Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (2): 415-427.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-050
• Research Article • Previous Articles
Hybrid systems of virus and nano-gold conducting networks for electrochemical analysis
LIANG Xiaosheng1( ), GUO Yongchao2, MEN Dong2,4, ZHANG Xian’en3,4
), GUO Yongchao2, MEN Dong2,4, ZHANG Xian’en3,4
- 1.College of Life Science,South-Central University for Nationalities,Wuhan 430074,Hubei,China
2.State Key Laboratory of Virology,Wuhan Institute of Virology,Center for Biosafety Mega-Science,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Wuhan 430071,Hubei,China
3.National Laboratory of Biomacromolecules,CAS Center for Excellence in Biomacromolecules,Institute of Biophysics,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100101,China
4.University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
-
Received:2021-04-26Revised:2021-11-14Online:2022-05-11Published:2022-04-30 -
Contact:LIANG Xiaosheng
病毒-纳米金杂合导电网络结构在电化学分析的应用
- 1.中南民族大学生命科学学院,湖北 武汉 430074
2.中国科学院武汉病毒研究所,生物安全大科学研究中心,病毒学国家重点实验室,湖北 武汉 430071
3.中国科学院生物物理研究所,生物大分子科教融合卓越中心,生物大分子国家重点实验室,北京 100101
4.中国科学院大学,北京 100049
-
通讯作者:梁晓声 -
作者简介:梁晓声 (1984—),男,博士,讲师。研究方向为纳米生物技术、纳米材料检测应用等。 E-mail:liangxs@mail.scuec.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2019YFA0904800)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LIANG Xiaosheng, GUO Yongchao, MEN Dong, ZHANG Xian’en. Hybrid systems of virus and nano-gold conducting networks for electrochemical analysis[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(2): 415-427.
梁晓声, 郭永超, 门冬, 张先恩. 病毒-纳米金杂合导电网络结构在电化学分析的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(2): 415-427.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2021-050
| 引物名称 | 序列(5'→3') |
|---|---|
| 6264mS | CGCCAAGCTTGCATGCCGCAGGTCCTC |
| 6264dn | GATAGCCTTTGTAGATCTCTC |
| 1381up | GGCATTACGTATTTTACCC |
| 1381S | CTTTCGCTGCAGAGGGTGAGGATC |
| 1381A | CTTTTGCGGGATCCTCACCCTCTGC |
| 1381dn | GCTATTAATTAATTTTCCC |
| GbS | GTATCGGGTTCTTCTCCTGATTCT |
| GbA | GATCAGAATCAGGAGAAGAACCCGATACTGCA |
Tab. 1 Primers for constructing of recombinant phage
