合成生物学 ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (6): 942-963.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-061
甾体化合物绿色生物制造:从生物转化到微生物从头合成
熊亮斌1,2, 宋璐1, 赵云秋1, 刘坤1, 刘勇军1, 王风清1, 魏东芝1
- 1.华东理工大学,鲁华生物技术研究所,生物反应器国家重点实验室,上海 200237
2.上海健康医学院,协同科研中心,上海 201318
-
收稿日期:2021-06-02修回日期:2021-07-20出版日期:2021-12-31发布日期:2022-01-21 -
通讯作者:王风清,魏东芝 -
作者简介:熊亮斌 (1986—),男,助理研究员。研究方向为代谢工程及合成生物学。E-mail:lbxiong2010@163.com宋璐 (1995—),女,博士研究生。研究方向为生物催化,代谢工程及合成生物学。E-mail:s13127579253@163.com王风清 (1977—),男,副教授,博士生导师。研究方向为生物催化,萜类、甾体类等天然活性化合物的微生物合成生物学研究。E-mail:fqwang@ecust.edu.cn魏东芝 (1963—),男,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为生物催化,萜类、甾体类等天然活性化合物的微生物合成生物学研究。E-mail:dzhwei@ecust.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(21776075);中国博士后基金面上项目(2020M671028)
Green biomanufacturing of steroids: from biotransformation to de novo synthesis by microorganisms
