Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (2): 347-372.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-069
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Research progress in mosquito-borne flaviviruses transmission and the development of vaccines and drugs
YU Xi1, LIU Jianying2, CHENG Gong1,2
- 1.Schoool of Medicine,Tsinghua University,Beijing 100084,China
2.Shenzhen Bay Laboratory,Shenzhen 518132,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2022-12-06Revised:2023-01-16Online:2023-04-27Published:2023-04-30 -
Contact:CHENG Gong
蚊媒黄病毒传播机制及疫苗与药物研发进展
余茜1, 刘建英2, 程功1,2
- 1.清华大学医学院,北京 100084
2.深圳湾实验室,广东 深圳 518132
-
通讯作者:程功 -
作者简介:余茜 (1994—),女,博士研究生。主要研究方向为蚊媒病毒的进化及其对病毒感染与传播能力的影响。E-mail:yuq16@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn程功 (1981—),男,长聘教授,博士生导师。长期开展针对虫媒病毒等新再发病毒性传染病致病机理、感染传播机制与抗病毒免疫及疫苗研发等领域的研究。E-mail:gongcheng@tsinghua.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(32188101);国家重点研发计划(2021YFC2300200)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YU Xi, LIU Jianying, CHENG Gong. Research progress in mosquito-borne flaviviruses transmission and the development of vaccines and drugs[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(2): 347-372.
余茜, 刘建英, 程功. 蚊媒黄病毒传播机制及疫苗与药物研发进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(2): 347-372.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2022-069
| 疫苗名称 | 疫苗种类 | 抗原 | 针对病毒种类 | 疫苗开发阶段 | 开发者 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17D | 减毒活疫苗 | E蛋白 | YFV | 已获得许可 | [ |
| SA14-14-2 | 减毒活疫苗 | E蛋白 | JEV | 已获得许可 | CDIBP |
| TV003 | 减毒活疫苗 | prM-E | DENV 1~4 | 临床三期 | NIAID |
| DENVax | 减毒活疫苗 | prM-E | DENV 1~4 | 临床三期 | Takeda |
| TDENV-PIV | 灭活疫苗 | C-prM-E-NS1/3/5 | DENV 1~4 | 临床一期 | GSK, Fiocruz & WRAIR |
| ZPIV | 灭活疫苗 | E蛋白 | ZIKV | 临床一期 | WRAIR/NIAID |
| CYD-TDV(Dengvaxia) | 重组疫苗 | prM-E | DENV 1~4 | 已获得许可 | Sanofi Pasteur |
| ChimeriVax-WN02 | 重组疫苗 | prM-E | WNV | 临床二期 | Sanofi Pasteur |
| V180 | 重组疫苗 | E蛋白 | DENV 1~4 | 临床一期 | Merck |
| ZIKV-VLP | VLPs | C-prM-E-NS2B/NS3 | ZIKV | 动物实验 | [ |
| DENV-VLP | VLPs | prM-E | DENV 1~4 | 临床前 | [ |
| GLS-5700 | DNA疫苗 | prM-E/NS1 | ZIKV | 临床一期 | Inovio GeneOne |
| IgEsig-prM-E-LNP | mRNA疫苗 | prM-E | ZIKV | 动物实验 | [ |
Table 1 Preventive vaccines against mosquito-borne flavivirus
| 疫苗名称 | 疫苗种类 | 抗原 | 针对病毒种类 | 疫苗开发阶段 | 开发者 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17D | 减毒活疫苗 | E蛋白 | YFV | 已获得许可 | [ |
| SA14-14-2 | 减毒活疫苗 | E蛋白 | JEV | 已获得许可 | CDIBP |
| TV003 | 减毒活疫苗 | prM-E | DENV 1~4 | 临床三期 | NIAID |
| DENVax | 减毒活疫苗 | prM-E | DENV 1~4 | 临床三期 | Takeda |
| TDENV-PIV | 灭活疫苗 | C-prM-E-NS1/3/5 | DENV 1~4 | 临床一期 | GSK, Fiocruz & WRAIR |
| ZPIV | 灭活疫苗 | E蛋白 | ZIKV | 临床一期 | WRAIR/NIAID |
| CYD-TDV(Dengvaxia) | 重组疫苗 | prM-E | DENV 1~4 | 已获得许可 | Sanofi Pasteur |
| ChimeriVax-WN02 | 重组疫苗 | prM-E | WNV | 临床二期 | Sanofi Pasteur |
| V180 | 重组疫苗 | E蛋白 | DENV 1~4 | 临床一期 | Merck |
| ZIKV-VLP | VLPs | C-prM-E-NS2B/NS3 | ZIKV | 动物实验 | [ |
| DENV-VLP | VLPs | prM-E | DENV 1~4 | 临床前 | [ |
| GLS-5700 | DNA疫苗 | prM-E/NS1 | ZIKV | 临床一期 | Inovio GeneOne |
| IgEsig-prM-E-LNP | mRNA疫苗 | prM-E | ZIKV | 动物实验 | [ |
| 候选因子 | 蚊虫媒介 | 对病毒感染的影响 | 机制与功能 |
|---|---|---|---|
| α-葡萄糖苷酶 | 埃及伊蚊 | 抑制DENV-2的复制和传播 | α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂能够抑制内质网出芽病毒的复制[ |
| 羧肽酶B-1(CPB-1) | 埃及伊蚊 | 抑制蚊子中的DENV-2感染 | 与沉积在内质网腔内膜上的E蛋白结合并抑制DENV-2的RNA封装,从而抑制病毒在内质网上的出芽,并可能干扰未成熟病毒向高尔基体网络的运输[ |
| 富含半胱氨酸的毒液蛋白 | 埃及伊蚊 | 登革病毒感染蚊虫的过程中需要这种蛋白 | 与抑制素蛋白相互作用;登革病毒对埃及伊蚊的感染需要这种蛋白质[ |
| 糖蛋白(Glycoproteins) | 蚊虫 | 阻断目标病毒 | 潜在的普遍疾病传播阻断目标[ |
| 热休克蛋白60(Hsp60) | 埃及伊蚊 | Hsp60 蛋白影响DENV-2对蚊虫的感染 | 感染了DENV-2的埃及伊蚊中Hsp60的水平上调[ |
| 蚊子半乳糖特异性C型凝集素-1(mosGCTL-1) | 埃及伊蚊、 致倦库蚊 | 抑制蚊子中西尼罗病毒的感染 | 参与西尼罗病毒对细胞的附着过程,免疫沉淀实验表明,该蛋白与西尼罗病毒颗粒相互作用并结合[ |
| 蚊子半乳糖特异性C型凝集素-3(mosGCTL-3) | 埃及伊蚊 | 抑制蚊子中登革病毒的感染 | 通过与登革病毒E蛋白相互作用调节病毒进入细胞的过程[ |
| 蚊子半乳糖特异性C型凝集素-7(mosGCTL-7) | 埃及伊蚊 | mosGCTL-7介导乙型脑炎病毒感染 | mosGCTL-7在乙型脑炎病毒E蛋白的N154位点与N-聚糖结合。病毒感染需要mosGCTL-7能够识别病毒N-聚糖[ |
| 蚊子半乳糖特异性C型凝集 素-15, 19, 20, 22, 23, 24, 26, 32 | 埃及伊蚊 | 抑制蚊子中登革病毒的感染 | 通过与登革病毒E蛋白相互作用调节病毒进入细胞的过程[ |
| 蚊子蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶-1 (mosPTP-1) | 伊蚊、库蚊 | mosPTP-1参与西尼罗病毒和乙型脑炎病毒的内吞作用 | 分泌蛋白mosGCTL-1通过与病毒相互作用并将其桥接至mosPTP-1细胞受体来增强西尼罗病毒感染[ |
| 唾液蛋白 | 埃及伊蚊 | 抑制或增强登革病毒感染 | 参考2.3.2节 |
Table 2 Candidates of transmission-blocking vaccines for mosquito-borne flavivirus
| 候选因子 | 蚊虫媒介 | 对病毒感染的影响 | 机制与功能 |
|---|---|---|---|
| α-葡萄糖苷酶 | 埃及伊蚊 | 抑制DENV-2的复制和传播 | α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂能够抑制内质网出芽病毒的复制[ |
| 羧肽酶B-1(CPB-1) | 埃及伊蚊 | 抑制蚊子中的DENV-2感染 | 与沉积在内质网腔内膜上的E蛋白结合并抑制DENV-2的RNA封装,从而抑制病毒在内质网上的出芽,并可能干扰未成熟病毒向高尔基体网络的运输[ |
| 富含半胱氨酸的毒液蛋白 | 埃及伊蚊 | 登革病毒感染蚊虫的过程中需要这种蛋白 | 与抑制素蛋白相互作用;登革病毒对埃及伊蚊的感染需要这种蛋白质[ |
| 糖蛋白(Glycoproteins) | 蚊虫 | 阻断目标病毒 | 潜在的普遍疾病传播阻断目标[ |
| 热休克蛋白60(Hsp60) | 埃及伊蚊 | Hsp60 蛋白影响DENV-2对蚊虫的感染 | 感染了DENV-2的埃及伊蚊中Hsp60的水平上调[ |
| 蚊子半乳糖特异性C型凝集素-1(mosGCTL-1) | 埃及伊蚊、 致倦库蚊 | 抑制蚊子中西尼罗病毒的感染 | 参与西尼罗病毒对细胞的附着过程,免疫沉淀实验表明,该蛋白与西尼罗病毒颗粒相互作用并结合[ |
| 蚊子半乳糖特异性C型凝集素-3(mosGCTL-3) | 埃及伊蚊 | 抑制蚊子中登革病毒的感染 | 通过与登革病毒E蛋白相互作用调节病毒进入细胞的过程[ |
| 蚊子半乳糖特异性C型凝集素-7(mosGCTL-7) | 埃及伊蚊 | mosGCTL-7介导乙型脑炎病毒感染 | mosGCTL-7在乙型脑炎病毒E蛋白的N154位点与N-聚糖结合。病毒感染需要mosGCTL-7能够识别病毒N-聚糖[ |
| 蚊子半乳糖特异性C型凝集 素-15, 19, 20, 22, 23, 24, 26, 32 | 埃及伊蚊 | 抑制蚊子中登革病毒的感染 | 通过与登革病毒E蛋白相互作用调节病毒进入细胞的过程[ |
| 蚊子蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶-1 (mosPTP-1) | 伊蚊、库蚊 | mosPTP-1参与西尼罗病毒和乙型脑炎病毒的内吞作用 | 分泌蛋白mosGCTL-1通过与病毒相互作用并将其桥接至mosPTP-1细胞受体来增强西尼罗病毒感染[ |
| 唾液蛋白 | 埃及伊蚊 | 抑制或增强登革病毒感染 | 参考2.3.2节 |
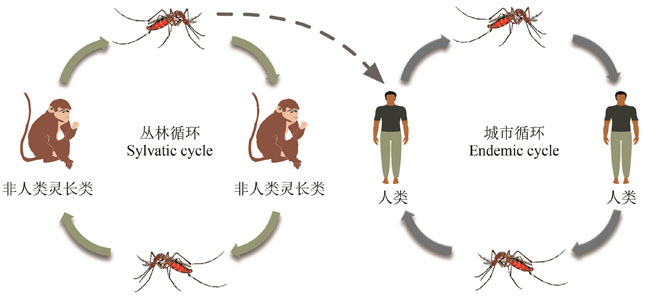
| 1 | WEAVER S C, REISEN W K. Present and future arboviral threats[J]. Antiviral Research, 2010, 85(2): 328-345. |
| 2 | WEAVER S C, BARRETT A D T. Transmission cycles, host range, evolution and emergence of arboviral disease[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2004, 2(10): 789-801. |
| 3 | BHATT S, GETHING P W, BRADY O J, et al. The global distribution and burden of dengue[J]. Nature, 2013, 496(7446): 504-507. |
| 4 | GAO G F. From "A"IV to "Z"IKV: attacks from emerging and re-emerging pathogens[J]. Cell, 2018, 172(6): 1157-1159. |
| 5 | PIERSON T C, DIAMOND M S. The emergence of Zika virus and its new clinical syndromes[J]. Nature, 2018, 560(7720): 573-581. |
| 6 | GOULD E A, SOLOMON T. Pathogenic flaviviruses[J]. Lancet, 2008, 371(9611): 500-509. |
| 7 | HEGDE N R, GORE M M. Japanese encephalitis vaccines: immunogenicity, protective efficacy, effectiveness, and impact on the burden of disease[J]. Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics, 2017, 13(6): 1320-1337. |
| 8 | ROEHRIG J T. West Nile virus in the United States - a historical perspective[J]. Viruses, 2013, 5(12): 3088-3108. |
| 9 | COLLINS M H, METZ S W. Progress and works in progress: update on flavivirus vaccine development[J]. Clinical Therapeutics, 2017, 39(8): 1519-1536. |
