合成生物学 ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (1): 185-203.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-035
基于核酸和蛋白质生物分子阵列传感器的构建及检测应用的研究进展
倪伟伟, 周玲佳, 王浩, 李飞, 韩进松
- 中国药科大学工学院食品质量与安全系,天然药物活性组分与药效国家重点实验室,国家中药材加工研发专业中心,江苏 南京 211109
-
收稿日期:2022-06-25修回日期:2022-08-26出版日期:2023-02-28发布日期:2023-03-07 -
通讯作者:李飞,韩进松 -
作者简介:倪伟伟 (1993—),男,博士研究生。研究方向为食品/药品质量控制及疾病的快速检测。E-mail:3120080256@stu.cpu.edu.cn
周玲佳(2000—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为食品/药品质量控制及疾病的快速检测。周玲佳 (2000—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为食品/药品质量控制及疾病的快速检测。E-mail:3221081884@stu.cpu.edu.cn李飞 (1990—),男,博士,特聘副研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为食品/药品安全及疾病快检与手性发光分子应用研究。E-mail:fei.li@cpu.edu.cn韩进松 (1987—),男,博士,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为食品/药品质量控制及疾病的快速检测与药物化学与新药研发。E-mail:Jinsong.han@cpu.edu.cn
第一联系人:倪伟伟(1993—),男,博士研究生。研究方向为食品/药品质量控制及疾病的快速检测。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(82072017)
Research progress in the construction of nucleic acid and protein biomolecular sensor arrays and their applications for rapid detection
NI Weiwei, ZHOU Lingjia, WANG Hao, LI Fei, HAN Jinsong
- State Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines and National R&D Center for Chinese Herbal Medicine Processing,Department of Food Quality and Safety,College of Engineering,China Pharmaceutical University,Nanjing 211109,Jiangsu,China
-
Received:2022-06-25Revised:2022-08-26Online:2023-02-28Published:2023-03-07 -
Contact:LI Fei, HAN Jinsong
摘要:
阵列传感器是组合多个传感元件,通过交叉反应机理来区分一类目标分析物的策略,不同于传统探针类传感器“锁-钥”结合模式,阵列传感器为非特异性结合,可实现一对多的识别。然而,传感元件的制备仍然存在设计困难、合成复杂、信号转换效率低等诸多挑战。核酸和蛋白具有优良的生物相容性、灵活的可编程性、易实现的功能化和优越的分子识别性质等优点。目前已经通过合理设计和可控化制备手段构建了多种基于核酸和蛋白类传感元件的阵列传感器,结合机器学习算法对所得数据进行处理,使数据可视化,构建待测物“指纹图谱”,对待测物进行区分。在此综述中,重点介绍了基于核酸和蛋白类传感元件构建的阵列传感器的多目标检测应用,并讨论了其合理的应用前景以及挑战。
中图分类号:
引用本文
倪伟伟, 周玲佳, 王浩, 李飞, 韩进松. 基于核酸和蛋白质生物分子阵列传感器的构建及检测应用的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 185-203.
NI Weiwei, ZHOU Lingjia, WANG Hao, LI Fei, HAN Jinsong. Research progress in the construction of nucleic acid and protein biomolecular sensor arrays and their applications for rapid detection[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 185-203.
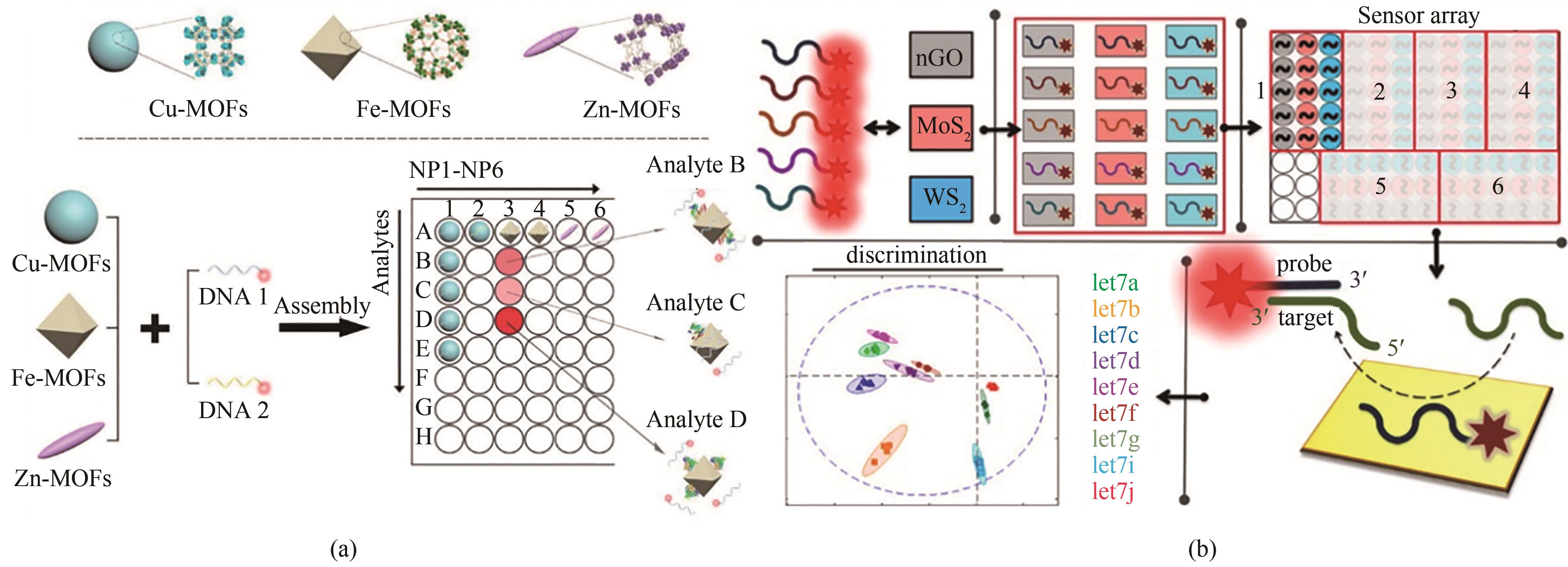
图2 (a) 基于含有不同金属离子和荧光团标记ssDNA的NMOF的传感器阵列方案[24][经许可后改编,版权所有(2019)美国化学学会];(b) 使用二维纳米颗粒(WS2、MoS2和nGO)和荧光团标记的 ssDNA的miRNA类似物识别方案[26][经许可后改编,版权所有(2018)美国化学学会]
Fig. 2 Diagrams for sensor arrays based on NMOFs containing different metal ions and fluorophore-labeled ssDNAs (a) [24], and miRNA analogues discrimination using two-dimensional nanoparticles (WS2, MoS2, and nGO) and fluorophore-labeled ssDNAs (b) [26], which were adapted with permission.