| 引物名称 | 序列(5'→3') |
|---|---|
| 6264mS | CGCCAAGCTTGCATGCCGCAGGTCCTC |
| 6264dn | GATAGCCTTTGTAGATCTCTC |
| 1381up | GGCATTACGTATTTTACCC |
| 1381S | CTTTCGCTGCAGAGGGTGAGGATC |
| 1381A | CTTTTGCGGGATCCTCACCCTCTGC |
| 1381dn | GCTATTAATTAATTTTCCC |
| GbS | GTATCGGGTTCTTCTCCTGATTCT |
| GbA | GATCAGAATCAGGAGAAGAACCCGATACTGCA |
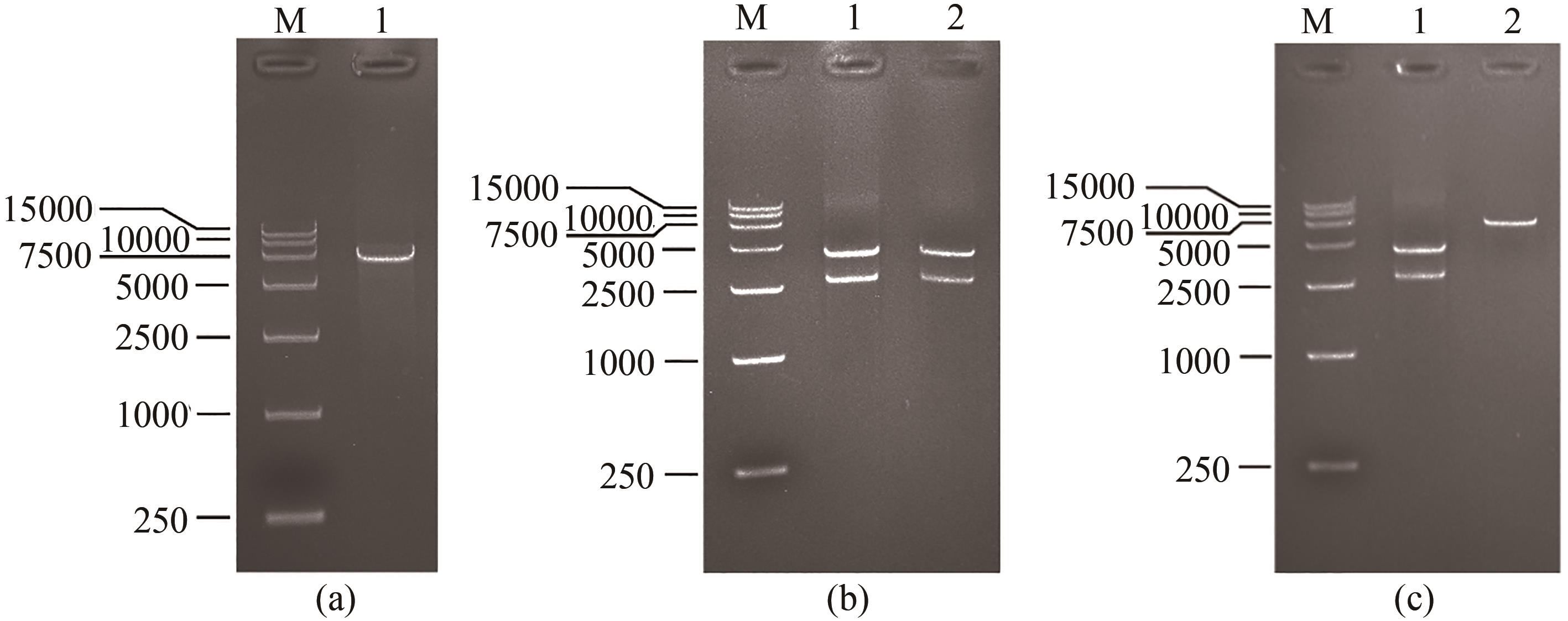
Fig. 2 Construction of gold-binding peptide displaying phage and its verificationM—Takara DL15000 DNA ladder. Lane (a) 1—Site 6264 mutated phage genome digested by PstⅠand BglⅡ. Lane (b) 1—Sites 1372 and 1381 mutated phage genome digested by PstⅠ and PacⅠ; 2—Sites 1372 and 1381 mutated phage genome digested by BamHⅠ and PacⅠ. Lane (c) 1—Gold-binding peptide sequence inserted phage genome digested by PstⅠ and PacⅠ; 2—Gold-binding peptide sequence inserted phage genome digested by BamHⅠ and PacⅠ
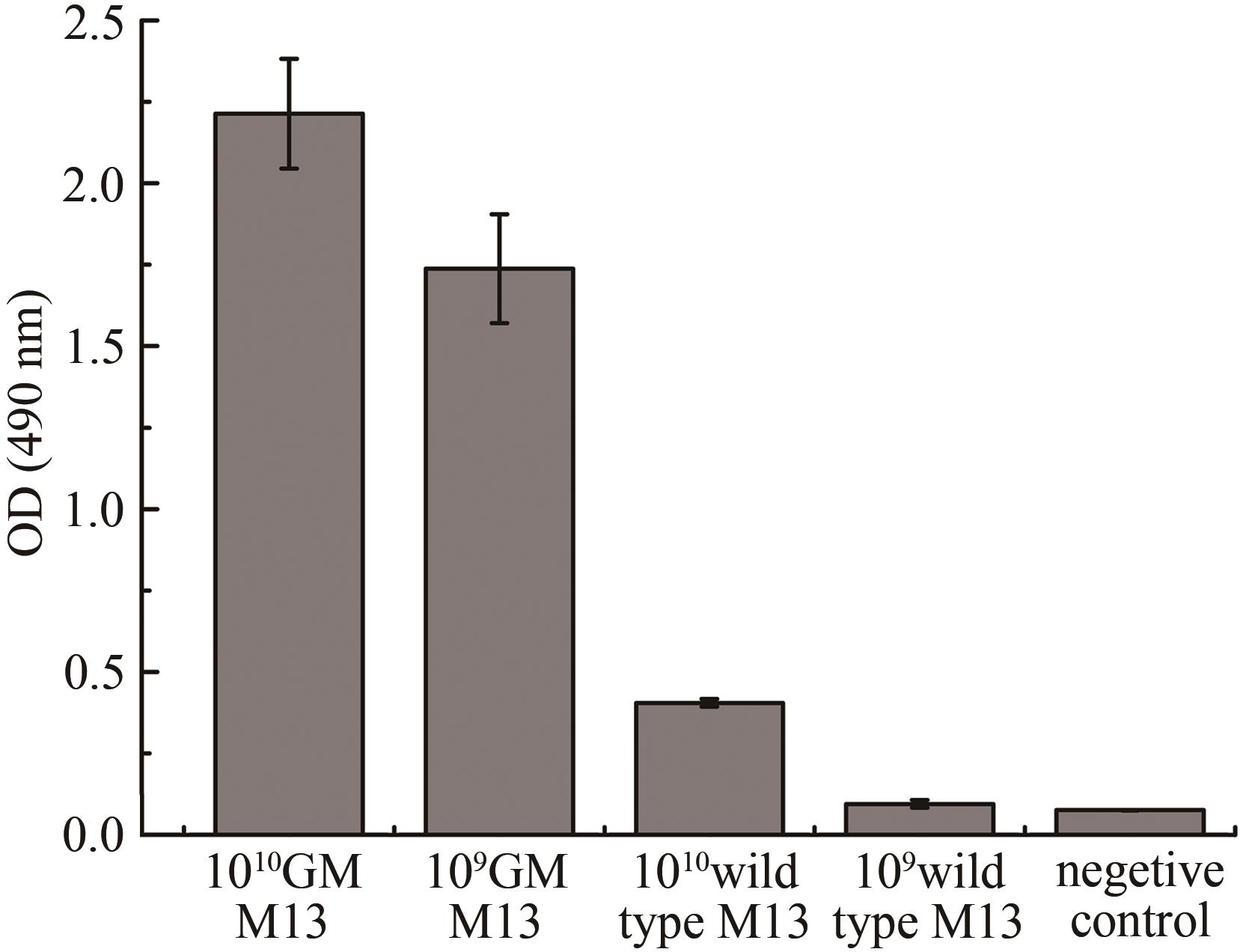
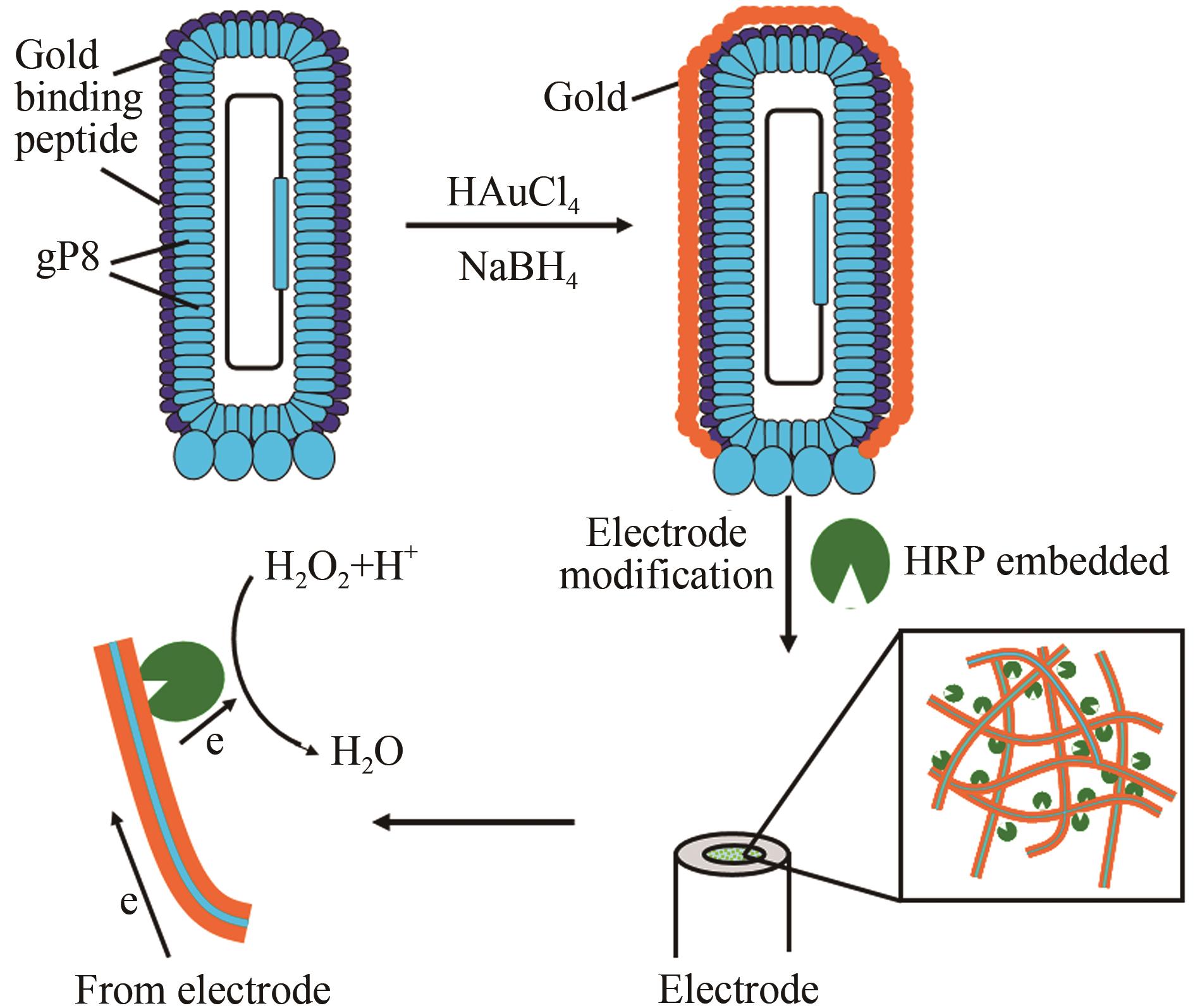
