• 特约评述 •
人乳寡糖的体外生物转化合成研究进展
李毅, 李因双, 李爽, 凌沛学, 房俊强
- 山东大学,国家糖工程技术研究中心,山东 青岛 266237
-
收稿日期:2025-05-29修回日期:2025-07-29出版日期:2025-07-30 -
通讯作者:房俊强 -
作者简介:李毅 (1996—),男,实验师。研究方向为分支人乳寡糖的多酶级联合成。E-mail:liyi1@sdu.edu.cn房俊强 (1979—),男,博士,教授,博士生导师,研究方向为糖核苷酸规模化制备和复杂寡糖的化学酶法合成及其应用。E-mail:fangjunqiang@sdu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发项目(2021YFC2103100);山东省重点研发计划(2022SFGC0103)
Recent Progress on the in vitro Bio-transformation Synthesis of Human Milk Oligosaccharides
LI Yi, LI Yinshuang, LI Shuang, LING Peixue, FANG Junqiang
- National Glycoengineering Research Center,Shandong University,Qingdao 266237,Shandong,China
-
Received:2025-05-29Revised:2025-07-29Online:2025-07-30 -
Contact:FANG Junqiang
摘要:
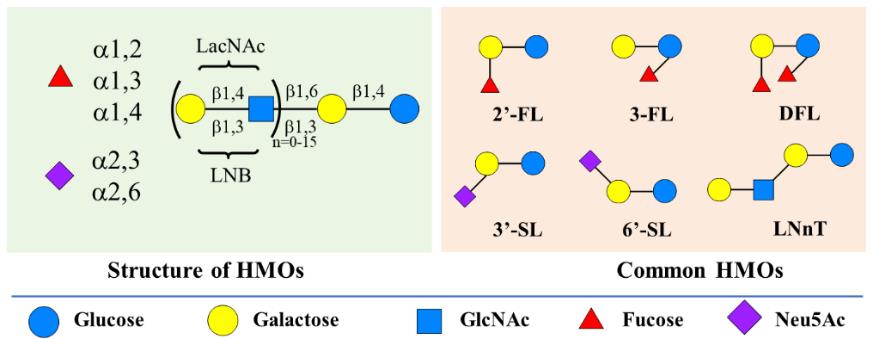
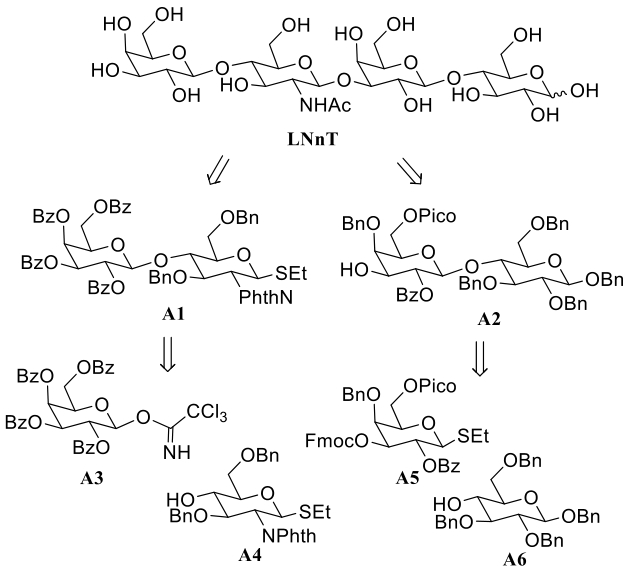
人乳寡糖是存在于人乳中的天然活性寡糖,对新生儿健康至关重要。人乳寡糖具有多种健康益处,如益生元活性、抗炎和抗菌特性、抗病毒以及促进新生儿认知发展作用等,已经成为婴儿配方奶粉、临床婴儿营养品、膳食补充剂或功能食品的重要组分。随着越来越多人乳寡糖获批应用于婴儿配方奶粉,其在商业领域的价值愈发凸显,人乳寡糖规模化制备技术也成为研究热点。鉴于人乳寡糖广阔的应用前景与市场需求,以及体外生物转化(ivBT)在大宗糖类产品生产中展现的高效、绿色、可规模化放大等显著优势,本文综述了人乳寡糖的结构组成、功能特性和合成方法,尤其是体外生物转化在人乳寡糖规模制备领域的研究进展,为相关基础研究与产业转化提供理论依据与技术参考。未来ivBT将向原料绿色化、酶元件改造智能化、过程连续化纵深发展,进一步降低人乳寡糖高效规模化生产的综合成本,为产业化注入新动能。
中图分类号:
引用本文
李毅, 李因双, 李爽, 凌沛学, 房俊强. 人乳寡糖的体外生物转化合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-052.
