| 8 |
ZOU Y K, YANG S, SANDERS J N, et al. Computational investigation of the mechanism of Diels-Alderase PyrI4[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(47): 20232-20239.
|
| 9 |
LI B, GUAN X Y, YANG S, et al. Mechanism of the stereoselective catalysis of Diels-Alderase PyrE3 involved in pyrroindomycin biosynthesis[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2022, 144(11): 5099-5107.
|
| 10 |
HASHIMOTO T, HASHIMOTO J, TERUYA K, et al. Biosynthesis of versipelostatin: identification of an enzyme-catalyzed [4+2]-cycloaddition required for macrocyclization of spirotetronate-containing polyketides[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(2): 572-575.
|
| 11 |
OHASHI M, LIU F, HAI Y, et al. SAM-dependent enzyme-catalysed pericyclic reactions in natural product biosynthesis[J]. Nature, 2017, 549(7673): 502-506.
|
| 12 |
ZHANG B, WANG K B, WANG W, et al. Enzyme-catalysed[6+4] cycloadditions in the biosynthesis of natural products[J]. Nature, 2019, 568(7750): 122-126.
|
| 13 |
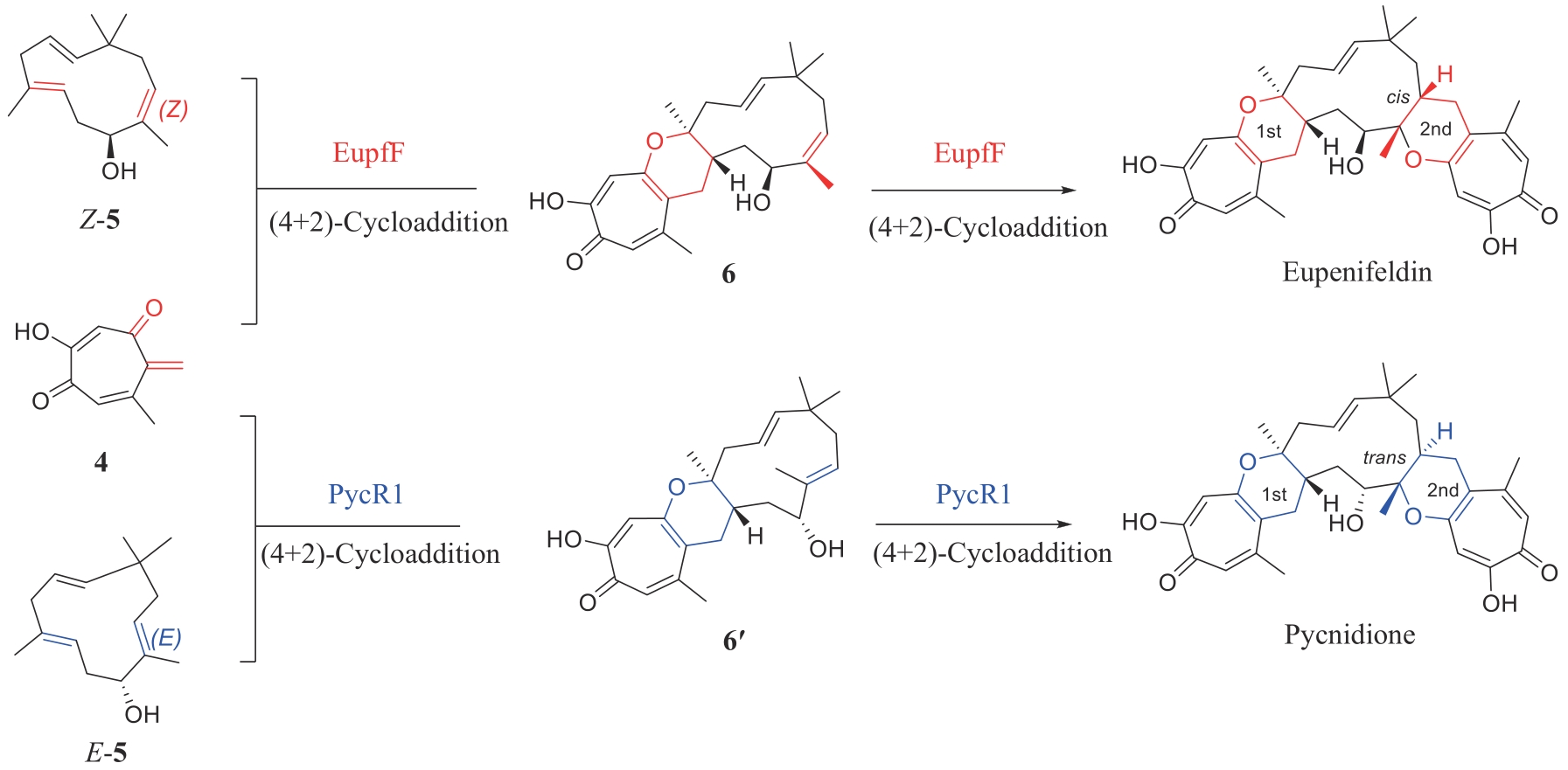
GAO L, SU C, DU X X, et al. FAD-dependent enzyme-catalysed intermolecular [4+2] cycloaddition in natural product biosynthesis[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2020, 12(7): 620-628.