图3 (a) 基于阳离子聚合物诱导的 AuNPs 聚集的传感器阵列方案[37][经许可后改编,版权所有(2018)美国化学学会];(b) 使用 DNA-AuNPs 区分细胞类型的示意图[39][经许可后改编,版权所有(2014)美国化学学会]
Fig. 3 (a) Diagrams for sensor arrays based on cationic polymer induced aggregation of AuNPs (a) [37], DNA-AuNPs for differentiating cell types (b) [39], which were adapted with permission
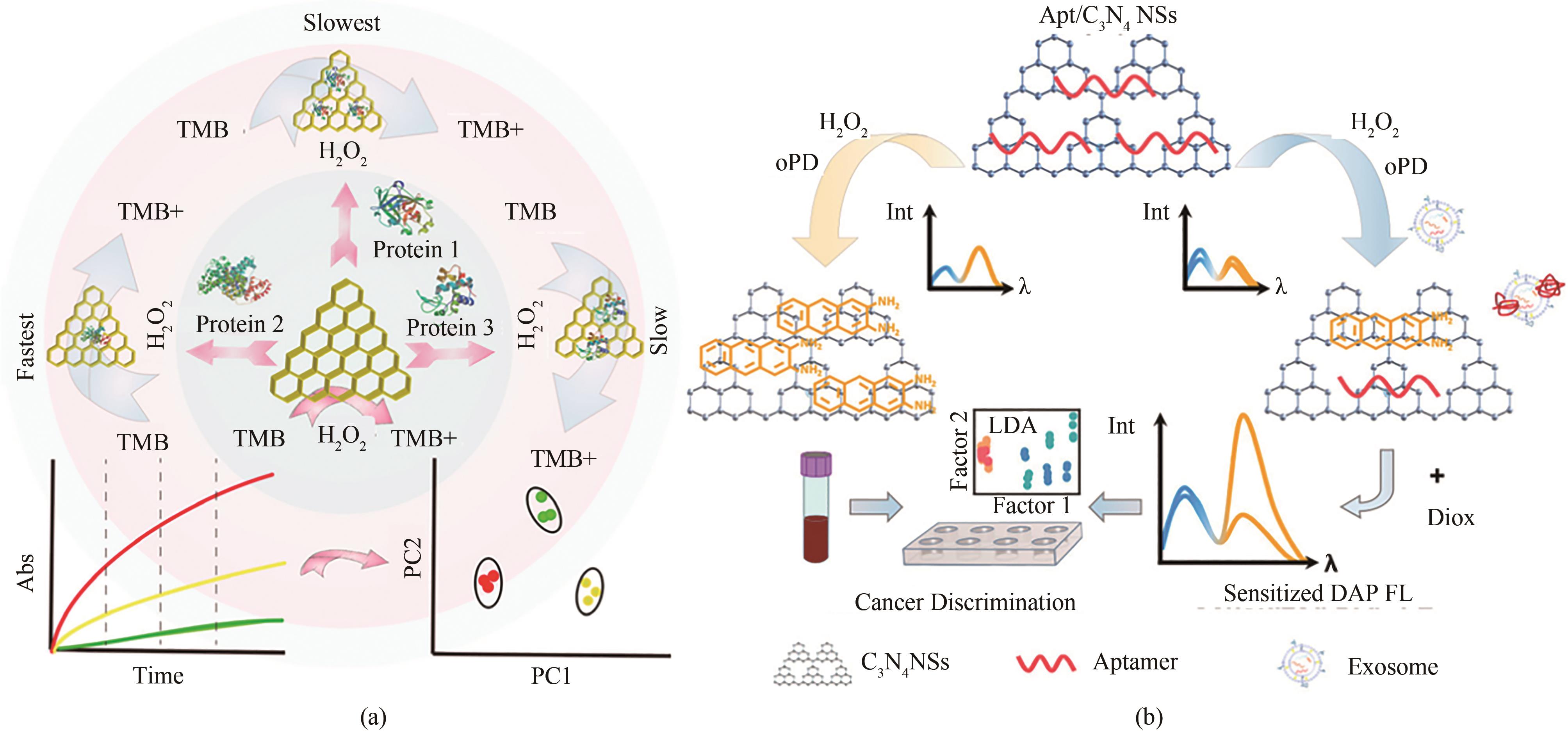
图4 (a)基于g-C3N4纳米片识别不同蛋白质的传感装置的代表性方案[61][经许可后改编,版权所有(2018)美国化学学会];(b)用于检测外泌体蛋白和癌症的纳米酶传感器阵列方案[62][经许可后改编,版权所有(2021)美国化学学会]
Fig. 4 Diagrams for sensing devices based on g-C3N4 nanosheets for discrimination of different proteins (a) [61], and detection of exosomal proteins and cancer identification with the nanozyme sensor array (b) [62], which were adapted with permission
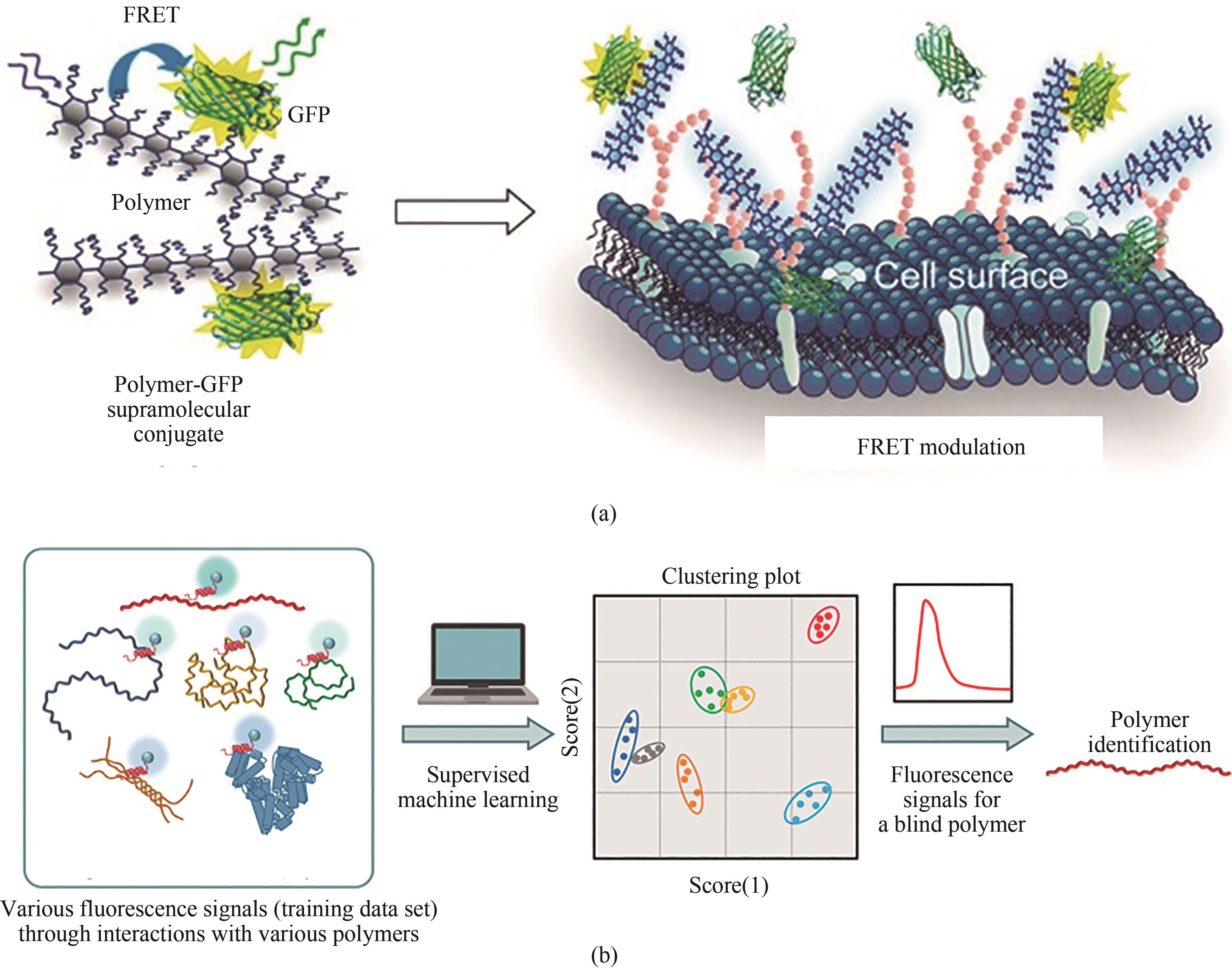
图5 (a)由共轭聚合物和GFP组成的基于FRET的比例生物阵列传感器示意图[108][经许可后改编,版权所有(2016)美国化学学会];(b)通过对来自基于肽的分子传感器和多变量分析进行聚合物分类的示意图[109][经许可后改编,版权所有(2021)美国化学学会]
Fig. 5 Diagrams for a FRET-based proportional bioarray sensor consisting of conjugated polymers and GFP (a) [108], and polymer classification through multivariable analysis of fluorescence signals based on a peptide-based molecular sensor and subsequent polymer identification (b) [109], which were adapted with permission.