Fig. 3 Evaluation of gold-binding ability for GM M13 with silver enhancement(1010 GM M13 and 109 GM M13 refer to the genetically modified M13 with the titer of 1010 PFU and 109 PFU, respectively, and the silver enhancement GM M13 without gold nanoparticles is used as the control.)
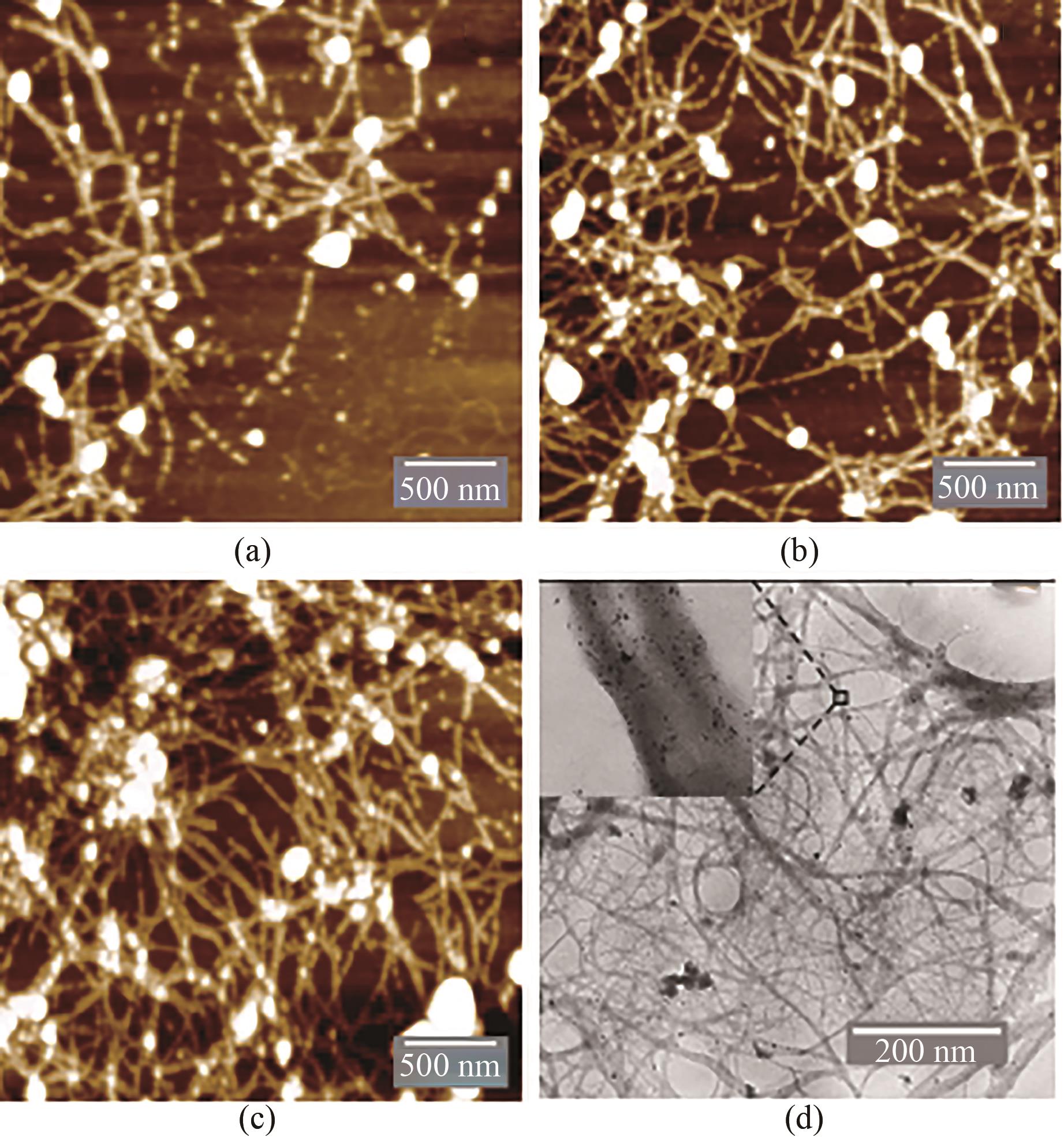
Fig. 4 AFM and TEM images for the Au-GM M13 complex formed under different reaction conditions(a) AFM images for 0.25 mmol/L HAuCl4, 1012 PFU/mL GM M13, 20 mmol/L Gly-Cl- and 2.5 mmol/L NaBH4; (b) AFM images for 0.375 mmol/L HAuCl4, 1012 PFU/mL GM M13, 20 mmol/L Gly-Cl- and 2.5 mmol/L NaBH4; (c) AFM images for 0.5 mmol/L HAuCl4, 1012 PFU/mL GM M13, 20 mmol/L Gly-Cl- and 2.5 mmol/L NaBH4; (d) TEM image for the Au-GM M13 complex. Complex forming conditions: 0.5 mmol/L HAuCl4, 1012 PFU/mL GM M13, 20 mmol/L Gly-Cl- and 2.5 mmol/L NaBH4
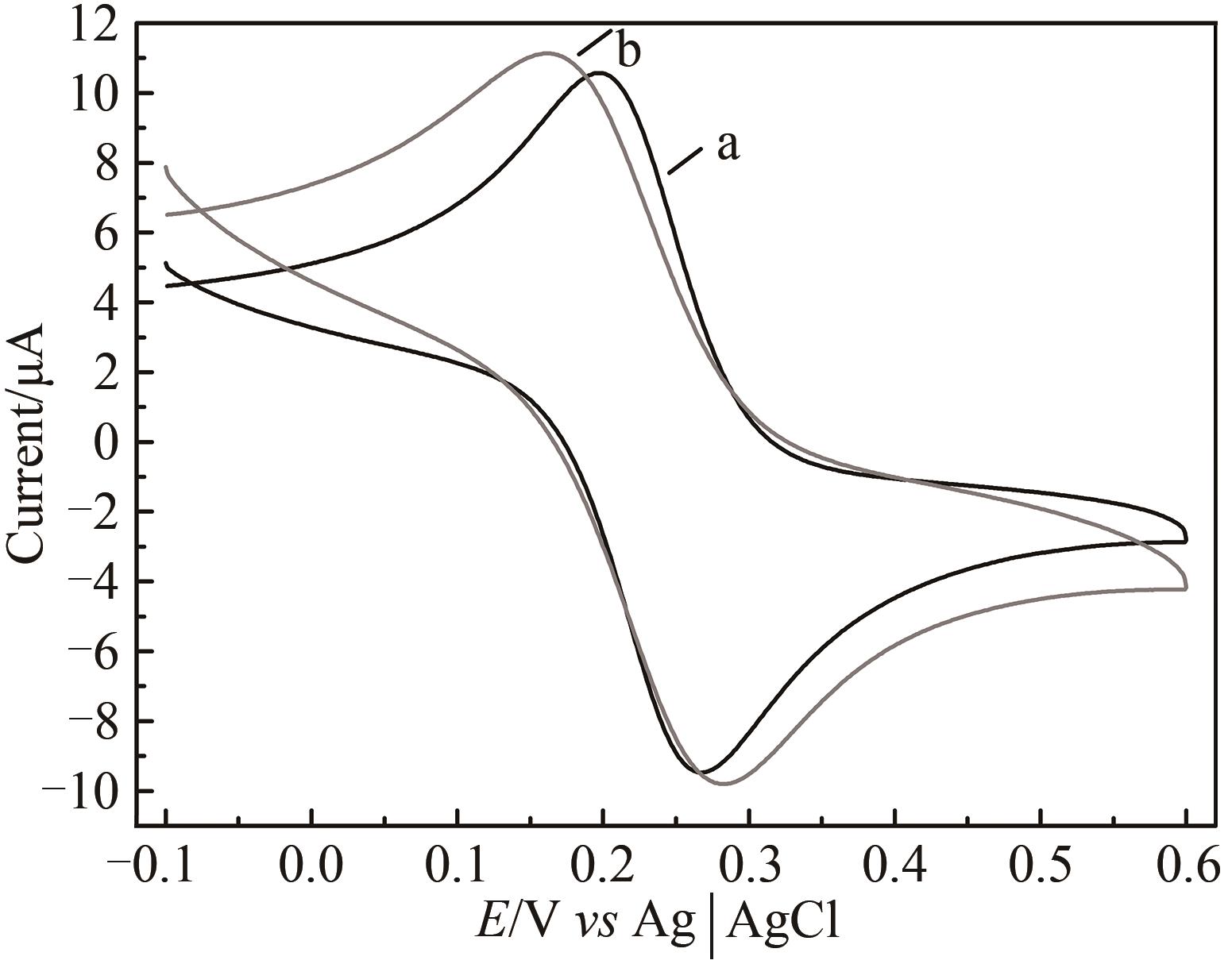
Fig. 5 Voltammograms of the HRP/Au-GM M13 electrode without (a) and with chitosan modifications (b)[Scan rate: 50 mV/s; buffer: PBS (10 mmol/L, pH 7.0) solution containing 0.1 mol/L KCl and 2 mmol/L [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-.]
