Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2020, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (6): 685-696.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-008
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Artificial enzyme designs and its application based on non-natural structural elements
YUAN Feiyan, YU Yang, LI Chun
- Department of Biochemical Engineering,Institute for Synthetic Biosystem,School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Beijing Institute of Technology,Beijing 100081,China
-
Received:2020-02-09Revised:2020-04-30Online:2021-01-15Published:2020-12-31 -
Contact:YU Yang, LI Chun
基于非天然结构组件的人工酶设计与应用
袁飞燕, 于洋, 李春
- 北京理工大学化学与化工学院生化工程系,合成生物系统研究所,北京 100081
-
通讯作者:于洋,李春 -
作者简介:袁飞燕(1993—),女,博士研究生。研究方向为蛋白质设计与酶工程。E-mail:feiyanyuan@163.com
于洋(1987—),男,博士,研究员、博士生导师。研究方向为蛋白质设计与酶工程。E-mail:yang_yu@outlook.com
李春(1970—),男,博士,教授、博士生导师。研究方向为合成生物学。E-mail:lichun@bit.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0903300)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YUAN Feiyan, YU Yang, LI Chun. Artificial enzyme designs and its application based on non-natural structural elements[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(6): 685-696.
袁飞燕, 于洋, 李春. 基于非天然结构组件的人工酶设计与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(6): 685-696.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2020-008
| 1 | MALATESTA F, ANTONINI G, SARTI P, et al. Structure and function of a molecular machine: cytochrome c oxidase[J]. Biophysical Chemistry, 1986, 68(3): 459-470. |
| 2 | REETZ M T. Directed evolution of artificial metalloenzymes: a universal means to tune the selectivity of transition metal catalysts?[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2019, 52(2): 336-344. |
| 3 | WANG J, HUANG Q, PENG W, et al. P450-BM3 catalyzed sulfoxidation versus hydroxylation : a common or two different catalytically active species? [J]. Journal of American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(4): 2068-2073. |
| 4 | NATOLI S N, HARTWIG J F. Noble-metal substitution in hemoproteins : an emerging strategy for abiological catalysis[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2019, 52(2): 326-335. |
| 5 | REETZ M T. Laboratory evolution of stereoselective enzymes: a prolific source of catalysts for asymmetric reactions[J]. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2011, 50(1): 138-174. |
| 6 | CHEN Q, CHEN X, FENG J, et al. Improving and inverting Cβ-stereoselectivity of threonine aldolase via substrate-binding-guided mutagenesis and a stepwise visual screening[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(5): 4462-4469. |
| 7 | CHEN X, ZHANG H, MARIA-SOLANO M A, et al. Efficient reductive desymmetrization of bulky 1,3-cyclodiketones enabled by structure-guided directed evolution of a carbonyl reductase[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2019, 2(10): 931-941. |
| 8 | BRANDENBERG O F, FASAN R, ARNOLD F H. Exploiting and engineering hemoproteins for abiological carbene and nitrene transfer reactions[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2017, 47(4): 102-111. |
| 9 | CHEN K, HUANG X, JENNIFER KAN S B, et al. Enzymatic construction of highly strained carbocycles[J]. Science, 2018, 360(6384): 71-75. |