XIONG Liangbin1,2, SONG Lu1, ZHAO Yunqiu1, LIU Kun1, LIU Yongjun1, WANG Fengqing1, WEI Dongzhi1
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering,Newworld Institute of Biotechnology,East China University of Science and Technology,Shanghai 200237,China
2.Collaborative Innovation Center for Biomedicine,Shanghai University of Medicine and Health Sciences,Shanghai 201318,China
-
Received:2021-06-02Revised:2021-07-20Online:2021-12-31Published:2022-01-21 -
Contact:WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi
摘要:
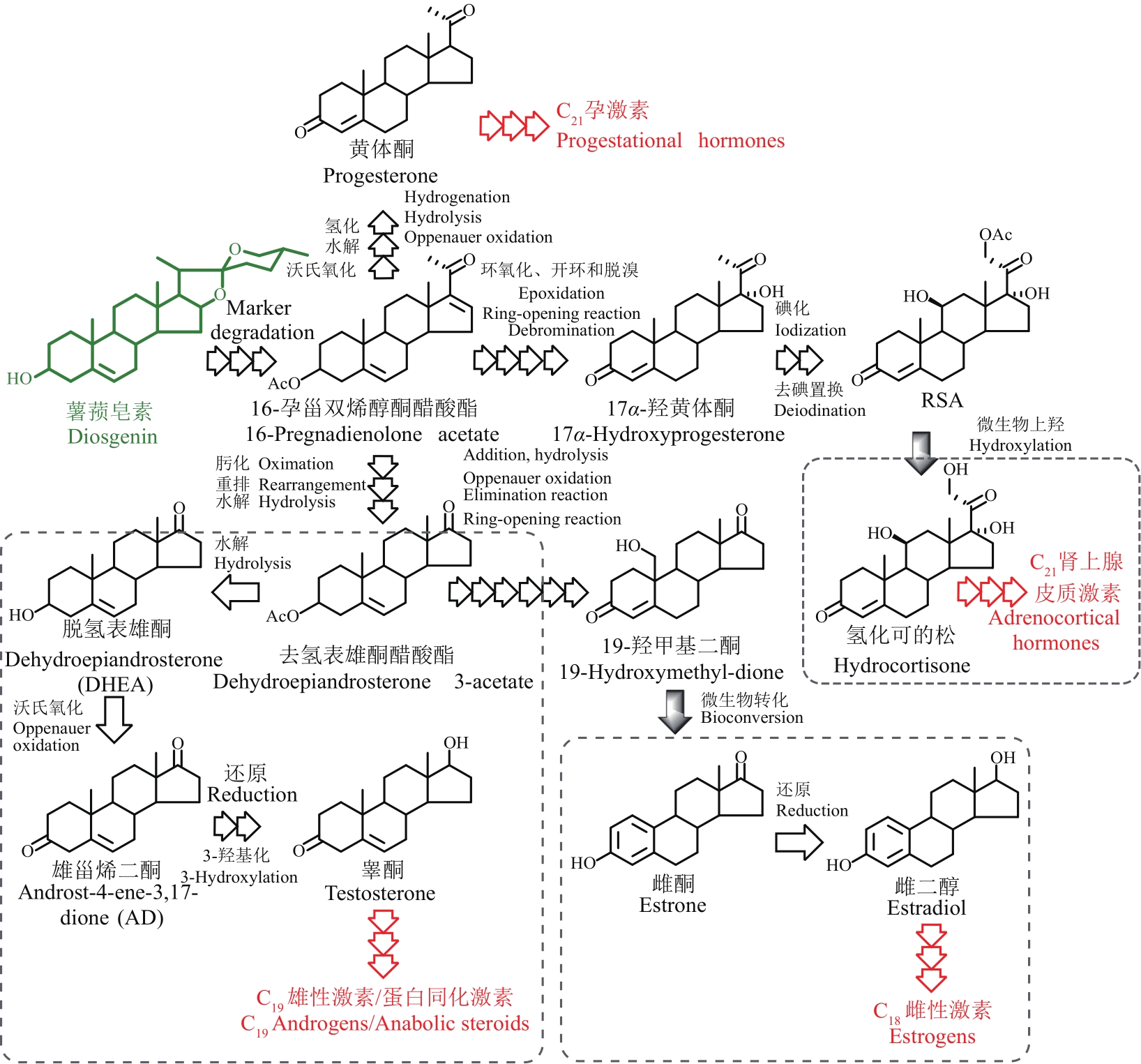
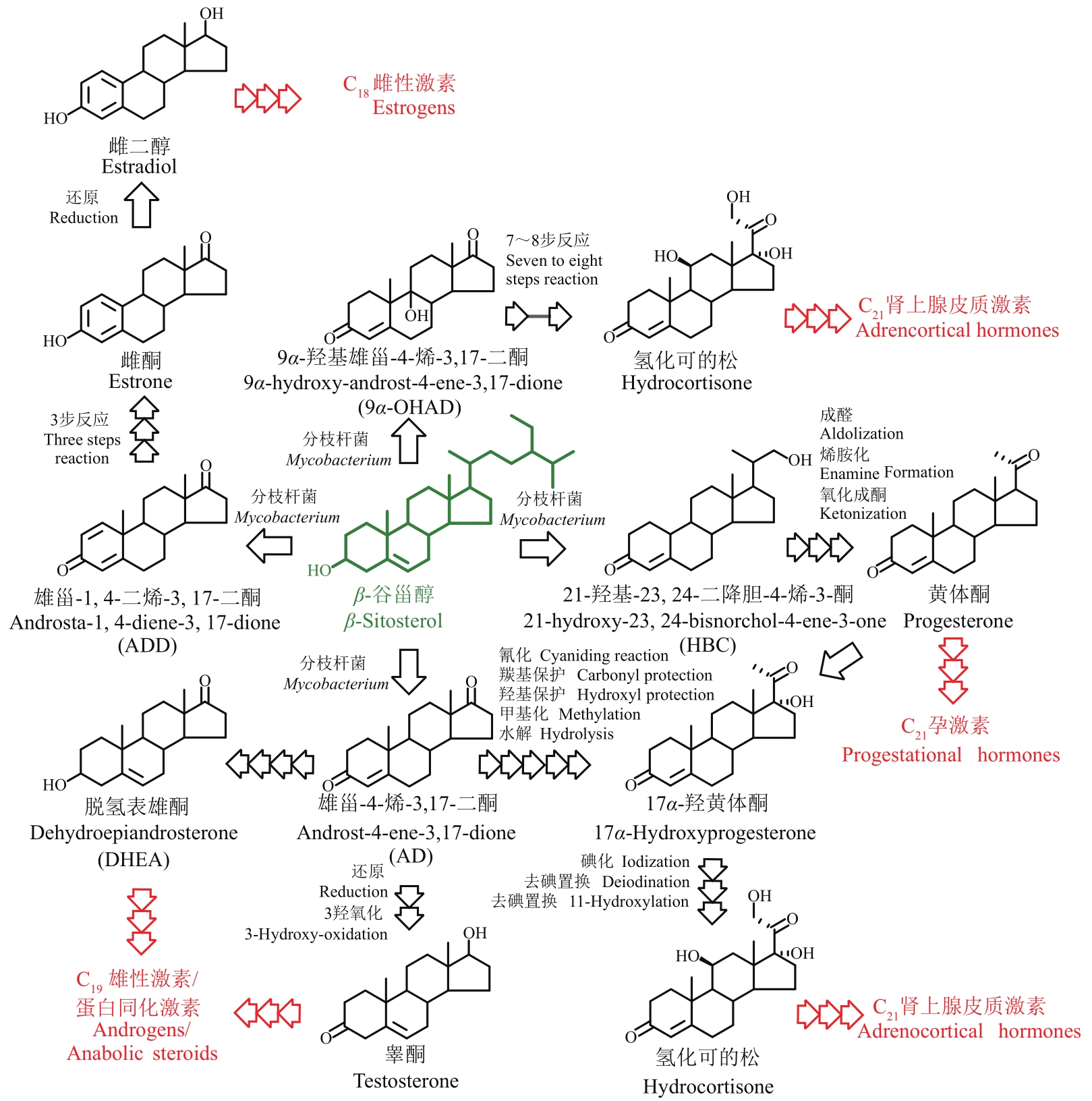
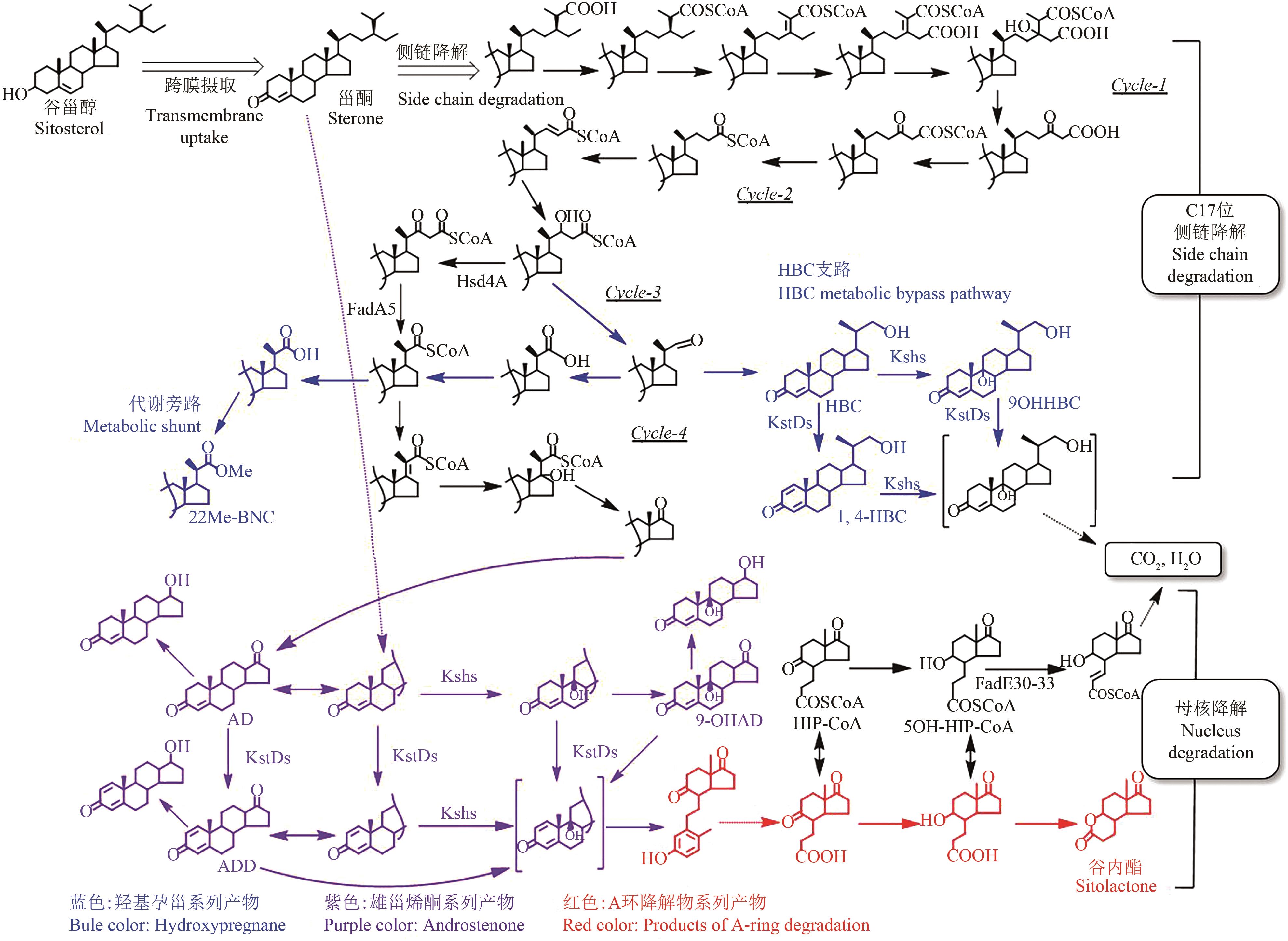
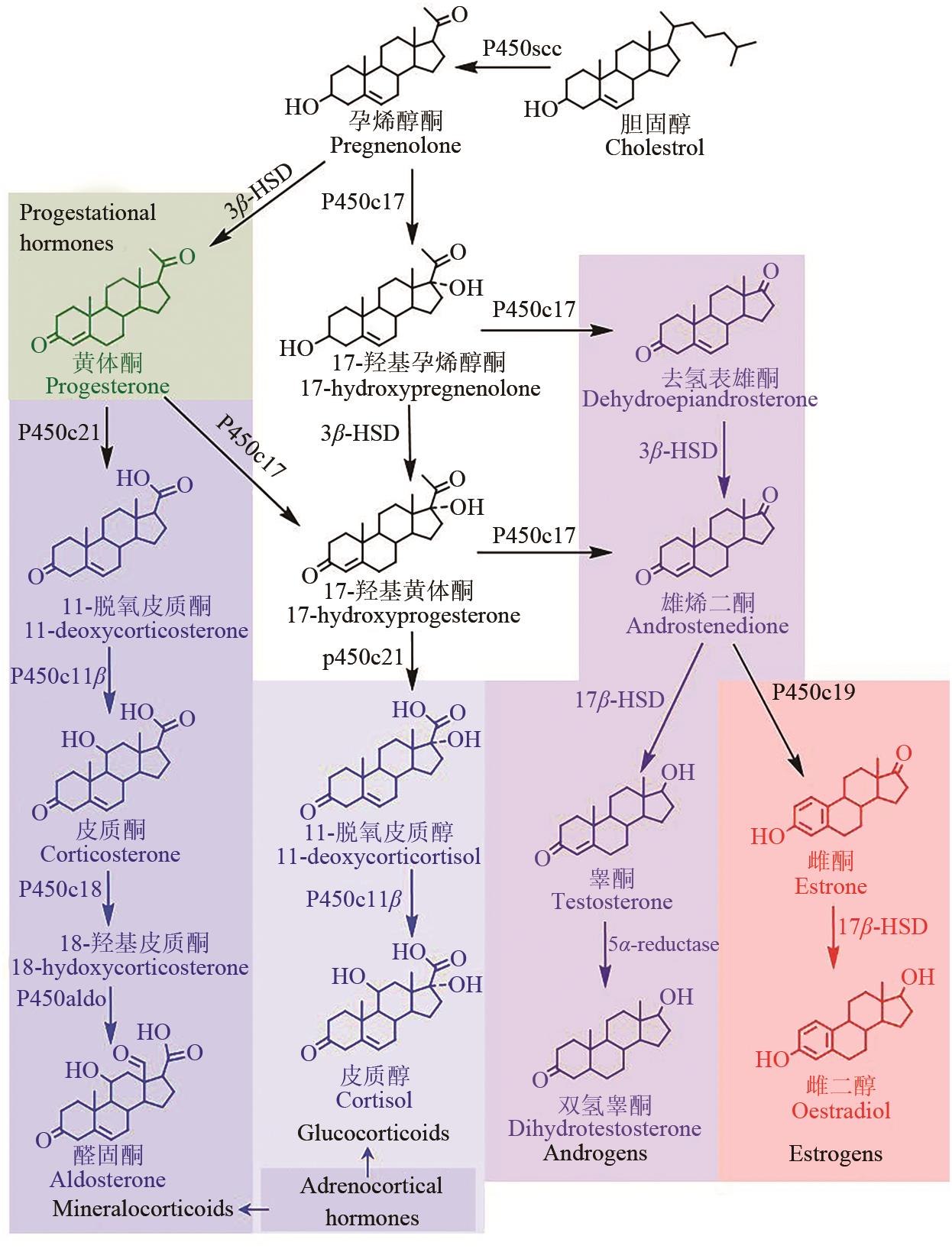
甾体化合物(简称甾体)分布广泛、功能卓越,在机体生长、物种繁育以及代谢调控等方面,发挥着难以取代的生理功能。因此,天然甾体及其衍生物被广泛用于生殖健康、内分泌调控等领域,是器官移植、重症感染等许多危重疾病的“刚需药”和“救命药”。甾体结构复杂、构型精巧,很难通过化学全合成来生产,当前主要以天然甾体皂素或甾醇为原料,通过化学与生物转化相结合的半合成法获得。