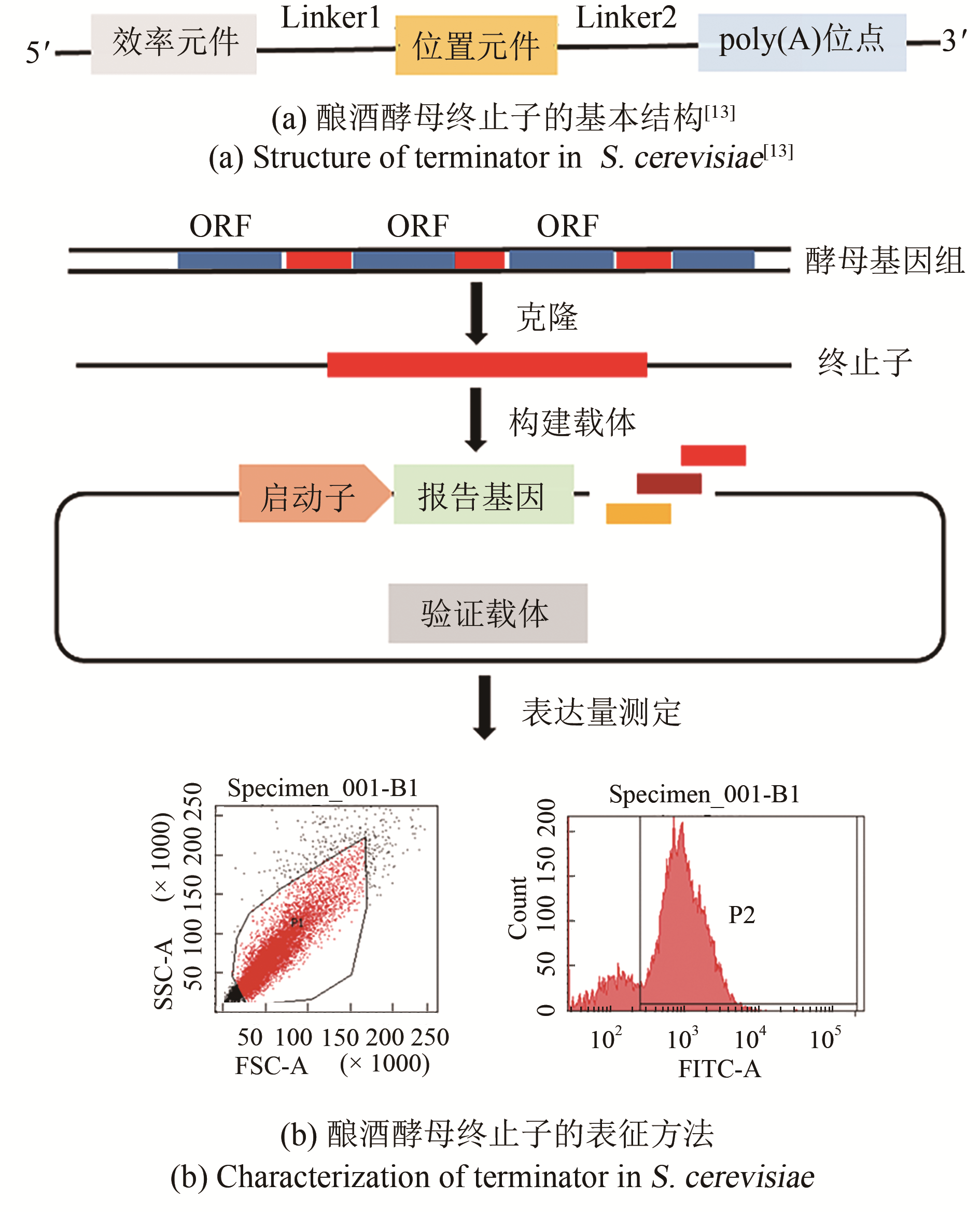
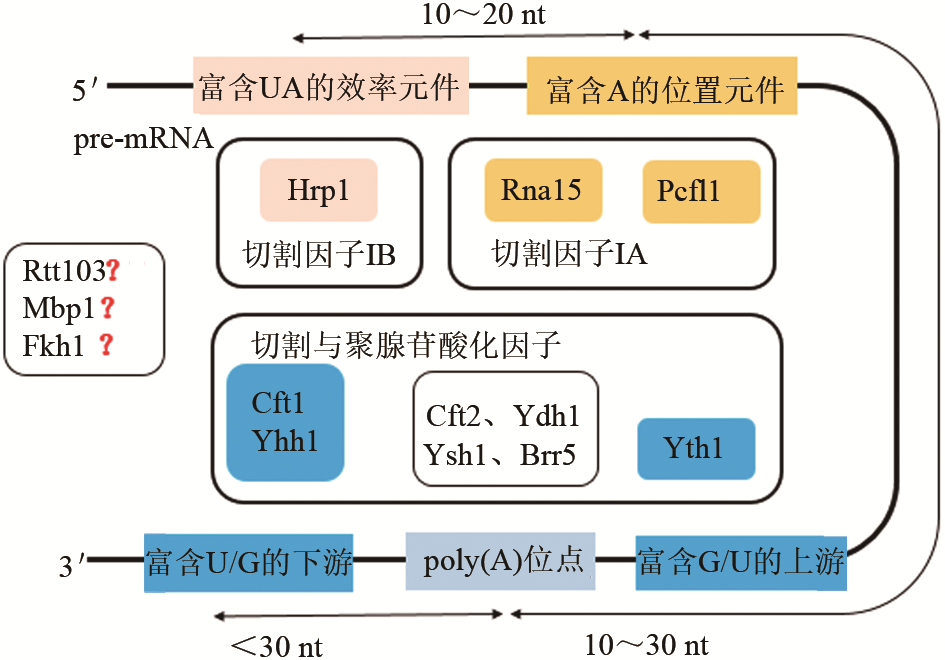
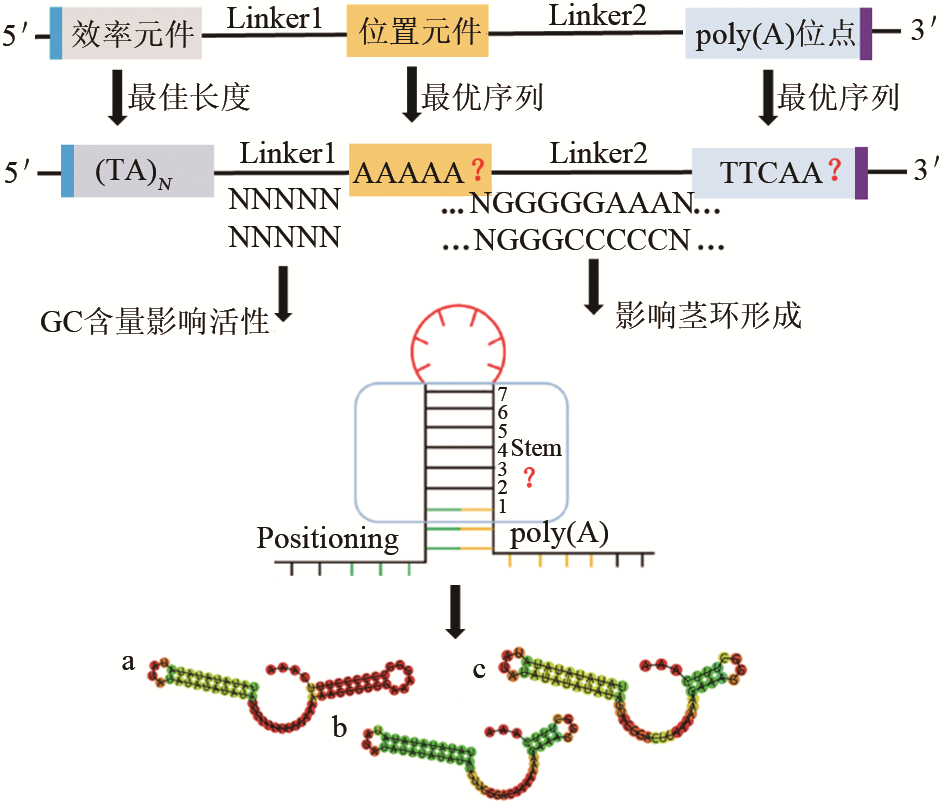
Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2020, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (6): 709-721.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-009
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yeast terminator engineering: from mechanism exploration to artificial design
SHENG Yue, ZHANG Genlin
- School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Key Laboratory for Green Processing of Chemical Engineering of Xinjiang Bingtuan,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832003,Xinjiang,China
-
Received:2020-02-29Revised:2020-04-15Online:2021-01-15Published:2020-12-31 -
Contact:ZHANG Genlin
酵母终止子工程:从机理探索到人工设计
盛月, 张根林
- 石河子大学化学化工学院,新疆兵团化工绿色过程重点实验室,新疆 石河子 832003
-
通讯作者:张根林 -
作者简介:盛月(1994— ),女,博士研究生,研究方向为酵母代谢工程。E-mail:syue_biol@163.com
张根林(1981— ),男,博士,教授,研究方向为酵母代谢工程。E-mail:zhgl_food@sina.com -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(21676167);兵团中青年科技创新领军人才计划(2017CB007)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
SHENG Yue, ZHANG Genlin. Yeast terminator engineering: from mechanism exploration to artificial design[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(6): 709-721.