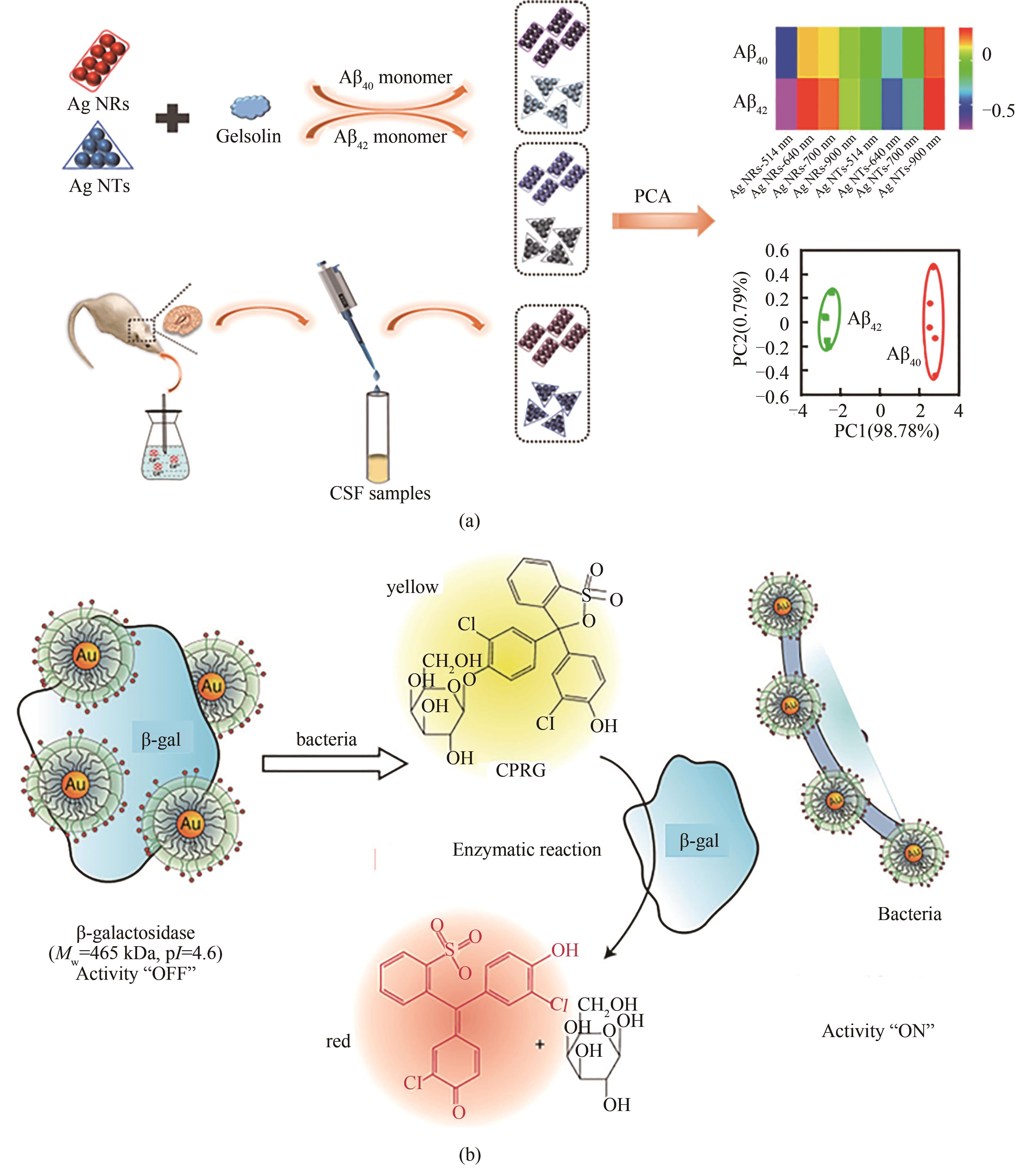
图6 (a)Aβ40和Aβ42由Gelsolin修饰的Ag NTs和Ag NRs组成的比色传感器阵列检测原理示意图[111] [经许可后改编,版权所有(2020)美国化学学会];(b)酶对细菌的放大传感,NPs和β-gal核心直径约为2 nm[112][经许可后改编,版权所有(2011)美国化学学会]
Fig.6 Diagrams for the detection principle of Aβ40 and Aβ42 by a colorimetric sensor array consisting of gelsolin-modified Ag NTs and Ag NRs (a) [111], and enzyme-amplified sensing of bacteria with the relative size of the 2 nm NPs andβ-gal particle (b) [112], which were adapted with permission
| 发表时间 | 传感元件 | 应用 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 适配体修饰的磁性纳米粒子 结合有核酸适配体的磁性纳米粒子(ACMNP) | 区分不同的细胞类型 癌细胞的模式识别 | [ |
| 2014 | 荧光标记的适配体 异硫氰酸荧光素酯(FITC)、花菁染料3(Cy3)和花菁染料5(Cy5)标记的核酸 | 区分癌细胞的类型 | [ |
| 1993 | 荧光团标记的单链DNA(ssDNA) | 检测蛋白酶 | [ |
| 2018 | DNA-染料-金属离子复合体系 | 区分硫醇 | [ |
| 2018 | 结合铕(Eu3+)的富含胞嘧啶和胸腺嘧啶的ssDNA(Eu-C16和Eu-T16) | 金属离子的检测 | [ |
| 2019 | 吸附荧光团标记的ssDNA的含有Cu、Fe、Zr离子的纳米级金属有机框架 | 对蛋白质和细胞的并行检测 | [ |
| 2018 | nGO、MoS2和WS2纳米片和多个荧光团标记的DNA | 对蛋白质、癌细胞、miRNA和不同结构状态的大分子的鉴定 | [ |
| 2018 | 5个荧光标记的ssDNA | 区分具有单核苷酸差异的let-7 miRNA 家族的9个成员 | [ |
| 2021 | GO、MoS2纳米片和一个DNA 库 | 细菌和蛋白质的检测 | [ |
| 2015 | 三个金属氧化物纳米颗粒与DNA 的复合物 | 磷酸根、砷酸根和亚砷酸根等常见阴离子的检测 | [ |
| 2020 | 纳米多孔阳极氧化铝 (NAA) 支架装载荧光指示剂罗丹明B,在孔入口用 DNA 适体进行覆盖 | 检测金黄色葡萄球菌 | [ |
| 2013 | AuNPs 和碱基形成的复合物 | 区分不同的蛋白质和细胞类型 | [ |
| 2017 | 含有两条不同长度的ssDNA的AuNPs | 识别残留的抗生素 | [ |
| 2018 | ssDNA-AuNPs复合物 | 识别牛奶中的抗生素 | [ |
| 2017 | 两条不同摩尔比的DNA修饰的AuNPs | 蛋白质测定 | [ |
| 2019 | 非特异性寡核苷酸修饰的AuNPs | 区分蛋白质 | [ |
| 2018 | 三个非特异性DNA链与不同的蛋白质混合后,加入阳离子聚-(二烯丙基二甲基氯化铵)(PDDA)和AuNPs | 区分不同的蛋白质 | [ |
| 2013 | 使用DNA修饰的催化AuNPs | 蛋白质识别 | [ |
| 2014 | DNA-AuNPs | 区分细胞类型 | [ |
| 2015 | DNA-AuNPs-GO | 区分不同亚型和等级的肿瘤细胞 | [ |
| 2019 | 锆金属-有机框架(Zr-MOFs)与固定有ssDNA 的 AuNPs 复合 | 识别蛋白质和人类精液样本 | [ |
| 2017 | 基于蛋白质和DNA 之间的相互作用 | 蛋白质识别 | [ |
| 2017 | 基于AuNPs在H2O2 存在下可催化3,3,5,5-四甲基联苯胺(TMB)产生蓝色,使用三种DNA 修饰的AuNPs | 蛋白质识别 | [ |
| 2015 | AuNPs 和非特异性染料标记的DNA | 蛋白质的区分 | [ |
| 2019 | AuNPs 与三个染料标记的ssDNA 序列复合 | 区分正常细胞与病理性细胞 | [ |
| 2016 | AuNPs-DNA复合物 | 检测并区分重金属离子 | [ |
| 2019 | 以DNA为模板的Cu纳米颗粒和金属介导的碱基对 | 区分生物硫醇 | [ |
| 2012 | GO和荧光染料标记的非特异性DNA序列 | 对蛋白质、细胞和细菌进行定性和定量分析 | [ |
| 2017 | 纳米氧化石墨烯(nGO)和荧光团修饰的单链DNA共轭 | 确定抗体降解途径 | [ |
| 2017 | nGO和三个表现出不同序列和荧光团的(ssDNA)共轭 | 识别蛋白质 | [ |
| 2015 | 表面固定有核酸适配体的磁性纳米粒子 | 检测氯霉素 | [ |
| 2019 | 核酸适配体共轭磁性纳米粒子 | 检测广泛存在的食源性病原体副溶血弧菌 | [ |
| 2020 | 适配体和抗体结合的双重识别单元 | 检测单核细胞增生李斯特菌 | [ |
| 2021 | 吸附三种靶向外泌体蛋白的核酸的C3N4纳米片 | 检测和诊断癌症 | [ |
| 2009 | 使用阳离子共轭低聚电解质(COE)与6-羧基荧光素(6-FAM)标记的ssDNA聚集体 | 蛋白质识别 | [ |
| 2021 | ssDNA 苝复合物 | 进行蛋白质的区分 | [ |
| 2010 | 共轭聚电解质和荧光素(FAM)标记的 ssDNA 的复合物 | 检测细菌 | [ |
| 2017 | DNA和两种染料的复合物 | 区分金属离子 | [ |
| 2017 | 苯并呋喃尿苷荧光团标记的RNA | RNA 结构模式识别分析 | [ |
| 2019 | 市售染料 | DNA 的高通量二级结构分析 | [ |
| 2020 | 核酸的自身荧光 | 探索 DNA 的二级结构 | [ |
| 2018 | 包含各种化学支架的30个已知核酸黏合剂库 | 筛选特定核酸结构的选择性配体 | [ |
| 2018 | 三种荧光蛋白(H-mTagBFP-H、H-EGFP-H、H-sfCherry-H) | 在水溶液中实现了对9种金属离子的区分 | [ |
| 2009 | 绿色荧光蛋白(GFP)和五种纳米颗粒形成的复合物 | 检测缓冲液和人血清中生物相关浓度的蛋白质 | [ |
| 2010 | 纳米粒子与GFP | 有效识别多种哺乳动物癌细胞 | [ |
| 2020 | 由金纳米粒子(AuNPs)和高效绿色荧光蛋白(EGFP)组成 | 低剂量条件下快速检测细胞异常的早期迹象 | [ |
| 2018 | 由功能化金纳米粒子(BenzNP)和三个荧光蛋白(EGFP, EBFP, tdTomato)组成 | 快速区分乳腺癌干细胞和非肿瘤干细胞 | [ |
| 2017 | 功能化的金纳米粒子(BenzNP)作为识别元件,GFP作为荧光报告传感器 | 在超低浓度下(兆分之一和千万亿分之一摩尔水平)检测细胞的雌激素EDC反应 | [ |
| 2018 | 聚亚苯基乙炔(PPE)和改性GFP(GFP-K72)的复合物 | 在25 mmol浓度下以100%的准确度识别20种天然氨基酸 | [ |
| 2016 | 由一系列共轭聚合物(CPs)和GFP构成的静电复合物 | 识别16种不同的细胞类型,并区分健康细胞、癌细胞和转移细胞 | [ |
| 2017 | 共轭荧光聚电解质与三种荧光蛋白(GFP、GFP-K36、GFP-E36)构建成传感元件 | 识别威士忌的关键品质信息,如麦芽状态、酒龄、原产地甚至口味等 | [ |
| 2021 | 胶溶蛋白(Gelsolin)修饰的Ag-NTs和Ag-NRs | 同时识别和检测复杂脑样本中的Aβ40和Aβ42 | [ |
| 2020 | 带负电的PPE与四种带正电的抗菌肽(AMPs)形成的静电复合物 | 准确识别和区分14种细菌 | [ |
| 2010 | 抗菌肽Ib-AMP4融合GFP形成的重组IGP蛋白 | 识别10种最常见的临床分离菌 | [ |
| 2011 | 基于GO猝灭的聚组氨酸适配器与AMPs融合体 | 细菌识别 | [ |
| 2017 | 基于肽单元和荧光团 | 识别溶解在水中的合成聚合物 | [ |
| 2019 | 由荧光肽和氧化石墨烯(GO)复合组成 | 可以靶向病毒半胱氨酸上的糖蛋白,利用主成分分析促进埃博拉病毒、马尔堡病毒和水泡性口炎病毒的鉴别 | [ |
| 2020 | 由1个含组氨酸的短肽、1个二价金属离子和1个pH比色指示剂组成 | 区分和预测红酒混合物成分 | [ |
| 2020 | 结合有β-半乳糖苷酶的AuNPs | 蛋白质的识别 | [ |
| 2015 | 结合有β-半乳糖苷酶的端基为季铵盐的AuNPs | 检测微生物污染 | [ |
表1 使用核酸和蛋白质类生物分子作为传感元件构建传感器阵列的总表
Table 1 Summary for sensor arrays using nucleic acids and proteins as sensing elements
| 发表时间 | 传感元件 | 应用 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 适配体修饰的磁性纳米粒子 结合有核酸适配体的磁性纳米粒子(ACMNP) | 区分不同的细胞类型 癌细胞的模式识别 | [ |
| 2014 | 荧光标记的适配体 异硫氰酸荧光素酯(FITC)、花菁染料3(Cy3)和花菁染料5(Cy5)标记的核酸 | 区分癌细胞的类型 | [ |
| 1993 | 荧光团标记的单链DNA(ssDNA) | 检测蛋白酶 | [ |
| 2018 | DNA-染料-金属离子复合体系 | 区分硫醇 | [ |
| 2018 | 结合铕(Eu3+)的富含胞嘧啶和胸腺嘧啶的ssDNA(Eu-C16和Eu-T16) | 金属离子的检测 | [ |
| 2019 | 吸附荧光团标记的ssDNA的含有Cu、Fe、Zr离子的纳米级金属有机框架 | 对蛋白质和细胞的并行检测 | [ |
| 2018 | nGO、MoS2和WS2纳米片和多个荧光团标记的DNA | 对蛋白质、癌细胞、miRNA和不同结构状态的大分子的鉴定 | [ |
| 2018 | 5个荧光标记的ssDNA | 区分具有单核苷酸差异的let-7 miRNA 家族的9个成员 | [ |
| 2021 | GO、MoS2纳米片和一个DNA 库 | 细菌和蛋白质的检测 | [ |
| 2015 | 三个金属氧化物纳米颗粒与DNA 的复合物 | 磷酸根、砷酸根和亚砷酸根等常见阴离子的检测 | [ |
| 2020 | 纳米多孔阳极氧化铝 (NAA) 支架装载荧光指示剂罗丹明B,在孔入口用 DNA 适体进行覆盖 | 检测金黄色葡萄球菌 | [ |
| 2013 | AuNPs 和碱基形成的复合物 | 区分不同的蛋白质和细胞类型 | [ |
| 2017 | 含有两条不同长度的ssDNA的AuNPs | 识别残留的抗生素 | [ |
| 2018 | ssDNA-AuNPs复合物 | 识别牛奶中的抗生素 | [ |
| 2017 | 两条不同摩尔比的DNA修饰的AuNPs | 蛋白质测定 | [ |
| 2019 | 非特异性寡核苷酸修饰的AuNPs | 区分蛋白质 | [ |
| 2018 | 三个非特异性DNA链与不同的蛋白质混合后,加入阳离子聚-(二烯丙基二甲基氯化铵)(PDDA)和AuNPs | 区分不同的蛋白质 | [ |
| 2013 | 使用DNA修饰的催化AuNPs | 蛋白质识别 | [ |
| 2014 | DNA-AuNPs | 区分细胞类型 | [ |
| 2015 | DNA-AuNPs-GO | 区分不同亚型和等级的肿瘤细胞 | [ |
| 2019 | 锆金属-有机框架(Zr-MOFs)与固定有ssDNA 的 AuNPs 复合 | 识别蛋白质和人类精液样本 | [ |
| 2017 | 基于蛋白质和DNA 之间的相互作用 | 蛋白质识别 | [ |
| 2017 | 基于AuNPs在H2O2 存在下可催化3,3,5,5-四甲基联苯胺(TMB)产生蓝色,使用三种DNA 修饰的AuNPs | 蛋白质识别 | [ |
| 2015 | AuNPs 和非特异性染料标记的DNA | 蛋白质的区分 | [ |
| 2019 | AuNPs 与三个染料标记的ssDNA 序列复合 | 区分正常细胞与病理性细胞 | [ |
| 2016 | AuNPs-DNA复合物 | 检测并区分重金属离子 | [ |
