合成生物学 ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (5): 916-931.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-036
超声移液及微量移液技术进展和展望
张志强1, 张扬1,2, 邱维宝1, 郑海荣1
- 1.中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院,保罗·C·劳特伯生物医学成像研究中心,广东 深圳 518055
2.南华大学电气工程学院,湖南 衡阳 421001
-
收稿日期:2023-05-10修回日期:2023-07-05出版日期:2023-10-31发布日期:2023-11-15 -
通讯作者:张志强 -
作者简介:张志强 (1988—),男,博士,副研究员,硕士生导师。研究方向为生物医学超声换能器及应用、超声移液技术研究。E-mail:zq.zhang@siat.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0902900)
Progress and prospect of ultrasonic liquid transfer and low-volume liquid transfer technology
ZHANG zhiqiang1, ZHANG Yang1,2, QIU Weibao1, ZHENG Hairong1
- 1.Paul C. Lauterbur Research Center for Biomedical Imaging,Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenzhen 518055,Guangdong,China
2.School of Electrical Engineering,University of South China,Hengyang 421001,Hunan,China
-
Received:2023-05-10Revised:2023-07-05Online:2023-10-31Published:2023-11-15 -
Contact:ZHANG zhiqiang
摘要:
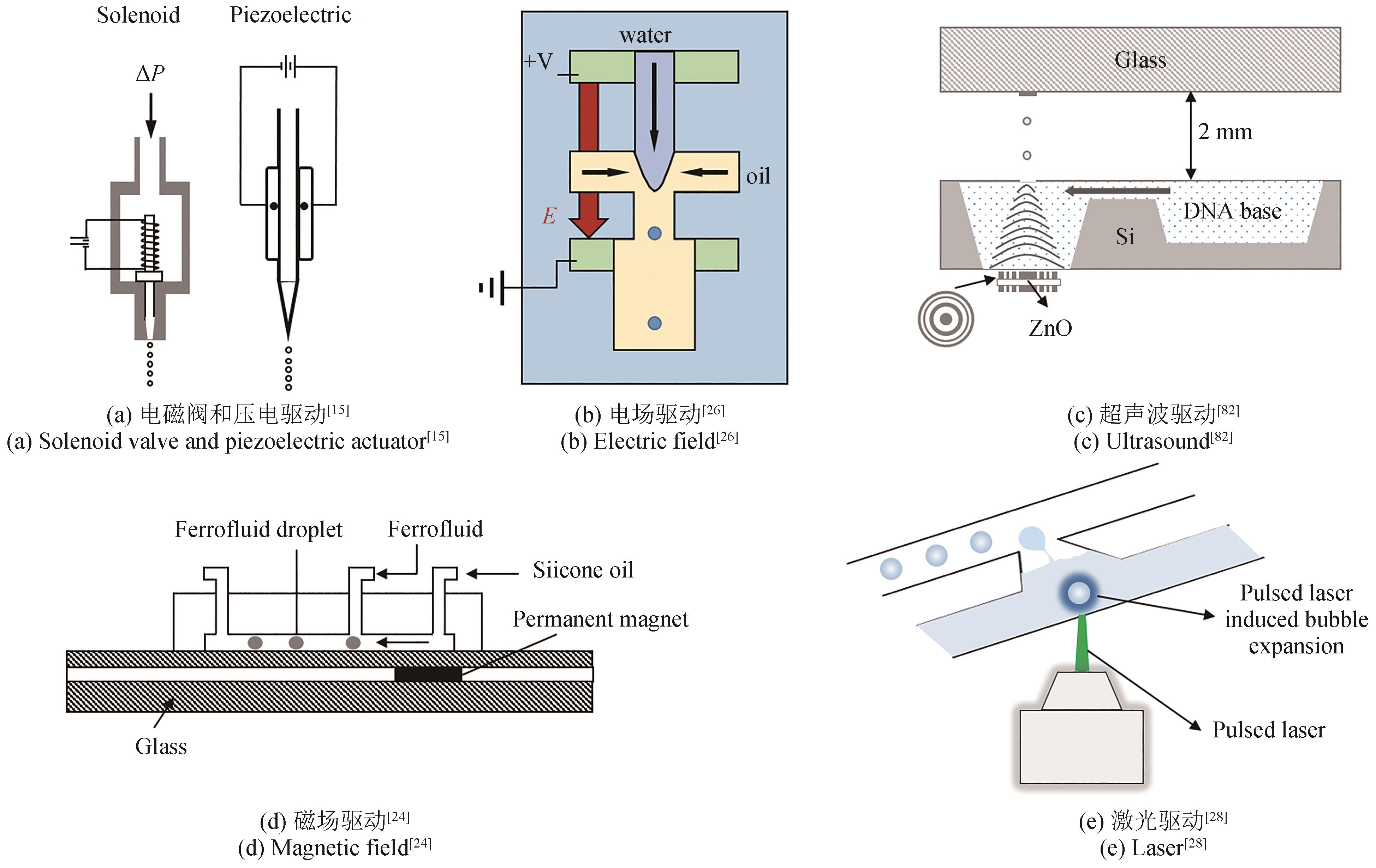
近年来,合成生物学、新药研究以及体外诊断等现代生物、医学技术的快速发展对微量移液技术的精准度、通量、成本等各方面提出了越来越高的要求。传统基于活塞原理的移液技术虽然可以做到自动化,通量可以很高,但是移液精度局限于亚微升级。基于电磁阀、压电驱动等移液技术可以大幅度提高移液精度,但是由于结构复杂,通量难以与活塞式移液技术相媲美。基于电场、磁场、激光等新型移液技术的移液精度可以实现纳升级和皮升级,但是这些技术主要基于微流控平台,针对一些特定应用,通用性差。此外,上述移液技术都需要使用吸头、毛细管、喷嘴等移液头,会与液体直接接触,存在移液头容易堵塞、液体残留、样品交叉污染的风险,而且移液头大都是一次性耗材,成本高,污染环境。非接触式超声移液技术是一种声镊技术,利用超声波声场调制的声辐射力实现对液滴的无接触式操控,无需一次性移液头辅助,无需与液体接触,且具有精度高、移液速度快等特点,是较为理想的精密微量移液技术,展现了重要的应用前景。本文对微量移液技术的发展和代表性研究进展进行了系统性介绍,重点介绍了非接触式超声移液技术的发展和研究进展,并分析讨论了微量移液技术值得关注的发展方向,比如高通量及高通用性的非接触式超声移液技术、智能化移液工作站,以及基于微流控平台的微量液体处理技术等。
中图分类号:
引用本文
张志强, 张扬, 邱维宝, 郑海荣. 超声移液及微量移液技术进展和展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 916-931.