| 10 | SCHERWITZL I, MONGKOLSAPAJA J, SCREATON G. Recent advances in human flavivirus vaccines[J]. Current Opinion in Virology, 2017, 23: 95-101. |
| 11 | SIMMONDS P, BECHER P, BUKH J, et al. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Flaviviridae[J]. The Journal of General Virology, 2017, 98(1): 2-3. |
| 12 | BURKE D S, MONATH T P. Flavivirus[M]//KNIPE D M and HOWLEY P M. Field virology, 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2001: 852-921. |
| 13 | KOSTYUCHENKO V A, LIM E X Y, ZHANG S J, et al. Structure of the thermally stable Zika virus[J]. Nature, 2016, 533(7603): 425-428. |
| 14 | BYK L A, GAMARNIK A V. Properties and functions of the dengue virus capsid protein[J]. Annual Review of Virology, 2016, 3(1): 263-281. |
| 15 | MUKHOPADHYAY S, KUHN R J, ROSSMANN M G. A structural perspective of the flavivirus life cycle[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2005, 3(1): 13-22. |
| 16 | FALGOUT B, PETHEL M, ZHANG Y M, et al. Both nonstructural proteins NS2B and NS3 are required for the proteolytic processing of dengue virus nonstructural proteins[J]. Journal of Virology, 1991, 65(5): 2467-2475. |
| 17 | PERERA R, KUHN R J. Structural proteomics of dengue virus[J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2008, 11(4): 369-377. |
| 18 | WESTAWAY E G, MACKENZIE J M, KHROMYKH A A. Kunjin RNA replication and applications of Kunjin replicons[J]. Advances in Virus Research, 2003, 59: 99-140. |
| 19 | LORENZ I C, ALLISON S L, HEINZ F X, et al. Folding and dimerization of tick-borne encephalitis virus envelope proteins prM and E in the endoplasmic reticulum[J]. Journal of Virology, 2002, 76(11): 5480-5491. |
| 20 | KELLY E P, GREENE J J, KING A D, et al. Purified dengue 2 virus envelope glycoprotein aggregates produced by baculovirus are immunogenic in mice[J]. Vaccine, 2000, 18(23): 2549-2559. |
| 21 | ZHANG Y, CORVER J, CHIPMAN P R, et al. Structures of immature flavivirus particles[J]. The EMBO Journal, 2003, 22(11): 2604-2613. |
| 22 | YU I M, ZHANG W, HOLDAWAY H A, et al. Structure of the immature dengue virus at low pH primes proteolytic maturation[J]. Science, 2008, 319(5871): 1834-1837. |
| 23 | LORENZ I C, KARTENBECK J, MEZZACASA A, et al. Intracellular assembly and secretion of recombinant subviral particles from tick-borne encephalitis virus[J]. Journal of Virology, 2003, 77(7): 4370-4382. |
| 24 | FARIA N R, KRAEMER M G, HILL S C, et al. Genomic and epidemiological monitoring of yellow fever virus transmission potential[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6405): 894-899. |
| 25 | INGELBEEN B, WEREGEMERE N A, NOEL H, et al. Urban yellow fever outbreak-Democratic Republic of the Congo, 2016: towards more rapid case detection[J]. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 2018, 12(12): e0007029. |
| 26 | LING Y, CHEN J, HUANG Q, et al. Yellow fever in a worker returning to China from Angola, March 2016[J]. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 2016, 22(7): 1317-1318. |
| 27 | YOUNG P. Arboviruses: a family on the move[M]// HILGENFELD R, VASUDEVAN S G. Dengue and Zika: control and antiviral treatment strategies. Singapore: Springer, 2018: 1-10. |
| 28 | TABACHNICK W J. Climate change and the arboviruses: lessons from the evolution of the dengue and yellow fever viruses[J]. Annual Review of Virology, 2016, 3(1): 125-145. |
| 29 | MANSFIELD K L, HERNÁNDEZ-TRIANA L M, BANYARD A C, et al. Japanese encephalitis virus infection, diagnosis and control in domestic animals[J]. Veterinary Microbiology, 2017, 201: 85-92. |
| 30 | MCLEAN R G, UBICO S R, BOURNE D, et al. West Nile virus in livestock and wildlife[M]//MACKENZIE J, BARRETT A, DEUBEL V eds. Japanese encephalitis and West Nile viruses. 2002, 267:271-308. |
| 31 | VENTER M. Assessing the zoonotic potential of arboviruses of African origin[J]. Current Opinion in Virology, 2018, 28: 74-84. |
| 32 | ZHANG W, CHEN S, MAHALINGAM S, et al. An updated review of avian-origin Tembusu virus: a newly emerging avian Flavivirus[J]. The Journal of General Virology, 2017, 98(10): 2413-2420. |
| 33 | PANDIT P S, DOYLE M M, SMART K M, et al. Predicting wildlife reservoirs and global vulnerability to zoonotic Flaviviruses[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 5425. |
| 34 | WHO. Global strategy for dengue prevention and control 2012-2020[EB/OL].[2022-12-01]. . |
| 35 | GUO C C, ZHOU Z X, WEN Z H, et al. Global epidemiology of dengue outbreaks in 1990—2015: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 2017, 7: 317. |
| 36 | STRUCHINER C J, ROCKLÖV J, WILDER-SMITH A, et al. Increasing dengue incidence in Singapore over the past 40 years: population growth, climate and mobility[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(8): e0136286. |
| 37 | BRATHWAITE DICK O, MARTÍN J L SAN, MONTOYA R H, et al. The history of dengue outbreaks in the americas[J]. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 2012, 87(4): 584-593. |
| 38 | DHIMAL M, GAUTAM I, JOSHI H D, et al. Risk factors for the presence of chikungunya and dengue vectors (Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus), their altitudinal distribution and climatic determinants of their abundance in central Nepal[J]. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 2015, 9(3): e0003545. |
| 39 | PANDEY B D, RAI S K, MORITA K, et al. First case of Dengue virus infection in Nepal[J]. Nepal Medical College Journal: NMCJ, 2004, 6(2): 157-159. |
| 40 | MALLA S, THAKUR G D, SHRESTHA S K, et al. Identification of all dengue serotypes in Nepal[J]. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 2008, 14(10): 1669-1670. |
| 41 | YANG L, CHEN Y, YAN H C, et al. A survey of the 2014 dengue fever epidemic in Guangzhou, China[J]. Emerging Microbes & Infections, 2015, 4(9): e57. |
| 42 | KOBAYASHI D, MUROTA K, FUJITA R, et al. Dengue virus infection in Aedes albopictus during the 2014 autochthonous dengue outbreak in Tokyo metropolis, Japan[J]. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 2018, 98(5): 1460-1468. |
| 43 | 関なおみ, 岩下裕子, 本涼子, ほか. 東京都におけるデング熱国内感染事例の発生について[J/OL]. 日本公衆衛生雑誌, 2015, 62(5): 238-250[2022-12-01]. . |
| SEKI N, IWASHITA Y, MOTO R, et al. An autochthonous outbreak of dengue type 1 in Tokyo, Japan 2014[J/OL]. Japanese Journal of Public Health, 2015, 62(5): 238-250[2022-12-01]. . | |
| 44 | DUCHEYNE E, TRAN MINH N N, HADDAD N, et al. Current and future distribution of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) in WHO Eastern Mediterranean Region[J]. International Journal of Health Geographics, 2018, 17(1): 4. |
| 45 | SUCCO T, LEPARC-GOFFART I, FERRÉ J B, et al. Autochthonous dengue outbreak in Nîmes, south of France, July to September 2015[J]. Eurosurveillance, 2016, 21(21): pii=30240. |
