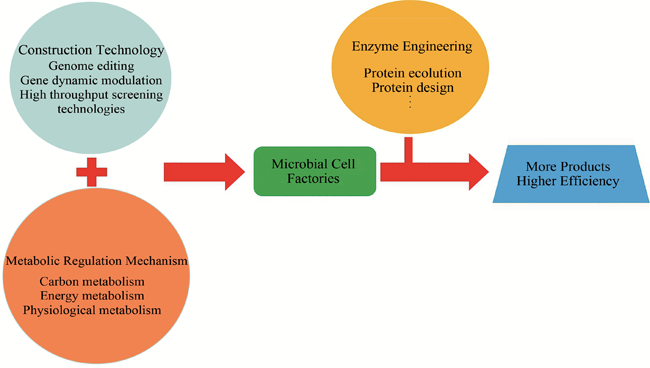
With the development of synthetic biology, more and more bulk chemicals can be produced through microbial cell factories, which can avoid the dependence on petroleum resources and decrease energy cost and pollution. In this review, the key technologies for construction of microbial cell factories were firstly introduced, including genome editing, simultaneous modulation of multiple genes, protein scaffold, gene dynamic modulation and high throughput screening technologies. How to characterize the metabolic regulation mechanisms for efficient production of chemicals was then introduced in three aspects: carbon metabolism, energy metabolism and physiological metabolism, and succinate cell factory was used as an example. Successful bulk chemical cell factories in recent years were then summarized, including L-alanine, L-methionine, succinate, D-lactate, malonate, L-malate, glutarate, adipate, 1,3-propanediol, 1,4-butanediol, isobutanol, etc. In the future, further increasing the efficiency of substrates utilization and broadening the range of products will be the directions of development of microbial cell factories, but the design and engineering of new enzymes are the key bottleneck limiting the design of metabolic pathways. It is believed that with the deepening of research, microbial cell factories will be more widely used in the production of bulk chemicals besides chemical methods.