Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (6): 1386-1403.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-030
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Clostridium pasteurianum as an industrial chassis for efficient production of 1,3-propanediol: from metabolic engineering to fermentation and product separation
LIU Jianming1,2,3,4, ZHANG Chijian5, ZHANG Bing1,2,3, ZENG Anping1,2,3,4
- 1.Center for Synthetic Biology and Biomanufacturing,Westlake University,Hangzhou 310030,Zhejiang,China
2.Engineering institute,Westlake University,Hangzhou 310030,Zhejiang,China
3.Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Low-Carbon Intelligent Synthetic Biology,Hangzhou 310030,Zhejiang,China
4.Research Center for Industries of the Future,Westlake University,Hangzhou 310030,Zhejiang,China
5.Guangdong C1 Life Biotech Co. ,Ltd. ,Guangzhou 510630,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2024-03-27Revised:2024-06-18Online:2025-01-10Published:2024-12-31 -
Contact:ZENG Anping
巴氏梭菌作为工业底盘细胞高效生产1,3-丙二醇——从代谢工程和菌种进化到过程工程和产品分离
刘建明1,2,3,4, 张炽坚5, 张冰1,2,3, 曾安平1,2,3,4
- 1.西湖大学合成生物学与生物智造中心,浙江 杭州 310030
2.西湖大学工学院,浙江 杭州 310030
3.浙江省全省智能低碳生物合成重点实验室,浙江 杭州 310030
4.西湖大学未来产业研究中心,浙江 杭州 310030
5.广东恒碳科技有限公司,广东 广州 510630
-
通讯作者:曾安平 -
作者简介:刘建明 (1985—),男,研究员。研究方向为合成生物学,低碳生物制造,代谢工程等。 E-mail:liujianming@westlake.edu.cn曾安平 (1963—),男,讲席教授,博士生导师,德国工程院院士,西湖大学合成生物学与生物智造中心创始主任。研究方向为生物化工、合成生物学、新型催化软物质和功能材料等。 E-mail:zenganping@westlake.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2023YFA09014003)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LIU Jianming, ZHANG Chijian, ZHANG Bing, ZENG Anping. Clostridium pasteurianum as an industrial chassis for efficient production of 1,3-propanediol: from metabolic engineering to fermentation and product separation[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1386-1403.
刘建明, 张炽坚, 张冰, 曾安平. 巴氏梭菌作为工业底盘细胞高效生产1,3-丙二醇——从代谢工程和菌种进化到过程工程和产品分离[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1386-1403.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2024-030

Fig. 1 Metabolic pathways for PDO bioproduction from various substratesC6—glucose; C3—glycerin; C2—ethanol; C1—CO2 and methanol; GPD—glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GPP—glycerol-3-phosphate phosphohydrolase; GDHt—glycerol dehydratase; YqhD—nonspecific alcohol dehydrogenase; DhaT—1,3-propanediol dehydrogenase; GDH—glutamate dehydrogenase; KDC—keto acid decarboxylase; ACC—acetyl-CoA carboxylase; MCR—malonyl-CoA reductase; ydfG—3-hydroxy acid dehydrogenase; Mdh2—methanol dehydrogenase; KHB—2-keto-4-hydroxybutyrate aldolase; PDC—pyruvate decarboxylase; ADH—alcohol dehydrogenase; DERA—deoxyribose-5-phosphate aldolase
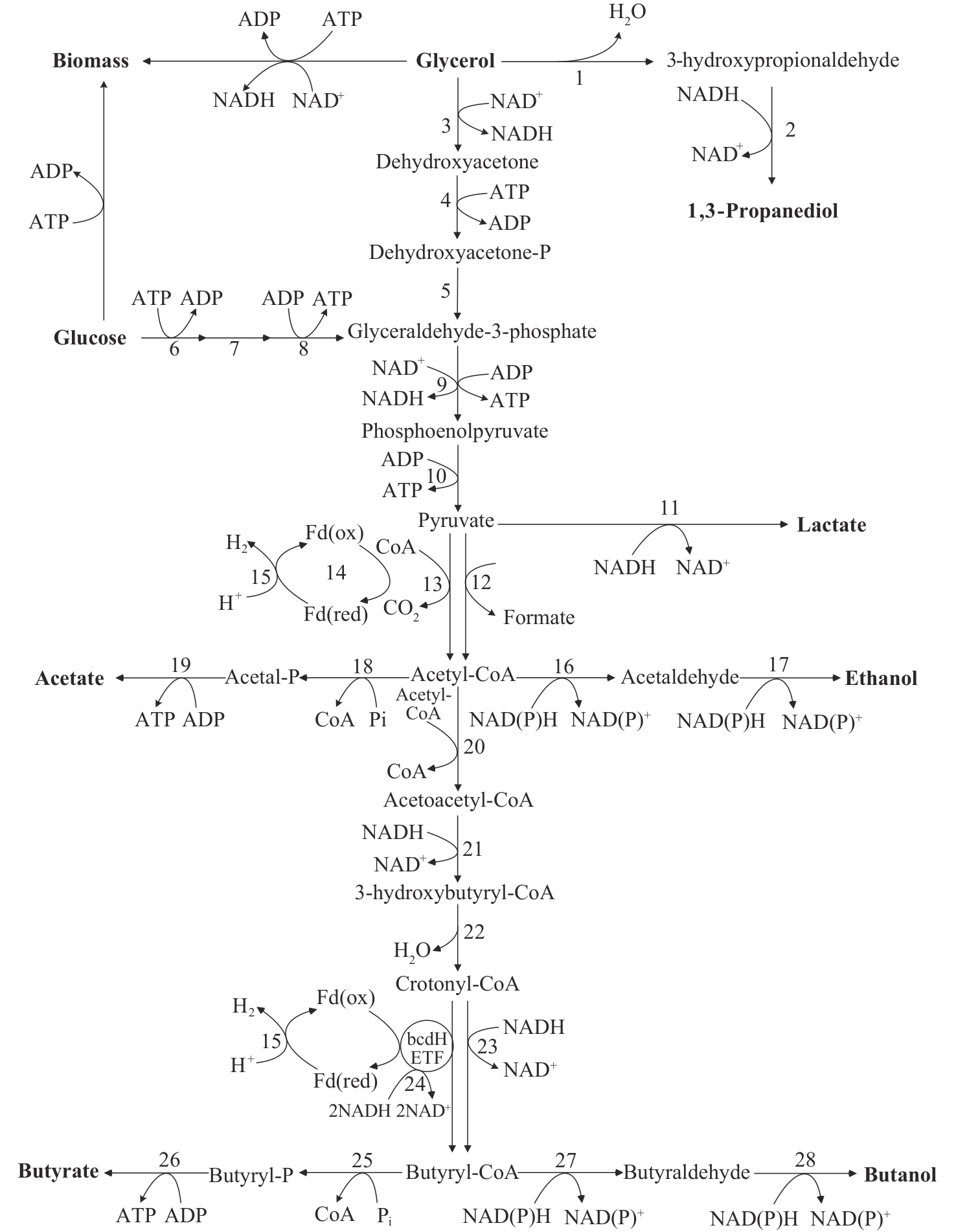
Fig. 2 Pathways of glucose and glycerol metabolism in C. pasteurianum[39]Enzymes involved in the metabolic pathways are numbered as follow: 1—Propanediol dehydratase; 2—1,3-Propanediol dehydrogenase; 3—Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; 4—Dihydroxyacetone kinase; 5—Triosephosphate isomerase; 6—Hexokinase; 7—Phosphoglucose isomerase; 8—Phosphofructokinase; 9—Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; 10—Pyruvate kinase; 11—Lactate dehydrogenase; 12—Pyruvate formate-lyase; 13—Pyruvate-flavodoxin oxidoreductase; 14—NADH-dependent reduced ferredoxin: NADP+ oxidoreductase; 15—Ferredoxin hydrogenase; 16—Acetaldehyde dehydrogenase; 17—Alcohol dehydrogenase; 18—Phosphate acetyltransferase; 19—Acetate kinase; 20—Acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase; 21—3-Hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase; 22—Crotonase; 23—2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase; 24—Ferredoxin dependent butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase/electron transferring flavoprotein complex (BCdH-ETF); 25—Phosphate butyryltransferase; 26—Butyrate kinase; 27—Aldehyde dehydrogenase; 28—Butanol dehydrogenase
| Substrate | End-product | Energy, reducing equivalents and product balances |
|---|---|---|
| glycerol | PDO | glycerol+NADH→PDO |
| lactate | glycerol→lactate+NADH+ATP | |
| acetate | glycerol→acetate+CO2+2ATP+2NADH+FdH2 | |
| ethanol | glycerol→ethanol+CO2+ATP+FdH2 | |
| butyrate | 2glycerol→butyrate+2CO2+3ATP+2NADH+2FdH2 | |
| *2glycerol→butyrate+2CO2+3ATP+NADH+3FdH2 | ||
| butanol | 2glycerol→butanol+2CO2+2ATP+2FdH2 | |
| *2glycerol+NADH→butanol+2CO2+2ATP+3FdH2 | ||
