合成生物学 ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (4): 763-780.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-089
现代生物技术推动塑料中聚对苯二甲酸乙二酯绿色降解的研究进展
李磊1,2, 高鑫2, 齐宏斌2, 李超2, 路福平1,2,3, 毛淑红1,2,3, 秦慧民1,2,3
- 1.工业发酵微生物教育部重点实验室,天津 300457
2.天津科技大学生物工程学院,天津 300457
3.工业酶国家工程实验室,天津 300457
-
收稿日期:2021-09-01修回日期:2022-02-17出版日期:2022-08-31发布日期:2022-09-08 -
通讯作者:毛淑红,秦慧民 -
作者简介:李磊 (1996—),男,硕士研究生。研究方向为酶工程与合成生物学。E-mail:lilei20190520@163.com毛淑红 (1977—),女,博士,教授。研究方向为微生物催化转化。E-mail:shuhongmao@tust.edu.cn秦慧民 (1980—),男,博士,教授。研究方向为酶制剂的结构与功能研究。E-mail:huiminqin@tust.edu.cn -
基金资助:天津市自然科学基金(18JCYBJC9140)
Research progress of modern biotechnology-promoted green degradation of polyethylene terephthalate in plastics
LI Lei1,2, GAO Xin2, QI Hongbin2, LI Chao2, LU Fuping1,2,3, MAO Shuhong1,2,3, QIN Huimin1,2,3
- 1.Key Laboratory of Industrial Fermentation Microbiology of the Ministry of Education,Tianjin 300457,China
2.College of Biotechnology,Tianjin University of Science and Technology,Tianjin 300457,China
3.National Engineering Laboratory for Industrial Enzymes,Tianjin 300457,China
-
Received:2021-09-01Revised:2022-02-17Online:2022-08-31Published:2022-09-08 -
Contact:MAO Shuhong, QIN Huimin
摘要:
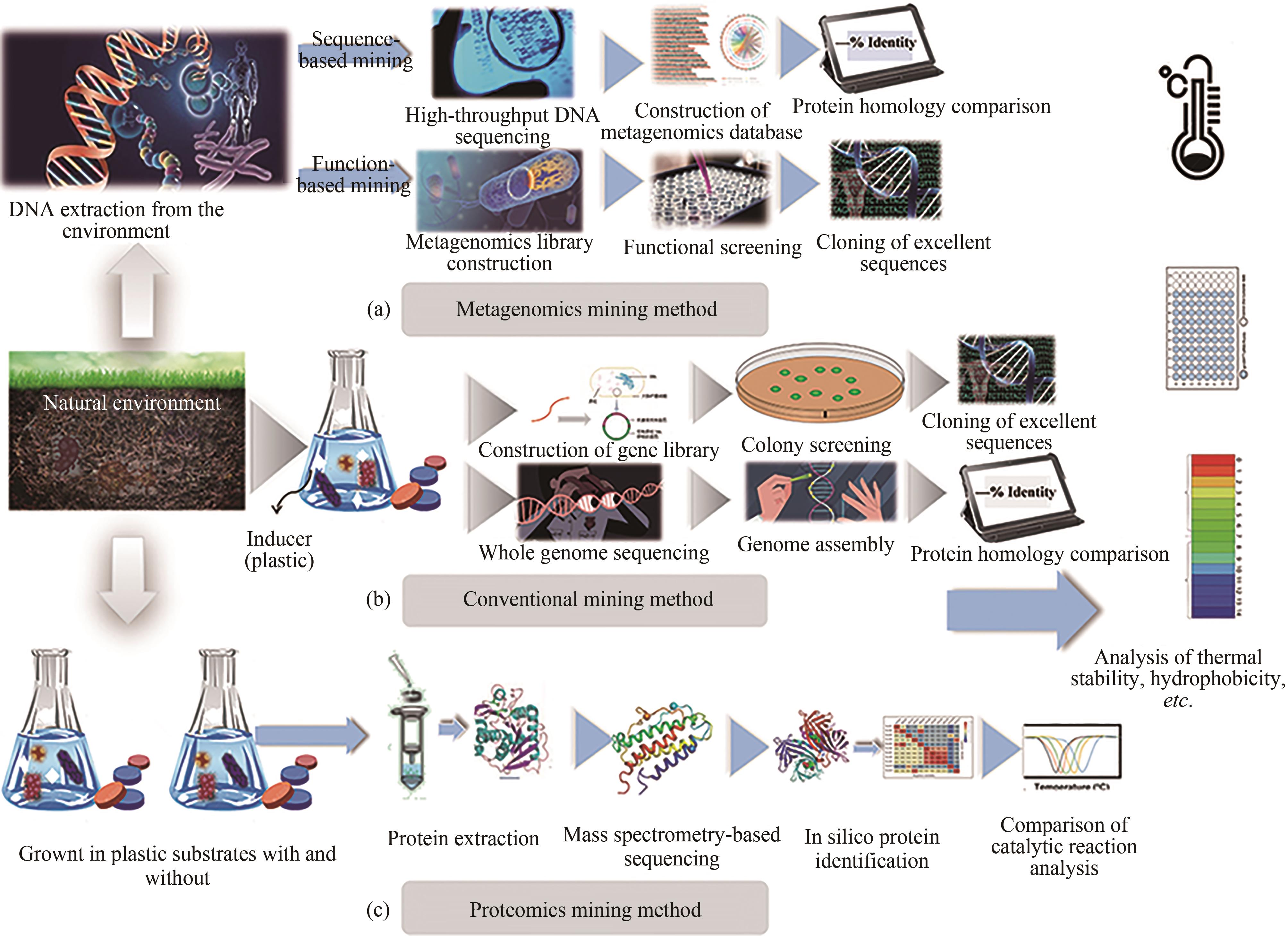
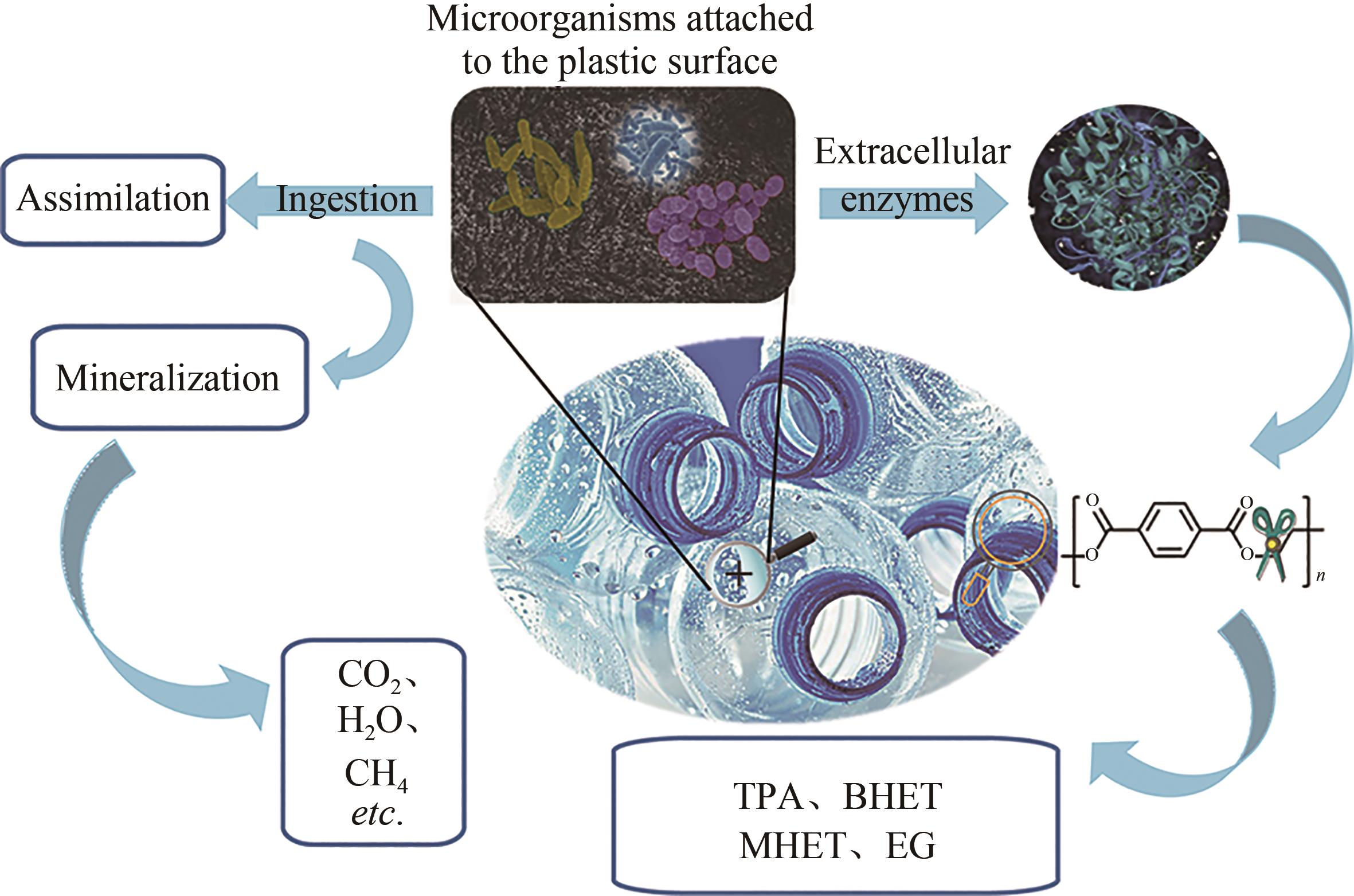
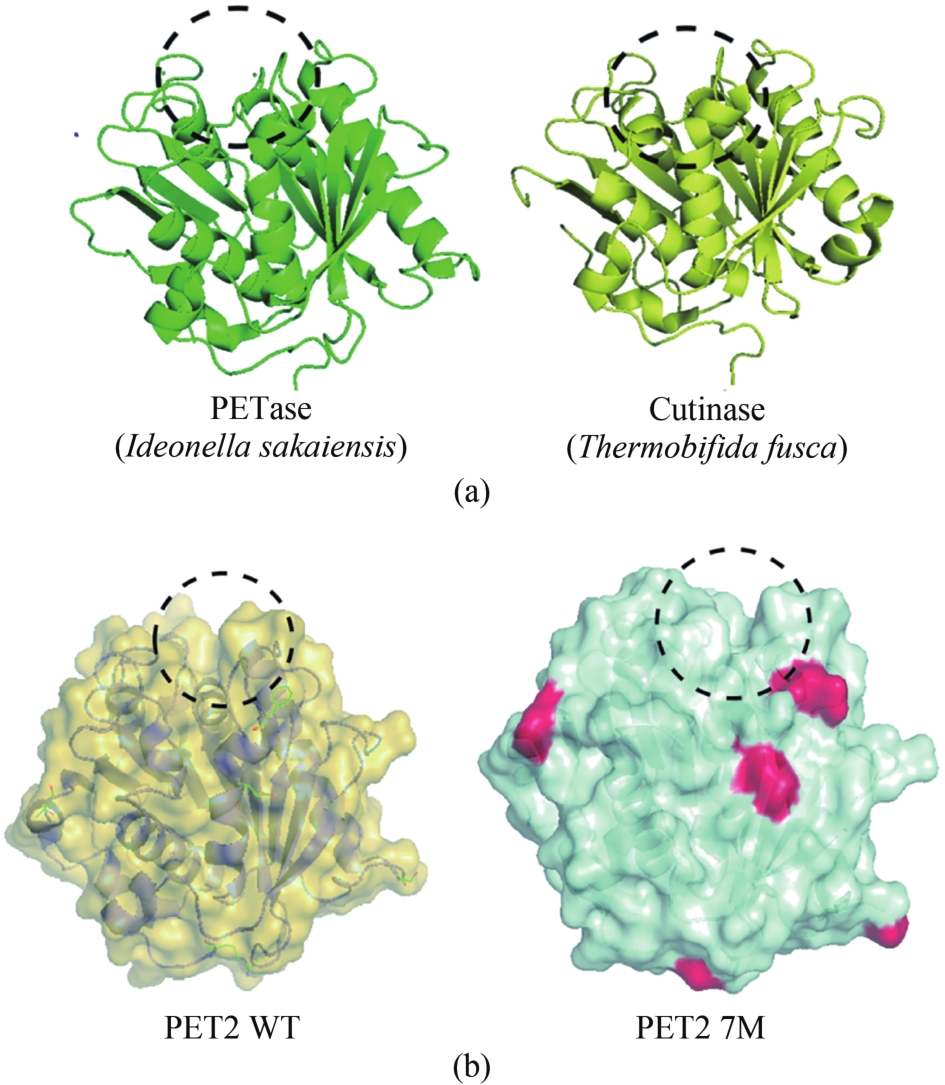
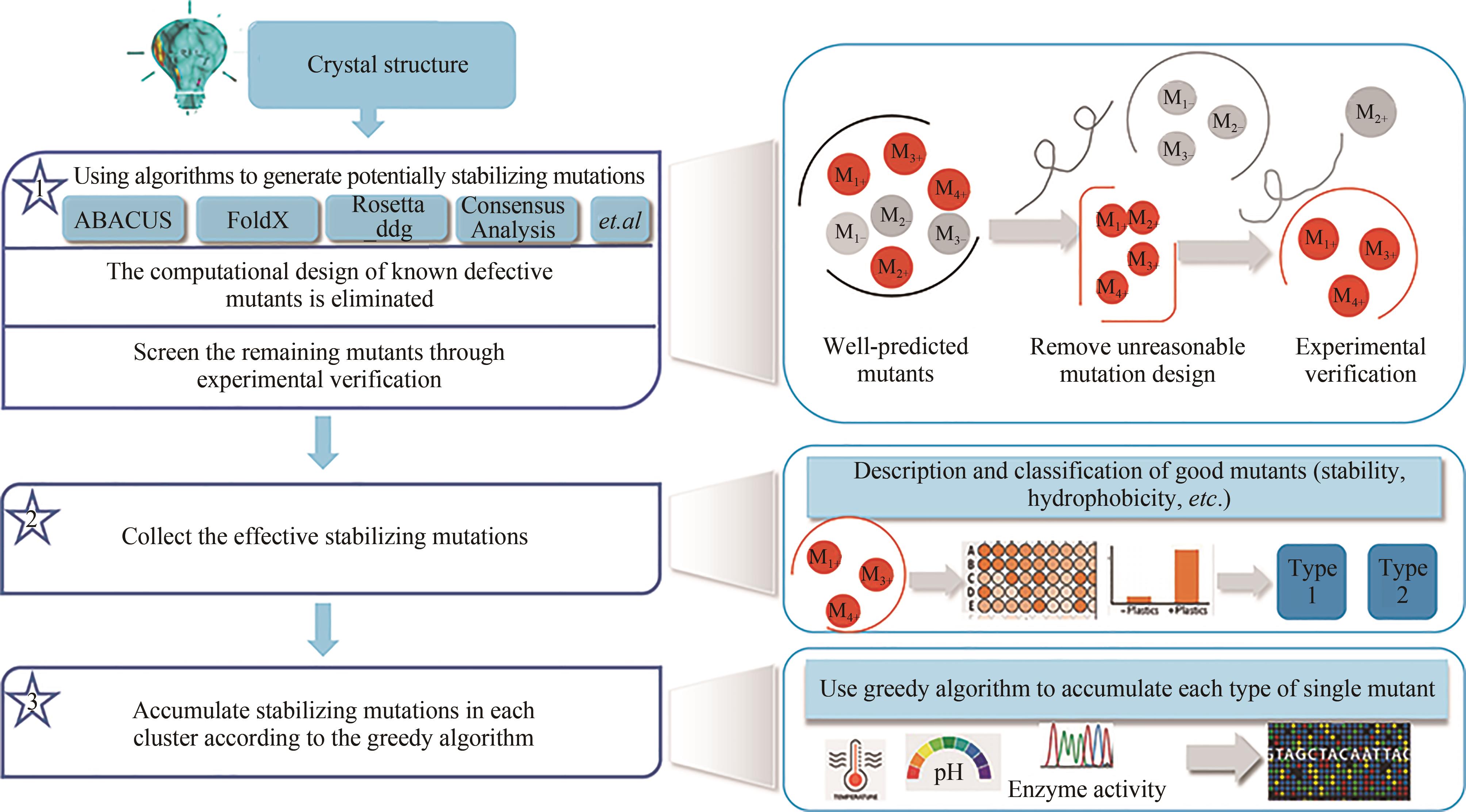
