合成生物学 ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (5): 904-915.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-026
高通量平行发酵技术的发展与应用
白仲虎1, 任和1, 聂简琪1, 孙杨2
- 1.江南大学粮食发酵与食品生物制造国家工程研究中心,江苏 无锡 214122
2.河南大学生命科学学院,河南 开封 475004
-
收稿日期:2023-03-30修回日期:2023-06-25出版日期:2023-10-31发布日期:2023-11-15 -
通讯作者:白仲虎 -
作者简介:白仲虎 (1965—),男,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为发酵工程、生物反应器、生物医药过程工程。E-mail:baizhonghu@jiangnan.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家高技术研究发展计划(2015A020802)
The recent progresses and applications of in-parallel fermentation technology
BAI Zhonghu1, REN He1, NIE Jianqi1, SUN Yang2
- 1.National Engineering Research Center of Cereal Fermentation and Food Biomanufacturing,Jiangnan University,Wuxi 214122,Jiangsu,China
2.School of Life Science,Henan University,Kaifeng 475004,Henan,China
-
Received:2023-03-30Revised:2023-06-25Online:2023-10-31Published:2023-11-15 -
Contact:BAI Zhonghu
摘要:
21世纪初,为解决生物医药过程工程研究所面临的微生物和哺乳动物细胞培养的实验通量、研发效率与成本方面的问题,更重要的是质量源于设计(QbD)导向的生物过程工程实验设计(DoE)的迫切需要,基于微、小型生物反应器的平行发酵(细胞培养)技术与产品得到了广泛应用。近年来微生物代谢工程与合成生物学的飞速发展,对高性能菌种库的高通量筛选与菌种表型过程表现的早期评价提出了更高实验通量的需求,这进一步拓展了不同培养体积的平行发酵培养装置在工业生物技术领域的应用。时至今日,可模拟工业培养条件并实施过程参数准确控制的微小型反应器的多联罐平行发酵装置、系统操作软件和数据处理的集成系统已成为生物过程工程研发的强大工具,它在生物医药创新、代谢工程和合成生物学等基础研究成果向工业化技术转化中起到重要的支撑作用。特别是在合成生物学领域中,基于“工业相似性“原则的平行发酵技术,可以解决培养板或摇瓶高通量菌种筛选无法表征克隆表型、在规模化培养中的表现受培养过程参数显著影响的痛点问题,实现过程工程导向的高通量、高效率的菌种筛选与评价。本文对高通量平行发酵与细胞培养技术的发展近况与其在合成生物学研究中的应用场景做了介绍,其中主要总结了平行发酵培养技术在高通量菌种筛选评价“三段论”中的价值、平行发酵培养如何支持菌种筛选的工业相似性原则的实施、平行发酵培养结合DoE实验策略实施高效的生物过程工程开发、使用平行发酵培养建立过程多变元批次模型的方法,以及平行发酵培养与建立生物培养过程缩小模型的关系等。
中图分类号:
引用本文
白仲虎, 任和, 聂简琪, 孙杨. 高通量平行发酵技术的发展与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 904-915.
BAI Zhonghu, REN He, NIE Jianqi, SUN Yang. The recent progresses and applications of in-parallel fermentation technology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(5): 904-915.
