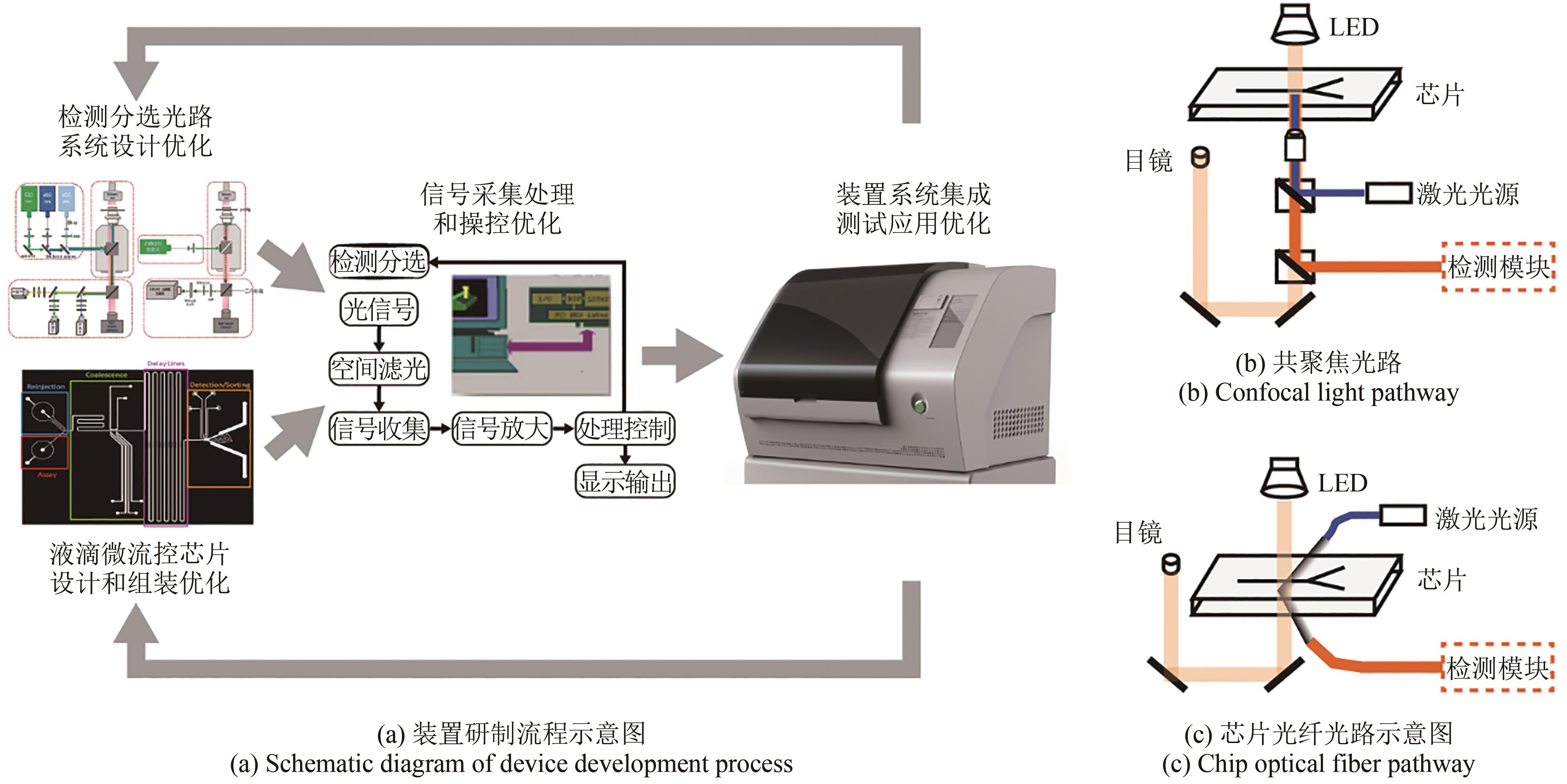
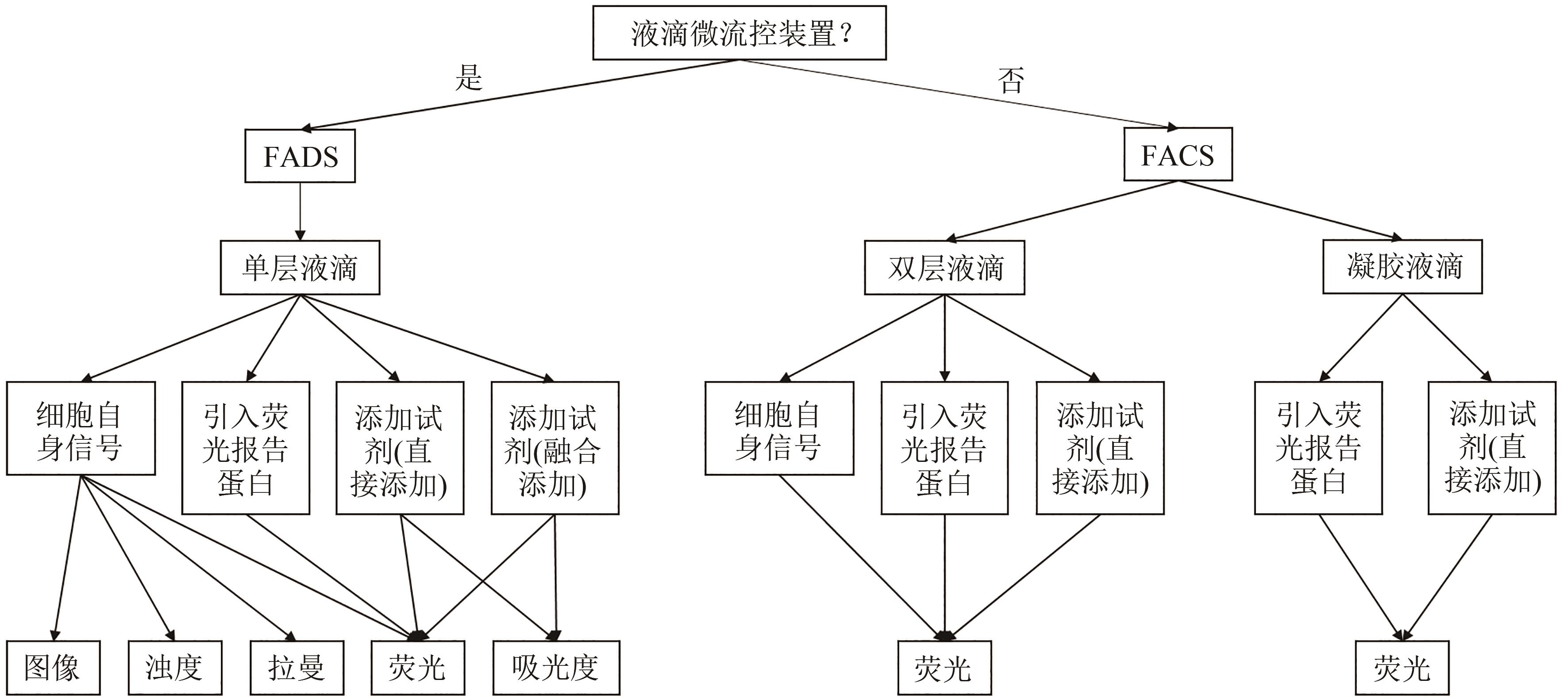
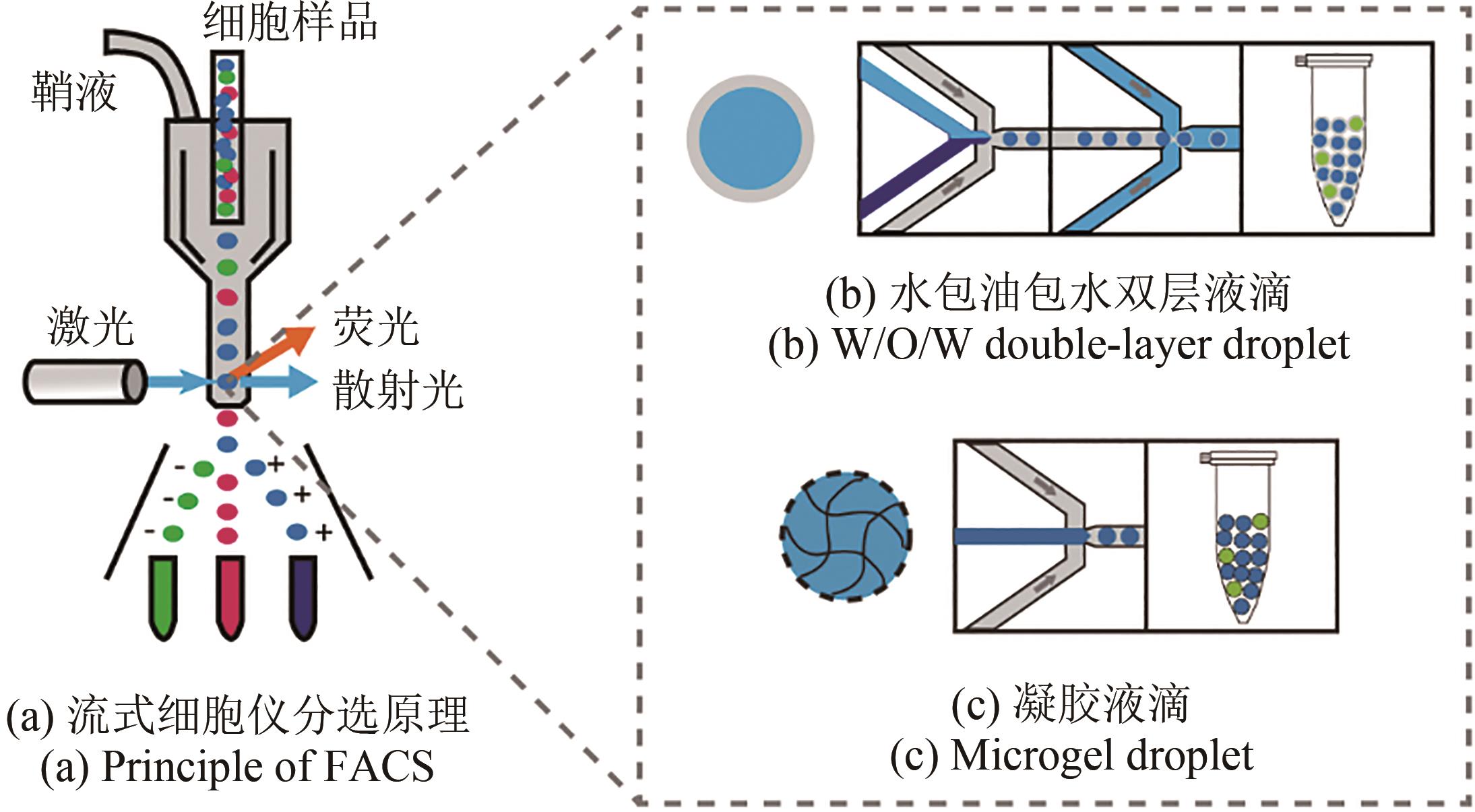
合成生物学 ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (1): 165-184.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-105
液滴微流控技术在微生物工程菌株选育中的应用进展
涂然1,2, 李世新3, 李昊霓3, 王猛2
- 1.重庆工商大学环境与资源学院,重庆 400067
2.中国科学院天津工业生物技术研究所,中国科学院低碳合成工程生物学重点实验室,天津 300308
3.天津科技大学生物工程学院,天津 300457
-
收稿日期:2021-12-05修回日期:2022-01-18出版日期:2023-02-28发布日期:2023-03-07 -
通讯作者:王猛 -
作者简介:涂然 (1979—),女,博士,正高级工程师,教授,硕士生导师。研究方向为合成生物学、高通量检测和筛选技术等。E-mail: tu_r@ctbu.edu.cn王猛 (1982—),男,博士,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为合成生物学、高通量自动化技术等。 E-mail: wangmeng@tib.cas.cn
第一联系人:涂然(1979—),女,博士,正高级工程师,教授,硕士生导师。研究方向为合成生物学、高通量检测和筛选技术等。 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划“绿色生物制造”重点专项(2021YFC2100201);天津市合成生物技术创新能力提升行动项目(TSBICIP-PTJS-003)
Advances and applications of droplet-based microfluidics in evolution and screening of engineered microbial strains
