Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (3): 335-353.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-088
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
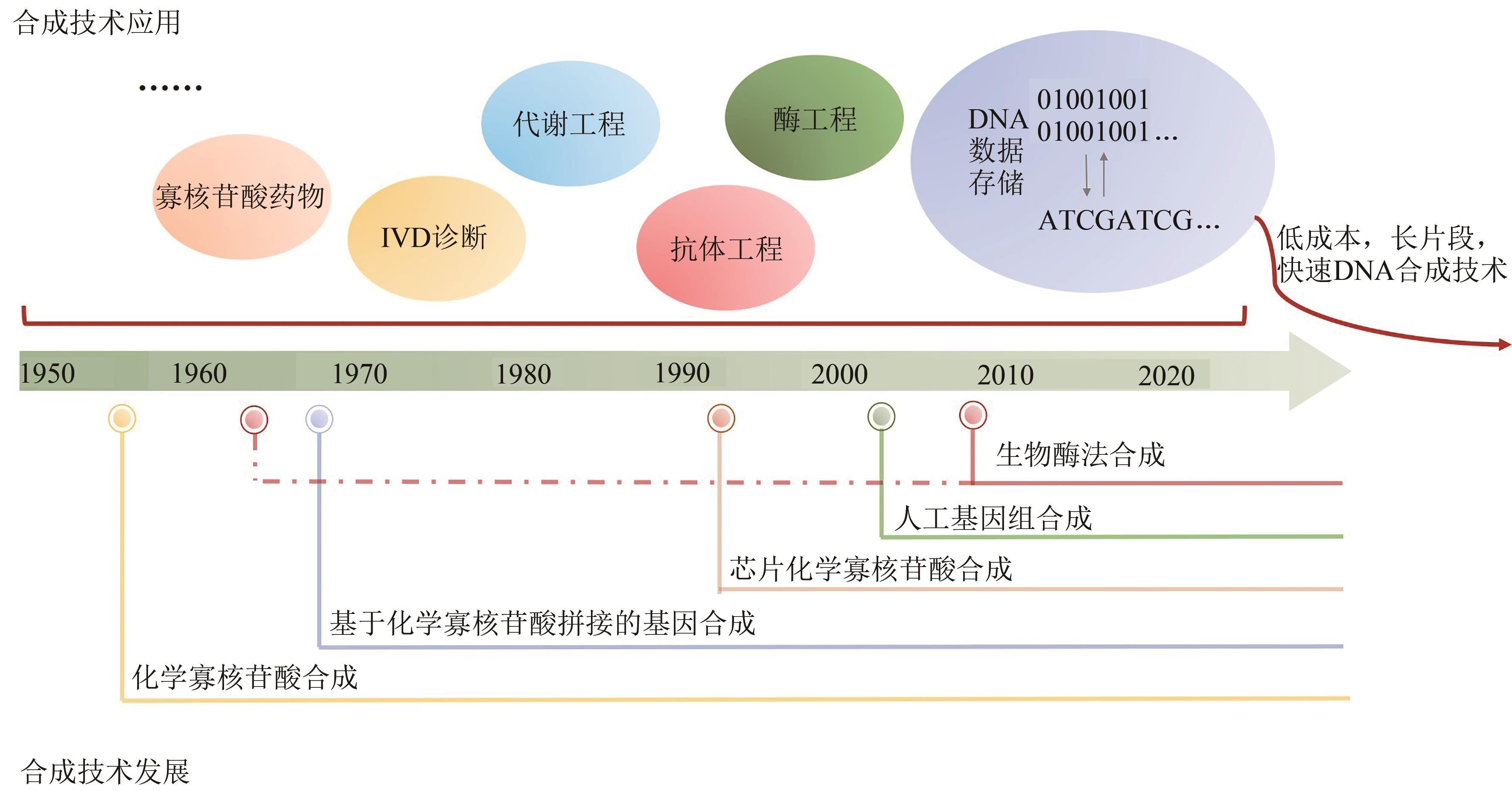
DNA synthesis technology: foundation of DNA data storage
HUANG Xiaoluo, DAI Junbiao
- Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Synthetic Genomics,Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Synthetic Genomics,Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology,Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenzhen 518055,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2020-12-14Revised:2021-04-07Online:2021-07-13Published:2021-06-30 -
Contact:DAI Junbiao
人工DNA合成技术:DNA数据存储的基石
黄小罗, 戴俊彪
- 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院,深圳合成生物学创新研究院,广东省合成基因组学重点实验室,深圳市合成基因组学重点实验室,广东 深圳 518055
-
通讯作者:戴俊彪 -
作者简介:黄小罗 (1988—),男,博士,高级工程师。研究方向为新一代DNA合成技术及DNA数据存储技术。E-mail:huangxl@siat.ac.cn戴俊彪 (1974—),男,博士,研究员。研究方向为合成基因组学及合成生物学相关使能技术。E-mail:junbiao.dai@siat.ac.cn -
基金资助:广东省合成基因组学重点实验室项目(2019B030301006);深圳市海外高层次人才创新创业专项资金项目(KQTD20180413181837372)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
HUANG Xiaoluo, DAI Junbiao. DNA synthesis technology: foundation of DNA data storage[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 335-353.