| glucose | lactate | glucose→2lactate+2ATP |
| acetate | glucose→2acetate+2CO2+4ATP+2NADH+2FdH2 | |
| ethanol | glucose+2NADH→2ethanol+2CO2+2ATP+2FdH2 | |
| butyrate | glucose→butyrate+2CO2+3ATP+2FdH2 | |
| *glucose+NADH→butyrate+2CO2+3ATP+3FdH2 | ||
| butanol | glucose+2NADH→butanol+2CO2+2ATP+2FdH2 | |
| *glucose+3NADH→butanol+2CO2+2ATP+3FdH2 |
Table 1 Energy, reducing equivalents and product balances in C. pasteurianum
| Substrate | End-product | Energy, reducing equivalents and product balances |
|---|---|---|
| glycerol | PDO | glycerol+NADH→PDO |
| lactate | glycerol→lactate+NADH+ATP | |
| acetate | glycerol→acetate+CO2+2ATP+2NADH+FdH2 | |
| ethanol | glycerol→ethanol+CO2+ATP+FdH2 | |
| butyrate | 2glycerol→butyrate+2CO2+3ATP+2NADH+2FdH2 | |
| *2glycerol→butyrate+2CO2+3ATP+NADH+3FdH2 | ||
| butanol | 2glycerol→butanol+2CO2+2ATP+2FdH2 | |
| *2glycerol+NADH→butanol+2CO2+2ATP+3FdH2 | ||
| glucose | lactate | glucose→2lactate+2ATP |
| acetate | glucose→2acetate+2CO2+4ATP+2NADH+2FdH2 | |
| ethanol | glucose+2NADH→2ethanol+2CO2+2ATP+2FdH2 | |
| butyrate | glucose→butyrate+2CO2+3ATP+2FdH2 | |
| *glucose+NADH→butyrate+2CO2+3ATP+3FdH2 | ||
| butanol | glucose+2NADH→butanol+2CO2+2ATP+2FdH2 | |
| *glucose+3NADH→butanol+2CO2+2ATP+3FdH2 |
| 分离步骤 | 作用与功能 | 存在的问题 | 分离物质 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 蒸馏 | 液态混合物中各组分沸点不同,去除残留甘油 | 残余甘油 | |
| 离心和微滤 | 有效去除所有微生物细胞(生物量) | 生物质 | |
| 低分子截留 | 有效去除高含量的可溶性蛋白质,避免其在水分蒸发过程中严重起泡从而导致过程效率降低 | 可溶性蛋白 | |
| 壳聚糖絮凝 | |||
| 活性炭吸附 | |||
| 纳滤 | 分离去除葡萄糖,避免葡萄糖在蒸发和蒸馏过程中发生沉淀 | 葡萄糖 | |
| 离子交换吸附 | 有效去除发酵液中的有机酸盐和无机盐,因为盐在水分蒸发过程中部分结晶,结晶盐的沉积导致蒸发器底部形成黏稠的浆液,进而导致高能耗和目标产品的低产量 | 树脂的快速饱和,需要大量的NaOH和HCl溶液进行再生 | 有机酸盐和无机盐 |
| 电渗析 | 电渗析的能源和材料成本通常非常高,阻碍了其在廉价大宗化学品的商业生产中的实际应用 | ||
| 醇沉淀和稀释结晶 | 不足以有效去除在醇类中溶解度高的有机酸盐 | ||
| 蒸发 | 蒸发去除水分 | 水 |
Table 2 PDO purification based on evaporation and distillation
| 分离步骤 | 作用与功能 | 存在的问题 | 分离物质 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 蒸馏 | 液态混合物中各组分沸点不同,去除残留甘油 | 残余甘油 | |
| 离心和微滤 | 有效去除所有微生物细胞(生物量) | 生物质 | |
| 低分子截留 | 有效去除高含量的可溶性蛋白质,避免其在水分蒸发过程中严重起泡从而导致过程效率降低 | 可溶性蛋白 | |
| 壳聚糖絮凝 | |||
| 活性炭吸附 | |||
| 纳滤 | 分离去除葡萄糖,避免葡萄糖在蒸发和蒸馏过程中发生沉淀 | 葡萄糖 | |
| 离子交换吸附 | 有效去除发酵液中的有机酸盐和无机盐,因为盐在水分蒸发过程中部分结晶,结晶盐的沉积导致蒸发器底部形成黏稠的浆液,进而导致高能耗和目标产品的低产量 | 树脂的快速饱和,需要大量的NaOH和HCl溶液进行再生 | 有机酸盐和无机盐 |
| 电渗析 | 电渗析的能源和材料成本通常非常高,阻碍了其在廉价大宗化学品的商业生产中的实际应用 | ||
| 醇沉淀和稀释结晶 | 不足以有效去除在醇类中溶解度高的有机酸盐 | ||
| 蒸发 | 蒸发去除水分 | 水 |
| 分离方法 | 作用与功能 | 存在的问题 | 提取率 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 液-液萃取 | 使用疏水有机溶剂乙酸乙酯 | 使用乙酸乙酯对生物合成的PDO进行溶剂萃取 | 从实际发酵液中回收PDO的最高分配系数仅达到0.14 | 12% |
| 基于化学反应的反应萃取 | 将PDO转化为疏水性PDO衍生物,有机溶剂萃取后,通过逆反应以获得PDO | 反应物和萃取剂都有毒,发酵液中与PDO具有相似化学结构的其他物质(如2,3-丁二醇、甘油、乙醇等)也会与反应物发生反应 | 91% | |
| 基于生物催化转化的反应萃取 | 利用与辛酸的酯化反应在脂肪酶催化下,将PDO转化为疏水酯 | PDO和脂肪酸之间的反应效率低,需要重复三次脂肪酶催化的酯化反应 | 90% | |
| 两相盐析萃取 | “K2CO3+K2HPO4”异丙醇盐析萃取系统 | 使用亲水有机溶剂的盐析萃取在从发酵液中回收亲水产品方面表现出显著更高的回收率 | 盐析萃取系统中形成两相所需的盐量大,且分离过程造成大量的废水排放 | 98% |
| 由乙醇和碳酸钠组成的盐析萃取系统 | 97% | |||
| 两步盐析萃取 | 第一步中,使用疏水性的正丁酸乙酯高效提丁酸,在第二步中,使用乙醇并添加NaH2PO4作为盐析剂,回收PDO | 95% | ||
Table 3 PDO purification based on extraction
| 分离方法 | 作用与功能 | 存在的问题 | 提取率 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 液-液萃取 | 使用疏水有机溶剂乙酸乙酯 | 使用乙酸乙酯对生物合成的PDO进行溶剂萃取 | 从实际发酵液中回收PDO的最高分配系数仅达到0.14 | 12% |
| 基于化学反应的反应萃取 | 将PDO转化为疏水性PDO衍生物,有机溶剂萃取后,通过逆反应以获得PDO | 反应物和萃取剂都有毒,发酵液中与PDO具有相似化学结构的其他物质(如2,3-丁二醇、甘油、乙醇等)也会与反应物发生反应 | 91% | |
| 基于生物催化转化的反应萃取 | 利用与辛酸的酯化反应在脂肪酶催化下,将PDO转化为疏水酯 | PDO和脂肪酸之间的反应效率低,需要重复三次脂肪酶催化的酯化反应 | 90% | |
| 两相盐析萃取 | “K2CO3+K2HPO4”异丙醇盐析萃取系统 | 使用亲水有机溶剂的盐析萃取在从发酵液中回收亲水产品方面表现出显著更高的回收率 | 盐析萃取系统中形成两相所需的盐量大,且分离过程造成大量的废水排放 | 98% |
| 由乙醇和碳酸钠组成的盐析萃取系统 | 97% | |||
| 两步盐析萃取 | 第一步中,使用疏水性的正丁酸乙酯高效提丁酸,在第二步中,使用乙醇并添加NaH2PO4作为盐析剂,回收PDO | 95% | ||
| 1 | 刘建明, 曾安平. 无细胞多酶分子机器赋能二氧化碳的高值利用及其挑战[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(5): 825-832. |
| LIU J M, ZENG A P. Cell-free multi-enzyme machines for CO2 capture, utilization and its associated challenges[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(5): 825-832. | |
| 2 | 杨苗苗, 员君华, 张欢欢, 等. 基于甘油的1,3-丙二醇生物合成的代谢局限及其改造策略[J]. 生物工程学报, 2018, 34(7): 1069-1080. |
| YANG M M, YUN J H, ZHANG H H, et al. Bottlenecks and modification strategies of 1,3-propanediol biosynthesis from glycerol[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2018, 34(7): 1069-1080. | |
| 3 | NAKAMURA C E, WHITED G M. Metabolic engineering for the microbial production of 1,3-propanediol[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2003, 14(5): 454-459. |