| 10 | ZHANG R K, CHEN K, HUANG X, et al. Enzymatic assembly of carbon-carbon bonds via iron-catalysed sp3 C-H functionalization[J]. Nature, 2019, 565(47): 67-72. |
| 11 | YANG Y, CHO I, QI X, et al. An enzymatic platform for the asymmetric amination of primary, secondary and tertiary C(sp3)-H bonds[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2019, 11(11): 987-993. |
| 12 | ZHANG J, HUANG X, ZHANG R K, et al. Enantiodivergent α-Amino C-H fluoroalkylation catalyzed by engineered cytochrome P450s[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(25): 9798-9802. |
| 13 | BRANDENBERG O F, CHEN K, ARNOLD F H. Directed evolution of a cytochrome P450 carbene transferase for selective functionalization of cyclic compounds[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(22): 8989-8995. |
| 14 | BRANDENBERG O F, MILLER D C, MARKEL U, et al. Engineering chemoselectivity in hemoprotein-catalyzed indole amidation[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(9): 8271-8275. |
| 15 | LI F L, KONG X D, CHEN Q, et al. Regioselectivity engineering of epoxide hydrolase: near-perfect enantioconvergence through a single site mutation[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(9): 8314-8317. |
| 16 | YAO P, CONG P, GONG R, et al. Biocatalytic route to chiral 2-substituted-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolines using cyclohexylamine oxidase muteins[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(3): 1648-1652. |
| 17 | CHEN X, ZHANG H, FENG J, et al. Molecular basis for the high activity and enantioselectivity of the carbonyl reductase from sporobolomyces salmonicolor toward α-haloacetophenones[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(4): 3525-3531. |
| 18 | GONG X M, QIN Z, LI F L, et al. Development of an engineered ketoreductase with simultaneously improved thermostability and activity for making a bulky atorvastatin precursor[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(1): 147-153. |
| 19 | 曲戈, 朱彤, 蒋迎迎, 等. 蛋白质工程: 从定向进化到计算设计[J]. 生物工程学报, 2019, 35(10): 1843-1856. |
| QU G, ZHU T, JIANG Y Y, et al. Protein engineering: from directional evolution to computational design[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2019, 35(10): 1843-1856. | |
| 20 | WANG L, BROCK A, HERBERICH B, et al. Expanding the genetic code of Escherichia coli [J]. Science, 2001, 292(5516): 498-500. |
| 21 | XIE J, SCHULTZ P G. An expanding genetic code[J]. Methods, 2005, 36(3): 227-238. |
| 22 | DUMAS A, LERCHER L, SPICER C D, et al. Designing logical codon reassignment-expanding the chemistry in biology[J]. Chemical Science, 2015, 6(1): 50-69. |
| 23 | DEITERS A, SCHULTZ P G. In vivo incorporation of an alkyne into proteins in Escherichia coli [J]. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2005, 15(5): 1521-1524. |
| 24 | DAY J W, KIM C H, SMIDER V V, et al. Identification of metal ion binding peptides containing unnatural amino acids by phage display[J]. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2013, 23(9): 2598-2600. |
| 25 | YU Y, CUI C, WANG J, et al. Biosynthetic approach to modeling and understanding metalloproteins using unnatural amino acids[J]. Science China Chemistry, 2017, 60(2): 188-200. |