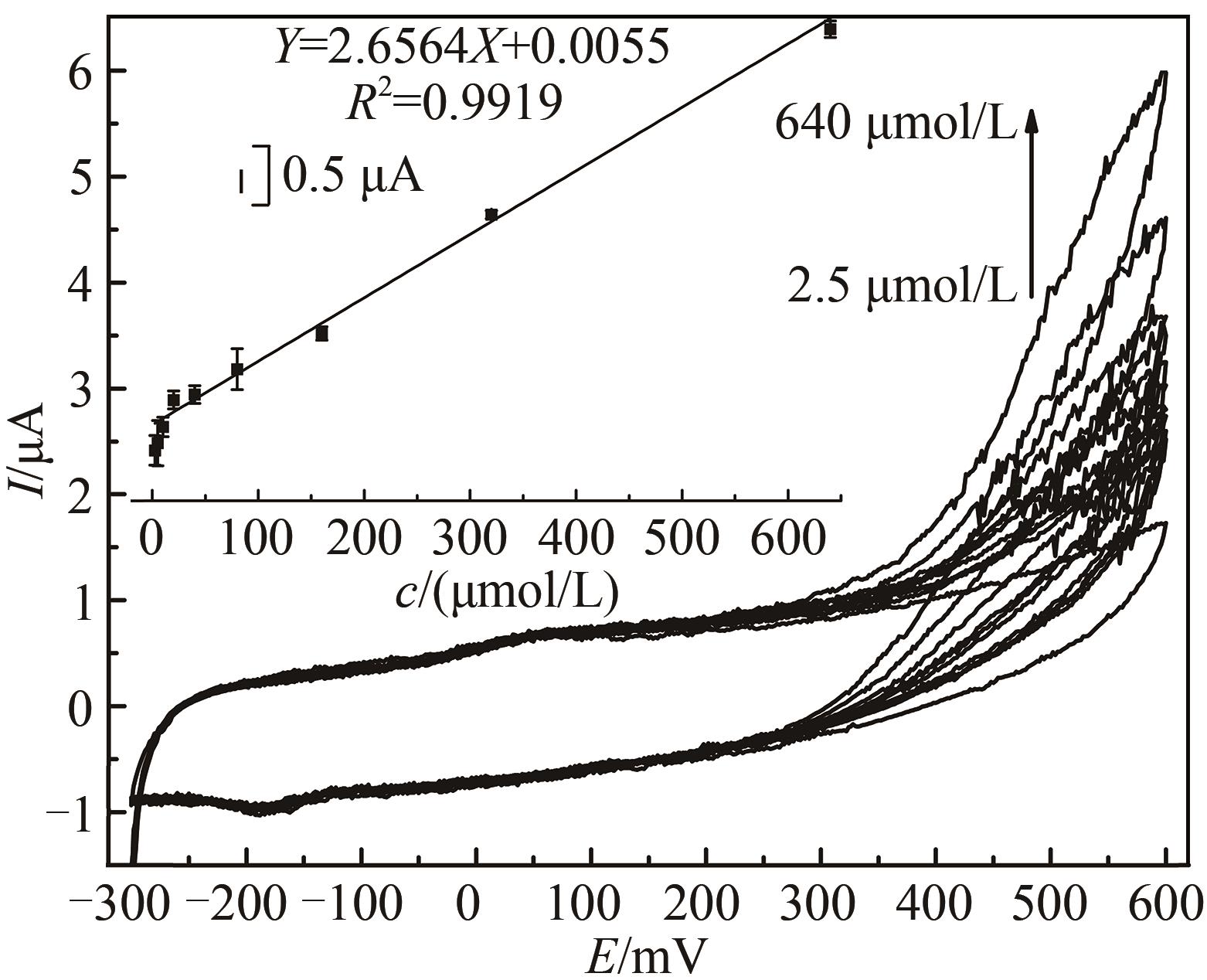
Fig. 6 Voltammograms of the HRP/Au-GM M13 electrode modified with chitosan at different concentrations of hydrogen peroxide[Scan rate: 20 mV/s for N2-saturated PBS (0.1 mol/L, pH 7.0). The curve peaks were obtained in response to H2O2 concentrations from 2.5 μmol/L to 640 μmol/L. The embedded image shows the calibration curve derived from the curves.]
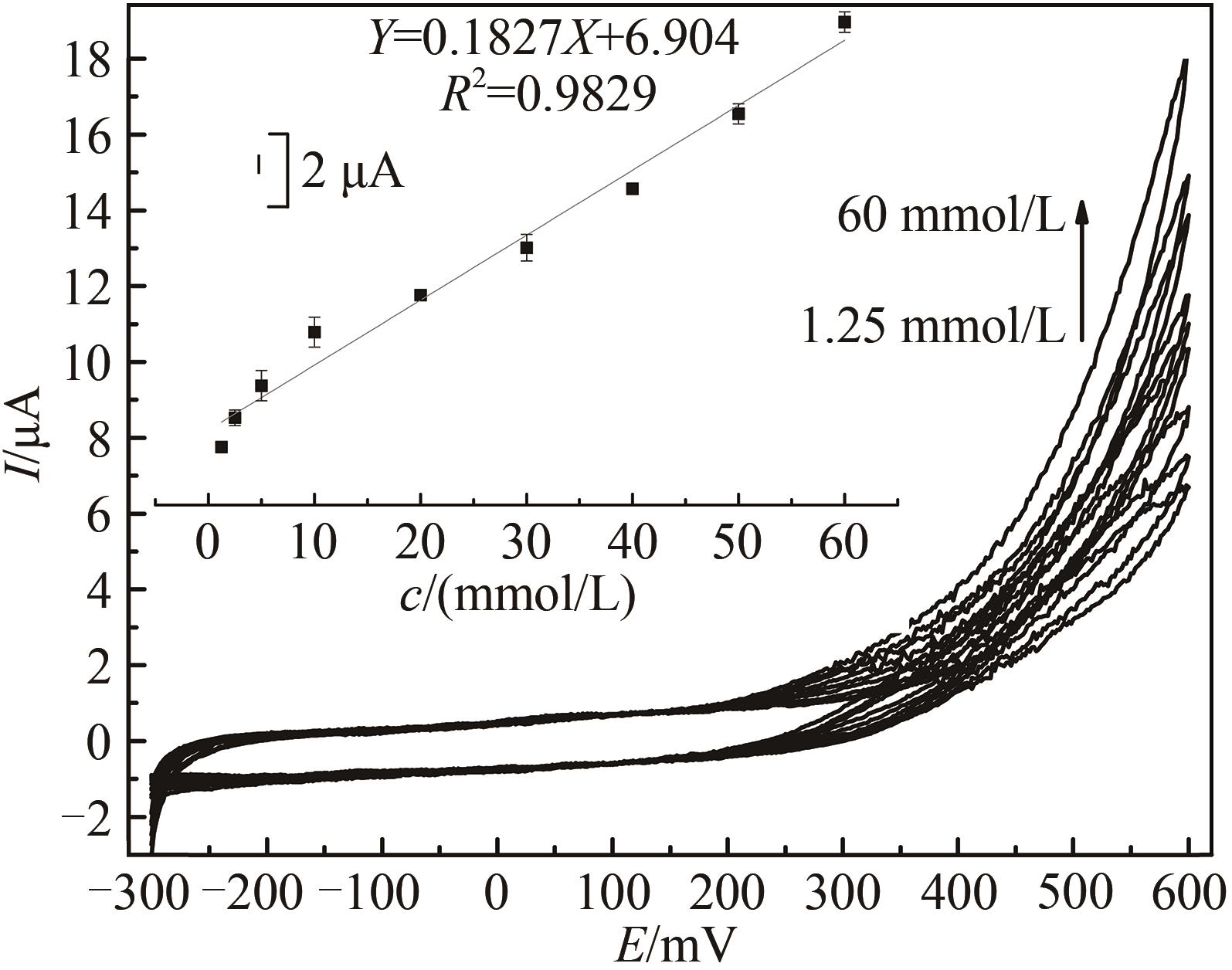
Fig. 7 Voltammograms of the HRP/Au-GM M13 electrode modified with chitosan at different concentrations of hydrogen peroxide from 640 μmol/L to 60 mmol/L[Scan rate: 20 mV/s for N2-saturated PBS (0.1 mol/L, pH 7.0). The embedded image shows the calibration curve derived from the curves.]