TU Ran1,2, LI Shixin3, LI Haoni3, WANG Meng2
- 1.College of Environmental and Resources,Chongqing Technology and Business University,Chongqing 400067,China
2.Key Laboratory of Engineering Biology for Low-Carbon Manufacturing,Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Tianjin 300308,China
3.College of Biotechnology,Tianjin University of Science & Technology,Tianjin 300457,China
-
Received:2021-12-05Revised:2022-01-18Online:2023-02-28Published:2023-03-07 -
Contact:WANG Meng
摘要:
微生物工程菌株是生物制造的重要基础,但大多数的工程菌株需要进化改造才能适用于生物制造。在菌种选育过程中,如何高效地筛选获得具有目标性状的微生物工程菌株是进行生物制造应用的关键影响因素之一。液滴微流控技术作为近年来发展起来的一种基于微芯片的高通量检测筛选技术,可以生成大小均一、相互独立的微体积液滴小室,并应用于单细胞的培养、检测和分离,在微生物菌株改造尤其是分泌型菌株的改造中得到广泛应用。本文首先概述液滴微流控技术的组成部分,对关键性的技术进行简要介绍;其次根据液滴检测信号的来源、液滴筛选流程的难易程度和液滴分选仪器的适用范围,对液滴微流控技术在工程菌株选育中的应用进行总结分析;最后对液滴微流控技术在应用中存在的问题和研究方向进行展望,为深化其在微生物合成生物学中的应用提供指导。
中图分类号:
引用本文
涂然, 李世新, 李昊霓, 王猛. 液滴微流控技术在微生物工程菌株选育中的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 165-184.