| 26 | LIU X, LI J, HU C, et al. Significant expansion of the fluorescent protein chromophore through the genetic incorporation of a metal-chelating unnatural amino acid[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2013, 52(18): 4805-4809. |
| 27 | DRIENOVSKÁ I, RIOZ-MARTÍNEZ A, DRAKSHARAPU A, et al. Novel artificial metalloenzymes by in vivo incorporation of metal-binding unnatural amino acids[J]. Chemical Science, 2015, 6(1): 770-776. |
| 28 | DRIENOVSKÁ I, ALONSO-COTCHICO L, VIDOSSICH P, et al. Design of an enantioselective artificial metallo-hydratase enzyme containing an unnatural metal-binding amino acid[J]. Chemical Science, 2017, 8(10): 7228-7235. |
| 29 | DRIENOVSKÁ I, MAYER C, DULSON C, et al. A designer enzyme for hydrazone and oxime formation featuring an unnatural catalytic aniline residue[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2018, 10(9): 946-952. |
| 30 | MAYER C, DULSON C, REDDEM E, et al. Directed evolution of a designer enzyme featuring an unnatural catalytic amino acid[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(7): 2083-2087. |
| 31 | WILSON M E, WHITESIDES G M. Conversion of a protein to a homogeneous asymmetric hydrogenation catalyst by site-specific modification with a diphosphinerhodium(I) moiety[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1978, 100(1): 306-307. |
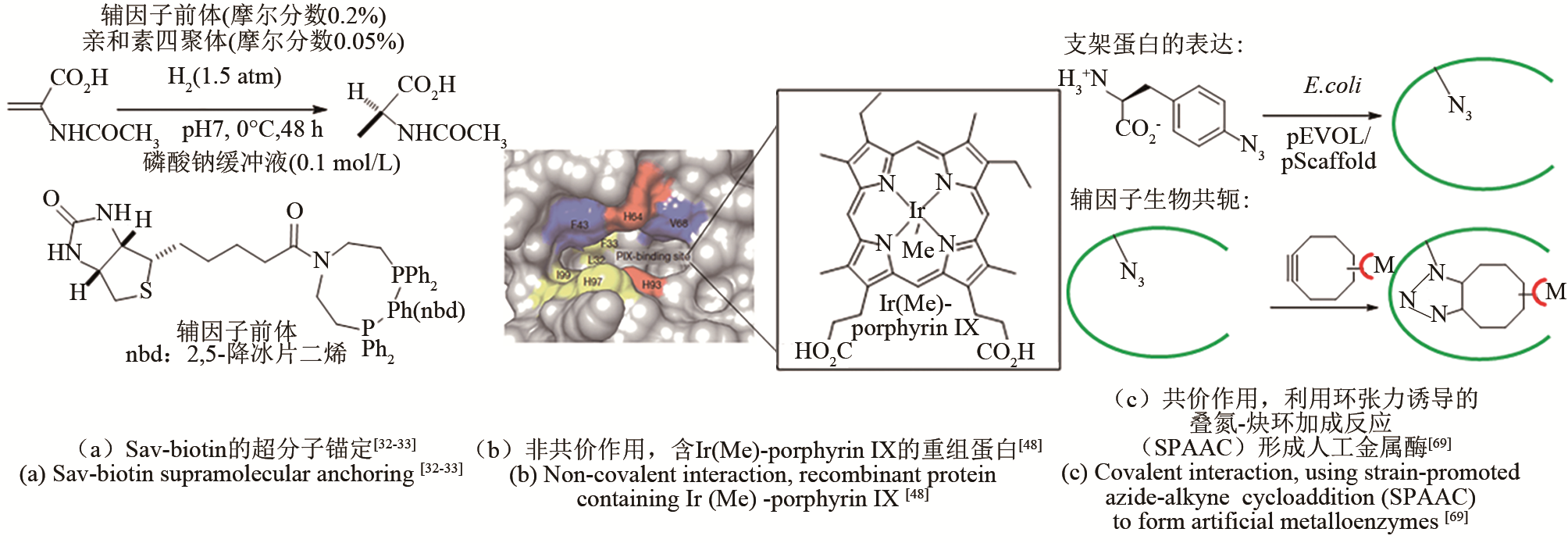
| 32 | HEINISCH T, WARD T R. Artificial metalloenzymes based on the biotin-streptavidin technology: challenges and opportunities[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2016, 49(9): 1711-1721. |
| 33 | WARD T R. Artificial metalloenzymes based on the biotin - avidin technology: enantioselective catalysis and beyond[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2011, 44(1): 47-57. |
| 34 | JESCHEK M, REUTER R, HEINISCH T, et al. Directed evolution of artificial metalloenzymes for in vivo metathesis[J]. Nature, 2016, 537(7622): 661-665. |
| 35 | 林英武. 人工金属酶分子设计新进展:肌红蛋白研究实例分析[J]. 化学进展, 2018, 30(10): 1464-1474. |
| LIN Y W. Rational design of artificial metalloenzymes: case studies in myoglobin[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2018, 30(10): 1464-1474. | |
| 36 | 林英武, 王江云, 陆艺. 蛋白质分子理性设计与肌红蛋白功能的调控及拓展[J]. 中国科学:化学, 2014, 2014, 57(3): 346-355. |
| LIN Y W, WANG J Y, LU Y. Functional tuning and expanding of myoglobin by rational protein design[J]. Science China Chemistry, 2014, 57(3): 346-355. | |
| 37 | 于洋. 基于肌红蛋白的氧激活蛋白的理性设计[J]. 生物加工过程, 2019, 17(1): 23-28. |
| YU Y. Rational design of oxygen-activating protein based on myoglobin[J]. Chinese Journal of Bioprocess Engineering, 2019, 17(1): 23-28. | |
| 38 | BHAGI-DAMODARAN A, PETRIK I D, MARSHALL N M, et al. Systematic tuning of heme redox potentials and its effects on O2 reduction rates in a designed oxidase in myoglobin[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(34): 11882-11885. |
| 39 | HILL R, HOLDEN H F. The preparation and some properties of the globin of oxyhaemoglobin[J]. Biochemical Journal, 1926, 20(6): 1326-1339. |
| 40 | OHASHI M, KOSHIYAMA T, UENO T, et al. Preparation of artificial metalloenzymes by insertion of chromium(III) schiff base complexes into apomyoglobin mutants[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2003, 42(9): 1005-1008. |