聚对苯二甲酸乙二酯(PET)因其耐用、可塑性强、安全性好等特点而广泛应用于食品包装和服装产业等领域,同时由于疏水性强、结晶度高等原因难以被微生物或酶降解利用,造成PET废弃物的不断积累,带来严重的环境和社会问题。部分高质量的PET净片可以再用到食品包装中,但绝大多数废弃PET通过常规的机械回收方法被降级利用,不能做到绿色高效回收。因此,解决“白色污染”,探索安全高效的生物降解方法成为急需攻克的重大研究课题。本文以石油基塑料的现状为背景,以PET的生物降解为切入点,综述了PET的生物降解研究现状,以宏基因组学、蛋白质组学为基础,重点总结了微生物和新酶基因的挖掘方法,并通过结构分析,以追溯不同来源的PET降解酶特性,利用定向改造和智能计算策略提高酶特性以及PET的降解效率。在改造降解酶的同时,探索对PET原材料的可降解性改良,提出了“双向改造”的思想。塑料降解酶新酶挖掘与工程改造、多酶催化体系开发以及塑料的可持续性能的改良等领域将成为塑料绿色降解的主流趋势,其为探索PET高效生物降解提供了新思路。
中图分类号:
引用本文
李磊, 高鑫, 齐宏斌, 李超, 路福平, 毛淑红, 秦慧民. 现代生物技术推动塑料中聚对苯二甲酸乙二酯绿色降解的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(4): 763-780.
LI Lei, GAO Xin, QI Hongbin, LI Chao, LU Fuping, MAO Shuhong, QIN Huimin. Research progress of modern biotechnology-promoted green degradation of polyethylene terephthalate in plastics[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(4): 763-780.

