Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (6): 1223-1245.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-050
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Microbial conversion and in vitro enzymatic catalysis for carbon dioxide utilization: a review
YE Wei1, LI Rui1,2, JIANG Weihong1, GU Yang1
- 1.CAS Center for Excellence in Molecular Plant Sciences,CAS-Key Laboratory of Synthetic Biology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shanghai 200032,China
2.College of Life Sciences,Henan University,Kaifeng 475004,Henan,China
-
Received:2023-07-11Revised:2023-09-18Online:2024-01-19Published:2023-12-31 -
Contact:GU Yang
二氧化碳微生物转化与体外酶催化体系研究进展
叶伟1, 李芮1,2, 姜卫红1, 顾阳1
- 1.中国科学院分子植物科学卓越创新中心,中国科学院合成生物学重点实验室,上海 200032
2.河南大学生命科学学院,河南 开封 475004
-
通讯作者:顾阳 -
作者简介:叶伟 (1995—),男,实验师。研究方向为微生物代谢调控与代谢工程。E-mail:wye@cemps.ac.cn李芮 (2001—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为微生物代谢调控与代谢工程。E-mail:lirui21@cemps.ac.cn顾阳 (1977—),男,研究员。研究方向为一碳生物转化。E-mail:ygu@cemps.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0901500);上海市科学技术委员会科研计划项目(21DZ1209100);中国科学院洁净能源创新研究院合作基金项目(DNL202013)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YE Wei, LI Rui, JIANG Weihong, GU Yang. Microbial conversion and in vitro enzymatic catalysis for carbon dioxide utilization: a review[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(6): 1223-1245.
叶伟, 李芮, 姜卫红, 顾阳. 二氧化碳微生物转化与体外酶催化体系研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(6): 1223-1245.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2023-050

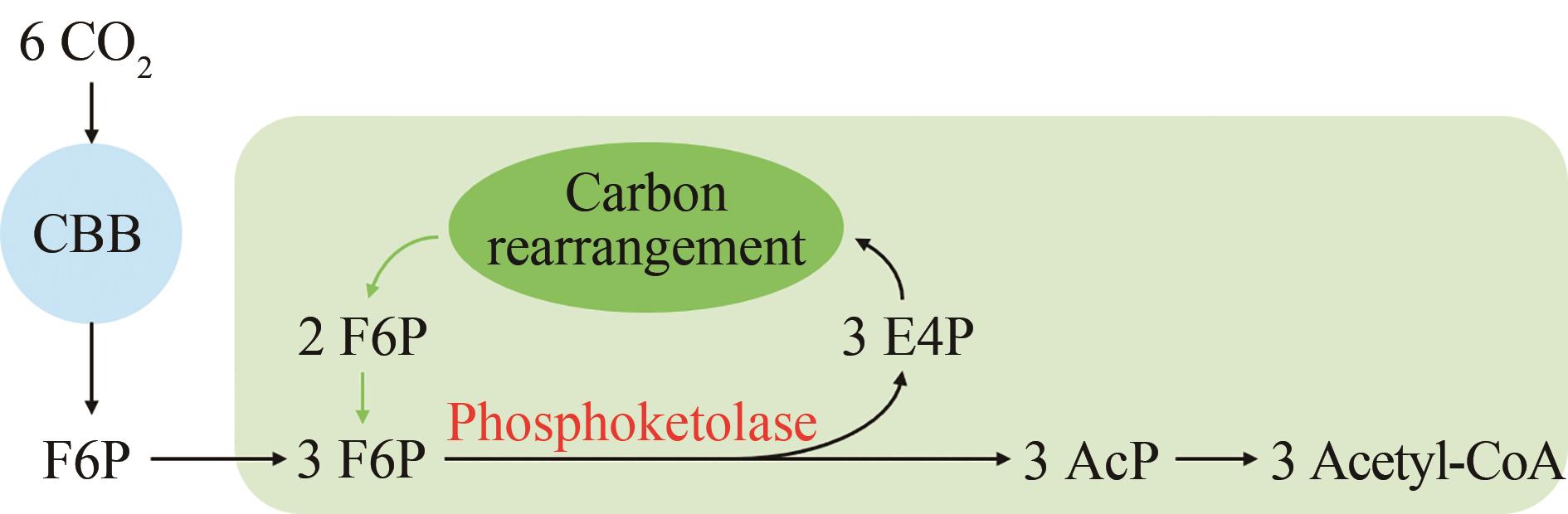
Fig. 3 Schematic diagram of the coupling of glycolysis pathway and Rubisco(Dashed arrows indicate multi-step reactions) 3-PGA—3-Phosphoglycerate;PEP—Phosphoenolpyruvate;Ru5P—Ribulose-5-phosphate;RuBP—Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate;PrkA—phosphoribulokinase
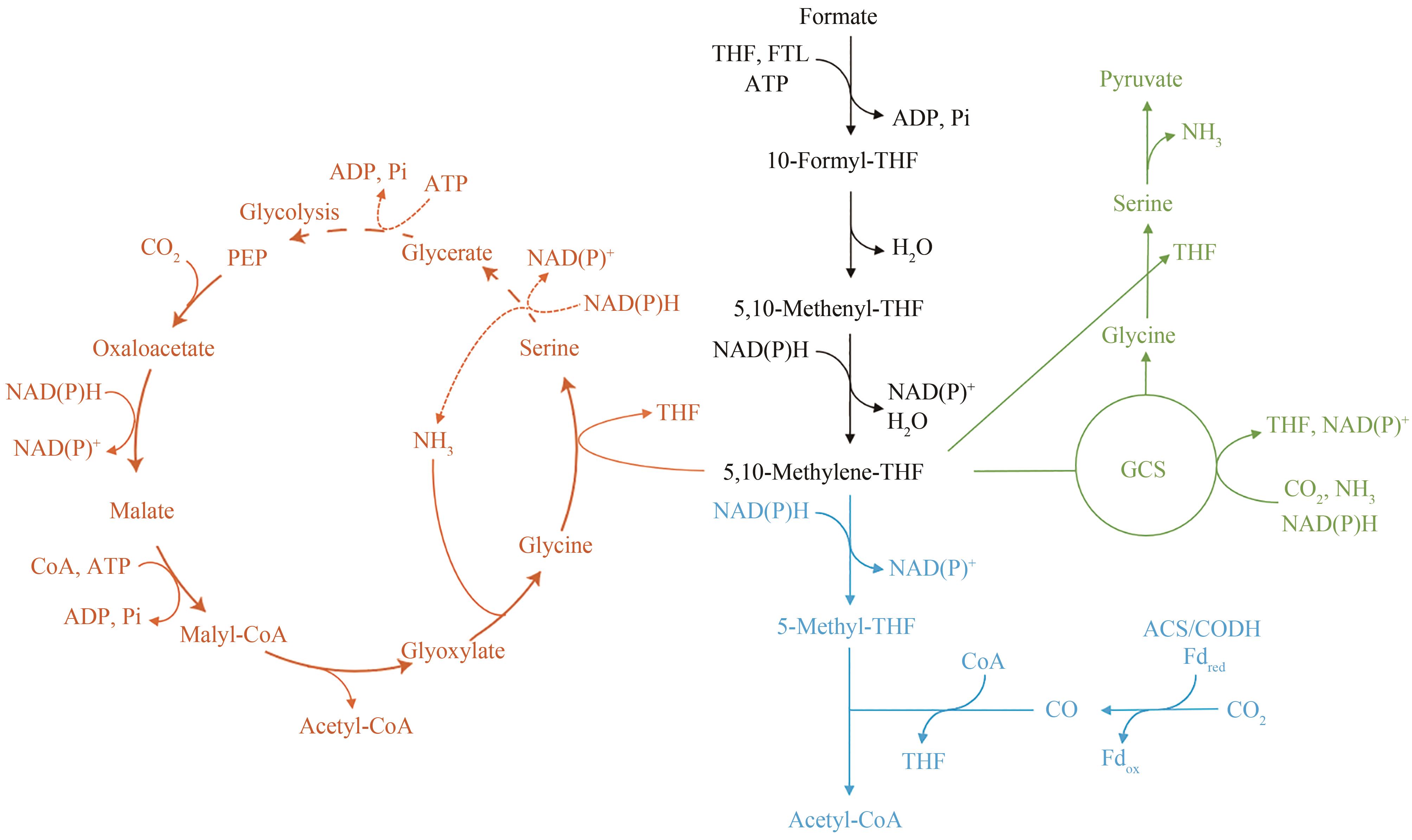
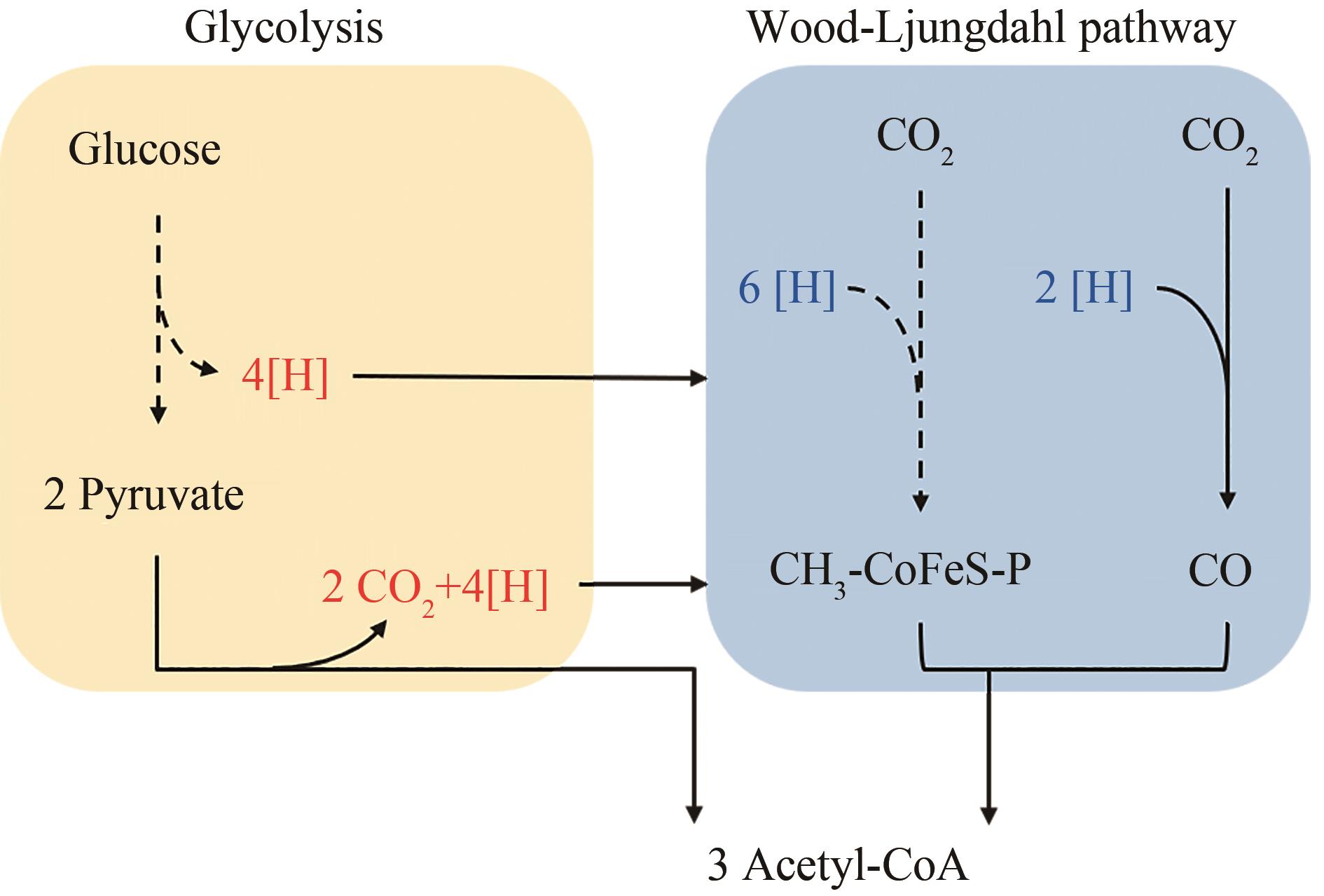
Fig. 4 Formate-assimilating pathwaysPEP—Phosphoenolpyruvate;GCS—Glycine cleavage system (Orange represents serine pathway; Blue indicates the Wood-Ljungdahl pathway; Green represents reducing glycine pathway. Dashed arrows indicate multi-step reactions)
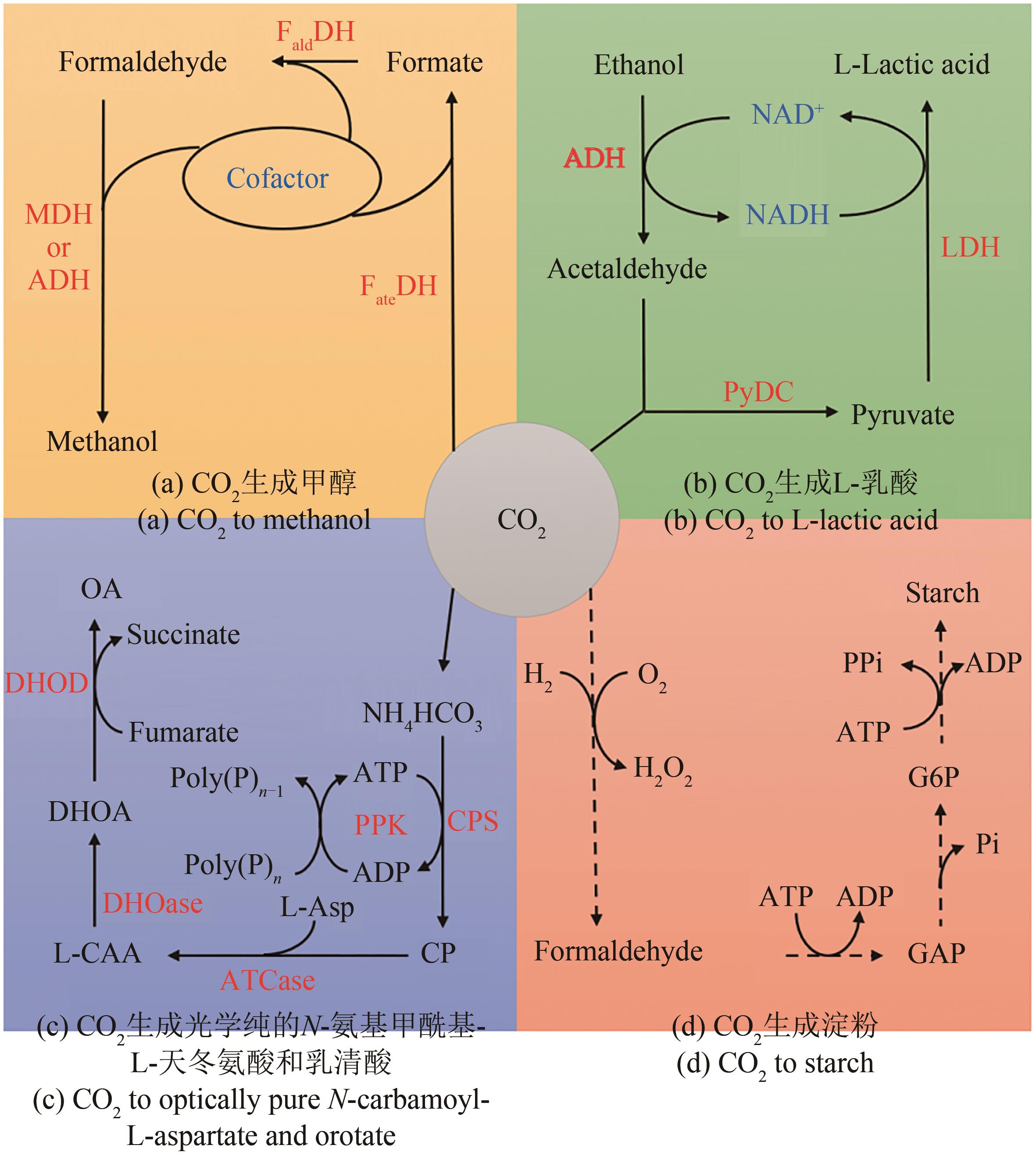
Fig. 5 Conversion of CO2 to various products bymulti-enzyme cascade catalysis in vitro(Dashed arrows indicate multi-step reactions) FateDH—Formate dehydrogenase; FaldDH—Formaldehyde dehydrogenase; MDH—Methanol dehydrogenase; ADH—Alcohol dehydrogenase; PyDC—Pyruvate decarboxylase; LDH—Lactate dehydrogenase; CPS—Carbamoyl phosphate synthase; PPK—Polyphosphate kinase; CP—Carbamoyl phosphate; ATCase—Aspartate carbamoyl-transferase; L-CAA—N-Carbamoyl-L-aspartate; DHOase—Dihydroorotase; DHOA—Dihydroorotate; DHOD—Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase; OA—Orotate; GAP—Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; G6P—Glucose 6-phosphate
| 1 | ARESTA M, DIBENEDETTO A. Utilisation of CO2 as a chemical feedstock: opportunities and challenges[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2007(28): 2975-2992. |
| 2 | GUPTA H, FAN L S. Carbonation-calcination cycle using high reactivity calcium oxide for carbon dioxide separation from flue gas[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2002, 41(16): 4035-4042. |
| 3 | LEUNG D Y C, CARAMANNA G, MAROTO-VALER M M. An overview of current status of carbon dioxide capture and storage technologies[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2014, 39: 426-443. |
| 4 | MARKEWITZ P, KUCKSHINRICHS W, LEITNER W, et al. Worldwide innovations in the development of carbon capture technologies and the utilization of CO2 [J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(6): 7281-7305. |
| 5 | MIKKELSEN M, JØRGENSEN M, KREBS F C. The teraton challenge. A review of fixation and transformation of carbon dioxide[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2010, 3(1): 43-81. |
| 6 | 李婉麒, 杨凤娟, 贾德臣, 等. 合成气的生物利用与定向转化[J]. 化工进展, 2023, 42(1): 73-85. |
| LI W Q, YANG F J, JIA D C, et al. Biological utilization and conversion of syngas[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2023, 42(1): 73-85. | |
| 7 | XIAO L, LIU G X, GONG F Y, et al. A minimized synthetic carbon fixation cycle[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2022, 12(1): 799-808. |
| 8 | ZHAO T T, FENG G H, CHEN W, et al. Artificial bioconversion of carbon dioxide[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2019, 40(10): 1421-1437. |
| 9 | MAHESHWARI N, KRISHNA P K, THAKUR I S, et al. Biological fixation of carbon dioxide and biodiesel production using microalgae isolated from sewage waste water[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(22): 27319-27329. |
| 10 | LIAO J C, MI L, PONTRELLI S, et al. Fuelling the future: microbial engineering for the production of sustainable biofuels[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2016, 14(5): 288-304. |
| 11 | 谢丽, 杜诗云, 卜凡. 同型产乙酸菌研究进展及其环境生物技术应用[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(1): 67-73, 108. |
| XIE L, DU S Y, BU F. Homoacetogen and its application in environmental biotechnology[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2018, 46(1): 67-73, 108. | |
| 12 | TAN X Y, NIELSEN J. The integration of bio-catalysis and electrocatalysis to produce fuels and chemicals from carbon dioxide[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2022, 51(11): 4763-4785. |
| 13 | TALEKAR S, JO B H, DORDICK J S, et al. Carbonic anhydrase for CO2 capture, conversion and utilization[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2022, 74: 230-240. |
| 14 | KAJLA S, KUMARI R, NAGI G K. Microbial CO2 fixation and biotechnology in reducing industrial CO2 emissions[J]. Archives of Microbiology, 2022, 204(2): 149. |
| 15 | MAHESHWARI N, THAKUR I S, SRIVASTAVA S. Role of carbon-dioxide sequestering bacteria for clean air environment and prospective production of biomaterials: a sustainable approach[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2022, 29(26): 38950-38971. |