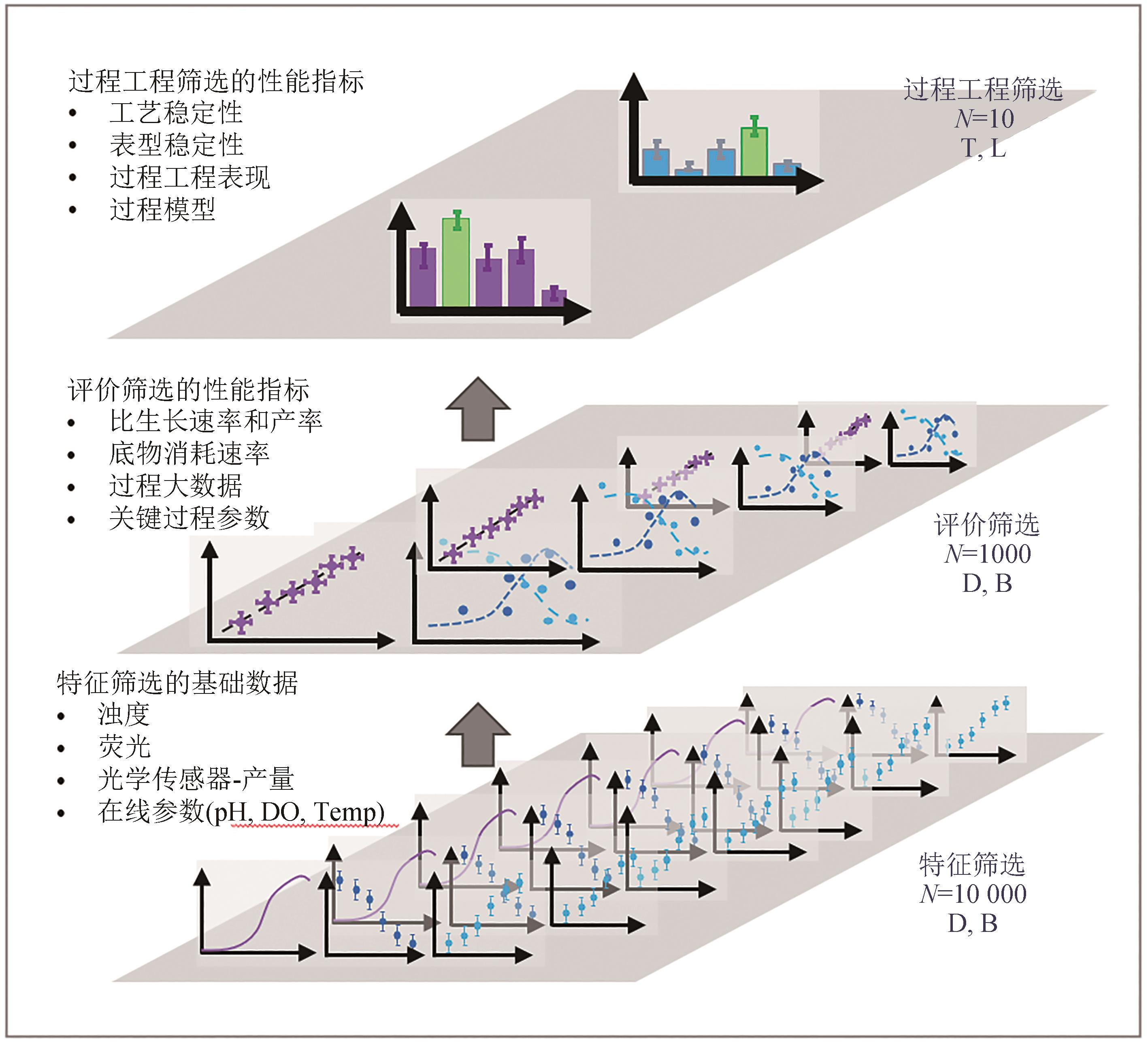
图1 平行培养技术的高通量高效率菌种筛选的三段论策略[13]
Fig. 1 Three-stage strategy for high-throughput and high-efficiency strain screening by in-parallel cultivation technology[13]
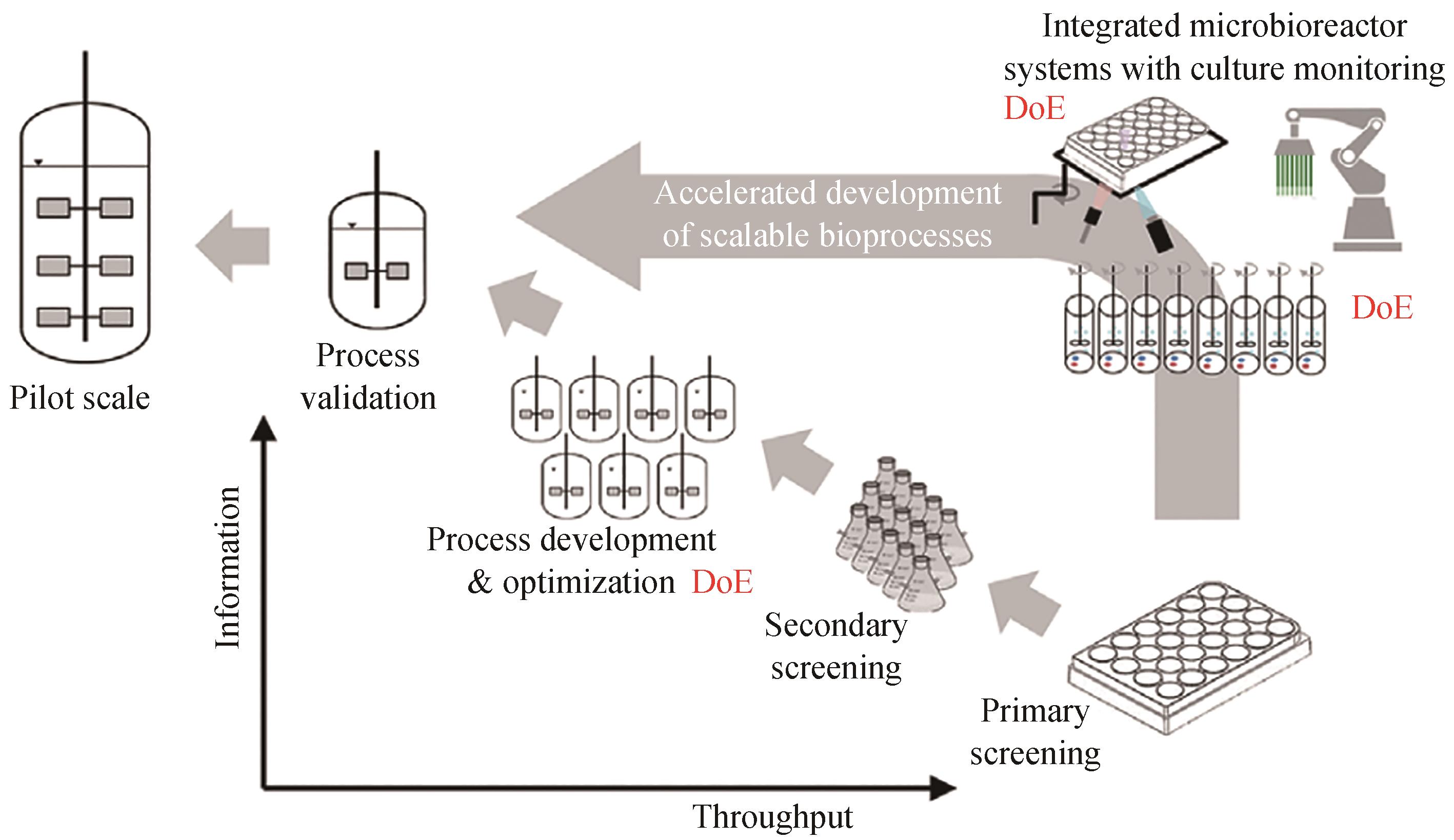
图2 传统的生物过程工程研发途径与使用平行发酵技术实施DoE的过程工程研发路径[13]
Fig. 2 Comparison between traditional roadmap of bioprocess R&D and the new approach using DoE implemented by in parallel fermentation system[13]
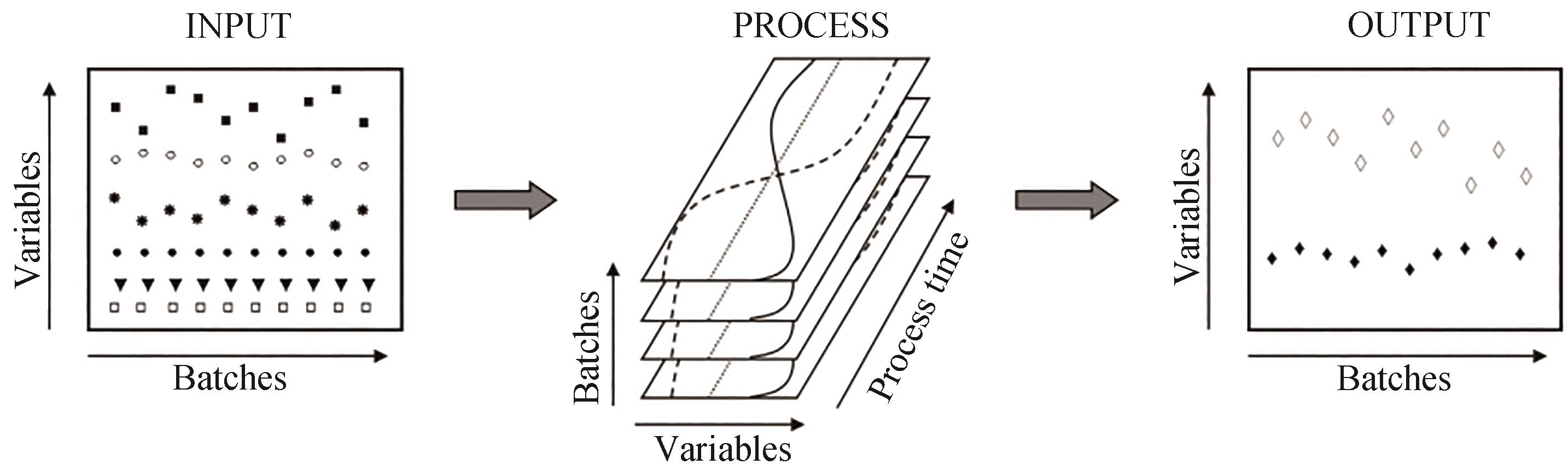
图3 培养过程数据采集的示意图[37][过程参数的输入是在预定受控的设定点范围内运行,这些参数的变化可能导致培养目标参数输出(产量或质量)的显著变化]
Fig. 3 Schematic diagram of data collection from bioprocesses[37][Inputs to the process parameters are operating within predetermined controlled set points. Changes in these parameters may result in significant changes in the output (yield or quality) of the culture target parameters.]
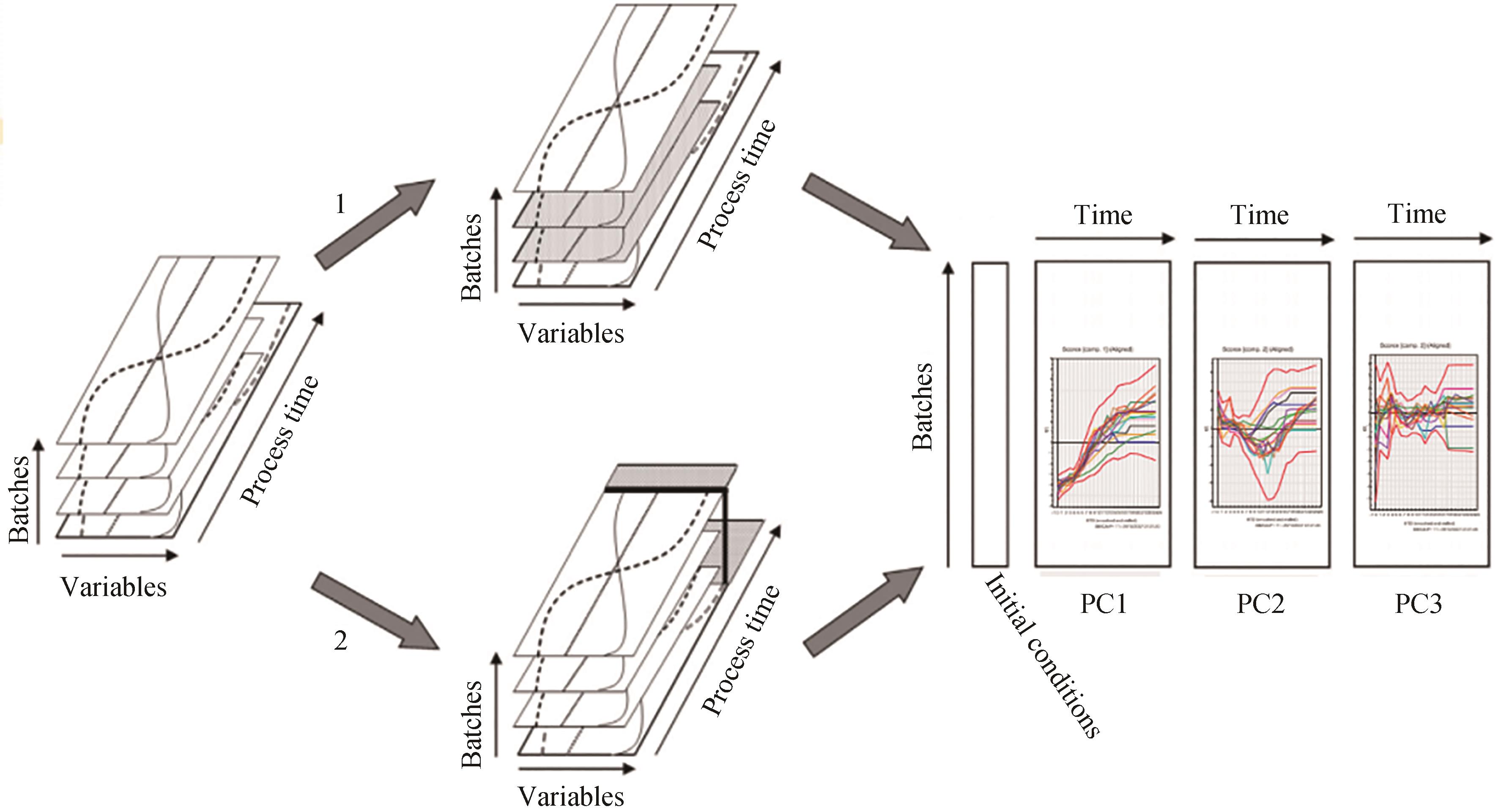
图 4 “好”的培养批次与“坏”批次培养的过程批次数据的展开,并进行模型对比示意图[37](在选项1中,只保留符合目标参数要求的所谓“好”的批次。在选项2中,所有批次均表现出不符合目标参数要求的所谓“坏”批次。可以基于好的批次建立PLS-MVA 批次模型,通过将坏批次的过程参数带入该批次模型,就可识别出坏批次发生问题的原因)
Fig. 4 Schematic diagram of unfolding and comparing the batch models of the processes of "good" and "bad" batches[37](In option 1, only the so-called "good" batches that meet the requirements of the target parameters are retained. In option 2, all batches exhibit the so-called "bad" batches that do not meet the target parameters. The PLS-MVA batch model can be built based on the good batches, and by bringing the process parameters of the bad batches into the batch model, the causes of the problems of the bad batches can be identified.)
| 1 | RIENZO M, JACKSON S J, CHAO L K, et al. High-throughput screening for high-efficiency small-molecule biosynthesis[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2021, 63: 102-125. |
| 2 | AKKERMANS S, NIMMEGEERS P, VAN IMPE J F. Comparing design of experiments and optimal experimental design techniques for modelling the microbial growth rate under static environmental conditions[J]. Food Microbiology, 2018, 76: 504-512. |
| 3 | WALSH I, MYINT M, NGUYEN-KHUONG T, et al. Harnessing the potential of machine learning for advancing "Quality by Design" in biomanufacturing[J]. mAbs, 2022, 14(1): 2013593. |