TU Ran, LI Shixin, LI Haoni, WANG Meng. Advances and applications of droplet-based microfluidics in evolution and screening of engineered microbial strains[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 165-184.
| 液滴类型 | 液滴信号来源 | 优缺点 | 通量 | 代表性应用案例 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单层液滴 | 细胞自身信号(荧光、拉曼、浊度、细胞图像) | 优点:操作简单,细胞直接包埋在液滴中 缺点:需要特殊软件,例如拉曼和图像识别软件 | 荧光300 Hz; 拉曼1~5 Hz; 图像识别5~10 Hz; 浊度240 Hz | 色素:核黄素 [ |
| 细胞荧光蛋白(目标蛋白和外源荧光蛋白融合、生产菌自身含生物传感器、生产菌和感应菌共包埋培养) | 优点:操作简单,细胞直接包埋在液滴中 缺点:需要构建特定生物传感器 | 150~300 Hz | 生产菌自身含生物传感器:3-脱氢莽草酸 [ | |
| 细胞和底物(同时共包埋在液滴) | 优点:操作简单,细胞和底物直接包埋在液滴中 缺点:不适合酶促反应快的样品 | 300~2000 Hz | 大肠杆菌:半乳糖苷酶 [ | |
| 细胞和底物(细胞先包埋在液滴,底物后加入) | 优点:可以通过液滴融合添加试剂,用于酶促反应快的样品 缺点:液滴融合操作复杂 | 300~1000 Hz | 漆酶 [ |
表1 基于液滴微流控装置的液滴筛选体系及应用
Table 1 Droplet-based screening systems and applications of FADS
| 液滴类型 | 液滴信号来源 | 优缺点 | 通量 | 代表性应用案例 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单层液滴 | 细胞自身信号(荧光、拉曼、浊度、细胞图像) | 优点:操作简单,细胞直接包埋在液滴中 缺点:需要特殊软件,例如拉曼和图像识别软件 | 荧光300 Hz; 拉曼1~5 Hz; 图像识别5~10 Hz; 浊度240 Hz | 色素:核黄素 [ |
| 细胞荧光蛋白(目标蛋白和外源荧光蛋白融合、生产菌自身含生物传感器、生产菌和感应菌共包埋培养) | 优点:操作简单,细胞直接包埋在液滴中 缺点:需要构建特定生物传感器 | 150~300 Hz | 生产菌自身含生物传感器:3-脱氢莽草酸 [ | |
| 细胞和底物(同时共包埋在液滴) | 优点:操作简单,细胞和底物直接包埋在液滴中 缺点:不适合酶促反应快的样品 | 300~2000 Hz | 大肠杆菌:半乳糖苷酶 [ | |
| 细胞和底物(细胞先包埋在液滴,底物后加入) | 优点:可以通过液滴融合添加试剂,用于酶促反应快的样品 缺点:液滴融合操作复杂 | 300~1000 Hz | 漆酶 [ |
| 液滴类型 | 液滴信号来源 | 优缺点 | 通量 | 代表性应用案例 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 双层液滴 | 细胞和底物(同时共包埋在液滴)、细胞代谢物自发荧光等 | 优点:液滴无需固化处理 缺点:制备双层液滴操作复杂;无法进行液滴融合添加其他试剂 | 3~20 kHz | 酯酶 [ |
| 凝胶液滴 | 细胞荧光蛋白(生产菌自身含生物传感器、生产菌和感应菌共包埋培养)、细胞和底物(同时共包埋在液滴) | 优点:操作简单,直接制备凝胶液滴 缺点:凝胶液滴需固化处理;无法进行液滴融合添加其他试剂 | 1~6 kHz (FACS分选仪); 30~40 Hz (COPAS大颗粒分选仪) | 脂肪酶 [ |
表2 基于流式细胞仪的液滴筛选体系及应用
Table 2 Droplet-based screening systems and applications of FACS
| 液滴类型 | 液滴信号来源 | 优缺点 | 通量 | 代表性应用案例 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 双层液滴 | 细胞和底物(同时共包埋在液滴)、细胞代谢物自发荧光等 | 优点:液滴无需固化处理 缺点:制备双层液滴操作复杂;无法进行液滴融合添加其他试剂 | 3~20 kHz | 酯酶 [ |
| 凝胶液滴 | 细胞荧光蛋白(生产菌自身含生物传感器、生产菌和感应菌共包埋培养)、细胞和底物(同时共包埋在液滴) | 优点:操作简单,直接制备凝胶液滴 缺点:凝胶液滴需固化处理;无法进行液滴融合添加其他试剂 | 1~6 kHz (FACS分选仪); 30~40 Hz (COPAS大颗粒分选仪) | 脂肪酶 [ |

图7 筛选方式与通量和应用关系图AADS—Absorbance-Activated Droplet Sorting; FACS—Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting; FADS—Fluorescence-Activated Droplet Sorting; IADS—Image-Activated Droplet Sorting; MADS—Mass-Activated Droplet Sorting; RADS—Raman-Activated Droplet Sorting
Fig. 7 Correlation for screening methods with throughput or application
| 1 | 唐婷, 付立豪, 郭二鹏, 等. 自动化合成生物技术与工程化设施平台[J]. 科学通报, 2021, 66( 3): 300- 309. |
| TANG T, FU L H, GUO E P, et al. Automation in synthetic biology using biological foundries[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2021, 66( 3): 300- 309. | |
| 2 | FAULON J L, FAURE L. In silico, in vitro, and in vivo machine learning in synthetic biology and metabolic engineering[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2021, 65: 85- 92. |
| 3 | BROOKS S M, ALPER H S. Applications, challenges, and needs for employing synthetic biology beyond the lab[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 1390. |
| 4 | 李洋, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 等. CRISPR基因编辑技术在微生物合成生物学领域的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2( 1): 106- 120. |
| LI Y, SHEN X L, SUN X X, et al. Advances of CRISPR gene editing in microbial synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2( 1): 106- 120. | |
| 5 | YANG J N, KIM B, KIM G Y, et al. Synthetic biology for evolutionary engineering: from perturbation of genotype to acquisition of desired phenotype[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2019, 12: 113. |
| 6 | SMITH K M, LIAO J C. An evolutionary strategy for isobutanol production strain development in Escherichia coli [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2011, 13( 6): 674- 681. |
| 7 | NEUENSCHWANDER M, BUTZ M, HEINTZ C, et al. A simple selection strategy for evolving highly efficient enzymes[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2007, 25( 10): 1145- 1147. |
| 8 | VALLEJO D, NIKOOMANZAR A, PAEGEL B M, et al. Fluorescence-activated droplet sorting for single-cell directed evolution[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8( 6): 1430- 1440. |
| 9 | LEAVELL M D, SINGH A H, KAUFMANN-MALAGA B B. High-throughput screening for improved microbial cell factories, perspective and promise[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2020, 62: 22- 28. |
| 10 | YANG J H, TU R, YUAN H L, et al. Recent advances in droplet microfluidics for enzyme and cell factory engineering[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2021, 41( 7): 1023- 1045. |
| 11 | LEAMON J H, LINK D R, EGHOLM M, et al. Overview: methods and applications for droplet compartmentalization of biology[J]. Nature Methods, 2006, 3( 7): 541- 543. |
| 12 | LINDSTRÖM S, ANDERSSON-SVAHN H. Overview of single-cell analyses: microdevices and applications[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2010, 10( 24): 3363- 3372. |
| 13 | VAN TATENHOVE-PEL R J, et al. Microdroplet screening and selection for improved microbial production of extracellular compounds[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2020, 61: 72- 81. |
| 14 | SESEN M, ALAN T, NEILD A. Droplet control technologies for microfluidic high throughput screening (μHTS)[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2017, 17( 14): 2372- 2394. |
| 15 | GUAN Z C, ZOU Y, ZHANG M X, et al. A highly parallel microfluidic droplet method enabling single-molecule counting for digital enzyme detection[J]. Biomicrofluidics, 2014, 8( 1): 014110. |
| 16 | AGRESTI J J, ANTIPOV E, ABATE A R, et al. Ultrahigh-throughput screening in drop-based microfluidics for directed evolution[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107( 9): 4004- 4009. |
| 17 | LI M, LIU H R, ZHUANG S Y, et al. Droplet flow cytometry for single-cell analysis[J]. RSC Advances, 2021, 11( 34): 20944- 20960. |
| 18 | SOLANKI S, PANDEY C M, GUPTA R K, et al. Emerging trends in microfluidics based devices[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 15( 5): e1900279. |
| 19 | DUSNY C, GRUNBERGER A. Microfluidic single-cell analysis in biotechnology: from monitoring towards understanding[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2020, 63: 26- 33. |
| 20 | BOWMAN E K, ALPER H S. Microdroplet-assisted screening of biomolecule production for metabolic engineering applications[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2020, 38( 7): 701- 714. |
| 21 | WENG L D, SPOONAMORE J E. Droplet microfluidics-enabled high-throughput screening for protein engineering[J]. Micromachines, 2019, 10( 11): 734. |
| 22 | GARCIA-CORDERO J L, MAERKL S J. Microfluidic systems for cancer diagnostics[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2020, 65: 37- 44. |
| 23 | FENG H H, ZHENG T T, LI M Y, et al. Droplet-based microfluidics systems in biomedical applications[J]. Electrophoresis, 2019, 40( 11): 1580- 1590. |
| 24 | CHIU F W Y, STAVRAKIS S. High-throughput droplet-based microfluidics for directed evolution of enzymes[J]. Electrophoresis, 2019, 40( 21): 2860- 2872. |