黄小罗, 戴俊彪. 人工DNA合成技术:DNA数据存储的基石[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(3): 335-353.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2020-088
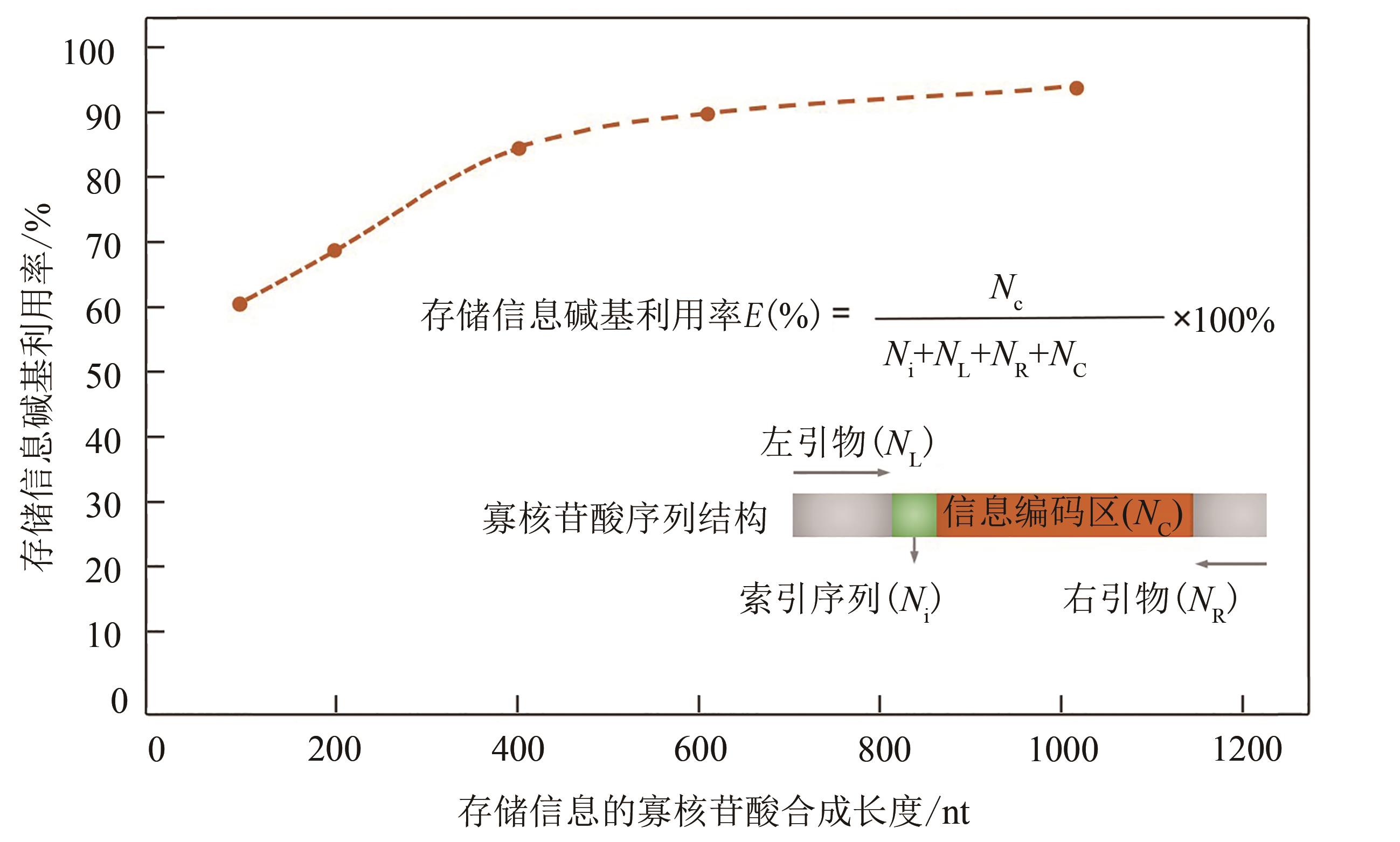
Fig. 4 Relationship between base utilization of data storage and oligo length [Referring to methods used by George Church et al., base utilization of data storage is calculated given that oligo length is different, while both the left and right flanking primers are 22 nt, and the index (address) sequence is 19 nt]
| 107 | TABATABAEI YAZDI S M H, YUAN Y, MA J, et al. A rewritable, random-access DNA-based storage system [J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 14138. |
| 108 | SONG L, ZENG A P. Orthogonal information encoding in living cells with high error-tolerance, safety, and fidelity [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(3): 866-874. |
| 109 | NGUYEN H H, PARK J, PARK S J, et al. Long-term stability and integrity of plasmid-based DNA data storage [J]. Polymers, 2018, 10(1): 28. |
| 110 | GRASS R N, HECKEL R, PUDDU M, et al. Robust chemical preservation of digital information on DNA in silica with error-correcting codes [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(8): 2552-2555. |
| 111 | LEE H H, KALHOR R, GOELA N, et al. Terminator-free template-independent enzymatic DNA synthesis for digital information storage [J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 2383. |
| 112 | STEPHANOPOULOS G. Synthetic biology and metabolic engineering [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2012, 1(11): 514-525. |
| 113 | CURRIN A, SWAINSTON N, DAY P J, et al. Synthetic biology for the directed evolution of protein biocatalysts: navigating sequence space intelligently [J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(5): 1172-1239. |
| 114 | SIDHU S S, FELLOUSE F A. Synthetic therapeutic antibodies [J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2006, 2(12): 682-688. |
| 115 | SLOMOVIC S, PARDEE K, COLLINS J J. Synthetic biology devices for in vitro and in vivo diagnostics [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(47): 14429-14435. |
| 116 | HILLSON N, CADDICK M, CAI Y, et al. Building a global alliance of biofoundries [J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 2040. |
| 117 | HAMEDIRAD M, CHAO R, WEISBERG S, et al. Towards a fully automated algorithm driven platform for biosystems design [J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 5150. |
| 118 | CHAO R, MISHRA S, SI T, et al. Engineering biological systems using automated biofoundries [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 42: 98-108. |
| 119 | STORCH M, HAINES M C, BALDWIN G S. DNA-BOT: a low-cost, automated DNA assembly platform for synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology, 2020, 5(1): ysaa010. |
| 120 | CHAO R, LIANG J, TASAN I, et al. Fully automated one-step synthesis of single-transcript TALEN pairs using a biological foundry [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(4): 678-685. |
| 1 | CEZE L, NIVALA J, STRAUSS K. Molecular digital data storage using DNA [J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2019, 20(8): 456-466. |
| 2 | DONG Y, SUN F, PING Z, et al. DNA storage: research landscape and future prospects [J]. National Science Review, 2020, 7(6): 1092-1107. |