| 酶电极修饰方法 | 检测限 | Kmapp | 线性范围 | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cerasomes with AuNPs@Poly(Ionic Liquid)s | 3.3 μmol/L | — | 10~70 μmol/L | [ |
| Silicahydroxyapatite hybrid film | 0.35 μmol/L | 21.8 μmol/L | 1.0~100 μmol/L | [ |
| Methanobactin functionalized gold nanoparticles | — | 0.787 mmol/L | 52.9 μmol/L~0.64 mmol/L | [ |
| Gold nanoparticles on indium/tin oxide electrode | 2 μmol/L | 0.4 mmol/L | 8.0 μmol/L~3.0 mmol/L | [ |
| Cerasome | 0.83 mmol/L | — | 2.5~325 mmol/L | [ |
| Carbon nanotubes | 0.1 μmol/L | — | 0.3~200 μmol/L | [ |
| 纳米金-噬菌体复合物 | 0.32 μmol/L | 0.3 mmol/L | 2.5 μmol/L~60 mmol/L | 本研究 |
Tab. 2 Comparison of the analytical performance of enzyme-phage-gold modified electrode with other electrochemical biosensors
| 酶电极修饰方法 | 检测限 | Kmapp | 线性范围 | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cerasomes with AuNPs@Poly(Ionic Liquid)s | 3.3 μmol/L | — | 10~70 μmol/L | [ |
| Silicahydroxyapatite hybrid film | 0.35 μmol/L | 21.8 μmol/L | 1.0~100 μmol/L | [ |
| Methanobactin functionalized gold nanoparticles | — | 0.787 mmol/L | 52.9 μmol/L~0.64 mmol/L | [ |
| Gold nanoparticles on indium/tin oxide electrode | 2 μmol/L | 0.4 mmol/L | 8.0 μmol/L~3.0 mmol/L | [ |
| Cerasome | 0.83 mmol/L | — | 2.5~325 mmol/L | [ |
| Carbon nanotubes | 0.1 μmol/L | — | 0.3~200 μmol/L | [ |
| 纳米金-噬菌体复合物 | 0.32 μmol/L | 0.3 mmol/L | 2.5 μmol/L~60 mmol/L | 本研究 |
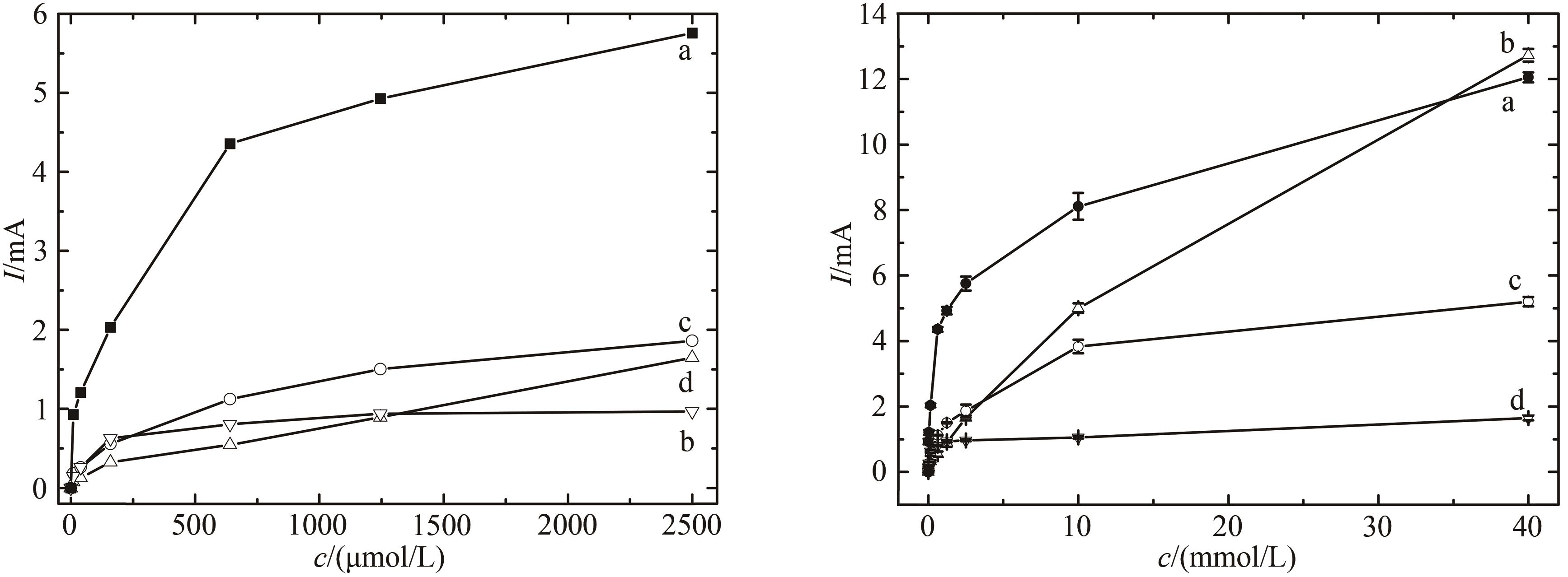
Fig. 8 Comparison of voltammograms for the electrode responses to increased H2O2 concentrations[The measurement was performed in the PBS without oxygen. HRP/Au-GM M13 electrode with (a) and without (b) chitosan modification, and HRP/Au nanoparticles electrode with (c) and without (d) chitosan modification]
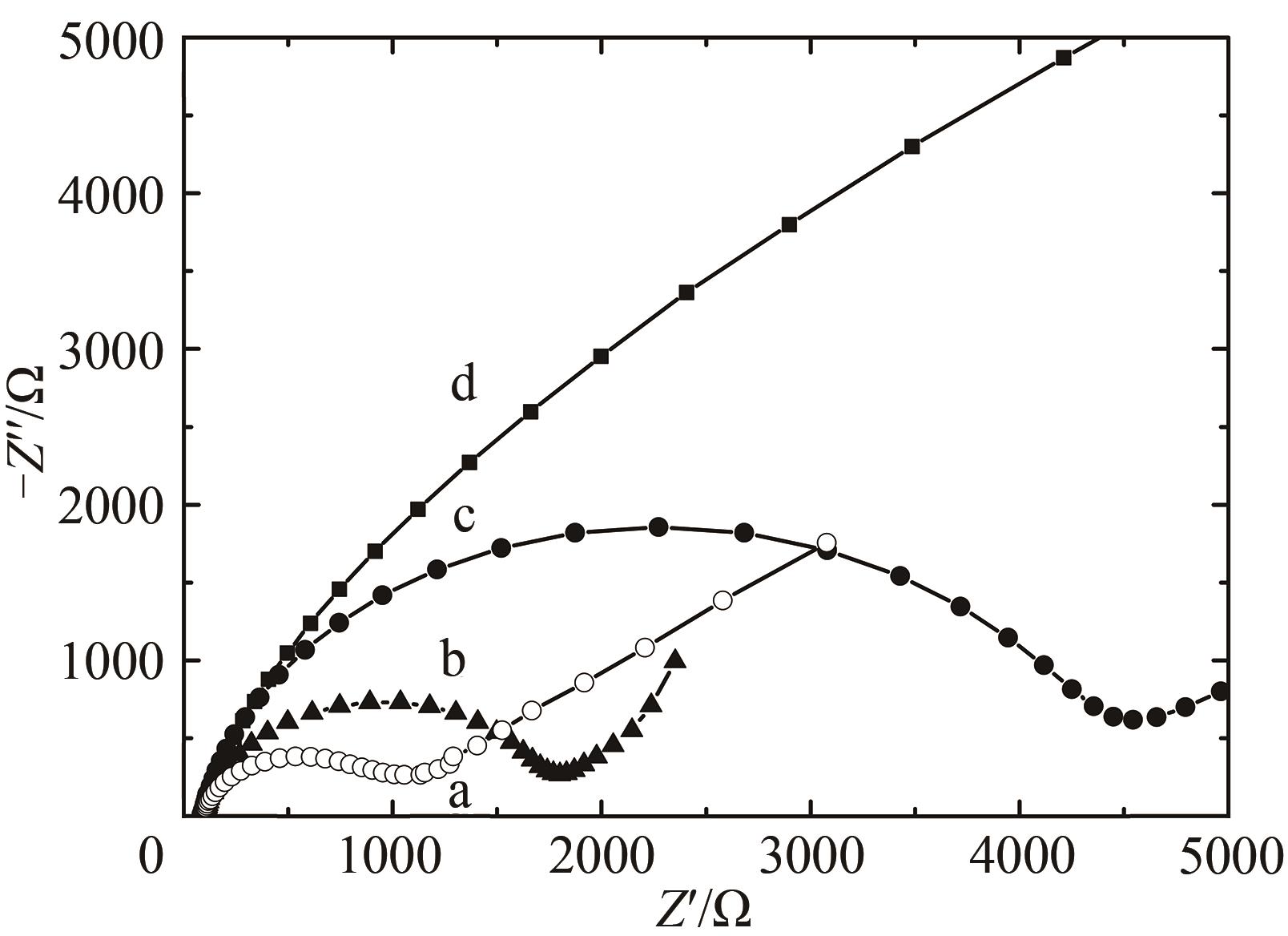
Fig. 9 Nyquist diagram (Z" vs Z') for Faradaic impedance spectra in the PBS (10 mmol/L, pH 7.0) containing 0.1 mol/L KCl and 2 mmol/L [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-a—HRP/Au-GM M13 electrode modified with chitosan; b—HRP/Au nanoparticles electrode modified with chitosan modified electrode; c—HRP electrode modified with chitosan; d—the glass-carbon electrode without the modification
| 1 | LUO H, SHI Z, LI N, et al. Investigation of the electrochemical and electrocatalytic behavior of single-wall carbon nanotube film on a glassy carbon electrode[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2001, 73(5): 915-920. |
| 2 | HU M L, ABBASI-AZAD M, MORSALI A, et al. Electrochemical applications of ferrocene-based coordination polymers[J]. Chempluschem, 2021, 85(11): 2397-2418. |
| 3 | HUANG X C, ZHANG J R, ZHANG L L, et al. A sensitive H2O2 biosensor based on carbon nanotubes/tetrathiafulvalene and its application in detecting NADH[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 2020, 589: 113493. |
| 4 | ITO K, OKUDA-SHIMAZAKI J, KOJIMA K, et al. Strategic design and improvement of the internal electron transfer of heme b domain-fused glucose dehydrogenase for use in direct electron transfer-type glucose sensors[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2021, 176: 112911. |
