合成生物学 ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (1): 204-224.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-043
拉曼光谱技术在单细胞表型检测与分选中的应用进展
王喜先, 孙晴, 刁志钿, 徐健, 马波
- 中国科学院青岛生物能源与过程研究所 单细胞中心,山东 青岛 266101
-
收稿日期:2022-08-03修回日期:2022-09-12出版日期:2023-02-28发布日期:2023-03-07 -
通讯作者:马波 -
作者简介:王喜先 (1988—), 男, 博士, 副研究员, 硕士生导师。研究方向为微流控、高通量拉曼流式分选技术等。E-mail:wangxx@qibebt.ac.cn马波 (1976—), 男, 博士, 研究员, 博士生导师。研究方向为单细胞关键技术与仪器、微流控技术等。E-mail:mabo@qibebt.ac.cn
第一联系人:王喜先(1988—), 男, 博士, 副研究员, 硕士生导师。研究方向为微流控、高通量拉曼流式分选技术等。 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划“合成生物学”重点专项(2018YFA090290);天津市合成生物技术创新能力提升行动项目(TSBICIP-PTJS-003-05)
Advances with applications of Raman spectroscopy in single-cell phenotype sorting and analysis
WANG Xixian, SUN Qing, DIAO Zhidian, XU Jian, MA Bo
- Single-cell Center,Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Qingdao 266101,Shandong,China
-
Received:2022-08-03Revised:2022-09-12Online:2023-02-28Published:2023-03-07 -
