合成生物学 ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (5): 1203-1223.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-078
小分子生物农药及其生物合成研究进展
宋开南1, 张礼文1, 王超2, 田平芳3, 李广悦4, 潘国辉5, 徐玉泉1
- 1.中国农业科学院生物技术研究所,北京 100081
2.国家粮食和物资储备局科学研究院,北京 100037
3.北京化工大学生命科学与技术学院,北京 100029
4.中国农业科学院植物保护研究所,北京 100081
5.中国科学院微生物研究所,北京 100101
-
收稿日期:2024-10-30修回日期:2024-12-18出版日期:2025-10-31发布日期:2025-11-05 -
通讯作者:徐玉泉 -
作者简介:宋开南 (1996—),男,博士研究生。研究方向为真菌次级代谢产物的挖掘与生物合成研究。E-mail:s15850653283@126.com徐玉泉 (1971—),男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为发明新技术发现在临床和农业生产中有重要应用价值的微生物天然产物,阐明聚酮和非核糖体多肽天然产物生物合成和合成后修饰机制,利用合成生物技术合成“非天然”聚酮化合物和非核糖体多肽等。E-mail:xuyuquan@caas.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划“合成生物学”重点专项(2023YFA0914700)
Advances in small-molecule biopesticides and their biosynthesis
SONG Kainan1, ZHANG Liwen1, WANG Chao2, TIAN Pingfang3, LI Guangyue4, PAN Guohui5, XU Yuquan1
- 1.Biotechnology Research Institute,Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Beijing 100081,China
2.Academy of National Food and Strategic Reserves Administration,Beijing 100037,China
3.College of Life Science and Technology,Beijing University of Chemical Technology,Beijing 100029,China
4.Institute of Plant Protection,Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Beijing 100081,China
5.Institute of Microbiology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100101,China
-
Received:2024-10-30Revised:2024-12-18Online:2025-10-31Published:2025-11-05 -
Contact:XU Yuquan
摘要:
利用对环境和非靶标生物友好的小分子生物农药防治病虫害,是一种可持续保障农作物安全生产的管理方法。然而,小分子生物农药的研发和应用也面临一些挑战,比如种类少、产量低等。通过合成生物学和代谢工程等方法,构建高产特定生物农药的微生物细胞工厂可以克服这些瓶颈问题。本文总结了2000年以来在我国新登记的小分子生物农药及部分半合成农药的化学结构与作用对象,并对代表性生物农药的生物合成机制与细胞工厂构建,如多杀霉素、白藜芦醇等进行了综述。对这些小分子生物农药的深入理解可为解析其生物合成途径与提高产量提供理论依据,并对新型生物农药的发现和应用提供借鉴。随着合成生物学与代谢工程等学科的不断发展,可以预见未来将设计和构建出更多高效、环保小分子生物农药的细胞工厂,并将其广泛应用于生产。
中图分类号:
引用本文
宋开南, 张礼文, 王超, 田平芳, 李广悦, 潘国辉, 徐玉泉. 小分子生物农药及其生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(5): 1203-1223.
SONG Kainan, ZHANG Liwen, WANG Chao, TIAN Pingfang, LI Guangyue, PAN Guohui, XU Yuquan. Advances in small-molecule biopesticides and their biosynthesis[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 1203-1223.
| 农药名称 | 主要来源 | 结构分类 | 用途 | 原药有效成分含量 | 登记证号① |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 聚酮类 | |||||
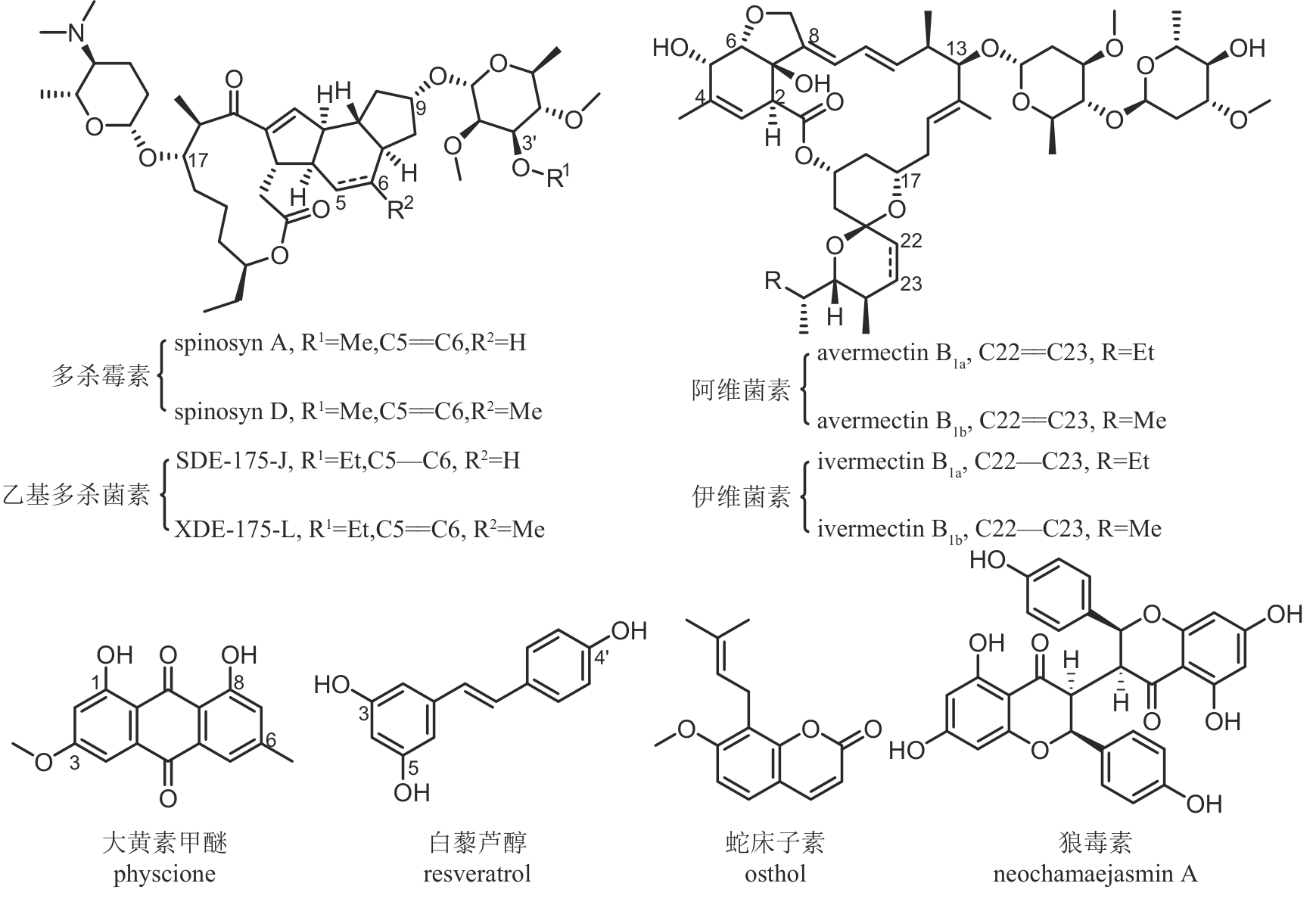