盛月, 张根林. 酵母终止子工程:从机理探索到人工设计[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(6): 709-721.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2020-009
| 终止子类型 | 名称 | FI值 | 活性 | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 天然 | IRS4t | 1.3501 | 弱 | [ |
| DNM1t | 0.6579 | 弱 | [ | |
| NFT1t | 0.1944 | 弱 | [ | |
| HOG1t | 3.3178 | 强 | [ | |
| SSD1t | 3.2127 | 强 | [ | |
| TPS1t | 3.0941 | 强 | [ | |
| ATP5t | 1.9912 | 中 | [ | |
| CYC1t | 1.7559 | 中 | [ | |
| SIR2t | 1.6812 | 中 | [ | |
| PGK1t | 1.5185 | 弱 | [ | |
| TDH3t | 1.4914 | 弱 | [ | |
| SLX5t | 1.3802 | 弱 | [ | |
| 人工 | T-Guo1 | 2.2000 | [ | |
| T0-T10 | 0.2~2.4400 | [ | ||
| Tsynth1-30 | 0.03~3.7000 | [ | ||
| T-1316 | 3.5270 | 强 | [ | |
| T-1299 | 3.5124 | 强 | [ | |
| T-1281 | 3.4866 | 强 | [ | |
| T-195 | 2.9325 | 中 | [ | |
| T-154 | 2.9370 | 中 | [ | |
| T-a9 | 2.9405 | 中 | [ | |
| T-509 | 2.6149 | 弱 | [ | |
| T-414 | 2.4048 | 弱 | [ | |
| T-d11 | 2.3648 | 弱 | [ |
Tab. 1 properties of commonly used yeast terminators
| 终止子类型 | 名称 | FI值 | 活性 | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 天然 | IRS4t | 1.3501 | 弱 | [ |
| DNM1t | 0.6579 | 弱 | [ | |
| NFT1t | 0.1944 | 弱 | [ | |
| HOG1t | 3.3178 | 强 | [ | |
| SSD1t | 3.2127 | 强 | [ | |
| TPS1t | 3.0941 | 强 | [ | |
| ATP5t | 1.9912 | 中 | [ | |
| CYC1t | 1.7559 | 中 | [ | |
| SIR2t | 1.6812 | 中 | [ | |
| PGK1t | 1.5185 | 弱 | [ | |
| TDH3t | 1.4914 | 弱 | [ | |
| SLX5t | 1.3802 | 弱 | [ | |
| 人工 | T-Guo1 | 2.2000 | [ | |
| T0-T10 | 0.2~2.4400 | [ | ||
| Tsynth1-30 | 0.03~3.7000 | [ | ||
| T-1316 | 3.5270 | 强 | [ | |
| T-1299 | 3.5124 | 强 | [ | |
| T-1281 | 3.4866 | 强 | [ | |
| T-195 | 2.9325 | 中 | [ | |
| T-154 | 2.9370 | 中 | [ | |
| T-a9 | 2.9405 | 中 | [ | |
| T-509 | 2.6149 | 弱 | [ | |
| T-414 | 2.4048 | 弱 | [ | |
| T-d11 | 2.3648 | 弱 | [ |
| 1 | 温栾, 卢俊南, 钟伟, 等. 合成生物学设计技术[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报, 2019,41(11): 2060-2071. |
| WEN L, LU J N, ZHONG W, et al. Design technology in synthetic biology[J]. Chinese Journal of Cell Biology, 2019, 41(11): 2060-2071. | |
| 2 | 赵禹, 赵雅坤, 刘士琦, 等. 非常规酵母的分子遗传学及合成生物学研究进展[J].微生物学报,2020,60(8): 1574-1591. |
| ZHAO Y, ZHAO Y K, LIU S Q, et al. Progress in molecular genetics and synthetic biology of unconventional yeast[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2020,60(8):1574-1591. | |
| 3 | 邢玉华, 谭俊杰, 李玉霞, 等. 合成生物学的关键技术及应用进展[J]. 中国医药生物技术, 2012, 7(5): 357-363. |
| XIN Y H, TAN J J, LI Y X, et al. Key technology and application progress of synthetic biology[J]. Chinese Medical Biotechnology, 2012, 7(5): 357-363. | |
| 4 | 赵国屏. 合成生物学:开启生命科学"会聚"研究新时代[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2018, 33(11): 1135-1149. |
| ZHAO G P. Synthetic biology:unsealing the convergence era of life science research[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018,33(11): 1135-1149. | |
| 5 | HEIDI R, NICHOLAS M, ALPER H S. The synthetic biology toolbox for tuning gene expression in yeast[J]. FEMS Yeast Research, 2014, 15(1): 1-12. |
| 6 | FISCHER V, SCHUMACHER K, TORA L, et al. Global role for coactivator complexes in RNA polymerase II transcription[J]. Transcription, 2019, 10(1): 29-36. |
| 7 | LAWSON M R, BERGER J M. Tuning the sequence specificity of a transcription terminator[J]. Current Genetics, 2019, 65(3): 729-733. |
| 8 | JEONG S W, LANG W H, REEDER R H. The release element of the yeast polymerase I transcription terminator can function independently of Reb1p.[J]. Molecular & Cellular Biology, 1995, 15(11): 5929-5936. |
| 9 | JEONG S W, LANG W H, REEDER R H. The yeast transcription terminator for RNA polymerase I is designed to prevent polymerase slippage.[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1996, 271(27): 16104-16110 |
| 10 | CHOO K B, WU S M, HUNG L, et al. Effect of vector type, host strains and transcription terminator on heterologous gene expression in yeast[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 1986, 140(2): 602-608. |
| 11 | WITTMANN A, SUESS B. Engineered riboswitches: expanding researchers′ toolbox with synthetic RNA regulator[J]. FEBS Letters, 2012, 586(15): 2076-2083. |
| 12 | BRENT R, PTASHNE M. A bacterial repressor protein or a yeast transcriptional terminator can block upstream activation of a yeast gene[J]. Nature, 1985, 314(5995): 198. |
| 13 | GUO Z, SHERMAN F. Signals sufficient for 3′-end formation of yeast mRNA[J]. Molecular & Cellular Biology, 1996, 16(6): 2772-2776. |
| 14 | THOMPSON C M, KOLESKE A J, CHAO D M, et al. A multisubunit complex associated with the RNA polymerase Ⅱ CTD and TATA-binding protein in yeast[J]. Cell, 1993, 73(7): 1361-1375. |