Contact:MA Bo
摘要:
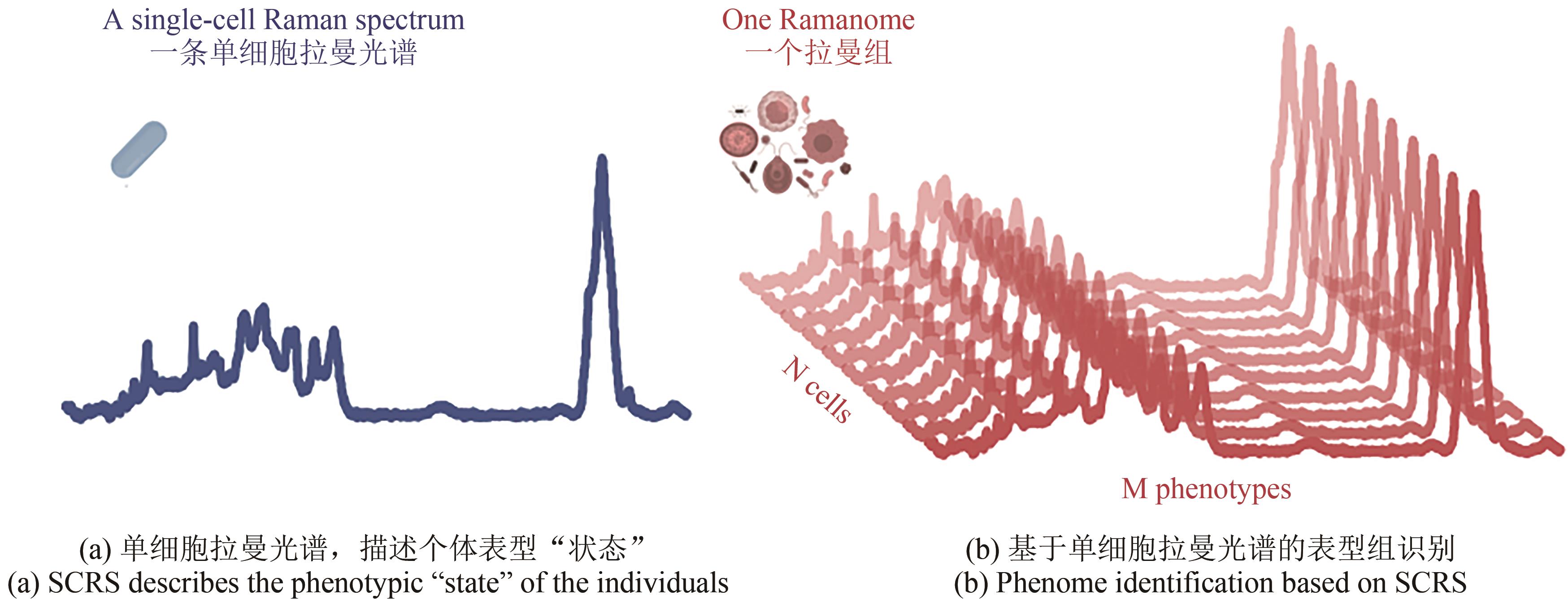
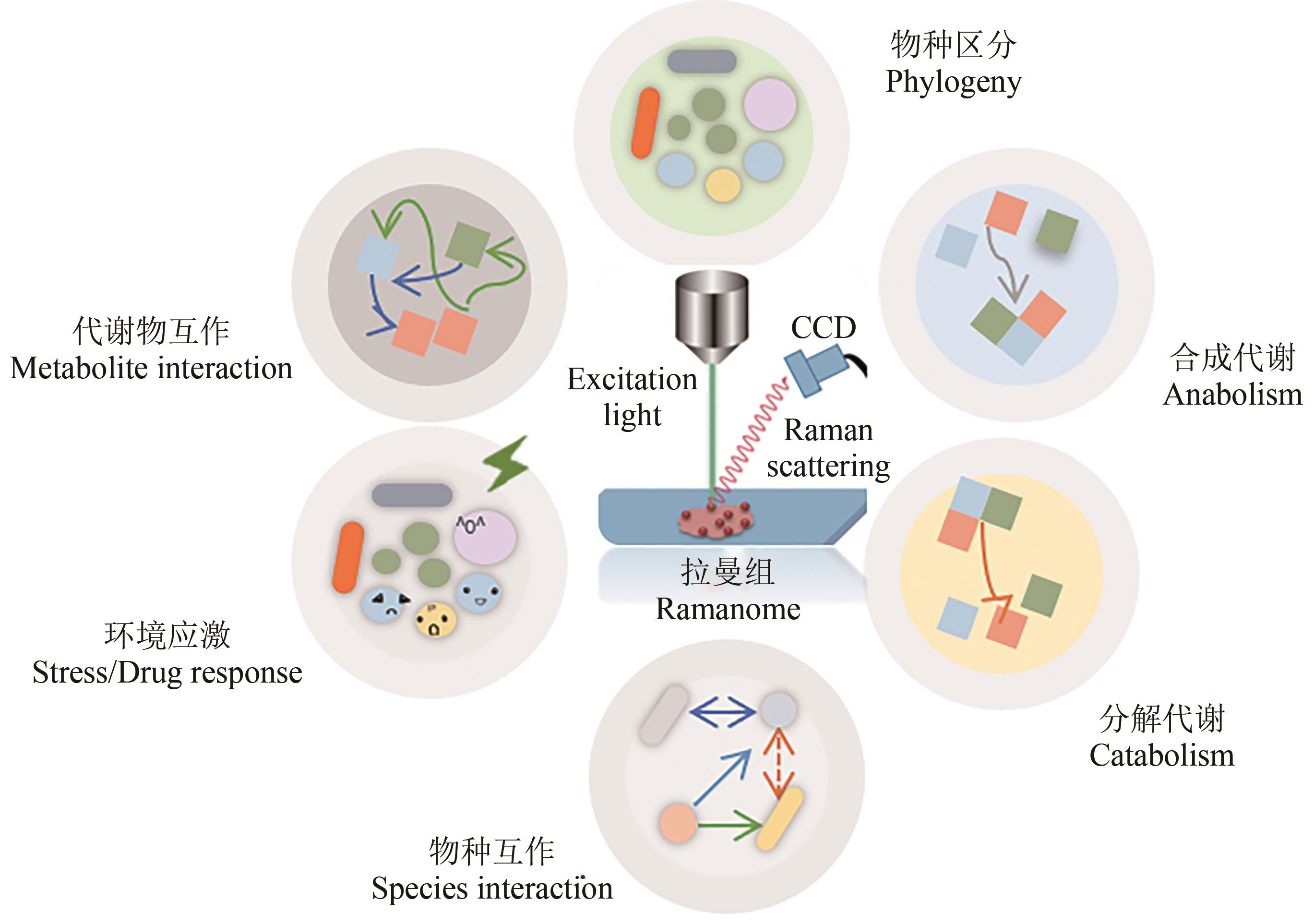
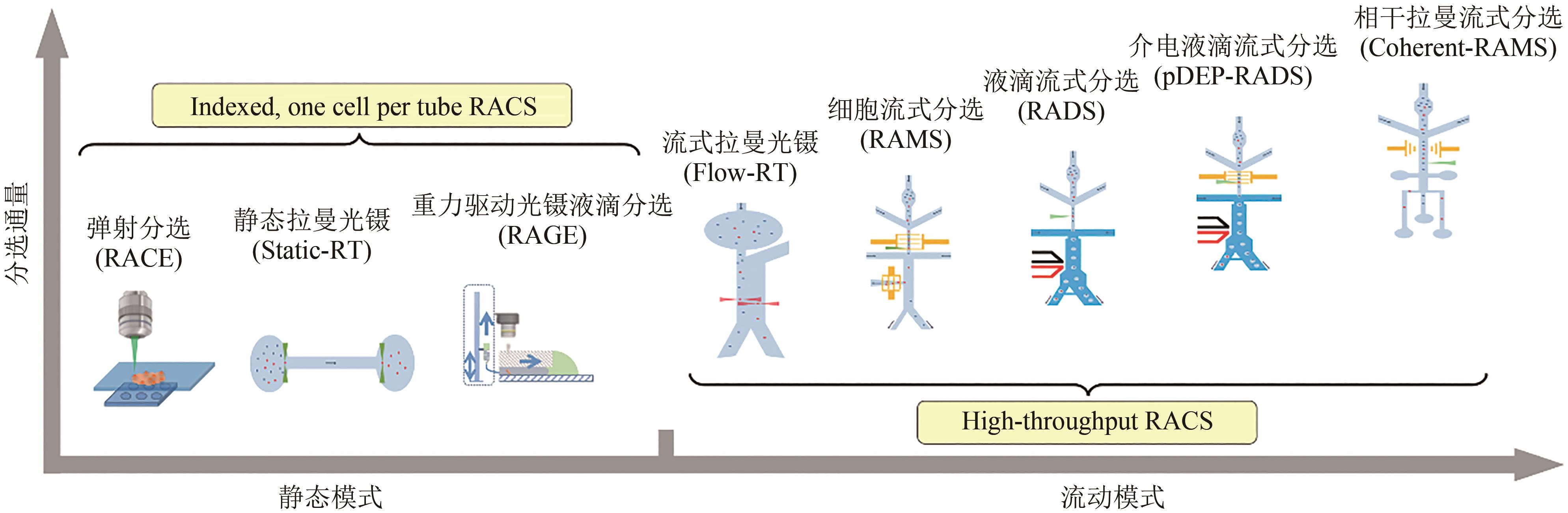
基因组测序、编辑与合成技术日新月异,推动了基因型“设计”和“合成”能力的突飞猛进,同时也使人工细胞的表型检测成为合成生物学发展的瓶颈之一。对于细胞功能的快速测试与评价,单细胞分析技术具有重要意义与前景,但理想的解决方案需要具备活体无损、非标记式、提供全景式表型、能分辨复杂功能、快速高通量且低成本、能与组学分析联动等特征。拉曼光谱技术具备上述所有特征,能够提供单细胞的化学成分组成及分子结构等信息,是一种高效的单细胞表型识别技术。本文首先概述了拉曼组概念和基于拉曼组的细胞功能表型识别,包括代谢产物定性和定量、底物代谢和互作表征、细胞种类和状态鉴定以及环境应激检测等;其次,根据拉曼信号的分类、拉曼信号检测模式和目标细胞分选策略,对现有的拉曼分选平台及其在细胞表型分选中的应用进行分析总结;最后,对单细胞拉曼光谱技术在合成细胞表型检测与分选面临的问题、潜在解决策略进行了探讨和展望。单细胞拉曼光谱技术不仅为细胞工厂的高通量、全景式表型检测与筛选提供了全新的解决方案,还将推动“单细胞精度的表型组-功能基因组”作为一种新的生物大数据类型,服务于“数据科学”驱动下的合成生物技术。
中图分类号:
引用本文
王喜先, 孙晴, 刁志钿, 徐健, 马波. 拉曼光谱技术在单细胞表型检测与分选中的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 204-224.
WANG Xixian, SUN Qing, DIAO Zhidian, XU Jian, MA Bo. Advances with applications of Raman spectroscopy in single-cell phenotype sorting and analysis[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 204-224.