然而,甾体药物的生产路线长、工艺复杂、收率低,涉及大量有毒有害试剂和重金属催化剂的使用,污水废渣排放量大、处理难度高,总体成本居高不下。为改变此局面,推动产业的转型升级,大力开发绿色生物制造技术是行业健康发展的大势所趋。当前,甾体制药工业正处于以生物催化转化取代化学合成的产业升级阶段,随着高效酶和细胞转化的成功应用,传统的甾体生产模式正发生着深刻变化。在此基础上,若能进一步利用合成生物学技术,创建可高效从头合成甾体的微生物细胞工厂,则将彻底改变甾体制药的工业模式,切实实现甾体药物的绿色制造。近年来,已有利用微生物从头合成部分甾体化合物的报道,然而由于甾体的天然合成机制异常复杂,如何实现细胞工厂的高效生产,仍是目前面临的主要挑战。本文从甾体药物生产方式的演变出发,系统综述了甾体生物催化转化和从头合成的最新进展,重点阐述了甾体生物催化转化酶的挖掘及改造、微生物代谢转化甾醇机制的解析及转化细胞工厂的开发、微生物从头合成甾体人工路线的创建三部分内容,以期对甾体药物绿色生物制造的现状和趋势做出合理的总结与展望。
中图分类号:
引用本文
熊亮斌, 宋璐, 赵云秋, 刘坤, 刘勇军, 王风清, 魏东芝. 甾体化合物绿色生物制造:从生物转化到微生物从头合成[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(6): 942-963.
XIONG Liangbin, SONG Lu, ZHAO Yunqiu, LIU Kun, LIU Yongjun, WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi. Green biomanufacturing of steroids: from biotransformation to de novo synthesis by microorganisms[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(6): 942-963.