LI Yi, LI Yinshuang, LI Shuang, LING Peixue, FANG Junqiang. Recent Progress on the in vitro Bio-transformation Synthesis of Human Milk Oligosaccharides[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-052.
| 合成方法 | 产物 | 技术路线的特点 | 产量/产率 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 酶法合成 | 3′-SL | 酶工程改造Trypanosoma rangeli sialidase,以CGMP为糖基供体,以乳糖为受体合成3’-SL | 31% | [ |
| 6′-SL | Bacteroides fragilis sialidase以多聚N-乙酰基神经氨酸为糖基供体,以乳糖为受体合成6’-SL | 22% | [ | |
| 2-FL | Fusarium graminearum fucosidase以木葡聚糖为糖基供体,以乳糖为受体合成2-FL | 14% | [ | |
| 3-FL | 重组表达岩藻糖基转移酶α1,3-HpFucT,以GDP-Fucose为糖基供体,以乳糖为糖基受体催化合成3-FL | 96% | [ | |
| LNFP I | 重组表达岩藻糖基转移酶α1,2-Te2FT,以一锅多酶合成的GDP-Fucose为糖基供体,以LNT为糖基受体催化合成LNFP I | 95% | [ | |
| 全细胞生物催化 | LNnT | E. coli K12 MG1655为工程菌,敲除lacZ、wcaJ、ugd;过表达galE、CpsIaJ、lgtA | 20.33 g/L | [ |
| 3′-SL | E. coli BL21(DE3)为工程菌,敲除lacZ、nanA、nanK;过表达neuC、neuB、neuA、α2,3-SiaT | 31.4 g/L | [ | |
| 6′-SL | E. coli DH1为工程菌,敲除lacZ、lacA、nanK、nanE、nanT、nanA;过表达neuB、neuC、neuA、ST6 | 30 g/L | [ | |
| 2′-FL | E. coli C41(DE3)为工程菌,敲除lacZ、wcaJ、nudD;过表达manB、manC、gmd、wcaG、wbgL、rcsA、rcsB | 79.23 g/L | [ | |
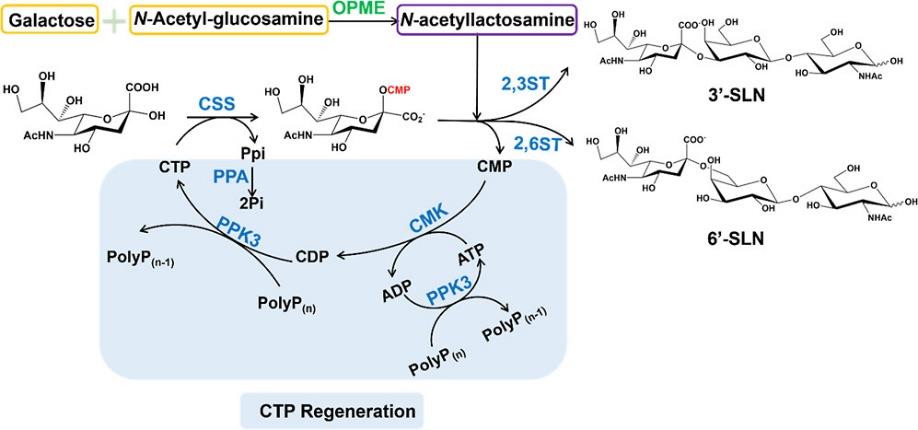
| ivBT | LacNAc | 构建多磷酸激酶(PPK)/多磷酸盐(polyPn)的NTP再生催化系统 | >90% | [ |
| LNT Ⅱ | 筛选新型酶元件HaHex74并进行酶元件定向进化和改造 | 15.0 g/L | [ | |
| LNT | 筛选新型β-半乳糖苷酶LzBgal35A并在E. coli中实现可溶性表达 | 6.4 g/L | [ | |
| LNnT | 多酶级联催化反应体系 | 93% | [ | |
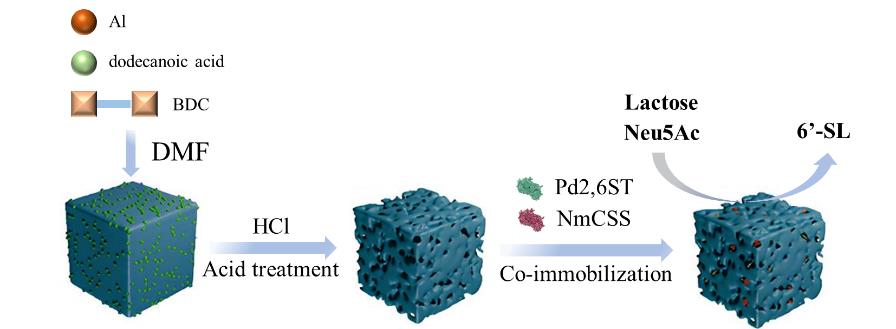
| 6′-SL | 多层级多孔材料用于共固定化CMP-唾液酸合成酶和α-2,6-唾液酸转移酶 | >80% | [ | |
| DSLNnT | 多酶级联催化反应体系 | 96% | [ | |
| 2′-FL | 体外多酶级联催化实现ATP和GTP的循环利用;筛选高效的α-1,2-岩藻糖基转移酶TeFucT | 27.07 g/L | [ | |
| LNFP I | 新型酶元件的筛选 | 91% | [ |
表1 HMOs主要合成方法对比
Table 1 Comparison of Major Synthesis Methods for HMOs
| 合成方法 | 产物 | 技术路线的特点 | 产量/产率 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 酶法合成 | 3′-SL | 酶工程改造Trypanosoma rangeli sialidase,以CGMP为糖基供体,以乳糖为受体合成3’-SL | 31% | [ |
| 6′-SL | Bacteroides fragilis sialidase以多聚N-乙酰基神经氨酸为糖基供体,以乳糖为受体合成6’-SL | 22% | [ | |
| 2-FL | Fusarium graminearum fucosidase以木葡聚糖为糖基供体,以乳糖为受体合成2-FL | 14% | [ | |
| 3-FL | 重组表达岩藻糖基转移酶α1,3-HpFucT,以GDP-Fucose为糖基供体,以乳糖为糖基受体催化合成3-FL | 96% | [ | |
| LNFP I | 重组表达岩藻糖基转移酶α1,2-Te2FT,以一锅多酶合成的GDP-Fucose为糖基供体,以LNT为糖基受体催化合成LNFP I | 95% | [ | |
| 全细胞生物催化 | LNnT | E. coli K12 MG1655为工程菌,敲除lacZ、wcaJ、ugd;过表达galE、CpsIaJ、lgtA | 20.33 g/L | [ |
| 3′-SL | E. coli BL21(DE3)为工程菌,敲除lacZ、nanA、nanK;过表达neuC、neuB、neuA、α2,3-SiaT | 31.4 g/L | [ | |
| 6′-SL | E. coli DH1为工程菌,敲除lacZ、lacA、nanK、nanE、nanT、nanA;过表达neuB、neuC、neuA、ST6 | 30 g/L | [ | |
| 2′-FL | E. coli C41(DE3)为工程菌,敲除lacZ、wcaJ、nudD;过表达manB、manC、gmd、wcaG、wbgL、rcsA、rcsB | 79.23 g/L | [ | |
| ivBT | LacNAc | 构建多磷酸激酶(PPK)/多磷酸盐(polyPn)的NTP再生催化系统 | >90% | [ |
| LNT Ⅱ | 筛选新型酶元件HaHex74并进行酶元件定向进化和改造 | 15.0 g/L | [ | |
| LNT | 筛选新型β-半乳糖苷酶LzBgal35A并在E. coli中实现可溶性表达 | 6.4 g/L | [ | |
| LNnT | 多酶级联催化反应体系 | 93% | [ | |
| 6′-SL | 多层级多孔材料用于共固定化CMP-唾液酸合成酶和α-2,6-唾液酸转移酶 | >80% | [ | |
| DSLNnT | 多酶级联催化反应体系 | 96% | [ | |
| 2′-FL | 体外多酶级联催化实现ATP和GTP的循环利用;筛选高效的α-1,2-岩藻糖基转移酶TeFucT | 27.07 g/L | [ | |
| LNFP I | 新型酶元件的筛选 | 91% | [ |
| [1] | AUTRAN C A, KELLMAN B P, KIM J H, et al. Human milk oligosaccharide composition predicts risk of necrotising enterocolitis in preterm infants [J]. Gut, 2018, 67: 1064-70. |
| [2] | DINLEYICI M, BARBIEUR J, DINLEYICI E C, et al. Functional effects of human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) [J]. Gut Microbes, 2023, 15(1): 2186115. |
| [3] | ESTORNINOS E, LAWENKO R B, PALESTROQUE E, et al. Term infant formula supplemented with milk-derived oligosaccharides shifts the gut microbiota closer to that of human milk-fed infants and improves intestinal immune defense: a randomized controlled trial [J]. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 2022, 115(1): 142-53. |
| [4] | AKKERMAN R, FAAS M M, DE VOS P. Non-digestible carbohydrates in infant formula as substitution for human milk oligosaccharide functions: Effects on microbiota and gut maturation [J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2019, 59(9): 1486-97. |