ZHANG zhiqiang, ZHANG Yang, QIU Weibao, ZHENG Hairong. Progress and prospect of ultrasonic liquid transfer and low-volume liquid transfer technology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(5): 916-931.

图4 非接触式超声移液技术[88](利用聚焦超声波的声辐射力实现微小尺寸液滴的无接触式操控)
Fig. 4 Non-contact ultrasonic liquid transfer technology[88](a) Schematic diagram of non-contact ultrasonic liquid transfer technology:using acoustic radiation force of focused ultrasonic wave to eject droplets from liquid surface; (b) Time sequences of droplet ejection from the surface of deionized water by acoustic radiation force
| 微量移液技术 | 原理 | 精度 | 通量 | 重复性 | 代表性应用领域 | 代表性工作 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 接触式 移液 | 移液器 | 活塞式 | 亚微升~微升 | 低 | 中 | 生物、医学、化学等实验室科学研究 | Marburg移液器 |
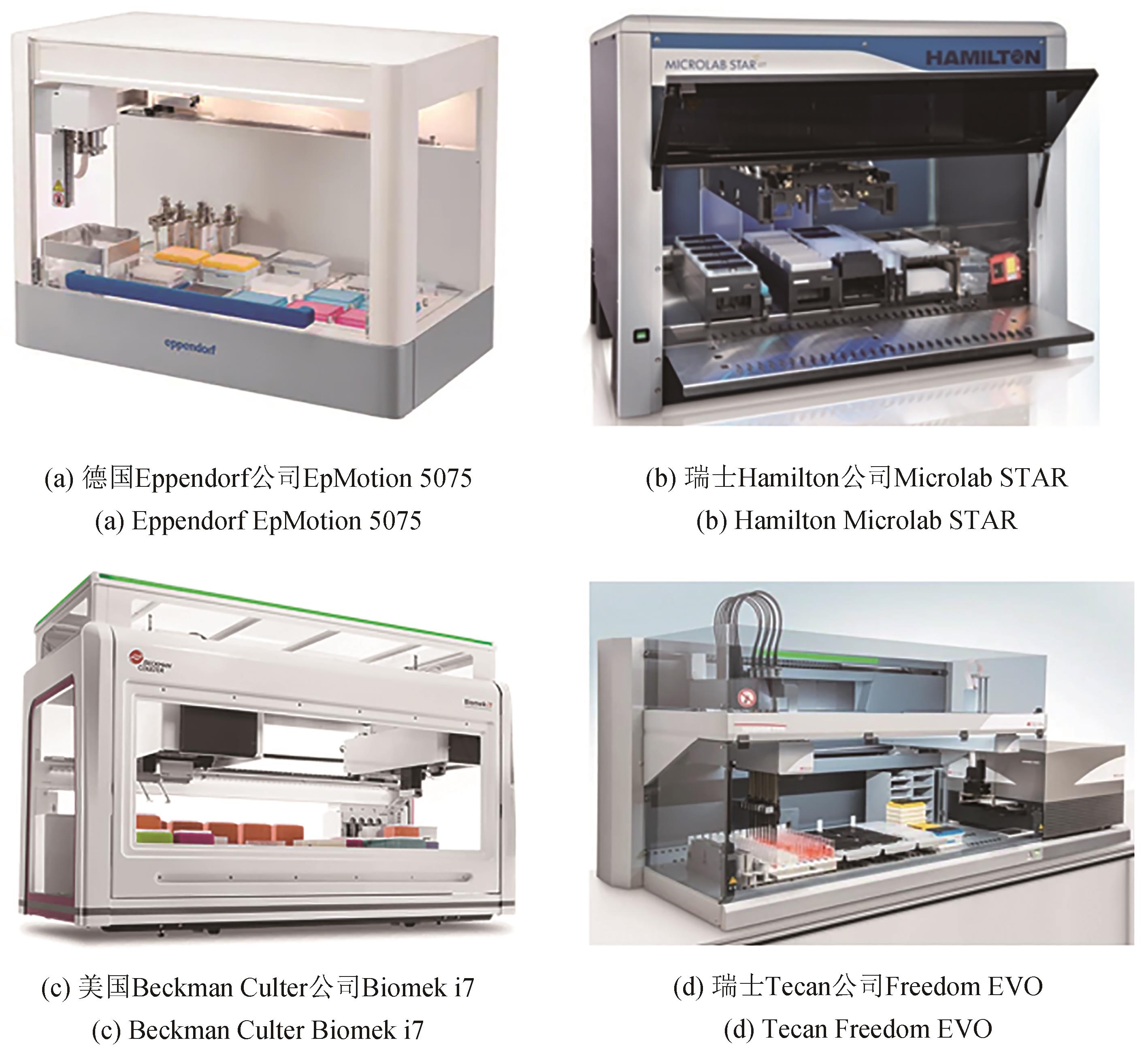
| 自动化移液工作站 | 活塞式 | 亚微升~微升 | 高 | 高 | 合成生物学、药物筛选、PCR预处理、DNA测序 | EpMotion系列,Biomek系列,Microlab STAR, Freedom EVO系列 | |
| 电磁阀移液 | 电磁阀驱动 | 纳升~微升 | 中 | 高 | 生物芯片点样 | PixSys | |
| 压电驱动移液 | 压电驱动 | 皮升~纳升 | 中 | 高 | 生物领域的样品处理,微型化分析,微阵列检测,制药生产 | BioChip,PipeJet TM | |
| 基于微流控平台的电、磁、光、声驱动液滴生成技术 | 电场/磁场/光辐射力、光致空化/声辐射力 | 皮升~纳升 | 中 | 高 | 基于微流控平台的体外诊断应用 | [ | |
| 非接触式 移液 | 超声移液 | 声辐射力 | 皮升~纳升 | 中 | 高 | 药物研发、基因组学、合成生物学 | Echo系列,Arrow系列 |
表1 不同微量移液技术对比
Table 1 Comparison of different low-volume liquid transfer technologies
| 微量移液技术 | 原理 | 精度 | 通量 | 重复性 | 代表性应用领域 | 代表性工作 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 接触式 移液 | 移液器 | 活塞式 | 亚微升~微升 | 低 | 中 | 生物、医学、化学等实验室科学研究 | Marburg移液器 |
| 自动化移液工作站 | 活塞式 | 亚微升~微升 | 高 | 高 | 合成生物学、药物筛选、PCR预处理、DNA测序 | EpMotion系列,Biomek系列,Microlab STAR, Freedom EVO系列 | |
| 电磁阀移液 | 电磁阀驱动 | 纳升~微升 | 中 | 高 | 生物芯片点样 | PixSys | |
| 压电驱动移液 | 压电驱动 | 皮升~纳升 | 中 | 高 | 生物领域的样品处理,微型化分析,微阵列检测,制药生产 | BioChip,PipeJet TM | |
| 基于微流控平台的电、磁、光、声驱动液滴生成技术 | 电场/磁场/光辐射力、光致空化/声辐射力 | 皮升~纳升 | 中 | 高 | 基于微流控平台的体外诊断应用 | [ | |
| 非接触式 移液 | 超声移液 | 声辐射力 | 皮升~纳升 | 中 | 高 | 药物研发、基因组学、合成生物学 | Echo系列,Arrow系列 |
| 30 | BATEMAN T A, AYERS R A, GREENWAY R B. An engineering evaluation of four fluid transfer devices for automated 384-well high throughput screening[J]. Laboratory Robotics and Automation, 1999, 11(5): 250-259. |
| 31 | GUO Q, SU X, ZHANG X G, et al. A review on acoustic droplet ejection technology and system[J]. Soft Matter, 2021, 17(11): 3010-3021. |
| 32 | CAIN-HOM C, PABALATE R, PHAM A, et al. Mammalian genotyping using acoustic droplet ejection for enhanced data reproducibility, superior throughput, and minimized cross-contamination[J]. Journal of Laboratory Automation, 2016, 21(1): 37-48. |
| 33 | MADOUX F, TANNER A, VESSELS M, et al. A 1536-well 3D viability assay to assess the cytotoxic effect of drugs on spheroids[J]. SLAS Discovery, 2017, 22(5): 516-524. |
| 34 | NAYLOR J, ROSSI A, HORNIGOLD D C. Acoustic dispensing preserves the potency of therapeutic peptides throughout the entire drug discovery workflow[J]. Journal of Laboratory Automation, 2016, 21(1): 90-96. |
| 35 | CROSS K, CRAGGS R, SWIFT D, et al. Delivering an automated and integrated approach to combination screening using acoustic-droplet technology[J]. Journal of Laboratory Automation, 2016, 21(1): 143-152. |
| 36 | SALZER E, NIXON E, DREWES G, et al. Screening pools of compounds against multiple endogenously expressed targets in a chemoproteomics binding assay[J]. Journal of Laboratory Automation, 2016, 21(1): 133-142. |
| 37 | PINHEIRO L B, O'BRIEN H, DRUCE J, et al. Interlaboratory reproducibility of droplet digital polymerase chain reaction using a new DNA reference material format[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 89(21): 11243-11251. |
| 38 | PIETIAINEN V, SAARELA J, VON SCHANTZ C, et al. The high throughput biomedicine unit at the institute for molecular medicine Finland: high throughput screening meets precision medicine[J]. Combinatorial Chemistry & High Throughput Screening, 2014, 17(4): 377-386. |