| 多杀霉素 | 刺糖多孢菌 Saccharopolyspora spinosa | 大环内酯类 | 杀虫 | 92.5% | PD20241953 LS20042235 |
乙基多杀菌素 (半合成) | 刺糖多孢菌 Saccharopolyspora spinosa | 大环内酯类 | 杀虫 | 81.2% | PD20181527 LS20091058 |
伊维菌素 (半合成) | 阿维链霉菌 Streptomyces avermitilis | 大环内酯类 | 杀虫 | 95% | PD20211308 PD20120410 |
甲氨基阿维菌素苯甲酸盐 (半合成) | 阿维链霉菌 Streptomyces avermitilis | 大环内酯类 | 杀虫 | 90% | PD20182180 LS20021924 |
| 大黄素甲醚 | 掌叶大黄 Rheum palmatum | 蒽醌类 | 杀菌 | 8.5% | PD20190139 LS20080104 |
| 狼毒素 | 狼毒 Stellera chamaejasme | 黄酮类 | 杀虫 | 9.5% | PD20120876 LS20053042 |
| 蛇床子素 | 蛇床花 Cnidium monnieri | 香豆素类 | 杀菌/杀虫 | 2% | PD20183068 LS20030489 |
| 白藜芦醇 | 藜芦 Veratrum sp. | 芪类 | 杀菌 | 10% | PD20212931 |
| 萜烯类 | |||||
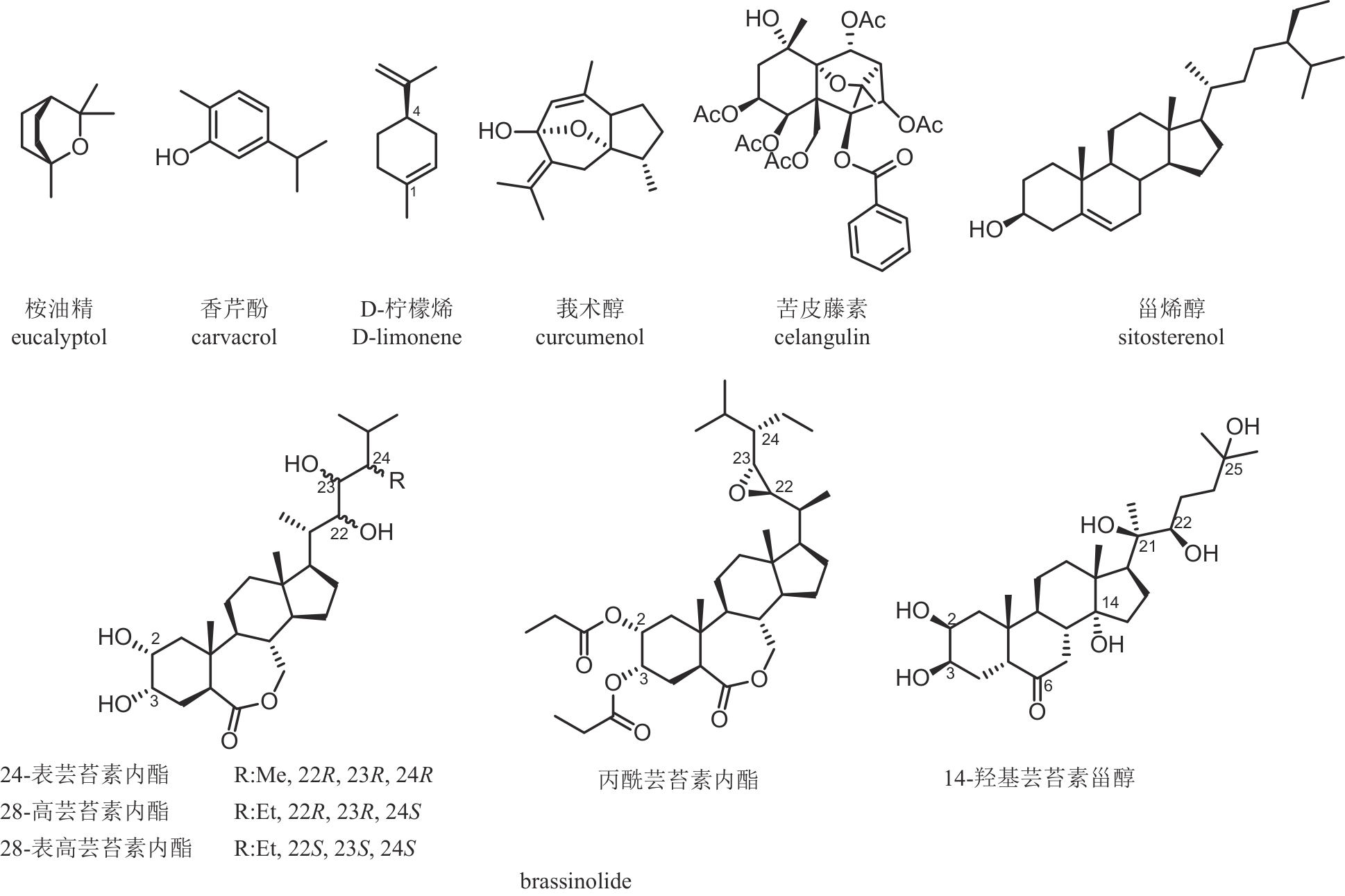
| 苦皮藤素 | 苦皮藤 Celastrus angulatus | 倍半萜类 | 杀虫 | 6% | PD20182273 LS20030503 |
| 甾烯醇 | 锦葵 Malva sp. | 甾体类 | 抗病毒 | 0.66% | PD20181615 LS20150137 |
| 螺威 | 油茶 Camellia oleifera | 三萜皂苷类 | 杀虫 | 50% | PD20131346 LS20080123 |
| 莪术醇 | 姜黄 Curcuma zedoaria | 倍半萜类 | 杀鼠 | 92% | PD20101276 LS20053774 |
| 桉油精 | 蓝桉 Eucalyptus globulus | 单萜类 | 杀虫 | 90% | PD20101270 LS20040664 |
| D-柠檬烯 | 柠檬 Citrus limon | 单萜类 | 杀虫/杀菌 | 92% | PD20220205 LS20160240 |
| 香芹酚 | 丁香 Syzygium aromaticum | 单萜类 | 杀虫/杀菌 | 16% | PD20200138 LS20011820 |
| 24-表芸苔素内酯 | 油菜 Brassica campestris | 甾醇类 | 植物生长调节剂 | 95% | PD20240892 PD20100303 |
| 28-高芸苔素内酯 | 油菜 Brassica campestris | 甾醇类 | 植物生长调节剂 | 95% | PD20241931 PD20080444 |
| 28-表高芸苔素内酯 | 油菜 Brassica campestris | 甾醇类 | 植物生长调节剂 | 90% | PD20241668 PD20082793 |
| 14-羟基芸苔素甾醇 | 油菜 Brassica campestris | 甾醇类 | 植物生长调节剂 | 80% | PD20242107 PD20070289 |
| 丙酰芸苔素内酯 | 油菜 Brassica campestris | 甾醇类 | 植物生长调节剂 | 80% | PD20242339 LS20011797 |
| 生物碱类 | |||||
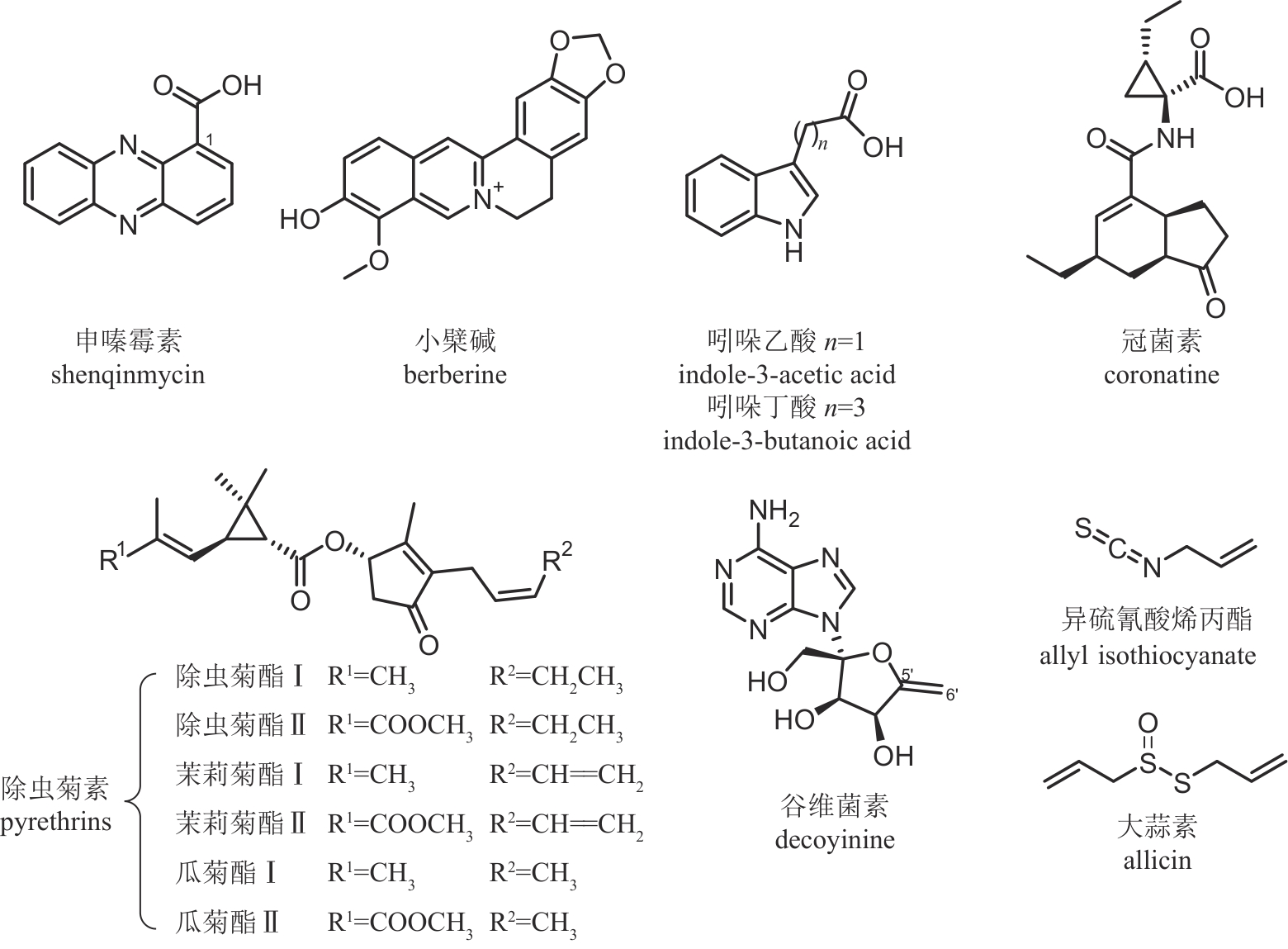
| 申嗪霉素 | 荧光假单胞菌 Pseudomonas fluorescens | 吩嗪类 | 杀菌 | 95% | PD20131515 LS20031381 |
| 小檗碱 | 黄连 Coptis chinensis | 喹啉生物碱类 | 杀菌 | 75% | PD20230660 LS20170288 |
| 吲哚乙酸 | 吲哚生物碱类 | 植物生长调节剂 | 97% | PD20241437 PD20081124 | |
| 吲哚丁酸 | 吲哚生物碱类 | 植物生长调节剂 | 95% | PD20230592 LS20050293 | |
| 其他类 | |||||
| 冠菌素 | 丁香假单胞菌 Pseudomonas syringae | 聚酮-非核糖体肽类 | 植物生长调节剂 | 98% | PD20211351 |
| 除虫菊素 | 除虫菊 Tanacetum cinerariifolium | 杂萜类 | 杀虫 | 60% | WP20210184 WL2001279 |
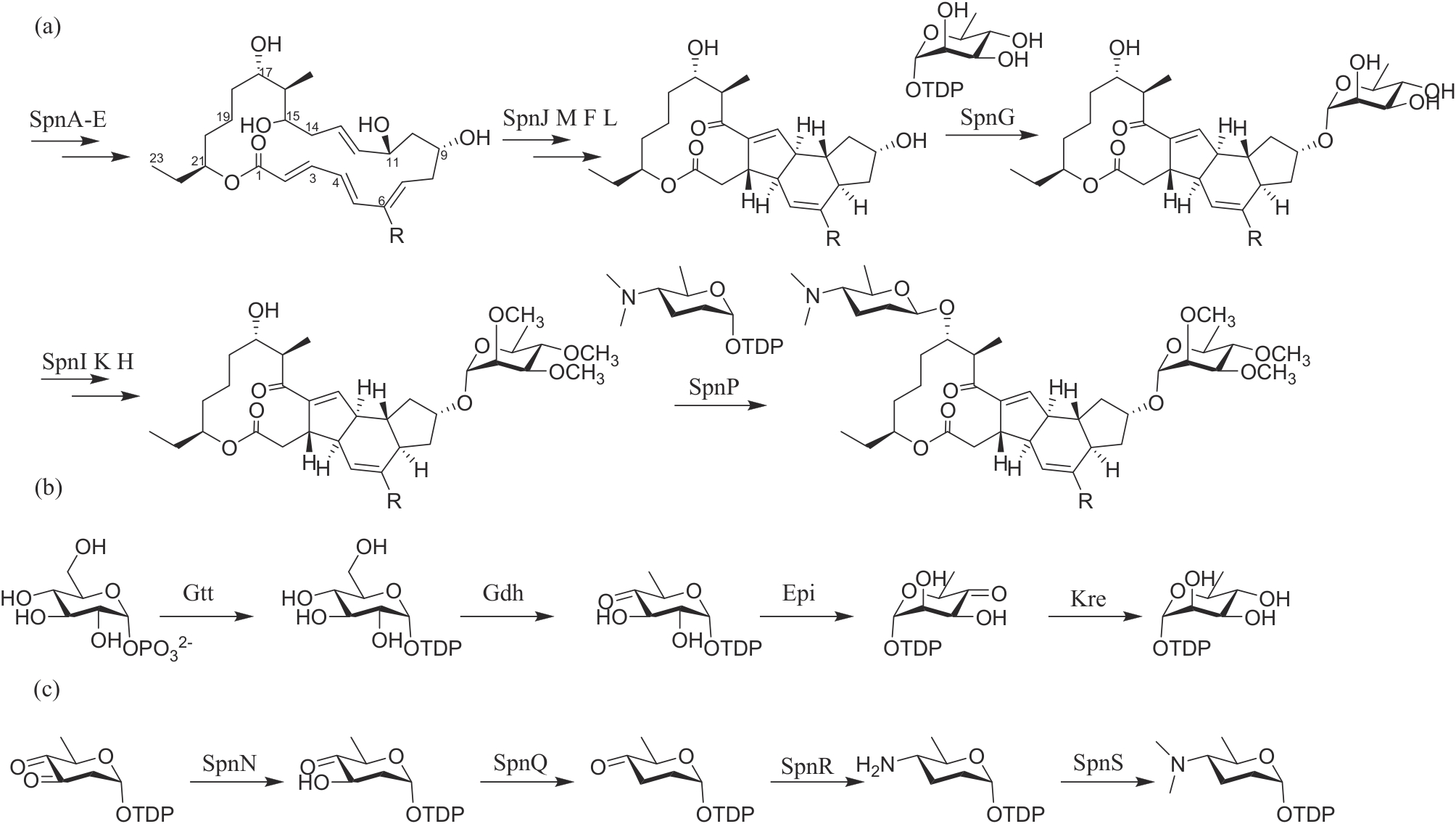
| 谷维菌素 | 链霉菌 Streptomyces sp. NEAU6 | 核苷类 | 植物生长调节剂 | 94% | PD20241925 PD20212929 |