| 46 | DUFFY M R, CHEN T H, HANCOCK W T, et al. Zika virus outbreak on Yap Island, Federated States of Micronesia[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 2009, 360(24): 2536-2543. |
| 47 | FOY B D, KOBYLINSKI K C, FOY J L C, et al. Probable non-vector-borne transmission of Zika virus, Colorado, USA[J]. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 2011, 17(5): 880-882. |
| 48 | KURSCHEIDT F A, MESQUITA C S S, DAMKE G M Z F, et al. Persistence and clinical relevance of Zika virus in the male genital tract[J]. Nature Reviews Urology, 2019, 16(4): 211-230. |
| 49 | OEHLER E, WATRIN L, LARRE P, et al. Zika virus infection complicated by Guillain-Barre syndrome — case report, French Polynesia, December 2013[J]. Euro Surveillance, 2014, 19(9): 20720. |
| 50 | HALSTEAD S B. Chapter 3-Chikungunya and Zika Disease[M/OL]// Chikungunya and Zika Viruses. HIGGS S, VANLANDINGHAM D L, POWERS A M, ed. Pittsburgh: Academic Press, 2018: 69-85 [2022-12-01]. . |
| 51 | VALIANT W G, LALANI T, YUN H C, et al. Human serum with high neutralizing antibody titers against both Zika and dengue virus shows delayed in vitro antibody-dependent enhancement of dengue virus infection[J]. Open Forum Infectious Diseases, 2018, 5(7): ofy151. |
| 52 | BRYANT J E, HOLMES E C, BARRETT A D T. Out of Africa: a molecular perspective on the introduction of yellow fever virus into the Americas[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2007, 3(5): e75. |
| 53 | VAN DER STUYFT P, GIANELLA A, PIRARD M, et al. Urbanisation of yellow fever in Santa Cruz, Bolivia[J]. Lancet, 1999, 353(9164): 1558-1562. |
| 54 | BARRETT A D T. Yellow fever live attenuated vaccine: a very successful live attenuated vaccine but still we have problems controlling the disease[J]. Vaccine, 2017, 35(44): 5951-5955. |
| 55 | SHEARER F M, MOYES C L, PIGOTT D M, et al. Global yellow fever vaccination coverage from 1970 to 2016: an adjusted retrospective analysis[J]. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 2017, 17(11): 1209-1217. |
| 56 | GARSKE T, VAN KERKHOVE M D, YACTAYO S, et al. Yellow fever in Africa: estimating the burden of disease and impact of mass vaccination from outbreak and serological data[J]. PLoS Medicine, 2014, 11(5): e1001638. |
| 57 | MONATH T P, VASCONCELOS P F C. Yellow fever[J]. Journal of Clinical Virology, 2015, 64: 160-173. |
| 58 | BARRETT A D T. Yellow fever in Angola and beyond — the problem of vaccine supply and demand[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 2016, 375(4): 301-303. |
| 59 | CASEY R M, HARRIS J B, AHUKA-MUNDEKE S, et al. Immunogenicity of fractional-dose vaccine during a yellow fever outbreak - final report[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 2019, 381(5): 444-454. |
| 60 | ZHENG Y Y, LI M H, WANG H Y, et al. Japanese encephalitis and Japanese encephalitis virus in mainland China[J]. Reviews in Medical Virology, 2012, 22(5): 301-322. |
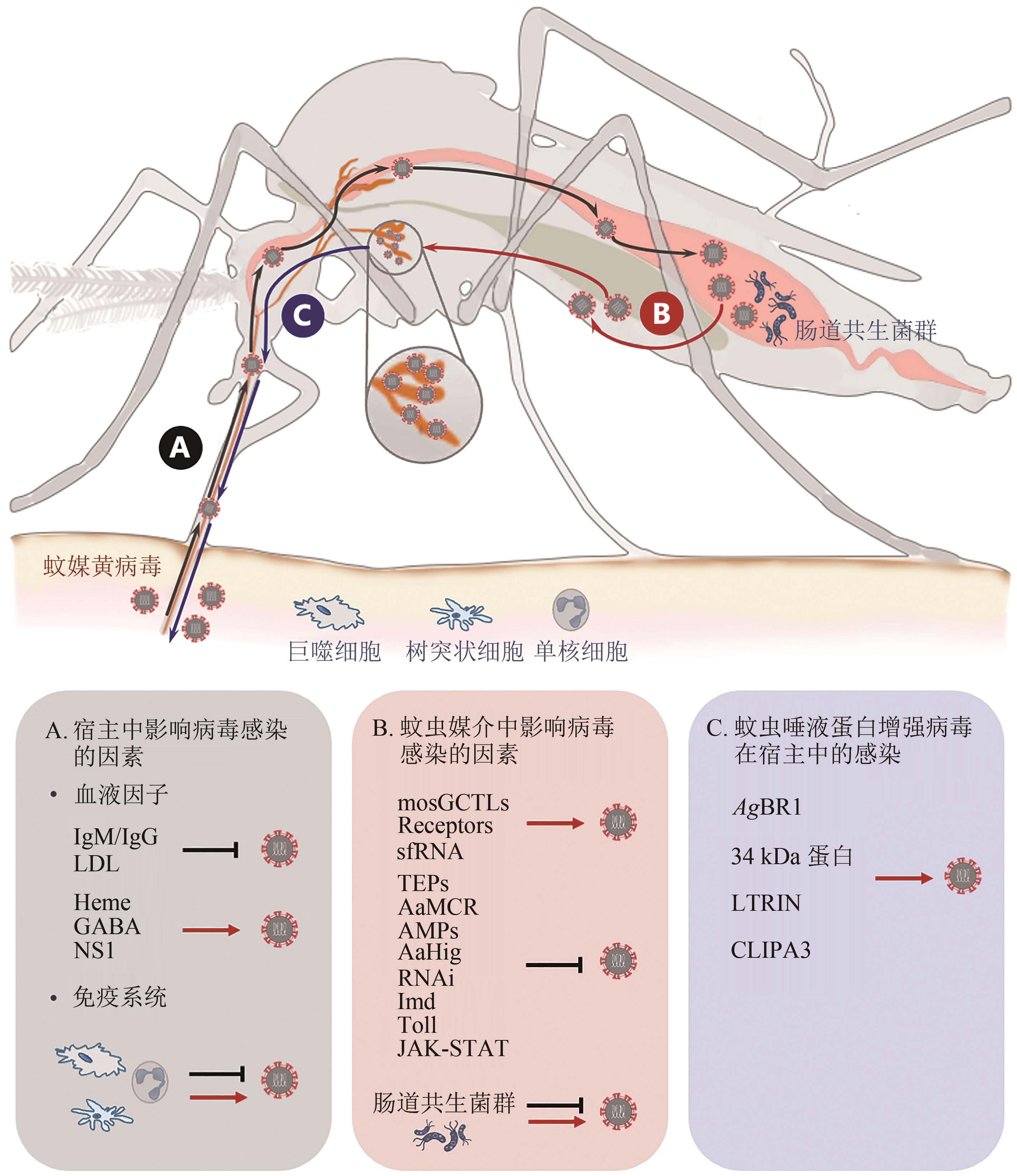
| 61 | DE WISPELAERE M, DESPRÈS P, CHOUMET V. European Aedes albopictus and culex pipiens are competent vectors for Japanese encephalitis virus[J]. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 2017, 11(1): e0005294. |
| 62 | HUANG Y J S, HETTENBACH S M, PARK S L, et al. Differential infectivities among different Japanese encephalitis virus genotypes in Culex quinquefasciatus mosquitoes[J]. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 2016, 10(10): e0005038. |
| 63 | SCHUH A J, WARD M J, LEIGH BROWN A J, et al. Dynamics of the emergence and establishment of a newly dominant genotype of Japanese encephalitis virus throughout Asia[J]. Journal of Virology, 2014, 88(8): 4522-4532. |
| 64 | FAN Y C, LIN J W, LIAO S Y, et al. Virulence of Japanese encephalitis virus genotypesⅠandⅢ, Taiwan[J/OL]. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 2017, 23(11): 1883-1886[2022-12-01]. . |
| 65 | PARK S L, HUANG Y J S, LYONS A C, et al. North American domestic pigs are susceptible to experimental infection with Japanese encephalitis virus[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 7951. |
| 66 | RICKLIN M E, GARCÌA-NICOLÀS O, BRECHBÜHL D, et al. Japanese encephalitis virus tropism in experimentally infected pigs[J]. Veterinary Research, 2016, 47: 34. |
| 67 | SUNWOO J S, JUNG K H, LEE S T, et al. Reemergence of Japanese encephalitis in South Korea, 2010-2015[J]. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 2016, 22(10): 1841-1843. |
| 68 | HEFFELFINGER J D, LI X, BATMUNKH N, et al. Japanese encephalitis surveillance and immunization-Asia and Western Pacific regions, 2016[J]. MMWR Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 2017, 66(22): 579-583. |
| 69 | NEMETH N, BOSCO-LAUTH A, OESTERLE P, et al. North American birds as potential amplifying hosts of Japanese encephalitis virus[J]. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 2012, 87(4): 760-767. |
| 70 | LYONS A C, HUANG Y J S, PARK S L, et al. Shedding of Japanese encephalitis virus in oral fluid of infected swine[J]. Vector Borne and Zoonotic Diseases, 2018, 18(9): 469-474. |
| 71 | RICKLIN M E, GARCÍA-NICOLÁS O, BRECHBÜHL D, et al. Vector-free transmission and persistence of Japanese encephalitis virus in pigs[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 10832. |
| 72 | CDC. West Nile virus final cumulative maps & data for 1999-2021 [EB/OL].[2023-01-10]. . |
| 73 | PETERSEN L R, BRAULT A C, NASCI R S. West Nile virus: review of the literature[J]. JAMA, 2013, 310(3): 308-315. |
| 74 | DAVIS C T, EBEL G D, LANCIOTTI R S, et al. Phylogenetic analysis of North American West Nile virus isolates, 2001-2004: evidence for the emergence of a dominant genotype[J]. Virology, 2005, 342(2): 252-265. |
| 75 | MAY F J, DAVIS C T, TESH R B, et al. Phylogeography of West Nile virus: from the cradle of evolution in Africa to Eurasia, Australia, and the Americas[J]. Journal of Virology, 2011, 85(6): 2964-2974. |
| 76 | REITER P. West Nile virus in Europe: understanding the present to gauge the future[J]. Euro Surveillance, 2010, 15(10): 19508. |
| 77 | GUBLER D J, TRENT D W. Emergence of epidemic dengue/dengue hemorrhagic fever as a public health problem in the Americas[J]. Infectious Agents and Disease, 1993, 2(6): 383-393. |
| 78 | GUBLER D J, NALIM S, TAN R, et al. Variation in susceptibility to oral infection with dengue viruses among geographic strains of Aedes aegypti [J]. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 1979, 28(6): 1045-1052. |
| 79 | GUBLER D J, ROSEN L. Variation among geographic strains of Aedes albopictus in susceptibility to infection with dengue viruses[J]. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 1976, 25(2): 318-325. |
| 80 | RICO-HESSE R. Molecular evolution and distribution of dengue viruses type 1 and 2 in nature[J]. Virology, 1990, 174(2): 479-493. |