| 15 | GUO Z, SHERMAN F. 3′-end-forming signals of yeast mRNA[J]. Molecular & Cellular Biology, 1995, 15(11): 5983-5990. |
| 16 | RYAN K, CALVO O, MANLEY J L. Evidence that polyadenylation factor CPSF-73 is the mRNA 3′ processing endonuclease[J]. RNA, 2004, 10(4): 565-573. |
| 17 | SHI Y S, MANLEY J L. The end of the message: multiple protein-RNA interactions define the mRNA polyadenylation site[J]. Genes & Development, 2015, 29(9): 889-897. |
| 18 | CHAN S L, HUPPERTZ I, YAO C G, et al. CPSF30 and Wdr33 directly bind to AAUAA in mammalian mRNA 3′ processing[J]. Genes & Development, 2014, 28(21): 2370-2380. |
| 19 | WHITELAW E, PROUDFOOT N. Alpha-thalassaemia caused by a poly(A) site mutation reveals that transcriptional termination is linked to 3′ end processing in the human alpha 2 globin gene[J]. The EMBO Journal, 1986, 5(11): 2915-2922. |
| 20 | GIBBS M D, REEVES R A, ANWAR S, et al. A yeast intron as a translational terminator in a plasmid shuttle vector[J]. FEMS Yeast Research, 2004, 4(6): 573-577. |
| 21 | DICHTL B. Recognition of polyadenylation sites in yeast pre-mRNAs by cleavage andpolyadenylation factor[J]. European Molecular Biology Organization Journal, 2001, 20(12): 3197-3209. |
| 22 | CHEN S, HYMAN L E. A specific RNA-protein interaction at yeast polyadenylation efficiency elements[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1998, 26(21): 4965-4974. |
| 23 | BROCKMAN J, SINGH P, LIU D, et al. PACdb: PolyA cleavage site and 3′-UTR database[J]. Bioinformatics, 2005, 21(18): 3691-3693. |
| 24 | KELLER W, MINVIELLE-SEBASTIA L. A comparison of mammalian and yeast pre-mRNA 3′-end processing[J]. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 1997, 9(3): 329-336. |
| 25 | MACDONALD C C, JOSÉ-LUIS R. Reexamining the polyadenylation signal: were we wrong about AAUAAA? [J]. Molecular & Cellular Endocrinology, 2002, 190(1): 1-8. |
| 26 | TULLER T, RUPPIN E, KUPIEC M. Properties of untranslated regions of the S. cerevisiae genome[J]. BMC Genomics, 2009, 10(1): 391. |
| 27 | CURRAN K A, MORSE N J, MARKHAM K A, et al. Short synthetic terminators for improved heterologous gene expression in yeast[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2015, 4(7): 824-832. |
| 28 | MACPHERSON M, SAKA Y. Short synthetic terminators for assembly of transcription units in vitro and stable chromosomal integration in yeast S. cerevisiae [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(1): 130-138. |
| 29 | SEOANE S, GUIARD B, RODRÍGUEZ-TORRES A M, et al. Effects of splitting alter native KlCYC1 3′-UTR regions on processing: metabolic consequences and biotech nological applications[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2005, 118(2): 149-156. |
| 30 | YAMANISHI M, ITO Y, KINTAKA R, et al. A genome-wide activity assessment of terminator regions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae provides a ‘Terminatome' toolbox[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2013, 2(6): 337-347. |
| 31 | YAMANISHI M, KATAHIRA S, MATSUYAMA T. TPS1 Terminator increases mRNA and protein yield in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae expression system[J]. Bioscience Biotechnology and Biochemistry,2011, 75(11): 2234-2236. |
| 32 | ITO Y, KITAGAWA T, YAMANISHI M, et al. Enhancement of protein production via the strong DIT1 terminator and two RNA-binding proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 197-214. |
| 33 | WEI L N, WANG Z X, ZHANG G L, et al. Characterization of terminators in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and exploration factors affecting their strength[J]. ChemBioChem, 2017, 18: 2422-2427. |
| 34 | KECMAN T, KUŚ K, HEO D H, et al. Elongation/termination factor exchange mediated by PP1 phosphatase orchestrates transcription termination[J]. Cell Reports, 2018, 25(1): 259-269. |
| 35 | CAMBRAY C, GUIMARAES J C, MUTALIK V K, et al. Measurement and modeling of intrinsic transcription terminators[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2013,41(9): 5139-5148. |
| 36 | LEAVITT J M, ALPER H S. Advances and current limitations in transcript-level control of gene expression[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2015, 34(3): 98-104. |
| 37 | SOUTOURINA J. Transcription regulation by the Mediator complex[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2017, 19(4): 262-274. |
| 38 | PORRUA O, LIBRI D. Transcription termination and the control of the transcriptome: why, where and how to stop[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2015, 16(3): 190-202. |