| 3 | CHURCH G M, GAO Y, KOSURI S. Next-generation digital information storage in DNA [J]. Science, 2012; 337(6102): 1628. |
| 4 | ERLICH Y, ZIELINSKI D. DNA fountain enables a robust and efficient storage architecture [J]. Science, 2017, 355(6328): 950-954. |
| 5 | ORGANICK L, ANG S D, CHEN Y J, et al. Random access in large-scale DNA data storage [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(3): 242-248. |
| 6 | GOLDMAN N, BERTONE P, CHEN S Y, et al. Towards practical, high-capacity, low-maintenance information storage in synthesized DNA [J]. Nature, 2013, 494(7435): 77-80. |
| 7 | WATSON J D, CRICK F H. Molecular structure of nucleic acids-a structure for deoxyribose nucleic acid [J]. Nature, 1953, 171(4356):737-738. |
| 8 | JUNG Y, PARK G S, MOON J H, et al. Comparative analysis of primer-probe sets for RT-qPCR of COVID-19 causative virus (SARS-CoV-2) [J]. ACS Infectious Diseases, 2020, 6(9): 2513-2523. |
| 9 | LIU Y P, YAO C Y. Rapid and quantitative detection of hepatitis B virus [J]. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 2015, 21(42): 11954-11963. |
| 10 | COARSEY C T, ESIOB N, NARAYANAN R, et al. Strategies in Ebola virus disease (EVD) diagnostics at the point of care [J]. Critical Reviews in Microbiology, 2017, 43(6): 779-798. |
| 11 | HU D M, HU S Y, WAN W, et al. Effective optimization of antibody affinity by phage display integrated with high-throughput DNA synthesis and sequencing technologies [J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(6): e0129125. |
| 12 | DUNBAR C E, HIGH K A, JOUNG J K, et al. Gene therapy comes of age [J]. Science, 2018, 359(6372): eaan4672. |
| 13 | NALDINI L. Gene therapy returns to centre stage [J]. Nature, 2015, 526(7573): 351-360. |
| 14 | LUNDIN K E, GISSBERG O, SMITH C I E. Oligonucleotide therapies: the past and the present [J]. Human Gene Therapy, 2015, 26(8): 475-485. |
| 15 | SUTTON D W, HAVSTAD P K, KEMP J D. Synthetic cryIIIA gene from Bacillus thuringiensis improved for high expression in plants [J]. Transgenic Research, 1992, 1(5): 228-236. |
| 16 | LI S P, JIANG Q, LIU S L, et al. A DNA nanorobot functions as a cancer therapeutic in response to a molecular trigger in vivo [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(3): 258-264. |
| 17 | MICHELSON A M, TODD A R. Nucleotides part XXXII. Synthesis of a dithymidine dinucleotide containing a 3′: 5′-internucleotidic linkage [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1955: 2632-2638. |
| 18 | CARUTHERS M H, BEAUCAGE S L, BECKER C, et al. Deoxyoligonucleotide synthesis via the phosphoramidite method [J]. Gene Amplification and Analysis, 1983, 3: 1-26. |
| 19 | CARUTHERS M H, BARONE A D, BEAUCAGE S L, et al. Chemical synthesis of deoxyoligonucleotides by the phosphoramidite method [J]. Methods in Enzymology, 1987, 154: 287-313. |
| 20 | REESE C B. The chemical synthesis of oligo- and poly-nucleotides by the phosphotriester approach [J]. Tetrahedron, 1978, 34: 3143-3179. |
| 21 | KHORANA H G, RAZZELL W E, GILHAM P T, et al. Syntheses of dideoxyribonucleotides [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1957, 79(4): 1002-1003. |
| 22 | REESE C B. Oligo- and poly-nucleotides: 50 years of chemical synthesis [J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2005, 3(21): 3851-3868. |