| 81 | RUDNICK A. Studies of the ecology of dengue in Malaysia: a preliminary report[J]. Journal of Medical Entomology, 1965, 2(2): 203-208. |
| 82 | RUDNICK A, MARCHETTE N J, GARCIA R. Possible jungle dengue — recent studies and hypotheses[J]. Japanese Journal of Medical Science & Biology, 1967, 20 Suppl: 69-74. |
| 83 | ZHU Y B, ZHANG R D, ZHANG B, et al. Blood meal acquisition enhances arbovirus replication in mosquitoes through activation of the GABAergic system[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 1262. |
| 84 | SOUZA-NETO J A, POWELL J R, BONIZZONI M. Aedes aegypti vector competence studies: a review[J]. Infection, Genetics and Evolution, 2019, 67: 191-209. |
| 85 | ROUNDY C M, AZAR S R, ROSSI S L, et al. Variation in Aedes aegypti mosquito competence for Zika virus transmission[J]. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 2017, 23(4): 625-632. |
| 86 | CHENG G, LIU Y, WANG P H, et al. Mosquito defense strategies against viral infection[J]. Trends in Parasitology, 2016, 32(3): 177-186. |
| 87 | FRANZ A W E, KANTOR A M, PASSARELLI A L, et al. Tissue barriers to arbovirus infection in mosquitoes[J]. Viruses, 2015, 7(7): 3741-3767. |
| 88 | STYER L M, KENT K A, ALBRIGHT R G, et al. Mosquitoes inoculate high doses of West Nile virus as they probe and feed on live hosts[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2007, 3(9): 1262-1270. |
| 89 | SANCHEZ-VARGAS I, HARRINGTON L C, W C Ⅳ BLACK, et al. Analysis of salivary glands and saliva from Aedes albopictus and Aedes aegypti infected with chikungunya viruses[J]. Insects, 2019, 10(2): 39. |
| 90 | DU S Y, LIU Y, LIU J Y, et al. Aedes mosquitoes acquire and transmit Zika virus by breeding in contaminated aquatic environments[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 1324. |
| 91 | MACIEL-DE-FREITAS R, CODEÇO C T, LOURENÇO-DE-OLIVEIRA R. Daily survival rates and dispersal of Aedes aegypti females in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil[J]. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 2007, 76(4): 659-665. |
| 92 | WHITEHORN J, KIEN D T H, NGUYEN N M, et al. Comparative susceptibility of Aedes albopictus and Aedes aegypti to dengue virus infection after feeding on blood of viremic humans: implications for public health[J]. The Journal of Infectious Diseases, 2015, 212(8): 1182-1190. |
| 93 | BARROWS N J, CAMPOS R K, LIAO K C, et al. Biochemistry and molecular biology of flaviviruses[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(8): 4448-4482. |
| 94 | CHENG G, COX J, WANG P H, et al. A C-type lectin collaborates with a CD45 phosphatase homolog to facilitate West Nile virus infection of mosquitoes[J]. Cell, 2010, 142(5): 714-725. |
| 95 | LIU Y, ZHANG F C, LIU J Y, et al. Transmission-blocking antibodies against mosquito C-type lectins for dengue prevention[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2014, 10(2): e1003931. |
| 96 | KUADKITKAN A, WIKAN N, FONGSARAN C, et al. Identification and characterization of prohibitin as a receptor protein mediating DENV-2 entry into insect cells[J]. Virology, 2010, 406(1): 149-161. |
| 97 | SALAS-BENITO J, REYES-DEL VALLE J, SALAS-BENITO M, et al. Evidence that the 45 kD glycoprotein, part of a putative dengue virus receptor complex in the mosquito cell line C6/36, is a heat-shock related protein[J]. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 2007, 77(2): 283-290. |
| 98 | SAKOONWATANYOO P, BOONSANAY V, SMITH D R. Growth and production of the dengue virus in C6/36 cells and identification of a laminin-binding protein as a candidate serotype 3 and 4 receptor protein[J]. Intervirology, 2006, 49(3): 161-172. |
| 99 | LONDONO-RENTERIA B, TROUPIN A, CONWAY M J, et al. Dengue virus infection of Aedes aegypti requires a putative cysteine rich venom protein[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2015, 11(10): e1005202. |
| 100 | KAKUMANI P K, PONIA S S, S R K, et al. Role of RNA interference (RNAi) in dengue virus replication and identification of NS4B as an RNAi suppressor[J]. Journal of Virology, 2013, 87(16): 8870-8883. |
| 101 | GÖERTZ G P, FROS J J, MIESEN P, et al. Noncoding subgenomic flavivirus RNA is processed by the mosquito RNA interference machinery and determines West Nile virus transmission by culex pipiens mosquitoes[J]. Journal of Virology, 2016, 90(22): 10145-10159. |
| 102 | MOON S L, DODD B J T, BRACKNEY D E, et al. Flavivirus sfRNA suppresses antiviral RNA interference in cultured cells and mosquitoes and directly interacts with the RNAi machinery[J]. Virology, 2015, 485: 322-329. |
| 103 | POMPON J, MANUEL M, NG G K, et al. Dengue subgenomic flaviviral RNA disrupts immunity in mosquito salivary glands to increase virus transmission[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2017, 13(7): e1006535. |
| 104 | PARIKH G R, OLIVER J D, BARTHOLOMAY L C. A haemocyte tropism for an arbovirus[J]. The Journal of General Virology, 2009, 90(Pt 2): 292-296. |
| 105 | GOIC B, STAPLEFORD K A, FRANGEUL L, et al. Virus-derived DNA drives mosquito vector tolerance to arboviral infection[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 12410. |
| 106 | XIAO X P, ZHANG R D, PANG X J, et al. A neuron-specific antiviral mechanism prevents lethal flaviviral infection of mosquitoes[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2015, 11(4): e1004848. |
| 107 | XIAO X P, LIU Y, ZHANG X Y, et al. Complement-related proteins control the flavivirus infection of Aedes aegypti by inducing antimicrobial peptides[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2014, 10(4): e1004027. |
| 108 | BLANDIN S, SHIAO S H, MOITA L F, et al. Complement-like protein TEP1 is a determinant of vectorial capacity in the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae [J]. Cell, 2004, 116(5): 661-670. |
| 109 | SHOKAL U, ELEFTHERIANOS I. Evolution and function of thioester-containing proteins and the complement system in the innate immune response[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2017, 8: 759. |
| 110 | KINGSOLVER M B, HUANG Z J, HARDY R W. Insect antiviral innate immunity: pathways, effectors, and connections[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2013, 425(24): 4921-4936. |
| 111 | TASSETTO M, KUNITOMI M, ANDINO R. Circulating immune cells mediate a systemic RNAi-based adaptive antiviral response in Drosophila [J]. Cell, 2017, 169(2): 314-325.e13. |
| 112 | GOIC B, VODOVAR N, MONDOTTE J A, et al. RNA-mediated interference and reverse transcription control the persistence of RNA viruses in the insect model Drosophila [J]. Nature Immunology, 2013, 14(4): 396-403. |
| 113 | WU P, YU X, WANG P, et al. Arbovirus lifecycle in mosquito: acquisition, propagation and transmission[J]. Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine, 2019, 21: e1. |