| 25 | LONGWELL C K, LABANIEH L, COCHRAN J R. High-throughput screening technologies for enzyme engineering[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2017, 48: 196- 202. |
| 26 | 马富强, 杨广宇. 基于液滴微流控技术的超高通量筛选体系及其在合成生物学中的应用[J]. 生物技术通报, 2017, 33( 1): 83- 92. |
| MA F Q, YANG G Y. Ultra-high-throughput screening system based on droplet microfluidics and its applications in synthetic biology[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2017, 33( 1): 83- 92. | |
| 27 | KINTSES B, VAN VLIET L D, DEVENISH S R, et al. Microfluidic droplets: new integrated workflows for biological experiments[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2010, 14( 5): 548- 555. |
| 28 | KAMINSKI T S, SCHELER O, GARSTECKI P. Droplet microfluidics for microbiology: techniques, applications and challenges[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2016, 16( 12): 2168- 2187. |
| 29 | SEEMANN R, BRINKMANN M, PFOHL T, et al. Droplet based microfluidics[J]. Reports on Progress in Physics, 2012, 75( 1): 016601. |
| 30 | SHANG L R, CHENG Y, ZHAO Y J. Emerging droplet microfluidics[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117( 12): 7964- 8040. |
| 31 | JOENSSON H N, ANDERSSON SVAHN H. Droplet microfluidics-a tool for single-cell analysis[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2012, 51( 49): 12176- 12192. |
| 32 | FERNANDES A C, GERNAEY K V, KRUHNE U, et al. " Connecting worlds-a view on microfluidics for a wider application"[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2018, 36( 4): 1341- 1366 |
| 33 | HASSAN S U, ZHANG X L, NIU X Z. Droplet-based microfluidics: formation, detection and analytical characterization[J]. Research & Development in Material Science, 2019, 11( 5): 1227- 1233. |
| 34 | KÖSTER S, ANGILÈ F E, DUAN H, et al. Drop-based microfluidic devices for encapsulation of single cells[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2008, 8( 7): 1110- 1115. |
| 35 | BAROUD C N, GALLAIRE F, DANGLA R. Dynamics of microfluidic droplets[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2010, 10( 16): 2032- 2045. |
| 36 | ANNA S L, BONTOUX N, STONE H A. Formation of dispersions using "flow focusing" in microchannels[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2003, 82( 3): 364- 366. |
| 37 | LAGERMAN C E, LOPEZ ACEVEDO S N, FAHAD A S, et al. Ultrasonically-guided flow focusing generates precise emulsion droplets for high-throughput single cell analyses[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2019, 128( 2): 226- 233. |
| 38 | TAN S H, NGUYEN N T. Generation and manipulation of monodispersed ferrofluid emulsions: the effect of a uniform magnetic field in flow-focusing and T-junction configurations[J]. Physical Review E, Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 2011, 84( 3 Pt 2): 036317. |
| 39 | ABATE A R, WEITZ D A. Syringe-vacuum microfluidics: a portable technique to create monodisperse emulsions[J]. Biomicrofluidics, 2011, 5( 1): 14107. |
| 40 | JIANG Y Y, DU L, LI Y M, et al. A novel mechanism for user-friendly and self-activated microdroplet generation capable of programmable control[J]. Analyst, 2018, 143( 16): 3798- 3807. |
| 41 | ZHU X D, CHU J, WANG Y H. Advances in microfluidics applied to single cell operation[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2018, 13( 2): 1700416. |
| 42 | ZHU P A, WANG L Q. Passive and active droplet generation with microfluidics: a review[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2016, 17( 1): 34- 75. |
| 43 | YOBAS L, MARTENS S, ONG W L, et al. High-performance flow-focusing geometry for spontaneous generation of monodispersed droplets[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2006, 6( 8): 1073- 1079. |
| 44 | ABATE A R, MARY P, VAN STEIJN V, et al. Experimental validation of plugging during drop formation in a T-junction[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2012, 12( 8): 1516- 1521. |
| 45 | JUUL S, NIELSEN C J F, LABOURIAU R, et al. Droplet microfluidics platform for highly sensitive and quantitative detection of malaria-causing Plasmodium parasites based on enzyme activity measurement[J]. ACS Nano, 2012, 6( 12): 10676- 10683. |
| 46 | HU B Y, XU B X, YUN J L, et al. High-throughput single-cell cultivation reveals the underexplored rare biosphere in deep-sea sediments along the Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2020, 20( 2): 363- 372. |
| 47 | VAN LOO B, HEBERLEIN M, MAIR P, et al. High-throughput, lysis-free screening for sulfatase activity using Escherichia coli autodisplay in microdroplets[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8( 12): 2690- 2700. |
| 48 | SJOSTROM S L, BAI Y P, HUANG M T, et al. High-throughput screening for industrial enzyme production hosts by droplet microfluidics[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2014, 14( 4): 806- 813. |
| 49 | LIM J, VRIGNON J, GRUNER P, et al. Ultra-high throughput detection of single cell β-galactosidase activity in droplets using micro-optical lens array[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2013, 103( 20): 203704. |
| 50 | BARET J C. Surfactants in droplet-based microfluidics[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2012, 12( 3): 422- 433. |
| 51 | HOLTZE C, ROWAT A C, AGRESTI J J, et al. Biocompatible surfactants for water-in-fluorocarbon emulsions[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2008, 8( 10): 1632- 1639. |
| 52 | OBEXER R, GODINA A, GARRABOU X, et al. Emergence of a catalytic tetrad during evolution of a highly active artificial aldolase[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2017, 9( 1): 50- 56. |
| 53 | BENEYTON T, WIJAYA I P M, POSTROS P, et al. High-throughput screening of filamentous fungi using nanoliter-range droplet-based microfluidics[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 27223. |
| 54 | NAKAGAWA Y, OHNUKI S, KONDO N, et al. Are droplets really suitable for single-cell analysis? A case study on yeast in droplets[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2021, 21( 19): 3793- 3803. |
| 55 | YU Z Y, BOEHM C R, HIBBERD J M, et al. Droplet-based microfluidic analysis and screening of single plant cells[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13( 5): e0196810. |
| 56 | KINTSES B, HEIN C, MOHAMED M, et al. Picoliter cell lysate assays in microfluidic droplet compartments for directed enzyme evolution[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2012, 19( 8): 1001- 1009. |
| 57 | COLIN P Y, KINTSES B, GIELEN F, et al. Ultrahigh-throughput discovery of promiscuous enzymes by picodroplet functional metagenomics[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 10008. |
| 58 | DAGKESAMANSKAYA A, LANGER K, TAUZIN A S, et al. Use of photoswitchable fluorescent proteins for droplet-based microfluidic screening[J]. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 2018, 147: 59- 65. |
| 59 | NEUN S, ZUREK P J, KAMINSKI T S, et al. Ultrahigh throughput screening for enzyme function in droplets[J]. Methods in Enzymology, 2020, 643: 317- 343. |
| 60 | BOUZETOS E, GANAR K A, MASTROBATTISTA E, et al. (R)evolution-on-a-chip[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2022, 40( 1): 60- 76. |
