|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Biosynthesis of xylo-oligosaccharides from wheat straw xylan via the synergistic hydrolysis by xylanase Xyn11A and arabinofuranosidase Abf62A
Synthetic Biology Journal
DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-037
Table 1
Analysis of Xyn11A enzymatic hydrolysis products of different WS xylan
Extracts from the Article
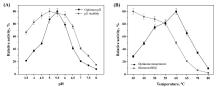
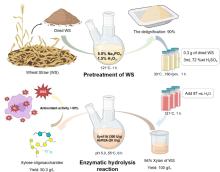
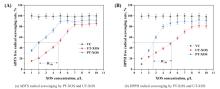
Recently, there is great interest to manufacture XOSs from biomass in a benign and sustainable way[1,33-34]. The integrated biorefinery process from wheat straw to XOSs is schematically illustrated in Fig. 6. Following delignification (90% efficiency) through optimized alkaline peroxide pretreatment (5% Na3PO4, 1.5% H2O2, 121 °C, 1 h), the cellulose-enriched residue of wheat straw was subjected to further extract xylan by NaOH method. Xylanase can hydrolyze xylan formed by the interconnection of xylan molecules, but other components in xylan will substantially influence the hydrolysis of xylan. The xylans extract from unpretreated (UTX) and pretreated (PTX) wheat straw were used as substrates for the enzyme hydrolysis by Xyn11A, and the results were displayed in Table 1. The Xylan (100 g/L) was mixed with xylanase (Xyn11A of 200 U/g substrate) and incubated at 60 ℃ and pH 5.0 for 6 h. It was observed that there was slight difference in the proportion of various sugars to total sugars in these two xylan-hydrolysates, but there was a substantial difference in concentration. After the enzyme hydrolysis of xylan extracted from unpretreated wheat straw (UTX), the total sugar concentration was 21.1 g/L. Among them, a total content of xylose, XOSs and arabinose was 20.8 g/L, and the hydrolysis efficiency of purified xylan was 26% (the xylan content in UTX was 79.9%). Through the enzymolysis of xylan extracted from unpretreated wheat straw (PTX), the total sugar content reached 36.6 g/L. It was detected that the content of XOSs was 33.3 g/L, including xylobiose (20.85 g/L), xylotriose (11.44 g/L), and xylotetraose (1.0 g/L). The hydrolysis efficiency of xylan was 38.6% (the content of xylan in PTX was 93.9%). The difference of enzymatic hydrolysis results between them might be due to their difference of lignin content [35]. In the previous research results, the main difference of xylan extracted from WS before and after pretreatment was the content of lignin. Direct extraction of xylan from WS will retain a large amount of lignin, produce irreversible adsorption to the enzyme in the process of hydrolysis, reduce enzyme activity, and the LCC structure formed by the combination of lignin and xylan will hinder the combination of xylanase and xylan, resulting in xylanase cannot play a role.
Other Images/Table from this Article
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||