| 39 | PROUDFOOT N. New perspectives on connecting messenger RNA 3′ end formation to transcription[J]. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 2004, 16(3): 272-278. |
| 40 | HARLEN K M, CHURCHMAN L S. The code and beyond: transcription regulation by the RNA polymerase Ⅱ carboxy-terminal domain[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2017, 18(4): 263-273. |
| 41 | STEURER B, JANSSENS R C, GEVERTS B, et al. Live-cell analysis of endogenous GFP-RPB1 uncovers rapid turnover of initiating and promoter-paused RNA polymerase Ⅱ[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Ences, 2018, 115(19): E4368-E4376. |
| 42 | EATON J D, DAVIDSON L, BAUER D L V, et al. Xrn2 accelerates termination by RNA polymerase Ⅱ, which is underpinned by CPSF73 activity[J]. Genes & Development, 2018, 32(2): 127. |
| 43 | PUIG S, PÉREZ-ORTÍN J, MATALLANA E. Transcriptional and structural study of a region of two convergent overlapping yeast genes[J]. Current Microbiology, 1999, 39(6): 369-373. |
| 44 | GRZYBOWSKA E A, WILCZYNSKA A, SIEDLECKI J A. Regulatory functions of 3′UTRs.[J]. Biochemical & Biophysical Research Communications, 2001, 288(2): 291-295. |
| 45 | DICHTL B. Yhh1p/Cft1p directly links poly(A) site recognition and RNA polymerase II transcription termination[J]. The EMBO Journal, 2014, 21(15): 4125-4135. |
| 46 | ITO Y, YAMANISHI M, IKEUCHI A, et al. Characterization of five terminator regions that increase the protein yield of a transgene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2013, 168(4): 486-492. |
| 47 | CURRAN K A, KARIM A S, GUPTA A, et al. Use of expression-enhancing terminators in Saccharomyces cerevisiae to increase mRNA half-life and improve gene expression control for metabolic engineering applications[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2013, 19(Complete): 88-97. |
| 48 | KELLER W, BIENROTH S, LANG K M, et al. Cleavage and polyadenylation factor CPF specifically interacts with the pre-mRNA 3′ processing signal AAUAAA[J]. The EMBO Journal,1991, 10(13):4241-4249. |
| 49 | TATOMER D C, ELROD N D, LIANG D, et al. The Integrator complex cleaves nascent mRNAs to attenuate transcription[J]. Genes & Development, 2019, 33(21/22): 1525-1538. |
| 50 | CHIU A C, SUZUKI H I, WU X B, et al. Transcriptional pause sites delineate stable nucleosome-associated premature polyadenylation suppressed by U1 snRNP[J]. Molecular Cell,2018, 69(4): 648-663, e7. |
| 51 | DEZAZZO J D, IMPERIALE M J. Sequences upstream of AAUAAA influence poly(A) site selection in a complex transcription unit[J]. Molecular & Cellular Biology, 1989, 9(11): 4951-4961. |
| 52 | SHAW G, KAMEN R. A conserved adenine uridine sequence from the 3′untranslated region of granulocyte-monocyte colony stimulating factor messenger RNA mediates selective messenger RNA degradation[J]. Cell, 1986, 46: 659-668. |
| 53 | WENG L, LI Y, XIE X, et al. Poly(A) code analyses reveal key determinants for tissue-specific mRNA alternative polyadenylation[J]. RNA, 2016, 22(6): 813-821 |
| 54 | MANDEL D R, TONG L, BAI Y. Protein factors in pre-mRNA 3′-end processing[J]. Cellular & Molecular Life Sciences, 2007, 65(7/8): 1099-1122. |
| 55 | CHAN S, CHOI E A, SHI Y. Pre-mRNA 3′-end processing complex assembly and function[J]. RNA, 2011,2(3): 321-335. |
| 56 | ERIKA L P, JOEL H G, SUSAN D, et al. Ipa1 Is an RNA polymerase II elongation factor that facilitates termination by maintaining levels of the poly(A) site endonuclease Ysh1[J]. Cell Reports, 2019, 26(7): 1919-1933. |
| 57 | TIAN B, MANLEY J L. Alternative cleavage and polyadenylation: the long and short of it[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 2013, 38(6): 312-320. |
| 58 | DAFNE C D G, KENSEI N, MANLEY J L, et al. Mechanisms and consequences of alternative polyadenylation[J]. Molecular Cell, 2011, 43(6): 853-866. |
| 59 | VIPHAKONE N, VOISINET-HAKIL F, MINVIELLE S L. Molecular dissection of mRNA poly(A) tail length control in yeast[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2008, 36(7): 2418-2433. |
| 60 | PORRUA O, HOBOR F, BOULAY J, et al. In vivo SELEX reveals novel sequence and structural determinants of Nrd1-Nab3-Sen1-dependent transcription termination.[J].The EMBO Journal, 2014, 31(19): 3935-3948. |
| 61 | SIERECKI E. The Mediator complex and the role of Protein-Protein interactions in the gene regulation machinery[J]. Seminars in Cell and Developmental Biology, 2020, 99: 20-30. |
| 62 | LEMAY J F, MARGUERAT S, LAROCHELLE M, et al. The Nrd1-like protein Seb1 coordinates cotranscriptional 3′ end processing and polyadenylation site selection[J]. Genes & Development, 2016, 30(13): 1558-1572. |