| 2019 | 以DNA为模板的Cu纳米颗粒和金属介导的碱基对 | 区分生物硫醇 | [ |
| 2012 | GO和荧光染料标记的非特异性DNA序列 | 对蛋白质、细胞和细菌进行定性和定量分析 | [ |
| 2017 | 纳米氧化石墨烯(nGO)和荧光团修饰的单链DNA共轭 | 确定抗体降解途径 | [ |
| 2017 | nGO和三个表现出不同序列和荧光团的(ssDNA)共轭 | 识别蛋白质 | [ |
| 2015 | 表面固定有核酸适配体的磁性纳米粒子 | 检测氯霉素 | [ |
| 2019 | 核酸适配体共轭磁性纳米粒子 | 检测广泛存在的食源性病原体副溶血弧菌 | [ |
| 2020 | 适配体和抗体结合的双重识别单元 | 检测单核细胞增生李斯特菌 | [ |
| 2021 | 吸附三种靶向外泌体蛋白的核酸的C3N4纳米片 | 检测和诊断癌症 | [ |
| 2009 | 使用阳离子共轭低聚电解质(COE)与6-羧基荧光素(6-FAM)标记的ssDNA聚集体 | 蛋白质识别 | [ |
| 2021 | ssDNA 苝复合物 | 进行蛋白质的区分 | [ |
| 2010 | 共轭聚电解质和荧光素(FAM)标记的 ssDNA 的复合物 | 检测细菌 | [ |
| 2017 | DNA和两种染料的复合物 | 区分金属离子 | [ |
| 2017 | 苯并呋喃尿苷荧光团标记的RNA | RNA 结构模式识别分析 | [ |
| 2019 | 市售染料 | DNA 的高通量二级结构分析 | [ |
| 2020 | 核酸的自身荧光 | 探索 DNA 的二级结构 | [ |
| 2018 | 包含各种化学支架的30个已知核酸黏合剂库 | 筛选特定核酸结构的选择性配体 | [ |
| 2018 | 三种荧光蛋白(H-mTagBFP-H、H-EGFP-H、H-sfCherry-H) | 在水溶液中实现了对9种金属离子的区分 | [ |
| 2009 | 绿色荧光蛋白(GFP)和五种纳米颗粒形成的复合物 | 检测缓冲液和人血清中生物相关浓度的蛋白质 | [ |
| 2010 | 纳米粒子与GFP | 有效识别多种哺乳动物癌细胞 | [ |
| 2020 | 由金纳米粒子(AuNPs)和高效绿色荧光蛋白(EGFP)组成 | 低剂量条件下快速检测细胞异常的早期迹象 | [ |
| 2018 | 由功能化金纳米粒子(BenzNP)和三个荧光蛋白(EGFP, EBFP, tdTomato)组成 | 快速区分乳腺癌干细胞和非肿瘤干细胞 | [ |
| 2017 | 功能化的金纳米粒子(BenzNP)作为识别元件,GFP作为荧光报告传感器 | 在超低浓度下(兆分之一和千万亿分之一摩尔水平)检测细胞的雌激素EDC反应 | [ |
| 2018 | 聚亚苯基乙炔(PPE)和改性GFP(GFP-K72)的复合物 | 在25 mmol浓度下以100%的准确度识别20种天然氨基酸 | [ |
| 2016 | 由一系列共轭聚合物(CPs)和GFP构成的静电复合物 | 识别16种不同的细胞类型,并区分健康细胞、癌细胞和转移细胞 | [ |
| 2017 | 共轭荧光聚电解质与三种荧光蛋白(GFP、GFP-K36、GFP-E36)构建成传感元件 | 识别威士忌的关键品质信息,如麦芽状态、酒龄、原产地甚至口味等 | [ |
| 2021 | 胶溶蛋白(Gelsolin)修饰的Ag-NTs和Ag-NRs | 同时识别和检测复杂脑样本中的Aβ40和Aβ42 | [ |
| 2020 | 带负电的PPE与四种带正电的抗菌肽(AMPs)形成的静电复合物 | 准确识别和区分14种细菌 | [ |
| 2010 | 抗菌肽Ib-AMP4融合GFP形成的重组IGP蛋白 | 识别10种最常见的临床分离菌 | [ |
| 2011 | 基于GO猝灭的聚组氨酸适配器与AMPs融合体 | 细菌识别 | [ |
| 2017 | 基于肽单元和荧光团 | 识别溶解在水中的合成聚合物 | [ |
| 2019 | 由荧光肽和氧化石墨烯(GO)复合组成 | 可以靶向病毒半胱氨酸上的糖蛋白,利用主成分分析促进埃博拉病毒、马尔堡病毒和水泡性口炎病毒的鉴别 | [ |
| 2020 | 由1个含组氨酸的短肽、1个二价金属离子和1个pH比色指示剂组成 | 区分和预测红酒混合物成分 | [ |
| 2020 | 结合有β-半乳糖苷酶的AuNPs | 蛋白质的识别 | [ |
| 2015 | 结合有β-半乳糖苷酶的端基为季铵盐的AuNPs | 检测微生物污染 | [ |
| 1 | CHEN J H, ANDLER S M, GODDARD J M, et al. Integrating recognition elements with nanomaterials for bacteria sensing[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(5): 1272-1283. |
| 2 | YOU L, ZHA D J, ANSLYN E V. Recent advances in supramolecular analytical chemistry using optical sensing[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2015, 115(15): 7840-7892. |
| 3 | LIN M, LI W S, WANG Y N, et al. Discrimination of hemoglobins with subtle differences using an aptamer based sensing array[J]. Chemical Communications, 2015, 51(39): 8304-8306. |
| 4 | GALE P A, CALTAGIRONE C. Anion sensing by small molecules and molecular ensembles[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(13): 4212-4227. |
| 5 | SUN J W, LU Y X, HE L Y, et al. Colorimetric sensor array based on gold nanoparticles: design principles and recent advances[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 122: 115754. |
| 6 | PU F, RAN X, GUAN M, et al. Biomolecule-templated photochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles: multiple readouts of localized surface plasmon resonance for pattern recognition[J]. Nano Research, 2018, 11(6): 3213-3221. |
| 7 | PU F, RAN X, REN J S, et al. Artificial tongue based on metal-biomolecule coordination polymer nanoparticles[J]. Chemical Communications, 2016, 52(16): 3410-3413. |
| 8 | ZHOU W H, SARAN R, LIU J W. Metal sensing by DNA[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(12): 8272-8325. |
| 9 | ZHENG J, YANG R H, SHI M L, et al. Rationally designed molecular beacons for bioanalytical and biomedical applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(10): 3036-3055. |
| 10 | TAN W H, DONOVAN M J, JIANG J H. Aptamers from cell-based selection for bioanalytical applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2013, 113(4): 2842-2862. |
| 11 | BELL N M, MICKLEFIELD J. Chemical modification of oligonucleotides for therapeutic, bioanalytical and other applications[J]. ChemBioChem, 2009, 10(17): 2691-2703. |
| 12 | HU L, XU J, QIN Z, et al. Detection of bitterness in vitro by a novel male mouse germ cell-based biosensor[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2016, 223: 461-469. |
| 13 | LI L, XU S J, YAN H, et al. Nucleic acid aptamers for molecular diagnostics and therapeutics: advances and perspectives[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(5): 2221-2231. |
| 14 | MOUTSIOPOULOU A, BROYLES D, DIKICI E, et al. Molecular aptamer beacons and their applications in sensing, imaging, and diagnostics[J]. Small, 2019, 15(35): 1902248. |
| 15 | BAMRUNGSAP S, CHEN T, SHUKOOR M I, et al. Pattern recognition of cancer cells using aptamer-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles[J]. ACS Nano, 2012, 6(5): 3974-3981. |
| 16 | WANG S, KONG H, GONG X Y, et al. Multicolor imaging of cancer cells with fluorophore-tagged aptamers for single cell typing[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 86(16): 8261-8266. |
| 17 | TOMITA S, SUGAI H, MIMURA M, et al. Optical fingerprints of proteases and their inhibited complexes provided by differential cross-reactivity of fluorophore-labeled single-stranded DNA[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(50): 47428-47436. |
| 18 | LI Z, ASKIM J R, SUSLICK K S. The optoelectronic nose: colorimetric and fluorometric sensor arrays[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2019, 119(1): 231-292. |
| 19 | OKADA M, SUGAI H, TOMITA S, et al. A multichannel pattern-recognition-based protein sensor with a fluorophore-conjugated single-stranded DNA set[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(18): 5110. |