| 41 | HAYASHI T, HISAEDA Y. New functionalization of myoglobin by chemical modification of heme-propionates[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2002, 35(1): 35-43. |
| 42 | CAREY J R, MA S K, PFISTER T D, et al. A site-selective dual anchoring strategy for artificial metalloprotein design[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004, 126(35): 10812-10813. |
| 43 | ZHANG J L, GARNER D K, LIANG L, et al. Noncovalent modulation of PH-dependent reactivity of a Mn-Salen cofactor in myoglobin with hydrogen peroxide[J]. Chemistry, 2009, 15(30): 7481-7489. |
| 44 | LIU J, CHAKRABORTY S, HOSSEINZADEH P, et al. Metalloproteins containing cytochrome, iron-sulfur, or copper redox centers[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(8): 4366-4369. |
| 45 | BHAGI-DAMODARAN A, KAHLE M, SHI Y, et al. Insights into how heme reduction potentials modulate enzymatic activities of a myoglobin-based functional oxidase[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(23): 6622-6626. |
| 46 | DYDIO P, KEY H M, NAZARENKO A, et al. An artificial metalloenzyme with the kinetics of native enzymes[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6308): 102-106. |
| 47 | KEY H M, DYDIO P, CLARK D S, et al. Abiological catalysis by artificial haem proteins containing noble metals in place of iron[J]. Nature, 2016, 534(7608): 534-537. |
| 48 | NATOLI S N, HARTWIG J F. Noble-metal substitution in hemoproteins: an emerging strategy for abiological catalysis[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2019, 52(2): 326-335. |
| 49 | DYDIO P, KEY H M, HAYASHI H, et al. Chemoselective, enzymatic C-H bond amination catalyzed by a cytochrome P450 containing an Ir(Me)-PIX cofactor[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(5): 1750-1753. |
| 50 | GU Y, NATOLI S N, LIU Z, et al. Site-selective functionalization of (sp3)C—H bonds catalyzed by artificial metalloenzymes containing an iridium-porphyrin cofactor[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(39): 13954-13960. |
| 51 | JI D Bin, WANG L, LIU W J, et al. Synthesis of NAD analogs to develop bioorthogonal redox system[J]. Science China Chemistry, 2013, 56(3): 296-300. |
| 52 | SEEFELDT L C, HOFFMAN B M, DEAN D R. Mechanism of mo-dependent nitrogenase[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2011, 78(1):701-722. |
| 53 | SHAH V K, BRILL W J. Isolation of an iron-molybdenum cofactor from nitrogenase[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1977, 74(8):3249-3253. |
| 54 | ČORIĆ I, HOLLAND P L. Insight into the iron-molybdenum cofactor of nitrogenase from synthetic iron complexes with sulfur, carbon, and hydride ligands[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(23): 7200-7211. |
| 55 | LIN Y W. Rational design of metalloenzymes: from single to multiple active sites[J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2017, 336(4):1-27. |
| 56 | STIEFEL E I, GEORGE G N. Ferredoxins, hydrogenases, and nitrogenases: metal-sulfide proteins[J]. Bioinorganic Chemistry, 1994: 365-453. |
| 57 | STAPPEN C VAN, DECAMPS L, CUTSAIL G E, et al. The spectroscopy of nitrogenases[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(12): 5005-5081. |