| [5] | WALKER A. Breast Milk as the Gold Standard for Protective Nutrients [J]. The Journal of Pediatrics, 2010, 156(2, ): S3-S7. |
| [6] | ZHU Y Y, CAO H Z, WANG H, et al. Biosynthesis of human milk oligosaccharides via metabolic engineering approaches: current advances and challenges [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2022, 78: 102841. |
| [7] | ZHANG Y H, ZHU Z G, YOU C, et al. In Vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): Definitions, Opportunities, and Challenges [J]. Synthetic Biology and Engineering, 2023, 1(2): 10013. |
| [8] | CHEN X. Human Milk Oligosaccharides (HMOS): Structure, Function, and Enzyme-Catalyzed Synthesis [J]. Advances in Carbohydrate Chemistry and Biochemistry, 2015, 72: 113-90. |
| [9] | JIN W J, LU Y, LI C, et al. Improved Glycoqueuing Strategy Reveals Novel alpha2,3-Linked Di-/Tri-Sialylated Oligosaccharide Isomers in Human Milk [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2022, 70(43): 13996-4004. |
| [10] | WU S, TAO N, GERMAN J B, et al. Development of an Annotated Library of Neutral Human Milk Oligosaccharides [J]. Journal of Proteome Research, 2010, 9(8): 4138-51. |
| [11] | BODE L. Human Milk Oligosaccharides: Structure and Functions [J]. Nestle Nutrition Institute Workshop Series, 2020, 94: 115-23. |
| [12] | NATHAN N N, PHILPOTT D J, GIRARDIN S E. The intestinal microbiota: from health to disease, and back [J]. Microbes Infect, 2021, 23(6-7): 104849. |
| [13] | GOEHRING K C, KENNEDY A D, PRIETO P A, et al. Direct evidence for the presence of human milk oligosaccharides in the circulation of breastfed infants [J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(7): e101692. |
| [14] | DOTZ V, RUDLOFF S, MEYER C, et al. Metabolic fate of neutral human milk oligosaccharides in exclusively breast-fed infants [J]. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 2015, 59(2): 355-64. |
| [15] | LIU Z M, SUBBARAJ A, FRASER K, et al. Human milk and infant formula differentially alters the microbiota composition and functional gene relative abundance in the small and large intestines in weanling rats [J]. European Journal of Nutrition, 2020, 59(5): 2131-43. |
| [16] | UNDERWOOD M A, GAERLAN S, DE LEOZ M L, et al. Human milk oligosaccharides in premature infants: absorption, excretion, and influence on the intestinal microbiota [J]. Pediatric research, 2015, 78(6): 670-7. |
| [17] | KITAOKA M. Bifidobacterial enzymes involved in the metabolism of human milk oligosaccharides [J]. Advances in Nutrition, 2012, 3(3): 422S-9S. |
| [18] | SINGH R P, NIHARIKA J, KONDEPUDI K K, et al. Recent understanding of human milk oligosaccharides in establishing infant gut microbiome and roles in immune system [J]. Food Research International, 2022, 151: 110884. |
| [19] | XIAO L, VAN DE WORP W R, STASSEN R, et al. Human milk oligosaccharides promote immune tolerance via direct interactions with human dendritic cells [J]. European Journal of Immunology 2019, 49(7): 1001-14. |
| [20] | KURAKEVICH E, HENNET T, HAUSMANN M, et al. Milk oligosaccharide sialyl(α2,3)lactose activates intestinal CD11c+ cells through TLR4 [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2013, 110(43): 17444-9. |
| [21] | VERMA R, LEE C, JEUN E J, et al. Cell surface polysaccharides of Bifidobacterium bifidum induce the generation of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells [J]. Science Immunology, 2018, 3(28): eaat6975. |
| [22] | GUO S S, GILLINGHAM T, GUO Y M, et al. Secretions of Bifidobacterium infantis and Lactobacillus acidophilus Protect Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function [J]. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, 2017, 64(3): 404-12. |
| [23] | CHUTIPONGTANATE S, MORROW A L, NEWBURG D S. Human Milk Oligosaccharides: Potential Applications in COVID-19 [J]. Biomedicines, 2022, 10(2): 346. |
| [24] | COSTERTON J W, IRVIN R T, CHENG K J. The Bacterial Glycocalyx in Nature and Disease [J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 1981, 35: 299-324. |