| 5 | ZHAO M, GAO Y, SUN J Y, et al. Mediatorless glucose biosensor and direct electron transfer type glucose/air biofuel cell enabled with carbon nanodots[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 87(5): 2615-2622. |
| 6 | 袁盛建, 马迎飞. 噬菌体合成生物学研究进展和应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(6): 635-655. |
| YUAN S J, MA Y F. Advances and applications of phage synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(6): 635-655. | |
| 7 | GUO Y C, ZHOU Y F, ZHANG X E, et al. Phage display mediated immuno-PCR[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2006, 34(8): e62. |
| 8 | SMITH G P. Filamentous fusion phage: novel expression vectors that display cloned antigens on the virion surface[J]. Science, 1985, 228(4705): 1315-1317. |
| 9 | KEHOE J W, KAY B K. Filamentous phage display in the new millennium[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2005, 105(11): 4056-4072. |
| 10 | SMITH G P, PETRENKO V A. Phage display[J]. Chemical Reviews, 1997, 97(2): 391-410. |
| 11 | OH D, QI J, LU Y C, et al. Biologically enhanced cathode design for improved capacity and cycle life for lithium-oxygen batteries[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 2756. |
| 12 | LEE Y J, YI H, KIM W J, et al. Fabricating genetically engineered high-power lithium-ion batteries using multiple virus genes[J]. Science, 2009, 324(5930): 1051-1055. |
| 13 | LEE S W, MAO C B, FLYNN C E, et al. Ordering of quantum dots using genetically engineered viruses[J]. Science, 2002, 296(5569): 892-895. |
| 14 | 张文静, 李明, 周维, 等. 基于病毒组件的纳米材料的自组装合成、功能化及应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(3): 298-318. |
| ZHANG W J, LI M, ZHOU W, et al. Self-assembly, biosynthesis, functionalization and applications of virus-based nanomaterials[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(3): 298-318. | |
| 15 | ZHANG J T, KANKALA R K, MA J Y, et al. Hollow tobacco mosaic virus coat protein assisted self-assembly of one-dimensional nanoarchitectures[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2021, 22(2): 540-545. |
| 16 | ZHANG W J, ZHANG X N, LI F. Virus-based nanoparticles of Simian virus 40 in the field of nanobiotechnology[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2018, 13(6): 1700619. |
| 17 | ZHANG S, YU H M, YANG J, et al. Design of the nanoarray pattern Fe-Ni bi-metal nanoparticles@M13 virus for the enhanced reduction of p-chloronitrobenzene through the micro-electrolysis effect[J]. Environmental Science: Nano, 2017, 4(4): 876-885. |
| 18 | YOO P J, NAM K T, QI J, et al. Spontaneous assembly of viruses on multilayered polymer surfaces[J]. Nature Materials, 2006, 5(3): 234-240. |
| 19 | CHO W, FOWLER J D, FURST E M, Targeted binding of the M 13 bacteriophage to thiamethoxam organic crystals[J]. Langmuir, 2012, 28(14): 6013-6020. |
| 20 | HUANG Y, CHIANG C Y, LEE S K, et al. Programmable assembly of nanoarchitectures using genetically engineered viruses[J]. Nano Letters, 2005, 5(7): 1429-1434. |
| 21 | YAMAMOTO K, SHI G Y, ZHOU T S, et al. Study of carbon nanotubes-HRP modified electrode and its application for novel on-line biosensors[J]. The Analyst, 2003, 128(3): 249-254. |
