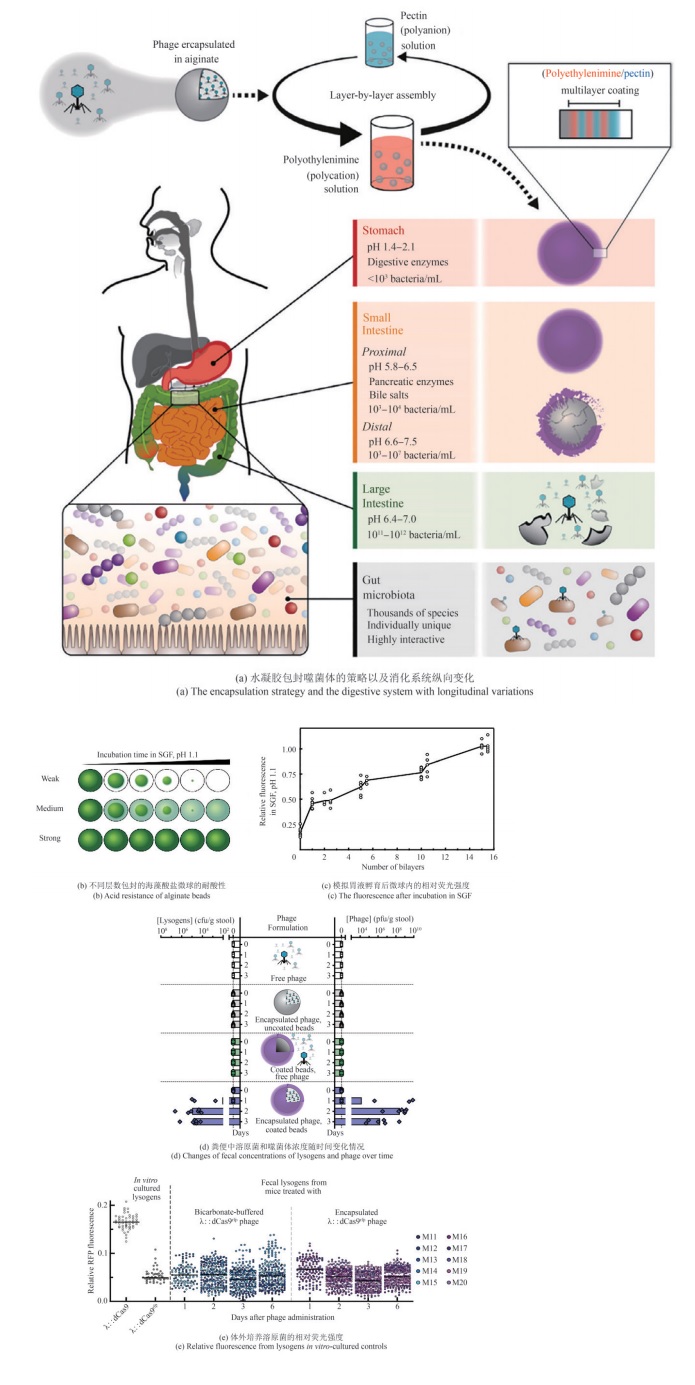
| [67] | WU D J, ZHAO Z J, LIU H, et al. Escherichia coli Nissle 1917-driven microrobots for effective tumor targeted drug delivery and tumor regression[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2023, 169: 477-488. |
| [68] | CHEN H T, LI Y Z, WANG Y J, et al. An engineered bacteria-hybrid microrobot with the magnetothermal bioswitch for remotely collective perception and imaging-guided cancer treatment[J]. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(4): 6118-6133. |
| [69] | TAN S W, WU T T, ZHANG D, et al. Cell or cell membrane-based drug delivery systems[J]. Theranostics, 2015, 5(8): 863-881. |
| [70] | XIA Z X, MU W W, YUAN S J, et al. Cell membrane biomimetic nano-delivery systems for cancer therapy[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2023, 15(12): 2770. |
| [71] | OROOJALIAN F, BEYGI M, BARADARAN B, et al. Immune cell membrane-coated biomimetic nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy[J]. Small, 2021, 17(12): 2006484. |
| [72] | HUANG L L, NIE W D, ZHANG J F, et al. Cell-membrane-based biomimetic systems with bioorthogonal functionalities[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2020, 53(1): 276-287. |
| [73] | CHEN H Y, DENG J, WANG Y, et al. Hybrid cell membrane-coated nanoparticles: a multifunctional biomimetic platform for cancer diagnosis and therapy[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2020, 112: 1-13. |
| [74] | ZHU L, ZHONG Y, WU S, et al. Cell membrane camouflaged biomimetic nanoparticles: focusing on tumor theranostics[J]. Materials Today Bio, 2022, 14: 100228. |
| [75] | NGUYEN P H D, JAYASINGHE M K, LE A H, et al. Advances in drug delivery systems based on red blood cells and their membrane-derived nanoparticles[J]. ACS Nano, 2023, 17(6): 5187-5210. |
| [76] | LIU B, WANG W M, FAN J L, et al. RBC membrane camouflaged Prussian blue nanoparticles for gamabutolin loading and combined chemo/photothermal therapy of breast cancer[J]. Biomaterials, 2019, 217: 119301. |
| [77] | XIE W, DENG W W, ZAN M H, et al. Cancer cell membrane camouflaged nanoparticles to realize starvation therapy together with checkpoint blockades for enhancing cancer therapy[J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(3): 2849-2857. |
| [78] | WU Y H, ZHU R T, ZHOU M Y, et al. Homologous cancer cell membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles target drug delivery and enhance the chemotherapy efficacy of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Letters, 2023, 558: 216106. |
| [79] | REN X L, YANG S P, YU N, et al. Cell membrane camouflaged bismuth nanoparticles for targeted photothermal therapy of homotypic tumors[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 591: 229-238. |
| [80] | HU Q, JIA L L, ZHANG X L, et al. Accurate construction of cell membrane biomimetic graphene nanodecoys via purposeful surface engineering to improve screening efficiency of active components of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2022, 12(1): 394-405. |
| [81] | NIE D, DAI Z, LI J L, et al. Cancer-cell-membrane-coated nanoparticles with a yolk-shell structure augment cancer chemotherapy[J]. Nano Letters, 2020, 20(2): 936-946. |
| [82] | WANG C X, WU B, WU Y T, et al. Camouflaging nanoparticles with brain metastatic tumor cell membranes: a new strategy to traverse blood-brain barrier for imaging and therapy of brain tumors[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(14): 1909369. |
| [83] | VIJAYAN V, UTHAMAN S, PARK I K. Cell membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles: a promising biomimetic strategy for cancer theragnostics[J]. Polymers, 2018, 10(9): 983. |