| [25] | RUIZ-PALACIOS G M, CERVANTES L E, RAMOS P, et al. Campylobacter jejuni binds intestinal H(O) antigen (Fuc alpha 1, 2Gal beta 1, 4GlcNAc), and fucosyloligosaccharides of human milk inhibit its binding and infection [J]. The Journal of biological chemistry, 2003, 278(16): 14112-20. |
| [26] | YU Z T, NANTHAKUMAR N N, NEWBURG D S. The Human Milk Oligosaccharide 2'-Fucosyllactose Quenches Campylobacter jejuni-Induced Inflammation in Human Epithelial Cells HEp-2 and HT-29 and in Mouse Intestinal Mucosa [J]. The Journal of nutrition, 2016, 146(10): 1980-90. |
| [27] | COPPA G V, ZAMPINI L, GALEAZZI T, et al. Human milk oligosaccharides inhibit the adhesion to Caco-2 cells of diarrheal pathogens: Escherichia coli, Vibrio cholerae, and Salmonella fyris [J]. Pediatric research, 2006, 59(3): 377-82. |
| [28] | RAMANI S, STEWART C J, LAUCIRICA D R, et al. Human milk oligosaccharides, milk microbiome and infant gut microbiome modulate neonatal rotavirus infection [J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 5010. |
| [29] | KOROMYSLOVA A, TRIPATHI S, MOROZOV V, et al. Human norovirus inhibition by a human milk oligosaccharide [J]. Virology, 2017, 508: 81-9. |
| [30] | LAUCIRICA D R, TRIANTIS V, SCHOEMAKER R, et al. Milk Oligosaccharides Inhibit Human Rotavirus Infectivity in MA104 Cells [J]. The Journal of nutrition, 2017, 147(9): 1709-14. |
| [31] | HANISCH F G, HANSMAN G S, MOROZOV V, et al. Avidity of α-fucose on human milk oligosaccharides and blood group-unrelated oligo/polyfucoses is essential for potent norovirus-binding targets [J]. The Journal of biological chemistry, 2018, 293(30): 11955–65. |
| [32] | CARR L E, VIRMANI M D, ROSA F, et al. Role of Human Milk Bioactives on Infants' Gut and Immune Health [J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2021, 12: 604080. |
| [33] | HOLSCHER H D, DAVIS S R, TAPPENDEN K A. Human milk oligosaccharides influence maturation of human intestinal Caco-2Bbe and HT-29 cell lines [J]. The Journal of nutrition, 2014, 144(5): 586-91. |
| [34] | KONG C L, ELDERMAN M, CHENG L H, et al. Modulation of Intestinal Epithelial Glycocalyx Development by Human Milk Oligosaccharides and Non-Digestible Carbohydrates [J]. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research 2019, 63(17): e1900303. |
| [35] | CHICHLOWSKI M, DE LARTIGUE G, GERMAN J B, et al. Bifidobacteria isolated from infants and cultured on human milk oligosaccharides affect intestinal epithelial function [J]. Journal of pediatric gastroenterology and nutrition 2012, 55(3): 321-7. |
| [36] | LIU F, SIMPSON A B, D'COSTA E, et al. Sialic acid, the secret gift for the brain [J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2022, 63(29): 9875-94. |
| [37] | COMSTOCK S S, LI M, WANG M, et al. Dietary Human Milk Oligosaccharides but Not Prebiotic Oligosaccharides Increase Circulating Natural Killer Cell and Mesenteric Lymph Node Memory T Cell Populations in Noninfected and Rotavirus-Infected Neonatal Piglets [J]. The Journal of nutrition, 2017, 147(6): 1041-7. |
| [38] | PISA E, MARTIRE A, CHIODI V, et al. Exposure to 3'Sialyllactose-Poor Milk during Lactation Impairs Cognitive Capabilities in Adulthood [J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13(12): 4191-211. |
| [39] | OLIVEROS E, VAZQUEZ E, BARRANCO A, et al. Sialic Acid and Sialylated Oligosaccharide Supplementation during Lactation Improves Learning and Memory in Rats [J]. Nutrients, 2018, 10(10): 1519. |
| [40] | BERGER P K, ONG M L, BODE L, et al. Human Milk Oligosaccharides and Infant Neurodevelopment: A Narrative Review [J]. Nutrients, 2023, 15(3): 719. |
| [41] | WILLEMSEN Y, BEIJERS R, GU F J, et al. Fucosylated Human Milk Oligosaccharides during the First 12 Postnatal Weeks Are Associated with Better Executive Functions in Toddlers [J]. Nutrients, 2023, 15(6): 1463. |