| 61 | MAZUTIS L, BARET J C, GRIFFITHS A D. A fast and efficient microfluidic system for highly selective one-to-one droplet fusion[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2009, 9( 18): 2665- 2672. |
| 62 | ABATE A R, HUNG T, MARY P, et al. High-throughput injection with microfluidics using picoinjectors[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107( 45): 19163- 19166. |
| 63 | 申峰, 李易, 刘赵淼, 等. 基于微流控技术的微液滴融合研究进展[J]. 分析化学, 2015, 43( 12): 1942- 1954. |
| SHEN F, LI Y, LIU Z M, et al. Advances in micro-droplets coalescence using microfluidics[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 43( 12): 1942- 1954. | |
| 64 | YOON D H, TANAKA D, SEKIGUCHI T, et al. Size-dependent and property-independent passive microdroplet sorting by droplet transfer on dot rails[J]. Micromachines, 2018, 9( 10): 513. |
| 65 | BAIGL D. Photo-actuation of liquids for light-driven microfluidics: state of the art and perspectives[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2012, 12( 19): 3637- 3653. |
| 66 | FANG T, SHANG W H, LIU C, et al. Nondestructive identification and accurate isolation of single cells through a chip with Raman optical tweezers[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91( 15): 9932- 9939. |
| 67 | AHN K, KERBAGE C, HUNT T P, et al. Dielectrophoretic manipulation of drops for high-speed microfluidic sorting devices[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 88( 2): 024104. |
| 68 | BURYK-IGGERS S, KIEDA J, TSAI S S H. Diamagnetic droplet microfluidics applied to single-cell sorting[J]. AIP Advances, 2019, 9( 7): 075106. |
| 69 | FRANKE T, ABATE A R, WEITZ D A, et al. Surface acoustic wave (SAW) directed droplet flow in microfluidics for PDMS devices[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2009, 9( 18): 2625- 2627. |
| 70 | WU L, CHEN P, DONG Y S, et al. Encapsulation of single cells on a microfluidic device integrating droplet generation with fluorescence-activated droplet sorting[J]. Biomedical Microdevices, 2013, 15( 3): 553- 560. |
| 71 | HOCHSTETTER A. Lab-on-a-chip technologies for the single cell level: separation, analysis, and diagnostics[J]. Micromachines, 2020, 11( 5): 468. |
| 72 | FU X Z, ZHANG Y Y, XU Q, et al. Recent advances on sorting methods of high-throughput droplet-based microfluidics in enzyme directed evolution[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2021, 9: 666867. |
| 73 | 林路遥, 林金明. 微流控芯片上细胞培养与分析方法研究进展[J]. 分析科学学报, 2017, 33( 5): 707- 714. |
| LIN L Y, LIN J M. Development of cell culture and analysis on microfluidic devices[J]. Journal of Analytical Science, 2017, 33( 5): 707- 714. | |
| 74 | 梁怡萧, 潘建章, 方群. 基于微流控技术的细胞水平高通量药物筛选系统的研究进展[J]. 色谱, 2021, 39( 6): 567- 577. |
| LIANG Y X, PAN J Z, FANG Q. Research advances of high-throughput cell-based drug screening systems based on microfluidic technique[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2021, 39( 6): 567- 577. | |
| 75 | MAO Z M, GUO F, XIE Y L, et al. Label-free measurements of reaction kinetics using a droplet-based optofluidic device[J]. Journal of Laboratory Automation, 2015, 20( 1): 17- 24. |
| 76 | ULLMAN G, WALLDEN M, MARKLUND E G, et al. High-throughput gene expression analysis at the level of single proteins using a microfluidic turbidostat and automated cell tracking[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B: Biological Sciences, 2013, 368( 1611): 20120025. |
| 77 | GU S Q, LU Y L, DING Y P, et al. Droplet-based microfluidics for dose-response assay of enzyme inhibitors by electrochemical method[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2013, 796: 68- 74. |
| 78 | WANG X X, REN L H, SU Y T, et al. Raman-activated droplet sorting (RADS) for label-free high-throughput screening of microalgal single-cells[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 89( 22): 12569- 12577. |
| 79 | WANG X X, XIN Y, REN L H, et al. Positive dielectrophoresis-based Raman-activated droplet sorting for culture-free and label-free screening of enzyme function in vivo [J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6( 32): eabb3521. |
| 80 | GUL B, ASHRAF S, KHAN S, et al. Cell refractive index: models, insights, applications and future perspectives[J]. Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy, 2021, 33: 102096. |
| 81 | LEBLANC-HOTTE A, CHABOT-ROY G, ODAGIU L, et al. High-throughput refractive index-based microphotonic sensor for enhanced cellular discrimination[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2018, 266: 255- 262. |
| 82 | LIU X, PAINTER R E, ENESA K, et al. High-throughput screening of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in picodroplets[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2016, 16( 9): 1636- 1643. |
| 83 | HAUSER P C, KUBÁŇ P. Capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection for analytical techniques-developments from 2018 to 2020[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2020, 1632: 461616. |
| 84 | KIRCHMAIR J, HOWLETT A, PEIRONCELY J E, et al. How do metabolites differ from their parent molecules and how are they excreted? [J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2013, 53( 2): 354- 367. |
| 85 | GU S Q, LU Y L, DING Y P, et al. A droplet-based microfluidic electrochemical sensor using platinum-black microelectrode and its application in high sensitive glucose sensing[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2014, 55: 106- 112. |
| 86 | SHAHAMIRIFARD S A, GHAEDI M, RAZMI Z, et al. A simple ultrasensitive electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of gallic acid and uric acid in human urine and fruit juices based on zirconia-choline chloride-gold nanoparticles-modified carbon paste electrode[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2018, 114: 30- 36. |
| 87 | ZHU Y, FANG Q. Analytical detection techniques for droplet microfluidics - a review[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2013, 787: 24- 35. |
| 88 | 李智磊, 李静岚, 陈缵光, 等. 微流控芯片技术在药物分析领域的研究进展[J]. 中国药房, 2019, 30( 16): 2279- 2284. |
| LI Z L, LI J L, CHEN Z G, et al. Research progress of microfluidic chip technology in the field of drug analysis [J]. China Pharmacy, 2019, 30( 16): 2279- 2284. | |
| 89 | WU J, WANG S Q, CHEN Q S, et al. Cell-patterned glass spray for direct drug assay using mass spectrometry[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2015, 892: 132- 139. |
| 90 | KEMPA E E, SMITH C A, LI X, et al. Coupling droplet microfluidics with mass spectrometry for ultrahigh-throughput analysis of complex mixtures up to and above 30 Hz[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 92( 18): 12605- 12612. |
| 91 | DIEFENBACH X W, FARASAT I, GUETSCHOW E D, et al. Enabling biocatalysis by high-throughput protein engineering using droplet microfluidics coupled to mass spectrometry[J]. ACS Omega, 2018, 3( 2): 1498- 1508. |
| 92 | BARET J C, MILLER O J, TALY V, et al. Fluorescence-activated droplet sorting (FADS): efficient microfluidic cell sorting based on enzymatic activity[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2009, 9( 13): 1850- 1858. |
| 93 | RAO L, CAI B, WANG J L, et al. A microfluidic electrostatic separator based on pre-charged droplets[J]. Sensors & Actuators B: Chemical, 2015, 210: 328- 335. |