| 4 | ICH Q8(R 2). Pharmaceutical Development[EB/OL]. 2009[2023-03-01]. . |
| 5 | LIAO X P, MA H W, TANG Y J. Artificial intelligence: a solution to involution of design-build-test-learn cycle[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2022, 75: 102712. |
| 6 | ORSI E, BEEKWILDER J, EGGINK G, et al. The transition of Rhodobacter sphaeroides into a microbial cell factory[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2021, 118(2): 531-541. |
| 7 | FLETCHER E, CHEN Y, CASPETA L, et al. Editorial: genomic strategies for efficient microbial cell factories[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2022, 10: 962828. |
| 8 | GURDO N, VOLKE D C, MCCLOSKEY D, et al. Automating the design-build-test-learn cycle towards next-generation bacterial cell factories[J]. New Biotechnology, 2023, 74: 1-15. |
| 9 | NAKAZAWA S, IMAICHI O, KOGURE T, et al. History-driven genetic modification design technique using a domain-specific lexical model for the acceleration of DBTL cycles for microbial cell factories[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2021, 10(9): 2308-2317. |
| 10 | ISETT K, GEORGE H, HERBER W, et al. Twenty-four-well plate miniature bioreactor high-throughput system: assessment for microbial cultivations[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2007, 98(5): 1017-1028. |
| 11 | MÜHLMANN M, KUNZE M, RIBEIRO J, et al. Cellulolytic RoboLector-towards an automated high-throughput screening platform for recombinant cellulase expression[J]. Journal of Biological Engineering, 2017, 11(1): 1. |
| 12 | VELEZ-SUBERBIE M L, BETTS J P J, WALKER K L, et al. High throughput automated microbial bioreactor system used for clone selection and rapid scale-down process optimization[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2018, 34(1): 58-68. |
| 13 | HEMMERICH J, NOACK S, WIECHERT W, et al. Microbioreactor systems for accelerated bioprocess development[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2018, 13(4): 1700141. |
| 14 | ABATE A R, HUNG T, MARY P, et al. High-throughput injection with microfluidics using picoinjectors[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(45): 19163-19166. |