| [42] | OLIVEROS E, RAMIREZ M, VAZQUEZ E, et al. Oral supplementation of 2'-fucosyllactose during lactation improves memory and learning in rats [J]. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 2016, 31: 20-7. |
| [43] | EFSA PANEL ON DIETETIC PRODUCTS N A A. Safety of 2′‐O‐fucosyllactose as a novel food ingredient pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 258/97 [J]. EFSA Journal, 2015, 13(7): 4184. |
| [44] | EFSA PANEL ON NUTRITION N F, FOOD A, TURCK D, et al. Safety of 3-FL (3-Fucosyllactose) as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 [J]. EFSA Journal, 2021, 19(6): 6662. |
| [45] | EFSA PANEL ON NUTRITION N F, FOOD A, TURCK D, et al. Safety of lacto-N-tetraose (LNT) as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 [J]. EFSA Journal, 2019, 17(12): 5907. |
| [46] | EFSA PANEL ON DIETETIC PRODUCTS N, ALLERGIES. Safety of lacto-N-neotetraose as a novel food ingredient pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 258/97 [J]. EFSA Journal, 2015, 13(7): 4183. |
| [47] | EFSA PANEL ON NUTRITION N F, FOOD A, TURCK D, et al. Safety of 3'-Sialyllactose (3'-SL) sodium salt as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 [J]. EFSA Journal, 2020, 18(5): 6098. |
| [48] | EFSA PANEL ON NUTRITION N F, FOOD A, TURCK D, et al. Safety of 6'-Sialyllactose (6'-SL) sodium salt as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 [J]. EFSA Journal, 2020, 18(5): 6097. |
| [49] | EFSA PANEL ON NUTRITION N F, FOOD A, TURCK D, et al. Safety of 2'-fucosyllactose/difucosyllactose mixture as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 [J]. EFSA Journal, 2019, 17(6): 5717. |
| [50] | TURCK D, BOHN T, CASTENMILLER J, et al. Safety of lacto-N-fucopentaose I/2'-fucosyllactose (LNFP-I/2'-FL) mixture as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 [J]. EFSA Journal, 2023, 21(12): 8412. |
| [51] | WANG S Y, YANG Y, ZHU Q, et al. Chemical synthesis of polysaccharides [J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2022, 69: 102154. |
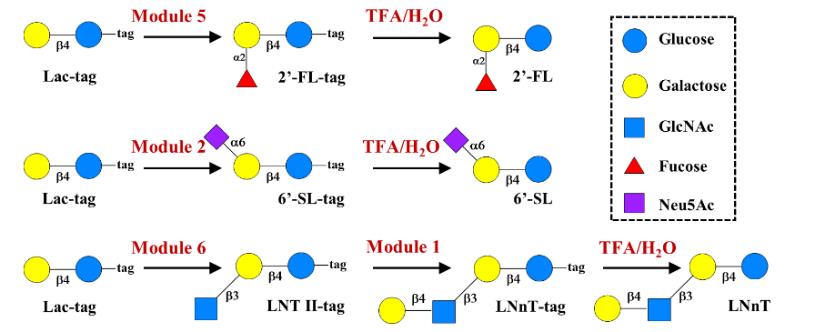
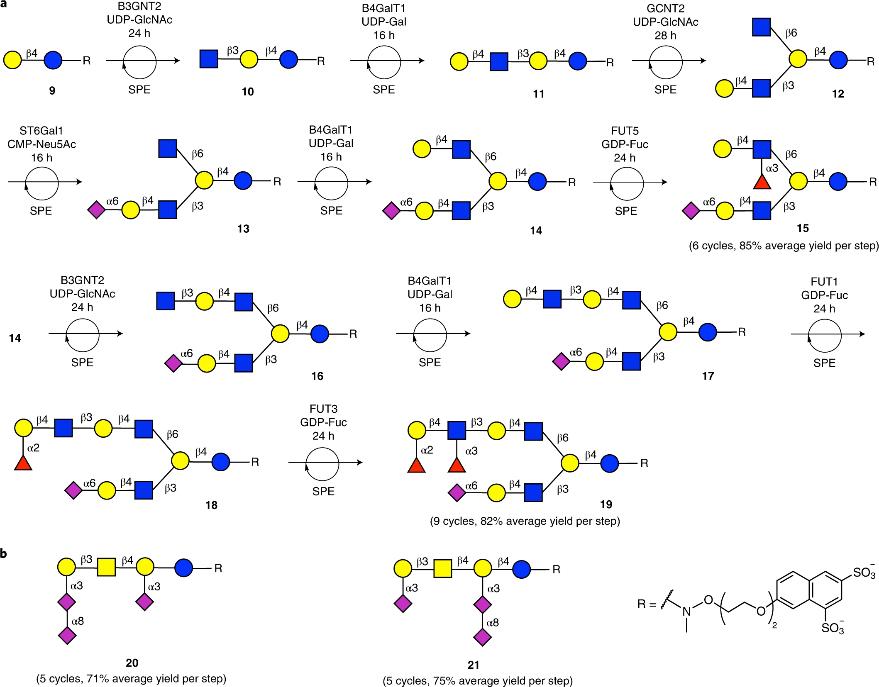
| [52] | AGOSTON K, HEDEROS M J, BAJZA I, et al. Kilogram scale chemical synthesis of 2'-fucosyllactose [J]. Carbohydrate Research, 2019, 476: 71-7. |
| [53] | BANDARA M D, STINE K J, DEMCHENKO A V. The chemical synthesis of human milk oligosaccharides: Lacto-N-neotetraose (Galbeta1-->4GlcNAcbeta1-->3Galbeta1-->4Glc) [J]. Carbohydrate Research, 2019, 483: 107743. |
| [54] | ESPOSITO D, HUREVICH M, CASTAGNER B, et al. Automated synthesis of sialylated oligosaccharides [J]. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2012, 8: 1601-9. |
| [55] | ARBOE JENNUM C, HAUCH FENGER T, BRUUN L M, et al. One-Pot Glycosylations in the Synthesis of Human Milk Oligosaccharides [J]. European Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2014, 2014(15): 3232-41. |
| [56] | XU L L, TOWNSEND S D. Synthesis as an Expanding Resource in Human Milk Science [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2021, 143(30): 11277-90. |
| [57] | SINGH Y, ESCOPY S, SHADRICK M, et al. Chemical Synthesis of Human Milk Oligosaccharides: para-Lacto-N-hexaose and para-Lacto-N-neohexaose [J]. Chemistry, 2023, 29(64): e202302288. |
| [58] | ZHAO M L, ZHU Y Y, WANG H, et al. An Overview of Sugar Nucleotide-Dependent Glycosyltransferases for Human Milk Oligosaccharide Synthesis [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2023, 71(33): 12390-402. |
| [59] | ZHENG J, XU H, FANG J Q, et al. Enzymatic and chemoenzymatic synthesis of human milk oligosaccharides and derivatives [J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2022, 291: 119564. |
| [60] | MA S Z, GAO J H, TIAN Y P, et al. Recent progress in chemoenzymatic synthesis of human glycans [J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2024, 22(38): 7767-85. |
| [61] | TAUJALE R, VENKAT A, HUANG L-C, et al. Deep evolutionary analysis reveals the design principles of fold A glycosyltransferases [J]. eLife, 2020, 9: e54532. |