| 63 | GRZECHNIK P, GDULA M R, PROUDFOOT N J. Pcf11 orchestrates transcription termination pathways in yeast[J]. Genes & Development, 2015, 29(8): 849-861. |
| 64 | NEMEC C M, YANG F, GILMORE J M, et al. Different phosphoisoforms of RNA polymerase II engage the Rtt103 termination factor in a structurally analogous manner[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(20): E3944-E3953. |
| 65 | LUNDE B M, REICHOW S, KIM M, et al. Cooperative interaction of transcription termination factors with the RNA polymerase Ⅱ C-terminal domain[J]. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 2010,17(10): 1195-1201. |
| 66 | KUMAR R, REYNOLDS D M, SHEVCHENKO A, et al. Forkhead transcription factors, Fkh1p and Fkh2p, collaborate with Mcm1p to control transcription required for M-phase[J]. Current Biology, 2000, 10(15): 896-906. |
| 67 | ZHANG Z, KLATT A, HENDERSON A J, et al. Transcription termination factor Pcf11 limits the processivity of Pol II on an HIV provirus to repress gene expression[J]. Genes & Development, 2007, 21(13): 1609-1614. |
| 68 | ZHANG Z, GILMOUR D S. Pcf11 is a termination factor in Drosophila that dismantles the elongation complex by bridging the CTD of RNA polymerase II to the nascent transcript[J]. Molecular Cell, 2006, 21(1): 65-74. |
| 69 | NOBLE C G, HOLLINGWORTH D, MARTIN S R, et al.Key features of the interaction between Pcf11 CID and RNA polymerase II CTD[J]. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 2005, 12(2): 144-151 |
| 70 | ZHANG Z. CTD-dependent dismantling of the RNA polymerase II elongation complex by the pre-mRNA 3′-end processing factor, Pcf11[J]. Genes & Development, 2005, 19(13): 1572-1580. |
| 71 | KAMIENIARZ-GDULA K, GDULA M R, PANSER K, et al. Selective roles of vertebrate PCF11 in premature and full-length transcript termination[J]. Molecular Cell, 2019,74(1): 158-172.e9. |
| 72 | RAPHAËL H, FRÉDÉRIQUE M, NICOLAS V, et al. An essential role for Clp1 in assembly of polyadenylation complex CF IA and Pol II transcription termination[J].Nucleic Acids Research. 2012, 40(3): 1226-1239. |
| 73 | LUNDE B M, REICHOW S L, KIM M,et al. Cooperative interaction of transcription termination factors with the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain[J]. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 2010, 17(10): 1195-1201. |
| 74 | NOBLE C G, BARBARA B, TAYLOR I A.Structure of a nucleotide-bound Clp1-Pcf11 polyadenylation factor[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2007, 35(1): 87-99. |
| 75 | SINGH N, MA Z, GEMMILL T, et al. The Ess1 prolyl isomerase is required for transcription termination of small noncoding RNAs via the Nrd1 pathway[J].Molecular Cell, 2009, 36(2): 255-266. |
| 76 | E- J CHO, KOBOR M S, KIM M, et al. Opposing effects of Ctk1 kinase and Fcp1 phosphatase at Ser 2 of the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain[J]. Genes & Development, 2002, 15(24): 3319-3329. |
| 77 | JONES J C, PHATNANI H P, HAYSTEAD T A,et al. C-terminal repeat domain kinase I phosphorylates Ser2 and Ser5 of RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain repeats[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2004, 279(24): 24957-24964. |
| 78 | OSTAPENKO D, SOLOMON M J. Phosphorylation by cak1 regulates the C-terminal domain kinase Ctk1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 2005, 25(10): 3906-3913. |
| 79 | XIAO T J, HALL H, KIZER K O, et al. Phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II CTD regulates H3 methylation in yeast[J]. Genes & Development, 2003, 17(5): 654-663. |
| 80 | EATON J D, DAVIDSON L, BAUER D L V, et al. Xrn2 accelerates termination by RNA polymerase II, which is underpinned by CPSF73 activity[J]. Genes & Development, 2018, 32(2): 127-139. |
| 81 | FONG N, BRANNAN K, ERICKSON B, et al. Effects of transcription elongation rate and Xrn2 exonuclease activity on RNA polymerase Ⅱ termination suggest widespread kinetic competition[J]. Molecular Cell, 2015, 60(2): 256-267. |
| 82 | NICOLAS V, FLORENCE V H, LIONEL M S. Molecular dissection of mRNA poly(A) tail length control in yeast[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2008, 36(7): 2418-33. |
| 83 | WEISS E A, GILMARTIN G M, NEVINS J R. Poly(A) site efficiency reflects the stability of complex formation involving the downstream element.[J]. The EMBO Journal, 1991, 10(1): 215-219. |
| 84 | FATICA A, MORLANDO M, BOZZONI I. Yeast snoRNA accumulation relies on a cleavage‐dependent/polyadenylation‐independent 3′‐processing apparatus[J]. The EMBO Journal, 2014, 19(22): 6218-6229. |