| 异硫氰酸烯丙酯 | 羽衣甘蓝 Brassica oleracea | 有机硫类 | 杀菌/杀线虫 | 70% | PD20190037 PD20181601 |
| 大蒜素 | 大蒜 Allium sativum | 有机硫类 | 杀菌 | 50% | PD20161252 |
表1 2000年以来我国新登记的小分子生物农药
Table 1 Summary of small molecule biological pesticides registered in China between 2000 and 2024
| 农药名称 | 主要来源 | 结构分类 | 用途 | 原药有效成分含量 | 登记证号① |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 聚酮类 | |||||
| 多杀霉素 | 刺糖多孢菌 Saccharopolyspora spinosa | 大环内酯类 | 杀虫 | 92.5% | PD20241953 LS20042235 |
乙基多杀菌素 (半合成) | 刺糖多孢菌 Saccharopolyspora spinosa | 大环内酯类 | 杀虫 | 81.2% | PD20181527 LS20091058 |
伊维菌素 (半合成) | 阿维链霉菌 Streptomyces avermitilis | 大环内酯类 | 杀虫 | 95% | PD20211308 PD20120410 |
甲氨基阿维菌素苯甲酸盐 (半合成) | 阿维链霉菌 Streptomyces avermitilis | 大环内酯类 | 杀虫 | 90% | PD20182180 LS20021924 |
| 大黄素甲醚 | 掌叶大黄 Rheum palmatum | 蒽醌类 | 杀菌 | 8.5% | PD20190139 LS20080104 |
| 狼毒素 | 狼毒 Stellera chamaejasme | 黄酮类 | 杀虫 | 9.5% | PD20120876 LS20053042 |
| 蛇床子素 | 蛇床花 Cnidium monnieri | 香豆素类 | 杀菌/杀虫 | 2% | PD20183068 LS20030489 |
| 白藜芦醇 | 藜芦 Veratrum sp. | 芪类 | 杀菌 | 10% | PD20212931 |
| 萜烯类 | |||||
| 苦皮藤素 | 苦皮藤 Celastrus angulatus | 倍半萜类 | 杀虫 | 6% | PD20182273 LS20030503 |
| 甾烯醇 | 锦葵 Malva sp. | 甾体类 | 抗病毒 | 0.66% | PD20181615 LS20150137 |
| 螺威 | 油茶 Camellia oleifera | 三萜皂苷类 | 杀虫 | 50% | PD20131346 LS20080123 |
| 莪术醇 | 姜黄 Curcuma zedoaria | 倍半萜类 | 杀鼠 | 92% | PD20101276 LS20053774 |
| 桉油精 | 蓝桉 Eucalyptus globulus | 单萜类 | 杀虫 | 90% | PD20101270 LS20040664 |
| D-柠檬烯 | 柠檬 Citrus limon | 单萜类 | 杀虫/杀菌 | 92% | PD20220205 LS20160240 |
| 香芹酚 | 丁香 Syzygium aromaticum | 单萜类 | 杀虫/杀菌 | 16% | PD20200138 LS20011820 |
| 24-表芸苔素内酯 | 油菜 Brassica campestris | 甾醇类 | 植物生长调节剂 | 95% | PD20240892 PD20100303 |
| 28-高芸苔素内酯 | 油菜 Brassica campestris | 甾醇类 | 植物生长调节剂 | 95% | PD20241931 PD20080444 |
| 28-表高芸苔素内酯 | 油菜 Brassica campestris | 甾醇类 | 植物生长调节剂 | 90% | PD20241668 PD20082793 |
| 14-羟基芸苔素甾醇 | 油菜 Brassica campestris | 甾醇类 | 植物生长调节剂 | 80% | PD20242107 PD20070289 |
| 丙酰芸苔素内酯 | 油菜 Brassica campestris | 甾醇类 | 植物生长调节剂 | 80% | PD20242339 LS20011797 |
| 生物碱类 | |||||
| 申嗪霉素 | 荧光假单胞菌 Pseudomonas fluorescens | 吩嗪类 | 杀菌 | 95% | PD20131515 LS20031381 |
| 小檗碱 | 黄连 Coptis chinensis | 喹啉生物碱类 | 杀菌 | 75% | PD20230660 LS20170288 |
| 吲哚乙酸 | 吲哚生物碱类 | 植物生长调节剂 | 97% | PD20241437 PD20081124 | |
| 吲哚丁酸 | 吲哚生物碱类 | 植物生长调节剂 | 95% | PD20230592 LS20050293 | |
| 其他类 | |||||
| 冠菌素 | 丁香假单胞菌 Pseudomonas syringae | 聚酮-非核糖体肽类 | 植物生长调节剂 | 98% | PD20211351 |