| 反应类型 | 羟基化酶 | 微生物来源 |
|---|---|---|
| 11β-OH[ | CYP103168 | 新月弯孢霉 |
| CYP5311B2 | 犁头霉菌 | |
| 11α-OH[ | CYP5311B1 CYP68L8、CYP68J5 | 蓝色犁头霉AS3.65 赭曲霉TCCC41060 |
| 9α-OH[ | KshA/B、TDO | 普提达假单胞菌F117 |
| 7β-OH[ | P450-BM3 | 巨大芽孢杆菌 |
| CYP107D1 | 链霉菌 | |
| 25-OH[ | CYP105A1 | 灰色链霉菌 |
| CYP107-Vdh | Pseudonocardia autotrophica | |
| 19-OH[ | STH10 | Thanatephorus cucumeris NBRC 6298 |
表1 甾体化合物羟基化反应的类型
Tab. 1 Types of steroidal hydroxylation
| 反应类型 | 羟基化酶 | 微生物来源 |
|---|---|---|
| 11β-OH[ | CYP103168 | 新月弯孢霉 |
| CYP5311B2 | 犁头霉菌 | |
| 11α-OH[ | CYP5311B1 CYP68L8、CYP68J5 | 蓝色犁头霉AS3.65 赭曲霉TCCC41060 |
| 9α-OH[ | KshA/B、TDO | 普提达假单胞菌F117 |
| 7β-OH[ | P450-BM3 | 巨大芽孢杆菌 |
| CYP107D1 | 链霉菌 | |
| 25-OH[ | CYP105A1 | 灰色链霉菌 |
| CYP107-Vdh | Pseudonocardia autotrophica | |
| 19-OH[ | STH10 | Thanatephorus cucumeris NBRC 6298 |
| 1 | DUFOURC E J. Sterols and membrane dynamics[J]. Journal of Chemical Biology, 2008, 1(1): 63-77. |
| 2 | FESTUCCI-BUSELLI RA, CONTIM LAS, BARBOSA LCA, et al. Biosynthesis and potential functions of the ecdysteroid 20-hydroxyecdysone—a review[J]. Botany, 2008, 86(9): 978-987. |
| 3 | KHRIPACH V, ZHABINSKII V, DE GROOT A. Twenty years of brassinosteroids: steroidal plant hormones warrant better crops for the XXI century[J]. Annals of Botany,2000, 86(3): 441-447. |
| 4 | TUCKEY R C. Progesterone synthesis by the human placenta[J]. Placenta, 2005, 26(4): 273-281. |
| 5 | PARISH E J, NES W D. Biochemistry and function of sterols[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1997. |
| 6 | WANG F Q, YAO K, WEI D Z. From soybean phytosterols to steroid hormones, soybean and health[M]. Rijeka, Croatia: Intech, 2011. |
| 7 | VALLÉE M, VITIELLO S, BELLOCCHIO L, et al. Pregnenolone can protect the brain from cannabis intoxication[J]. Science, 2014, 343(6166): 94-98. |
| 8 | XIONG L B, LIU H H, ZHAO M, et al. Enhancing the bioconversion of phytosterols to steroidal intermediates by the deficiency of kasB in the cell wall synthesis of Mycobacterium neoaurum [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2020, 19(1): 80. |
| 9 | FERNÁNDEZ-CABEZÓN L, GALÁN B, GARCÍA J L. New insights on steroid biotechnology[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9: 958. |
| 10 | HOGG JA. Steroids, the steroid community, and Upjohn in perspective: a profile of innovation[J]. Steroids, 1992, 57(12): 593-616. |
| 11 | MAHATO SB, GARAI S. Advances in microbial steroid biotransformation[J]. Steroids, 1997, 62(4): 332-345. |
| 12 | FERNÁNDEZ-CRUZ A, RUIZ-ANTORÁN B, MUÑOZ-GÓMEZ A, et al. A retrospective controlled cohort study of the impact of glucocorticoid treatment in SARS-CoV-2 infection mortality[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2020, 64(9): e01168-01120. |
| 13 | MAHASE E. Covid-19: Low dose steroid cuts death in ventilated patients by one third, trial finds[J]. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed), 2020, 369: m2422. |
| 14 | LU C, LIU Y, CHEN B, et al. Prognostic value of lymphocyte count in severe COVID-19 patients with corticosteroid treatment[J]. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 2021, 6(1): 106. |
| 15 | BARNES P J. Corticosteroids: the drugs to beat[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2006, 533(1/2/3): 2-14. |
| 16 | STONG R A, KOLODNY E, KELSEY R G, et al. Effect of plant sterols and tannins on Phytophthora ramorum growth and sporulation[J]. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 2013, 39(6): 733-743. |
| 17 | CHIANG Y R, WEI S T, WANG P H, et al. Microbial degradation of steroid sex hormones: Implications for environmental and ecological studies[J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 2020, 13(4): 926-949. |
| 18 | ROWLAND S J, WEST C E, JONES D, et al. Steroidal aromatic ‘naphthenic acids’ in oil sands process-affected water: structural comparisons with environmental estrogens[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(22): 9806-9815. |
| 19 | NICOLAOU KC, MONTAGNON T: Molecules that changed the world : a brief history of the art and science of synthesis and its impact on society[M]. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, 2008. |
| 20 | 郭瑞霞, 李力更, 王于方, 等. 天然药物化学史话: 甾体化合物[J]. 中草药, 2016, 47(8): 1251-1264. |
| GUO R X, LI L G, WANG Y F, et al. Historical story on natural medicinal chemistry: steroids[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2016, 47(8): 1251-1264. | |
| 21 | MARKER R E, Sterols KRUEGER J.. CXII. sapogenins. XLI. the preparation of trillin and its conversion to progesterone[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1940, 62(12): 3349-3350. |
| 22 | 韩广甸, 金善炜, 吴毓林. 黄鸣龙——我国有机化学的一位先驱[J]. 化学进展, 2012, 24(7): 1229-1235. |
| HAN G D, JIN S W, WU Y L. Huang Ming-Long—A pioneer of organic chemistry in China[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2012, 24(7): 1229-1235. | |
| 23 | 王印. 浅析黄姜产业的发展对策[J]. 农村经济与科技, 2013, 24(8): 44-46. |
| WANG Y. Development countermeasure of turmeric industry [J]. Rural Economy and Science-Technology, 2013, 24(8): 44-46. | |
| 24 | 熊亮斌. 分枝杆菌甾醇代谢途径的解析及高产甾体医药中间体工程菌株的构建[D]. 上海: 华东理工大学, 2017. |
| XIONG L B. Analysis of the sterol metabolic pathway in mycobacteria and the modification of high-yield steroidal pharmaceutical precursors producing strains[D].Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2017. | |
| 25 | DUPORT C, SPAGNOLI R, DEGRYSE E, et al. Self-sufficient biosynthesis of pregnenolone and progesterone in engineered yeast[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 1998, 16(2): 186-189. |
| 26 | SZCZEBARA F M, CHANDELIER C, VILLERET C, et al. Total biosynthesis of hydrocortisone from a simple carbon source in yeast[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2003, 21(2): 143-149. |
| 27 | RESETIĆ J, REINER Z, LÜDECKE D, et al. The effects of cortisol, 11-epicortisol, and lysine vasopressin on DNA and RNA synthesis in isolated human adrenocorticotropic hormone-secreting pituitary tumor cells[J]. Steroids, 1990, 55(3): 98-100. |
| 28 | MAO S, ZHANG L, GE Z, et al. Microbial hydroxylation of steroids by Penicillium decumbens [J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic 2016, 133: S346-S351. |
| 29 | KOZŁOWSKA E, HOC N, SYCZ J, et al. Biotransformation of steroids by entomopathogenic strains of Isaria farinosa [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2018, 17(1): 71. |
| 30 | LI Q, SHI L, LIU Y, et al. Improved 11α-hydroxycanrenone production by modification of cytochrome P450 monooxygenase gene in Aspergillus ochraceus [J]. Acta Pharmaceutica, 2021, 71(1): 99-114. |
| 31 | ZHOU X L, ZHANG Y, SHEN Y B, et al. Efficient production of androstenedione by repeated batch fermentation in waste cooking oil media through regulating NAD+/NADH ratio and strengthening cell vitality of Mycobacterium neoaurum [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 279: 209-217. |