|
| 14 |
LITTLE R, PAIVA F C R, JENKINS R, et al. Unexpected enzyme-catalysed [4+2] cycloaddition and rearrangement in polyether antibiotic biosynthesis[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2019, 2(11): 1045-1054.
|
| 15 |
SATO M, KISHIMOTO S, YOKOYAMA M, et al. Catalytic mechanism and endo-to-exo selectivity reversion of an octalin-forming natural Diels-Alderase[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2021, 4(3): 223-232.
|
| 16 |
OHASHI M, TAN D, LU J Y, et al. Enzymatic cis-decalin formation in natural product biosynthesis[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(6): 3301-3305.
|
| 17 |
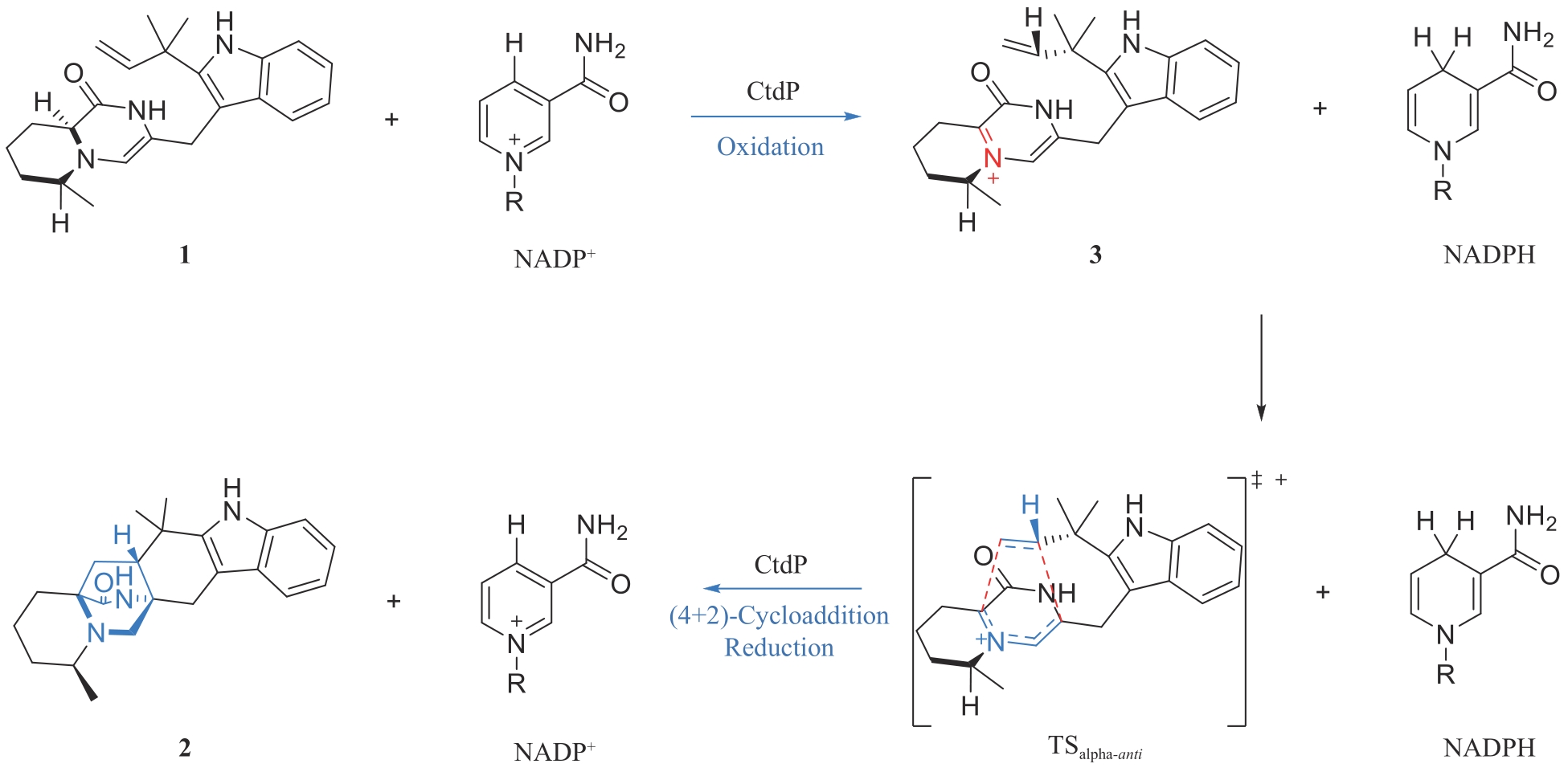
LIU Z W, RIVERA S, NEWMISTER S A, et al. An NmrA-like enzyme-catalysed redox-mediated Diels-Alder cycloaddition with anti-selectivity[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2023, 15(4): 526-534.