| 23 | MCBRIDE L J, CARUTHERS M H. An investigation of several deoxynucleoside phosphoramidites useful for synthesizing deoxyoligonucleotides [J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 1983, 24(3): 245-248. |
| 24 | KOZLOV I A, DANG M, SIKES K, et al. Significant improvement of quality for long oligonucleotides by using controlled pore glass with large pores [J]. Nucleosides, Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids, 2005, 24(5/6/7): 1037-1041. |
| 25 | ALUL R H, SINGMAN C N, ZHANG G, et al. Oxalyl-CPG: a labile support for synthesis of sensitive oligonucleotide derivatives [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1991, 19(7): 1527-1532. |
| 26 | FODOR S P A, RAVA R P, HUANG X H C, et al. Multiplexed biochemical assays with biological chips [J]. Nature, 1993, 364(6437): 555-556. |
| 27 | LOCKHART D J, DONG H L, BYRNE M C, et al. Expression monitoring by hybridization to high-density oligonucleotide arrays [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 1996, 14(13): 1675-1680. |
| 28 | GAO X L, LEPROUST E, ZHANG H, et al. A flexible light-directed DNA chip synthesis gated by deprotection using solution photogenerated acids [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2001, 29(22): 4744-4750. |
| 29 | SINGH-GASSON S, GREEN R D, YUE Y J, et al. Maskless fabrication of light-directed oligonucleotide microarrays using a digital micromirror array [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 1999, 17(10): 974-978. |
| 30 | GHINDILIS A L, SMITH M W, SCHWARZKOPF K R, et al. CombiMatrix oligonucleotide arrays: genotyping and gene expression assays employing electrochemical detection [J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2007, 22(9/10): 1853-1860. |
| 31 | HUGHES T R, MAO M, JONES A R, et al. Expression profiling using microarrays fabricated by an ink-jet oligonucleotide synthesizer [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2001, 19(4): 342-347. |
| 32 | QUAN J Y, SAAEM I, TANG N, et al. Parallel on-chip gene synthesis and application to optimization of protein expression [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2011, 29(5): 449-452. |
| 33 | LAUSTED C, DAHL T, WARREN C, et al. POSaM: a fast, flexible, open-source, inkjet oligonucleotide synthesizer and microarrayer [J]. Genome Biology, 2004, 5(8): R58. |
| 34 | IVANETICH K M, AKIYAMA J, SANTI D V, et al. Automated purification of synthetic oligonucleotides [J]. Biotechniques, 1991, 10(6): 704-708. |
| 35 | LOPEZ-GOMOLLON S, NICOLAS F E. Purification of DNA oligos by denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) [J]. Methods in Enzymology, 2013, 529: 65-83. |
| 36 | SINHA N D, JUNG K E. Analysis and purification of synthetic nucleic acids using HPLC [J]. Current Protocols in Nucleic Acid Chemistry, 2015, 61: 10.5.1-10.5.39. |
| 37 | SEPTAK M. Kinetic studies on depurination and detritylation of CPG-bound intermediates during oligonucleotide synthesis [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1996, 24(15): 3053-3058. |
| 38 | EFCAVITCH J W, HEINER C. Depurination as a yield decreasing mechanism in oligodeoxynucleotide synthesis [J]. Nucleosides Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids, 1985, 4(1/2): 267. |
| 39 | LEPROUST E M, PECK B J, SPIRIN K, et al. Synthesis of high-quality libraries of long (150mer) oligonucleotides by a novel depurination controlled process [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, 38(8): 2522-2540. |