| 4 | 刘永飞, 刘建明, 聂晶磊, 等. 基于CO2等碳一底物的化学品生物合成技术进展及挑战[J]. 科学通报, 2023, 68(19): 2470-2488. |
| LIU Y F, LIU J M, NIE J L, et al. Advances and perspectives of biosynthesis of chemicals based on CO2 and other one-carbon feedstocks[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2023, 68(19): 2470-2488. | |
| 5 | VIVEK N, PANDEY A, BINOD P. Production and applications of 1,3-propanediol[M/OL]// Current Developments in biotechnology and bioengineering. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2017: 719-738. [2024-03-11]. . |
| 6 | KALISA N Y, GAO X D. Current trends in efficient production of 1,3-propanediol[J]. Journal of Academia and Industrial Research, 2018, 6(8): 137-148. |
| 7 | ZHANG Y J, MA C W, DISCHERT W, et al. Engineering of phosphoserine aminotransferase increases the conversion of l-homoserine to 4-hydroxy-2-ketobutyrate in a glycerol-independent pathway of 1,3-propanediol production from glucose[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 14(9): e1900003. |
| 8 | LI Z H, WU Z Y, CEN X C, et al. Efficient production of 1,3-propanediol from diverse carbohydrates via a non-natural pathway using 3-hydroxypropionic acid as an intermediate[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2021, 10(3): 478-486. |
| 9 | WANG C, REN J, ZHOU L B, et al. An aldolase-catalyzed new metabolic pathway for the assimilation of formaldehyde and methanol to synthesize 2-keto-4-hydroxybutyrate and 1,3-propanediol in Escherichia coli [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(11): 2483-2493. |
| 10 | MENG H, WANG C, YUAN Q P, et al. An aldolase-based new pathway for bioconversion of formaldehyde and ethanol into 1,3-propanediol in Escherichia coli [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2021, 10(4): 799-809. |
| 11 | SUN X M, REN L J, BI Z Q, et al. Development of a cooperative two-factor adaptive-evolution method to enhance lipid production and prevent lipid peroxidation in Schizochytrium sp[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2018, 11: 65. |
| 12 | ZHU Y T, WANG Y X, GAO H, et al. Current advances in microbial production of 1,3-propanediol[J]. Biofuels, Bioproducts and Biorefining, 2021, 15(5): 1566-1583. |
| 13 | FOKUM E, ZABED H M, YUN J, et al. Recent technological and strategical developments in the biomanufacturing of 1,3-propanediol from glycerol[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 2021, 18(8): 2467-2490. |
| 14 | MA J S, JIANG H, HECTOR S B, et al. Adaptability of Klebsiella pneumoniae 2e, a newly isolated 1,3-propanediol-producing strain, to crude glycerol as revealed by genomic profiling[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2019, 85(10): e00254-19. |
| 15 | XU Y Z, GUO N N, ZHENG Z M, et al. Metabolism in 1,3-propanediol fed-batch fermentation by a D-lactate deficient mutant of Klebsiella pneumoniae [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2009, 104(5): 965-972. |
| 16 | JUN S A, MOON C, KANG C H, et al. Microbial fed-batch production of 1,3-propanediol using raw glycerol with suspended and immobilized Klebsiella pneumoniae [J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2010, 161(1-8): 491-501. |
| 17 | WANG X L, ZHOU J J, SHEN J T, et al. Sequential fed-batch fermentation of 1,3-propanediol from glycerol by Clostridium butyricum DL07[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2020, 104(21): 9179-9191. |
| 18 | MARTINS F F, LIBERATO V D S S, RIBEIRO C M S, et al. Low-cost medium for 1,3-propanediol production from crude glycerol by Clostridium butyricum [J]. Biofuels, Bioproducts and Biorefining, 2020, 14(5): 1125-1134. |
| 19 | WISCHRAL D, ZHANG J Z, CHENG C, et al. Production of 1,3-propanediol by Clostridium beijerinckii DSM 791 from crude glycerol and corn steep liquor: process optimization and metabolic engineering[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 212: 100-110. |
| 20 | DE SANTANA J S, SILVA J L DA, DUTRA E D, et al. Production of 1,3-propanediol by Lactobacillus diolivorans from agro-industrial residues and cactus cladode acid hydrolyzate[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2021, 193(5): 1585-1601. |
| 21 | CASSIR N, BENAMAR S, KHALIL J B, et al. Clostridium butyricum strains and dysbiosis linked to necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm neonates[J]. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 2015, 61(7): 1107-1115. |