| 114 | RAMIREZ J L, SHORT S M, BAHIA A C, et al. Chromobacterium Csp_P reduces malaria and dengue infection in vector mosquitoes and has entomopathogenic and in vitro anti-pathogen activities[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2014, 10(10): e1004398. |
| 115 | SARAIVA R G, FANG J R, KANG S, et al. Aminopeptidase secreted by Chromobacterium sp. Panama inhibits dengue virus infection by degrading the E protein[J]. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 2018, 12(4): e0006443. |
| 116 | YU X, TONG L Q, ZHANG L M, et al. Lipases secreted by a gut bacterium inhibit arbovirus transmission in mosquitoes[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2022, 18(6): e1010552. |
| 117 | RAMIREZ J L, SOUZA-NETO J, TORRES COSME R, et al. Reciprocal tripartite interactions between the Aedes aegypti midgut microbiota, innate immune system and dengue virus influences vector competence[J]. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 2012, 6(3): e1561. |
| 118 | APTE-DESHPANDE A, PAINGANKAR M, GOKHALE M D, et al. Serratia odorifera a midgut inhabitant of Aedes aegypti mosquito enhances its susceptibility to dengue-2 virus[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(7): e40401. |
| 119 | ANGLERÓ-RODRÍGUEZ Y I, TALYULI O A, BLUMBERG B J, et al. An Aedes aegypti-associated fungus increases susceptibility to dengue virus by modulating gut trypsin activity[J]. eLife, 2017, 6: e28844. |
| 120 | DONG Y M, MORTON J C Jr, RAMIREZ J L, et al. The entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana activate toll and JAK-STAT pathway-controlled effector genes and anti-dengue activity in Aedes aegypti [J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2012, 42(2): 126-132. |
| 121 | GARZA-HERNÁNDEZ J A, RODRÍGUEZ-PÉREZ M A, SALAZAR M I, et al. Vectorial capacity of Aedes aegypti for dengue virus type 2 is reduced with co-infection of Metarhizium anisopliae [J]. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 2013, 7(3): e2013. |
| 122 | NGUYEN N M, KIEN D THI HUE, TUAN T V, et al. Host and viral features of human dengue cases shape the population of infected and infectious Aedes aegypti mosquitoes[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(22): 9072-9077. |
| 123 | WAGAR Z L, TREE M O, MPOY M C, et al. Low density lipopolyprotein inhibits flavivirus acquisition in Aedes aegypti [J]. Insect Molecular Biology, 2017, 26(6): 734-742. |
| 124 | BOTTINO-ROJAS V, TALYULI O A, JUPATANAKUL N, et al. Heme signaling impacts global gene expression, immunity and dengue virus infectivity in Aedes aegypti [J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(8): e0135985. |
| 125 | LIU J Y, LIU Y, NIE K X, et al. Flavivirus NS1 protein in infected host sera enhances viral acquisition by mosquitoes[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2016, 1: 16087. |
| 126 | LIU Y, LIU J Y, DU S Y, et al. Evolutionary enhancement of Zika virus infectivity in Aedes aegypti mosquitoes[J]. Nature, 2017, 545(7655): 482-486. |
| 127 | WU P, YU X, WANG P H, et al. Arbovirus lifecycle in mosquito: acquisition, propagation and transmission[J]. Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine, 2019, 21: e1. |
| 128 | WICHIT S, DIOP F, HAMEL R, et al. Aedes aegypti saliva enhances chikungunya virus replication in human skin fibroblasts via inhibition of the typeⅠinterferon signaling pathway[J]. Infection, Genetics and Evolution, 2017, 55: 68-70. |
| 129 | CERNY D, HANIFFA M, SHIN A, et al. Selective susceptibility of human skin antigen presenting cells to productive dengue virus infection[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2014, 10(12): e1004548. |
| 130 | SCHMID M A, HARRIS E. Monocyte recruitment to the dermis and differentiation to dendritic cells increases the targets for dengue virus replication[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2014, 10(12): e1004541. |
| 131 | HAMEL R, DEJARNAC O, WICHIT S, et al. Biology of Zika virus infection in human skin cells[J]. Journal of Virology, 2015, 89(17): 8880-8896. |
| 132 | SCHAEFFER E, FLACHER V, PAPAGEORGIOU V, et al. Dermal CD14+ dendritic cell and macrophage infection by dengue virus is stimulated by interleukin-4[J]. The Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 2015, 135(7): 1743-1751. |
| 133 | MACDONALD G H, JOHNSTON R E. Role of dendritic cell targeting in Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus pathogenesis[J]. Journal of Virology, 2000, 74(2): 914-922. |
| 134 | GARDNER C L, BURKE C W, TESFAY M Z, et al. Eastern and Venezuelan equine encephalitis viruses differ in their ability to infect dendritic cells and macrophages: impact of altered cell tropism on pathogenesis[J]. Journal of Virology, 2008, 82(21): 10634-10646. |
| 135 | DAVISON A M, KING N J C. Accelerated dendritic cell differentiation from migrating Ly6C(lo) bone marrow monocytes in early dermal West Nile virus infection[J]. Journal of Immunology, 2011, 186(4): 2382-2396. |
| 136 | WU S J L, GROUARD-VOGEL G, SUN W, et al. Human skin Langerhans cells are targets of dengue virus infection[J]. Nature Medicine, 2000, 6(7): 816-820. |
| 137 | DIAMOND M S, SHRESTHA B, MEHLHOP E, et al. Innate and adaptive immune responses determine protection against disseminated infection by West Nile encephalitis virus[J]. Viral Immunology, 2003, 16(3): 259-278. |
| 138 | STYER L M, LIM P Y, LOUIE K L, et al. Mosquito saliva causes enhancement of West Nile virus infection in mice[J]. Journal of Virology, 2011, 85(4): 1517-1527. |
| 139 | SCHNEIDER B S, SOONG L, GIRARD Y A, et al. Potentiation of West Nile encephalitis by mosquito feeding[J]. Viral Immunology, 2006, 19(1): 74-82. |
| 140 | COX J, MOTA J, SUKUPOLVI-PETTY S, et al. Mosquito bite delivery of dengue virus enhances immunogenicity and pathogenesis in humanized mice[J]. Journal of Virology, 2012, 86(14): 7637-7649. |
| 141 | SCHNEIDER B S, HIGGS S. The enhancement of arbovirus transmission and disease by mosquito saliva is associated with modulation of the host immune response[J]. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 2008, 102(5): 400-408. |
| 142 | PINGEN M, SCHMID M A, HARRIS E, et al. Mosquito biting modulates skin response to virus infection[J]. Trends in Parasitology, 2017, 33(8): 645-657. |
| 143 | URAKI R, HASTINGS A K, MARIN-LOPEZ A, et al. Aedes aegypti AgBR1 antibodies modulate early Zika virus infection of mice[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2019, 4(6): 948-955. |
| 144 | URAKI R, HASTINGS A K, BRACKNEY D E, et al. AgBR1 antibodies delay lethal Aedes aegypti-borne West Nile virus infection in mice[J]. Npj Vaccines, 2019, 4: 23. |
| 145 | SURASOMBATPATTANA P, EKCHARIYAWAT P, HAMEL R, et al. Aedes aegypti saliva contains a prominent 34 kDa protein that strongly enhances dengue virus replication in human keratinocytes[J]. The Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 2014, 134(1): 281-284. |