| 32 | SU L Q, SHEN Y B, ZHANG W K, et al. Cofactor engineering to regulate NAD+/NADH ratio with its application to phytosterols biotransformation[J]. Microbial Cell Factories,2017, 16(1): 182. |
| 33 | FELPETO-SANTERO C, GALAN B, LUENGO J M, et al. Identification and expression of the 11β-steroid hydroxylase from Cochliobolus lunatus in Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Microbial Biotechnologys, 2019, 12(5): 856-868. |
| 34 | CHEN J, FAN F, QU G, et al. Identification of Absidia orchidis steroid 11β-hydroxylation system and its application in engineering Saccharomyces cerevisiae for one-step biotransformation to produce hydrocortisone[J]. Metabolic Engineering,2020, 57: 31-42. |
| 35 | FENYVESI É, PUSKÁS I, SZENTE L. Applications of steroid drugs entrapped in cyclodextrins[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2019, 17(1): 375-391. |
| 36 | ZHU Z, GAO X, SONG Z, et al. Development of engineered ferredoxin reductase systems for the efficient hydroxylation of steroidal substrates[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020, 8(44): 16720-16730. |
| 37 | WANG R, SUI P, HOU X, et al. Cloning and identification of a novel steroid 11α-hydroxylase gene from Absidia coerulea [J]. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2017, 171: 254-261. |
| 38 | WANG X, YANG X, JIA X, et al. Determination of steroid hydroxylation specificity of an industrial strain Aspergillus ochraceus TCCC41060 by cytochrome P450 gene CYP68J5 [J]. Annals of Microbiology,2020, 70(1): 45. |
| 39 | LI A, ACEVEDO-ROCHA C G, D'AMORE L, et al. Regio-and stereoselective steroid hydroxylation at C7 by cytochrome P450 monooxygenase mutants[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2020, 59(30): 12499-12505. |
| 40 | GROBE S, BADENHORST C P S, BAYER T, et al. Engineering regioselectivity of a P450 monooxygenase enables the synthesis of ursodeoxycholic acid via 7β-hydroxylation of lithocholic acid[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2021, 60(2): 753-757. |
| 41 | SAKAKI T, SUGIMOTO H, HAYASHI K, et al. Bioconversion of vitamin D to its active form by bacterial or mammalian cytochrome P450[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2011, 1814(1): 249-256. |
| 42 | YASUTAKE Y, NISHIOKA T, IMOTO N, et al. A single mutation at the ferredoxin binding site of P450 Vdh enables efficient biocatalytic production of 25-hydroxyvitamin D(3)[J]. Chembiochem, 2013, 14(17): 2284-2291. |
| 43 | LU W, CHEN X, FENG JH, et al. A fungal P450 enzyme from Thanatephorus cucumeris with steroid hydroxylation capabilities[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2018, 84(13): e00503-18. |
| 44 | WANG J, ZHANG Y, LIU H, et al. A biocatalytic hydroxylation-enabled unified approach to C19-hydroxylated steroids[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 3378. |
| 45 | MAO S H, WANG J W, LIU F F, et al. Engineering of 3-ketosteroid-Δ 1-dehydrogenase based site-directed saturation mutagenesis for efficient biotransformation of steroidal substrates[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2018, 17(1): 141. |
| 46 | ZHANG R J, LIU X C, WANG Y S, et al. Identification, function, and application of 3-ketosteroid Δ 1-dehydrogenase isozymes in Mycobacterium neoaurum DSM 1381 for the production of steroidic synthons[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2018, 17(1): 77. |
| 47 | LUO J M, CUI H L, JIA H C, et al. Identification, biological characteristics and the active site residues of 3-ketosteroid Δ 1-dehydrogenase homologues from Arthrobacter simplex [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2020, 68(35): 9496-9512. |
| 48 | YOSHIYAMA-YANAGAWA T, ENYA S, SHIMADA-NIWA Y, et al. The conserved rieske oxygenase DAF-36/Neverland is a novel cholesterol-metabolizing enzyme[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2011, 286(29): 25756-25762. |
| 49 | ZHU Z, LI C, CHENG X, et al. Soluble expression, purification and biochemical characterization of a C-7 cholesterol dehydrogenase from Drosophila melanogaster [J]. Steroids, 2019, 152: 108495. |
| 50 | MAO S, SONG Z, WU M, et al. Expression, purification, refolding, and characterization of a Neverland protein from Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2020, 8: 593041. |
| 51 | OPPERMANN UCT, MASER E. Characterization of a 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/carbonyl reductase from the gram-negative bacterium Comamonas testosteroni [J]. European Journal of Biochemistry, 1996, 241(3): 744-749. |
| 52 | FERNANDES P, CRUZ A, ANGELOVA B, et al. Microbial conversion of steroid compounds: recent developments[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2003, 32(6): 688-705. |
| 53 | LEVY H R, TALALAY P. Bacterial oxidation of steroids I. Ring A dehydrogenations by intact cells[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1959, 234(8): 2009-2013. |
| 54 | DHAR A, SAMANTHA TB. Novel oxidative cleavage of C 17-C 20 bond in pregnane by a Pseudomonas sp.[J]. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,1993, 44(1): 101-104. |
| 55 | TENNESON M E, BATY J D, BILTON R F, et al. The degradation of cholic acid by Pseudomonas sp. NCIB 10590[J]. The Biochemical Journal, 1979, 184(3): 613-618. |
| 56 | TURFITT G E. Microbiological agencies in the degradation of steroids: I. the cholesterol-decomposing organisms of soils[J]. Journal of Bacteriology 1944, 47(6): 487-493. |
| 57 | HORVATH J, KRAMLI A. Microbiological oxidation of cholesterol with Azotobacter [J]. Nature, 1947, 160(4071): 639-639. |
| 58 | SIH C J, WANG K C, TAI H H. C-22 acid intermediates in the microbiological cleavage of the cholesterol side chain[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1967, 89(8): 1956-1957. |
| 59 | DRZYZGA O, LLORENS J M N, DE LAS HERAS L F, et al. Gordonia cholesterolivorans sp. nov., a cholesterol-degrading actinomycete isolated from sewage sludge[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2009, 59(5): 1011-1015. |
| 60 | FERREIRA N P, TRACEY R P. Numerical taxonomy of cholesterol-degrading soil bacteria[J]. Journal of Applied Bacteriology, 1984, 57(3): 429-446. |
| 61 | YAO K, XU L Q, WANG F Q, et al. Characterization and engineering of 3-ketosteroid-Δ 1-dehydrogenase and 3-ketosteroid-9α-hydroxylase in Mycobacterium neoaurum ATCC 25795 to produce 9α-hydroxy-4-androstene-3, 17-dione through the catabolism of sterols[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2014, 24: 181-191. |
| 62 | LIU H H, XU L Q, YAO K, et al. Characterization and engineering of 3-ketosteroid 9α-hydroxylases in Mycobacterium neoaurum ATCC 25795 for the development of androst-1, 4-diene-3, 17-dione and 9α-hydroxy-androst-4-ene-3,17-dione--producing strains[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2018, 84(14): e-02777-17. |
