|
||
|
Applications of protein engineering in pharmaceutical industry
Synthetic Biology Journal
2025, 6 (1):
65-86.
DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-061
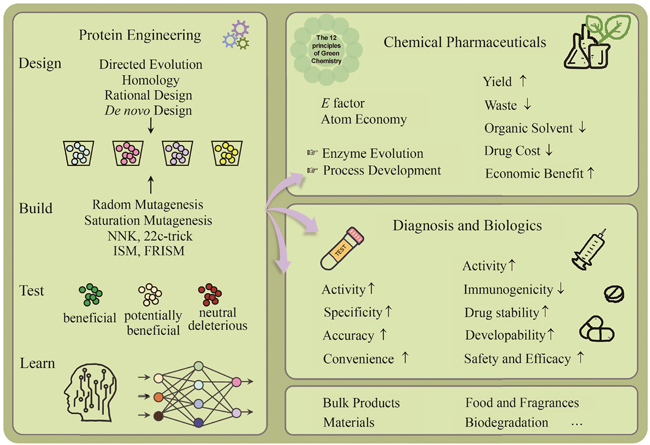
Protein engineering performs specific designs and modifications on proteins through directed evolution, semi-rational or rational design, computer-assisted design, and so on. The engineered proteins, with improved properties, have significant applications in food, medicine, fuel, and material industries. For the chemical and pharmaceutical industry, engineered enzymes can serve as efficient biocatalysts for the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) and their intermediates, aligning with the concepts and principles of green chemistry and manufacturing. For the biopharmaceutical industry, the engineering of peptide or protein modifying enzymes can boost the efficiency in preparing drug candidates, while engineered diagnostic enzymes can make detection more accurate and sensitive. Moreover, protein engineering can improve the bioactivities of biological drugs such as therapeutic enzymes and antibodies, increase stability, and mitigate immunogenic response for their safety and efficacy. Here, we review the tremendous progress in protein engineering, elucidate its importance in the research and development of chemically derived drugs and biologics, and provide examples of its applications. These examples encompass the discovery of enzymes or antibodies, the process of protein engineering, and the subsequent economic advantages. We aim to showcase the practical implementation of protein engineering in the pharmaceutical industry and facilitate technology transfer, thereby fostering seamless integration between research, development, and industrial production. Furthermore, we discuss challenges such as cost-effectiveness and market changes in the synthesis of API, and multi-target optimization, long cycle and high risk in the discovery and development of biopharmaceuticals. Finally, we look forward to the prospects of protein engineering in pharmaceutical industry. In the future, automated pipelines consisting artificial intelligence and self-driving laboratories will accelerate the design-build-test-learn cycle, leading to rapid progress in molecular design and discovery.

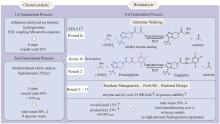
Fig. 4
Transformation of 2-chloronicotinamide to 2-chloronicotinic acid catalyzed by the amidase Pa-Ami
Extracts from the Article
其中一种具有吸引力的2-氯烟酸生产方式是用酰胺酶催化2-氯烟酰胺(图4),但是过去已有的酰胺酶对该反应的催化活性均较低。郑裕国院士团队致力于筛选和改造催化该反应的酰胺酶。2018年,团队从Pantoea sp.中筛选出新的酰胺酶Pa-Ami,对烟酰胺及其氯代衍生物具有较好的活性,其催化2-氯烟酰胺产生2-氯烟酸的酶活为16.4 U/mg[85],比之前从Delftia tsuruhatensis ZJB-05174[86]、Brevibacterium epidermidis ZJB-07021[87]和Rhodococcus erythropolis[88]中鉴定的酰胺酶的活性更好,且对底物的耐受程度更高。通过适当降低反应温度使产物析出解除产物抑制,Pa-Ami对底物的转化率可达94.2%,产生370 mmol/L的2-氯烟酸,但其活性仍然偏低。
活性↑,稳定性↑,收率↑ ... Exploitation and characterization of three versatile amidase super family members from Delftia tsuruhatensis ZJB-05174 1 2016 ... 其中一种具有吸引力的2-氯烟酸生产方式是用酰胺酶催化2-氯烟酰胺( Mining and characterization of two amidase signature family amidases from Brevibacterium epidermidis ZJB-07021 by an efficient genome mining approach 1 2016 ... 其中一种具有吸引力的2-氯烟酸生产方式是用酰胺酶催化2-氯烟酰胺( Efficient biocatalytic hydrolysis of 2-chloronicotinamide for production of 2-chloronicotinic acid by recombinant amidase 1 2013 ... 其中一种具有吸引力的2-氯烟酸生产方式是用酰胺酶催化2-氯烟酰胺( Structure-based engineering of amidase from Pantoea sp. for efficient 2-chloronicotinic acid biosynthesis 2 2019 ... Pa-Ami具有保守的催化三联体Ser177-Ser153-Lys80,通过分子对接分析发现,吡啶环上2位氯取代基改变了亲核进攻残基Ser177与底物之间的距离,也影响了Ser153对底物的质子化,而氯的电子效应又增加了反应的活化能.这种由于邻位氯取代引起的强空间位阻和电子效应导致Pa-Ami催化2-氯烟酰胺的kcat/Km只有催化烟酰胺kcat/Km的0.79%[
Other Images/Table from this Article
|