| 20 | SIGEL H. Interactions of metal ions with nucleotides and nucleic acids and their constituents[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 1993, 22(4): 255-267. |
| 21 | QIU H, PU F, RAN X, et al. Fingerprint-like pattern for recognition of thiols[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2018, 260: 183-188. |
| 22 | XUE S F, CHEN Z H, HAN X Y, et al. DNA encountering terbium(Ⅲ): a smart "Chemical nose/tongue" for large-scale time-gated luminescent and lifetime-based sensing[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 90(5): 3443-3451. |
| 23 | XUE S F, HAN X Y, CHEN Z H, et al. The chemistry of europium(Ⅲ) encountering DNA: sprouting unique sequence-dependent performances for multifunctional time-resolved luminescent assays[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 90(17): 10614-10620. |
| 24 | WU S, HAN Y W, WANG L, et al. Sensor array fabricated with nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for the histopathological examination of colon cancer[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(16): 10772-10778. |
| 25 | HIZIR M S, ROBERTSON N M, BALCIOGLU M, et al. Universal sensor array for highly selective system identification using two-dimensional nanoparticles[J]. Chemical Science, 2017, 8(8): 5735-5745. |
| 26 | HIZIR M S, NANDU N, YIGIT M V. Homologous miRNA analyses using a combinatorial nanosensor array with two-dimensional nanoparticles[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 90(10): 6300-6306. |
| 27 | NANDU N, HIZIR M S, YIGIT M V. Systematic investigation of two-dimensional DNA nanoassemblies for construction of a nonspecific sensor array[J]. Langmuir, 2018, 34(49): 14983-14992. |
| 28 | AUGSPURGER E E, RANA M, YIGIT M V. Chemical and biological sensing using hybridization chain reaction[J]. ACS Sensors, 2018, 3(5): 878-902. |
| 29 | QI J W, RAO P H, WANG L L, et al. Development of pattern recognition based on nanosheet-DNA probes and an extendable DNA library[J]. Analyst, 2021, 146(15): 4803-4810. |
| 30 | LIU B W, LIU J W. Comprehensive screen of metal oxide nanoparticles for DNA adsorption, fluorescence quenching, and anion discrimination[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(44): 24833-24838. |
| 31 | PLA L, SANTIAGO-FELIPE S, TORMO-MAS M Á, et al. Aptamer-capped nanoporous anodic alumina for staphylococcus aureus detection[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2020, 320: 128281. |
| 32 | LU Y X, LIU Y Y, ZHANG S G, et al. Aptamer-based plasmonic sensor array for discrimination of proteins and cells with the naked eye[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 85(14): 6571-6574. |
| 33 | WEI X C, WANG Y X, ZHAO Y X, et al. Colorimetric sensor array for protein discrimination based on different DNA chain length-dependent gold nanoparticles aggregation[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2017, 97: 332-337. |
| 34 | YAN S, LAI X X, DU G R, et al. Identification of aminoglycoside antibiotics in milk matrix with a colorimetric sensor array and pattern recognition methods[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2018, 1034: 153-160. |
| 35 | WANG F Y, ZHANG X, LU Y X, et al. Continuously evolving 'chemical tongue' biosensor for detecting proteins[J]. Talanta, 2017, 165: 182-187. |
| 36 | JIA F F, LIU Q Y, WEI W, et al. Colorimetric sensor assay for discrimination of proteins based on exonuclease Ⅰ-triggered aggregation of DNA-functionalized gold nanoparticles[J]. Analyst, 2019, 144(16): 4865-4870. |
| 37 | XI H Y, HE W W, LIU Q Y, et al. Protein discrimination using a colorimetric sensor array based on gold nanoparticle aggregation induced by cationic polymer[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(8): 10751-10757. |
| 38 | YANG X F, LI J, PEI H, et al. Pattern recognition analysis of proteins using DNA-decorated catalytic gold nanoparticles[J]. Small, 2013, 9(17): 2844-2849. |
| 39 | YANG X F, LI J, PEI H, et al. DNA-gold nanoparticle conjugates-based nanoplasmonic probe for specific differentiation of cell types[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 86(6): 3227-3231. |
| 40 | LI C, YANG Y C, WEI L M, et al. An array-based approach to determine different subtype and differentiation of non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Theranostics, 2015, 5(1): 62-70. |
| 41 | SUN Z W, WU S, MA J H, et al. Colorimetric sensor array for human semen identification designed by coupling zirconium metal-organic frameworks with DNA-modified gold nanoparticles[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(40): 36316-36323. |
| 42 | WEI X C, CHEN Z B, TAN L L, et al. DNA-catalytically active gold nanoparticle conjugates-based colorimetric multidimensional sensor array for protein discrimination[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 89(1): 556-559. |
| 43 | YANG J E, LU Y X, AO L, et al. Colorimetric sensor array for proteins discrimination based on the tunable peroxidase-like activity of AuNPs-DNA conjugates[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2017, 245: 66-73. |
| 44 | SUN W B, LU Y X, MAO J P, et al. Multidimensional sensor for pattern recognition of proteins based on DNA-gold nanoparticles conjugates[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 87(6): 3354-3359. |
| 45 | SAHA N DAS, SASMAL R, MEETHAL S K, et al. Multichannel DNA sensor array fingerprints cell states and identifies pharmacological effectors of catabolic processes[J]. ACS Sensors, 2019, 4(12): 3124-3132. |