| 15 | BROMIG L, VON DEN EICHEN N, WEUSTER-BOTZ D. Control of parallelized bioreactorsⅠ: dynamic scheduling software for efficient bioprocess management in high-throughput systems[J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2022, 45(12): 1927-1937. |
| 16 | LONG Q, LIU X X, YANG Y K, et al. The development and application of high throughput cultivation technology in bioprocess development[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2014, 192 Pt B: 323-338. |
| 17 | SANDNER V, PYBUS L P, MCCREATH G, et al. Scale-down model development in ambr systems: an industrial perspective[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 14(4): 1700766. |
| 18 | CRUZ BOURNAZOU M N, BARZ T, NICKEL D B, et al. Online optimal experimental re-design in robotic parallel fed-batch cultivation facilities[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2017, 114(3): 610-619. |
| 19 | JANSEN R, TENHAEF N, MOCH M, et al. FeedER: a feedback-regulated enzyme-based slow-release system for fed-batch cultivation in microtiter plates[J].Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2019, 42(11): 1843-1852. |
| 20 | HEMMERICH J, WIECHERT W, OLDIGES M. Automated growth rate determination in high-throughput microbioreactor systems[J].BMC Research Notes, 2017, 10(1): 617. |
| 21 | MORSCHETT H, JANSEN R, NEUENDORF C, et al. Parallelized microscale fed-batch cultivation in online-monitored microtiter plates: implications of media composition and feed strategies for process design and performance[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2020, 47(1): 35-47. |
| 22 | HEMMERICH J, TENHAEF N, STEFFENS C, et al. Less sacrifice, more insight: repeated low-volume sampling of microbioreactor cultivations enables accelerated deep phenotyping of microbial strain libraries[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 14(9): 1800428. |
| 23 | UNTHAN S, RADEK A, WIECHERT W, et al. Bioprocess automation on a Mini Pilot Plant enables fast quantitative microbial phenotyping[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2015, 14: 32. |
| 24 | LAWSON C E, HARCOMBE W R, HATZENPICHLER R, et al. Common principles and best practices for engineering microbiomes[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2019, 17(12): 725-741. |