| 85 | EGECIOGLU D E, HENRAS A K, CHANFREAU G F. Contributions of Trf4p- and Trf5p-dependent polyadenylation to the processing and degradative functions of the yeast nuclear exosome[J]. RNA, 2006, 12(1): 26-32. |
| 86 | GHAZAL G, GAGNON J, JACQUES P E, et al. Yeast rNase Ⅲ triggers polyadenylation-independent transcription termination[J]. Molecular Cell, 2009, 36(1): 99-109. |
| 87 | MATA J. Genome-wide mapping of polyadenylation sites in fission yeast reveals widespread alternative polyadenylation[J]. RNA Biology, 2013, 10(8): 1407-1414. |
| 88 | YAMANAKA S, YAMASHITA A, HARIGAYA Y, et al. Importance of polyadenylation in the selective elimination of meiotic mRNAs in growing S. pombe cells.[J]. The EMBO Journal, 2010, 29(13): 2173-2181. |
| 89 | MORALES J C, RICHARD P, ROMMEL A, et al. Kub5-Hera, the human Rtt103 homolog, plays dual functional roles in transcription termination and DNA repair[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2014, 42(8): 4996-5006. |
| 90 | QIU H, HU C, HINNEBUSCH A G. Phosphorylation of the Pol II CTD by KIN28 enhances BUR1/BUR2 recruitment and Ser2 CTD phosphorylation near promoters[J]. Molecular Cell, 2009, 33(6): 752-762. |
| 91 | MIRNA J, HINZE H, HOLZER H. Inactivation of Yeast Enzymes by proteinase A and B and carboxypeptidase Y from yeast[J]. Hoppe-Seyler´s Zeitschrift für Physiologische Chemie, 1976, 357(1): 735-740. |
| 92 | HOUSELEY J, RUBBI L, GRUNSTEIN M, et al. A ncRNA modulates histone modification and mRNA induction in the yeast GAL gene cluster[J]. Molecular Cell, 2008, 32(5): 685-695. |
| 93 | STEVEN P, MARCIN G. FRACZEK, JIAN WU, et al . A resource for functional profiling of noncoding RNA in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae[J]. RNA, 2017, 23(8): 1166-1171. |
| 94 | RUSSO P, SHERMAN F. Transcription terminates near the poly(A) site in the CYC1 gene of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1989, 86(21): 8348-8352. |
| 95 | EMBO R. Yeast Trf5p is a nuclear poly(A) polymerase[J]. The EMBO Reports, 2006, 7(2): 205-211. |
| 96 | CARROLL K L, PRADHAN D A, GRANEK J A, et al. Identification of cis elements directing termination of yeast nonpolyadenylated snoRNA transcripts[J]. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 2004, 24(14): 6241-6252. |
| 97 | WILSON S M. Characterization of nuclear polyadenylated RNA-binding proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. The Journal of Cell Biology, 1994, 127(5): 1173-1184. |
| 98 | STEINMETZ E J, CONRAD N K, BROW D A, et al. RNA-binding protein Nrd1 directs poly(A)-independent 3′-end formation of RNA polymerase II transcripts[J]. Nature, 2001, 413(6853): 327-331. |
| 99 | ZHANG W, LIU H, LI X, et al. Production of naringenin from D-xylose with co-culture of E. coli and S. cerevisiae [J]. Engineering in Life Sciences, 2017, 17: 1021-1029. |
| 100 | LIAN J, SI T, NAIR N U, ZHAO H. Design and construction of acetyl-CoA overproducing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2014, 24: 139-149. |
| 101 | RENDA B A, HAMMERLING M J, BARRICK J E. Engineering reduced evolutionary potential for synthetic biology[J]. Molecular Biosystems, 2014, 10(7): 1668-1678. |
| 102 | CURRAN K A, KARIM A S, GUPTA A, et al. Use of expression-enhancing terminators in Saccharomyces cerevisiae to increase mRNA half-life and improve gene expression control for metabolic engineering applications[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2013, 19: 88-97. |
| 103 | LEBER C, SILVA N A D. Engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the synthesis of short chain fatty acids[J]. Biotechnology & Bioengineering, 2014, 111(2). |
| 104 | ITO Y, YAMANISHI M, IKEUCHI A, et al. Combinatorial screening for transgenic yeasts with high cellulase activities in combination with a tunable expression system[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(12): e0144870. |
| 105 | CHEN Y J, LIU P, NIELSEN A A K, et al. Characterization of 582 natural and synthetic terminators and quantification of their design constraints[J]. Nature Methods, 2013, 10(7): 659-664. |
| 106 | WANG Z X, WEI L N, SHENG Y, et al. Yeast synthetic terminators: fine regulation of strength through linker sequences[J]. ChemBioChem, 2019, 20(18): 2383-2389. |
| 107 | CHEN Y, XIAO W H, WANG Y, et al. Lycopene overproduction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae through combining pathway engineering with host engineering[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2016, 15(1): 113. |
| 108 | JOSEPH V G, ZARMIK M, XIAO C F, et al. Global analysis of mRNA isoform half-lives reveals stabilizing and destabilizing elements in yeast[J]. Cell, 2014, 156(4): 812-824. |
