Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2020, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (6): 674-684.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-049
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Construction and application of microbial cell factories for production of bulk chemicals
YU Yong, ZHU Xinna, ZHANG Xueli
- Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology,Chinese Academy of Science,Tianjin 300308,China
-
Received:2020-04-16Revised:2020-09-25Online:2021-01-19Published:2020-12-31 -
Contact:ZHANG Xueli
大宗化学品细胞工厂的构建与应用
于勇, 朱欣娜, 张学礼
- 中国科学院天津工业生物技术研究所,天津 300308
-
通讯作者:张学礼 -
作者简介:于勇(1992—),男,博士,博士后。研究方向为代谢工程、合成生物学。E-mail:yu_yong@tib.cas.cn
朱欣娜(1975—),女,博士,副研究员。研究方向为代谢工程、合成生物学。E-mail:zhu_xn@tib.cas.cn
张学礼(1981—),男,博士,研究员。研究方向为代谢工程、合成生物学。E-mail:zhang_xl@tib.cas.cn
第一联系人:共同第一作者 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2019YFA0904900)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YU Yong, ZHU Xinna, ZHANG Xueli. Construction and application of microbial cell factories for production of bulk chemicals[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(6): 674-684.
于勇, 朱欣娜, 张学礼. 大宗化学品细胞工厂的构建与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(6): 674-684.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2020-049
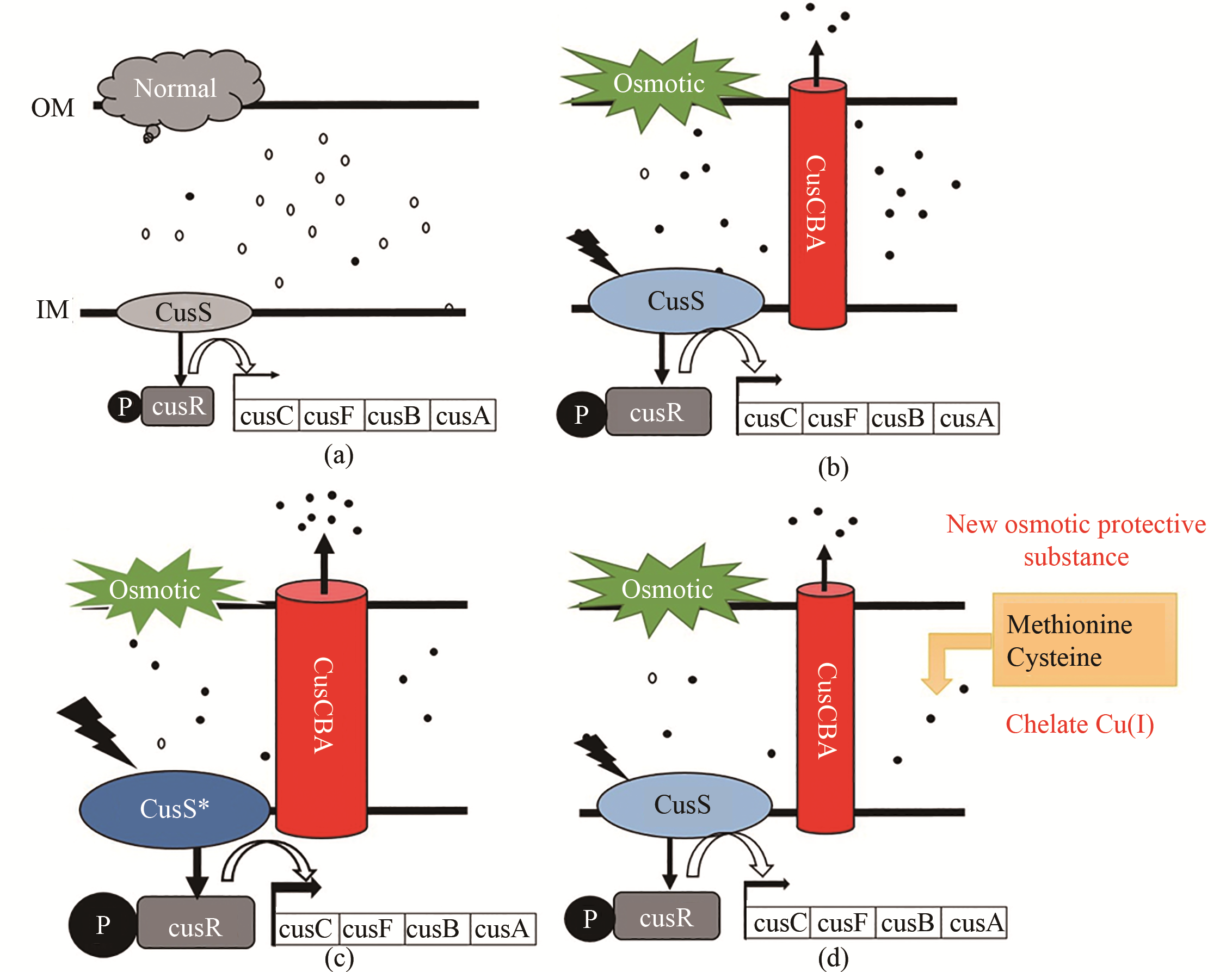
Fig. 5 New osmotolerance mechanism of Escherichia coli(a) Under normal conditions (5% glucose), copper exists mostly in the form of less-toxic Cu(Ⅱ), and the CopA and Cus system was not induced; (b) Under high osmotic pressure (12% glucose), increasing free Cu(Ⅰ) in the periplasmic space activates the expression of copA, cusS, cusR and cusCFAB to expel toxic Cu(Ⅰ); (c) Under high osmotic pressure (12% glucose), expression levels of cusS and cusCFAB are increased to expel more Cu(Ⅰ) from the periplasmic space; (d) Osmotic protective substances such as methionine and cysteine can chelate valence copper ions.
| 1 | 于勇, 朱欣娜, 刘萍萍, 等. 微生物细胞工厂生产大宗化学品及其产业化进展[J]. 生物产业技术, 2019(1): 13-18. |
| YU Y, ZHU X N, LIU P P, et al. Production of bulk chemicals through microbial cell factories and its Industrialization[J]. Biotechnology & Business, 2019(1):13-18. | |
| 2 | MURPHY K C. Use of bacteriophage lambda recombination functions to promote gene replacement in Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1998, 180(8): 2063-2071. |
| 3 | ZHANG Y M, BUCHHOLZ F, MUYRERS J P P, et al. A new logic for DNA engineering using recombination in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature Genetics, 1998, 20(2): 123-128. |
| 4 | URNOV F D, REBAR E J, HOLMES M C, et al. Genome editing with engineered zinc finger nucleases[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2010, 11(9): 636-646. |
| 5 | MILLER J C, TAN S, QIAO G, et al. A TALE nuclease architecture for efficient genome editing[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2011, 29(2): 143-148. |
| 6 | 何庆, 王茜, 朱清华, 等. 基因组工程在微生物细胞工厂构建中的应用进展 [J]. 生物产业技术, 2017(1): 31-36. |
| HE Q, WANG Q, ZHU Q H, et al. Application progress of genome engineering for construction of microbial cell factories[J]. Biotechnology & Business, 2017(1): 31-36. | |