| 25 | ZHU X F, DU C C, MOHSIN A, et al. An efficient high-throughput screening of high gentamicin-producing mutants based on titer determination using an integrated computer-aided vision technology and machine learning[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 94(33): 11659-11669. |
| 26 | KAMMINGA T, SLAGMAN S J, MARTINS DOS SANTOS V A P, et al. Risk-based bioengineering strategies for reliable bacterial vaccine production[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2019, 37(8): 805-816. |
| 27 | LIU Y, NIELSEN J. Recent trends in metabolic engineering of microbial chemical factories[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2019, 60: 188-197. |
| 28 | SARNAIK A, LIU A, NIELSEN D, et al. High-throughput screening for efficient microbial biotechnology[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2020, 64: 141-150. |
| 29 | ZENG W Z, GUO L K, XU S, et al. High-throughput screening technology in industrial biotechnology[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2020, 38(8): 888-906. |
| 30 | RAJ K, VENAYAK N, DIEP P, et al. Automation assisted anaerobic phenotyping for metabolic engineering[J].Microbial Cell Factories, 2021, 20(1): 184. |
| 31 | RIENZO M, LIN K C, MOBILIA K C, et al. High-throughput optofluidic screening for improved microbial cell factories via real-time micron-scale productivity monitoring[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2021, 21(15): 2901-2912. |
| 32 | POLITIS S N, COLOMBO P, COLOMBO G, et al. Design of experiments (DoE) in pharmaceutical development[J]. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 2017, 43(6): 889-901. |
| 33 | SWAIN S, PARHI R, JENA B R, et al. Quality by design: concept to applications[J]. Current Drug Discovery Technologies, 2019, 16(3): 240-250. |
| 34 | NOLD V, JUNGHANS L, BISGEN L, et al. Applying intensified design of experiments to mammalian cell culture processes[J]. Engineering in Life Sciences, 2022, 22(12): 784-795. |
| 35 | TAI M, LY A, LEUNG I, et al. Efficient high-throughput biological process characterization: definitive screening design with the ambr250 bioreactor system[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2015, 31(5): 1388-1395. |