| 除虫菊素 | 除虫菊 Tanacetum cinerariifolium | 杂萜类 | 杀虫 | 60% | WP20210184 WL2001279 |
| 谷维菌素 | 链霉菌 Streptomyces sp. NEAU6 | 核苷类 | 植物生长调节剂 | 94% | PD20241925 PD20212929 |
| 异硫氰酸烯丙酯 | 羽衣甘蓝 Brassica oleracea | 有机硫类 | 杀菌/杀线虫 | 70% | PD20190037 PD20181601 |
| 大蒜素 | 大蒜 Allium sativum | 有机硫类 | 杀菌 | 50% | PD20161252 |
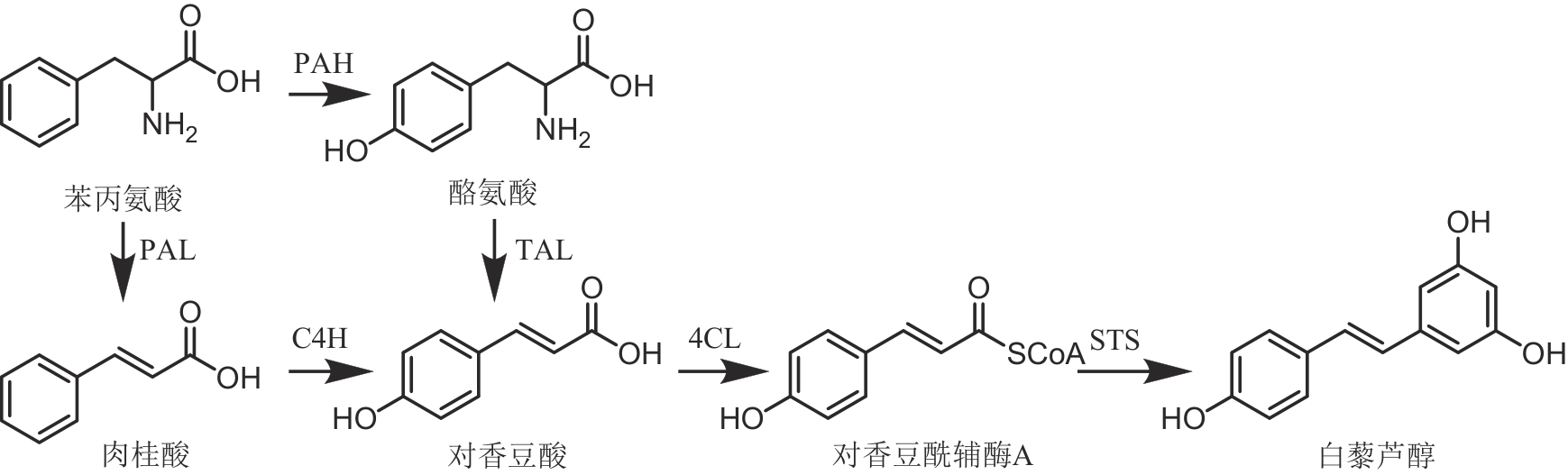
图5 白藜芦醇的生物合成通路(PAH—苯丙氨酸羟化酶;PAL—苯丙氨酸氨解酶;C4H—肉桂酸-4-羟化酶;TAL—酪氨酸氨解酶;4CL—对香豆酰辅酶A连接酶;STS—芪合酶)
Fig. 5 Biosynthetic pathway of resveratrol(PAH—phenylalanine hydroxylase; PAL—phenylalanine ammonia lyase; C4H—cinnamate-4-hydroxylase; TAL—tyrosine ammonia lyase; 4CL—4-coumarate CoA ligase; STS—stilbene synthase)
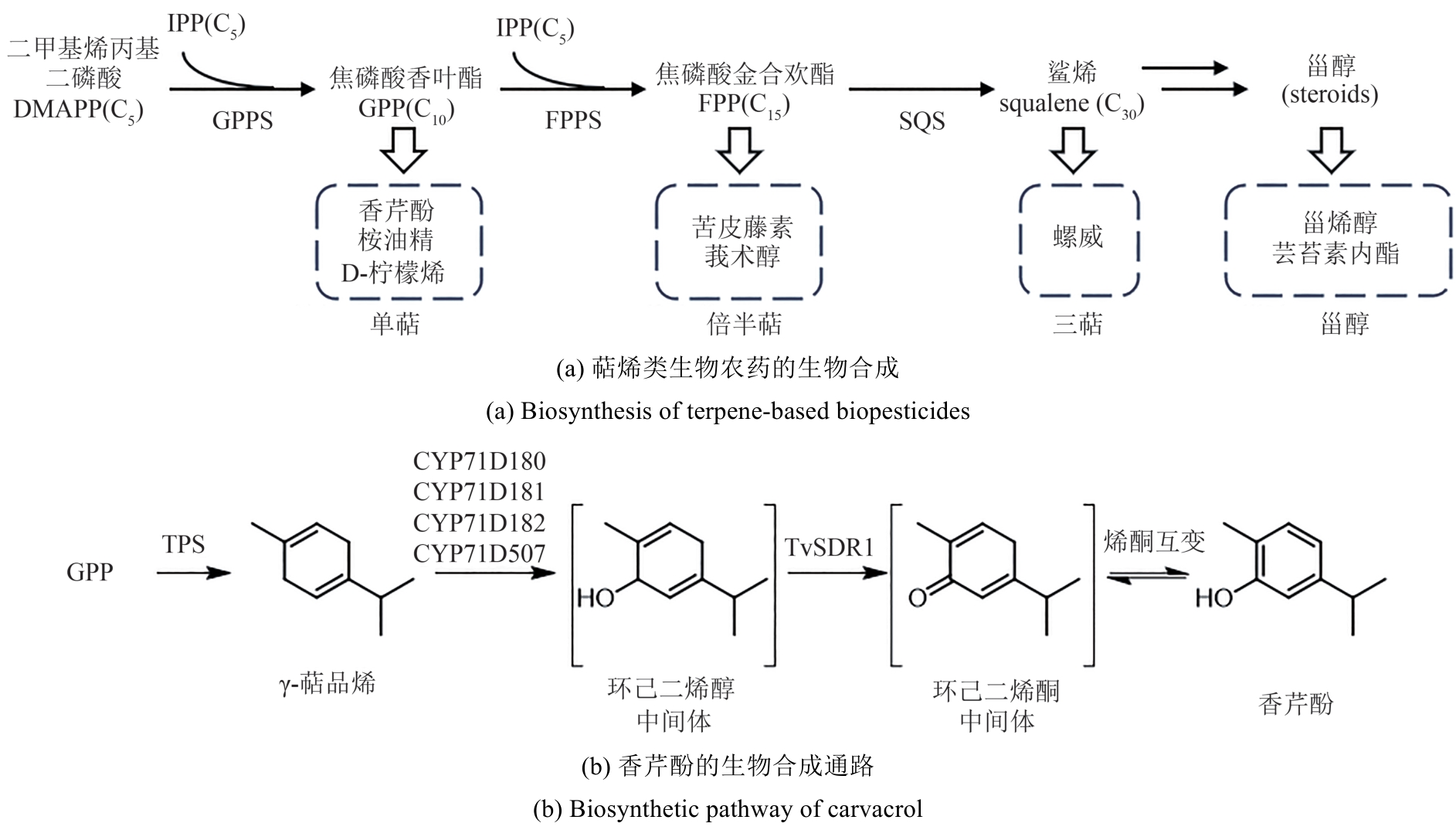
图6 萜烯类农药(TPS—γ-萜品烯合酶;CYP71D180等—P450单加氧酶;TvSDR1—短链还原酶1)
Fig. 6 Terpenes-based biopesticides(TPS—γ-terpinene synthase; CYP71D180, etc—cytochrome P450 monooxygenase; TvSDR1—short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase 1)
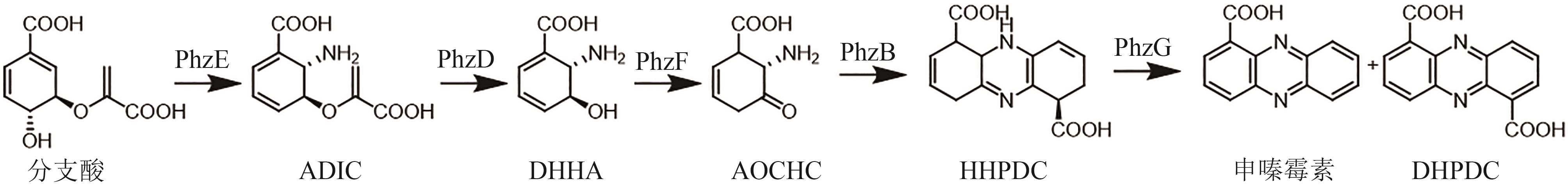
图7 申嗪霉素的生物合成途径(PhzE—2-氨基脱氧分支酸合酶;PhzD—异分支酸酶;PhzF—DHHA异构酶;PhzB—3-类固醇异构酶;PhzG—FMN依赖氧化酶)
Fig. 7 Biosynthetic pathway of shenqinmycin(PhzE—2-amino-2-desoxyisochorismate synthase; PhzD—isochorismatase; PhzF—DHHA isomerase; PhzB—Δ5-3-ketosteroid isomerase; PhzG—FMN-dependent oxidase)
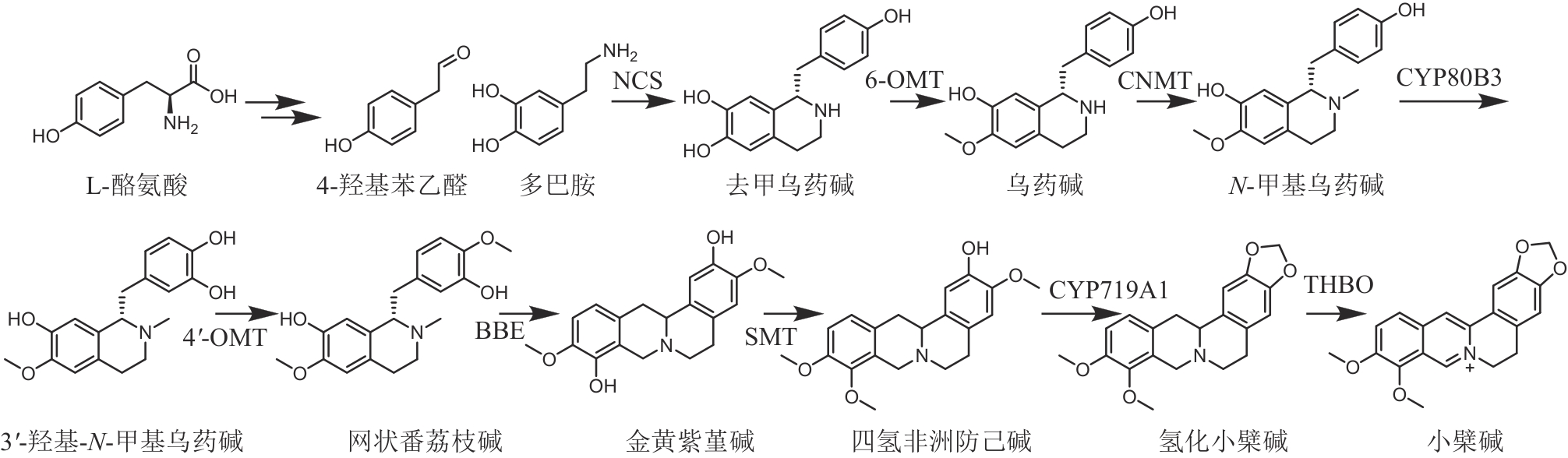
图8 小檗碱的生物合成途径(NCS—去甲乌药碱合酶;6-OMT—去甲乌药碱-6-O-甲基转移酶;CNMT—乌药碱-N-甲基转移酶;CYP80B3—N-甲基乌药碱-3′-羟化酶;4′-OMT—3′-羟基-N-甲基乌药碱-4′-O-甲基转移酶;BBE—小檗碱桥酶;SMT—金黄紫堇碱-9-O-甲基转移酶;CYP719A1—氢化小檗碱合酶;THBO—四氢小檗碱氧化酶)
Fig. 8 Biosynthetic pathway of berberine(NCS—noraconitine synthase; 6-OMT—noraconitine 6-O-methyltransferase; CNMT—coclaurine N-methyltransferase; CYP80B3—N-methylcoclaurine 3′-hydroxylase; 4′-OMT—3′-hydroxy-N-methylcoclaurine 4′-O-methyltransferase; BBE—berberine bridge enzyme; SMT—scoulerine-9-O-methyltransferase; CYP719A1—canadine synthase; THBO—tetrahydroberberine oxidase)
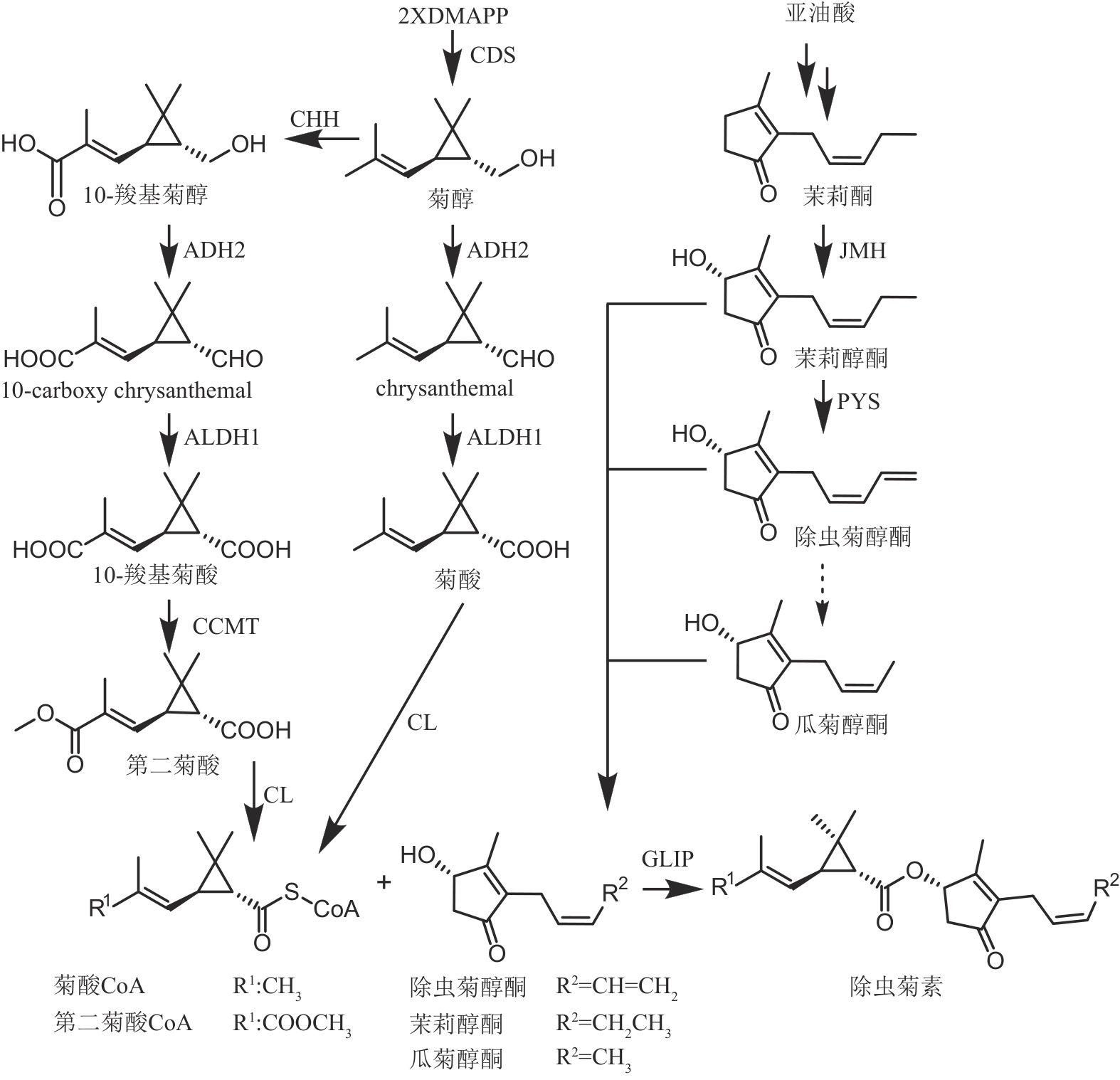
图9 除虫菊素的生物合成途径(CDS—菊基二磷酸合成酶;CHH—chrysanthemol羟化酶;ADH2—乙醇脱氢酶2;ALDH1—醛脱氢酶1;CCMT—10-羧基菊酸10-甲基转移酶;CL—辅酶A连接酶;JMH—茉莉酮羟化酶;PYS—除虫菊醇酮合酶;GLIP—GDSL脂肪酶)
Fig. 9 Biosynthetic pathway of pyrethrins(CDS—chrysanthemyl diphosphate synthase; CHH—chrysanthemol 10-hydroxylase; ADH2—alcohol dehydrogenase 2; ALDH1—aldehyde dehydrogenase 1; CCMT—10-carboxychrysanthemic acid 10-methyltransferase; CL—CoA ligase; JMH—jasmone hydroxylase; PYS—pyrethrolone synthase; GLIP—GDSL lipase)
