|
||
|
CRISPR/Cas systems and their applications in gene editing with filamentous fungi
Synthetic Biology Journal
2024, 5 (3):
672-693.
DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-097
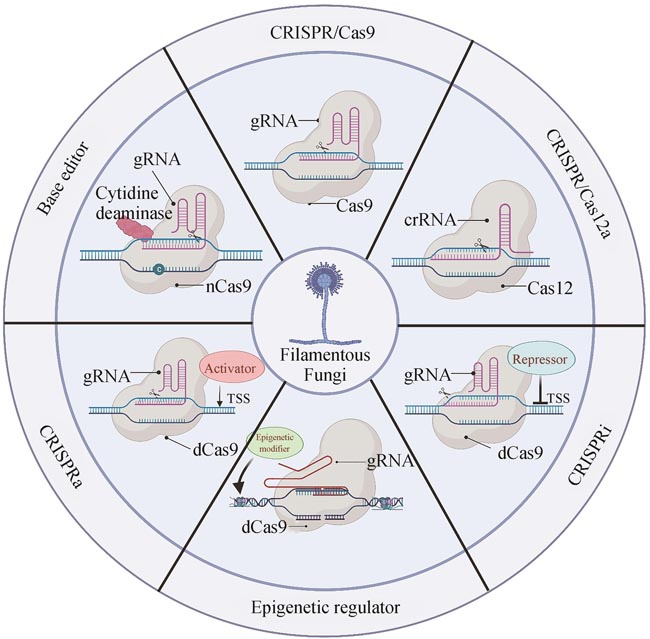
Filamentous fungi, which present distinct morphology and cell structure, play a critical role in human health as well as industrial and agricultural production. However, the unique characteristics of filamentous fungi make them difficult to be manipulated with traditional genetic engineering methods. Thus, the development of an efficient gene editing system is essential for exploring biological resources and understanding metabolic processes in filamentous fungi. The development of the Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats/CRISPR associated protein (CRISPR/Cas) system promotes more efficient and effective gene editing in different species, and brings a revolutionary breakthrough in fungal fundamental research and applications. In this review, we first briefly introduce the history, working mechanism, and classifications of the CRISPR/Cas mediated gene editing system. Next, we comment the functional components of CRISPR/Cas9 such as selective marker, Cas9 and gRNA and the delivery methods of these components in various filamentous fungi. Furthermore, we systematically discuss the applications of CRISPR related technologies, including CRISPR/Cas12, base-editor, CRISPRa, CRISPRi and CRISPR mediated epigenetic regulation, in the genetic engineering of filamentous fungi, particularly in marine-derived filamentous fungi. Finally, we address challenges with relative low gene editing efficiency and off-targets effects in engineering filamentous fungi, and highlight the potential solutions for developing novel CRISPR/Cas-based gene editing systems. This review can provide guidance for developing an efficient gene editing platform in filamentous fungi and pave the way for further exploration of the secondary metabolites and establishment of robust fungal cell factories.

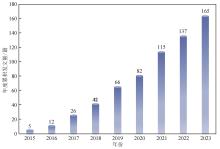
Fig. 2
Applications of different Cas9 with codons optimized in engineering filamentous fungi
(Colors representing different Cas9 with codon sequences optimized)
Extracts from the Article
Cas9蛋白是CRISPR/Cas9系统的重要组成部分,具有切割目标靶点的作用。目前被广泛应用的CRISPR/Cas9系统来自于原核生物化脓性链球菌。由于不同的物种在编码蛋白质时具有密码子偏好性,当CRISPR/Cas9系统被用于丝状真菌的基因编辑时,需根据真菌密码子偏好性,重新设计优化Cas9基因序列。在丝状真菌中,常用的Cas9的氨基酸序列主要有人类密码子优化和真菌密码子优化来源(图2)。人源密码子优化的Cas9在烟曲霉(A. fumigatus)、大豆疫霉(P. sojae)、产黄青霉(Penicillium. chrysogenum)等菌株中都可以正常表达并发挥DNA剪切功能[43,47,73]。然而,人源密码子优化的Cas9在一些真菌中无法正常表达,研究者们因此根据不同真菌的密码子的偏好性,又合成了一系列不同真菌密码子优化的Cas9序列,包括里氏木霉(T. reesei)、黑曲霉(A. niger)、米曲霉(A. oryzae)、白僵菌(B. bassiana)等[40,45,55,74]。其中,根据里氏木霉和黑曲霉进行密码子优化的Cas9在其他真菌种属中有着较为广泛的应用,不同种属密码子优化的Cas9在丝状真菌中的应用情况已总结于图2。
Other Images/Table from this Article
|