| 16 | BARATI B, ZENG K, BAEYENS J, et al. Recent progress in genetically modified microalgae for enhanced carbon dioxide sequestration[J]. Biomass and Bioenergy, 2021, 145: 105927. |
| 17 | 王竞, 周集体, 张晶晶, 等. 固定CO2氢细菌的筛选及其培养条件优化[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2000, 6(3): 271-275. |
| WANG J, ZHOU J T, ZHANG J J, et al. Screening and culture conditions of hydrogen oxidizing bacteria[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2000, 6(3): 271-275. | |
| 18 | WANG B, LI Y Q, WU N, et al. CO2 bio-mitigation using microalgae[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2008, 79(5): 707-718. |
| 19 | KUMAR K, DASGUPTA C N, NAYAK B, et al. Development of suitable photobioreactors for CO2 sequestration addressing global warming using green algae and cyanobacteria[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(8): 4945-4953. |
| 20 | SKJÅNES K, REBOURS C, LINDBLAD P. Potential for green microalgae to produce hydrogen, pharmaceuticals and other high value products in a combined process[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2013, 33(2): 172-215. |
| 21 | CHENG J, HUANG Y, FENG J, et al. Improving CO2 fixation efficiency by optimizing Chlorella PY-ZU1 culture conditions in sequential bioreactors[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 144: 321-327. |
| 22 | CHEAH W Y, SHOW P L, CHANG J S, et al. Biosequestration of atmospheric CO2 and flue gas-containing CO2 by microalgae[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 184: 190-201. |
| 23 | SOLOVCHENKO A, KHOZIN-GOLDBERG I. High-CO2 tolerance in microalgae: possible mechanisms and implications for biotechnology and bioremediation[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2013, 35(11): 1745-1752. |
| 24 | ZHANG A, CARROLL A L, ATSUMI S. Carbon recycling by cyanobacteria: improving CO2 fixation through chemical production[J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2017, 364(16): fnx165. |
| 25 | 康瑞娟. 蓝藻的光合碳代谢特征及调控[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2004. |
| KANG R J. Characteristics and regulation of photosynthetic carbon metabolism in cyanobacteria[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Science, 2004. | |
| 26 | ZHAO B T, SU Y X. Process effect of microalgal-carbon dioxide fixation and biomass production: a review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2014, 31: 121-132. |
| 27 | GAO Z X, ZHAO H, LI Z M, et al. Photosynthetic production of ethanol from carbon dioxide in genetically engineered cyanobacteria[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(12): 9857-9865. |
| 28 | WANG Y P, SUN T, GAO X Y, et al. Biosynthesis of platform chemical 3-hydroxypropionic acid (3-HP) directly from CO2 in cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2016, 34: 60-70. |
| 29 | ANGERMAYR S A, VAN DER WOUDE A D, CORREDDU D, et al. Exploring metabolic engineering design principles for the photosynthetic production of lactic acid by Synechocystis sp. PCC6803[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2014, 7: 99. |
| 30 | ATSUMI S, HIGASHIDE W, LIAO J C. Direct photosynthetic recycling of carbon dioxide to isobutyraldehyde[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2009, 27(12): 1177-1180. |
| 31 | DE MORAIS M G, DE MORAIS E G, DUARTE J H, et al. Biological CO2 mitigation by microalgae: technological trends, future prospects and challenges[J]. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2019, 35(5): 78. |
| 32 | GUPTA P L, LEE S M, CHOI H J. A mini review: photobioreactors for large scale algal cultivation[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 31(9): 1409-1417. |
| 33 | SUH I S, LEE C G. Photobioreactor engineering: design and performance[J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 2003, 8(6): 313-321. |
| 34 | CHEN C Y, YEH K L, AISYAH R, et al. Cultivation, photobioreactor design and harvesting of microalgae for biodiesel production: a critical review[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(1): 71-81. |
| 35 | YEN H W, HU I C, CHEN C Y, et al. Microalgae-based biorefinery—from biofuels to natural products[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 135: 166-174. |
| 36 | 李金洋, 刘荣厚, 袁海荣. 沼气生物脱硫反应器的选择和设计[J]. 农机化研究, 2007, 29(3): 174-177. |
| LI J Y, LIU R H, YUAN H R. Selection and design of the biogas biological desulphurization reactor[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2007, 29(3): 174-177. | |
| 37 | 李金洋, 敖永华, 刘庆玉. 沼气脱硫方法的研究[J]. 农机化研究, 2008, 30(8): 228-230. |
| LI J Y, AO Y H, LIU Q Y. The research of biogas desulphurization technology[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2008, 30(8): 228-230. | |
| 38 | SRISAWAT P, HIGUCHI-TAKEUCHI M, NUMATA K. Microbial autotrophic biorefineries: perspectives for biopolymer production[J]. Polymer Journal, 2022, 54(10): 1139-1151. |
| 39 | WU X M, MA G, LIU C Y, et al. Biosynthesis of pinene in purple non-sulfur photosynthetic bacteria[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2021, 20(1): 101. |
| 40 | BEEKWILDER J, VAN HOUWELINGEN A, CANKAR K, et al. Valencene synthase from the heartwood of Nootka cypress (Callitropsis nootkatensis) for biotechnological production of valencene[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2014, 12(2): 174-182. |
| 41 | KHAN N E, NYBO S E, CHAPPELL J, et al. Triterpene hydrocarbon production engineered into a metabolically versatile host—Rhodobacter capsulatus [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2015, 112(8): 1523-1532. |
| 42 | REVELLES O, TARAZONA N, GARCÍA J L, et al. Carbon roadmap from syngas to polyhydroxyalkanoates in Rhodospirillum rubrum [J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2016, 18(2): 708-720. |
| 43 | REVELLES O, BENEROSO D, MENÉNDEZ J A, et al. Syngas obtained by microwave pyrolysis of household wastes as feedstock for polyhydroxyalkanoate production in Rhodospirillum rubrum [J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 2017, 10(6): 1412-1417. |