|
| 18 |
LIU J W, LU J Y, ZHANG C, et al. Tandem intermolecular[4+2] cycloadditions are catalysed by glycosylated enzymes for natural product biosynthesis[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2023, 15(8): 1083-1090.
|
| 19 |
CHEN Q B, GAO J, JAMIESON C, et al. Enzymatic intermolecular Hetero-Diels-Alder reaction in the biosynthesis of tropolonic sesquiterpenes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(36): 14052-14056.
|
| 20 |
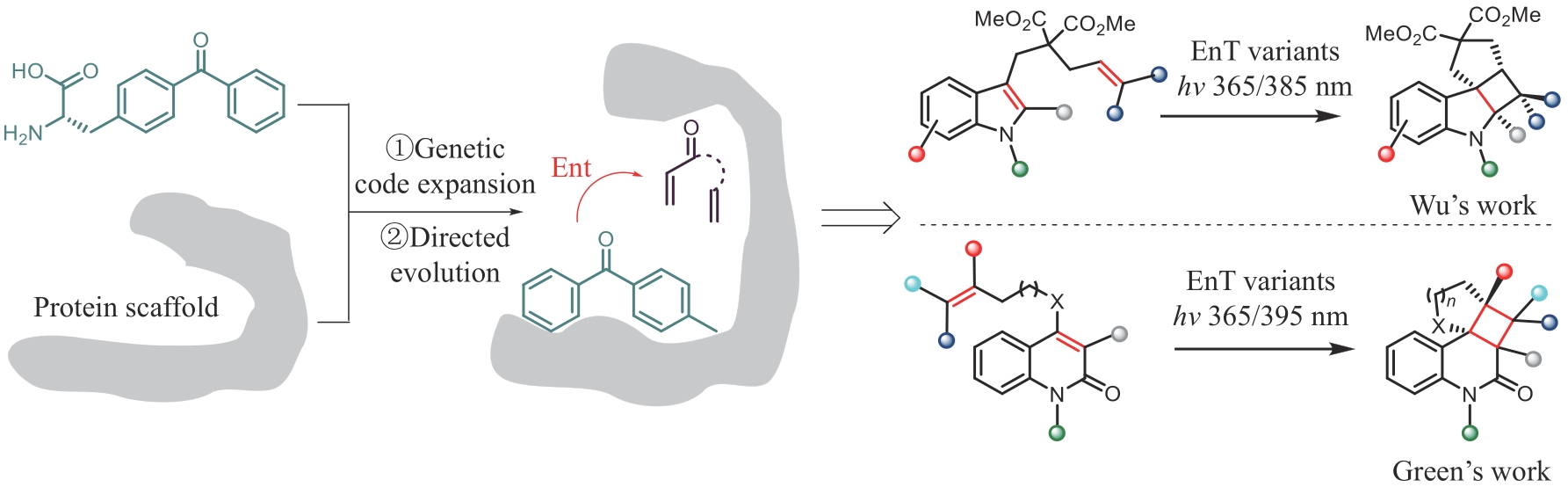
SUN N N, HUANG J J, QIAN J Y, et al. Enantioselective[2+2]-cycloadditions with triplet photoenzymes[J]. Nature, 2022, 611(7937): 715-720.
|
| 21 |
TRIMBLE J S, CRAWSHAW R, HARDY F J, et al. A designed photoenzyme for enantioselective [2+2] cycloadditions[J]. Nature, 2022, 611(7937): 709-714.