| 40 | SEKIYA T, CONTRERAS R, TAKEYA T, et al. Total synthesis of a tyrosine suppressor transfer RNA gene. XVII. Transcription, in vitro, of the synthetic gene and processing of the primary transcript to transfer RNA [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1979, 254(13): 5802-5816. |
| 41 | AGARWAL K L, BÜCHI H, CARUTHERS M H, et al. Total synthesis of the gene for an alanine transfer ribonucleic acid from yeast [J]. Nature, 1970, 227(5253): 27-34. |
| 42 | GUPTA N K, OHTSUKA E, WEBER H, et al. Studies on polynucleotides. LXXXVII. The joining of short deoxyribopolynucleotides by DNA-joining enzymes [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1968, 60(1): 285-292. |
| 43 | GUPTA N K, OHTSUKA E, SGARAMELLA V, et al. Studies on polynucleotides, 88. Enzymatic joining of chemically synthesized segments corresponding to the gene for alanine-tRNA [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1968, 60(4): 1338-1344. |
| 44 | XIONG A, PENG R, ZHUANG J, et al. Non-polymerase-cycling-assembly-based chemical gene synthesis: strategies, methods, and progress [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2008, 26(2): 121-134. |
| 45 | GRUNDSTRÖM T, ZENKE W M, WINTZERITH M, et al. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis by microscale 'shot-gun' gene synthesis [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1985, 13(9): 3305-3316. |
| 46 | EREN M, SWENSON R P. Chemical synthesis and expression of a synthetic gene for the flavodoxin from Clostridium MP [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1989, 264(25): 14874-14879. |
| 47 | BARANY F. The ligase chain reaction in a PCR world [J]. Genome Research, 1991, 1: 5-16. |
| 48 | AU L C, YANG F Y, YANG W J, et al. Gene synthesis by a LCR-based approach: high-level production of leptin-L54 using synthetic gene in Escherichia coli [J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 1998, 248(1): 200-203. |
| 49 | JAYARAMAN K, FINGAR S A, SHAH J, et al. Polymerase chain reaction-mediated gene synthesis: synthesis of a gene coding for isozyme c of horseradish peroxidase [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1991, 88(10): 4084-4088. |
| 50 | XIONG A. YAO Q, PENG R,et al. A simple, rapid, high-fidelity and cost-effective PCR-based two-step DNA synthesis method for long gene sequences [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2004, 32(12): e98. |
| 51 | STEMMER W P C, CRAMERI A, HA K D, et al. Single-step assembly of a gene and entire plasmid from large numbers of oligodeoxyribonucleotides [J]. Gene, 1995, 164(1): 49-53. |
| 52 | XIONG A, PENG R, ZHUANG J, et al. Chemical gene synthesis: strategies, softwares, error corrections, and applications [J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2008, 32(3): 522-540. |
| 53 | YOUNG L, DONG Q. Two-step total gene synthesis method [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2004, 32(7): e59. |
| 54 | 林继伟, 张晓东, 曹雪雁, 等. 一种新的等温单向基因的合成方法[J]. 遗传, 2007, 29(6): 765-770. |
| LIN J W, ZHANG X D, CAO X Y,et al. Isothermal unidirectional elongation method of gene synthesis [J]. Hereditas (Beijing), 2007, 29(6): 765-770. | |
| 55 | 林继伟, 李海阔, 王小兵, 等. 等温单向生长的基因合成方法: CN 200610028886 [P]. 2007-02-07. |