| [84] | CAO Z C, LIU X, ZHANG W Q, et al. Biomimetic macrophage membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles induce ferroptosis by promoting mitochondrial damage in glioblastoma[J]. ACS Nano, 2023, 17(23): 23746-23760. |
| [85] | JIANG Q, LIU Y, GUO R R, et al. Erythrocyte-cancer hybrid membrane-camouflaged melanin nanoparticles for enhancing photothermal therapy efficacy in tumors[J]. Biomaterials, 2019, 192: 292-308. |
| [86] | GONG P, WANG Y F, ZHANG P F, et al. Immunocyte membrane-coated nanoparticles for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Cancers, 2020, 13(1): 77. |
| [87] | ZHAO Y, ZHANG H G, ZHANG Q X, et al. Research progress of neutrophil-mediated drug delivery strategies for inflammation-related disease[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2023, 15(7): 1881. |
| [88] | CHU D F, DONG X Y, SHI X T, et al. Neutrophil-based drug delivery systems[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(22): 1706245. |
| [89] | CHU D F, DONG X Y, ZHAO Q, et al. Photosensitization priming of tumor microenvironments improves delivery of nanotherapeutics via neutrophil infiltration[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(27): 1701021. |
| [90] | SU Y J, GAO J, DONG X Y, et al. Neutrophil-mediated delivery of nanocrystal drugs via photoinduced inflammation enhances cancer therapy[J]. ACS Nano, 2023, 17(16): 15542-15555. |
| [91] | KUMBHOJKAR N, PRAKASH S, FUKUTA T, et al. Neutrophils bearing adhesive polymer micropatches as a drug-free cancer immunotherapy[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2024, 8(5): 579-592. |
| [92] | VENTURINI C, PETROVIC FABIJAN A, FAJARDO LUBIAN A, et al. Biological foundations of successful bacteriophage therapy[J]. EMBO Molecular Medicine, 2022, 14(7): e12435. |
| [93] | LOH B, GONDIL V S, MANOHAR P, et al. Encapsulation and delivery of therapeutic phages[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2021, 87(5): e01979-20. |
| [94] | SAMANANDA SINGH L. Nano-emulsion encapsulation for the efficient delivery of bacteriophage therapeutics[J]. Biologicals, 2024, 85: 101725. |
| [95] | OTERO J, GARCÍA-RODRÍGUEZ A, CANO-SARABIA M, et al. Biodistribution of liposome-encapsulated bacteriophages and their transcytosis during oral phage therapy[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10: 689. |
| [96] | ŚLIWKA P, SKARADZIŃSKI G, DUSZA I, et al. Freeze-drying of encapsulated bacteriophage T4 to obtain shelf-stable dry preparations for oral application[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2023, 15(12): 2792. |
| [97] | HSU B B, PLANT I N, LYON L, et al. In situ reprogramming of gut bacteria by oral delivery[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 5030. |
| [98] | KARIMI M, MIRSHEKARI H, MOOSAVI BASRI S M, et al. Bacteriophages and phage-inspired nanocarriers for targeted delivery of therapeutic cargos[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2016, 106: 45-62. |
| [99] | ATHANASOPOULOU K, DANEVA G N, ADAMOPOULOS P G, et al. Artificial intelligence: the milestone in modern biomedical research[J]. BioMedInformatics, 2022, 2(4): 727-744. |
| [100] | VASINA M, VELECKÝ J, PLANAS-IGLESIAS J, et al. Tools for computational design and high-throughput screening of therapeutic enzymes[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2022, 183: 114143. |
| [101] | MILLER K, JOLDES G R, BOURANTAS G, et al. Biomechanical modeling and computer simulation of the brain during neurosurgery[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Biomedical Engineering, 2019, 35(10): e3250. |