| [1] | FENIBO E O, IJOMA G N, MATAMBO T. Biopesticides in sustainable agriculture: current status and future prospects[M/OL]//MANDAL S D, RAMKUMAR G, KARTHI S, et al. New and future development in biopesticide research: biotechnological exploration. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 2022: 1-53. (2022-05-04)[2024-12-01]. . |
| [2] | AIOUB A A A, GHOSH S, AL-FARGA A, et al. Back to the origins: biopesticides as promising alternatives to conventional agrochemicals[J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2024, 169(4): 697-713. |
| [3] | ARORA N K, VERMA M, PRAKASH J, et al. Regulation of biopesticides: global concerns and policies[M/OL]//ARORA N K, MEHNAZ S, BALESTRINI R. Bioformulations: for sustainable agriculture. New Delhi: Springer India, 2016: 283-299. (2016-06-07)[2024-12-01]. . |
| [4] | WANG Q, WANG Z S. Chapter 10 - Biopesticides in China: development, commercialization, and regulation [M/OL]// KOUL O. Development and commercialization of biopesticides. New York: Academic Press, 2023: 203-12. (2023-04-21)[2024-12-01]. . |
| [5] | FENIBO E O, IJOMA G N, MATAMBO T. Biopesticides in sustainable agriculture: a critical sustainable development driver governed by green chemistry principles[J]. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems, 2021, 5: 619058. |
| [6] | LI J, RONG L X, ZHAO Y, et al. Next-generation metabolic engineering of non-conventional microbial cell factories for carboxylic acid platform chemicals[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2020, 43: 107605. |
| [7] | LÜBECK M, LÜBECK P S. Fungal cell factories for efficient and sustainable production of proteins and peptides[J]. Microorganisms, 2022, 10(4): 753. |
| [8] | GAYEN A K, NICHOLS L, WILLIAMS G J. An artificial pathway for polyketide biosynthesis[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2020, 3(7): 536-538. |
| [9] | JANAS A, PRZYBYLSKI P. 14- and 15-Membered lactone macrolides and their analogues and hybrids: structure, molecular mechanism of action and biological activity[J]. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2019, 182: 111662. |
| [10] | WANG R L, LIU S X, MA Z Y. Recent development of versatile polyphenol platforms in fertilizers and pesticides[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2023, 71(25): 9599-9608. |