图4 二酰基甘油酰基转移酶体内活性筛选的传统方法和FlowRACS方法的流程比较[146]
Fig. 4 Workflows for in vivo screening of DGAT activities through traditional methods and FlowRACS strategies[146]
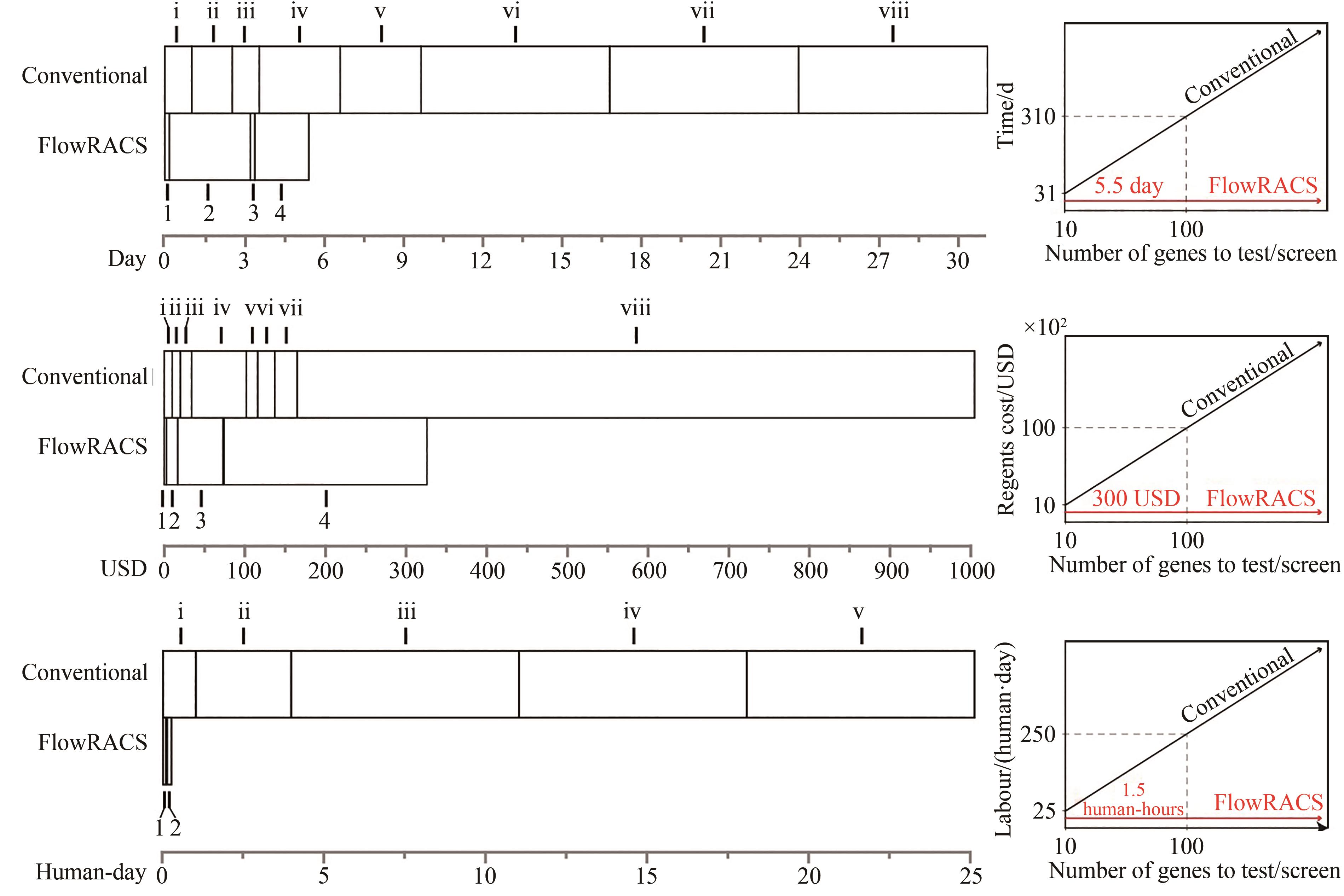
图5 二酰基甘油酰基转移酶体内活性筛选的传统方法和FlowRACS方法在时间成本、试剂耗材消耗和人工成本的比较[146]
Fig. 5 Consumption of time, labor and reagents for in vivo screening of DGAT activities through traditional methods and FlowRACS strategies[146]
| 1 | GARDNER T S, CANTOR C R, COLLINS J J. Construction of a genetic toggle switch in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6767): 339-342. |
| 2 | BENNER S A, SISMOUR A M. Synthetic biology[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2005, 6(7): 533-543. |
| 3 | 欧阳颀. 合成生物学的发展与面临的科学任务[J]. 科学与社会, 2014, 4(4): 1-10. |
| OUYANG Q. The development of synthetic biology and scientific tasks it faced[J]. Science and Society, 2014, 4(4): 1-10. | |
| 4 | CHECK E. Synthetic biology:designs on life [J]. Nature, 2005, 438(7067): 417-418. |
| 5 | AUSLÄNDER S, AUSLÄNDER D, FUSSENEGGER M. Synthetic biology—the synthesis of biology[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(23): 6396-6419. |
| 6 | KOSURI S, CHURCH G M. Large-scale de novo DNA synthesis:technologies and applications[J]. Nature Methods, 2014, 11(5): 499-507. |
| 7 | KOSURI S, EROSHENKO N, LEPROUST E M, et al. Scalable gene synthesis by selective amplification of DNA pools from high-fidelity microchips[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2010, 28(12): 1295-1299. |
| 8 | PALLUK S, ARLOW D H, DE ROND T, et al. De novo DNA synthesis using polymerase-nucleotide conjugates[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(7): 645-650. |
| 9 | WANG H H, ISAACS F J, CARR P A, et al. Programming cells by multiplex genome engineering and accelerated evolution[J]. Nature, 2009, 460(7257): 894-898. |
| 10 | SANDER J D, JOUNG J K. CRISPR-Cas systems for editing, regulating and targeting genomes[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2014, 32(4): 347-355. |
| 11 | SMITH H O, C A Ⅲ HUTCHISON, PFANNKOCH C, et al. Generating a synthetic genome by whole genome assembly: φX174 bacteriophage from synthetic oligonucleotides[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2003, 100(26): 15440-15445. |
| 12 | GIBSON D G, YOUNG L, CHUANG R Y, et al. Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases[J]. Nature Methods, 2009, 6(5): 343-345. |
| 13 | SHAO Y Y, LU N, WU Z F, et al. Creating a functional single-chromosome yeast[J]. Nature, 2018, 560(7718): 331-335. |
| 14 | 卢俊南, 褚鑫, 潘燕平, 等. 基因编辑技术: 进展与挑战[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2018, 33(11): 1184-1192. |
| LU J N, CHU X, PAN Y P, et al. Advances and challenges in gene editing technologies[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 33(11): 1184-1192. | |
| 15 | RO D K, PARADISE E M, OUELLET M, et al. Production of the antimalarial drug precursor artemisinic acid in engineered yeast[J]. Nature, 2006, 440(7086): 940-943. |
| 16 | KWOK R. Five hard truths for synthetic biology[J]. Nature, 2010, 463(7279): 288-290. |
| 17 | KUSSELL E, LEIBLER S. Phenotypic diversity, population growth, and information in fluctuating environments[J]. Science, 2005, 309(5743): 2075-2078. |
| 18 | MÜLLER S, HARMS H, BLEY T. Origin and analysis of microbial population heterogeneity in bioprocesses[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2010, 21(1): 100-113. |
| 19 | PASZEK P, RYAN S, ASHALL L, et al. Population robustness arising from cellular heterogeneity[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(25): 11644-11649. |
| 20 | SCHUBERT C. Single-cell analysis:the deepest differences[J]. Nature, 2011, 480(7375): 133-137. |
| 21 | ZENOBI R. Single-cell metabolomics: analytical and biological perspectives[J]. Science, 2013, 342(6163): 1243259. |
| 22 | KASHTAN N, ROGGENSACK S E, RODRIGUE S, et al. Single-cell genomics reveals hundreds of coexisting subpopulations in wild Prochlorococcus [J]. Science, 2014, 344(6182): 416-420. |
| 23 | LEWIS W H, TAHON G, GEESINK P, et al. Innovations to culturing the uncultured microbial majority[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2021, 19(4): 225-240. |
| 24 | HE Y H, WANG X X, MA B, et al. Ramanome technology platform for label-free screening and sorting of microbial cell factories at single-cell resolution[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2019, 37(6): 107388. |
| 25 | 马波, 徐健. 人工细胞的表型测试与分选: 构建从光谱学到遗传学的桥梁[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2018, 33(11): 1193-1204. |
| MA B, XU J. Phenotyping and sorting of synthetic cells: building bridge from spectroscopy to genetics[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 33(11): 1193-1204. | |
| 26 | PERKEL J M. Single-cell proteomics takes centre stage[J]. Nature, 2021, 597(7877): 580-582. |
| 27 | SEYDEL C. Single-cell metabolomics hits its stride[J]. Nature Methods, 2021, 18(12): 1452-1456. |
| 28 | NAWY T. Integrated single-cell profiles[J]. Nature Methods, 2016, 13(1): 36. |
| 29 | NIELSEN J, OLIVER S. The next wave in metabolome analysis[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2005, 23(11): 544-546. |
| 30 | WISHART D S. Emerging applications of metabolomics in drug discovery and precision medicine[J]. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2016, 15(7): 473-484. |
| 31 | BENDALL S C, SIMONDS E F, QIU P, et al. Single-cell mass cytometry of differential immune and drug responses across a human hematopoietic continuum[J]. Science, 2011, 332(6030): 687-696. |
| 32 | ALI A, ABOULEILA Y, SHIMIZU Y, et al. Single-cell metabolomics by mass spectrometry: advances, challenges, and future applications[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 120: 115436. |
| 33 | SPITZER M H, NOLAN G P. Mass cytometry: single cells, many features[J]. Cell, 2016, 165(4): 780-791. |
| 34 | AMANTONICO A, URBAN P L, ZENOBI R. Analytical techniques for single-cell metabolomics: state of the art and trends[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2010, 398(6): 2493-2504. |
| 35 | BREHM-STECHER B F, JOHNSON E A. Single-cell microbiology: tools, technologies, and applications[J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews: MMBR, 2004, 68(3): 538-559. |