| 146 | MCCRACKEN M K, CHRISTOFFERSON R C, CHISENHALL D M, et al. Analysis of early dengue virus infection in mice as modulated by Aedes aegypti probing[J]. Journal of Virology, 2014, 88(4): 1881-1889. |
| 147 | JIN L, GUO X M, SHEN C B, et al. Salivary factor LTRIN from Aedes aegypti facilitates the transmission of Zika virus by interfering with the lymphotoxin-β receptor[J]. Nature Immunology, 2018, 19(4): 342-353. |
| 148 | CONWAY M J, WATSON A M, COLPITTS T M, et al. Mosquito saliva serine protease enhances dissemination of dengue virus into the mammalian host[J]. Journal of Virology, 2014, 88(1): 164-175. |
| 149 | SCHMID M A, GLASNER D R, SHAH S, et al. Mosquito saliva increases endothelial permeability in the skin, immune cell migration, and dengue pathogenesis during antibody-dependent enhancement[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2016, 12(6): e1005676. |
| 150 | MOYA A, HOLMES E C, GONZÁLEZ-CANDELAS F. The population genetics and evolutionary epidemiology of RNA viruses[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2004, 2(4): 279-288. |
| 151 | DOLAN P T, WHITFIELD Z J, ANDINO R. Mechanisms and concepts in RNA virus population dynamics and evolution[J]. Annual Review of Virology, 2018, 5(1): 69-92. |
| 152 | MUSTAFA M S, RASOTGI V, JAIN S, et al. Discovery of fifth serotype of dengue virus (DENV-5): a new public health dilemma in dengue control[J]. Medical Journal Armed Forces India, 2015, 71(1): 67-70. |
| 153 | DÍAZ F J, BLACK W C IV, FARFÁN-ALE J A, et al. Dengue virus circulation and evolution in Mexico: a phylogenetic perspective[J]. Archives of Medical Research, 2006, 37(6): 760-773. |
| 154 | ZHANG C L, MAMMEN M P Jr, CHINNAWIROTPISAN P, et al. Clade replacements in dengue virus serotypes 1 and 3 are associated with changing serotype prevalence[J]. Journal of Virology, 2005, 79(24): 15123-15130. |
| 155 | LEWIS J A, CHANG G J, LANCIOTTI R S, et al. Phylogenetic relationships of dengue-2 viruses[J]. Virology, 1993, 197(1): 216-224. |
| 156 | RICO-HESSE R, HARRISON L M, NISALAK A, et al. Molecular evolution of dengue type 2 virus in Thailand[J]. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 1998, 58(1): 96-101. |
| 157 | MESSER W B, GUBLER D J, HARRIS E, et al. Emergence and global spread of a dengue serotype 3, subtype Ⅲvirus[J]. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 2003, 9(7): 800-809. |
| 158 | LANCIOTTI R S, LEWIS J G, GUBLER D J, et al. Molecular evolution and epidemiology of dengue-3 viruses[J]. The Journal of General Virology, 1994, 75 ( Pt 1): 65-75. |
| 159 | WANG E, NI H, XU R, et al. Evolutionary relationships of endemic/epidemic and sylvatic dengue viruses[J]. Journal of Virology, 2000, 74(7): 3227-3234. |
| 160 | LANCIOTTI R S, GUBLER D J, TRENT D W. Molecular evolution and phylogeny of dengue-4 viruses[J]. The Journal of General Virology, 1997, 78 ( Pt 9): 2279-2284. |
| 161 | BALMASEDA A, HAMMOND S N, PÉREZ L, et al. Serotype-specific differences in clinical manifestations of dengue[J]. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 2006, 74(3): 449-456. |
| 162 | BURKE D S, NISALAK A, JOHNSON D E, et al. A prospective study of dengue infections in Bangkok[J]. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 1988, 38(1): 172-180. |
| 163 | GUZMÁN M G, KOURÍ G, VALDÉS L, et al. Enhanced severity of secondary dengue-2 infections: death rates in 1981 and 1997 Cuban outbreaks[J]. Revista Panamericana De Salud Publica=Pan American Journal of Public Health, 2002, 11(4): 223-227. |
| 164 | NISALAK A, ENDY T P, NIMMANNITYA S, et al. Serotype-specific dengue virus circulation and dengue disease in Bangkok, Thailand from 1973 to 1999[J]. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 2003, 68(2): 191-202. |
| 165 | SANGKAWIBHA N, ROJANASUPHOT S, AHANDRIK S, et al. Risk factors in dengue shock syndrome: a prospective epidemiologic study in rayong, Thailand:Ⅰ. the 1980 outbreak[J]. American Journal of Epidemiology, 1984, 120(5): 653-669. |
| 166 | THEIN S, AUNG M M, SHWE T N, et al. Risk factors in dengue shock syndrome[J]. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 1997, 56(5): 566-572. |
| 167 | GRAHAM R R, JUFFRIE M, TAN R, et al. A prospective seroepidemiologic study on dengue in children four to nine years of age in Yogyakarta, IndonesiaⅠ. studies in 1995—1996[J]. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 1999, 61(3): 412-419. |
| 168 | HARRIS E, VIDEA E, PÉREZ L, et al. Clinical, epidemiologic, and virologic features of dengue in the 1998 epidemic in Nicaragua[J]. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 2000, 63(1/2): 5-11. |
| 169 | MESSER W B, VITARANA U T, SIVANANTHAN K, et al. Epidemiology of dengue in Sri Lanka before and after the emergence of epidemic dengue hemorrhagic fever[J]. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 2002, 66(6): 765-773. |
| 170 | LEITMEYER K C, VAUGHN D W, WATTS D M, et al. Dengue virus structural differences that correlate with pathogenesis[J]. Journal of Virology, 1999, 73(6): 4738-4747. |
| 171 | COLOGNA R, RICO-HESSE R. American genotype structures decrease dengue virus output from human monocytes and dendritic cells[J]. Journal of Virology, 2003, 77(7): 3929-3938. |
| 172 | PRYOR M J, CARR J M, HOCKING H, et al. Replication of dengue virus type 2 in human monocyte-derived macrophages: comparisons of isolates and recombinant viruses with substitutions at amino acid 390 in the envelope glycoprotein[J]. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 2001, 65(5): 427-434. |
| 173 | OHAINLE M, BALMASEDA A, MACALALAD A R, et al. Dynamics of dengue disease severity determined by the interplay between viral genetics and serotype-specific immunity[J]. Science Translational Medicine, 2011, 3(114): 114-128. |
| 174 | CHEN H L, LIN S R, LIU H F, et al. Evolution of dengue virus type 2 during two consecutive outbreaks with an increase in severity in southern Taiwan in 2001—2002[J]. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 2008, 79(4): 495-505. |
| 175 | MUSSO D, GUBLER D J. Zika virus[J]. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 2016, 29(3): 487-524. |
| 176 | ENFISSI A, CODRINGTON J, ROOSBLAD J, et al. Zika virus genome from the americas[J]. Lancet, 2016, 387(10015): 227-228. |
| 177 | WINKLER G, RANDOLPH V B, CLEAVES G R, et al. Evidence that the mature form of the flavivirus nonstructural protein NS1 is a dimer[J]. Virology, 1988, 162(1): 187-196. |
| 178 | ALCON S, TALARMIN A, DEBRUYNE M, et al. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay specific to Dengue virus type 1 nonstructural protein NS1 reveals circulation of the antigen in the blood during the acute phase of disease in patients experiencing primary or secondary infections[J]. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 2002, 40(2): 376-381. |