| 44 | 王西俜, 刘之慧, 詹毅, 等. 净化有机废水的光合细菌S1和S2菌株的分离鉴定[J]. 太阳能学报, 1993, 14(1): 43-47. |
| WANG X P, LIU Z H, ZHAN Y, et al. The isolation and identification of photosynthetic bacteria S1 and S2 in purifing process of organic waste water[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 1993, 14(1): 43-47. | |
| 45 | 杜翠红. 沼泽红假单胞菌RubisCO基因的克隆与表达及其固定二氧化碳特性的研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2003. |
| DU C H. Cloning and expression of RubisCO gene from Rhodopseudomonas palustris for CO2 fixation[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2003. | |
| 46 | HEINRICH D, RABERG M, STEINBÜCHEL A. Synthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) from unrelated carbon sources in engineered Rhodospirillum rubrum [J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2015, 362(8): fnv038. |
| 47 | 李艳丽, 胡佳俊, 付小花, 等. 非光合微生物菌群好氧固定CO2的研究[J]. 工业微生物, 2009, 39(5): 1-6. |
| LI Y L, HU J J, FU X H, et al. CO2 fixation with non-photosynthetic microbial flora under aerobic condition[J]. Industrial Microbiology, 2009, 39(5): 1-6. | |
| 48 | 彭艳丽, 赵华章, 杨亲正, 等. 微生物及酶固定二氧化碳的研究进展[J]. 化学与生物工程, 2010, 27(7): 10-13. |
| PENG Y L, ZHAO H Z, YANG Q Z, et al. Progress in microbial and enzyme immobilization of carbon dioxide[J]. Chemistry & Bioengineering, 2010, 27(7): 10-13. | |
| 49 | BOWIEN B, SCHLEGEL H G. Physiology and biochemistry of aerobic hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 1981, 35: 405-452. |
| 50 | NISHIHARA H, IGARASHI Y, KODAMA T, et al. Production and properties of glycogen in the marine obligate chemolithoautotroph, Hydrogenovibrio marinus [J]. Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering, 1993, 75(6): 414-416. |
| 51 | NGUYEN B T, KODAMA T, MINODA Y. Extracellular polysaccharide formed by Pseudomonas hydrogenovorain autotrophic culture and its physiological activities[J]. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 1980, 44(12): 2925-2930. |
| 52 | VOLOVA T G, ZHILA N O, KALACHEVA G S, et al. Effects of intracellular poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) reserves on physiological-biochemical properties and growth of Ralstonia eutropha [J]. Research in Microbiology, 2013, 164(2): 164-171. |
| 53 | BAE S, KWAK K, KIM S, et al. Isolation and characterization of CO2-fixing hydrogen-oxidizing marine bacteria[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2001, 91(5): 442-448. |
| 54 | CLAASSENS N J, BORDANABA-FLORIT G, COTTON C A R, et al. Replacing the Calvin cycle with the reductive glycine pathway in Cupriavidus necator [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 62: 30-41. |
| 55 | ISHIZAKI A, TANAKA K, TAGA N. Microbial production of poly-D-3-hydroxybutyrate from CO2 [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2001, 57(1/2): 6-12. |
| 56 | KIM S W, KIM J H, JEON S, et al. Eftect of hyperthermophilic Aeropyrum pernix chaperonins on the soluble expression of Pseudoalteromonas elyakovii alginate lyase in E .coli[C/OL]. 한국생물공학회 학술대회 학술대회자료: 2011 추계학술대회 및 국제심포지움, 2011: 225[2023-06-01]. . |
| KIM S W, KIM J H, JEON S, et al. Eftect of hyperthermophilic Aeropyrum pernix chaperonins on the soluble expression of Pseudoalteromonas elyakovii alginate lyase in E .coli[C/OL]. Proceedings of the Korean Society of Biotechnology: 2011 Autumn Conference and International Symposium, 2011: 225[2023-06-01]. . | |
| 57 | YU J. Fixation of carbon dioxide by a hydrogen-oxidizing bacterium for value-added products[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 34(7): 89. |
| 58 | IGARASHI K, KATO S. Extracellular electron transfer in acetogenic bacteria and its application for conversion of carbon dioxide into organic compounds[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 101(16): 6301-6307. |
| 59 | BENGELSDORF F R, BECK M H, ERZ C, et al. Bacterial anaerobic synthesis gas (syngas) and CO2 + H2 fermentation[M/OL]//Advances in applied microbiology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2018: 143-221 [2023-06-01]. . |
| 60 | SCHUCHMANN K, MÜLLER V. Energetics and application of heterotrophy in acetogenic bacteria[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2016, 82(14): 4056-4069. |
| 61 | SCHIEL-BENGELSDORF B, DÜRRE P. Pathway engineering and synthetic biology using acetogens[J]. FEBS Letters, 2012, 586(15): 2191-2198. |
| 62 | 贾德臣, 姜卫红, 顾阳. 食气梭菌的研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 2019, 46(2): 374-387. |
| JIA D C, JIANG W H, GU Y. Research progresses in gas-fermenting clostridia[J]. Microbiology China, 2019, 46(2): 374-387. | |
| 63 | HUANG H, CHAI C S, LI N, et al. CRISPR/Cas9-based efficient genome editing in Clostridium ljungdahlii, an autotrophic gas-fermenting bacterium[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2016, 5(12): 1355-1361. |
| 64 | LIEW F, HENSTRA A M, KӦPKE M, et al. Metabolic engineering of Clostridium autoethanogenum for selective alcohol production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 40: 104-114. |
| 65 | STRAUB M, DEMLER M, WEUSTER-BOTZ D, et al. Selective enhancement of autotrophic acetate production with genetically modified Acetobacterium woodii [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2014, 178: 67-72. |
| 66 | 姚伦, 周雍进. 一碳化合物生物利用和转化研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2023, 42(1): 16-29. |
| YAO L, ZHOU Y J. Progress in microbial utilization of one-carbon feedstocks for biomanufacturing[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2023, 42(1): 16-29. | |
| 67 | HOFFMEISTER S, GERDOM M, BENGELSDORF F R, et al. Acetone production with metabolically engineered strains of Acetobacterium woodii [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2016, 36: 37-47. |
| 68 | BANERJEE A, LEANG C, UEKI T, et al. Lactose-inducible system for metabolic engineering of Clostridium ljungdahlii [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2014, 80(8): 2410-2416. |