图1 2020年中国塑料生产及处理情况(The data in the figure come from the National Bureau of Statistics. In 2020, the output of plastic products in China was 76.032 million tons, and the consumption of plastics was 90.877 million tons. Compared with 2019, this was a 12.2% increase. Plastic waste was 38.4 million tons. Green recycling accounts for 17.6% of the total waste)
Fig. 1 Plastic production and processing in China in 2020
| 降解塑料类型 | 降解酶来源 | 降解酶名称 | 最佳降解温度/℃ | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET | Fosmid基因文库 | LCC | 50 | [ |
| Sphagnummagellanicum | EstC7 | 50 | [ | |
| Thermobifida alba AHK119 | Est119 | 45~55 | [ | |
| T.alba DSM43185 | Tha_Cut1 | 88.7 | [ | |
| T.cellulosilytica DSM44535 | Tc_Cut1 | 50 | [ | |
| Humicola insolens | HiC | 70 | [ | |
| Sminthurusviridis AHK190 | Cut190 | 65 | [ | |
| T. fusca DSM43793 | TfH | 55 | [ | |
| T. halotolerans DSM44931 | Thh_Est | 50 | [ | |
| T.insolens | pulA | 80 | [ | |
| Thermomyces lanuginosus | TLL | 37 | [ | |
| Acidovorax delafieldii BS-3 | PETase | 30 | [ | |
| Ideonella sakaiensis 201-F6 | IsPETase | 30 | [ | |
| T.fusca KW3 | TfCut2 | 70 | [ |
表1 PET降解酶研究进展
Tab. 1 Research progress of PET degrading enzymes
| 降解塑料类型 | 降解酶来源 | 降解酶名称 | 最佳降解温度/℃ | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET | Fosmid基因文库 | LCC | 50 | [ |
| Sphagnummagellanicum | EstC7 | 50 | [ | |
| Thermobifida alba AHK119 | Est119 | 45~55 | [ | |
| T.alba DSM43185 | Tha_Cut1 | 88.7 | [ | |
| T.cellulosilytica DSM44535 | Tc_Cut1 | 50 | [ | |
| Humicola insolens | HiC | 70 | [ | |
| Sminthurusviridis AHK190 | Cut190 | 65 | [ | |
| T. fusca DSM43793 | TfH | 55 | [ | |
| T. halotolerans DSM44931 | Thh_Est | 50 | [ | |
| T.insolens | pulA | 80 | [ | |
| Thermomyces lanuginosus | TLL | 37 | [ | |
| Acidovorax delafieldii BS-3 | PETase | 30 | [ | |
| Ideonella sakaiensis 201-F6 | IsPETase | 30 | [ | |
| T.fusca KW3 | TfCut2 | 70 | [ |
| 降解塑料类型 | 微生物名称 | 最适降解温度/℃ | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PET | Aspergillusoryzae CCUG33812 | 30 | [ |
| Clostridium botulinum ATCC3502 | 50 | [ | |
| Pseudomonas aestusnigri VGXO14T | 30 | [ | |
| Fusarium oxysporum | 30 | [ | |
| Fusarium solani | 30 | [ | |
| Streptomyces scabies | 37 | [ | |
| Penicillium citrinum | 30 | [ | |
| Trichoderma reesei | 37 | [ | |
| Burkholderiacepacia | 37 | [ | |
| Candida antarctica | 60 | [ |
表2 PET降解微生物研究进展
Tab. 2 Research progress of microorganisms in PET degradation
| 降解塑料类型 | 微生物名称 | 最适降解温度/℃ | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PET | Aspergillusoryzae CCUG33812 | 30 | [ |
| Clostridium botulinum ATCC3502 | 50 | [ | |
| Pseudomonas aestusnigri VGXO14T | 30 | [ | |
| Fusarium oxysporum | 30 | [ | |
| Fusarium solani | 30 | [ | |
| Streptomyces scabies | 37 | [ | |
| Penicillium citrinum | 30 | [ | |
| Trichoderma reesei | 37 | [ | |
| Burkholderiacepacia | 37 | [ | |
| Candida antarctica | 60 | [ |
| 1 | FEIL A, PRETZ T. Mechanical recycling of packaging waste[M]. Plastic Waste and Recycling. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2020: 283-319. |
| 2 | BORRELLE S B, RINGMA J, LAW K L, et al. Predicted growth in plastic waste exceeds efforts to mitigate plastic pollution[J]. Science, 2020, 369(6510): 1515-1518. |
| 3 | MOORE C J. Synthetic polymers in the marine environment: a rapidly increasing, long-term threat[J]. Environmental Research, 2008, 108(2): 131-139. |
| 4 | TEUTEN E L, SAQUING J M, KNAPPE D R U, et al. Transport and release of chemicals from plastics to the environment and to wildlife[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B, Biological Sciences, 2009, 364(1526): 2027-2045. |
| 5 | 许楹, 殷超凡, 岳纹龙, 等. 石油基塑料的微生物降解[J]. 生物工程学报, 2019, 35(11): 2092-2103. |
| XU Y, YIN C F, YUE W L, et al. Microbial degradation of petroleum-based plastics[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2019, 35(11): 2092-2103. | |
| 6 | CATHERINE, NOVELLI. Rethinking the future of plastics [J]. Waste Management World, 2016, 17(1): 15-15. |
| 7 | GEYER R, JAMBECK J R, LAW K L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made[J]. Science Advances, 2017, 3(7): e1700782. |
| 8 | 魏鑫嘉, 刘博洋, 王鸣, 等. 废塑料裂解及塑料油精制研究进展[J]. 工业催化, 2019, 27(2): 31-34. |
| WEI X J, LIU B Y, WANG M, et al. Progress in pyrolysis of waste plastics and refining of waste plastic oil [J]. Industrial Catalysis, 2019, 27(2): 31-34. | |
| 9 | GU J D. Microbiological deterioration and degradation of synthetic polymeric materials: recent research advances[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2003, 52(2): 69-91. |
| 10 | LEAHY J G, COLWELL R R. Microbial degradation of hydrocarbons in the environment[J]. Microbiological Reviews, 1990, 54(3): 305-315. |
| 11 | SATTI S M, SHAH A A. Polyester-based biodegradable plastics: an approach towards sustainable development[J]. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 2020, 70(6): 413-430. |
| 12 | STEFFAN R. Consequences of microbial interactions with hydrocarbons, oils, and lipids: biodegradation and bioremediation[M]. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2018. |
| 13 | TANIGUCHI I, YOSHIDA S, HIRAGA K, et al. Biodegradation of PET: current status and application aspects[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(5): 4089-4105. |
| 14 | ZHU B T, WANG D, WEI N. Enzyme discovery and engineering for sustainable plastic recycling[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2022, 40(1): 22-37. |
| 15 | CARDENAS E, TIEDJE J M. New tools for discovering and characterizing microbial diversity[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2008, 19(6): 544-549. |
| 16 | DEVARAPALLI P, KUMAVATH R N. Metagenomics—a technological drift in bioremediation[M]// SHIOMI N. Advances in bioremediation of wastewater and polluted soil. IntechOpen, 2015. |
| 17 | SANKARA SUBRAMANIAN S H, BALACHANDRAN K R S, RANGAMARAN V R, et al. RemeDB: tool for rapid prediction of enzymes involved in bioremediation from high-throughput metagenome data sets[J]. Journal of Computational Biology: a Journal of Computational Molecular Cell Biology, 2020, 27(7): 1020-1029. |