| 179 | GUO M J, HUI L X, NIE Y W, et al. ZIKV viral proteins and their roles in virus-host interactions[J]. Science China Life Sciences, 2021, 64(5): 709-719. |
| 180 | YU X, SHAN C, ZHU Y B, et al. A mutation-mediated evolutionary adaptation of Zika virus in mosquito and mammalian host[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2021, 118(42): e2113015118. |
| 181 | ZHU Z, CHAN J F W, TEE K M, et al. Comparative genomic analysis of pre-epidemic and epidemic Zika virus strains for virological factors potentially associated with the rapidly expanding epidemic[J]. Emerging Microbes & Infections, 2016, 5(1): 1-12. |
| 182 | YUAN L, HUANG X Y, LIU Z Y, et al. A single mutation in the prM protein of Zika virus contributes to fetal microcephaly[J]. Science, 2017, 358(6365): 933-936. |
| 183 | SHAN C, XIA H J, HALLER S L, et al. A Zika virus envelope mutation preceding the 2015 epidemic enhances virulence and fitness for transmission[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(33): 20190-20197. |
| 184 | GEERLING E, STEFFEN T L, BRIEN J D, et al. Current flavivirus research important for vaccine development[J]. Vaccines, 2020, 8(3): 477. |
| 185 | THEILER M, SMITH H H. The use of yellow fever virus modified by in vitro cultivation for human immunization[J]. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 1937, 65(6): 787-800. |
| 186 | BOIGARD H, ALIMOVA A, MARTIN G R, et al. Zika virus-like particle (VLP) based vaccine[J]. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 2017, 11(5): e0005608. |
| 187 | URAKAMI A, NGWE TUN M M, MOI M L, et al. An envelope-modified tetravalent dengue virus-like-particle vaccine has implications for flavivirus vaccine design[J]. Journal of Virology, 2017, 91(23): e01181-e01117. |
| 188 | RICHNER J M, HIMANSU S, DOWD K A, et al. Modified mRNA vaccines protect against Zika virus infection[J]. Cell, 2017, 168(6): 1114-1125.e10. |
| 189 | COLLINS N D, BARRETT A D T. Live attenuated yellow fever 17D vaccine: a legacy vaccine still controlling outbreaks in modern day[J]. Current Infectious Disease Reports, 2017, 19(3): 14. |
| 190 | SATCHIDANANDAM V. Japanese encephalitis vaccines[J]. Current Treatment Options in Infectious Diseases, 2020, 12(4): 375-386. |
| 191 | GUY B, BARRERE B, MALINOWSKI C, et al. From research to phaseⅢ: preclinical, industrial and clinical development of the Sanofi Pasteur tetravalent dengue vaccine[J]. Vaccine, 2011, 29(42): 7229-7241. |
| 192 | THOMAS R E. Yellow fever vaccine-associated viscerotropic disease: current perspectives[J]. Drug Design, Development and Therapy, 2016, 10: 3345-3353. |
| 193 | DEM MARTINS R, PAVÃO A L B, DE OLIVEIRA P M N, et al. Adverse events following yellow fever immunization: report and analysis of 67 neurological cases in Brazil[J]. Vaccine, 2014, 32(49): 6676-6682. |
| 194 | BREUGELMANS J G, LEWIS R F, AGBENU E, et al. Adverse events following yellow fever preventive vaccination campaigns in eight African countries from 2007 to 2010[J]. Vaccine, 2013, 31(14): 1819-1829. |
| 195 | MCMAHON A W, EIDEX R B, MARFIN A A, et al. Neurologic disease associated with 17D-204 yellow fever vaccination: a report of 15 cases[J]. Vaccine, 2007, 25(10): 1727-1734. |
| 196 | BURCHARD G D, CAUMES E, CONNOR B A, et al. Expert opinion on vaccination of travelers against Japanese encephalitis[J]. Journal of Travel Medicine, 2009, 16(3): 204-216. |
| 197 | HADINEGORO S R, ARREDONDO-GARCÍA J L, CAPEDING M R, et al. Efficacy and long-term safety of a dengue vaccine in regions of endemic disease[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 2015, 373(13): 1195-1206. |
| 198 | SRIDHAR S, LUEDTKE A, LANGEVIN E, et al. Effect of dengue serostatus on dengue vaccine safety and efficacy[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 2018, 379(4): 327-340. |
| 199 | GEORGE J, VALIANT W G, MATTAPALLIL M J, et al. Prior exposure to Zika virus significantly enhances peak dengue-2 viremia in rhesus macaques[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 10498. |
| 200 | DEJNIRATTISAI W, SUPASA P, WONGWIWAT W, et al. Dengue virus sero-cross-reactivity drives antibody-dependent enhancement of infection with Zika virus[J]. Nature Immunology, 2016, 17(9): 1102-1108. |
| 201 | BARDINA S V, BUNDUC P, TRIPATHI S, et al. Enhancement of Zika virus pathogenesis by preexisting antiflavivirus immunity[J]. Science, 2017, 356(6334): 175-180. |
| 202 | FOWLER A M, TANG W W, YOUNG M P, et al. Maternally acquired Zika antibodies enhance dengue disease severity in mice[J]. Cell Host & Microbe, 2018, 24(5): 743-750. |
| 203 | KATZELNICK L C, GRESH L, HALLORAN M E, et al. Antibody-dependent enhancement of severe dengue disease in humans[J]. Science, 2017, 358(6365): 929-932. |
| 204 | KATZELNICK L C, NARVAEZ C, ARGUELLO S, et al. Zika virus infection enhances future risk of severe dengue disease[J]. Science, 2020, 369(6507): 1123-1128. |
| 205 | RAVIPRAKASH K, PORTER K R, KOCHEL T J, et al. Dengue virus type 1 DNA vaccine induces protective immune responses in rhesus macaques[J]. The Journal of General Virology, 2000, 81(Pt 7): 1659-1667. |
| 206 | KHETARPAL N, KHANNA I. Dengue fever: causes, complications, and vaccine strategies[J]. Journal of Immunology Research, 2016, 2016: 6803098. |
| 207 | WONG G, GAO G F. An mRNA-based vaccine strategy against Zika[J]. Cell Research, 2017, 27(9): 1077-1078. |
| 208 | JIMÉNEZ DE OYA N, ESCRIBANO-ROMERO E, BLÁZQUEZ A B, et al. Current progress of avian vaccines against west Nile virus[J]. Vaccines, 2019, 7(4): 126. |
| 209 | KHOU C, PARDIGON N. Identifying attenuating mutations: tools for a new vaccine design against flaviviruses[J]. Intervirology, 2017, 60(1/2): 8-18. |
| 210 | LONDONO-RENTERIA B, TROUPIN A, COLPITTS T M. Arbovirosis and potential transmission blocking vaccines[J]. Parasites & Vectors, 2016, 9(1): 516. |
| 211 | WU S F, LEE C J, LIAO C L, et al. Antiviral effects of an iminosugar derivative on flavivirus infections[J]. Journal of Virology, 2002, 76(8): 3596-3604. |
| 212 | TCHANKOUO-NGUETCHEU S, KHUN H, PINCET L, et al. Differential protein modulation in midguts of Aedes aegypti infected with chikungunya and dengue 2 viruses[J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5(10): e13149. |
| 213 | THAM H W, BALASUBRAMANIAM V R M T, TEJO B A, et al. CPB1 of Aedes aegypti interacts with DENV2 E protein and regulates intracellular viral accumulation and release from midgut cells[J]. Viruses, 2014, 6(12): 5028-5046. |
| 214 | DINGLASAN R R, VALENZUELA J G, AZAD A F. Sugar epitopes as potential universal disease transmission blocking targets[J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2005, 35(1): 1-10. |