| 22 | LIU D L, WU Q, ZOU S, et al. Surface modification of cerasomes with AuNPs@poly(ionic liquid)s for an enhanced stereo biomimetic membrane electrochemical platform[J]. Bioelectrochemistry, 2020, 132: 107411. |
| 23 | WANG B, ZHANG J J, PAN Z Y, et al. A novel hydrogen peroxide sensor based on the direct electron transfer of horseradish peroxidase immobilized on silica-hydroxyapatite hybrid film[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2009, 24(5): 1141-1145. |
| 24 | XIN J Y, DOU B X, WANG Z X, et al. Direct electrochemistry of methanobactin functionalized gold nanoparticles on Au electrode[J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2018, 18(7): 4805-4813. |
| 25 | WANG J W, WANG L P, DI J W, et al. Electrodeposition of gold nanoparticles on indium/tin oxide electrode for fabrication of a disposable hydrogen peroxide biosensor[J]. Talanta, 2009, 77(4): 1454-1459. |
| 26 | QIAO Y, TAHARA K, ZHANG Q, et al. Cerasomes: soft interface for redox enzyme electrochemical signal transmission[J]. Chemistry - A European Journal, 2016, 22(4): 1340-1348. |
| 27 | HAMES B D, HOOPER N M, HOUGHTON J D. Instant Notes in Biochemistry [M]. London: Taylor & Francis, 1997: 67. |
| 28 | ZHANG H L, LAI G S, HAN D Y, et al. An amperometric hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on immobilization of horseradish peroxidase on an electrode modified with magnetic dextran microspheres[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2008, 390(3): 971-977. |
| 29 | MARCUS R A, SUTIN N. Electron transfers in chemistry and biology[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1985, 811(3): 265-322. |
| 30 | CHEN H, JIANG J H, HUANG Y, et al. An electrochemical impedance immunosensor with signal amplification based on Au-colloid labeled antibody complex[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2006, 117(1): 211-218. |
| 31 | HLELI S, MARTELET C, ABDELGHANI A, et al. An immunosensor for haemoglobin based on impedimetric properties of a new mixed self-assembled monolayer[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2006, 26(2/3): 322-327. |
| [1] | ZHAO Jingyu, ZHANG Jian, QI Qingsheng, WANG Qian. Research progress in biosensors based on bacterial two-component systems [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(1): 38-52. |
| [2] | DU Yao, GAO Hongdan, LIU Jiakun, LIU Xiaorong, XING Zhihao, ZHANG Tao, MA Dongli. Research progress of the CRISPR-Cas system in the detecting pathogen nucleic acids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(1): 202-216. |
| [3] | Lu YANG, Nan WU, Rongrong BAI, Weiliang DONG, Jie ZHOU, Min JIANG. Design, optimization and application of whole-cell microbial biosensors with engineered genetic circuits [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(6): 1061-1080. |
| [4] | Ping ZHANG, Wenping WEI, Ying ZHOU, Bangce YE. Construction of a light-controlled expression system and its application in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(5): 778-791. |
| [5] | Bo ZHANG, Yongshuo MA, Yi SHANG, Sanwen HUANG. Recent advances in plant synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(2): 121-140. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||