| 18 | MÜLLER C A, PERZ V, PROVASNEK C, et al. Discovery of polyesterases from moss-associated microorganisms[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2017, 83(4): e02641-e02616. |
| 19 | SULAIMAN S, YAMATO S, KANAYA E, et al. Isolation of a novel cutinase homolog with polyethylene terephthalate-degrading activity from leaf-branch compost by using a metagenomic approach[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2012, 78(5): 1556-1562. |
| 20 | GAYTÁN I, SÁNCHEZ-REYES A, BURELO M, et al. Degradation of recalcitrant polyurethane and xenobiotic additives by a selected landfill microbial community and its biodegradative potential revealed by proximity ligation-based metagenomic analysis[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, 10: 2986. |
| 21 | HAJIGHASEMI M, TCHIGVINTSEV A, NOCEK B, et al. Screening and characterization of novel polyesterases from environmental metagenomes with high hydrolytic activity against synthetic polyesters[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(21): 12388-12401. |
| 22 | WEINBERGER S, BEYER R, SCHÜLLER C, et al. High throughput screening for new fungal polyester hydrolyzing enzymes[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, 11: 554. |
| 23 | URBANEK A K, MIROŃCZUK A M, GARCÍA-MARTÍN A, et al. Biochemical properties and biotechnological applications of microbial enzymes involved in the degradation of polyester-type plastics[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Proteins and Proteomics, 2020, 1868(2): 140315. |
| 24 | DANSO D, SCHMEISSER C, CHOW J, et al. New insights into the function and global distribution of polyethylene terephthalate (PET)-degrading bacteria and enzymes in marine and terrestrial metagenomes[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2018, 84(8): e02773-e02717. |
| 25 | KANG C H, OH K H, LEE M H, et al. A novel family VII esterase with industrial potential from compost metagenomic library[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2011, 10: 41. |
| 26 | UFARTÉ L, LAVILLE É, DUQUESNE S, et al. Metagenomics for the discovery of pollutant degrading enzymes[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2015, 33(8): 1845-1854. |
| 27 | MAYUMI D, AKUTSU-SHIGENO Y, UCHIYAMA H, et al. Identification and characterization of novel poly(DL-lactic acid) depolymerases from metagenome[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2008, 79(5): 743-750. |
| 28 | JACQUIN J, CHENG J G, ODOBEL C, et al. Microbial ecotoxicology of marine plastic debris: a review on colonization and biodegradation by the "plastisphere"[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10: 865. |
| 29 | SANDER M, KOHLER H P E, MCNEILL K. Assessing the environmental transformation of nanoplastic through 13C-labelled polymers[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2019, 14(4): 301-303. |
| 30 | STURMBERGER L, WALLACE P W, GLIEDER A, et al. Synergism of proteomics and mRNA sequencing for enzyme discovery[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2016, 235: 132-138. |
| 31 | SCHNEIDER T, GERRITS B, GASSMANN R, et al. Proteome analysis of fungal and bacterial involvement in leaf litter decomposition[J]. Proteomics, 2010, 10(9): 1819-1830. |
| 32 | BISWAS R, SARKAR A. 'Omics' tools in soil microbiology: the state of the art[M]// Advances in soil microbiology: recent trends and future prospects. Springer, 2018: 35-64. |
| 33 | TESEI D, QUARTINELLO F, GUEBITZ G M, et al. Shotgun proteomics reveals putative polyesterases in the secretome of the rock-inhabiting fungus Knufia chersonesos [J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 9770. |
| 34 | ZADJELOVIC V, CHHUN A, QUARESHY M, et al. Beyond oil degradation: Enzymatic potential of Alcanivorax to degrade natural and synthetic polyesters[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2020, 22(4): 1356-1369. |
| 35 | WALLACE P W, HAERNVALL K, RIBITSCH D, et al. PpEst is a novel PBAT degrading polyesterase identified by proteomic screening of Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 101(6): 2291-2303. |
| 36 | JHONG J H, CHI Y H, LI W C, et al. dbAMP: an integrated resource for exploring antimicrobial peptides with functional activities and physicochemical properties on transcriptome and proteome data[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 47(D1): D285-D297. |
| 37 | 钱秀娟, 刘嘉唯, 薛瑞, 等. 合成生物学助力废弃塑料资源生物解聚与升级再造[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(2): 161-180. |
| QIAN X J, LIU J W, XUE R, et al. Synthetic biology boosts biological depolymerization and upgrading of waste plastics[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(2): 161-180. | |
| 38 | RONKVIST Å M, XIE W C, LU W H, et al. Cutinase-catalyzed hydrolysis of poly(ethylene terephthalate)[J]. Macromolecules, 2009, 42(14): 5128-5138. |
| 39 | FEUERHACK A, ALISCH-MARK M, KISNER A, et al. Biocatalytic surface modification of knitted fabrics made of poly(ethylene terephthalate) with hydrolytic enzymes from Thermobifida fusca KW3b[J]. Biocatalysis and Biotransformation, 2008, 26(5):357-364. |
| 40 | MÜLLER R J, SCHRADER H, PROFE J, et al. Enzymatic degradation of poly(ethylene terephthalate): rapid hydrolyse using a hydrolase fromT. fusca[J]. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 2005, 26(17): 1400-1405. |
| 41 | KLEEBERG I, WELZEL K, VANDENHEUVEL J, et al. Characterization of a new extracellular hydrolase from Thermobifida fusca degrading aliphatic-aromatic copolyesters[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2005, 6(1): 262-270. |
| 42 | BAKER P J, POULTNEY C, LIU Z Q, et al. Identification and comparison of cutinases for synthetic polyester degradation[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2012, 93(1): 229-240. |