| [11] | SPARKS T C, CROUSE G D, BENKO Z, et al. The spinosyns, spinosad, spinetoram, and synthetic spinosyn mimics-discovery, exploration, and evolution of a natural product chemistry and the impact of computational tools[J]. Pest Management Science, 2021, 77(8): 3637-3649. |
| [12] | GALM U, SPARKS T C. Natural product derived insecticides: discovery and development of spinetoram[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2016, 43(2): 185-193. |
| [13] | TANG J L, ZHU Z R, HE H C, et al. Bacterioferritin: a key iron storage modulator that affects strain growth and butenyl-spinosyn biosynthesis in Saccharopolyspora pogona [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2021, 20(1): 157. |
| [14] | WATSON G B. Actions of insecticidal spinosyns on γ-aminobutyric acid responses from small-diameter cockroach neurons[J]. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 2001, 71(1): 20-28. |
| [15] | LEWER P, HAHN D R, KARR L L, et al. Discovery of the butenyl-spinosyn insecticides: novel macrolides from the new bacterial strain Saccharopolyspora pogona [J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2009, 17(12): 4185-4196. |
| [16] | JOHNSON-ARBOR K. Ivermectin: a mini-review[J]. Clinical Toxicology, 2022, 60(5): 571-575. |
| [17] | GHORBANI A, AMIRI M S, HOSSEINI A. Pharmacological properties of Rheum turkestanicum janisch[J]. Heliyon, 2019, 5(6): e01986. |
| [18] | HAREERI R H, ALDURDUNJI M M, ABDALLAH H M, et al. Aspergillus ochraceus: metabolites, bioactivities, biosynthesis, and biotechnological potential[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(19): 6759. |
| [19] | LI X, LIU Y J, CHU S F, et al. Physcion and physcion 8-O-β-glucopyranoside: a review of their pharmacology, toxicities and pharmacokinetics[J]. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 2019, 310: 108722. |
| [20] | VIKAL A, MAURYA R, BHOWMIK S, et al. Resveratrol: a comprehensive review of its multifaceted health benefits, mechanisms of action, and potential therapeutic applications in chronic disease[J]. Pharmacological Research-Natural Products, 2024, 3: 100047. |
| [21] | SHARIFI-RAD J, QUISPE C, DURAZZO A, et al. Resveratrol’ biotechnological applications: enlightening its antimicrobial and antioxidant properties[J]. Journal of Herbal Medicine, 2022, 32: 100550. |