| 22 | CASSIR N, BENAMAR S, LA SCOLA B. Clostridium butyricum: from beneficial to a new emerging pathogen[J]. Clinical Microbiology and Infection, 2016, 22(1): 37-45. |
| 23 | SUN Y Q, SHEN J T, YAN L, et al. Advances in bioconversion of glycerol to 1,3-propanediol: prospects and challenges[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2018, 71: 134-146. |
| 24 | RAMAKRISHNAN G G, NEHRU G, SUPPURAM P, et al. Bio-transformation of glycerol to 3-hydroxypropionic acid using resting cells of Lactobacillus reuteri [J]. Current Microbiology, 2015, 71(4): 517-523. |
| 25 | LINDLBAUER K A, MARX H, SAUER M. Effect of carbon pulsing on the redox household of Lactobacillus diolivorans in order to enhance 1,3-propanediol production[J]. New Biotechnology, 2017, 34: 32-39. |
| 26 | JU J H, WANG D X, HEO S Y, et al. Enhancement of 1,3-propanediol production from industrial by-product by Lactobacillus reuteri CH53[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2020, 19(1): 6. |
| 27 | KAEDING T, DALUZ J, KUBE J, et al. Integrated study of fermentation and downstream processing in a miniplant significantly improved the microbial 1,3-propanediol production from raw glycerol[J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2015, 38(3): 575-586. |
| 28 | BIEBL H. Fermentation of glycerol by Clostridium pasteurianum: batch and continuous culture studies[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2001, 27(1): 18-26. |
| 29 | GROEGER C, WANG W, SABRA W, et al. Metabolic and proteomic analyses of product selectivity and redox regulation in Clostridium pasteurianum grown on glycerol under varied iron availability[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2017, 16(1): 64. |
| 30 | SARCHAMI T, MUNCH G, JOHNSON E, et al. A review of process-design challenges for industrial fermentation of butanol from crude glycerol by non-biphasic Clostridium pasteurianum [J]. Fermentation, 2016, 2(2): 13. |
| 31 | JENSEN T O, KVIST T, MIKKELSEN M J, et al. Fermentation of crude glycerol from biodiesel production by Clostridium pasteurianum [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2012, 39(5): 709-717. |
| 32 | SANDOVAL N R, VENKATARAMANAN K P, GROTH T S, et al. Whole-genome sequence of an evolved Clostridium pasteurianum strain reveals Spo0A deficiency responsible for increased butanol production and superior growth[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2015, 8: 227. |
| 33 | ZHANG C J, SHARMA S, MA C W, et al. Strain evolution and novel downstream processing with integrated catalysis enable highly efficient coproduction of 1,3-propanediol and organic acid esters from crude glycerol[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2022, 119(6): 1450-1466. |
| 34 | ZHANG C J, SHARMA S, WANG W, et al. A novel downstream process for highly pure 1,3-propanediol from an efficient fed-batch fermentation of raw glycerol by Clostridium pasteurianum [J]. Engineering in Life Sciences, 2021, 21(6): 351-363. |
| 35 | ZHANG C J, TRAITRONGSAT P, ZENG A P. Electrochemically mediated bioconversion and integrated purification greatly enhanced co-production of 1,3-propanediol and organic acids from glycerol in an industrial bioprocess[J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2023, 46(4): 565-575. |
| 36 | BIEBL H, MENZEL K, ZENG A P, et al. Microbial production of 1,3-propanediol[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 1999, 52(3): 289-297. |
| 37 | JOHNSON E E, REHMANN L. The role of 1,3-propanediol production in fermentation of glycerol by Clostridium pasteurianum [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 209: 1-7. |
| 38 | SARCHAMI T, JOHNSON E, REHMANN L. Optimization of fermentation condition favoring butanol production from glycerol by Clostridium pasteurianum DSM 525[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 208: 73-80. |
| 39 | SCHWARZ K M, GROSSE-HONEBRINK A, DERECKA K, et al. Towards improved butanol production through targeted genetic modification of Clostridium pasteurianum [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 40: 124-137. |
| 40 | SUN J B, VAN DEN HEUVEL J, SOUCAILLE P, et al. Comparative genomic analysis of dha regulon and related genes for anaerobic glycerol metabolism in bacteria[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2003, 19(2): 263-272. |
| 41 | WESTBROOK A W, MISCEVIC D, KILPATRICK S, et al. Strain engineering for microbial production of value-added chemicals and fuels from glycerol[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2019, 37(4): 538-568. |