| 43 | HU X P, THUMARAT U, ZHANG X, et al. Diversity of polyester-degrading bacteria in compost and molecular analysis of a thermoactive esterase from Thermobifida alba AHK119[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2010, 87(2): 771-779. |
| 44 | RIBITSCH D, ACERO E H, GREIMEL K, et al. Characterization of a new cutinase from Thermobifida alba for PET-surface hydrolysis[J]. Biocatalysis and Biotransformation, 2012, 30(1): 2-9. |
| 45 | ACERO H E, RIBITSCH D, STEINKELLNER G, et al. Enzymatic surface hydrolysis of PET: effect of structural diversity on kinetic properties of cutinases from Thermobifida [J]. Macromolecules, 2011, 44(12): 4632-4640. |
| 46 | RONKVIST Å M, XIE W C, LU W H, et al. Cutinase-catalyzed hydrolysis of poly(ethylene terephthalate)[J]. Macromolecules, 2009, 42(14): 5128-5138. |
| 47 | ODA M, YAMAGAMI Y, INABA S, et al. Enzymatic hydrolysis of PET: functional roles of three Ca2+ ions bound to a cutinase-like enzyme, Cut190*, and its engineering for improved activity[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(23): 10067-10077. |
| 48 | SULAIMAN S, YOU D J, KANAYA E, et al. Crystal structure and thermodynamic and kinetic stability of metagenome-derived LC-cutinase[J]. Biochemistry, 2014, 53(11): 1858-1869. |
| 49 | KLEEBERG I, WELZEL K, VANDENHEUVEL J, et al. Characterization of a new extracellular hydrolase from Thermobifida fusca degrading aliphatic-aromatic copolyesters[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2005, 6(1): 262-270. |
| 50 | RIBITSCH D, HERRERO ACERO E, GREIMEL K, et al. A new esterase from Thermobifida halotolerans hydrolyses polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polylactic acid (PLA)[J]. Polymers, 2012, 4(1): 617-629. |
| 51 | RUIZ C, HOWARD G T. Nucleotide sequencing of a polyurethanase gene (pulA) from Pseudomonas fluorescens [J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 1999, 44(2/3): 127-131. |
| 52 | ANDERSEN B K, BORCH K, ABO M, et al. Method of treating polyester fabrics: US5997584[P]. 1999-12-07. |
| 53 | FERNANDEZ-LAFUENTE R. Lipase from Thermomyces lanuginosus: uses and prospects as an industrial biocatalyst[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 2010, 62(3/4): 197-212. |
| 54 | WANG X, LU D, JÖNSSON L J, et al. Preparation of a PET-hydrolyzing lipase from Aspergillus oryzae by the addition of bis (2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalate to the culture medium and enzymatic modification of PET fabrics[J]. Engineering in Life Sciences, 2008, 8(3): 268-276. |
| 55 | UCHIDA H, SHIGENO-AKUTSU Y, NOMURA N, et al. Cloning and sequence analysis of poly(tetramethylene succinate) depolymerase from Acidovorax delafieldii strain BS-3[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2002, 93(2): 245-247. |
| 56 | YOSHIDA S, HIRAGA K, TAKEHANA T, et al. A bacterium that degrades and assimilates poly(ethylene terephthalate)[J]. Science, 2016, 351(6278): 1196-1199. |
| 57 | YANG Y, YANG J, JIANG L. Comment on "A bacterium that degrades and assimilates poly(ethylene terephthalate)"[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6301): 759. |
| 58 | FECKER T, GALAZ-DAVISON P, ENGELBERGER F, et al. Active site flexibility as a hallmark for efficient PET degradation by I. sakaiensis PETase[J]. Biophysical Journal, 2018, 114(6): 1302-1312. |
| 59 | JOO S, CHO I J, SEO H, et al. Structural insight into molecular mechanism of poly(ethylene terephthalate) degradation[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 382. |
| 60 | HAN X, LIU W D, HUANG J W, et al. Structural insight into catalytic mechanism of PET hydrolase[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 2106. |
| 61 | PERZ V, BAUMSCHLAGER A, BLEYMAIER K, et al. Hydrolysis of synthetic polyesters by Clostridium botulinum esterases[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2016, 113(5): 1024-1034. |
| 62 | KITADOKORO K, THUMARAT U, NAKAMURA R, et al. Crystal structure of cutinase Est119 from Thermobifida alba AHK119 that can degrade modified polyethylene terephthalate at 1.76 Å resolution[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2012, 97(5): 771-775. |
| 63 | NUMOTO N, KAMIYA N, BEKKER G J, et al. Structural dynamics of the PET-degrading cutinase-like enzyme from Saccharomonospora viridis AHK190 in substrate-bound states elucidates the Ca2+-driven catalytic cycle[J]. Biochemistry, 2018, 57(36): 5289-5300. |
| 64 | INABA S, KAMIYA N, BEKKER G J, et al. Folding thermodynamics of PET-hydrolyzing enzyme Cut190 depending on Ca2+ concentration[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2019, 135(5): 2655-2663. |
| 65 | BOLLINGER A, THIES S, KNIEPS-GRÜNHAGEN E, et al. A novel polyester hydrolase from the marine bacterium Pseudomonas aestusnigri-structural and functional insights[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, 11: 114. |
| 66 | NIMCHUA T, EVELEIGH D E, SANGWATANAROJ U, et al. Screening of tropical fungi producing polyethylene terephthalate-hydrolyzing enzyme for fabric modification[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2008, 35(8): 843. |
| 67 | NIMCHUA T, PUNNAPAYAK H, ZIMMERMANN W. Comparison of the hydrolysis of polyethylene terephthalate fibers by a hydrolase from Fusarium oxysporum LCH I and Fusarium solani f.sp. pisi [J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2007, 2(3): 361-364. |
| 68 | DE CASTRO A M, CARNIEL A, NICOMEDES JUNIOR J, et al. Screening of commercial enzymes for poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) hydrolysis and synergy studies on different substrate sources[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 44(6): 835-844. |
| 69 | JABLOUNE R, KHALIL M, MOUSSA I E BEN, et al. Enzymatic degradation of p-nitrophenyl esters, polyethylene terephthalate, cutin, and suberin by Sub1, a suberinase encoded by the plant pathogen Streptomyces scabies [J]. Microbes and Environments, 2020, 35(1): ME19086. |