| 69 | UEKI T, NEVIN K P, WOODARD T L, et al. Converting carbon dioxide to butyrate with an engineered strain of Clostridium ljungdahlii [J]. mBio, 2014, 5(5): e01636-14. |
| 70 | BOMAR M, HIPPE H, SCHINK B. Lithotrophic growth and hydrogen metabolism by Clostridium magnum [J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 1991, 83(3): 347-349. |
| 71 | FLÜCHTER S, FOLLONIER S, SCHIEL-BENGELSDORF B, et al. Anaerobic production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and its precursor 3-hydroxybutyrate from synthesis gas by autotrophic clostridia[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2019, 20(9): 3271-3282. |
| 72 | BOGORAD I W, LIN T S, LIAO J C. Synthetic non-oxidative glycolysis enables complete carbon conservation[J]. Nature, 2013, 502(7473): 693-697. |
| 73 | LIN P P, JAEGER A J, WU T Y, et al. Construction and evolution of an Escherichia coli strain relying on nonoxidative glycolysis for sugar catabolism[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(14): 3538-3546. |
| 74 | YANG X Y, YUAN Q Q, ZHENG Y Y, et al. An engineered non-oxidative glycolysis pathway for acetone production in Escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2016, 38(8): 1359-1365. |
| 75 | MIYOSHI K, KAWAI R, NIIDE T, et al. Functional evaluation of non-oxidative glycolysis in Escherichia coli in the stationary phase under microaerobic conditions[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2023, 135(4): 291-297. |
| 76 | FAST A G, SCHMIDT E D, JONES S W, et al. Acetogenic mixotrophy: novel options for yield improvement in biofuels and biochemicals production[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2015, 33: 60-72. |
| 77 | LIU Z H, WANG K, CHEN Y, et al. Third-generation biorefineries as the means to produce fuels and chemicals from CO2 [J]. Nature Catalysis, 2020, 3(3): 274-288. |
| 78 | JONES S W, FAST A G, CARLSON E D, et al. CO2 fixation by anaerobic non-photosynthetic mixotrophy for improved carbon conversion[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 12800. |
| 79 | DINER B A, FAN J, SCOTCHER M C, et al. Synthesis of heterologous mevalonic acid pathway enzymes in Clostridium ljungdahlii for the conversion of fructose and of syngas to mevalonate and isoprene[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2018, 84(1): e01723-17. |
| 80 | GREENE D N, WHITNEY S M, MATSUMURA I. Artificially evolved Synechococcus PCC 6301 Rubisco variants exhibit improvements in folding and catalytic efficiency[J]. The Biochemical Journal, 2007, 404(3): 517-524. |
| 81 | MUELLER-CAJAR O, MORELL M, WHITNEY S M. Directed evolution of rubisco in Escherichia coli reveals a specificity-determining hydrogen bond in the form Ⅱ enzyme[J]. Biochemistry, 2007, 46(49): 14067-14074. |
| 82 | ZHUANG Z Y, LI S Y. Rubisco-based engineered Escherichia coli for in situ carbon dioxide recycling[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 150: 79-88. |
| 83 | LI Y H, OUYANG F Y, YANG C H, et al. The coupling of glycolysis and the Rubisco-based pathway through the non-oxidative pentose phosphate pathway to achieve low carbon dioxide emission fermentation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 187: 189-197. |
| 84 | PARIKH M R, GREENE D N, WOODS K K, et al. Directed evolution of RuBisCO hypermorphs through genetic selection in engineered E.coli [J]. Protein Engineering, Design and Selection, 2006, 19(3): 113-119. |
| 85 | KANNO M, CARROLL A L, ATSUMI S. Global metabolic rewiring for improved CO2 fixation and chemical production in cyanobacteria[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 14724. |
| 86 | KAMKENG A D N, WANG M H, HU J, et al. Transformation technologies for CO2 utilisation: current status, challenges and future prospects[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 409: 128138. |
| 87 | QUAYLE J R, FERENCI T. Evolutionary aspects of autotrophy[J]. Microbiological Reviews, 1978, 42(2): 251-273. |
| 88 | PFEIFENSCHNEIDER J, BRAUTASET T, WENDISCH V F. Methanol as carbon substrate in the bio-economy: metabolic engineering of aerobic methylotrophic bacteria for production of value-added chemicals[J]. Biofuels, Bioproducts and Biorefining, 2017, 11(4): 719-731. |
| 89 | LEDEBOER A M, EDENS L, MAAT J, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of a gene coding for methanol oxidase in Hansenula polymorpha [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1985, 13(9): 3063-3082. |
| 90 | CREGG J M, MADDEN K R, BARRINGER K J, et al. Functional characterization of the two alcohol oxidase genes from the yeast Pichia pastoris [J]. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 1989, 9(3): 1316-1323. |
| 91 | SAKAI Y, TANI Y. Cloning and sequencing of the alcohol oxidase-encoding gene (AOD1) from the formaldehyde-producing asporogeneous methylotrophic yeast, Candida boidinii S2[J]. Gene, 1992, 114(1): 67-73. |
| 92 | YURIMOTO H, SAKAI Y, KATO N. Methanol metabolism[M/OL]//Hansenula polymorpha: biology and applications. Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley, 2002: 61-75 [2023-06-01]. . |
| 93 | CHEN F Y H, JUNG H W, TSUEI C Y, et al. Converting Escherichia coli to a synthetic methylotroph growing solely on methanol[J]. Cell, 2020, 182(4): 933-946.e14. |
| 94 | YURIMOTO H, OKU M, SAKAI Y. Yeast methylotrophy: metabolism, gene regulation and peroxisome homeostasis[J]. International Journal of Microbiology, 2011, 2011: 101298. |
| 95 | YURIMOTO H, KATO N, SAKAI Y. Assimilation, dissimilation, and detoxification of formaldehyde, a central metabolic intermediate of methylotrophic metabolism[J]. Chemical Record, 2005, 5(6): 367-375. |
| 96 | ZHANG W M, ZHANG T, WU S H, et al. Guidance for engineering of synthetic methylotrophy based on methanol metabolism in methylotrophy[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(7): 4083-4091. |
| 97 | FILLET S, ADRIO J L. Microbial production of fatty alcohols[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2016, 32(9): 152. |
| 98 | 熊向华, 刘志敏, 陈惠鹏. 多形汉逊酵母研究进展[J]. 生物技术通讯, 2006, 17(5): 771-774. |