| LIN J W, LI H K, WANG X B, et al. Isothermal unidirectional elongation method of gene synthesis: CN 200610028886 [P]. 2007-02-07. | |
| 56 | 林继伟, 戴俊彪. 一种基于双向等温延伸的核酸合成方法: CN201310219029. 4 [P]. 2019-03-08. LIN J W, DAI J B. Isothermal bidirectional elongation method of nucleic acid synthesis. CN201310219029. 4 [P]. 2019-03-08. |
| 57 | TIAN J, GONG H, SHENG N, et al. Accurate multiplex gene synthesis from programmable DNA microchips [J]. Nature, 2004, 432(7020): 1050-1054. |
| 58 | KOSURI S, EROSHENKO N, LEPROUST E M, et al. Scalable gene synthesis by selective amplification of DNA pools from high-fidelity microchips [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2010, 28(12): 1295-1299. |
| 59 | PLESA C, SIDORE A M, LUBOCK N B, et al. Multiplexed gene synthesis in emulsions for exploring protein functional landscapes [J]. Science, 2018, 359(6373): 343-347. |
| 60 | SIDORE A M, PLESA C, SAMSON J A, et al. DropSynth 2.0: high-fidelity multiplexed gene synthesis in emulsions [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 48(16): e95. |
| 61 | JENSEN M A, FUKUSHIMA M, DAVIS R W. DMSO and betaine greatly improve amplification of GC-rich constructs in de novo synthesis [J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5(6): e11024. |
| 62 | HOOVER D M, LUBKOWSKI J. DNAWorks: an automated method for designing oligonucleotides for PCR-based gene synthesis [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2002, 30(10): e43. |
| 63 | CARR P A, PARK J S, LEE Y J, et al. Protein-mediated error correction for de novo DNA synthesis [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2004, 32(20): e162. |
| 64 | SMITH J, MODRICH P. Removal of polymerase-produced mutant sequences from PCR products [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1997, 94(13): 6847-6850. |
| 65 | ZHANG J, WANG Y F, CHAI B H, et al. Efficient and low-Cost error removal in DNA synthesis by a high-durability MutS [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(4): 940-952. |
| 66 | MA S, SAAEM I, TIAN J. Error correction in gene synthesis technology [J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2012, 30(3): 147-154. |
| 67 | SAAEM I, MA S, QUAN J, et al. Error correction of microchip synthesized genes using surveyor nuclease [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2012, 40(3): e23. |
| 68 | LUBOCK N B, ZHANG D, SIDORE A M, et al. A systematic comparison of error correction enzymes by next-generation sequencing [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, 45(15): 9206-9217. |
| 69 | ENGLER C, KANDZIA R, MARILLONNET S. A one pot, one step, precision cloning method with high throughput capability [J]. PLoS One, 2008, 3(11): e3647. |
| 70 | ENGLER C, GRUETZNER R, KANDZIA R, et al. Golden gate shuffling: a one-pot DNA shuffling method based on Type IIS restriction enzymes [J]. PLoS One, 2009, 4(5): e5553. |
| 71 | GIBSON D G, YOUNG L, CHUANG R Y, et al. Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases [J]. Nature Methods, 2009, 6(5): 343-345. |
| 72 | ROBINSON C J, DUNSTAN M S, SWAINSTON N, et al. Multifragment DNA assembly of biochemical pathways via automated ligase cycling reaction [J]. Methods in Enzymology, 2018, 608: 369-392. |
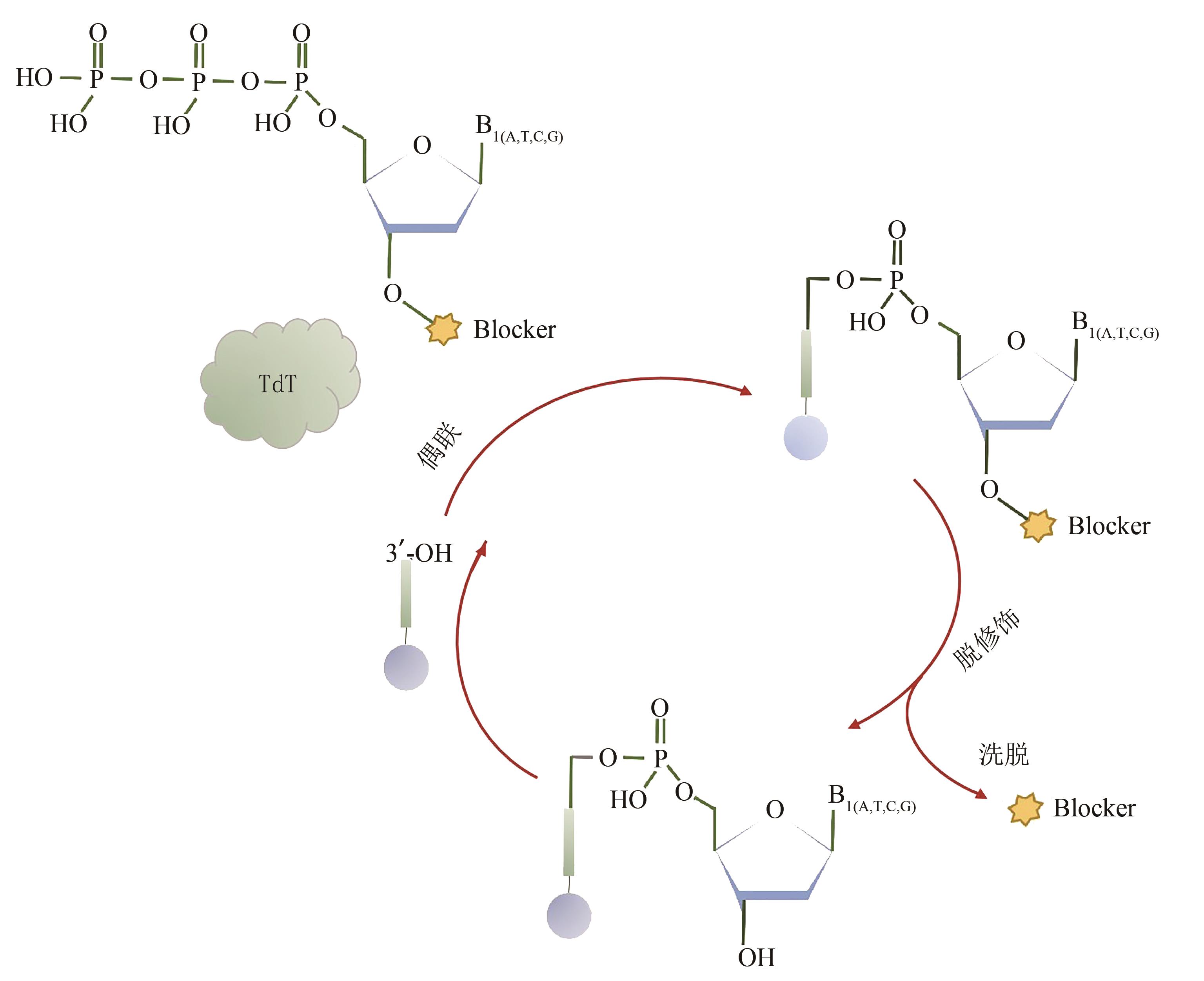
| 73 | DE KOK S, STANTON L H, SLABY T, et al. Rapid and reliable DNA assembly via ligase cycling reaction [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2014, 3(2): 97-106. |