| 70 | FARZI A, DEHNAD A, FOTOUHI A F. Biodegradation of polyethylene terephthalate waste using Streptomyces species and kinetic modeling of the process[J]. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 2019, 17: 25-31. |
| 71 | BEAULIEU C, SIDIBÉ A, JABLOUNE R, et al. Physical, chemical and proteomic evidence of potato suberin degradation by the plant pathogenic bacterium Streptomyces scabiei [J]. Microbes and Environments, 2016, 31(4): 427-434. |
| 72 | LIEBMINGER S, EBERL A, SOUSA F, et al. Hydrolysis of PET and bis-(benzoyloxyethyl) terephthalate with a new polyesterase from Penicillium citrinum [J]. Biocatalysis and Biotransformation, 2007, 25(2/3/4): 171-177. |
| 73 | KONTKANEN H, SALOHEIMO M, PERE J, et al. Characterization of Melanocarpus albomyces steryl esterase produced in Trichoderma reesei and modification of fibre products with the enzyme[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2006, 72(4): 696-704. |
| 74 | HEUMANN S, EBERL A, POBEHEIM H, et al. New model substrates for enzymes hydrolysing polyethyleneterephthalate and polyamide fibres[J]. Journal of Biochemical and Biophysical Methods, 2006, 69(1/2): 89-99. |
| 75 | KIKKAWA Y, FUJITA M, ABE H, et al. Effect of water on the surface molecular mobility of poly(lactide) thin films: an atomic force microscopy study[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2004, 5(4): 1187-1193. |
| 76 | KAWAI F, ODA M, TAMASHIRO T, et al. A novel Ca2+-activated, thermostabilized polyesterase capable of hydrolyzing polyethylene terephthalate from Saccharomonospora viridis AHK190[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2014, 98(24): 10053-10064. |
| 77 | KAZA S, YAO L C, BHADA-TATA P, et al. What a waste 2.0:a global snapshot of solid waste management to 2050[M]. Washington: World Bank Group, 2018. |
| 78 | BARTH M, HONAK A, OESER T, et al. A dual enzyme system composed of a polyester hydrolase and a carboxylesterase enhances the biocatalytic degradation of polyethylene terephthalate films[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2016, 11(8): 1082-1087. |
| 79 | QIAO Y X, HU R, CHEN D W, et al. Fluorescence-activated droplet sorting of polyethylene terephthalate degrading enzymes[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 424:127417. |
| 80 | SILVA C, DA S, SILVA N, et al. Engineered Thermobifida fusca cutinase with increased activity on polyester substrates[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2011, 6(10): 1230-1239. |
| 81 | ARAÚJO R, SILVA C, O'NEILL A, et al. Tailoring cutinase activity towards polyethylene terephthalate and polyamide 6,6 fibers[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2007, 128(4): 849-857. |
| 82 | CHEN Z Z, WANG Y Y, CHENG Y Y, et al. Efficient biodegradation of highly crystallized polyethylene terephthalate through cell surface display of bacterial PETase[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 709: 136138. |
| 83 | CARNIEL A, VALONI É, NICOMEDES J, et al. Lipase from Candida antarctica (CALB) and cutinase from Humicola insolens act synergistically for PET hydrolysis to terephthalic acid[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2017, 59: 84-90. |
| 84 | MIYAKAWA T, MIZUSHIMA H, OHTSUKA J, et al. Structural basis for the Ca2+-enhanced thermostability and activity of PET-degrading cutinase-like enzyme from Saccharomonospora viridis AHK190[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 99(10): 4297-4307. |
| 85 | THEN J, WEI R, OESER T, et al. Ca2+ and Mg2+ binding site engineering increases the degradation of polyethylene terephthalate films by polyester hydrolases from Thermobifida fusca [J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2015, 10(4): 592-598. |
| 86 | BIUNDO A, REICH J, RIBITSCH D, et al. Synergistic effect of mutagenesis and truncation to improve a polyesterase from Clostridium botulinum for polyester hydrolysis[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 3745. |
| 87 | SENGA A, HANTANI Y, BEKKER G J, et al. Metal binding to cutinase-like enzyme from Saccharomonospora viridis AHK190 and its effects on enzyme activity and stability[J]. The Journal of Biochemistry, 2019, 166(2): 149-156. |
| 88 | AUSTIN H P, ALLEN M D, DONOHOE B S, et al. Characterization and engineering of a plastic-degrading aromatic polyesterase[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(19): E4350-E4357. |
| 89 | SON H F, CHO I J, JOO S, et al. Rational protein engineering of thermo-stable PETase from Ideonella sakaiensis for highly efficient PET degradation[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(4): 3519-3526. |
| 90 | SON H F, JOO S, SEO H, et al. Structural bioinformatics-based protein engineering of thermo-stable PETase from Ideonella sakaiensis [J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2020, 141: 109656. |
| 91 | BIUNDO A, SUBAGIA R, MAURER M, et al. Switched reaction specificity in polyesterases towards amide bond hydrolysis by enzyme engineering[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(62): 36217-36226. |
| 92 | NAKAMURA A, KOBAYASHI N, KOGA N, et al. Positive charge introduction on the surface of thermostabilized PET hydrolase facilitates PET binding and degradation[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2021, 11(14): 8550-8564. |
| 93 | TOURNIER V, TOPHAM C M, GILLES A, et al. An engineered PET depolymerase to break down and recycle plastic bottles[J]. Nature, 2020, 580(7802): 216-219. |
| 94 | THEN J, WEI R, OESER T, et al. A disulfide bridge in the calcium binding site of a polyester hydrolase increases its thermal stability and activity against polyethylene terephthalate[J]. Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, 2016, 6(5): 425-32. |
| 95 | RIBITSCH D, HERRERO ACERO E, PRZYLUCKA A, et al. Enhanced cutinase-catalyzed hydrolysis of polyethylene terephthalate by covalent fusion to hydrophobins[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 81(11): 3586-3592. |