| 7 | SHI S, LIANG Y, ZHANG M M, et al. A highly efficient single-step, markerless strategy for multi-copy chromosomal integration of large biochemical pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2016, 33: 19-27. |
| 8 | HEO M J, JUNG H M, UM J, et al. Controlling citrate synthase expression by CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing for n-butanol production in Escherichia coli [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(2): 182-189. |
| 9 | BASSALO M C, GARST A D, HALWEG-EDWARDS A L, et al. Rapid and efficient one-step metabolic pathway integration in E. coli [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2016, 5(7): 561-568. |
| 10 | WASELS F, JEAN-MARIE J, COLLAS F, et al. A two-plasmid inducible CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing tool for Clostridium acetobutylicum [J]. Journal of Microbiol Methods, 2017, 140: 5-11. |
| 11 | CHO J S, CHOI K R, PRABOWO C P S, et al. CRISPR/Cas9-coupled recombineering for metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 42: 157-167. |
| 12 | ANZALONE A V, RANDOLPH P B, DAVIS J R, et al. Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand breaks or donor DNA[J]. Nature, 2019, 576(7785): 149-157. |
| 13 | WANG H H, ISAACS F J, CARR P A, et al. Programming cells by multiplex genome engineering and accelerated evolution[J]. Nature, 2009, 460(7257): 894-898. |
| 14 | PFLEGER B F, PITERA D J, SMOLKE C D, et al. Combinatorial engineering of intergenic regions in operons tunes expression of multiple genes[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2006, 24(8): 1027-1032. |
| 15 | WARNER J R, REEDER P J, KARIMPOUR-FARD A, et al. Rapid profiling of a microbial genome using mixtures of barcoded oligonucleotides[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2010, 28(8): 856-862. |
| 16 | ISAACS F J, CARR P A, WANG H H, et al. Precise manipulation of chromosomes in vivo enables genome-wide codon replacement[J]. Science, 2011, 333(6040): 348-353. |
| 17 | ZHU X N, ZHAO D D, QIU H N, et al. The CRISPR/Cas9-facilitated multiplex pathway optimization (CFPO) technique and its application to improve the Escherichia coli xylose utilization pathway[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 43: 37-45. |
| 18 | LEE M J, MANTELL J, HODGSON L, et al. Engineered synthetic scaffolds for organizing proteins within the bacterial cytoplasm[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2018, 14(2): 142. |
| 19 | DUEBER J E, WU G C, MALMIRCHEGINI G R, et al. Synthetic protein scaffolds provide modular control over metabolic flux[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2009, 27(8): 753. |
| 20 | KANG W, MA T, LIU M, et al. Modular enzyme assembly for enhanced cascade biocatalysis and metabolic flux[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 4248. |
| 21 | ZHANG F Z, CAROTHERS J M, KEASLING J D. Design of a dynamic sensor-regulator system for production of chemicals and fuels derived from fatty acids[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2012, 30(4): 354. |