| 94 | GIELEN F, HOURS R, EMOND S, et al. Ultrahigh-throughput-directed enzyme evolution by absorbance-activated droplet sorting (AADS)[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113( 47): E7383- E7389. |
| 95 | HELLMICH W, PELARGUS C, LEFFHALM K, et al. Single cell manipulation, analytics, and label-free protein detection in microfluidic devices for systems nanobiology[J]. Electrophoresis, 2005, 26( 19): 3689- 3696. |
| 96 | HENGOJU S, WOHLFEIL S, MUNSER A S, et al. Optofluidic detection setup for multi-parametric analysis of microbiological samples in droplets[J]. Biomicrofluidics, 2020, 14( 2): 024109. |
| 97 | CHABINYC M L, CHIU D T, MCDONALD J C, et al. An integrated fluorescence detection system in poly(dimethylsiloxane) for microfluidic applications[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2001, 73( 18): 4491- 4498. |
| 98 | HUANG N T, TRUXAL S C, TUNG Y C, et al. Multiplexed spectral signature detection for microfluidic color-coded bioparticle flow[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2010, 82( 22): 9506- 9512. |
| 99 | 涂然, 王钦宏. 新一代高通量筛选系统:液滴微流控分选系统研究进展[M]//马延和. 2013工业生物技术发展报告. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013: 155- 165. |
| TU R, WANG Q H. Next generation of high-throughput screening system: research advances in droplet microfluidic screening system[M]//MA Y H. 2013 Industrial biotechnology development report. Beijing: Science Press, 2013: 155- 165. | |
| 100 | JOSEPHIDES D, DAVOLI S, WHITLEY W, et al. Cyto-mine: an integrated, picodroplet system for high-throughput single-cell analysis, sorting, dispensing, and monoclonality assurance[J]. SLAS Technology, 2020, 25( 2): 177- 189. |
| 101 | OTA Y, SAITO K, TAKAGI T, et al. Fluorescent nucleic acid probe in droplets for bacterial sorting (FNAP-sort) as a high-throughput screening method for environmental bacteria with various growth rates[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14( 4): e0214533. |
| 102 | BEST R J, LYCZAKOWSKI J J, ABALDE-CELA S, et al. Label-free analysis and sorting of microalgae and cyanobacteria in microdroplets by intrinsic chlorophyll fluorescence for the identification of fast growing strains[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 88( 21): 10445- 10451. |
| 103 | CHEN J, VESTERGAARD M, JENSEN T G, et al. Finding the needle in the haystack-the use of microfluidic droplet technology to identify vitamin-secreting lactic acid bacteria[J]. mBio, 2017, 8( 3): e00526- e00517. |
| 104 | HOLLAND-MORITZ D A, WISMER M K, MANN B F, et al. Mass activated droplet sorting (MADS) enables high-throughput screening of enzymatic reactions at nanoliter scale[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59( 11): 4470- 4477. |
| 105 | GIRAULT M, KIM H, ARAKAWA H, et al. An on-chip imaging droplet-sorting system: a real-time shape recognition method to screen target cells in droplets with single cell resolution[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 40072. |
| 106 | SESEN M, WHYTE G. Image-based single cell sorting automation in droplet microfluidics[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 8736. |
| 107 | TU R, LI L P, YUAN H L, et al. Biosensor-enabled droplet microfluidic system for the rapid screening of 3-dehydroshikimic acid produced in Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2020, 47( 12): 1155- 1160. |
| 108 | KIM S, JIN S H, LIM H G, et al. Synthetic cellular communication-based screening for strains with improved 3-hydroxypropionic acid secretion[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2021, 21( 22): 4455- 4463. |
| 109 | SIEDLER S, KHATRI N K, ZSOHÁR A, et al. Development of a bacterial biosensor for rapid screening of yeast p-coumaric acid production[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6( 10): 1860- 1869. |
| 110 | SALESKI T E, KERNER A R, CHUNG M T, et al. Syntrophic co-culture amplification of production phenotype for high-throughput screening of microbial strain libraries[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 54: 232- 243. |
| 111 | FALLAH-ARAGHI A, BARET J C, RYCKELYNCK M, et al. A completely in vitro ultrahigh-throughput droplet-based microfluidic screening system for protein engineering and directed evolution[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2012, 12( 5): 882- 891. |
| 112 | BENEYTON T, COLDREN F, BARET J C, et al. CotA laccase: high-throughput manipulation and analysis of recombinant enzyme libraries expressed in E. coli using droplet-based microfluidics[J]. Analyst, 2014, 139( 13): 3314- 3323. |
| 113 | NAJAH M, CALBRIX R, MAHENDRA-WIJAYA I P, et al. Droplet-based microfluidics platform for ultra-high-throughput bioprospecting of cellulolytic microorganisms[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2014, 21( 12): 1722- 1732. |
| 114 | ZHANG G Q, CHEN Y K, LI Q H, et al. Growth-coupled evolution and high-throughput screening assisted rapid enhancement for amylase-producing Bacillus licheniformis [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 337: 125467. |
| 115 | HUANG M T, BAI Y P, SJOSTROM S L, et al. Microfluidic screening and whole-genome sequencing identifies mutations associated with improved protein secretion by yeast[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112( 34): E4689- E4696. |
| 116 | NAJAH M, MAYOT E, MAHENDRA-WIJAYA I P, et al. New glycosidase substrates for droplet-based microfluidic screening[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 85( 20): 9807- 9814. |
| 117 | OBEXER R, POTT M, ZEYMER C, et al. Efficient laboratory evolution of computationally designed enzymes with low starting activities using fluorescence-activated droplet sorting[J]. Protein Engineering, Design and Selection, 2016, 29( 9): 355- 366. |
| 118 | MA F Q, CHUNG M T, YAO Y, et al. Efficient molecular evolution to generate enantioselective enzymes using a dual-channel microfluidic droplet screening platform[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 1030. |
| 119 | HE R L, DING R H, HEYMAN J A, et al. Ultra-high-throughput picoliter-droplet microfluidics screening of the industrial cellulase-producing filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2019, 46( 11): 1603- 1610. |
| 120 | KIM H S, HSU S C, HAN S I, et al. High-throughput droplet microfluidics screening platform for selecting fast-growing and high lipid-producing microalgae from a mutant library[J]. Plant Direct, 2017, 1( 3): e00011. |
| 121 | BENEYTON T, THOMAS S, GRIFFITHS A D, et al. Droplet-based microfluidic high-throughput screening of heterologous enzymes secreted by the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2017, 16( 1): 18. |
| 122 | QIAO Y X, ZHAO X Y, ZHU J, et al. Fluorescence-activated droplet sorting of lipolytic microorganisms using a compact optical system[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2017, 18( 1): 190- 196. |
| 123 | ABALDE-CELA S, GOULD A, LIU X, et al. High-throughput detection of ethanol-producing cyanobacteria in a microdroplet platform[J]. Journal of the Royal Society, Interface, 2015, 12( 106): 20150216. |
| 124 | DEBS B EL, UTHARALA R, BALYASNIKOVA I V, et al. Functional single-cell hybridoma screening using droplet-based microfluidics[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109( 29): 11570- 11575. |