| 42 | MOON C L, LEE C H, SANG B I, et al. Optimization of medium compositions favoring butanol and 1,3-propanediol production from glycerol by Clostridium pasteurianum [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(22): 10561-10568. |
| 43 | MALAVIYA A, JANG Y S, LEE S Y. Continuous butanol production with reduced byproducts formation from glycerol by a hyper producing mutant of Clostridium pasteurianum [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2012, 93(4): 1485-1494. |
| 44 | SABRA W, GROEGER C, SHARMA P N, et al. Improved n-butanol production by a non-acetone producing Clostridium pasteurianum DSMZ 525 in mixed substrate fermentation[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2014, 98(9): 4267-4276. |
| 45 | SABRA W, WANG W, SURANDRAM S, et al. Fermentation of mixed substrates by Clostridium pasteurianum and its physiological, metabolic and proteomic characterizations[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2016, 15(1): 114. |
| 46 | LAN E I, LIAO J C. Metabolic engineering of cyanobacteria for L-butanol production from carbon dioxide[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2011, 13(4): 353-363. |
| 47 | BUCKEL W, THAUER R K. Energy conservation via electron bifurcating ferredoxin reduction and proton/Na+ translocating ferredoxin oxidation[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics, 2013, 1827(2): 94-113. |
| 48 | DEMMER J K, CHOWDHURY N PAL, SELMER T, et al. The semiquinone swing in the bifurcating electron transferring flavoprotein/butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase complex from Clostridium difficile[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 1577. |
| 49 | GALLARDO R, ALVES M, RODRIGUES L R. Modulation of crude glycerol fermentation by Clostridium pasteurianum DSM 525 towards the production of butanol[J]. Biomass and Bioenergy, 2014, 71: 134-143. |
| 50 | GROEGER C, SABRA W, ZENG A P. Simultaneous production of 1,3-propanediol and n-butanol by Clostridium pasteurianum: in situ gas stripping and cellular metabolism[J]. Engineering in Life Sciences, 2016, 16(7): 664-674. |
| 51 | GALLAZZI A, BRANSKA B, MARINELLI F, et al. Continuous production of n-butanol by Clostridium pasteurianum DSM 525 using suspended and surface-immobilized cells[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2015, 216: 29-35. |
| 52 | KHANNA S, GOYAL A, MOHOLKAR V S. Effect of fermentation parameters on bio-alcohols production from glycerol using immobilized Clostridium pasteurianum: an optimization study[J]. Preparative Biochemistry & Biotechnology, 2013, 43(8): 828-847. |
| 53 | KHANNA S, GOYAL A, MOHOLKAR V S. Production of n-butanol from biodiesel derived crude glycerol using Clostridium pasteurianum immobilized on amberlite[J]. Fuel, 2013, 112: 557-561. |
| 54 | TAN J P, TEE Z K, ISAHAK W N R W, et al. Improved fermentability of pretreated glycerol enhanced bioconversion of 1,3-propanediol[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(37): 12565-12573. |
| 55 | JOHNSON E E, REHMANN L. Self-synchronized oscillatory metabolism of Clostridium pasteurianum in continuous culture[J]. Processes, 2020, 8(2): 137. |
| 56 | CHOI O Y, KIM T, WOO H M, et al. Electricity-driven metabolic shift through direct electron uptake by electroactive heterotroph Clostridium pasteurianum [J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 6961. |
| 57 | KAO W C, LIN D S, CHENG C L, et al. Enhancing butanol production with Clostridium pasteurianum CH4 using sequential glucose-glycerol addition and simultaneous dual-substrate cultivation strategies[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 135: 324-330. |
| 58 | EZEJI T C, QURESHI N, BLASCHEK H P. Production of acetone, butanol and ethanol by Clostridium beijerinckii BA101 and in situ recovery by gas stripping[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2003, 19(6): 595-603. |
| 59 | UTESCH T, SABRA W, PRESCHER C, et al. Enhanced electron transfer of different mediators for strictly opposite shifting of metabolism in Clostridium pasteurianum grown on glycerol in a new electrochemical bioreactor[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2019, 116(7): 1627-1643. |