| 22 | ZHANG X D. Optimal high-throughput screening: practical experimental design and data analysis for genome-scale RNAi research[M]. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2011. |
| 23 | SALIS H M, MIRSKY E A, VOIGT C A. Automated design of synthetic ribosome binding sites to control protein expression[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2009, 27(10): 946-950. |
| 24 | KAN S B, LEWIS R D, CHEN K, et al. Directed evolution of cytochrome c for carbon-silicon bond formation: bringing silicon to life[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6315): 1048-1051. |
| 25 | SCHMIDL S R, EKNESS F, SOFJAN K, et al. Rewiring bacterial two-component systems by modular DNA-binding domain swapping[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2019, 15(7): 690-698. |
| 26 | SIKORA A E, TEHAN R, MCPHAIL K. Utilization of Vibrio cholerae as a model organism to screen natural product libraries for identification of new antibiotics[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2018, 1839: 135-146. |
| 27 | LU J, TANG J L, LIU Y, et al. Combinatorial modulation of galP and glk gene expression for improved alternative glucose utilization[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2012, 93(6): 2455-2462. |
| 28 | ZHANG X L, JANTAMA K, MOORE J C, et al. Metabolic evolution of energy-conserving pathways for succinate production in Escherichia coli [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(48): 20180-20185. |
| 29 | CHEN J, ZHU X N, TAN Z G, et al. Activating C-4-dicarboxylate transporters DcuB and DcuC for improving succinate production[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2014, 98(5): 2197-2205. |
| 30 | ZHU X N, TAN Z G, XU H T, et al. Metabolic evolution of two reducing equivalent-conserving pathways for high-yield succinate production in Escherichia coli [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2014, 24: 87-96. |
| 31 | TAN Z G, CHEN J, ZHANG X L. Systematic engineering of pentose phosphate pathway improves Escherichia coli succinate production[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2016, 9: 13. |
| 32 | YU Y, ZHU X N, XU H T, et al. Construction of an energy-conserving glycerol utilization pathways for improving anaerobic succinate production in Escherichia coli [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 56: 181-189. |
| 33 | XIAO M Y, ZHU X N, FAN F Y, et al. Osmotolerance in Escherichia coli is improved by activation of copper efflux genes or supplementation with sulfur-containing amino acids[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2017, 83(7): 11. |
| 34 | 张学礼, 张冬竹. 一种高产L-丙氨酸的XZ-A26菌株及构建方法与应用: CN102329765A[P]. 2011-08-17. |
| ZHANG X L, ZHANG D Z. High-yield L-alanine XZ-A26 and construction method and application thereof: CN102329765A[P]. 2011-08-17. | |
| 35 | 马桂燕. 2015年蛋氨酸市场回顾及2016年趋势展望[J]. 中国畜牧业, 2016(10): 50-51. |
| MA G Y. Review of methionine market in 2015 and prospect of trend in 2016[J]. China Animal Industry, 2016(10): 50-51. | |
| 36 | 希杰L-蛋氨酸生物利用率高出 40 %[J]. 中国食品工业, 2015(2): 27. |
| The bioavailability of CJ L-methionine was 40 % higher[J]. China Food, 2015(2): 27. | |