| 125 | RYCKELYNCK M, BAUDREY S, RICK C, et al. Using droplet-based microfluidics to improve the catalytic properties of RNA under multiple-turnover conditions[J]. RNA, 2015, 21( 3): 458- 469. |
| 126 | HOLSTEIN J M, GYLSTORFF C, HOLLFELDER F. Cell-free directed evolution of a protease in microdroplets at ultrahigh throughput[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2021, 10( 2): 252- 257. |
| 127 | 陈朱波, 曹雪涛. 流式细胞术——原理、操作及应用[M]. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014. |
| CHEN Z B, CAO X T. Flow cytometry-principles, operation and applications [M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Science Press, 2014. | |
| 128 | MILLER O J, BERNATH K, AGRESTI J J, et al. Directed evolution by in vitro compartmentalization[J]. Nature Methods, 2006, 3( 7): 561- 570. |
| 129 | MOHAMED M G A, AMBHORKAR P, SAMANIPOUR R, et al. Microfluidics-based fabrication of cell-laden microgels[J]. Biomicrofluidics, 2020, 14( 2): 021501. |
| 130 | KAMPERMAN T, KARPERIEN M, LE GAC S, et al. Single-cell microgels: technology, challenges, and applications[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2018, 36( 8): 850- 865. |
| 131 | BERNATH K, HAI M, MASTROBATTISTA E, et al. In vitro compartmentalization by double emulsions: sorting and gene enrichment by fluorescence activated cell sorting[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 2004, 325( 1): 151- 157. |
| 132 | MASTROBATTISTA E, TALY V, CHANUDET E, et al. High-throughput screening of enzyme libraries: in vitro evolution of a β-galactosidase by fluorescence-activated sorting of double emulsions[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2005, 12( 12): 1291- 1300. |
| 133 | WU N, OAKESHOTT J G, EASTON C J, et al. A double-emulsion microfluidic platform for in vitro green fluorescent protein expression[J]. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 2011, 21( 5): 054032. |
| 134 | AHARONI A, AMITAI G, BERNATH K, et al. High-throughput screening of enzyme libraries: thiolactonases evolved by fluorescence-activated sorting of single cells in emulsion compartments[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2005, 12( 12): 1281- 1289. |
| 135 | GUPTA R D, GOLDSMITH M, ASHANI Y, et al. Directed evolution of hydrolases for prevention of G-type nerve agent intoxication[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2011, 7( 2): 120- 125. |
| 136 | MA F Q, XIE Y, HUANG C, et al. An improved single cell ultrahigh throughput screening method based on in vitro compartmentalization[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9( 2): e89785. |
| 137 | MA F Q, FISCHER M, HAN Y B, et al. Substrate engineering enabling fluorescence droplet entrapment for IVC-FACS-based ultrahigh-throughput screening[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 88( 17): 8587- 8595. |
| 138 | MA F Q, GUO T J, ZHANG Y F, et al. An ultrahigh-throughput screening platform based on flow cytometric droplet sorting for mining novel enzymes from metagenomic libraries[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2021, 23( 2): 996- 1008. |
| 139 | ZINCHENKO A, DEVENISH S R A, KINTSES B, et al. One in a million: flow cytometric sorting of single cell-lysate assays in monodisperse picolitre double emulsion droplets for directed evolution[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 86( 5): 2526- 2533. |
| 140 | LARSEN A C, DUNN M R, HATCH A, et al. A general strategy for expanding polymerase function by droplet microfluidics[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 11235. |
| 141 | ZHANG Y, HO Y P, CHIU Y L, et al. A programmable microenvironment for cellular studies via microfluidics-generated double emulsions[J]. Biomaterials, 2013, 34( 19): 4564- 4572. |
| 142 | CHAN H F, MA S, TIAN J, et al. High-throughput screening of microchip-synthesized genes in programmable double-emulsion droplets[J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9( 10): 3485- 3495. |
| 143 | TU R, MARTINE Z R, PRODANOVIC R, et al. A flow cytometry-based screening system for directed evolution of proteases[J]. Journal of Biomolecular Screening, 2011, 16( 3): 285- 294. |
| 144 | OSTAFE R, PRODANOVIC R, COMMANDEUR Uet al. Flow cytometry-based ultra-high-throughput screening assay for cellulase activity[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 2013, 435( 1): 93- 98. |
| 145 | TEREKHOV S S, SMIRNOV I V, STEPANOVA A V, et al. Microfluidic droplet platform for ultrahigh-throughput single-cell screening of biodiversity[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114( 10): 2550- 2555. |
| 146 | WAGNER J M, LIU L, YUAN S F, et al. A comparative analysis of single cell and droplet-based FACS for improving production phenotypes: riboflavin overproduction in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 47: 346- 356. |
| 147 | ZHU X D, SHI X, WANG S W, et al. High-throughput screening of high lactic acid-producing Bacillus coagulans by droplet microfluidic based flow cytometry with fluorescence activated cell sorting[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9( 8): 4507- 4513. |
| 148 | GRIFFITHS A D, TAWFIK D S. Man-made enzymes — from design to in vitro compartmentalisation[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2000, 11( 4): 338- 353. |
| 149 | KÖRFER G, PITZLER C, VOJCIC L, et al. In vitro flow cytometry-based screening platform for cellulase engineering[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 26128. |
| 150 | LIM S W, ABATE A R. Ultrahigh-throughput sorting of microfluidic drops with flow cytometry[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2013, 13( 23): 4563- 4572. |
| 151 | BROWER K K, CARSWELL-CRUMPTON C, KLEMM S, et al. Double emulsion flow cytometry with high-throughput single droplet isolation and nucleic acid recovery[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2020, 20( 12): 2062- 2074. |
| 152 | 白立宽, 袁会领, 涂然, 等. 一种基于微芯片快速生成双层乳化液滴的方法[J]. 生物工程学报, 2020, 36( 7): 1405- 1413. |
| BAI L K, YUAN H L, TU R, et al. Rapid generation of double-layer emulsion droplets based on microfluidic chip[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2020, 36( 7): 1405- 1413. | |
| 153 | LENG X F, ZHANG W H, WANG C M, et al. Agarose droplet microfluidics for highly parallel and efficient single molecule emulsion PCR[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2010, 10( 21): 2841- 2843. |
| 154 | BEER N R, WHEELER E K, LEE-HOUGHTON L, et al. On-chip single-copy real-time reverse-transcription PCR in isolated picoliter droplets[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2008, 80( 6): 1854- 1858. |
| 155 | ZHANG H F, JENKINS G, ZOU Y, et al. Massively parallel single-molecule and single-cell emulsion reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction using agarose droplet microfluidics[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 84( 8): 3599- 3606. |
| 156 | FITZSIMONS M S, NOVOTNY M, LO C C, et al. Nearly finished genomes produced using gel microdroplet culturing reveal substantial intraspecies genomic diversity within the human microbiome[J]. Genome Research, 2013, 23( 5): 878- 888. |