| 63 | XU L Q, LIU Y J, YAO K, et al. Unraveling and engineering the production of 23, 24-bisnorcholenic steroids in sterol metabolism[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 21928. |
| 64 | LIN C W, WANG P H, ISMAIL W, et al. Substrate uptake and subcellular compartmentation of anoxic cholesterol catabolism in Sterolibacterium denitrificans[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2015, 290(2): 1155-1169. |
| 65 | GEIZE R VAN DER, YAM K, HEUSER T, et al. A gene cluster encoding cholesterol catabolism in a soil actinomycete provides insight into Mycobacterium tuberculosis survival in macrophages[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2007, 104(6): 1947-1952. |
| 66 | OUELLET H, JOHNSTON J B, DE MONTELLANO P R. Cholesterol catabolism as a therapeutic target in Mycobacterium tuberculosis [J]. Trends in Microbiology, 2011, 19(11): 530-539. |
| 67 | FERNÁNDEZ-CABEZÓN L, GARCÍA-FERNÁNDEZ E, GALÁN B, et al. Molecular characterization of a new gene cluster for steroid degradation in Mycobacterium smegmatis [J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2017, 19(7): 2546-2563. |
| 68 | YAO K, WANG F Q, ZHANG H C, et al. Identification and engineering of cholesterol oxidases involved in the initial step of sterols catabolism in Mycobacterium neoaurum [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2013, 15(1): 75-87. |
| 69 | WARNKE M, JUNG T, JACOBY C, et al. Functional characterization of three specific acyl-coenzyme A synthetases involved in anaerobic cholesterol degradation in Sterolibacterium denitrificans [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2018, 84: e02721-17. |
| 70 | CAPYK J K, CASABON I, GRUNINGER R, et al. Activity of 3-ketosteroid 9α-hydroxylase (KshAB) indicates cholesterol side chain and ring degradation occur simultaneously in Mycobacterium tuberculosis [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2011, 286(47): 40717-40724. |
| 71 | YANG X X, DUBNAU E, SMITH I, et al. Rv1106c from Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase[J]. Biochemistry,2007, 46(31): 9058-9067. |
| 72 | UHÍA I, GALÁN B, MORALES V, et al. Initial step in the catabolism of cholesterol by Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 13(4): 943-959. |
| 73 | UHÍA I, GALÁN B, MEDRANO F J, et al. Characterization of the KstR-dependent promoter of the gene for the first step of the cholesterol degradative pathway in Mycobacterium smegmatis [J]. Microbiology (Reading, England), 2011, 157(pt 9): 2670-2680. |
| 74 | DRESEN C, LIN L Y, D'ANGELO I, et al. A flavin-dependent monooxygenase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis involved in cholesterol catabolism[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2010, 285(29): 22264-22275. |
| 75 | FERNÁNDEZ-CABEZÓN L, GALÁN B, GARCÍA J L. Unravelling a new catabolic pathway of C-19 steroids in Mycobacterium smegmatis [J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2018, 20(5): 1815-1827. |
| 76 | YUE Q K, KASS I J, SAMPSON N S, et al. Crystal structure determination of cholesterol oxidase from Streptomyces and structural characterization of key active site mutants[J]. Biochemistry, 1999, 38(14): 4277-4286. |
| 77 | LARIO P I, SAMPSON N, VRIELINK A. Sub-atomic resolution crystal structure of cholesterol oxidase: what atomic resolution crystallography reveals about enzyme mechanism and the role of the FAD cofactor in redox activity[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2003, 326(5): 1635-1650. |
| 78 | VRIELINK A, LLOYD L F, BLOW D M. Crystal structure of cholesterol oxidase from Brevibacterium sterolicum refined at 1.8 Å resolution[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology,1991, 219(3): 533-554. |
| 79 | GUEVARA G, FERNÁNDEZ DE LAS HERAS L, PERERA J, et al. Functional differentiation of 3-ketosteroid Δ 1-dehydrogenase isozymes in Rhodococcus ruber strain Chol-4[J]. Microbial Cell Factories 2017, 16(1): 42. |
| 80 | WANG X J, FENG J H, ZHANG D L, et al. Characterization of new recombinant 3-ketosteroid-Δ 1-dehydrogenases for the biotransformation of steroids[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 101(15): 6049-6060. |
| 81 | ZHANG R J, XU X X, CAO H J, et al. Purification, characterization, and application of a high activity 3-ketosteroid-Δ 1-dehydrogenase from Mycobacterium neoaurum DSM 1381[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2019, 103(16): 6605-6616. |
| 82 | ZHANG X, ZHU M, HAN R, et al. A novel 3-phytosterone-9α-hydroxylase oxygenation component and its application in bioconversion of 4-androstene-3, 17-dione to 9α-hydroxy-4-androstene-3, 17-dione coupling with a NADH regeneration formate dehydrogenase[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(14): 2534. |
| 83 | BRAGIN E Y, SHTRATNIKOVA V Y, SCHELKUNOV M I, et al. Genome-wide response on phytosterol in 9-hydroxyandrostenedione-producing strain of Mycobacterium sp. VKM Ac-1817D[J]. BMC Biotechnology, 2019, 19(1): 39. |
| 84 | LIU N, FENG JH, ZHANG R, et al. Efficient microbial synthesis of key steroidal intermediates from bio-renewable phytosterols by genetically modified Mycobacterium fortuitum strains[J]. Green Chemistry,2019, 21: 4076-4085. |
| 85 | WILBRINK M H, PETRUSMA M, DIJKHUIZEN L, et al. FadD19 of Rhodococcus rhodochrous DSM43269, a steroid-coenzyme A ligase essential for degradation of C-24 branched sterol side chains[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2011, 77(13): 4455-4464. |
| 86 | DERMER J, FUCHS G. Molybdoenzyme that catalyzes the anaerobic hydroxylation of a tertiary carbon atom in the side chain of cholesterol[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2012, 287(44): 36905-36916. |
| 87 | WÓJCIK P, GLANOWSKI M, WOJTKIEWICZ A M, et al. Universal capability of 3-ketosteroid Δ 1-dehydrogenases to catalyze Δ 1-dehydrogenation of C17-substituted steroids[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2021, 20(1): 119. |
| 88 | GARCÍA J L, UHÍA I, GALÁN B. Catabolism and biotechnological applications of cholesterol degrading bacteria[J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 2012, 5(6): 679-699. |
| 89 | DONOVA M V, EGOROVA O V. Microbial steroid transformations: current state and prospects[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2012, 94(6): 1423-1447. |
| 90 | YUAN T, WERMAN JM, YIN X, et al. Enzymatic β-oxidation of the cholesterol side chain in Mycobacterium tuberculosis bifurcates stereospecifically at hydration of 3-oxo-cholest-4, 22-dien-24-oyl-CoA[J]. ACS Infectious Diseases,2021, doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.1021c00069 . |
| 91 | DRAPER P. The outer parts of the mycobacterial envelope as permeability barriers[J]. Frontiers in Bioscience, 1998, 3(3): D1253-1261. |
| 92 | TAHLAN K, WILSON R, KASTRINSKY D B, et al. SQ109 targets MmpL3, a membrane transporter of trehalose monomycolate involved in mycolic acid donation to the cell wall core of Mycobacterium tuberculosis [J]. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 2012, 56(4): 1797-1809. |