|
| 1 |
HUISGEN R. Cycloadditions—Definition, classification, and characterization[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 1968, 7(5): 321-328.
|
| 2 |
JEON B S, WANG S A, RUSZCZYCKY M W, et al. Natural[4+2]-cyclases[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(8): 5367-5388.
|
| 3 |
TANG Z J, WANG H B, LIU W. Enzyme-associated pericyclic reactions[M/OL]//Comprehensive natural products Ⅲ. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2020: 187-227 [2023-10-01]. .
|
| 4 |
KIM H J, RUSZCZYCKY M W, CHOI S H, et al. Enzyme-catalysed [4+2] cycloaddition is a key step in the biosynthesis of spinosyn A[J]. Nature, 2011, 473(7345): 109-112.
|
| 5 |
TIAN Z H, SUN P, YAN Y, et al. An enzymatic [4+2]cyclization cascade creates the pentacyclic core of pyrroindomycins[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2015, 11(4): 259-265.
|
| 6 |
ZHENG Q F, GUO Y J, YANG L L, et al. Enzyme-dependent[4+2] cycloaddition depends on lid-like interaction of the N-terminal sequence with the catalytic core in PyrI4[J]. Cell Chemical Biology, 2016, 23(3): 352-360.
|
| 7 |
ZHENG Q F, GONG Y K, GUO Y J, et al. Structural insights into a flavin-dependent [4+2] cyclase that catalyzes trans-decalin formation in pyrroindomycin biosynthesis[J]. Cell Chemical Biology, 2018, 25(6): 718-727.e3.
|
| 22 |
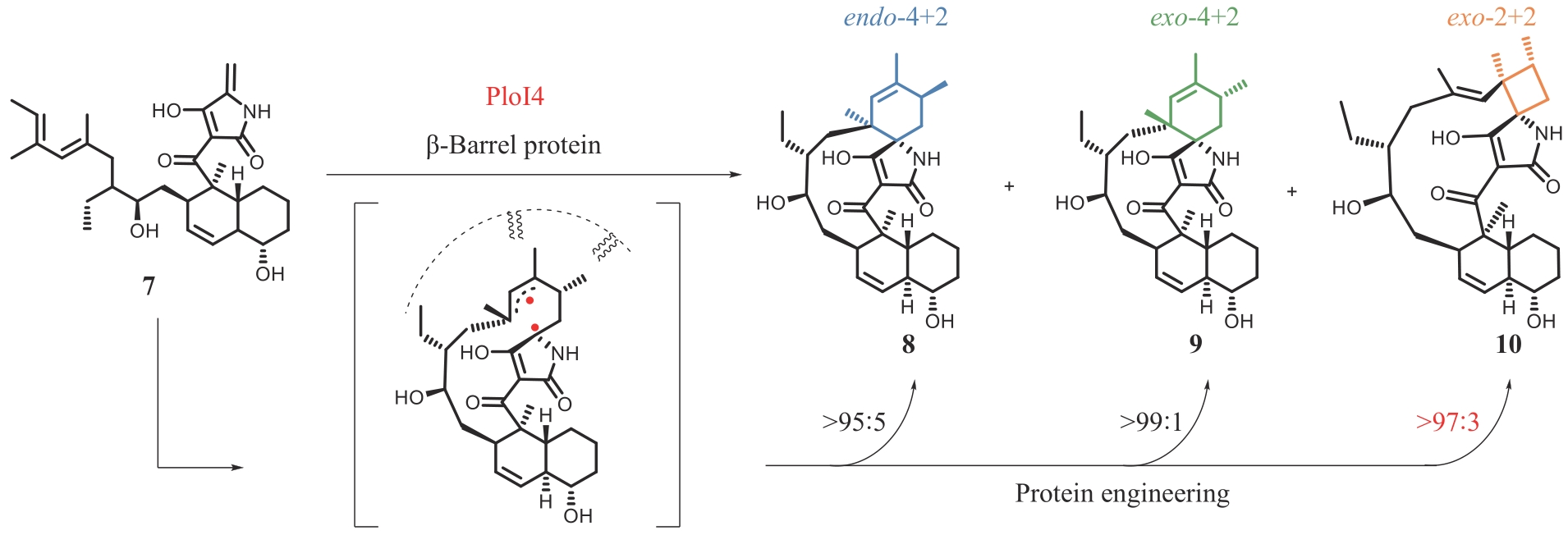
WANG H B, ZOU Y K, LI M, et al. A cyclase that catalyses competing 2+2 and 4+2 cycloadditions[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2023, 15(2): 177-184.
|