| 46 | TAN L L, CHEN Z B, ZHAO Y. Dual channel sensor for detection and discrimination of heavy metal ions based on colorimetric and fluorescence response of the AuNPs-DNA conjugates[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2016, 85: 414-421. |
| 47 | ZHOU L, REN J S, QU X G. Nucleic acid-templated functional nanocomposites for biomedical applications[J]. Materials Today, 2017, 20(4): 179-190. |
| 48 | KUMAR A, KUMAR V. Biotemplated inorganic nanostructures: supramolecular directed nanosystems of semiconductor(s)/metal(s) mediated by nucleic acids and their properties[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(14): 7044-7078. |
| 49 | XU F Z, QING T P, QING Z H. DNA-coded metal nano-fluorophores: preparation, properties and applications in biosensing and bioimaging[J]. Nano Today, 2021, 36: 101021. |
| 50 | CHEN Y X, PHIPPS M L, WERNER J H, et al. DNA templated metal nanoclusters: from emergent properties to unique applications[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2018, 51(11): 2756-2763. |
| 51 | XI H Y, LI X, LIU Q Y, et al. Fluorescent sensor array for discrimination of biothiols based on poly(thymine/cytosine)-templated copper nanoparticles[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2019, 1051: 147-152. |
| 52 | QING Z H, HE X X, HE D G, et al. Poly(thymine)-templated selective formation of fluorescent copper nanoparticles[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2013, 125(37): 9901-9904. |
| 53 | CLEVER G, KAUL C, CARELL T. DNA-metal base pairs[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2007, 46(33): 6226-6236. |
| 54 | CHUNG C, KIM Y K, SHIN D, et al. Biomedical applications of graphene and graphene oxide[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2013, 46(10): 2211-2224. |
| 55 | PEI H, LI J, LV M, et al. A graphene-based sensor array for high-precision and adaptive target identification with ensemble aptamers[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(33): 13843-13849. |
| 56 | TOMITA S, MATSUDA A, NISHINAMI S, et al. One-step identification of antibody degradation pathways using fluorescence signatures generated by cross-reactive DNA-based arrays[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 89(15): 7818-7822. |
| 57 | TOMITA S, ISHIHARA S, KURITA R. A multi-fluorescent DNA/graphene oxide conjugate sensor for signature-based protein discrimination[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(10): 2194. |
| 58 | WU S J, ZHANG H, SHI Z. Aptamer-based fluorescence biosensor for chloramphenicol determination using upconversion nanoparticles[J]. Food Control, 2015, 50: 597-604. |
| 59 | SUN Y H, DUAN N, MA P F, et al. Colorimetric aptasensor based on truncated aptamer and trivalent DNAzyme for Vibrio parahemolyticus determination[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2019, 67(8): 2313-2320. |
| 60 | GUO Y Y, ZHAO C, LIU Y S, et al. A novel fluorescence method for the rapid and effective detection of Listeria monocytogenes using aptamer-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles and aggregation-induced emission dots[J]. Analyst, 2020, 145(11): 3857-3863. |
| 61 | QIU H, PU F, RAN X, et al. Nanozyme as artificial receptor with multiple readouts for pattern recognition[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 90(20): 11775-11779. |
| 62 | LIU M X, ZHANG H, ZHANG X W, et al. Nanozyme sensor array plus solvent-mediated signal amplification strategy for ultrasensitive ratiometric fluorescence detection of exosomal proteins and cancer identification[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 93(25): 9002-9010. |
| 63 | LI H P, BAZAN G C. Conjugated oligoelectrolyte/ssDNA aggregates: self-assembled multicomponent chromophores for protein discrimination[J]. Advanced Materials, 2009, 21(9): 964-967. |
| 64 | ZHOU W, HOU J Z, LI Y X, et al. Protein discrimination based on DNA induced perylene probe self-assembly[J]. Talanta, 2021, 224: 121897. |
| 65 | DUARTE A, CHWOROS A, FLAGAN S F, et al. Identification of bacteria by conjugated oligoelectrolyte/single-stranded DNA electrostatic complexes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(36): 12562-12564. |
| 66 | QIU H, PU F, RAN X, et al. A DNA-based label-free artificial tongue for pattern recognition of metal ions[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2017, 23(39): 9258-9261. |
| 67 | LI L, LIU B, CHEN Z B. Heavy metal ion discrimination based on distinct interaction between single-stranded DNA and methylene blue[J]. Analytical Methods, 2019, 11(1): 17-20. |
| 68 | EUBANKS C S, FORTE J E, KAPRAL G J, et al. Small molecule-based pattern recognition to classify RNA structure[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(1): 409-416. |
| 69 | EUBANKS C S, ZHAO B, PATWARDHAN N N, et al. Visualizing RNA conformational changes via pattern recognition of RNA by small molecules[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(14): 5692-5698. |
| 70 | EUBANKS C S, HARGROVE A E. RNA structural differentiation: opportunities with pattern recognition[J]. Biochemistry, 2019, 58(4): 199-213. |
| 71 | EUBANKS C S, HARGROVE A E. Sensing the impact of environment on small molecule differentiation of RNA sequences[J]. Chemical Communications, 2017, 53(100): 13363-13366. |
| 72 | ZUFFO M, XIE X, GRANZHAN A. Strength in numbers: development of a fluorescence sensor array for secondary structures of DNA[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2019, 25(7): 1812-1818. |