| 93 | THOMAS S T, VANDERVEN B C, SHERMAN D R, et al. Pathway profiling in Mycobacterium tuberculosis:elucidation of cholesterol-derived catabolite and enzymes that catalyze its metabolism[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2011, 286(51): 43668-43678. |
| 94 | THOMAS S T, SAMPSON N S. Mycobacterium tuberculosis utilizes a unique heterotetrameric structure for dehydrogenation of the cholesterol side chain[J]. Biochemistry, 2013, 52(17): 2895-2904. |
| 95 | OUELLET H, GUAN S, JOHNSTON J B, et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis CYP125A1, a steroid C27 monooxygenase that detoxifies intracellularly generated cholest-4-en-3-one[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2010, 77(3): 730-742. |
| 96 | GARCÍA-FERNÁNDEZ E, FRANK DJ, GALÁN B, et al. A highly conservedmycobacterial cholesterol catabolic pathway[J]. Environmental Microbiology,2013, 15(8): 2342-2359. |
| 97 | XIONG L B, LIU H H, XU L Q, et al. Improving the production of 22-hydroxy-23, 24-bisnorchol-4-ene-3-one from sterols in Mycobacterium neoaurum by increasing cell permeability and modifying multiple genes[J]. Microbial Cell Factories,2017, 16(1): 89. |
| 98 | DAFFE M, DRAPER P. The envelope layers of mycobacteria with reference to their pathogenicity[J]. Advances in Microbial Physiology, 1997, 39(1): 131-203. |
| 99 | KAUR D, GUERIN M E, ŠKOVIEROVÁ H, et al. Chapter 2: biogenesis of the cell wall and other glycoconjugates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis [J]. Advances in Applied Microbiology, 2009, 69(1): 23-78. |
| 100 | JANKUTE M, GROVER S, RANA A K, et al. Arabinogalactan and lipoarabinomannan biosynthesis: structure, biogenesis and their potential as drug targets[J]. Future Microbiology,2012, 7(1): 129-147. |
| 101 | LISOWSKA K, KORYCKA M, HADŁAW-KLIMASZEWSKA O, et al. Permeability of mycobacterial cell envelopes to sterols: peptidoglycan as the diffusion barrier[J]. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 1996, 36(6): 407-419. |
| 102 | SEDLACZEK L, LISOWSKA K, KORYCKA M, et al. The effect of cell wall components on glycine-enhanced sterol side chain degradation to androstene derivatives by Mycobacteria [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 1999, 52(4): 563-571. |
| 103 | RUMIJOWSKA A, LISOWSKA K, ZIÓTKOWSKI A, et al. Transformation of sterols by Mycobacterium vaccae: effect of lecithin on the permeability of cell envelopes to sterols[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology,1997, 13(1): 89-95. |
| 104 | GRZEGORZEWICZ A E, PHAM H, GUNDI V A, et al. Inhibition of mycolic acid transport across the Mycobacterium tuberculosis plasma membrane[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2012, 8(4): 334-341. |
| 105 | XIONG L B, LIU H H, SONG X W, et al. Improving the biotransformation of phytosterols to 9α-hydroxy-4-androstene-3, 17-dione by deleting embC associated with the assembly of cell envelope in Mycobacterium neoaurum [J]. Journal of Biotechnology 2020, 323(2020): 341-346. |
| 106 | SHTRATNIKOVA V Y, SСHELKUNOV M I, FOKINA V V, et al. Different genome-wide transcriptome responses of Nocardioides simplex VKM Ac-2033D to phytosterol and cortisone 21-acetate[J]. BMC Biotechnology, 2021, 21(1): 7. |
| 107 | SHTRATNIKOVA V Y, SCHELKUNOV M I, FOKINA V V, et al. Genome-wide bioinformatics analysis of steroid metabolism-associated genes in Nocardioides simplex VKM Ac-2033D[J]. Current Genetics, 2016, 62(3): 643-656. |
| 108 | XIONG L B, LIU H H, XU L Q, et al. Role identification and application of SigD in the transformation of soybean phytosterol to 9α-hydroxy-4-androstene-3,17-dione in Mycobacterium neoaurum [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2017, 65(3): 626-631. |
| 109 | XIONG L B, SUN W J, LIU Y J, et al. Enhancement of 9α-hydroxy-4-androstene-3,17-dione production from soybean phytosterols by deficiency of a regulated intramembrane proteolysis metalloprotease in Mycobacterium neoaurum [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2017, 65(48): 10520-10525. |
| 110 | SUN W J, WANG L, LIU H H, et al. Characterization and engineering control of the effects of reactive oxygen species on the conversion of sterols to steroid synthons in Mycobacterium neoaurum [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 56: 97-110. |
| 111 | RUSSELL D W. Cholesterol biosynthesis and metabolism[J]. Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy, 1992, 6(2): 103-110. |
| 112 | SONAWANE PD, POLLIER J, PANDA S, et al. Plant cholesterol biosynthetic pathway overlaps with phytosterol metabolism[J]. Nature Plants, 2016, 3(1): 16205. |
| 113 | DUPONT S, LEMETAIS G, FERREIRA T, et al. Ergosterol biosynthesis: a fungal pathway for life on land?[J]. Evolution: International Journal of Organic Evolution, 2012, 66(9): 2961-2968. |
| 114 | BROWN A C, EBERL M, CRICK D C, et al. The nonmevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis is essential and transcriptionally regulated by Dxs[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2010, 192(9): 2424-2433. |
| 115 | LIU G S, LI T, ZHOU W, et al. The yeast peroxisome: a dynamic storage depot and subcellular factory for squalene overproduction[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 57: 151-161. |
| 116 | PEARSON A, BUDIN M, BROCKS J J. Phylogenetic and biochemical evidence for sterol synthesis in the bacterium Gemmata obscuriglobus [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2003, 100(26): 15352-15357. |
| 117 | NES W D. Biosynthesis of cholesterol and other sterols[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2011, 111(10): 6423-6451. |
| 118 | LAMB D C, JACKSON C J, WARRILOW A G S, et al. Lanosterol biosynthesis in the prokaryote Methylococcus capsulatus: insight into the evolution of sterol biosynthesis[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2007, 24(8): 1714-1721. |
| 119 | SOUZA C M, SCHWADE T M, PICHLER H, et al. A stable yeast strain efficiently producing cholesterol instead of ergosterol is functional for tryptophan uptake, but not weak organic acid resistance[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2011, 13(5): 555-569. |
| 120 | PAYNE A H, HALES D B. Overview of steroidogenic enzymes in the pathway from cholesterol to active steroid hormones[J]. Endocrine Reviews, 2004, 25(6): 947-970. |
| 121 | MILLER W L. Disorders in the initial steps of steroid hormone synthesis[J]. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2017, 165: 18-37. |
| 122 | JENKINSON C. The vitamin D metabolome: an update on analysis and function[J]. Cell Biochemistry and Function, 2019, 37(6): 408-423. |