| 215 | LIU K, QIAN Y J, JUNG Y S, et al. mosGCTL-7, a C-type lectin protein, mediates Japanese encephalitis virus infection in mosquitoes[J]. Journal of Virology, 2017, 91(10): e01348-e01316. |
| 216 | PERERA-LECOIN M, MEERTENS L, CARNEC X, et al. Flavivirus entry receptors: an update[J]. Viruses, 2014, 6(1): 69-88. |
| 217 | PERERA R, KHALIQ M, KUHN R J. Closing the door on flaviviruses: entry as a target for antiviral drug design[J]. Antiviral Research, 2008, 80(1): 11-22. |
| 218 | LI P C, JANG J, HSIA C Y, et al. Small molecules targeting the flavivirus E protein with broad-spectrum activity and antiviral efficacy in vivo [J]. ACS Infectious Diseases, 2019, 5(3): 460-472. |
| 219 | KAMPMANN T, YENNAMALLI R, CAMPBELL P, et al. In silico screening of small molecule libraries using the dengue virus envelope E protein has identified compounds with antiviral activity against multiple flaviviruses[J]. Antiviral Research, 2009, 84(3): 234-241. |
| 220 | ZHANG W, CHIPMAN P R, CORVER J, et al. Visualization of membrane protein domains by cryo-electron microscopy of dengue virus[J]. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 2003, 10(11): 907-912. |
| 221 | COSTIN J M, JENWITHEESUK E, LOK S M, et al. Structural optimization and de novo design of dengue virus entry inhibitory peptides[J]. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 2010, 4(6): e721. |
| 222 | ALTMEYER R. Virus attachment and entry offer numerous targets for antiviral therapy[J]. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2004, 10(30): 3701-3712. |
| 223 | DIGHE S N, EKWUDU O, DUA K, et al. Recent update on anti-dengue drug discovery[J]. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2019, 176: 431-455. |
| 224 | KANG C B, KELLER T H, LUO D H. Zika virus protease: an antiviral drug target[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 2017, 25(10): 797-808. |
| 225 | NITSCHE C. Proteases from dengue, West Nile and Zika viruses as drug targets[J]. Biophysical Reviews, 2019, 11(2): 157-165. |
| 226 | KOK W M. New developments in flavivirus drug discovery[J]. Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery, 2016, 11(5): 433-445. |
| 227 | RAY D, SHI P Y. Recent advances in flavivirus antiviral drug discovery and vaccine development[J]. Recent Patents on Anti-Infective Drug Discovery, 2006, 1(1): 45-55. |
| 228 | MASTRANGELO E, PEZZULLO M, DE BURGHGRAEVE T, et al. Ivermectin is a potent inhibitor of flavivirus replication specifically targeting NS3 helicase activity: new prospects for an old drug[J]. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 2012, 67(8): 1884-1894. |
| 229 | BOLLATI M, ALVAREZ K, ASSENBERG R, et al. Structure and functionality in flavivirus NS-proteins: perspectives for drug design[J]. Antiviral Research, 2010, 87(2): 125-148. |
| 230 | CHATRIN C, TALAPATRA S K, CANARD B, et al. The structure of the binary methyltransferase-SAH complex from Zika virus reveals a novel conformation for the mechanism of mRNA capping[J]. Oncotarget, 2018, 9(3): 3160-3171. |
| 231 | ZHOU Y S, RAY D, ZHAO Y W, et al. Structure and function of flavivirus NS5 methyltransferase[J]. Journal of Virology, 2007, 81(8): 3891-3903. |
| 232 | AFAQ S, ATIYA A, MALIK A, et al. Analysis of methyltransferase (MTase) domain from Zika virus (ZIKV)[J]. Bioinformation, 2020, 16(3): 229-235. |
| 233 | BRECHER M, CHEN H, LI Z, et al. Identification and characterization of novel broad-spectrum inhibitors of the flavivirus methyltransferase[J]. ACS Infectious Diseases, 2015, 1(8): 340-349. |
| 234 | NOBLE C G, LI S H, DONG H P, et al. Crystal structure of dengue virus methyltransferase without S-adenosyl-L-methionine[J]. Antiviral Research, 2014, 111: 78-81. |
| 235 | WANG B X, THURMOND S, HAI R, et al. Structure and function of Zika virus NS5 protein: perspectives for drug design[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2018, 75(10): 1723-1736. |
| 236 | JAIN R, BUTLER K V, COLOMA J, et al. Development of a S-adenosylmethionine analog that intrudes the RNA-cap binding site of Zika methyltransferase[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 1632. |
| 237 | LIM S V, RAHMAN M B A, TEJO B A. Structure-based and ligand-based virtual screening of novel methyltransferase inhibitors of the dengue virus[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2011, 12(): S24. |
| 238 | BRECHER M, CHEN H, LIU B B, et al. Novel broad spectrum inhibitors targeting the flavivirus methyltransferase[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(6): e0130062. |
| 239 | SIQUEIRA-BATISTA R, DE SOUZA BAYÃO T, CARMO CUPERTINO M DO, et al. Sofosbuvir use for yellow fever: a new perspective treatment[J]. Pathogens and Global Health, 2019, 113(5): 207-208. |
| 240 | BULLARD-FEIBELMAN K M, GOVERO J, ZHU Z, et al. The FDA-approved drug sofosbuvir inhibits Zika virus infection[J]. Antiviral Research, 2017, 137: 134-140. |
| 241 | FERREIRA A C, ZAVERUCHA-DO-VALLE C, REIS P A, et al. Sofosbuvir protects Zika virus-infected mice from mortality, preventing short- and long-term sequelae[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 9409. |
| 242 | JACOBS S, DELANG L E, VERBEKEN E, et al. A viral polymerase inhibitor reduces Zika virus replication in the reproductive organs of male mice[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(9): 2122. |
| 243 | IVANOVA T, HARDES K, KALLIS S, et al. Optimization of substrate-analogue furin inhibitors[J]. ChemMedChem, 2017, 12(23): 1953-1968. |
| 244 | SKRZYPEK R, CALLAGHAN R. The "pushmi-pullyu" of resistance to chloroquine in malaria[J]. Essays in Biochemistry, 2017, 61(1): 167-175. |
| 245 | BYRD C M, DAI D C, GROSENBACH D W, et al. A novel inhibitor of dengue virus replication that targets the capsid protein[J]. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 2013, 57(1): 15-25. |
| 246 | QIN C F, QIN E D. Capsid-targeted viral inactivation can destroy dengue 2 virus from within in vitro [J]. Archives of Virology, 2006, 151(2): 379-385. |
| 247 | STOERMER K A, MORRISON T E. Complement and viral pathogenesis[J]. Virology, 2011, 411(2): 362-373. |
| 248 | AKEY D L, BROWN W C, JOSE J, et al. Structure-guided insights on the role of NS1 in flavivirus infection[J]. BioEssays: News and Reviews in Molecular, Cellular and Developmental Biology, 2015, 37(5): 489-494. |
| 249 | SOMNUKE P, HAUHART R E, ATKINSON J P, et al. N-linked glycosylation of dengue virus NS1 protein modulates secretion, cell-surface expression, hexamer stability, and interactions with human complement[J]. Virology, 2011, 413(2): 253-264. |
| 250 | WATTERSON D, MODHIRAN N, YOUNG P R. The many faces of the flavivirus NS1 protein offer a multitude of options for inhibitor design[J]. Antiviral Research, 2016, 130: 7-18. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||