| 60 | LI J Z, ZHANG Y F, SUN K, et al. Optimization of a cathodic electro-fermentation process for enhancing co-production of butanol and hydrogen via acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation of Clostridium beijerinckii [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2022, 251: 114987. |
| 61 | ZENG A P. New bioproduction systems for chemicals and fuels: needs and new development[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2019, 37(4): 508-518. |
| 62 | JIANG Y, LU L, WANG H, et al. Electrochemical control of redox potential arrests methanogenesis and regulates products in mixed culture electro-fermentation[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(7): 8650-8658. |
| 63 | ARBTER P, SABRA W, UTESCH T, et al. Metabolomic and kinetic investigations on the electricity-aided production of butanol by Clostridium pasteurianum strains[J]. Engineering in Life Sciences, 2021, 21(3/4): 181-195. |
| 64 | ARBTER P, WIDDERICH N, UTESCH T, et al. Control of redox potential in a novel continuous bioelectrochemical system led to remarkable metabolic and energetic responses of Clostridium pasteurianum grown on glycerol[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2022, 21(1): 178. |
| 65 | SU L Q, SHEN Y B, ZHANG W K, et al. Cofactor engineering to regulate NAD+/NADH ratio with its application to phytosterols biotransformation[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2017, 16(1): 182. |
| 66 | UTESCH T, ZENG A P. A novel All-in-one electrolysis electrode and bioreactor enable better study of electrochemical effects and electricity-aided bioprocesses[J]. Engineering in Life Sciences, 2018, 18(8): 600-610. |
| 67 | PYNE M E, MOO-YOUNG M, CHUNG D A, et al. Development of an electrotransformation protocol for genetic manipulation of Clostridium pasteurianum [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2013, 6(1): 50. |
| 68 | PYNE M E, MOO-YOUNG M, CHUNG D A, et al. Expansion of the genetic toolkit for metabolic engineering of Clostridium pasteurianum: chromosomal gene disruption of the endogenous CpaAI restriction enzyme[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2014, 7(1): 163. |
| 69 | SARMA S, ORTEGA D, MINTON N P, et al. Homologous overexpression of hydrogenase and glycerol dehydrogenase in Clostridium pasteurianum to enhance hydrogen production from crude glycerol[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 284: 168-177. |
| 70 | VEES C A, NEUENDORF C S, PFLÜGL S. Towards continuous industrial bioprocessing with solventogenic and acetogenic clostridia: challenges, progress and perspectives[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2020, 47(9/10): 753-787. |
| 71 | HONG Y, ARBTER P, WANG W, et al. Introduction of glycine synthase enables uptake of exogenous formate and strongly impacts the metabolism in Clostridium pasteurianum [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2021, 118(3): 1366-1380. |
| 72 | GALLARDO R, ALVES M, RODRIGUES L R. Influence of nutritional and operational parameters on the production of butanol or 1,3-propanediol from glycerol by a mutant Clostridium pasteurianum [J]. New Biotechnology, 2017, 34: 59-67. |
| 73 | YANG M M, AN Y F, ZABED H M, et al. Random mutagenesis of Clostridium butyricum strain and optimization of biosynthesis process for enhanced production of 1,3-propanediol[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 284: 188-196. |
| 74 | JENSEN T O, KVIST T, MIKKELSEN M J, et al. Production of 1,3-PDO and butanol by a mutant strain of Clostridium pasteurianum with increased tolerance towards crude glycerol[J]. AMB Express, 2012, 2(1): 44. |
| 75 | SIVARAMAKRISHNAN R, INCHAROENSAKDI A. Enhancement of lipid production in Scenedesmus sp. by UV mutagenesis and hydrogen peroxide treatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 235: 366-370. |
| 76 | YANG Y P, NIE X Q, JIANG Y Q, et al. Metabolic regulation in solventogenic clostridia: regulators, mechanisms and engineering[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2018, 36(4): 905-914. |
| 77 | YU Q H, LI Y C, WU B, et al. Novel mutagenesis and screening technologies for food microorganisms: advances and prospects[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2020, 104(4): 1517-1531. |
| 78 | EOM G E, LEE H B, KIM S H. Development of a genome-targeting mutator for the adaptive evolution of microbial cells[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2022, 50(7): e38. |