| 36 | PEREIRA R F S, DE CARVALHO C C C R. Optimization of multiparameters for increased yields of cytochrome B5 in bioreactors[J]. Molecules, 2021, 26(14): 4148. |
| 37 | MERCIER S M, DIEPENBROEK B, DALM M C F, et al. Multivariate data analysis as a PAT tool for early bioprocess development data[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2013, 167(3): 262-270. |
| 38 | MERCIER S M, DIEPENBROEK B, WIJFFELS R H, et al. Multivariate PAT solutions for biopharmaceutical cultivation: current progress and limitations[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2014, 32(6): 329-336. |
| 39 | RATHORE A S, MITTAL S, PATHAK M, et al. Guidance for performing multivariate data analysis of bioprocessing data: pitfalls and recommendations[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2014, 30(4): 967-973. |
| 40 | XU P, CLARK C, RYDER T, et al. Characterization of TAP Ambr 250 disposable bioreactors, as a reliable scale-down model for biologics process development[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2017, 33(2): 478-489. |
| 41 | NIKITA S, MISHRA S, GUPTA K, et al. Advances in bioreactor control for production of biotherapeutic products[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2023, 120(5): 1189-1214. |
| 42 | SÃO PEDRO M N, SILVA T C, PATIL R, et al. White paper on high-throughput process development for integrated continuous biomanufacturing[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2021, 118(9): 3275-3286. |
| 43 | KHANAL O, LENHOFF A M. Developments and opportunities in continuous biopharmaceutical manufacturing[J]. mAbs, 2021, 13(1): 1903664. |
| 44 | ANANE E, GARCÍA Á C, HABY B, et al. A model-based framework for parallel scale-down fed-batch cultivations in mini-bioreactors for accelerated phenotyping[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2019, 116(11): 2906-2918. |
| 45 | TAPIA F, VÁZQUEZ-RAMÍREZ D, GENZEL Y, et al. Bioreactors for high cell density and continuous multi-stage cultivations: options for process intensification in cell culture-based viral vaccine production[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2016, 100(5): 2121-2132. |