| 73 | ZUFFO M, GANDOLFINI A, HEDDI B, et al. Harnessing intrinsic fluorescence for typing of secondary structures of DNA[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 48(11): e61. |
| 74 | DEL VILLAR-GUERRA R, GRAY R D, TRENT J O, et al. A rapid fluorescent indicator displacement assay and principal component/cluster data analysis for determination of ligand-nucleic acid structural selectivity[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 46(7): e41. |
| 75 | LIU Q J, WU C S, CAI H, et al. Cell-based biosensors and their application in biomedicine[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(12): 6423-6461. |
| 76 | WU C S, DU L P, WANG D, et al. A biomimetic olfactory-based biosensor with high efficiency immobilization of molecular detectors[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2012, 31(1): 44-48. |
| 77 | 庄柳静, 周俊, 董琪, 等. 利用动物嗅觉诊断癌症技术的研究进展[J]. 科学通报, 2013, 58(15): 1369-1378. |
| ZHUANG L J, ZHOU J, DONG Q, et al. The research progress of using the mammalian olfaction for cancer diagnosis[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(15): 1369-1378. | |
| 78 | LIM J H, PARK J H, AHN J H, et al. A peptide receptor-based bioelectronic nose for the real-time determination of seafood quality[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2013, 39(1): 244-249. |
| 79 | SMITH R G, D'SOUZA N, NICKLIN S. A review of biosensors and biologically-inspired systems for explosives detection[J]. Analyst, 2008, 133(5): 571-584. |
| 80 | PAULING L, ROBINSON A B, TERANISHI R, et al. Quantitative analysis of urine vapor and breath by gas-liquid partition chromatography[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1971, 68(10): 2374-2376. |
| 81 | GORDON S M, SZIDON J P, KROTOSZYNSKI B K, et al. Volatile organic compounds in exhaled air from patients with lung cancer[J]. Clinical Chemistry, 1985, 31(8): 1278-1282. |
| 82 | SHCHERBO D, SHEMIAKINA I I, RYABOVA A V, et al. Near-infrared fluorescent proteins[J]. Nature Methods, 2010, 7(10): 827-829. |
| 83 | YU D, GUSTAFSON W C, HAN C, et al. An improved monomeric infrared fluorescent protein for neuronal and tumour brain imaging[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 3626. |
| 84 | MCISAAC R S, ENGQVIST M K M, WANNIER T, et al. Directed evolution of a far-red fluorescent rhodopsin[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(36): 13034-13039. |
| 85 | ZHAO L Y, ZOU Q L, YAN X H. Self-assembling peptide-based nanoarchitectonics[J]. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 2019, 92(1): 70-79. |
| 86 | SAWADA T, MIHARA H, SERIZAWA T. Peptides as new smart bionanomaterials: molecular-recognition and self-assembly capabilities[J]. The Chemical Record, 2013, 13(2): 172-186. |
| 87 | FUKUNAGA K, TSUTSUMI H, MIHARA H. Self-assembling peptides as building blocks of functional materials for biomedical applications[J]. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 2019, 92(2): 391-399. |
| 88 | SERIZAWA T, SAWADA T, MATSUNO H. Highly specific affinities of short peptides against synthetic polymers[J]. Langmuir, 2007, 23(22): 11127-11133. |
| 89 | MATSUNO H, SEKINE J, YAJIMA H, et al. Biological selection of peptides for poly(L-lactide) substrates[J]. Langmuir, 2008, 24(13): 6399-6403. |
| 90 | DATE T, SEKINE J, MATSUNO H, et al. Polymer-binding peptides for the noncovalent modification of polymer surfaces: effects of peptide density on the subsequent immobilization of functional proteins[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2011, 3(2): 351-359. |
| 91 | SERIZAWA T, FUKUTA H, DATE T, et al. Affinity-based release of polymer-binding peptides from hydrogels with the target segments of peptides[J]. Chemical Communications, 2016, 52(11): 2241-2244. |
| 92 | ZASLOFF M. Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms[J]. Nature, 2002, 415(6870): 389-395. |
| 93 | HALE J D, HANCOCK R E. Alternative mechanisms of action of cationic antimicrobial peptides on bacteria[J]. Expert Review of Anti-Infective Therapy, 2007, 5(6): 951-959. |
| 94 | UZARSKI J R, MELLO C M. Detection and classification of related lipopolysaccharides via a small array of immobilized antimicrobial peptides[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 84(17): 7359-7366. |
| 95 | YUAN H X, LIU Z, LIU L B, et al. Cationic conjugated polymers for discrimination of microbial pathogens[J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(25): 4333-4338. |
| 96 | BORNSCHEUER U T, HUISMAN G W, KAZLAUSKAS R J, et al. Engineering the third wave of biocatalysis[J]. Nature, 2012, 485(7397): 185-194. |
| 97 | LIN Y H, REN J S, QU X G. Nano-gold as artificial enzymes: hidden talents[J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(25): 4200-4217. |
| 98 | LIPPINCOTT-SCHWARTZ J, SNAPP E, KENWORTHY A. Studying protein dynamics in living cells[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2001, 2(6): 444-456. |
| 99 | KANDA T, , SULLIVAN K F, WAHL G M. Histone-GFP fusion protein enables sensitive analysis of chromosome dynamics in living mammalian cells[J]. Current Biology, 1998, 8(7): 377-385. |
| 100 | CLARK J, GRZNAROVA P, STANSELL E, et al. A Mason-Pfizer Monkey virus Gag-GFP fusion vector allows visualization of capsid transport in live cells and demonstrates a role for microtubules[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(12): e83863. |
| 101 | HU S F, CHEN X Y, LEI C Y, et al. Charge designable and tunable GFP as a target pH-responsive carrier for intracellular functional protein delivery and tracing[J]. Chemical Communications, 2018, 54(56): 7806-7809. |