| 74 | LIANG J, LIU Z, LOW X Z, et al. Twin-primer non-enzymatic DNA assembly: an efficient and accurate multi-part DNA assembly method [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, 45(11): e94. |
| 75 | SHETTY R P, ENDY D, KNIGHT T F. Engineering bioBrick vectors from bioBrick parts [J]. Journal of Biological Engineering, 2008, 2: 5. |
| 76 | WEBER E, ENGLER C, GRUETZNER R, et al. A modular cloning system for standardized assembly of multigene constructs [J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(2): e16765. |
| 77 | LI L, JIANG W, LU Y. A modified Gibson assembly method for cloning large DNA fragments with high GC contents [J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2018, 1671: 203-209. |
| 78 | KUIJPERS N G, SOLIS-ESCALANTE D, BOSMAN L . et al. A versatile, efficient strategy for assembly of multi-fragment expression vectors in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using 60 bp synthetic recombination sequences [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2013, 12: 47. |
| 79 | GIBSON D G, BENDERS G A, AXELROD K C, et al. One-step assembly in yeast of 25 overlapping DNA fragments to form a complete synthetic Mycoplasma genitalium genome [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2008, 105(51): 20404-20409. |
| 80 | SHAO Z, ZHAO H, ZHAO H M. DNA assembler, an in vivo genetic method for rapid construction of biochemical pathways [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2009, 37(2): e16. |
| 81 | WILD J, HRADECNA Z, SZYGBALSKI W. Conditionally amplifiable BACs: switching from single-copy to high-copy vectors and genomic clones [J]. Genome Research, 2002, 12(9): 1434-1444. |
| 82 | SHIZUYA H, BIRREN B, KIM U J, et al. Cloning and stable maintenance of 300-kilobase-pair fragments of human DNA in Escherichia coli using an F-factor-based vector [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1992, 89(18): 8794-8797. |
| 83 | CELLO J, PAUL A V, WIMMER E. Chemical synthesis of poliovirus cDNA: generation of infectious virus in the absence of natural template [J]. Science, 2002, 297(5583): 1016-1018. |
| 84 | SMITH H O, HUTCHISON C A, PFANNKOCH C, et al. Generating a synthetic genome by whole genome assembly: ϕX174 bacteriophage from synthetic oligonucleotides [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2003, 100(26): 15440-15445. |
| 85 | THAO T T N, LABROUSSAA F, EBERT N, et al. Rapid reconstruction of SARS-CoV-2 using a synthetic genomics platform [J]. Nature, 2020, 582(7813): 561-565. |
| 86 | GIBSON D G, BENDERS G A, ANDREWS-PFANNKOCH C, et al. Complete chemical synthesis, assembly, and cloning of a Mycoplasma genitalium genome [J]. Science, 2008, 319(5867): 1215-1220. |
| 87 | GIBSON D G, GLASS J I, LARTIGUE C, et al. Creation of a bacterial cell controlled by a chemically synthesized genome [J]. Science, 2010, 329(5987): 52-56. |
| 88 | ANNALURU N, MULLER H, MITCHELL L A, et al. Total synthesis of a functional designer eukaryotic chromosome [J]. Science, 2014, 344(6179): 55-58. |
| 89 | RICHARDSON S M, MITCHELL L A, STRACQUADANIO G, et al. Design of a synthetic yeast genome [J]. Science, 2017, 355(6329): 1040-1044. |
| 90 | WANG L, JIANG S, CHEN C, et al. Synthetic genomics: from DNA synthesis to genome design [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(7): 1748-1756. |