| 109 | MISCHO H E, PROUDFOOT N J. Disengaging polymerase: terminating RNA polymerase II transcription in budding yeast [J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Gene Regulatory Mechanisms, 2013,1829(1): 174-185. |
| 110 | LIAN J Z, SI T, NAIR N U, et al. Design and construction of acetyl-CoA overproducing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains.[J]. Metabolic Engineering,2014, 24: 139-149. |
| 111 | SILVA N A DA, SRIKRISHNAN S. Introduction and expression of genes for metabolic engineering applications in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. FEMS Yeast Research, 2012,12(2): 197-214. |
| 112 | HONG S P, SEIP J, WALTERS P D, et al. Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica to express secretory invertase with strong FBA1IN promoter[J]. Yeast, 2012, 29(2): 59-72. |
| 113 | LI X, WANG Z X, ZHANG G l, et al. Improving lycopene production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae through optimizing pathway and chassis metabolism[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 193: 364-369. |
| 114 | AHMED M S, IKRAM S, RASOOL A, et al. Design and construction of short synthetic terminators for β-amyrin production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 146: 105-116. |
| 115 | XIE Z X, LIU D, LI B Z, et al. Design and chemical synthesis of eukaryotic chromosomes[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(23): 7191-7207. |
| 116 | SONG H, DING M Z, JIA X Q, et al. Synthetic microbial consortia: from systematic analysis to construction and applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2014, 43(20): 6954-6981. |
| 117 | ZHANG Y, GU L F, HOU Y F, et al. Integrative genome-wide analysis reveals HLP1, a novel RNA-binding protein, regulates plant flowering by targeting alternative polyadenylation[J]. Cell Research, 2015, 25(7): 864-876. |
| 118 | ZHANG X, ZUO X, YANG B, et al. MicroRNA directly enhances mitochondrial translation during muscle differentiation[J]. Cell, 2014, 158(3): 607-619. |
| 119 | XUE Y C, ZHOU Y, WU T B, et al. Genome-wide analysis of PTB-RNA interactions reveals a strategy used by the general splicing repressor to modulate exon inclusion or skipping[J]. Molecular Cell,2009, 36(6): 996-1006. |
| 120 | XIAO R, TANG P, YANG B, et al. Nuclear matrix factor hnRNP U/SAF-A exerts a global control of alternative splicing by regulating U2 snRNP maturation[J]. Molecular Cell. 2012, 45(5): 656-668. |
| 121 | FENG S, XU M, LIU F, et al. Reconstruction of the full-length transcriptome atlas using PacBio Iso-Seq provides insight into the alternative splicing in Gossypium australe [J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 365. |
| 122 | PICELLI S, FARIDANI O R, BJÖRKLUND A K, et al. Full-length RNA-seq from single cells using Smart-seq2[J]. Nature Protocols, 2014, 9(1): 171-181. |
| 123 | PRIELHOFER R, BARRERO J J, STEUER S, et al. GoldenPiCS: a Golden Gate-derived modular cloning system for applied synthetic biology in the yeast Pichia pastoris [J]. BMC Systems Biology, 2017, 11(1): 123. |
| 124 | SARAYA R, KRIKKEN A M, VEENHUIS M, et al. Novel genetic tools for Hansenula polymorpha [J]. FEMS Yeast Research,2012,12(3): 271-278. |
| 125 | LARROUDE M, ROSSIGNOL T, NICAUD J M, et al. Synthetic biology tools for engineering Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2018, 36(8): 2150-2164. |
| [1] | REN Jiawei, ZHANG Jinpeng, XU Guoqiang, ZHANG Xiaomei, XU Zhenghong, ZHANG Xiaojuan. Effect of terminators on the downstream transcript unit with gene expression in Escherichiacoli [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 213-227. |
| [2] | PAN Yingjia, XIA Siyang, DONG Chang, CAI Jin, LIAN Jiazhang. Mutator-driven continuous genome evolution of Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 225-240. |
| [3] | SUN Wentao, ZHANG Xinzhe, WAN Shengtong, WANG Ruwen, LI Chun. Regulation on oxidation selectivity for β-amyrin by Class Ⅱ cytochrome P450 enzymes [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(5): 804-814. |
| [4] | LI Xiaodong, YANG Chengshuai, WANG Pingping, YAN Xing, ZHOU Zhihua. Production of sesquiterpenoids α-neoclovene and β-caryophyllene by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(5): 792-803. |
| [5] | LI Yi, LIN Zhenquan, LIU Zihe. Advances in yeast based adaptive laboratory evolution [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(2): 287-301. |
| [6] | Siyang XIA, Lihong JIANG, Jin CAI, Lei HUANG, Zhinan XU, Jiazhang LIAN. Advances in genome evolution of Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(5): 556-569. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||