| 37 | HUANG J F, SHEN Z Y, MAO Q L, et al. Systematic analysis of bottlenecks in a multibranched and multilevel regulated pathway: the molecular fundamentals of L-methionine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(11): 2577-2589. |
| 38 | DIETRICH J A, FORTMAN J L, STEEN E J. Recombinant host cells for the production of malonate: US 10472653[P]. 2019-11-12. |
| 39 | KNUF C, NOOKAEW I, REMMERS I, et al. Physiological characterization of the high malic acid-producing Aspergillus oryzae strain 2103a-68[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2014, 98(8): 3517-3527. |
| 40 | LI W N, MA L, SHEN X L, et al. Targeting metabolic driving and intermediate influx in lysine catabolism for high-level glutarate production[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 8. |
| 41 | ZHAO M, HUANG D X, ZHANG X J, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for producing adipic acid through the reverse adipate-degradation pathway[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 47: 254-262. |
| 42 | NAKAMURA C E, WHITED G M. Metabolic engineering for the microbial production of 1,3-propanediol[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2003, 14(5): 454-459. |
| 43 | YIM H, HASELBECK R, NIU W, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for direct production of 1,4-butanediol[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2011, 7(7): 445-452. |
| 44 | DIEN S J VAN, BURGARD A P, HASELBECK R, et al. Microorganisms for the production of 1,4 -butanediol and related methods: US 10273508[P]. 2019-04-30. |
| 45 | ATSUMI S, HANAI T, LIAO J C. Non-fermentative pathways for synthesis of branched-chain higher alcohols as biofuels[J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7174): 86-89. |
| 46 | SHELDON R A, PEREIRA P C. Biocatalysis engineering: the big picture[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(10): 2678-2691. |
| 47 | 曲戈, 朱彤, 蒋迎迎, 等. 蛋白质工程:从定向进化到计算设计[J]. 生物工程学报, 2019, 35(10): 1843-1856. |
| QU G, ZHU T, JIANG Y Y, et al. Protein engineering: from directed evolution to computational design[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2019, 35(10): 1843-1856. | |
| 48 | YU D, WANG J B, REETZ M T. Exploiting designed oxidase-peroxygenase mutual benefit system for asymmetric cascade reactions[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(14): 5655-5658. |
| 49 | The runners-up[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6319): 1518-1523. |
| 50 | LEAVER-FAY A, TYKA M, LEWIS S M, et al. ROSETTA3: an object-oriented software suite for the simulation and design of macromolecules[J]. Methods in Enzymology, 2011, 487: 545-574. |
| 51 | SIEGEL J B, SMITH A L, POUST S, et al. Computational protein design enables a novel one-carbon assimilation pathway[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(12): 3704-3709. |
| 52 | JIANG L, ALTHOFF E A, CLEMENTE F R, et al. De novo computational design of retro-aldol enzymes[J]. Science, 2008, 319(5868): 1387-1391. |
| 53 | SIEGEL J B, ZANGHELLINI A, LOVICK H M, et al. Computational design of an enzyme catalyst for a stereoselective bimolecular Diels-Alder reaction[J]. Science, 2010, 329(5989): 309-313. |