| 39 | MAYDAY M Y, KHAN L M, CHOW E D, et al. Miniaturization and optimization of 384-well compatible RNA sequencing library preparation[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(1): e0206194. |
| 40 | ZHANG J Z, CHEN Y C, FU L H, et al. Accelerating strain engineering in biofuel research via build and test automation of synthetic biology[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2021, 67: 88-98. |
| 41 | KLINGENBERG M. When a common problem meets an ingenious mind[J]. EMBO Reports, 2005, 6(9): 797-800. |
| 42 | FELDMANN R, LOCHNER K H. Influences on volume in piston-operated air-displacement pipettes[J]. Accreditation and Quality Assurance, 2016, 21(1): 69-82. |
| 43 | EWALD K, EPPENDORF A. Impact of pipetting techniques on precision and accuracy [EB/OL]. Eppendorf Userguide, 2015[2023-03-01]. . |
| 44 | MARTEAU D E. Positive-displacement pipette: US4362064[P]. 1982-12-07. |
| 45 | BAMMESBERGER S B, MALKI I, ERNST A, et al. A calibration-free, noncontact, disposable liquid dispensing cartridge featuring an online process control[J]. SLAS Technology, 2014, 19(4): 394-402. |
| 46 | CHENG S, CHANDRA S. A pneumatic droplet-on-demand generator[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2003, 34(6): 755-762. |
| 47 | KHASTSAEV B D. Single channel and multichannel adjustable micropipettes[J]. Biomedical Engineering, 1993, 27(5): 285-291. |
| 48 | AINLA A, JEFFRIES G D M, BRUNE R, et al. A multifunctional pipette[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2012, 12(7): 1255-1261. |
| 49 | BHEEMAVARAPU L P, SHAH M I, RAMANATHAN R, et al. Intelligent pipetting system towards automatic liquid handling applications[C/OL]//2018 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA). June 11-13, 2018, Rome, Italy. IEEE, 2018: 1-6 [2023-03-01]. . |
| 50 | TUROŇOVÁ D, KUJOVSKÁ KRČMOVÁ L, ŠVEC F. Application of microextraction in pipette tips in clinical and forensic toxicology[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 143: 116404. |
| 51 | GREIVELL N E, HANNAFORD B. The design of a ferrofluid magnetic pipette[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 1997, 44(3): 129-135. |
| 52 | RAININ K, KELLY C, PETREK J S. Electronic pipette: US29101531 [P]. 2000-06-13. |
| 53 | WILLIAMS J, WILSON K. Automated pipetting apparatus having a combined liquid pump and pipette head system: US8287820[P]. 2012-10-16. |
| 54 | DUNN D A, FEYGIN I. Challenges and solutions to ultra-high-throughput screening assay miniaturization: submicroliter fluid handling[J]. Drug Discovery Today, 2000, 5(12): 84-91. |
| 55 | TAYLOR P B, ASHMAN S, BADDELEY S M, et al. A standard operating procedure for assessing liquid handler performance in high-throughput screening[J]. Journal of biomolecular screening, 2002, 7(6): 554-569. |
| 56 | YOKOBAYASHI Y. High-throughput analysis and engineering of ribozymes and deoxyribozymes by sequencing[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2020, 53(12): 2903-2912. |
| 57 | ZENG W Z, GUO L K, XU S, et al. High-throughput screening technology in industrial biotechnology[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2020, 38(8): 888-906. |
| 58 | BLAY V, TOLANI B, HO S P, et al. High-Throughput Screening: today's biochemical and cell-based approaches[J]. Drug Discovery Today, 2020, 25(10): 1807-1821. |
| 59 | 张亭, 冷梦甜, 金帆, 等. 合成生物研究重大科技基础设施概述[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(1): 184-194. |
| ZHANG T, LENG M T, JIN F, et al. Overview on platform for synthetic biology research at Shenzhen[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022(1): 184-194. | |
| 60 | FLEISCHER H, BAUMANN D, JOSHI S, et al. Analytical measurements and efficient process generation using a dual-arm robot equipped with electronic pipettes[J]. Energies, 2018, 11(10): 2567. |
| 61 | BESSEMANS L, JULLY V, DE RAIKEM C, et al. Automated gravimetric calibration to optimize the accuracy and precision of TECAN freedom EVO liquid handler[J]. Journal of Laboratory Automation, 2016, 21(5): 693-705. |