| 91 | FREDENS J, WANG K, DE LA TORRE D, et al. Total synthesis of Escherichia coli with a recoded genome [J]. Nature, 2019, 569(7757): 514-518. |
| 92 | VENETZ J E, MEDICO L DEL, WÖLFLE A, et al. Chemical synthesis rewriting of a bacterial genome to achieve design flexibility and biological functionality [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(16): 8070-8079. |
| 93 | FULLER C W, MIDDENDORF L R, BENNER S A, et al. The challenges of sequencing by synthesis [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2009, 27(11): 1013-1023. |
| 94 | BOLLUM F J. Thermal conversion of nonpriming deoxyribonucleic acid to primer [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1959, 234: 2733-2734. |
| 95 | BOLLUM F J. Calf thymus polymerase [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1960, 235: 2399-2403. |
| 96 | BOLLUM F J. Oligodeoxyribonucleotide-primed reactions catalyzed by calf thymus polymerase [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1962, 237: 1945-1949. |
| 97 | YAMTICH J, SWEASY J B. DNA polymerase family X: function, structure, and cellular roles [J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2010, 1804(5): 1136-1150. |
| 98 | RAMADAN K, SHEVELEV I, HÜBSCHER U. The DNA-polymerase-X family: controllers of DNA quality [J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2004, 5(12): 1038-1043. |
| 99 | UD-DEAN S M M. A theoretical model for template-free synthesis of long DNA sequence [J]. Systems and Synthetic Biology, 2008, 2(3/4): 67-73. |
| 100 | MATHEWS A S, YANG H, MONTEMAGNO C. Photo-cleavable nucleotides for primer free enzyme mediated DNA synthesis [J]. Organic and Biomolecular Chemistry, 2016, 14(35): 8278-8288. |
| 101 | EFCAVITCH W J, SIDDIQI S. Methods and apparatus for synthesizing nucleic acids: US8808989B1 [P]. 2018-08-07. |
| 102 | PALLUK S, ARLOW DH, DE ROND T, et al. De novo DNA synthesis using polymerasenucleotide conjugates [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(7): 645-650. |
| 103 | CLARK J M. Novel non-templated nucleotide addition reactions catalyzed by procaryotic and eucaryotic DNA polymerases [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1988, 16(20): 9677-9686. |
| 104 | HOFF K, HALPAIN M, GARBAGNATI G, et al. Rapid and dynamic nucleic acid hybridization enables enzymatic oligonucleotide synthesis by cyclic reversible termination: a novel mechanism for enzymatic DNA synthesis [EB/OL]. [2021-05-13]. . |
| 105 | ENGL T E, UHLENBECK O C. Enzymatic oligoribonucleotide synthesis with T4 RNA ligase [J]. Biochemistry, 1978, 17(11): 2069-2076. |
| 106 | SCHMITZ C, REETZ M T. Solid-phase enzymatic synthesis of oligonucleotides [J]. Organic Letters, 1999, 1(11): 1729-1731. |
| [1] | JIAO Hongtao, QI Meng, SHAO Bin, JIANG Jinsong. Legal issues for the storage of DNA data [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [2] | CHEN Weigang, GE Qi, WANG Panpan, HAN Mingzhe, GUO Jian. Multiple interleaved RS codes for data storage using up to Mb-scale synthetic DNA in living cells [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 428-443. |
| [3] | GAO Yanmin, TANG Mengtong, LIU Qian, QIAO Hongyan, WANG Taoxue, QI Hao. The pivotal biochemical methods in DNA data storage [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 384-398. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||