| 102 | DE M, RANA S, AKPINAR H, et al. Sensing of proteins in human serum using conjugates of nanoparticles and green fluorescent protein[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2009, 1(6): 461-465. |
| 103 | BAJAJ A, RANA S, MIRANDA O R, et al. Cell surface-based differentiation of cell types and cancer states using a gold nanoparticle-GFP based sensing array[J]. Chemical Science, 2010, 1(1): 134-138. |
| 104 | GENG Y Y, CHATTOPADHYAY A N, ZHANG X Z, et al. Nano assessing nano: nanosensor-enabled detection of cell phenotypic changes identifies nanoparticle toxicological effects at ultra-low exposure levels[J]. Small, 2020, 16(36): 2002084. |
| 105 | GENG Y Y, , GOEL H L, LE N B, et al. Rapid phenotyping of cancer stem cells using multichannel nanosensor arrays[J]. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, 2018, 14(6): 1931-1939. |
| 106 | LE N D B, WANG X, GENG Y Y, et al. Rapid and ultrasensitive detection of endocrine disrupting chemicals using a nanosensor-enabled cell-based platform[J]. Chemical Communications, 2017, 53(62): 8794-8797. |
| 107 | WANG B H, HAN J S, BOJANOWSKI N M, et al. An optimized sensor array identifies all natural amino acids[J]. ACS Sensors, 2018, 3(8): 1562-1568. |
| 108 | RANA S, ELCI S G, MOUT R, et al. Ratiometric array of conjugated polymers-fluorescent protein provides a robust mammalian cell sensor[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(13): 4522-4529. |
| 109 | SUZUKI S, SAWADA T, SERIZAWA T. Identification of water-soluble polymers through discrimination of multiple optical signals from a single peptide sensor[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(47): 55978-55987. |
| 110 | HAN J S, MA C, WANG B H, et al. A hypothesis-free sensor array discriminates whiskies for brand, age, and taste[J]. Chem, 2017, 2(6): 817-824. |
| 111 | LIU C, YOU X R, LU D K, et al. Gelsolin encountering Ag nanorods/triangles: an aggregation-based colorimetric sensor array for in vivo monitoring the cerebrospinal Aβ42% as an indicator of Cd2+ exposure-related Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis[J]. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 2020, 3(11): 7965-7973. |
| 112 | MIRANDA O R, CHEN H T, YOU C C, et al. Enzyme-amplified array sensing of proteins in solution and in biofluids[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(14): 5285-5289. |
| 113 | MIRANDA O R, LI X N, GARCIA-GONZALEZ L, et al. Colorimetric bacteria sensing using a supramolecular enzyme-nanoparticle biosensor[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(25): 9650-9653. |
| 114 | HAN J S, CHENG H R, WANG B H, et al. A polymer/peptide complex-based sensor array that discriminates bacteria in urine[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(48): 15246-15251. |
| 115 | FAN X B, XU W, HAN J S, et al. Antimicrobial peptide hybrid fluorescent protein based sensor array discriminate ten most frequent clinic isolates[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects, 2019, 1863(6): 1158-1166. |
| 116 | FAN X B, XU W, GAO W, et al. A facile method to classify clinic isolates with a turn-off sensor array based on graphene oxide and antimicrobial peptides[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2020, 307: 127607. |
| 117 | FU M Q, WANG X C, DOU W T, et al. Supramolecular fluorogenic peptide sensor array based on graphene oxide for the differential sensing of ebola virus[J]. Chemical Communications, 2020, 56(43): 5735-5738. |
| 118 | GHANEM E, HOPFER H, NAVARRO A, et al. Predicting the composition of red wine blends using an array of multicomponent peptide-based sensors[J]. Molecules, 2015, 20(5): 9170-9182. |
| [1] | 董颖, 马孟丹, 黄卫人. CRISPR-Cas系统的小型化研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 105-117. |
| [2] | 郑益坤, 郑婕, 胡国鹏. 光遗传学工具在学习记忆中的应用研究[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 87-104. |
| [3] | 温艳华, 刘合栋, 曹春来, 巫瑞波. 蛋白质工程在医药产业中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 65-86. |
| [4] | 赵亮, 李振帅, 付丽平, 吕明, 王士安, 张全, 刘立成, 李福利, 刘自勇. 生物转化一碳化合物原料产油脂与单细胞蛋白研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1300-1318. |
| [5] | 王子渊, 杨立荣, 吴坚平, 郑文隆. 酶促合成手性氨基酸的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1319-1349. |
| [6] | 李庚, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 王佳, 袁其朋. 过氧化物酶的重组表达和应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1498-1517. |
| [7] | 杨皓然, 叶发荣, 黄平, 王平. 糖蛋白合成的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1072-1101. |
| [8] | 张宣梁, 李青婷, 王飞. DNA存储系统中的数据写入[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1125-1141. |
| [9] | 叶精勤, 黄文华, 潘超, 朱力, 王恒樑. 合成生物学在多糖结合疫苗研发中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(2): 338-352. |
| [10] | 刘泽众, 周洁, 朱赟, 陆路, 姜世勃. 基于重组人Ⅲ型胶原蛋白的三聚体抗原疫苗策略在新冠和流感疫苗中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(2): 385-395. |
| [11] | 杜瑶, 高宏丹, 刘家坤, 刘孝荣, 邢志浩, 张涛, 马东礼. CRISPR-Cas系统在病原核酸检测中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 202-216. |
| [12] | 朱景勇, 李钧翔, 李旭辉, 张瑾, 毋文静. 深度学习在基于序列的蛋白质互作预测中的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 88-106. |
| [13] | 吴玉洁, 刘欣欣, 刘健慧, 杨开广, 随志刚, 张丽华, 张玉奎. 基于高通量液相色谱质谱技术的菌株筛选与关键分子定量分析研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 1000-1019. |
| [14] | 刘晚秋, 季向阳, 许慧玲, 卢屹聪, 李健. 限制性内切酶的无细胞快速制备研究[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(4): 840-851. |
| [15] | 马孟丹, 尚梦宇, 刘宇辰. CRISPR-Cas9系统在肿瘤生物学中的应用及前景[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(4): 703-719. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