| 62 | LIU Y X, CHEN L G, SUN L N, et al. A self-adjusted precise liquid handling system[C/OL]//2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. May 12-17, 2009, Kobe, Japan. IEEE, 2009: 538-543 [2023-03-01]. . |
| 63 | KOLTAY P, STEGER R, BIRKLE G, et al. Microdispenser array for highly parallel and accurate liquid handling[C/OL]//Proc. SPIE 4590, BioMEMS and Smart Nanostructures, San Diego, CA, USA, 2001, 4590: 195-203 [2023-03-01]. . |
| 64 | KARP D G, CUDA D, TANDEL D, et al. Sensitive and specific detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies using a high-throughput, fully automated liquid-handling robotic system[J]. SLAS Technology, 2020, 25(6): 545-552. |
| 65 | OSTENDORF N, NIEFHOFF D, CASSENS U, et al. Automated serological compatibility testing using a solid-phase test and standard laboratory equipment[J]. Vox Sanguinis, 2001, 80(4): 225-229. |
| 66 | BASU I, NAGAPPAN R, FOX-LEWIS S, et al. Evaluation of extraction and amplification assays for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 at Auckland Hospital laboratory during the COVID-19 outbreak in New Zealand[J]. Journal of Virological Methods, 2021, 289: 114042. |
| 67 | BACH A, FLEISCHER H, WIJAYAWARDENA B, et al. Optimization of automated sample preparation for vitamin D determination on a biomek i7 workstation[J]. SLAS Technology, 2021, 26(6): 615-629. |
| 68 | LAURO M L, BOWMAN A M, SMITH J P, et al. Overcoming biopharmaceutical interferents for quantitation of host cell DNA using an automated, high-throughput methodology[J]. The AAPS Journal, 2023, 25(1): 10. |
| 69 | TRUONG V, VIKEN K, GENG Z H, et al. Automating human induced pluripotent stem cell culture and differentiation of iPSC-derived retinal pigment epithelium for personalized drug testing[J]. SLAS Technology, 2021, 26(3): 287-299. |
| 70 | KIMURA J, KAWANA Y, KURIYAMA T. An immobilized enzyme membrane fabrication method using an ink jet nozzle[J]. Biosensors, 1989, 4(1): 41-52. |
| 71 | BERNARDINI G L, RAMPY B A, HOWELL G A, et al. Applications of piezoelectric fluid jetting devices to neuroscience research[J]. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 1991, 38(1): 81-88. |
| 72 | NILES W D, COASSIN P J. Piezo- and solenoid valve-based liquid dispensing for miniaturized assays[J]. ASSAY and Drug Development Technologies, 2005, 3(2): 189-202. |
| 73 | BAILEY A G. Electrostatic spraying of liquids[J]. Physics Bulletin, 1984, 35(4): 146-148. |
| 1 | HE N Y, LIU T, LIU B. Technologies and applications in micro-volume liquid handling[J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2016, 16(1): 58-66. |
| 2 | KONG F W, YUAN L, ZHENG Y F, et al. Automatic liquid handling for life science: a critical review of the current state of the art[J]. Journal of Laboratory Automation, 2012, 17(3): 169-185. |
| 3 | SCOWN C D, KEASLING J D. Sustainable manufacturing with synthetic biology[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2022, 40(3): 304-307. |
| 4 | MCCARTY N S, LEDESMA-AMARO R Synthetic biology tools to engineer microbial communities for biotechnology[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2019, 37(2): 181-197. |
| 5 | TANG T C, AN B L, HUANG Y Y, et al. Materials design by synthetic biology[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2021, 6(4): 332-350. |
| 6 | YU J X, HUBBARD-LUCEY V M, TANG J. Immuno-oncology drug development goes global[J]. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2019, 18(12): 899-900. |
| 7 | ATHAR T, BALUSHI K AL, KHAN S A. Recent advances on drug development and emerging therapeutic agents for Alzheimer's disease[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2021, 48(7): 5629-5645. |
| 8 | DARTOIS V A, RUBIN E J. Anti-tuberculosis treatment strategies and drug development: challenges and priorities[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2022, 20(11): 685-701. |