| [102] | FIGUEIRAS A, DOMINGUES C, JARAK I, et al. New advances in biomedical application of polymeric micelles[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2022, 14(8): 1700. |
| [103] | ROGACKA J, LABUS K. Metal-organic frameworks as highly effective platforms for enzyme immobilization-current developments and future perspectives[J/OL]. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2024[2025-07-01]. . |
| [104] | GUO F, XU Z H, ZHANG W D, et al. Facile synthesis of catalase@ZIF-8 composite by biomimetic mineralization for efficient biocatalysis[J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2021, 44(6): 1309-1319. |
| [105] | WÖRHEIDE M A, KRUMSIEK J, KASTENMÜLLER G, et al. Multi-omics integration in biomedical research - a metabolomics-centric review[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2021, 1141: 144-162. |
| [106] | REEL P S, REEL S, PEARSON E, et al. Using machine learning approaches for multi-omics data analysis: a review[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2021, 49: 107739. |
| [107] | VANELLA R, KOVACEVIC G, DOFFINI V, et al. High-throughput screening, next generation sequencing and machine learning: advanced methods in enzyme engineering[J]. Chemical Communications, 2022, 58(15): 2455-2467. |
| [108] | KANEHISA M, FURUMICHI M, SATO Y, et al. KEGG: biological systems database as a model of the real world[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2025, 53(D1): D672-D677. |
| [109] | KORTEMME T. De novo protein design—from new structures to programmable functions[J]. Cell, 2024, 187(3): 526-544. |
| [110] | HRISTOZOV D, GOTTARDO S, SEMENZIN E, et al. Frameworks and tools for risk assessment of manufactured nanomaterials[J]. Environment International, 2016, 95: 36-53. |
| [111] | NASIR R. Developing CRISPR-based therapies for genetic diseases: Clinical trials and regulatory challenges [J]. Indus Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 2025, 4(1): 13-26. |
| [1] | 钟奶才, 陈缘, 潘文锋, 苏小凤, 廖景文, 翟英雷, 钟近艺. 等离子体微生物育种技术在生物制造中的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(4): 789-805. |
| [2] | 张以恒, 陈雪梅, 韩平平. 生物制造的PE值与PX值:定义与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(4): 715-727. |
| [3] | 吴晓燕, 宋琪, 许睿, 丁陈君, 陈方, 郭勍, 张波. 合成生物学研发竞争态势对比分析[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(4): 940-955. |
| [4] | 马牧青, 吴彦, 曲茂华, 卢夏锋, 曹敏, 杜峰, 季荣涛, 董磊迟, 罗志波. 体外多酶组装与生物级联催化:进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(4): 920-939. |
| [5] | 黄怡, 司同, 陆安静. 生物制造标准体系建设的现状、问题与建议[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(3): 701-714. |
| [6] | 应汉杰, 柳东, 王振宇, 沈涛, 庄伟, 朱晨杰. 工业生物制造与“碳中和”目标探讨[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 1-7. |
| [7] | 张以恒, 陈雪梅, 石婷. 生物制造的市本率(PC值):定义与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 8-17. |
| [8] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [9] | 张以恒. 中国哲学思想“道法术器”对生物制造的启示[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1231-1241. |
| [10] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [11] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [12] | 赵亮, 李振帅, 付丽平, 吕明, 王士安, 张全, 刘立成, 李福利, 刘自勇. 生物转化一碳化合物原料产油脂与单细胞蛋白研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1300-1318. |
| [13] | 刘建明, 张炽坚, 张冰, 曾安平. 巴氏梭菌作为工业底盘细胞高效生产1,3-丙二醇——从代谢工程和菌种进化到过程工程和产品分离[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1386-1403. |
| [14] | 程峰, 邹树平, 徐建妙, 汤恒, 薛亚平, 郑裕国. 生物高纯精草:高光学纯L-草铵膦生物制造的创新与发展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1404-1418. |
| [15] | 张晨悦, 马英群, 王兴, 傅容湛, 黄技伟, 花秀夫, 范代娣, 费强. 全碳素生物转化沼气制备生物航煤制造路线研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(6): 1246-1258. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||