| 36 | YANG J H, SU X L, ZHU L L. Advances of high-throughput screening system in reengineering of biological entities[J]. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao, 2021, 37(7): 2197-2210. |
| 37 | CHEN J, VESTERGAARD M, JENSEN T G, et al. Finding the needle in the haystack-the use of microfluidic droplet technology to identify vitamin-secreting lactic acid bacteria[J]. mBio, 2017, 8(3): e00526-e00517. |
| 38 | WAGNER J M, LIU L Q, YUAN S F, et al. A comparative analysis of single cell and droplet-based FACS for improving production phenotypes: riboflavin overproduction in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 47: 346-356. |
| 39 | BEST R J, LYCZAKOWSKI J J, ABALDE-CELA S, et al. Label-free analysis and sorting of microalgae and cyanobacteria in microdroplets by intrinsic chlorophyll fluorescence for the identification of fast growing strains[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 88(21): 10445-10451. |
| 40 | AN G H, BIELICH J, AUERBACH R, et al. Isolation and characterization of carotenoid hyperproducing mutants of yeast by flow cytometry and cell sorting[J]. Bio/Technology, 1991, 9(1): 70-73. |
| 41 | HUANG M T, BAI Y P, SJOSTROM S L, et al. Microfluidic screening and whole-genome sequencing identifies mutations associated with improved protein secretion by yeast[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(34): E4689-E4696. |
| 42 | SJOSTROM S L, BAI Y P, HUANG M T, et al. High-throughput screening for industrial enzyme production hosts by droplet microfluidics[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2014, 14(4): 806-813. |
| 43 | KINTSES B, HEIN C, MOHAMED M F, et al. Picoliter cell lysate assays in microfluidic droplet compartments for directed enzyme evolution[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2012, 19(8): 1001-1009. |
| 44 | RODRIGUEZ E A, CAMPBELL R E, LIN J Y, et al. The growing and glowing toolbox of fluorescent and photoactive proteins[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 2017, 42(2): 111-129. |
| 45 | KREMERS G J, GILBERT S G, CRANFILL P J, et al. Fluorescent proteins at a glance[J]. Journal of Cell Science, 2011, 124(Pt 2): 157-160. |
| 46 | MANNAN A A, LIU D, ZHANG F Z, et al. Fundamental design principles for transcription-factor-based metabolite biosensors[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(10): 1851-1859. |
| 47 | FOWLER C C, BROWN E D, LI Y F. Using a riboswitch sensor to examine coenzyme B12 metabolism and transport in E. coli [J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2010, 17(7): 756-765 |
| 48 | ABATEMARCO J, SARHAN M F, WAGNER J M, et al. RNA-aptamers-in-droplets (RAPID) high-throughput screening for secretory phenotypes[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 332. |
| 49 | VALLEJO D, NIKOOMANZAR A, PAEGEL B M, et al. Fluorescence-activated droplet sorting for single-cell directed evolution[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(6): 1430-1440. |
| 50 | YANG G Y, WITHERS S G. Ultrahigh-throughput FACS-based screening for directed enzyme evolution[J]. ChemBioChem, 2009, 10(17): 2704-2715. |
| 51 | AGRESTI J J, ANTIPOV E, ABATE A R, et al. Ultrahigh-throughput screening in drop-based microfluidics for directed evolution[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(9): 4004-4009. |
| 52 | BARET J C, MILLER O J, TALY V, et al. Fluorescence-activated droplet sorting (FADS): efficient microfluidic cell sorting based on enzymatic activity[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2009, 9(13): 1850-1858. |
| 53 | SCIAMBI A, ABATE A R. Accurate microfluidic sorting of droplets at 30 kHz[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2015, 15(1): 47-51. |
| 54 | BROUZES E, MEDKOVA M, SAVENELLI N, et al. Droplet microfluidic technology for single-cell high-throughput screening[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(34): 14195-14200. |
| 55 | WANG Y, JIN R N, SHEN B Q, et al. High-throughput functional screening for next-generation cancer immunotherapy using droplet-based microfluidics[J]. Science Advances, 2021, 7(24): eabe3839. |
| 56 | QIAO Y X, HU R, CHEN D W, et al. Fluorescence-activated droplet sorting of PET degrading microorganisms[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 424: 127417. |
| 57 | TEREKHOV S S, SMIRNOV I V, STEPANOVA A V, et al. Microfluidic droplet platform for ultrahigh-throughput single-cell screening of biodiversity[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(10): 2550-2555. |
| 58 | MA F Q, CHUNG M T, YAO Y, et al. Efficient molecular evolution to generate enantioselective enzymes using a dual-channel microfluidic droplet screening platform[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 1030. |
| 59 | NITTA N, SUGIMURA T, ISOZAKI A, et al. Intelligent image-activated cell sorting[J]. Cell, 2018, 175(1): 266-276. |
| 60 | SCHRAIVOGEL D, KUHN T M, RAUSCHER B, et al. High-speed fluorescence image-enabled cell sorting[J]. Science, 2022, 375(6578): 315-320. |
| 61 | ROBINSON J P. Spectral flow cytometry-quo vadimus? [J]. Cytometry Part A: the Journal of the International Society for Analytical Cytology, 2019, 95(8): 823-824. |
| 62 | CHENG J X, XIE X S. Vibrational spectroscopic imaging of living systems: an emerging platform for biology and medicine[J]. Science, 2015, 350(6264): aaa8870. |
| 63 | PETIBOIS C, CESTELLI-GUIDI M, PICCININI M, et al. Synchrotron radiation FTIR imaging in minutes: a first step towards real-time cell imaging[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2010, 397(6): 2123-2129. |
| 64 | RAMAN C V, KRISHNAN K S. A new type of secondary radiation[J]. Nature, 1928, 121(3048): 501-502. |
| 65 | XU J, MA B, SU X Q, et al. Emerging trends for microbiome analysis: from single-cell functional imaging to microbiome big data[J]. Engineering, 2017, 3(1): 66-70. |
| 66 | LEE K S, LANDRY Z, PEREIRA F C, et al. Raman microspectroscopy for microbiology[J]. Nature Reviews Methods Primers, 2021, 1: 80. |
| 67 | YAN S S, QIU J X, GUO L, et al. Development overview of Raman-activated cell sorting devoted to bacterial detection at single-cell level[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2021, 105(4): 1315-1331. |