| [62] | BAI L, LI H. Protein N-glycosylation and O-mannosylation are catalyzed by two evolutionarily related GT-C glycosyltransferases [J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2021, 68: 66-73. |
| [63] | PEREZ C, SZYMANSKI C M. More than one way to add a sugar into bacterial polysaccharides [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2024, 121(25): e2408556121 |
| [64] | NISHIMOTO M. Large scale production of lacto-N-biose I, a building block of type I human milk oligosaccharides, using sugar phosphorylases [J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2020, 84(1): 17-24. |
| [65] | NEKVASILOVá P, HOVORKOVá M, MéSZáROS Z, et al. Engineered Glycosidases for the Synthesis of Analogs of Human Milk Oligosaccharides [J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(8): 4106. |
| [66] | LIU Y H, WANG L, HUANG P, et al. Efficient sequential synthesis of lacto-N-triose II and lacto-N-neotetraose by a novel beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase from Tyzzerella nexilis [J]. Food Chemistry, 2020, 332: 127438. |
| [67] | BENSIMON J, LU X N. Human milk oligosaccharides produced by synthetic biology [J]. Journal of Agriculture and Food Research, 2024, 18: 101361. |
| [68] | TENG Y X, JIANG T, YAN Y J. The expanded CRISPR toolbox for constructing microbial cell factories [J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2024, 42(1): 104-18. |
| [69] | GUPTA R, GUPTA N, SHARMA R. ABC Transporters and Group Translocation [M]. Fundamentals of Bacterial Physiology and Metabolism. Springer Singapore. 2021: 209-33. |
| [70] | DREW D, NORTH R A, NAGARATHINAM K, et al. Structures and General Transport Mechanisms by the Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2021, 121(9): 5289-335. |
| [71] | JECKELMANN J M, ERNI B. Transporters of glucose and other carbohydrates in bacteria [J]. Pflugers Archiv : European journal of physiology, 2020, 472(9): 1129-53. |
| [72] | SUGITA T, KOKETSU K. Transporter Engineering Enables the Efficient Production of Lacto-N-triose II and Lacto-N-tetraose in Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2022, 70(16): 5106-14. |
| [73] | LI Y S, LI Y, LI P F, et al. Whole-Cell Biosynthesis of Branched Human Milk Hexasaccharide Lacto-N-neohexaose [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2025, 73(28): 17814-23. |
| [74] | LI N, YAN S F, XIA H Z, et al. Metabolic Engineering of Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) for 2'-Fucosyllactose Synthesis in a Higher Productivity [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2025, 14(2): 441-52. |
| [75] | LIAO Y X, LAO C W, WU J Y, et al. High-Yield Synthesis of Lacto-N-Neotetraose from Glycerol and Glucose in Engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024, 72(10): 5325-38. |
| [76] | HUANG H Y, YU W W, XU X H, et al. Combinatorial Engineering of Escherichia coli for Enhancing 3-Fucosyllactose Production [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2024, 13(6): 1866-78. |
| [77] | QIAN Q Y, YANG L H, ZHAO C H, et al. Highly efficient production of lacto-N-tetraose in plasmid-free Escherichia coli through chromosomal integration of multicopy key glycosyltransferase genes [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2025, 284(Pt 1): 137987. |
| [78] | LI C C, LI M L, HU M M, et al. Metabolic Engineering of Escherichia coli for High-Titer Biosynthesis of 3'-Sialyllactose [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024, 72(10): 5379-90. |
| [79] | LIU Y L, QIAO L P, YU L M, et al. Highly efficient biosynthesis of 6′-sialyllactose in a metabolically engineered plasmid-free Escherichia coli using a novel α2,6-sialyltransferase from Nicoletella semolina [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2025, 284: 138151. |
| [80] | LIANG S Q, QUAN Q, LIU D, et al. Regulation of Metabolic Pathways to Enhance Difucosyllactose Biosynthesis in Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2025, 73(1): 727-34. |