| 96 | CHEN K, HU Y, DONG X Y, et al. Molecular insights into the enhanced performance of EKylated PETase toward PET degradation[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2021, 11(12): 7358-7370. |
| 97 | LIU B, HE L H, WANG L P, et al. Protein crystallography and site-direct mutagenesis analysis of the poly(ethylene terephthalate) hydrolase PETase from Ideonella sakaiensis [J]. Chembiochem, 2018, 19(14): 1471-1475. |
| 98 | REN W, OESER T, SCHMIDT J, et al. Engineered bacterial polyester hydrolases efficiently degrade polyethylene terephthalate due to relieved product inhibition[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2016, 113(8): 1658-1665. |
| 99 | HUANG Q Y, HIYAMA M, KABE T, et al. Enzymatic self-biodegradation of poly (L-lactic acid) films by embedded heat-treated and immobilized proteinase K[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2020, 21(8): 3301-3307. |
| 100 | HUANG B, XU Y, HU X H, et al. A backbone-centred energy function of neural networks for protein design[J]. Nature, 2022, 602(7897): 523-528. |
| 101 | GUEROIS R, NIELSEN J E, SERRANO L. Predicting changes in the stability of proteins and protein complexes: a study of more than 1000 mutations[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2002, 320(2): 369-387. |
| 102 | MENG X X, YANG L X, LIU H Q, et al. Protein engineering of stable IsPETase for PET plastic degradation by Premuse[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2021, 180: 667-676. |
| 103 | CUI Y L, CHEN Y C, LIU X Y, et al. Computational redesign of a PETase for plastic biodegradation under ambient condition by the GRAPE strategy[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2021, 11(3): 1340-1350. |
| 104 | KNOTT B C, ERICKSON E, ALLEN M D, et al. Characterization and engineering of a two-enzyme system for plastics depolymerization[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(41): 25476-25485. |
| 105 | PINTO A V, FERREIRA P, NEVES R P P, et al. Reaction mechanism of MHETase, a PET degrading enzyme[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2021, 11(16): 10416-10428. |
| 106 | HUANG P S, BOYKEN S E, BAKER D. The coming of age of de novo protein design[J]. Nature, 2016, 537(7620): 320-327. |
| 107 | DELRE C, JIANG Y F, KANG P, et al. Near-complete depolymerization of polyesters with nano-dispersed enzymes[J]. Nature, 2021, 592(7855): 558-563. |
| 108 | OSTERHOUT R E, BURGARD A P, PHARKYA P, et al. Microorganisms and methods for the biosynthesis of aromatics, 2,4-pentadienoate and 1,3-butadiene: US8715957 [J]. 2012. |
| 109 | GRAGLIA M, KANNA N, ESPOSITO D. Lignin refinery: towards the preparation of renewable aromatic building blocks[J]. ChemBioEng Reviews, 2015, 2(6): 377-392. |
| 110 | LUO Z W, LEE S Y. Biotransformation of p-xylene into terephthalic acid by engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 15689. |
| 111 | SALUSJÄRVI L, HAVUKAINEN S, KOIVISTOINEN O, et al. Biotechnological production of glycolic acid and ethylene glycol: current state and perspectives[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 103(6): 2525-2535. |
| 112 | PANG J F, ZHENG M Y, WANG A Q, et al. Catalytic hydrogenation of corn stalk to ethylene glycol and 1,2-propylene glycol[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2011, 50(11): 6601-6608. |
| 113 | 张可, 胡芮绮, 蔡珉敏, 等. 黄粉虫取食和消化降解PE塑料薄膜的研究[J]. 化学与生物工程, 2017, 34(4): 47-49. |
| ZHANG K, HU R Q, CAI M M, et al. Degradation of plastic film containing polyethylene(PE) by yellow meal worms[J]. Chemistry & Bioengineering, 2017, 34(4): 47-49. | |
| 114 | KHAN I, NAGARJUNA R, DUTTA J R, et al. Enzyme-embedded degradation of poly(ε-caprolactone) using lipase-derived from probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum [J]. ACS Omega, 2019, 4(2): 2844-2852. |
| 115 | CHEN X Q, GUO Z Y, WANG L, et al. Directional-path modification strategy enhances PET hydrolase catalysis of plastic degradation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 433: 128816. |
| 116 | PALM G J, REISKY L, BÖTTCHER D, et al. Structure of the plastic-degrading Ideonella sakaiensis MHETase bound to a substrate[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 1717. |
| 117 | LU H, DIAZ DJ, CZARNECKI NJ, et al. Machine learning-aided engineering of hydrolases for PET depolymerization[J]. Nature, 2022, 604(7907) :662-667. |
| [1] | 张成辛. 基于文本数据挖掘的蛋白功能预测的机遇与挑战[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, (): 1-14. |
| [2] | 李倩, James E. Ferrell, 陈于平. 细胞质浓度:细胞生物学的老问题、新参数[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, (): 1-18. |
| [3] | 姜百翼, 钱珑. 活细胞记录器在细胞谱系追踪中的应用和前景[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, (): 1-17. |
| [4] | 温艳华, 刘合栋, 曹春来, 巫瑞波. 蛋白质工程在医药产业中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 65-86. |
| [5] | 董颖, 马孟丹, 黄卫人. CRISPR-Cas系统的小型化研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 105-117. |
| [6] | 张日新, 田晓军. 合成基因回路面临的细胞‘经济学窘境’[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, (): 1-14. |
| [7] | 谭骁天, 李睿涵, 杨慧. 生物分子传感中的抗体探针:由碳基计算走向硅基计算[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, (): 1-9. |
| [8] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | 刘建明, 张炽坚, 张冰, 曾安平. 巴氏梭菌作为工业底盘细胞高效生产1,3-丙二醇——从代谢工程和菌种进化到过程工程和产品分离[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1386-1403. |
| [10] | 刘益宁, 蒲伟, 杨金星, 王钰. ω-氨基酸与内酰胺的生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1350-1366. |
| [11] | 赵亮, 李振帅, 付丽平, 吕明, 王士安, 张全, 刘立成, 李福利, 刘自勇. 生物转化一碳化合物原料产油脂与单细胞蛋白研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1300-1318. |
| [12] | 宋开南, 张礼文, 王超, 田平芳, 李广悦, 潘国辉, 徐玉泉. 小分子生物农药及其生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, (): 1-21. |
| [13] | 伊进行, 唐宇琳, 李春雨, 吴鹤云, 马倩, 谢希贤. 氨基酸衍生物在化妆品中的应用及其生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, (): 1-36. |
| [14] | 瞿旭东, 唐功利, 丁奎岭. 打破学科界限——合成科学的新发展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 909-912. |
| [15] | 张守祺, 王涛, 孔尧, 邹家胜, 刘元宁, 徐正仁. 天然产物的化学-酶法合成:方法与策略的演进[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 913-940. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||