| 68 | GUO J X, LIU Y, JU H X, et al. From lab to field: surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based sensing strategies for on-site analysis[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 146: 116488. |
| 69 | QIAN X M, PENG X H, ANSARI D O, et al. In vivo tumor targeting and spectroscopic detection with surface-enhanced Raman nanoparticle tags[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2008, 26(1): 83-90. |
| 70 | LIN L, TIAN X D, HONG S L, et al. A bioorthogonal Raman reporter strategy for SERS detection of glycans on live cells[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(28): 7266-7271. |
| 71 | CHEN Y L, DING L, SONG W Y, et al. Protein-specific Raman imaging of glycosylation on single cells with zone-controllable SERS effect[J]. Chemical Science, 2016, 7(1): 569-574. |
| 72 | ZONG S F, CHEN C, WANG Z Y, et al. Surface enhanced Raman scattering based in situ hybridization strategy for telomere length assessment[J]. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(2): 2950-2959. |
| 73 | ZHU R, FENG H J, LI Q Q, et al. Asymmetric core-shell gold nanoparticles and controllable assemblies for SERS ratiometric detection of microRNA[J]. Angewandte Chemie International ed. in English, 2021, 60(22): 12560-12568. |
| 74 | YANG Y J, CHEN Y L, GUO J X, et al. A pore-forming protein-induced surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic strategy for dynamic tracing of cell membrane repair[J]. iScience, 2021, 24(9): 102980. |
| 75 | YANG Y J, CHEN Y L, ZHAO S Y, et al. O-GlcNAcylation mapping of single living cells by in situ quantitative SERS imaging[J]. Chemical Science, 2022, 13(33): 9701-9705. |
| 76 | BERRY D, MADER E, LEE T K, et al. Tracking heavy water (D2O) incorporation for identifying and sorting active microbial cells[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(2): E194-E203. |
| 77 | JING X Y, GOU H L, GONG Y H, et al. Raman-activated cell sorting and metagenomic sequencing revealing carbon-fixing bacteria in the ocean[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2018, 20(6): 2241-2255. |
| 78 | SONG Y Z, KASTER A K, VOLLMERS J, et al. Single-cell genomics based on Raman sorting reveals novel carotenoid-containing bacteria in the Red Sea[J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 2017, 10(1): 125-137. |
| 79 | WANG T T, JI Y T, WANG Y, et al. Quantitative dynamics of triacylglycerol accumulation in microalgae populations at single-cell resolution revealed by Raman microspectroscopy[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2014, 7: 58. |
| 80 | JI Y T, HE Y H, CUI Y B, et al. Raman spectroscopy provides a rapid, non-invasive method for quantitation of starch in live, unicellular microalgae[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2014, 9(12): 1512-1518. |
| 81 | HE Y H, ZHANG P, HUANG S, et al. Label-free, simultaneous quantification of starch, protein and triacylglycerol in single microalgal cells[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2017, 10: 275. |
| 82 | TAO Y F, WANG Y, HUANG S, et al. Metabolic-activity-based assessment of antimicrobial effects by D2O-labeled single-cell Raman microspectroscopy[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 89(7): 4108-4115. |
| 83 | TENG L, WANG X, WANG X J, et al. Label-free, rapid and quantitative phenotyping of stress response in E. coli via ramanome[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 34359. |
| 84 | HEKMATARA M, HEIDARI BALADEHI M, JI Y T, et al. D2O-probed Raman microspectroscopy distinguishes the metabolic dynamics of macromolecules in organellar anticancer drug response[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 93(4): 2125-2134. |
| 85 | WANG Y, SONG Y Z, TAO Y F, et al. Reverse and multiple stable isotope probing to study bacterial metabolism and interactions at the single cell level[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 88(19): 9443-9450. |
| 86 | HE Y H, HUANG S, ZHANG P, et al. Intra-ramanome correlation analysis unveils metabolite conversion network from an isogenic population of cells[J]. mBio, 2021, 12(4): e0147021. |
| 87 | HEIDARI BALADEHI M, HEKMATARA M, HE Y H, et al. Culture-free identification and metabolic profiling of microalgal single cells via ensemble learning of ramanomes[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 93(25): 8872-8880. |
| 88 | CHRISTAKI E, BONOS E, GIANNENAS I, et al. Functional properties of carotenoids originating from algae[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2013, 93(1): 5-11. |
| 89 | RODRIGUEZ-CONCEPCION M, AVALOS J, BONET M L, et al. A global perspective on carotenoids: metabolism, biotechnology, and benefits for nutrition and health[J]. Progress in Lipid Research, 2018, 70: 62-93. |
| 90 | ROBERT B. Resonance Raman spectroscopy[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2009, 101(2/3): 147-155. |
| 91 | GUEDES A C, AMARO H M, MALCATA F X. Microalgae as sources of carotenoids[J]. Marine Drugs, 2011, 9(4): 625-644. |
| 92 | COLLINS A M, JONES H D T, HAN D X, et al. Carotenoid distribution in living cells of Haematococcus pluvialis (Chlorophyceae)[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(9): e24302. |
| 93 | KACZOR A, BARANSKA M. Structural changes of carotenoid astaxanthin in a single algal cell monitored in situ by Raman spectroscopy[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2011, 83(20): 7763-7770. |
| 94 | LI K. In vivo kinetics of lipids and astaxanthin evolution in Haematococcus pluvialis mutant under 15% CO2 using Raman microspectroscopy[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 244(Pt 2): 1439-1444. |
| 95 | ALEXANDRE M T A, GUNDERMANN K, PASCAL A A, et al. Probing the carotenoid content of intact Cyclotella cells by resonance Raman spectroscopy[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2014, 119(3): 273-281. |
| 96 | WU H W, VOLPONI J V, OLIVER A E, et al. In vivo lipidomics using single-cell Raman spectroscopy[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108(9): 3809-3814. |
| 97 | LEE T H, CHANG J S, WANG H Y. Rapid and in vivo quantification of cellular lipids in Chlorella vulgaris using near-infrared Raman spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 85(4): 2155-2160. |