| 157 | DICHOSA A E K, DAUGHTON A R, REITENGA K G, et al. Capturing and cultivating single bacterial cells in gel microdroplets to obtain near-complete genomes[J]. Nature Protocols, 2014, 9( 3): 608- 621. |
| 158 | FISCHLECHNER M, SCHAERLI Y, MOHAMED M F, et al. Evolution of enzyme catalysts caged in biomimetic gel-shell beads[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2014, 6( 9): 791- 796. |
| 159 | HOSOKAWA M, , HOSHINO Y, NISHIKAWA Y, et al. Droplet-based microfluidics for high-throughput screening of a metagenomic library for isolation of microbial enzymes[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2015, 67: 379- 385. |
| 160 | MA C X, TAN Z L, LIN Y, et al. Gel microdroplet-based high-throughput screening for directed evolution of xylanase-producing Pichia pastoris [J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2019, 128( 6): 662- 668. |
| 161 | LI M, VAN ZEE M, RICHE C T, et al. A gelatin microdroplet platform for high-throughput sorting of hyperproducing single-cell-derived microalgal clones[J]. Small, 2018, 14( 44): e1803315. |
| 162 | AKBARI S, PIRBODAGHI T. A droplet-based heterogeneous immunoassay for screening single cells secreting antigen-specific antibodies[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2014, 14( 17): 3275- 3280. |
| 163 | UTECH S, PRODANOVIC R, MAO A S, et al. Microfluidic generation of monodisperse, structurally homogeneous alginate microgels for cell encapsulation and 3D cell culture[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2015, 4( 11): 1628- 1633. |
| 164 | SHAO F, YU L, ZHANG Y, et al. Microfluidic encapsulation of single cells by alginate microgels using a trigger-gellified strategy[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2020, 8: 583065. |
| 165 | CHA C, OH J, KIM K, et al. Microfluidics-assisted fabrication of gelatin-silica core-shell microgels for injectable tissue constructs[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2014, 15( 1): 283- 290. |
| 166 | WANG H, LIU H T, LIU H, et al. One-step generation of core-shell gelatin methacrylate (GelMA) microgels using a droplet microfluidic system[J]. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2019, 4( 6): 1800632. |
| 167 | WANG J T, WANG J, HAN J J. Fabrication of advanced particles and particle-based materials assisted by droplet-based microfluidics[J]. Small, 2011, 7( 13): 1728- 1754. |
| 168 | MARKEL U, ESSANI K D, BESIRLIOGLU V, et al. Advances in ultrahigh-throughput screening for directed enzyme evolution[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49( 1): 233- 262. |
| 169 | DELGADO-RAMOS L, MARCOS A T, RAMOS-GUELFO M S, et al. Flow cytometry of microencapsulated colonies for genetics analysis of filamentous fungi[J]. G 3 Genes|Genomes|Genetics, 2014, 4( 11): 2271- 2278. |
| 170 | MEYER A, PELLAUX R, POTOT S, et al. Optimization of a whole-cell biocatalyst by employing genetically encoded product sensors inside nanolitre reactors[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2015, 7( 8): 673- 678. |
| 171 | PAYNE E M, HOLLAND-MORITZ D A, SUN S W, et al. High-throughput screening by droplet microfluidics: perspective into key challenges and future prospects[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2020, 20( 13): 2247- 2262. |
| 172 | BUNZEL H A, GARRABOU X, POTT M, et al. Speeding up enzyme discovery and engineering with ultrahigh-throughput methods[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2018, 48: 149- 156. |
| 173 | BJORK S M, JOENSSON H N. Microfluidics for cell factory and bioprocess development[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2019, 55: 95- 102. |
| 174 | JIAN X J, GUO X J, WANG J, et al. Microbial microdroplet culture system (MMC): an integrated platform for automated, high-throughput microbial cultivation and adaptive evolution[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2020, 117( 6): 1724- 1737. |
| 175 | MAZUTIS L, GILBERT J, UNG W L, et al. Single-cell analysis and sorting using droplet-based microfluidics[J]. Nature Protocols, 2013, 8( 5): 870- 891. |
| 176 | LING S D, GENG Y H, CHEN A, et al. Enhanced single-cell encapsulation in microfluidic devices: from droplet generation to single-cell analysis[J]. Biomicrofluidics, 2020, 14( 6): 061508. |
| 177 | COLLINS D J, NEILD A, DEMELLO A, et al. The Poisson distribution and beyond: methods for microfluidic droplet production and single cell encapsulation[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2015, 15( 17): 3439- 3459. |
| 178 | MUTAFOPULOS K, LU P J, GARRY R, et al. Selective cell encapsulation, lysis, pico-injection and size-controlled droplet generation using traveling surface acoustic waves in a microfluidic device[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2020, 20( 21): 3914- 3921. |
| 179 | ABATE A R, CHEN C H, AGRESTI J J, et al. Beating poisson encapsulation statistics using close-packed ordering[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2009, 9( 18): 2628- 2631. |
| 180 | HU B Y, XU P, MA L, et al. One cell at a time: droplet-based microbial cultivation, screening and sequencing[J]. Marine Life Science & Technology, 2021, 3( 2): 169- 188. |
| 181 | TU R, ZHANG Y, HUA E B, et al. Droplet-based microfluidic platform for high-throughput screening of Streptomyces [J]. Communications Biology, 2021, 4: 647. |
| [1] | 应汉杰, 柳东, 王振宇, 沈涛, 庄伟, 朱晨杰. 工业生物制造与“碳中和”目标探讨[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 1-7. |
| [2] | 郭肖杰, 剪兴金, 王立言, 张翀, 邢新会. 合成生物学表型测试生物反应器及其装备化研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 16-37. |
| [3] | 晏雄鹰, 王振, 娄吉芸, 张皓瑜, 黄星宇, 王霞, 杨世辉. 生物燃料高效生产微生物细胞工厂构建研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(6): 1082-1121. |
| [4] | 赵国淼, 杨鑫, 张媛, 王靖, 谭剑, 魏超, 周娜娜, 李凡, 王小艳. 生物设施平台及其工业应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 892-903. |
| [5] | 孙梦楚, 陆亮宇, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 王佳, 袁其朋. 基于荧光检测的高通量筛选技术和装备助力细胞工厂构建[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 947-965. |
| [6] | 刁志钿, 王喜先, 孙晴, 徐健, 马波. 单细胞拉曼光谱测试分选装备研制及应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 1020-1035. |
| [7] | 秦伟彤, 杨广宇. 微液滴高通量筛选方法的研究与应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 966-979. |
| [8] | 吴玉洁, 刘欣欣, 刘健慧, 杨开广, 随志刚, 张丽华, 张玉奎. 基于高通量液相色谱质谱技术的菌株筛选与关键分子定量分析研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 1000-1019. |
| [9] | 刘欢, 崔球. 原位电离质谱技术在微生物菌株筛选中的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 980-999. |
| [10] | 陈永灿, 司同, 张建志. 自动化合成生物技术在DNA组装与微生物底盘操作中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 857-876. |
| [11] | 孙美莉, 王凯峰, 陆然, 纪晓俊. 解脂耶氏酵母底盘细胞的工程改造及应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(4): 779-807. |
| [12] | 高纤云, 牛灵雪, 见妮, 管宁子. 微生物合成生物学在疾病诊疗上的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(2): 263-282. |
| [13] | 王喜先, 孙晴, 刁志钿, 徐健, 马波. 拉曼光谱技术在单细胞表型检测与分选中的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 204-224. |
| [14] | 刘启, 钱芷兰, 宋丽丽, 要超颖, 徐名强, 任燕娜, 蔡孟浩. 巴斯德毕赤酵母底盘细胞的工程化改造及应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(6): 1150-1173. |
| [15] | 陶飞, 孙韬, 王钰, 魏婷, 倪俊, 许平. “双碳”背景下聚球藻底盘研究的挑战与机遇[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(5): 932-952. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||