| 9 | 唐婷, 付立豪, 郭二鹏, 等. 自动化合成生物技术与工程化设施平台[J]. 科学通报, 2021, 66(3): 300-309. |
| TANG T, FU L H, GUO E P, et al. Automation in synthetic biology using biological foundries[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2021, 66(3): 300-309. | |
| 10 | 高倩, 江洪, 陈禹保. 我国体外诊断行业发展现状与对策建议[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 2022, 42(10): 105-111. |
| GAO Q, JIANG H, CHEN Y B. In vitro diagnostics industry in China: current status and development strategies[J]. China Biotechnology, 2022, 42(10): 105-111. | |
| 11 | VASHIST S K. In vitro diagnostic assays for COVID-19: recent advances and emerging trends[J]. Diagnostics, 2020, 10(4): 202. |
| 12 | YING W, LEVONS J K, CARNEY A, et al. Semiautomated sample preparation for protein stability and formulation screening via buffer exchange[J]. Journal of Laboratory Automation, 2016, 21(3): 378-386. |
| 13 | OUYANG W, BOWMAN R W, WANG H R, et al. An open-source modular framework for automated pipetting and imaging applications[J]. Advanced Biology, 2022, 6(4): 2101063. |
| 14 | LEMMO A V, FISHER J T, GEYSEN H M, et al. Characterization of an inkjet chemical microdispenser for combinatorial library synthesis[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1997, 69(4): 543-551. |
| 74 | VONNEGUT B, NEUBAUER R L. Production of monodisperse liquid particles by electrical atomization[J]. Journal of Colloid Science, 1952, 7(6): 616-622. |
| 75 | LOVELADY K T, TOYE L F. Liquid drop emitter: US4308547[P]. 1981-12-29. |
| 76 | SU W T, GAO X H, JIANG L, et al. Microfluidic platform towards point-of-care diagnostics in infectious diseases[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2015, 1377: 13-26. |
| 77 | CHEN X M, REN C L. A microfluidic chip integrated with droplet generation, pairing, trapping, merging, mixing and releasing[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(27): 16738-16750. |
| 78 | YEO L Y, CHANG H C, CHAN P P Y, et al. Microfluidic devices for bioapplications[J]. Small, 2011, 7(1): 12-48. |
| 79 | KWON J W, YU H Y, KIM E S. Film transfer and bonding techniques for covering single-chip ejector array with microchannels and reservoirs[J]. Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems, 2005, 14(6): 1399-1408. |
| 80 | KIM H, LUO D W, LINK D, et al. Controlled production of emulsion drops using an electric field in a flow-focusing microfluidic device[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2007, 91(13): 133106. |
| 81 | TAN S H, SEMIN B, BARET J C. Microfluidic flow-focusing in ac electric fields[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2014, 14(6): 1099-1106. |
| 82 | KWON J W, KAMAL-BAHL S, KIM E S. In situ DNA synthesis on glass substrate for microarray fabrication using self-focusing acoustic transducer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2006, 3(2): 152-158. |
| 83 | OEFTERING R. Acoustic liquid manipulation[C/OL]//1999 IEEEUltrasonics Symposium. Proceedings. International Symposium (Cat. No.99CH37027). October 17-20, 1999, Tahoe, NV, USA. IEEE, 2002: 675-678 [2023-03-01]. . |
| 84 | MEACHAM J M, VARADY M J, DEGERTEKIN F L, et al. Droplet formation and ejection from a micromachined ultrasonic droplet generator: visualization and scaling[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2005, 17(10): 100605. |
| 85 | ZHANG Y Z, ZHU B L, LIU Y H, et al. Hydrodynamic dispensing and electrical manipulation of attolitre droplets[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 12424. |
| 86 | TAN M K, FRIEND J R, YEO L Y. Interfacial jetting phenomena induced by focused surface vibrations[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 103(2): 024501. |
| 15 | LEMMO A V, ROSE D J, TISONE T C. Inkjet dispensing technology: applications in drug discovery[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 1998, 9(6): 615-617. |