| 58 | MIRTS E N, PETRIK I D, HOSSEINZADEH P, et al. A designed heme-[4Fe-4S] metalloenzyme catalyzes sulfite reduction like the native enzyme[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6407): 1098-1101. |
| 59 | MIRTS E N, DIKANOV S A, JOSE A, et al. A binuclear cuA center designed in an all α-helical protein scaffold[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(32): 13779-13794. |
| 60 | MIRTS E N, BHAGI-DAMODARAN A, LU Y. Understanding and modulating metalloenzymes with unnatural amino acids, non-native metal ions, and non-native metallocofactors[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2019, 52(4): 935-944. |
| 61 | MULLIEZ E, DUARTE V, ARRAGAIN S, et al. On the role of additional [4Fe-4S] clusters with a free coordination site in radical-SAM enzymes[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2017, 5(17): 1-13. |
| 62 | SMITH A T, LINKOUS R O, MAX N J, et al. The FeoC [4Fe-4S] cluster is redox-active and rapidly oxygen-sensitive[J]. Biochemistry, 2019, 58(49): 4935-4949. |
| 63 | SHOJI O, FUJISHIRO T, NAKAJIMA H, et al. Hydrogen peroxide dependent monooxygenations by tricking the substrate recognition of cytochrome P450BSβ [J]. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2007, 46(20): 3656-3659. |
| 64 | SHOJI O, AIBA Y, WATANABE Y. Hoodwinking cytochrome P450BM3 into hydroxylating non-native substrates by exploiting its substrate misrecognition[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2019, 52(4): 925-934. |
| 65 | ZHANG W, MA M, HUIJBERS M M E, et al. Hydrocarbon synthesis via photoenzymatic decarboxylation of carboxylic acids[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(7): 3116-3120. |
| 66 | DEMMING R M, HAMMER S C, NESTL B M, et al. Asymmetric enzymatic hydration of unactivated, aliphatic alkenes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(1): 173-177. |
| 67 | CHEN J, KONG F, MA N, et al. Peroxide-driven hydroxylation of small alkanes catalyzed by an artificial P450BM3 peroxygenase system[J]. ACS Catalysis, American Chemical Society, 2019, 9(8): 7350-7355. |
| 68 | MA N, CHEN Z, CHEN J, et al. Dual-functional small molecules for generating an efficient cytochrome P450BM3 peroxygenase[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(26): 7628-7633. |
| 69 | YANG H, SRIVASTAVA P, ZHANG C, et al. A general method for artificial metalloenzyme formation through strain-promoted azide-alkyne cycloaddition[J]. ChemBioChem, 2014, 15(2): 223-227. |
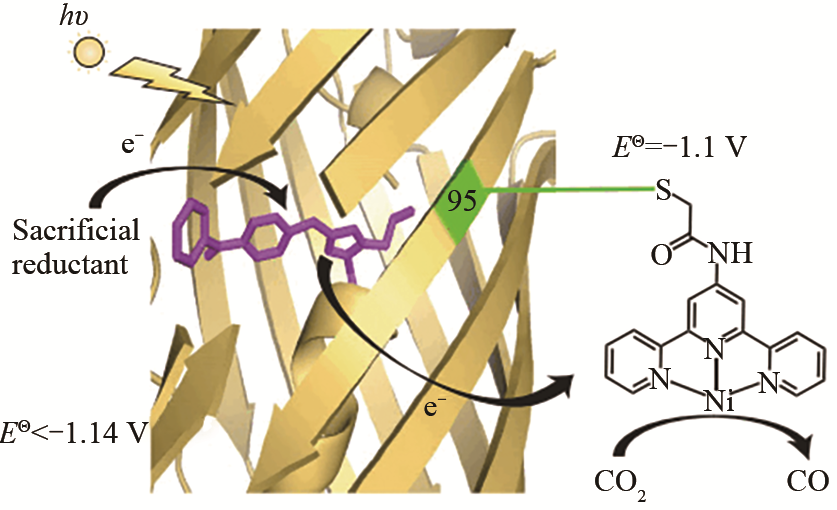
| 70 | LIU X, KANG F, HU C, et al. A genetically encoded photosensitizer protein facilitates the rational design of a miniature photocatalytic CO2-reducing enzyme[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2018, 10(12): 1201-1206. |
| 71 | CHATTERJEE A, SUN S B, FURMAN J L, et al. A versatile platform for single- and multiple-unnatural amino acid mutagenesis in Escherichia coli [J]. Biochemistry, 2013, 52(10): 1828-1837. |
| 72 | GUO J, MELANÇON C E, LEE H S, et al. Evolution of amber suppressor tRNAs for efficient bacterial production of proteins containing nonnatural amino acids[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2009, 48(48): 9148-9151. |