| 123 | TUCKEY R C, CHENG C Y S, SLOMINSKI A T. The serum vitamin D metabolome: what we know and what is still to discover[J]. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2019, 186: 4-21. |
| 124 | SLOMINSKI A T, LI W, KIM T-K, et al. Novel activities of CYP11A1 and their potential physiological significance[J]. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,2015, 151: 25-37. |
| 125 | SLOMINSKI A, SEMAK I, ZJAWIONY J, et al. The cytochrome P450scc system opens an alternate pathway of vitamin D3 metabolism[J]. The FEBS Journal,2005, 272(16): 4080-4090. |
| 126 | GURYEV O, CARVALHO RA, USANOV S, et al. A pathway for the metabolism of vitamin D: unique hydroxylated metabolites formed during catalysis with cytochrome P450scc (CYP11A1)[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2003, 100(25): 14754-14759. |
| 127 | GUO Y D, STRUGNELL S, BACK D W, et al. Transfected human liver cytochrome P-450 hydroxylates vitamin D analogs at different side-chain positions[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1993, 90(18): 8668-8672. |
| 128 | PANDAK W M, KAKIYAMA G. The acidic pathway of bile acid synthesis: not just an alternative pathway[J]. Liver Research, 2019, 3(2): 88-98. |
| 129 | ZHU M, WANG C X, SUN W T, et al. Boosting 11-oxo-β-amyrin and glycyrrhetinic acid synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae via pairing novel oxidation and reduction system from legume plants[J]. Metabolic Engineering,2018, 45: 43-50. |
| 130 | YEE D A, DENICOLA A B, BILLINGSLEY J M, et al. Engineered mitochondrial production of monoterpenes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 55: 76-84. |
| 131 | JIANG J J, YIN H, WANG S, et al. Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for high-level production of salidroside from glucose[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2018, 66(17): 4431-4438. |
| 132 | GOLD N D, FOSSATI E, HANSEN C C, et al. A combinatorial approach to study cytochrome P450 enzymes for de novo production of steviol glucosides inbaker's yeast[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(12): 2918-2929. |
| 133 | LIU X, CHENG J, ZHANG G, et al. Engineering yeast for the production of breviscapine by genomic analysis and synthetic biology approaches[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 448. |
| 134 | EICHENBERGER M, LEHKA B J, FOLLY C, et al. Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for de novo production of dihydrochalcones with known antioxidant, antidiabetic, and sweet tasting properties[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 39: 80-89. |
| 135 | SHEN X L, MAHAJANI M, WANG J, et al. Elevating 4-hydroxycoumarin production through alleviating thioesterase-mediated salicoyl-CoA degradation[J]. Metabolic Engineering,2017, 42: 59-65. |
| 136 | LI Z J, HONG P H, DA Y Y, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of L-malate from xylose[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 48: 25-32. |
| 137 | B-M CORINNE, ISABELLE B, BRUNO D. Process for preparing genetically transformed yeasts capable of producing a molecule of interest at a high titre: WO2012175453[P]. 2012. |
| 138 | SU W, XIAO W H, WANG Y, et al. Alleviating redox imbalance enhances 7-dehydrocholesterol production in engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(6): e0130840. |
| 139 | DU H X, XIAO W H, YING W, et al. Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica for campesterol overproduction[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(1): e0146773. |
| 140 | ZHANG Y, WANG Y, YAO M D, et al. Improved campesterol production in engineered Yarrowia lipolytica strains[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2017, 39(7): 1033-1039. |
| 141 | ZHANG R, ZHANG Y, WANG Y, et al. Pregnenolone overproduction in Yarrowia lipolytica by integrative components pairing of the cytochrome P450scc system[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(12): 2666-2678. |
| 142 | MA B X, KE X, TANG X L, et al. Rate-limiting steps in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ergosterol pathway: towards improved ergosta-5, 7-dien-3β-ol accumulation by metabolic engineering[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 34(4): 55. |
| 143 | DAI Z, WANG B, LIU Y, et al. Producing aglycons of ginsenosides in bakers' yeast[J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 3698. |
| 144 | WU Y, XU S, GAO X, et al. Enhanced protopanaxadiol production from xylose by engineered Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2019, 18: 83. |
| 145 | WANG P, WEI W, YE W, et al. Synthesizing ginsenoside Rh2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell factory at high-efficiency[J]. Cell Discovery, 2019, 5: 5. |
| 146 | YANG C, LI C, WEI W, et al. The unprecedented diversity of UGT94-family UDP-glycosyltransferases in Panax plants and their contribution to ginsenoside biosynthesis[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 15394. |
| 147 | YAN X, FAN Y, WEI W, et al. Production of bioactive ginsenoside compound K in metabolically engineered yeast[J]. Cell Research, 2014, 24(6): 770-773. |
| 148 | WANG P, WANG J, ZHAO G, et al. Systematic optimization of the yeast cell factory for sustainable and high efficiency production of bioactive ginsenoside compound K[J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology,2021, 6(2): 69-76. |
| [1] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [2] | 郑梦梦, 刘犇犇, 林芝, 瞿旭东. 重要甾体化合物的化学酶法合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 941-959. |
| [3] | 晏雄鹰, 王振, 娄吉芸, 张皓瑜, 黄星宇, 王霞, 杨世辉. 生物燃料高效生产微生物细胞工厂构建研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(6): 1082-1121. |
| [4] | 吴玉洁, 刘欣欣, 刘健慧, 杨开广, 随志刚, 张丽华, 张玉奎. 基于高通量液相色谱质谱技术的菌株筛选与关键分子定量分析研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 1000-1019. |
| [5] | 孙梦楚, 陆亮宇, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 王佳, 袁其朋. 基于荧光检测的高通量筛选技术和装备助力细胞工厂构建[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 947-965. |
| [6] | 高纤云, 牛灵雪, 见妮, 管宁子. 微生物合成生物学在疾病诊疗上的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(2): 263-282. |
| [7] | 任师超, 孙秋艳, 冯旭东, 李春. 微生物细胞工厂合成五环三萜皂苷类化合物[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(1): 168-183. |
| [8] | 郭亮, 高聪, 柳亚迪, 陈修来, 刘立明. 大肠杆菌生产饲用氨基酸的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(6): 964-981. |
| [9] | 陈久洲, 王钰, 蒲伟, 郑平, 孙际宾. 5-氨基乙酰丙酸生物合成技术的发展及展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(6): 1000-1016. |
| [10] | 吕建明, 赵欢, 胡丹, 高昊. 天然产物中炔基的生物合成机制研究及其应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(5): 734-750. |
| [11] | 袁姚梦, 邢新会, 张翀. 微生物细胞工厂的设计构建:从诱变育种到全基因组定制化创制[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(6): 656-673. |
| [12] | 夏思杨, 江丽红, 蔡谨, 黄磊, 徐志南, 连佳长. 酿酒酵母基因组进化的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(5): 556-569. |
| [13] | 许可, 王靖楠, 李春. 智能抗逆微生物细胞工厂与绿色生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(4): 427-439. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||