| [81] | LI Z Y, ZHU Y Y, HUANG Z L, et al. Engineering Escherichia coli for high-level production of lacto-N-fucopentaose I by stepwise de novo pathway construction [J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2023, 315: 121028. |
| [82] | XU M Y, MENG X F, ZHANG W X, et al. Improved production of 2'-fucosyllactose in engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing a putative alpha-1, 2-fucosyltransferase from Bacillus cereus [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2021, 20(1): 165-78. |
| [83] | LI Y, WANG X, CHEN K D, et al. Efficient production of 2'-fucosyllactose in Pichia pastoris through metabolic engineering and constructing an orthogonal energy supply system [J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2025, 10(3): 807-15. |
| [84] | DONG X M, LI N, LIU Z M, et al. Modular pathway engineering of key precursor supply pathways for lacto-N-neotetraose production in Bacillus subtilis [J]. Biotechnology for biofuels, 2019, 12: 212. |
| [85] | LEE Y G, JO H Y, LEE D H, et al. De novo biosynthesis of 2'-fucosyllactose by bioengineered Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Biotechnology journal, 2024, 19(1): e2300461. |
| [86] | JERS C, MICHALAK M, LARSEN D M, et al. Rational design of a new Trypanosoma rangeli trans-sialidase for efficient sialylation of glycans [J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(1): e83902. |
| [87] | GUO L C, CHEN X D, XU L, et al. Enzymatic Synthesis of 6'-Sialyllactose, a Dominant Sialylated Human Milk Oligosaccharide, by a Novel exo-α-Sialidase from Bacteroides fragilis NCTC9343 [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2018, 84(13): e00071-18. |
| [88] | ZEUNER B, MUSCHIOL J, HOLCK J, et al. Substrate specificity and transfucosylation activity of GH29 α-l-fucosidases for enzymatic production of human milk oligosaccharides [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 41: 34-45. |
| [89] | CHOI Y H, KIM J H, PARK B S, et al. Solubilization and Iterative Saturation Mutagenesis of α1,3-fucosyltransferase from Helicobacter pylori to enhance its catalytic efficiency [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2016, 113(8): 1666-75. |
| [90] | ZHAO C, WU Y J, YU H, et al. The one-pot multienzyme (OPME) synthesis of human blood group H antigens and a human milk oligosaccharide (HMOS) with highly active Thermosynechococcus elongates α1-2-fucosyltransferase [J]. Chemical Communications, 2016, 52(20): 3899-902. |
| [91] | TAO M T, YANG L H, ZHAO C H, et al. Implementation of a Quorum-Sensing System for Highly Efficient Biosynthesis of Lacto-N-neotetraose in Engineered Escherichia coli MG1655 [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024, 72(13): 7179-86. |
| [92] | ZHANG J M, ZHU Y Y, ZHANG W L, et al. Efficient Production of a Functional Human Milk Oligosaccharide 3'-Sialyllactose in Genetically Engineered Escherichia coli [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2022, 11(8): 2837-45. |
| [93] | DROUILLARD S, MINE T, KAJIWARA H, et al. Efficient synthesis of 6'-sialyllactose, 6,6'-disialyllactose, and 6'-KDO-lactose by metabolically engineered E. coli expressing a multifunctional sialyltransferase from the Photobacterium sp. JT-ISH-224 [J]. Carbohydrate Research, 2010, 345(10): 1394-9. |
| [94] | LIU Y L, ZHU Y Y, WAN L, et al. High-Level De Novo Biosynthesis of 2'-Fucosyllactose by Metabolically Engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2022, 70(29): 9017-25. |
| [95] | JIAO R, ZHANG L, YOU R, et al. Efficient and Cost-Effective Synthesis of N-Acetyllactosamine by Sequential Modular Enzymatic Cascade Reactions Involving NTP Regeneration [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024, 72(50): 28060-71. |
| [96] | LIU Y H, YAN Q J, MA J W, et al. Directed evolution of a beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase from Haloferula sp. for lacto-N-triose II and lacto-N-neotetraose synthesis from chitin [J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2023, 164: 110177. |