| XIONG X H, LIU Z M, CHEN H P. Advances in the research of Hansenula polymorpha [J]. Letters in Biotechnology, 2006, 17(5): 771-774. | |
| 99 | KATA I, SEMKIV M V, RUCHALA J, et al. Overexpression of the genes PDC1 and ADH1 activates glycerol conversion to ethanol in the thermotolerant yeast Ogataea (Hansenula) polymorpha [J]. Yeast, 2016, 33(8): 471-478. |
| 100 | 钱卫东, 施春阳, 王婷. 多形汉逊酵母作为细胞工厂的应用研究进展[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2012, 39(4): 55-59. |
| QIAN W D, SHI C Y, WANG T. Progress in research on the methylotrophic yeast Hansenula polymaorph cell factory[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2012, 39(4): 55-59. | |
| 101 | 刘爽, 高教琪, 薛闯, 等. 多形汉逊酵母提高生长性能的培养基优化[J]. 生物加工过程, 2020, 18(1): 117-125. |
| LIU S, GAO J Q, XUE C, et al. Medium optimization for growth of Ogataea polymorpha [J]. Chinese Journal of Bioprocess Engineering, 2020, 18(1): 117-125. | |
| 102 | GAO J Q, LI Y X, YU W, et al. Rescuing yeast from cell death enables overproduction of fatty acids from sole methanol[J]. Nature Metabolism, 2022, 4(7): 932-943. |
| 103 | ZHAI X X, GAO J Q, LI Y X, et al. Peroxisomal metabolic coupling improves fatty alcohol production from sole methanol in yeast[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2023, 120(12): e2220816120. |
| 104 | BECKER J, WITTMANN C. Advanced biotechnology: metabolically engineered cells for the bio-based production of chemicals and fuels, materials, and health-care products[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(11): 3328-3350. |
| 105 | DAI Z X, GU H L, ZHANG S J, et al. Metabolic construction strategies for direct methanol utilization in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 245: 1407-1412. |
| 106 | ZHU W L, CUI J Y, CUI L Y, et al. Bioconversion of methanol to value-added mevalonate by engineered Methylobacterium extorquens AM1 containing an optimized mevalonate pathway[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2016, 100(5): 2171-2182. |
| 107 | MA Z X, ZHANG M, ZHANG C T, et al. Metabolomic analysis improves bioconversion of methanol to isobutanol in Methylorubrum extorquens AM1[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2021, 16(6): e2000413. |
| 108 | CHEN C T, CHEN F Y H, BOGORAD I W, et al. Synthetic methanol auxotrophy of Escherichia coli for methanol-dependent growth and production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 49: 257-266. |
| 109 | YISHAI O, LINDNER S N, DE LA CRUZ J G, et al. The formate bio-economy[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2016, 35: 1-9. |
| 110 | Engineered E. coli using formic acid and CO2 as a C1-refinery platform strain[R/OL]. (2018-09-18) [2023-05-01]. . |
| 111 | BAR-EVEN A, NOOR E, FLAMHOLZ A, et al. Design and analysis of metabolic pathways supporting formatotrophic growth for electricity-dependent cultivation of microbes[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics, 2013, 1827(8/9): 1039-1047. |
| 112 | 徐蓉, 邓王姝颖, 姜卫红, 等. 甲酸生物利用的研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2020, 36(6): 1031-1040. |
| XU R, DENG W S Y, JIANG W H, et al. Progress in biological utilization of formic acid[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2020, 36(6): 1031-1040. | |
| 113 | CROWTHER G J, KOSÁLY G, LIDSTROM M E. Formate as the main branch point for methylotrophic metabolism in Methylobacterium extorquens AM1[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2008, 190(14): 5057-5062. |
| 114 | DRAKE H L, KÜSEL K, MATTHIES C. Acetogenic prokaryotes[M/OL]// DWORKIN M, FALKOW S, ROSENBERG E, et al. The Prokaryotes. New York: Springer, 2006[2023-06-01]. . |
| 115 | 郭峰, 张尚杰, 蒋羽佳, 等. 一碳资源在酵母中的利用与转化[J]. 化工进展, 2023, 42(1): 30-39. |
| GUO F, ZHANG S J, JIANG Y J, et al. Biotransformation of one-carbon resources by yeast[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2023, 42(1): 30-39. | |
| 116 | 毛雯. 利用定向进化提高基因工程大肠杆菌的甲酸利用能力[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2020. |
| MAO W. Directed evolution to improve formate utilization in genetically engineered E .coli[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2020. | |
| 117 | KIM S J, YOON J, IM D K, et al. Adaptively evolved Escherichia coli for improved ability of formate utilization as a carbon source in sugar-free conditions[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2019, 12: 207. |
| 118 | YISHAI O, BOUZON M, DÖRING V, et al. In vivo assimilation of one-carbon via a synthetic reductive glycine pathway in Escherichia coli [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(9): 2023-2028. |
| 119 | BANG J, HWANG C H, AHN J H, et al. Escherichia coli is engineered to grow on CO2 and formic acid[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2020, 5(12): 1459-1463. |
| 120 | HONG Y, ARBTER P, WANG W, et al. Introduction of glycine synthase enables uptake of exogenous formate and strongly impacts the metabolism in Clostridium pasteurianum [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2021, 118(3): 1366-1380. |
| 121 | LAMA S M, KIM Y, NGUYEN D T, et al. Production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid from acetate using metabolically-engineered and glucose-grown Escherichia coli [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 320(Pt A): 124362. |
| 122 | CHANG Z S, DAI W, MAO Y F, et al. Enhanced 3-hydroxypropionic acid production from acetate via the malonyl-CoA pathway in Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2022, 9: 808258. |
| 123 | YANG S Y, LI S H, JIA X Q. Production of medium chain length polyhydroxyalkanoate from acetate by engineered Pseudomonas putida KT2440[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2019, 46(6): 793-800. |
| 124 | WEI N, QUARTERMAN J, KIM S R, et al. Enhanced biofuel production through coupled acetic acid and xylose consumption by engineered yeast[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 2580. |