| 79 | SANDBERG T E, SALAZAR M J, WENG L L, et al. The emergence of adaptive laboratory evolution as an efficient tool for biological discovery and industrial biotechnology[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 56: 1-16. |
| 80 | ZHANG A H, ZHUANG X Y, CHEN K N, et al. Adaptive evolution of Clostridium butyricum and scale-up for high-concentration 1,3-propanediol production[J]. AIChE Journal, 2019, 65(1): 32-39. |
| 81 | LACROIX R A, SANDBERG T E, O’BRIEN E J, et al. Use of adaptive laboratory evolution to discover key mutations enabling rapid growth of Escherichia coli K-12 MG1655 on glucose minimal medium[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 81(1): 17-30. |
| 82 | SANDBERG T E, PEDERSEN M, LACROIX R A, et al. Evolution of Escherichia coli to 42 ℃ and subsequent genetic engineering reveals adaptive mechanisms and novel mutations[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2014, 31(10): 2647-2662. |
| 83 | WONG B G, MANCUSO C P, KIRIAKOV S, et al. Precise, automated control of conditions for high-throughput growth of yeast and bacteria with eVOLVER[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(7): 614-623. |
| 84 | SZYMANOWSKA-POWAŁOWSKA D, KUBIAK P. Effect of 1,3-propanediol, organic acids, and ethanol on growth and metabolism of Clostridium butyricum DSP1[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 99(7): 3179-3189. |
| 85 | SZYMANOWSKA-POWAŁOWSKA D. The effect of high concentrations of glycerol on the growth, metabolism and adaptation capacity of Clostridium butyricum DSP1[J]. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology, 2015, 18(2): 128-133. |
| 86 | NEMATI F, GOLMAKANI M T, NIAKOUSARI M, et al. Optimization of solvent free ohmic-assisted heating as a promising esterification tool for ethyl butyrate synthesis[J]. LWT: Food Science and Technology, 2021, 141: 110890. |
| 87 | XUE D S, YAO D H, YOU X H, et al. Green synthesis of the flavor esters with a marine Candida parapsilosis esterase expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Indian Journal of Microbiology, 2020, 60(2): 175-181. |
| 88 | XIU Z L, ZENG A P. Present state and perspective of downstream processing of biologically produced 1,3-propanediol and 2,3-butanediol[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2008, 78(6): 917-926. |
| 89 | LEEJEERAJUMNEAN A, AMES J M, OWENS J D. Effect of ammonia on the growth of Bacillus species and some other bacteria[J]. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 2000, 30(5): 385-389. |
| 90 | WANG K L, LI J, LIU P, et al. Pressure swing distillation for the separation of methyl acetate-methanol azeotrope[J]. Asia-Pacific Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2019, 14(3): e2319. |
| 91 | WANG S Z, QIU L H, DAI H F, et al. Highly pure 1,3-propanediol: separation and purification from crude glycerol-based fermentation[J]. Engineering in Life Sciences, 2015, 15(8): 788-796. |
| 92 | GONG Y, TANG Y, WANG X L, et al. The possibility of the desalination of actual 1,3-propanediol fermentation broth by electrodialysis[J]. Desalination, 2004, 161(2): 169-178. |
| 93 | ADKESSON D M, ALSOP A W, AMES T T, et al. Purification of biologically-produced 1,3-propanediol: US2011015281A1[P]. 2011-06-23. |
| 94 | WU R C, XU Y Z, SONG Y Q, et al. A novel strategy for salts recovery from 1,3-propanediol fermentation broth by bipolar membrane electrodialysis[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2011, 83: 9-14. |
| 95 | GONG Y, DAI L M, WANG X L, et al. Effects of transport properties of ion-exchange membranes on desalination of 1,3-propanediol fermentation broth by electrodialysis[J]. Desalination, 2006, 191(1-3): 193-199. |
| 96 | GAO S J, ZHANG D J, SUN Y Q, et al. Separation of 1,3-propanediol from glycerol-based fermentations of Klebsiella pneumoniae by alcohol dilution crystallization[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Engineering in China, 2007, 1: 202-207. |
| 97 | BOONSONGSAWAT T, SHOTIPRUK A, TANTAYAKOM V, et al. Solvent extraction of biologically derived 1,3-propanediol with ethyl acetate and ethanol cosolvent[J]. Separation Science and Technology, 2010, 45(4): 541-547. |
| 98 | BOONOUN P, LAOSIRIPOJANA N, MUANGNAPOH C, et al. Application of sulfonated carbon-based catalyst for reactive extraction of 1,3-propanediol from model fermentation mixture[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2010, 49: 12352-12357. |