| 98 | SHAO Y N, FANG H, ZHOU H, et al. Detection and imaging of lipids of Scenedesmus obliquus based on confocal Raman microspectroscopy[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2017, 10: 300. |
| 99 | CHIU L D, HO S H, SHIMADA R, et al. Rapid in vivo lipid/carbohydrate quantification of single microalgal cell by Raman spectral imaging to reveal salinity-induced starch-to-lipid shift[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2017, 10: 9. |
| 100 | MOUDŘÍKOVÁ Š, SADOWSKY A, METZGER S, et al. Quantification of polyphosphate in microalgae by Raman microscopy and by a reference enzymatic assay[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 89(22): 12006-12013. |
| 101 | XU J B, WEBB I, POOLE P, et al. Label-free discrimination of rhizobial bacteroids and mutants by single-cell Raman microspectroscopy[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 89(12): 6336-6340. |
| 102 | GIERLINGER N, SCHWANNINGER M. Chemical imaging of poplar wood cell walls by confocal Raman microscopy[J]. Plant Physiology, 2006, 140(4): 1246-1254. |
| 103 | CHYLIŃSKA M, SZYMAŃSKA-CHARGOT M, ZDUNEK A. Imaging of polysaccharides in the tomato cell wall with Raman microspectroscopy[J]. Plant Methods, 2014, 10: 14. |
| 104 | LUPOI J S, SINGH S, DAVIS M, et al. High-throughput prediction of eucalypt lignin syringyl/guaiacyl content using multivariate analysis: a comparison between mid-infrared, near-infrared, and Raman spectroscopies for model development[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2014, 7: 93. |
| 105 | SAMEK O, OBRUČA S, ŠILER M, et al. Quantitative Raman spectroscopy analysis of polyhydroxyalkanoates produced by cupriavidus necator H16[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(11): 1808. |
| 106 | WEISS T L, CHUN H J, OKADA S, et al. Raman spectroscopy analysis of botryococcene hydrocarbons from the green microalga Botryococcus braunii [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2010, 285(42): 32458-32466. |
| 107 | MIYAOKA R, HOSOKAWA M, ANDO M, et al. In situ detection of antibiotic amphotericin B produced in Streptomyces nodosus using Raman microspectroscopy[J]. Marine Drugs, 2014, 12(5): 2827-2839. |
| 108 | BERRY D, LOY A. Stable-isotope probing of human and animal microbiome function[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 2018, 26(12): 999-1007. |
| 109 | UHLIK O, LEEWIS M C, STREJCEK M, et al. Stable isotope probing in the metagenomics era: a bridge towards improved bioremediation[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2013, 31(2): 154-165. |
| 110 | HUANG W E, LI M Q, JARVIS R M, et al. Shining light on the microbial world: the application of Raman microspectroscopy[J]. Advances in Applied Microbiology, 2010, 70: 153-186. |
| 111 | HUANG W E, STOECKER K, GRIFFITHS R, et al. Raman-FISH: combining stable-isotope Raman spectroscopy and fluorescence in situ hybridization for the single cell analysis of identity and function[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2007, 9(8): 1878-1889. |
| 112 | WANG Y, HUANG W E, CUI L, et al. Single cell stable isotope probing in microbiology using Raman microspectroscopy[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2016, 41: 34-42. |
| 113 | LI M Q, CANNIFFE D P, JACKSON P J, et al. Rapid resonance Raman microspectroscopy to probe carbon dioxide fixation by single cells in microbial communities[J]. The ISME Journal, 2012, 6(4): 875-885. |
| 114 | NOOTHALAPATI VENKATA H N, SHIGETO S. Stable isotope-labeled Raman imaging reveals dynamic proteome localization to lipid droplets in single fission yeast cells[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2012, 19(11): 1373-1380. |
| 115 | VINAY K B N, GUO S X, BOCKLITZ T, et al. Demonstration of carbon catabolite repression in naphthalene degrading soil bacteria via Raman spectroscopy based stable isotope probing[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 88(15): 7574-7582. |
| 116 | ANGEL R, PANHÖLZL C, GABRIEL R, et al. Application of stable-isotope labelling techniques for the detection of active diazotrophs[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2018, 20(1): 44-61. |
| 117 | CUI L, YANG K, LI H Z, et al. Functional single-cell approach to probing nitrogen-fixing bacteria in soil communities by resonance Raman spectroscopy with 15N2 labeling[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 90(8): 5082-5089. |
| 118 | HAN Z L, SHI X S, JI Y T, et al. Stable isotope labeling to study the nitrogen metabolism in microcystin biosynthesis[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(52): 46806-46812. |
| 119 | YONAMINE Y, SUZUKI Y, ITO T, et al. Monitoring photosynthetic activity in microalgal cells by Raman spectroscopy with deuterium oxide as a tracking probe[J]. ChemBioChem, 2017, 18(20): 2063-2068. |
| 120 | OLANIYI O O, YANG K, ZHU Y G, et al. Heavy water-labeled Raman spectroscopy reveals carboxymethylcellulose-degrading bacteria and degradation activity at the single-cell level[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 103(3): 1455-1464. |
| 121 | LORENZ B, WICHMANN C, STOCKEL S, et al. Cultivation-free Raman spectroscopic investigations of bacteria[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 2017, 25(5): 413-424. |
| 122 | PAHLOW S, MEISEL S, CIALLA-MAY D, et al. Isolation and identification of bacteria by means of Raman spectroscopy[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2015, 89: 105-120. |
| 123 | KOCHAN K, PENG H D, WOOD B R, et al. Single cell assessment of yeast metabolic engineering for enhanced lipid production using Raman and AFM-IR imaging[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2018, 11: 106. |
| 124 | STÖCKEL S, MEISEL S, ELSCHNER M, et al. Identification of Bacillus anthracis via Raman spectroscopy and chemometric approaches[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 84(22): 9873-9880. |
| 125 | CHOO-SMITH L P, MAQUELIN K, VAN VREESWIJK T, et al. Investigating microbial (micro)colony heterogeneity by vibrational spectroscopy[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2001, 67(4): 1461-1469. |