| 16 | DIJKSMAN J F. Hydrodynamics of small tubular pumps[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1984, 139: 173-191. |
| 17 | WU H C, HWANG W S, LIN H J. Development of a three-dimensional simulation system for micro-inkjet and its experimental verification[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2004, 373(1/2): 268-278. |
| 18 | DAS C, WANG G C, NGUYEN C. A low-cost, accurate, and high-precision fluid dispensing system for microscale application[J]. SLAS Technology, 2017, 22(2): 144-152. |
| 19 | NGUYEN Q H, YUN B Y, CHOI S B. Performance characteristics of a high frequency jetting dispenser featuring piezoelectric actuator[C/OL]//Proc. SPIE 6928, Active and Passive Smart Structures and Integrated Systems, San Diego, CA, USA, SPIE, 2008, 6928: 69281U[2023-03-01]. . |
| 20 | YIN Z Q, HUANG Z M, LIN X H, et al. Droplet generation in a flow-focusing microfluidic device with external mechanical vibration[J]. Micromachines, 2020, 11(8): 743. |
| 21 | YANG J C, CHIEN W, KING M, et al. A simple piezoelectric droplet generator[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 1997, 23(5): 445-447. |
| 22 | MINOV S V, COINTAULT F, VANGEYTE J, et al. Droplet generation and characterization using a piezoelectric droplet generator and high speed imaging techniques[J]. Crop Protection, 2015, 69: 18-27. |
| 23 | MAO Y X, PAN Y, LI X, et al. High-precision digital droplet pipetting enabled by a plug-and-play microfluidic pipetting chip[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2018, 18(18): 2720-2729. |
| 24 | TAN S H, NGUYEN N T, YOBAS L, et al. Formation and manipulation of ferrofluid droplets at a microfluidic T-junction[J]. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 2010, 20(4): 045004. |
| 25 | WU Y N, FU T T, MA Y G, et al. Ferrofluid droplet formation and breakup dynamics in a microfluidic flow-focusing device[J]. Soft Matter, 2013, 9(41): 9792-9798. |
| 26 | LINK D R, GRASLAND-MONGRAIN E, DURI A, et al. Electric control of droplets in microfluidic devices[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2006, 45(16): 2556-2560. |
| 27 | MANDAR D, LAXMAN S. Light-driven actuation of fluids at microscale[C/OL]. Proc. SPIE 5389, Smart Structures and Materials 2004: ElectronicsSmart, MEMS, BioMEMS, and Nanotechnology, DiegoSan, CA, USA, 2004, 5389: 286-297[2023-03-01]. . |
| 28 | PARK S Y, WU T H, CHEN Y, et al. High-speed droplet generation on demand driven by pulse laser-induced cavitation[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2011, 11(6): 1010-1012. |
| 29 | ENTEN A, YANG Y J, YE Z H, et al. A liquid-handling robot for automated attachment of biomolecules to microbeads[J]. Journal of Laboratory Automation, 2016, 21(4): 526-532. |
| 87 | HON S F, KWOK K W. Study of piezoelectric transducer for liquid ejection[C/OL]//2009 IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium Joint with the 22nd European Frequency and Time forum. April 20-24, 2009, Besancon, France. IEEE, 2009: 1050-1054 [2023-03-01]. . |
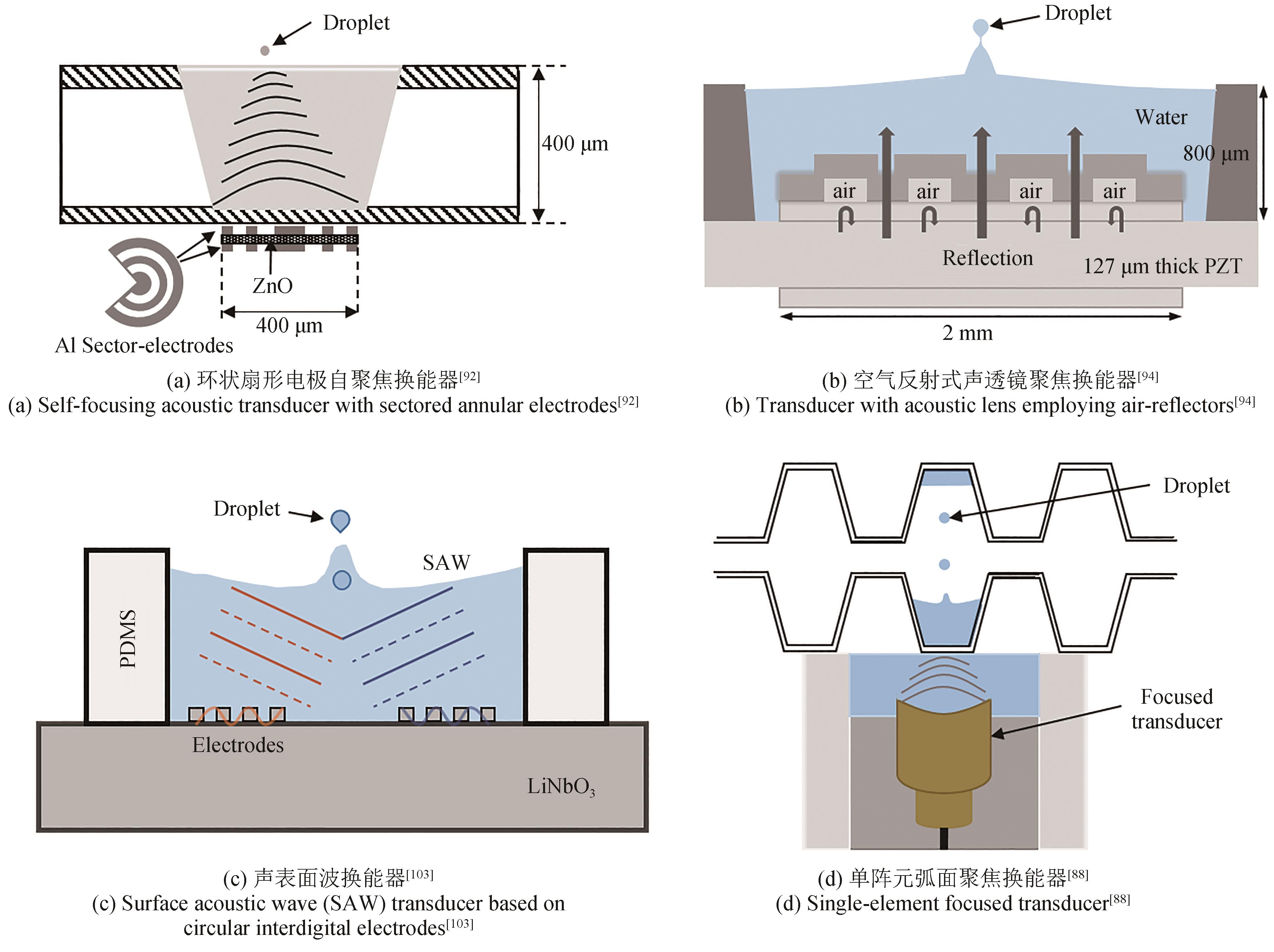
| 88 | LIANG S Z, ZHANG Z Q, WANG X Y, et al. Flexible pico-liter acoustic droplet ejection based on high-frequency ultrasound transducer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 2021, 68(6): 2212-2218. |
| 89 | RAYLEIGH L . ⅩⅩⅩⅣ. On the pressure of vibrations//Philosophical magazine series 6 (1901-1925)[M]. London: Taylor & Francis, 2012: 338-346. |
| 90 | QUATE C F, KHURI-YAKUB B T. Nozzleless liquid droplet ejectors: US4697195[P]. 1987-09-29. |
| 91 | ELROD S A, HADIMIOGLU B, KHURI-YAKUB B T, et al. Nozzleless droplet formation with focused acoustic beams[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1989, 65(9): 3441-3447. |
| 92 | KWON J W, YU H Y, ZOU Q, et al. Directional droplet ejection by nozzleless acoustic ejectors built on ZnO and PZT[J]. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 2006, 16(12): 2697-2704. |