| 99 | CUI C X, ZHANG Z, CHEN B Q. Environmentally-friendly strategy for separation of 1,3-propanediol using biocatalytic conversion[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 245: 477-482. |
| 100 | VIVEK N, PANDEY A, BINOD P. An efficient aqueous two phase systems using dual inorganic electrolytes to separate 1,3-propanediol from the fermented broth[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 254: 239-246. |
| 101 | LI Z G, SUN Y Q, ZHENG W L, et al. A novel and environment-friendly bioprocess of 1,3-propanediol fermentation integrated with aqueous two-phase extraction by ethanol/sodium carbonate system[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 80: 68-75. |
| 102 | LI Z, YAN L, ZHOU J J, et al. Two-step salting-out extraction of 1,3-propanediol, butyric acid and acetic acid from fermentation broths[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 209: 246-253. |
| 103 | DAI J Y, LIU C J, XIU Z L. Sugaring-out extraction of 2,3-butanediol from fermentation broths[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2015, 50(11): 1951-1957. |
| [1] | YING Hanjie, LIU Dong, WANG Zhenyu, SHEN Tao, ZHUANG Wei, ZHU Chenjie. Exploring industrial biomanufacturing and the goal of “carbon neutrality” [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 1-7. |
| [2] | ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job, CHEN Xuemei, SHI Ting. Price to Cost-of-raw-materials Ratio (PC) of biomanufacturing: definition and application [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 8-17. |
| [3] | CHENG Feng, ZOU Shuping, XU Jianmiao, TANG Heng, XUE Yaping, ZHENG Yuguo. BioHPP®: a benchmark of biomanufacturing for high optically pure L-phosphinothricin [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1404-1418. |
| [4] | ZHAO Liang, LI Zhenshuai, FU Liping, LYU Ming, WANG Shi’an, ZHANG Quan, LIU Licheng, LI Fuli, LIU Ziyong. Progress in biomanufacturing of lipids and single cell protein from one-carbon compounds [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1300-1318. |
| [5] | CHAI Meng, WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi. Synthesis of organic acids from lignocellulose by biotransformation [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [6] | SHI Ting, SONG Zhan, SONG Shiyi, ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job. In vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): a new frontier of industrial biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job. The enlightenment of the Chinese philosophy “Tao-Fa-Shu-Qi” to industrial biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1231-1241. |
| [8] | SUN Huili, CUI Jinyu, LUAN Guodong, LYU Xuefeng. Progress of cyanobacterial synthetic biotechnology for efficient light-driven carbon fixation and ethanol production [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(6): 1161-1177. |
| [9] | SUN Meili, WANG Kaifeng, LU Ran, JI Xiaojun. Rewiring and application of Yarrowia lipolytica chassis cell [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(4): 779-807. |
| [10] | CUI Jinyu, ZHANG Aidi, LUAN Guodong, LYU Xuefeng. Engineering microalgae for photosynthetic biosynthesis: progress and prospect [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(5): 884-900. |
| [11] | ZHANG Can, SHI Liyang, DAI Jianwu. Cultured meat from biomaterials: challenges and prospects [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(4): 676-689. |
| [12] | REN Jie, ZENG Anping. CO2 based biomanufacturing: from basic research to industrial application [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(6): 854-862. |
| [13] | ZHANG Xiaolong, WANG Chenyun, LIU Yanfeng, LI Jianghua, LIU Long, DU Guocheng. Research progress of constructing efficient biomanufacturing system based on synthetic biotechnology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(6): 863-875. |
| [14] | XIONG Liangbin, SONG Lu, ZHAO Yunqiu, LIU Kun, LIU Yongjun, WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi. Green biomanufacturing of steroids: from biotransformation to de novo synthesis by microorganisms [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(6): 942-963. |
| [15] | ZHANG Yi-Heng. Remembering Professor Daniel I.C. Wang’s contribution to biorefining and my perspective on the progress [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(4): 497-508. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||