| [22] | KANG J E, YOO N, JEON B J, et al. Resveratrol oligomers, plant-produced natural products with anti-virulence and plant immune-priming roles[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 885625. |
| [23] | CHEN J C, LIAO X F, GAN J W. Review on the protective activity of osthole against the pathogenesis of osteoporosis[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2023, 14: 1236893. |
| [24] | SUN M N, SUN M J, ZHANG J Y. Osthole: an overview of its sources, biological activities, and modification development[J]. Medicinal Chemistry Research, 2021, 30(10): 1767-1794. |
| [25] | 石志琦, 沈寿国, 徐朗莱, 等. 蛇床子素对植物病原真菌抑制机制的初步研究[J]. 农药学学报, 2004, 6(4): 28-32. |
| SHI Z Q, SHEN S G, XU L L, et al. Inhibition mechanism of osthol to plant fungus pathogens[J]. Chinese Journal of Pesticide Science, 2004, 6(4): 28-32. | |
| [26] | 阴旗俊, 孙海峰. 蛇床子素的药理作用和作为生物农药的研究[J]. 中医药信息, 2009, 26(2): 13-15, 93. |
| YIN Q J, SUN H F. Pharmacological effects and research of osthole as a biological pesticide[J]. Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2009, 26(2): 13-15, 93. | |
| [27] | YANG G H, LIAO Z X, XU Z Y, et al. Antimitotic and antifungal C-3/C-3″-biflavanones from Stellera chamaejasme [J]. ChemInform, 2005, 36(52): 200552196. |
| [28] | 宋丽雯, 张新虎, 沈慧敏. 1.6%瑞香狼毒素水乳剂对4种蔬菜害虫的作用方式比较[J]. 植物保护, 2017, 43(1): 218-223. |
| SONG L W, ZHANG X H, SHEN H M. Comparison of different actions of 1.6% daphneantoxin EW on four vegetable pests[J]. Plant Protection, 2017, 43(1): 218-223. | |
| [29] | ZHOU C M, ZHOU J Y, WU Y J, et al. Mugwort essential oil and its major constituent, eucalyptol, elicits oviposition avoidance of Drosophila suzukii [J]. Entomologia Generalis, 2024, 44(3): 673-683. |
| [30] | MĄCZKA W, TWARDAWSKA M, GRABARCZYK M, et al. Carvacrol - a natural phenolic compound with antimicrobial properties[J]. Antibiotics, 2023, 12(5): 824. |
| [31] | SILVA E R, DE CARVALHO F O, TEIXEIRA L G B, et al. Pharmacological effects of carvacrol in in vitro studies: a review[J]. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2018, 24(29): 3454-3465. |
| [32] | 李烨青, 张昌朋, 方楠, 等. 柠檬烯在农业病虫草害防控中的应用研究进展[J]. 农药学学报, 2023, 25(5): 1004-1016. |