| 125 | HUANG X F, SHEN Y, LUO H J, et al. Enhancement of extracellular lipid production by oleaginous yeast through preculture and sequencing batch culture strategy with acetic acid[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 247: 395-401. |
| 126 | GONG G P, ZHANG X, TAN T W. Simultaneously enhanced intracellular lipogenesis and β-carotene biosynthesis of Rhodotorula glutinis by light exposure with sodium acetate as the substrate[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 295: 122274. |
| 127 | CHEN L, YAN W, QIAN X J, et al. Increased lipid production in Yarrowia lipolytica from acetate through metabolic engineering and cosubstrate fermentation[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2021, 10(11): 3129-3138. |
| 128 | KÖVILEIN A, UMPFENBACH J, OCHSENREITHER K. Acetate as substrate for L-malic acid production with Aspergillus oryzae DSM 1863[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2021, 14(1): 48. |
| 129 | LI Y J, HUANG B, WU H, et al. Production of succinate from acetate by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2016, 5(11): 1299-1307. |
| 130 | HUANG B, YANG H, FANG G C, et al. Central pathway engineering for enhanced succinate biosynthesis from acetate in Escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2018, 115(4): 943-954. |
| 131 | LI W, CHEN J, LIU C X, et al. Microbial production of glycolate from acetate by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2019, 291: 41-45. |
| 132 | YU Y, SHAO M Y, LI D, et al. Construction of a carbon-conserving pathway for glycolate production by synergetic utilization of acetate and glucose in Escherichia coli [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 61: 152-159. |
| 133 | DA Y Y, LIU Z H, ZHU R, et al. Coutilization of glucose and acetate for the production of pyruvate by engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 170: 107990. |
| 134 | NOH M H, LIM H G, WOO S H, et al. Production of itaconic acid from acetate by engineering acid-tolerant Escherichia coli W[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2018, 115(3): 729-738. |
| 135 | MERKEL M, KIEFER D, SCHMOLLACK M, et al. Acetate-based production of itaconic acid with Corynebacterium glutamicum using an integrated pH-coupled feeding control[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 351: 126994. |
| 136 | ZHOU S F, LAMA S M, JIANG J H, et al. Use of acetate for the production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid by metabolically-engineered Pseudomonas denitrificans [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 307: 123194. |
| 137 | LAI N Y, LUO Y C, FEI P, et al. One stone two birds: biosynthesis of 3-hydroxypropionic acid from CO2 and syngas-derived acetic acid in Escherichia coli [J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2021, 6(3): 144-152. |
| 138 | LEE J, CHA S, KANG C E, et al. Efficient conversion of acetate to 3-hydroxypropionic acid by engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Catalysts, 2018, 8(11): 525. |
| 139 | XU X, XIE M, ZHAO Q A, et al. Microbial production of mevalonate by recombinant Escherichia coli using acetic acid as a carbon source[J]. Bioengineered, 2018, 9(1): 116-123. |
| 140 | LEE H M, JEON B Y, OH M K. Microbial production of ethanol from acetate by engineered Ralstonia eutropha [J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 2016, 21(3): 402-407. |
| 141 | YANG H, ZHANG C, LAI N Y, et al. Efficient isopropanol biosynthesis by engineered Escherichia coli using biologically produced acetate from syngas fermentation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 296: 122337. |
| 142 | SONG H S, SEO H M, JEON J M, et al. Enhanced isobutanol production from acetate by combinatorial overexpression of acetyl-CoA synthetase and anaplerotic enzymes in engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2018, 115(8): 1971-1978. |
| 143 | NOVAK K, KUTSCHA R, PFLÜGL S. Microbial upgrading of acetate into 2,3-butanediol and acetoin by E. coli W[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2020, 13: 177. |
| 144 | CHEN J, LI W, ZHANG Z Z, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the synthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates using acetate as a main carbon source[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2018, 17(1): 102. |
| 145 | SHI L L, DA Y Y, ZHENG W T, et al. Production of polyhydroxyalkanoate from acetate by metabolically engineered Aeromonas hydrophilia [J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2020, 130(3): 290-294. |
| 146 | GONG Z W, ZHOU W T, SHEN H W, et al. Co-fermentation of acetate and sugars facilitating microbial lipid production on acetate-rich biomass hydrolysates[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 207: 102-108. |
| 147 | LIU L J, ZHAO Y, JIANG X X, et al. Lipid accumulation of Chlorella pyrenoidosa under mixotrophic cultivation using acetate and ammonium[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 262: 342-346. |
| 148 | HU P, CHAKRABORTY S, KUMAR A, et al. Integrated bioprocess for conversion of gaseous substrates to liquids[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(14): 3773-3778. |
| 149 | QIAN X J, GORTE O, CHEN L, et al. Continuous self-provided fermentation for microbial lipids production from acetate by using oleaginous yeasts Cryptococcus podzolicus and Trichosporon porosum [J]. Renewable Energy, 2020, 146: 737-743. |
| 150 | ZHANG W, WU J, ZHOU Y J, et al. Enhanced lipid production by Rhodotorula glutinis CGMCC 2.703 using a two-stage pH regulation strategy with acetate as the substrate[J]. Energy Science & Engineering, 2019, 7(5): 2077-2085. |
| 151 | TASHIRO Y, DESAI S H, ATSUMI S. Two-dimensional isobutyl acetate production pathways to improve carbon yield[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 7488. |
| 152 | GONG G P, WU B, LIU L P, et al. Metabolic engineering using acetate as a promising building block for the production of bio-based chemicals[J]. Engineering Microbiology, 2022, 2(4): 100036. |