| 46 | JANOSCHEK S, SCHULZE M, ZIJLSTRA G, et al. A protocol to transfer a fed-batch platform process into semi-perfusion mode: the benefit of automated small-scale bioreactors compared to shake flasks as scale-down model[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2019, 35(2): e2757. |
| 47 | LIN H, LEIGHTY R W, GODFREY S, et al. Principles and approach to developing mammalian cell culture media for high cell density perfusion process leveraging established fed-batch media[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2017, 33(4): 891-901. |
| 48 | XU J L, OU J F, MCHUGH K P, et al. Upstream cell culture process characterization and in-process control strategy development at pandemic speed[J]. mAbs, 2022, 14(1): 2060724. |
| 49 | WOLF M K F, LORENZ V, KARST D J, et al. Development of a shake tube-based scale-down model for perfusion cultures[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2018, 115(11): 2703-2713. |
| 50 | MACDONALD M A, NÖBEL M, ROCHE RECINOS D, et al. Perfusion culture of Chinese Hamster Ovary cells for bioprocessing applications[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2022, 42(7): 1099-1115. |
| 51 | KUIPER M, SPENCER C, FÄLDT E, et al. Repurposing fed-batch media and feeds for highly productive CHO perfusion processes[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2019, 35(4): e2821. |
| 52 | JANAKIRAMAN V, KWIATKOWSKI C, KSHIRSAGAR R, et al. Application of high-throughput mini-bioreactor system for systematic scale-down modeling, process characterization, and control strategy development[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2015, 31(6): 1623-1632. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | 赵亮, 李振帅, 付丽平, 吕明, 王士安, 张全, 刘立成, 李福利, 刘自勇. 生物转化一碳化合物原料产油脂与单细胞蛋白研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1300-1318. |
| [10] | 刘建明, 张炽坚, 张冰, 曾安平. 巴氏梭菌作为工业底盘细胞高效生产1,3-丙二醇——从代谢工程和菌种进化到过程工程和产品分离[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1386-1403. |
| [11] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [12] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [13] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [14] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [15] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