| 54 | LU X Y, LIU Y W, YANG Y Q, et al. Constructing a synthetic pathway for acetylcoenzyme A from one-carbon through enzyme design[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 1-10. |
| 55 | LI R, WIJMA H J, SONG L, et al. Computational redesign of enzymes for regio- and enantioselective hydroamination[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2018, 14(7): 664-670. |
| [1] | GUO Shuyuan, ZHANG Qiannan, Gulikezi· MAIMAITIREXIATI, YANG Yiqun, YU Tao. Advances in microbial production of liquid biofuels [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 18-44. |
| [2] | GAO Ge, BIAN Qi, WANG Baojun. Synthetic genetic circuit engineering: principles, advances and prospects [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [3] | LI Jiyuan, WU Guosheng. Two hypothesises for the origins of organisms from the synthetic biology perspective [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [4] | JIAO Hongtao, QI Meng, SHAO Bin, JIANG Jinsong. Legal issues for the storage of DNA data [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [5] | TANG Xinghua, LU Qianneng, HU Yilin. Philosophical reflections on synthetic biology in the Anthropocene [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [6] | XU Huaisheng, SHI Xiaolong, LIU Xiaoguang, XU Miaomiao. Key technologies for DNA storage: encoding, error correction, random access, and security [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [7] | SHI Ting, SONG Zhan, SONG Shiyi, ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job. In vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): a new frontier of industrial biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [8] | CHAI Meng, WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi. Synthesis of organic acids from lignocellulose by biotransformation [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [9] | SHAO Mingwei, SUN Simian, YANG Shimao, CHEN Guoqiang. Bioproduction based on extremophiles [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [10] | ZHAO Liang, LI Zhenshuai, FU Liping, LYU Ming, WANG Shi’an, ZHANG Quan, LIU Licheng, LI Fuli, LIU Ziyong. Progress in biomanufacturing of lipids and single cell protein from one-carbon compounds [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1300-1318. |
| [11] | ZHU Fanghuan, CEN Xuecong, CHEN Zhen. Research progress of diols production by microbes [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1367-1385. |
| [12] | CHEN Yu, ZHANG Kang, QIU Yijing, CHENG Caiyun, YIN Jingjing, SONG Tianshun, XIE Jingjing. Progress of microbial electrosynthesis for conversion of CO2 [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [13] | ZHENG Haotian, LI Chaofeng, LIU Liangxu, WANG Jiawei, LI Hengrun, NI Jun. Design, optimization and application of synthetic carbon-negative phototrophic community [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [14] | YU Wei, GAO Jiaoqi, ZHOU Yongjin. Bioconversion of one carbon feedstocks for producing organic acids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1169-1188. |
| [15] | CHEN Ziling, XIANG Yangfei. Integrated development of organoid technology and synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||