| 153 | KESSLER D, LEIBRECHT I, KNAPPE J. Pyruvate-formate-lyase-deactivase and acetyl-CoA reductase activities of Escherichia coli reside on a polymeric protein particle encoded by adhE [J]. FEBS Letters, 1991, 281(1/2): 59-63. |
| 154 | MEMBRILLO-HERNÁNDEZ J, ECHAVE P, CABISCOL E, et al. Evolution of the adhE gene product of Escherichia coli from a functional reductase to a dehydrogenase. Genetic and biochemical studies of the mutant proteins [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2000, 275(43): 33869-33875. |
| 155 | LIANG H, MA X Q, NING W B, et al. Constructing an ethanol utilization pathway in Escherichia coli to produce acetyl-CoA derived compounds[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2021, 65: 223-231. |
| 156 | LU J F, WANG Y Y, XU M C, et al. Efficient biosynthesis of 3-hydroxypropionic acid from ethanol in metabolically engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 363: 127907. |
| 157 | WANG Y Y, LU J F, XU M C, et al. Efficient biosynthesis of isopropanol from ethanol by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli [J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2022, 10(41): 13857-13864. |
| 158 | LI G W, WEI X L, WU R, et al. Stoichiometric conversion of maltose for biomanufacturing by in vitro synthetic enzymatic biosystems[J]. BioDesign Research, 2022, 2022: 9806749. |
| 159 | ARESTA M, DIBENEDETTO A, QUARANTA E. Reaction mechanisms in carbon dioxide conversion[M/OL]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2016[2023-06-01]. . |
| 160 | ARESTA M, QUARANTA E, LIBERIO R, et al. Enzymatic synthesis of 4-OH-benzoic acid from phenol and CO2: the first example of a biotechnological application of a carboxylase enzyme[J]. Tetrahedron, 1998, 54(30): 8841-8846. |
| 161 | OBERT R, DAVE B C. Enzymatic conversion of carbon dioxide to methanol: enhanced methanol production in silica sol-gel matrices[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1999, 121(51): 12192-12193. |
| 162 | SHI J F, JIANG Y J, JIANG Z Y, et al. Enzymatic conversion of carbon dioxide[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(17): 5981-6000. |
| 163 | LU Y, JIANG Z Y, XU S W, et al. Efficient conversion of CO2 to formic acid by formate dehydrogenase immobilized in a novel alginate-silica hybrid gel[J]. Catalysis Today, 2006, 115(1/2/3/4): 263-268. |
| 164 | YADAV R K, BAEG J O, OH G H, et al. A photocatalyst–enzyme coupled artificial photosynthesis system for solar energy in production of formic acid from CO2 [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(28): 11455-11461. |
| 165 | YADAV R K, BAEG J O, KUMAR A, et al. Graphene-BODIPY as a photocatalyst in the photocatalytic-biocatalytic coupled system for solar fuel production from CO2 [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(14): 5068-5076. |
| 166 | SULTANA S, SAHOO P C, MARTHA S, et al. A review of harvesting clean fuels from enzymatic CO2 reduction[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(50): 44170-44194. |
| 167 | APPEL A M, BERCAW J E, BOCARSLY A B, et al. Frontiers, opportunities, and challenges in biochemical and chemical catalysis of CO2 fixation[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2013, 113(8): 6621-6658. |
| 168 | PARKIN A, SERAVALLI J, VINCENT K A, et al. Rapid and efficient electrocatalytic CO2/CO interconversions by carboxydothermus hydrogenoformans CO dehydrogenase Ⅰ on an electrode[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2007, 129(34): 10328-10329. |
| 169 | ÜNLÜ A, DUMAN-ÖZDAMAR Z E, ÇALOĞLU B, et al. Enzymes for efficient CO2 conversion[J]. The Protein Journal, 2021, 40(4): 489-503. |
| 170 | SHIN W, LEE S H, SHIN J W, et al. Highly selective electrocatalytic conversion of CO2 to CO at -0.57 V (NHE) by carbon monoxide dehydrogenase from Moorella thermoacetica [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(48): 14688-14689. |
| 171 | WOOLERTON T W, SHEARD S, REISNER E, et al. Efficient and clean photoreduction of CO2 to CO by enzyme-modified TiO2 nanoparticles using visible light[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(7): 2132-2133. |
| 172 | WOOLERTON T W, SHEARD S, PIERCE E, et al. CO2 photoreduction at enzyme-modified metal oxidenanoparticles[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2011, 4(7): 2393-2399. |
| 173 | SEEFELDT L C, RASCHE M E, ENSIGN S A. Carbonyl sulfide and carbon dioxide as new substrates, and carbon disulfide as a new inhibitor, of nitrogenase[J]. Biochemistry, 1995, 34(16): 5382-5389. |
| 174 | YANG Z Y, MOURE V R, DEAN D R, et al. Carbon dioxide reduction to methane and coupling with acetylene to form propylene catalyzed by remodeled nitrogenase[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(48): 19644-19648. |
| 175 | MELDRUM N U, ROUGHTON F J W. Carbonic anhydrase. its preparation and properties[J]. The Journal of Physiology, 1933, 80(2): 113-142. |
| 176 | GIRI A, CHAUHAN S, SHARMA T, et al. Recent advances in enzymatic conversion of carbon dioxide into value-added product[M/OL]//PANT D, KUMAR NADDA A, PANT K K, et al. Advances in carbon capture and utilization. Singapore: Springer, 2021: 313-326 [2023-06-01]. . |
| 177 | VEITCH F P, BLANKENSHIP L C. Carbonic anhydrase in bacteria[J]. Nature, 1963, 197(4862): 76-77. |
| 178 | JENSEN E L, CLEMENT R, KOSTA A, et al. A new widespread subclass of carbonic anhydrase in marine phytoplankton[J]. The ISME Journal, 2019, 13(8): 2094-2106. |
| 179 | WU Z H, NAN Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Immobilization of carbonic anhydrase for facilitated CO2 capture and separation[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2020, 28(11): 2817-2831. |
| 180 | DEL PRETE S, NOCENTINI A, SUPURAN C T, et al. Bacterial ι-carbonic anhydrase: a new active class of carbonic anhydrase identified in the genome of the Gram-negative bacterium Burkholderia territorii [J]. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, 2020, 35(1): 1060-1068. |