| 126 | WEI X, JIE D F, CUELLO J J, et al. Microalgal detection by Raman microspectroscopy[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 53: 33-40. |
| 127 | GUO J X, LIU Y, YANG Y J, et al. A filter supported surface-enhanced Raman scattering "nose" for point-of-care monitoring of gaseous metabolites of bacteria[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 92(7): 5055-5063. |
| 128 | CHIU Y F, HUANG C K, SHIGETO S. In vivo probing of the temperature responses of intracellular biomolecules in yeast cells by label-free Raman microspectroscopy[J]. ChemBioChem, 2013, 14(8): 1001-1005. |
| 129 | SINGH G P, CREELY C M, VOLPE G, et al. Real-time detection of hyperosmotic stress response in optically trapped single yeast cells using Raman microspectroscopy[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2005, 77(8): 2564-2568. |
| 130 | HERAUD P, BEARDALL J, MCNAUGHTON D, et al. In vivo prediction of the nutrient status of individual microalgal cells using Raman microspectroscopy[J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2007, 275(1): 24-30. |
| 131 | ATHAMNEH A I M, ALAJLOUNI R A, WALLACE R S, et al. Phenotypic profiling of antibiotic response signatures in Escherichia coli using Raman spectroscopy[J]. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 2014, 58(3): 1302-1314. |
| 132 | GERMOND A, ICHIMURA T, HORINOUCHI T, et al. Raman spectral signature reflects transcriptomic features of antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli [J]. Communications Biology, 2018, 1: 85. |
| 133 | ZU T N K, ATHAMNEH A I M, WALLACE R S, et al. Near-real-time analysis of the phenotypic responses of Escherichia coli to 1-butanol exposure using Raman spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2014, 196(23): 3983-3991. |
| 134 | GUO J X, LIU Y, CHEN Y L, et al. A multifunctional SERS sticky note for real-time quorum sensing tracing and inactivation of bacterial biofilms[J]. Chemical Science, 2018, 9(27): 5906-5911. |
| 135 | LI M Q, HUANG W E, GIBSON C M, et al. Stable isotope probing and Raman spectroscopy for monitoring carbon flow in a food chain and revealing metabolic pathway[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 85(3): 1642-1649. |
| 136 | MIECZAN T, MICHAŁ N, ADAMCZUK M, et al. Stable isotope analyses revealed high seasonal dynamics in the food web structure of a peatbog[J]. International Review of Hydrobiology, 2015, 100(5/6): 141-150. |
| 137 | SONG Y Z, YIN H B, HUANG W E. Raman activated cell sorting[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2016, 33: 1-8. |
| 138 | GALA DE PABLO J, LINDLEY M, HIRAMATSU K, et al. High-throughput Raman flow cytometry and beyond[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2021, 54(9): 2132-2143. |
| 139 | WANG Y, JI Y T, WHARFE E S, et al. Raman activated cell ejection for isolation of single cells[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 85(22): 10697-10701. |
| 140 | HUANG W E, WARD A D, WHITELEY A S. Raman tweezers sorting of single microbial cells[J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 2009, 1(1): 44-49. |
| 141 | XIE C G, CHEN D, LI Y Q. Raman sorting and identification of single living micro-organisms with optical tweezers[J]. Optics Letters, 2005, 30(14): 1800-1802. |
| 142 | XU T, GONG Y H, SU X L, et al. Phenome-genome profiling of single bacterial cell by Raman-activated gravity-driven encapsulation and sequencing[J]. Small, 2020, 16(30): 2001172. |
| 143 | LEE K S, PALATINSZKY M, PEREIRA F C, et al. An automated Raman-based platform for the sorting of live cells by functional properties[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2019, 4(6): 1035-1048. |
| 144 | ZHANG P R, REN L H, ZHANG X, et al. Raman-activated cell sorting based on dielectrophoretic single-cell trap and release[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 87(4): 2282-2289. |
| 145 | WANG X X, REN L H, SU Y T, et al. Raman-activated droplet sorting (RADS) for label-free high-throughput screening of microalgal single-cells[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 89(22): 12569-12577. |
| 146 | WANG X X, XIN Y, REN L H, et al. Positive dielectrophoresis-based Raman-activated droplet sorting for culture-free and label-free screening of enzyme function in vivo [J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(32): eabb3521. |
| 147 | NITTA N, IINO T, ISOZAKI A, et al. Raman image-activated cell sorting[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 3452. |
| 148 | LINDLEY M, DE PABLO J G, PETERSON J W, et al. High-throughput Raman-activated cell sorting in the fingerprint region[J]. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2022, 7(10): 2101567. |
| 149 | SONG Y Z, CUI L, LÓPEZ J Á S, et al. Raman-Deuterium Isotope Probing for in situ identification of antimicrobial resistant bacteria in Thames River[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 16648. |
| 150 | WANG Y, XU J B, KONG L C, et al. Raman-activated sorting of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in human gut microbiota[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2020, 22(7): 2613-2624. |
| 151 | YUAN X F, SONG Y Q, SONG Y Z, et al. Effect of laser irradiation on cell function and its implications in Raman spectroscopy[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2018, 84(8): e02508-e02517. |
| 152 | LIANG P, LIU B, WANG Y, et al. Isolation and culture of single microbial cells by laser ejection sorting technology[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2022, 88(3): e0116521. |
| 153 | SU X L, GONG Y H, GOU H L, et al. Rational optimization of Raman-activated cell ejection and sequencing for bacteria[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 92(12): 8081-8089. |
| 154 | ZHANG H, LIU K K. Optical tweezers for single cells[J]. Journal of the Royal Society, Interface, 2008, 5(24): 671-690. |
| 155 | XIE C G, DINNO M A, LI Y Q. Near-infrared Raman spectroscopy of single optically trapped biological cells[J]. Optics Letters, 2002, 27(4): 249-251. |
| 156 | FANG T, SHANG W H, LIU C, et al. Nondestructive identification and accurate isolation of single cells through a chip with Raman optical tweezers[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(15): 9932-9939. |