| 93 | KWON J W, ZOU Q, KIM E S. Directional ejection of liquid droplets through sectoring half-wave-band sources of self-focusing acoustic transducer[C/OL]//Technical Digest. MEMS 2002 IEEE International Conference. Fifteenth IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (Cat. No.02CH37266). January 24-24, 2002, Las Vegas, NV, USA. IEEE, 2002: 121-124 [2023-03-01]. . |
| 94 | LEE C Y, YU H Y, KIM E S. Acoustic ejector with novel lens employing air-reflectors[C/OL]//19th IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems. January 22-26, 2006, Istanbul, Turkey. IEEE, 2006: 170-173 [2023-03-01]. . |
| 95 | LEE C Y, YU H Y, KIM E S. Nanoliter droplet coalescence in air by directional acoustic ejection[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 89(22): 223902. |
| 96 | LEE C Y, YU H Y, KIM E S. Harmonic operation of acoustic transducer for droplet ejection application[C/OL]//TRANSDUCERS 2007-2007 International Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Conference. June 10-14, 2007, Lyon, France. IEEE, 2007: 1283-1286 [2023-03-01]. . |
| 97 | LEE C Y, PANG W, HILL S C, et al. Airborne particle generation through acoustic ejection of particles-in-droplets[J]. Aerosol Science and Technology, 2008, 42(10): 832-841. |
| 98 | CHOE Y, CHEN S J, KIM E S. Peptide synthesis on glass substrate using acoustic droplet ejector[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2014, 61(3): 705-710. |
| 99 | TANG Y K, WANG L T, WANG Y F, et al. On-demand, heatless ejection of sub-MM-sized liquid droplets[C/OL]//2017 IEEE 30th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS). January 22-26, 2017, Las Vegas, NV, USA. IEEE, 2017: 1196-1199 [2023-03-01]. . |
| 100 | TANG Y K, KIM E S. Nozzleless acoustic droplet ejector with electrically tunable droplet size for picking and placing semiconductor chips[J]. Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems, 2021, 30(2): 262-270. |
| 101 | CASTRO J O, RAMESAN S, REZK A R, et al. Continuous tuneable droplet ejection via pulsed surface acoustic wave jetting[J]. Soft Matter, 2018, 14(28): 5721-5727. |
| 102 | CASTRO J O, RAMESAN S R, DANG H D, et al. Acoustopipetting: tunable nanoliter sample dispensing using surface acoustic waves[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(9): 5621-5628. |
| 103 | CHEN K K, SUI C X, WU Y, et al. A digital acoustofluidic device for on-demand and oil-free droplet generation[J]. Nanotechnology, 2019, 30(8): 084001. |
| 104 | CHEN K K, JIANG E H, WEI X Y, et al. The acoustic droplet printing of functional tumor microenvironments[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2021, 21(8): 1604-1612. |
| 105 | NING Y, ZHANG M L, ZHANG H X, et al. Mechanism and stability investigation of a nozzle-free droplet-on-demand acoustic ejector[J]. Analyst, 2021, 146(18): 5650-5657. |
| 106 | FANG Y, FRAMPTON J P, RAGHAVAN S, et al. Rapid generation of multiplexed cell cocultures using acoustic droplet ejection followed by aqueous two-phase exclusion patterning[J]. Tissue Engineering Part C, Methods, 2012, 18(9): 647-657. |
| 107 | TANAKA H, MIZUNO Y, NAKAMURA K. Ejection of small droplet from microplate using focused ultrasound[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2017, 56(8): 087202. |
| 108 | GUO Q, SHAO M C, SU X, et al. Controllable droplet ejection of multiple reagents through focused acoustic beams[J]. Langmuir, 2021, 37(51): 14805-14812. |
| 109 | AERNI H R, CORNETT D S, CAPRIOLI R M. Automated acoustic matrix deposition for MALDI sample preparation[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2006, 78(3): 827-834. |
| 110 | VILLASEÑOR A G, WONG A, SHAO A D, et al. Nanolitre-scale crystallization using acoustic liquid-transfer technology[J]. Acta Crystallographica Section D Biological Crystallography, 2012, 68(8): 893-900. |