| 181 | SAVILE C K, LALONDE J J. Biotechnology for the acceleration of carbon dioxide capture and sequestration[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2011, 22(6): 818-823. |
| 182 | ZHANG S H, LU H, LU Y Q. Enhanced stability and chemical resistance of a new nanoscale biocatalyst for accelerating CO2 absorption into a carbonate solution[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(23): 13882-13888. |
| 183 | 梁珊, 宗敏华, 娄文勇. 酶法催化二氧化碳制备高附加值化学品研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(11): 1099-1114. |
| LIANG S, ZONG M H, LOU W Y. Recent advances in enzymatic catalysis for preparation of high value-added chemicals from carbon dioxide[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2019, 77(11): 1099-1114. | |
| 184 | GLUECK S M, GÜMÜS S, FABIAN W M F, et al. Biocatalytic carboxylation[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2010, 39(1): 313-328. |
| 185 | ALLEN J R, ENSIGN S A. Carboxylation of epoxides to beta-keto acids in cell extracts of Xanthobacter strain Py2[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1996, 178(5): 1469-1472. |
| 186 | ARESTA M, DIBENEDETTO A. Development of environmentally friendly syntheses: use of enzymes and biomimetic systems for the direct carboxylation of organic substrates[J]. Reviews in Molecular Biotechnology, 2002, 90(2): 113-128. |
| 187 | OMURA H, WIESER M, NAGASAWA T. Pyrrole-2-carboxylate decarboxylase from Bacillus megaterium PYR2910, an organic-acid-requiring enzyme[J]. European Journal of Biochemistry, 1998, 253(2): 480-484. |
| 188 | MIYAZAKI M, SHIBUE M, OGINO K, et al. Enzymatic synthesis of pyruvic acid from acetaldehyde and carbon dioxide[J]. Chemical Communications, 2001(18): 1800-1801. |
| 189 | KUWABATA S, TSUDA R, YONEYAMA H. Electrochemical conversion of carbon dioxide to methanol with the assistance of formate dehydrogenase and methanol dehydrogenase as biocatalysts[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1994, 116(12): 5437-5443. |
| 190 | BASKAYA F S, ZHAO X Y, FLICKINGER M C, et al. Thermodynamic feasibility of enzymatic reduction of carbon dioxide to methanol[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2010, 162(2): 391-398. |
| 191 | XU S W, LU Y, LI J A, et al. Efficient conversion of CO2 to methanol catalyzed by three dehydrogenases co-encapsulated in an alginate-silica (ALG-SiO2) hybrid gel[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2006, 45(13): 4567-4573. |
| 192 | SUN Q Y, JIANG Y J, JIANG Z Y, et al. Green and efficient conversion of CO2 to methanol by biomimetic coimmobilization of three dehydrogenases in protamine-templated titania[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2009, 48(9): 4210-4215. |
| 193 | JIANG Y J, SUN Q Y, ZHANG L, et al. Capsules-in-bead scaffold: a rational architecture for spatially separated multienzyme cascade system[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2009, 19(47): 9068-9074. |
| 194 | WANG X L, LI Z, SHI J F, et al. Bioinspired approach to multienzyme cascade system construction for efficient carbon dioxide reduction[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2014, 4(3): 962-972. |
| 195 | EL-ZAHAB B, DONNELLY D, WANG P. Particle-tethered NADH for production of methanol from CO2 catalyzed by coimmobilized enzymes[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2008, 99(3): 508-514. |
| 196 | CAZELLES R, DRONE J, FAJULA F, et al. Reduction of CO2 to methanol by a polyenzymatic system encapsulated in phospholipids-silica nanocapsules[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2013, 37(11): 3721-3730. |
| 197 | TONG X D, EL-ZAHAB B, ZHAO X Y, et al. Enzymatic synthesis of L-lactic acid from carbon dioxide and ethanol with an inherent cofactor regeneration cycle[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2011, 108(2): 465-469. |
| 198 | SCHWANDER T, SCHADA VON BORZYSKOWSKI L, BURGENER S, et al. A synthetic pathway for the fixation of carbon dioxide in vitro [J]. Science, 2016, 354(6314): 900-904. |
| 199 | SUNDARAM S, DIEHL C, CORTINA N S, et al. A modular in vitro platform for the production of terpenes and polyketides from CO2 [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(30): 16420-16425. |
| 200 | DIEHL C, GERLINGER P D, PACZIA N, et al. Synthetic anaplerotic modules for the direct synthesis of complex molecules from CO2 [J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2023, 19(2): 168-175. |
| 201 | LI Z L, SHEN S, LI Z M. Towards the conversion of CO2 into optically pure N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate and orotate by an in vitro multi-enzyme cascade[J]. Green Chemistry, 2020, 22(17): 5798-5805. |
| 202 | CAI T, SUN H B, QIAO J, et al. Cell-free chemoenzymatic starch synthesis from carbon dioxide[J]. Science, 2021, 373(6562): 1523-1527. |
| [1] | LIU Kuanqing, ZHANG Yi-Heng P.Job. Biological degradation and utilization of lignin [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1264-1278. |
| [2] | Zhongliang SUN, Hui CHEN, Qiang WANG. From CO2 to value-added products—carbon neutral microalgal green biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(5): 953-965. |
| [3] | Jie REN, Anping ZENG. CO2 based biomanufacturing: from basic research to industrial application [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(6): 854-862. |
| [4] | Qingzhuo WANG, Ping SONG, He HUANG. Synthetic biotechnology drives the development of natural eukaryotic lipid cell factories [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(6): 920-941. |
| [5] | Kai WANG, Zihe LIU, Biqiang CHEN, Meng WANG, Yang ZHANG, Haoran BI, Yali ZHOU, Yiying HUO, Tianwei TAN. Microbial utilization of carbon dioxide to synthesize fuels and chemicals——third-generation biorefineries [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(1): 60-70. |
| [6] | Shuobo SHI, Qiongyu MENG, Weibo QIAO, Huimin ZHAO. Establishing carbon dioxide-based third-generation biorefinery for a sustainable low-carbon economy [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(1): 44-59. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||