| 157 | FANG T, SHANG W H, LIU C, et al. Single-cell multimodal analytical approach by integrating Raman optical tweezers and RNA sequencing[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 92(15): 10433-10441. |
| 158 | JING X Y, GONG Y H, XU T, et al. One-cell metabolic phenotyping and sequencing of soil microbiome by Raman-activated gravity-driven encapsulation (RAGE)[J]. mSystems, 2021, 6(3): e0018121. |
| 159 | LAU A Y, LEE L P, CHAN J W. An integrated optofluidic platform for Raman-activated cell sorting[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2008, 8(7): 1116-1120. |
| 160 | DOCHOW S, KRAFFT C, NEUGEBAUER U, et al. Tumour cell identification by means of Raman spectroscopy in combination with optical traps and microfluidic environments[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2011, 11(8): 1484-1490. |
| 161 | DOCHOW S, BELEITES C, HENKEL T, et al. Quartz microfluidic chip for tumour cell identification by Raman spectroscopy in combination with optical traps[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2013, 405(8): 2743-2746. |
| 162 | CASABELLA S, SCULLY P, GODDARD N, et al. Automated analysis of single cells using Laser Tweezers Raman Spectroscopy[J]. Analyst, 2016, 141(2): 689-696. |
| 163 | LI M Q, ASHOK P C, DHOLAKIA K, et al. Raman-activated cell counting for profiling carbon dioxide fixing microorganisms[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2012, 116(25): 6560-6563 |
| 164 | MCILVENNA D, HUANG W E, DAVISON P, et al. Continuous cell sorting in a flow based on single cell resonance Raman spectra[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2016, 16(8): 1420-1429. |
| 165 | 涂然, 李世新, 李昊霓, 等. 液滴微流控技术在微生物工程菌株选育中的应用进展[J].合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 165-184. |
| TU R, LI S X, LI H N, et al. Application of droplet microfluidic technology in the breeding of microbial engineering strains [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 165-184. | |
| 166 | CRISTOBAL G, ARBOUET L, SARRAZIN F, et al. On-line laser Raman spectroscopic probing of droplets engineered in microfluidic devices [J]. Lab on a Chip, 2006, 6(9): 1140-1146. |
| 167 | EVANS C L, POTMA E O, PUORIS'HAAG M, et al. Chemical imaging of tissue in vivo with video-rate coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopy[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2005, 102(46): 16807-16812. |
| 168 | HU F H, SHI L X, MIN W. Biological imaging of chemical bonds by stimulated Raman scattering microscopy[J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(9): 830-842. |
| 169 | WANG H W, BAO N, LE T L, et al. Microfluidic CARS cytometry[J]. Optics Express, 2008, 16(8): 5782-5789. |
| 170 | CAMP C H Jr, YEGNANARAYANAN S, EFTEKHAR A A, et al. Label-free flow cytometry using multiplex coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering (MCARS) for the analysis of biological specimens[J]. Optics Letters, 2011, 36(12): 2309-2311. |
| 171 | HIRAMATSU K, IDEGUCHI T, YONAMINE Y, et al. High-throughput label-free molecular fingerprinting flow cytometry[J]. Science Advances, 2019, 5(1): eaau0241. |
| 172 | ZHANG C, HUANG K C, RAJWA B, et al. Stimulated Raman scattering flow cytometry for label-free single-particle analysis[J]. Optica, 2017, 4(1): 103-109. |
| 173 | SUZUKI Y, KOBAYASHI K, WAKISAKA Y, et al. Label-free chemical imaging flow cytometry by high-speed multicolor stimulated Raman scattering[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(32): 15842-15848. |
| 174 | XIN Y, SHEN C, SHE Y T, et al. Biosynthesis of triacylglycerol molecules with a tailored PUFA profile in industrial microalgae[J]. Molecular Plant, 2019, 12(4): 474-488. |
| 175 | XIN Y, LU Y D, LEE Y Y, et al. Producing designer oils in industrial microalgae by rational modulation of co-evolving type-2 diacylglycerol acyltransferases[J]. Molecular Plant, 2017, 10(12): 1523-1539. |
| 176 | ZENG W Z, GUO L K, XU S, et al. High-throughput screening technology in industrial biotechnology[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2020, 38(8): 888-906. |
| 177 | HO C S, JEAN N, HOGAN C A, et al. Rapid identification of pathogenic bacteria using Raman spectroscopy and deep learning[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 4927. |
| 178 | TANG T, LIU X, KIYA R, et al. Microscopic impedance cytometry for quantifying single cell shape[J]. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 2021, 193: 113521. |
| 179 | ISLAM M, BRINK H, BLANCHE S, et al. Microfluidic sorting of cells by viability based on differences in cell stiffness[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 1997. |
| 180 | ZHANG Y, ZHAO Y, CHEN D Y, et al. Crossing constriction channel-based microfluidic cytometry capable of electrically phenotyping large populations of single cells[J]. Analyst, 2019, 144(3): 1008-1015. |
| 181 | LABELLE C A, MASSARO A, CORTES-LLANOS B, et al. Image-based live cell sorting[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2021, 39(6): 613-623. |
| 182 | KONG K, ROWLANDS C J, VARMA S, et al. Diagnosis of tumors during tissue-conserving surgery with integrated autofluorescence and Raman scattering microscopy [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(38): 15189-15194. |
| [1] | 应汉杰, 柳东, 王振宇, 沈涛, 庄伟, 朱晨杰. 工业生物制造与“碳中和”目标探讨[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 1-7. |
| [2] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [3] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [4] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [5] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [6] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [7] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [8] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [9] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [10] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [11] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [12] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [13] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [14] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [15] | 谢皇, 郑义蕾, 苏依婷, 阮静怡, 李永泉. 放线菌聚酮类化合物生物合成体系重构研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||