| 111 | KANIGOWSKA P, SHEN Y, ZHENG Y J, et al. Smart DNA fabrication using sound waves: applying acoustic dispensing technologies to synthetic biology[J]. Journal of Laboratory Automation, 2016, 21(1): 49-56. |
| 112 | JENTSCH S, NASEHI R, KUCKELKORN C, et al. Multiscale 3D bioprinting by nozzle-free acoustic droplet ejection[J]. Small Methods, 2021, 5(6): 2000971. |
| 113 | HADIMIOGLU B, STEARNS R, ELLSON R. Moving liquids with sound: the physics of acoustic droplet ejection for robust laboratory automation in life sciences[J]. Journal of Laboratory Automation, 2016, 21(1): 4-18. |
| 114 | STEARNS R G, QURESHI S A. Method for acoustically ejecting a droplet of fluid from a reservoir by an acoustic fluid ejection apparatus: US07717544B2[P]. 2010-05-18. |
| 115 | STEARNS R G, DATWANI S S. Acoustic fluid height monitoring using dynamic surface perturbations: US8107319[P]. 2012-01-31. |
| 116 | HARRIS D, MUTZ M, SONNTAG M, et al. Low nanoliter acoustic transfer of aqueous fluids with high precision and accuracy of volume transfer and positional placement[J]. Journal of the Association for Laboratory Automation, 2008, 13(2): 97-102. |
| 117 | HARRIS D L, MUTZ M. Debunking the myth: validation of fluorescein for testing the precision of nanoliter dispensing[J]. Journal of the Association for Laboratory Automation, 2006, 11(4): 233-239. |
| 118 | SACKMANN E K, MAJLOF L, HAHN-WINDGASSEN A, et al. Technologies that enable accurate and precise nano- to milliliter-scale liquid dispensing of aqueous reagents using acoustic droplet ejection[J]. Journal of Laboratory Automation, 2016, 21(1): 166-177. |
| 119 | GRANT R J, ROBERTS K, POINTON C, et al. Achieving accurate compound concentration in cell-based screening: validation of acoustic droplet ejection technology[J]. Journal of Biomolecular Screening, 2009, 14(5): 452-459. |
| 120 | TURMEL M, ITKIN Z, LIU D, et al. An innovative way to create assay ready plates for concentration response testing using acoustic technology[J]. Journal of the Association for Laboratory Automation, 2010, 15(4): 297-305. |
| 121 | EDWARDS B, LESNICK J, WANG J, et al. Miniaturization of high-throughput epigenetic methyltransferase assays with acoustic liquid handling[J]. Journal of Laboratory Automation, 2016, 21(1): 208-216. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 雷茹, 陶慧, 刘天罡. 基因组深度挖掘驱动微生物萜类化合物高效发现[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 507-526. |
| [3] | 郭肖杰, 剪兴金, 王立言, 张翀, 邢新会. 合成生物学表型测试生物反应器及其装备化研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 16-37. |
| [4] | 陈永灿, 司同, 张建志. 自动化合成生物技术在DNA组装与微生物底盘操作中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 857-876. |
| [5] | 刘欢, 崔球. 原位电离质谱技术在微生物菌株筛选中的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 980-999. |
| [6] | 胡哲辉, 徐娟, 卞光凯. 自动化高通量技术在天然产物生物合成中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 932-946. |
| [7] | 马翠, 杨凡, 张君泰, 何凯. 面向自动化铸造平台的多功能微孔板检测系统[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 1036-1049. |
| [8] | 吴玉洁, 刘欣欣, 刘健慧, 杨开广, 随志刚, 张丽华, 张玉奎. 基于高通量液相色谱质谱技术的菌株筛选与关键分子定量分析研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 1000-1019. |
| [9] | 秦伟彤, 杨广宇. 微液滴高通量筛选方法的研究与应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 966-979. |
| [10] | 白仲虎, 任和, 聂简琪, 孙杨. 高通量平行发酵技术的发展与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 904-915. |
| [11] | 卢挥, 张芳丽, 黄磊. 合成生物学自动化装置iBioFoundry的构建与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 877-891. |
| [12] | 刁志钿, 王喜先, 孙晴, 徐健, 马波. 单细胞拉曼光谱测试分选装备研制及应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 1020-1035. |
| [13] | 赵国淼, 杨鑫, 张媛, 王靖, 谭剑, 魏超, 周娜娜, 李凡, 王小艳. 生物设施平台及其工业应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 892-903. |
| [14] | 王喜先, 孙晴, 刁志钿, 徐健, 马波. 拉曼光谱技术在单细胞表型检测与分选中的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 204-224. |
| [15] | 涂然, 李世新, 李昊霓, 王猛. 液滴微流控技术在微生物工程菌株选育中的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 165-184. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||