| [97] | LI T, LI J, YAN Q J, et al. Biochemical characterization of a novel beta-galactosidase from Lacticaseibacillus zeae and its application in synthesis of lacto-N-tetraose [J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2023, 106(10): 6623-34. |
| [98] | CHEN C C, ZHANG Y, XUE M Y, et al. Sequential one-pot multienzyme (OPME) synthesis of lacto-N-neotetraose and its sialyl and fucosyl derivatives [J]. Chemical Communications, 2015, 51(36): 7689-92. |
| [99] | PENG X, PEI C X, QIAN E W, et al. Co-immobilization of a bi-enzymatic cascade into hierarchically porous MIL-53 for efficient 6'-sialyllactose production [J]. Nanoscale, 2024, 16(31): 14932-9. |
| [100] | YU H, YAN X B, AUTRAN C A, et al. Enzymatic and Chemoenzymatic Syntheses of Disialyl Glycans and Their Necrotizing Enterocolitis Preventing Effects [J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2017, 82(24): 13152-60. |
| [101] | LI C, WU M, GAO X, et al. Efficient Biosynthesis of 2'-Fucosyllactose Using an In Vitro Multienzyme Cascade [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2020, 68(39): 10763-71. |
| [102] | YANG Y Y, THORHALLSSON A T, ROVIRA C, et al. Improved Enzymatic Production of the Fucosylated Human Milk Oligosaccharide LNFP II with GH29B alpha-1,3/4-l-Fucosidases [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024, 72(19): 11013-28. |
| [103] | ZHANG Y H. Production of biofuels and biochemicals by in vitro synthetic biosystems: Opportunities and challenges [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2015, 33(7): 1467-83. |
| [104] | ZHANG Y H P, SUN J B, MA Y H. Biomanufacturing: history and perspective [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 44(4-5): 773-84. |
| [105] | MENG J W, ZHU Y Y, WANG H, et al. Biosynthesis of Human Milk Oligosaccharides: Enzyme Cascade and Metabolic Engineering Approaches [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2023, 71(5): 2234-43. |
| [106] | YU H, CHOKHAWALA H, KARPEL R, et al. A Multifunctional Pasteurella multocida Sialyltransferase: A Powerful Tool for the Synthesis of Sialoside Libraries [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2005, 127(50): 17618-9. |
| [107] | XU Y Y, FAN Y Y, YE J F, et al. Successfully Engineering a Bacterial Sialyltransferase for Regioselective α2,6-sialylation [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(8): 7222-7. |
| [108] | JIAO R M, PENG X, WANG B, et al. Highly Efficient and Economical One-Pot Two-Step Multienzymatic Synthesis of 6'/3'-Sialyllactosamine from In Situ-Produced N-Acetyllactosamine [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2025, 73(23): 14444-52. |
| [109] | TAN Y M, ZHANG Y, HAN Y B, et al. Directed evolution of an α1,3-fucosyltransferase using a single-cell ultrahigh-throughput screening method [J]. Science Advances, 2019, 5(10): eaaw8451. |
| [110] | BOTELHO V A, MATEUS M, PETRUS J C C, et al. Membrane Bioreactor for Simultaneous Synthesis and Fractionation of Oligosaccharides [J]. Membranes (Basel), 2022, 12(2): 17397–405 |
| [111] | RUZIC L, BOLIVAR J M, NIDETZKY B. Glycosynthase reaction meets the flow: Continuous synthesis of lacto-N-triose II by engineered beta-hexosaminidase immobilized on solid support [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2020, 117(5): 1597-602. |
| [112] | WU Y R, SUN Y Z, PEI C X, et al. Automated chemoenzymatic modular synthesis of human milk oligosaccharides on a digital microfluidic platform [J]. RSC Advances, 2024, 14(25): 17397-405. |
| [113] | LI T H, LIU L, WEI N, et al. An automated platform for the enzyme-mediated assembly of complex oligosaccharides [J]. Nature Chemistry, 2019, 11(3): 229-36. |
| [1] | 盛周煌, 陈智仙, 张彦. 酵母甘露糖蛋白的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(2): 408-421. |
| [2] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [3] | 史然, 江正强. 2'-岩藻糖基乳糖的酶法合成研究进展和展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(4): 481-494. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||