| 73 | XIE J, WANG L, WU N, et al. The site-specific incorporation of p-iodo-L-phenylalanine into proteins for structure determination[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2004, 22(10): 1297-1301. |
| 74 | LI F, SHI P, LI J S, et al. A genetically encoded 19F NMR probe for tyrosine phosphorylation[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52 (14): 3958-3962. |
| 75 | MEHL R A, ANDERSON J C, SANTORO S W, et al. Generation of a bacterium with a 21 amino acid genetic code[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(4): 935-939. |
| 76 | EHRLICH M, GATTNER M J, VIVERGE B, et al. Orchestrating the biosynthesis of an unnatural pyrrolysine amino acid for its direct incorporation into proteins inside living cells[J]. Chemistry, 2015, 21(21): 7701-7704. |
| 77 | MARCHAND J A, NEUGEBAUER M E, ING M C, et al. Discovery of a pathway for terminal-alkyne amino acid biosynthesis[J]. Nature, 2019, 567(7748): 420-424. |
| 78 | WANG N, YANG B, FU C, et al. Genetically encoding fluorosulfate-L-tyrosine to react with lysine, histidine, and tyrosine via SuFEx in proteins in vivo [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(15): 4995-4999. |
| 79 | YANG B, WANG N, SCHNIER P D, et al. Genetically introducing biochemically reactive amino acids dehydroalanine and dehydrobutyrine in proteins[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(19): 7698-7703. |
| 80 | PARK J, SELVARAJ B, MCSHAN A C, et al. De novo design of a homo-trimeric amantadine-binding protein[J]. eLife, 2019, 8: e47839. |
| 81 | MILLS J H, KHARE S D, BOLDUC J M, et al. Computational design of an unnatural amino acid dependent metalloprotein with atomic level accuracy[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(36): 13393-13399. |
| 82 | YANG J, ANISHCHENKO I, PARK H, et al. Improved protein structure prediction using predicted interresidue orientations[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(3): 1496-1503. |
| 83 | 崔颖璐, 吴边. 符合工程化需求的生物元件设计[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2018, 33(11): 1150-1157. |
| CUI Y L, WU B. Biological components design for engineering requirements[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 33(11): 1150-1157. | |
| 84 | 刘海燕. 工业酶研究中的计算化学方法[J]. 生物工程学报, 2019, 35(10): 1819-1828. |
| LIU H Y. Computational chemistry approaches in studies on industrial enzymes[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2019, 35(10): 1819-1828. | |
| 85 | REYNOLDS E W, MCHENRY M W, CANNAC F, et al. An evolved orthogonal enzyme/cofactor pair[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(38): 12451-12458. |
| 86 | HUANG J, LIU Z, BLOOMER B, et al. Artificial biosynthetic pathway for an unnatural terpenoid with an iridium-containing P450[EB/OL].[2020-03-18]. . |
| [1] | WANG Junting, GUO Xiaojia, LI Qing, WAN Li, ZHAO Zongbao. Creation of non-natural cofactor-dependent methanol dehydrogenase [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(4): 651-661. |
| [2] | Xian FU, Tao LIN, Fan ZHANG, Huiming ZHANG, Wenwei ZHANG, Huanming YANG, Shida ZHU, Xun XU, Yue SHEN. Progress in the study of genetic code expansion related methods, principles and applications [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(1): 103-119. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||