| LI Y Q, ZHANG C P, FANG N, et al. Research progress of limonene in the prevention and control of agricultural diseases, pests and weeds[J]. Chinese Journal of Pesticide Science, 2023, 25(5): 1004-1016. | |
| [33] | DENKOVA-KOSTOVA R, TENEVA D, TOMOVA T, et al. Chemical composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of essential oils from tangerine (Citrus reticulata L.), grapefruit (Citrus paradisi L.), lemon (Citrus lemon L.) and cinnamon (Cinnamomum zeylanicum Blume)[J]. Zeitschrift Fur Naturforschung C, 2021, 76(5-6): 175-185. |
| [34] | QIAN H, HU Y K, WANG Z Y, et al. In-depth structural simplification of celangulin Ⅴ: design, synthesis, and biological activity[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024, 72(27): 15142-15150. |
| [35] | ROY G, CHAKRABORTY K, NANDY P, et al. Pros and cons of curcumin as bioactive phyto- compound for effective management of insect pests[J]. American Scientific Research Journal for Engineering, Technology, and Sciences, 2014, 7(1): 31-43. |
| [36] | FU Y S, CHEN T H, WENG L B, et al. Pharmacological properties and underlying mechanisms of curcumin and prospects in medicinal potential[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2021, 141: 111888. |
| [37] | 官威, 洪青标, 吕山, 等. 钉螺控制技术研究进展[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2017, 29(2): 246-251. |
| GUAN W, HONG Q B, LÜ S, et al. Research progress of control techniques on Oncomelania hupensis [J]. Chinese Journal of Schistosomiasis Control, 2017, 29(2): 246-251. | |
| [38] | 吴洪初, 马玉才, 张正球, 等. 3种常用灭螺药大规模现场应用效果与费用评价[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2018, 30(6): 619-624. |
| WU H C, MA Y C, ZHANG Z Q, et al. Effect and cost-effectiveness of three commonly used molluscicides in largescale field application[J]. Chinese Journal of Schistosomiasis Control, 2018, 30(6): 619-624. | |
| [39] | 曹磊, 顾爱国, 王莉. 高效液相色谱法测定0.06%甾烯醇微乳剂中有效成分含量方法研究[J]. 现代农业科技, 2018(2): 125-126. |
| CAO L, GU A G, WANG L. Determination of active component content in 0.06% β-sitosterol ME by HPLC[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018(2): 125-126. | |
| [40] | 张上林, 毕艳, 张祝华, 等. 0.06%甾烯醇微乳剂防治番茄病毒病田间药效试验[J]. 天津农林科技, 2019(5): 25-26. |
| ZHANG S L, BI Y, ZHANG Z H, et al. Field efficacy of 0.06% sterol microemulsion against tomato virus disease[J]. Science and Technology of Tianjin Agriculture and Forestry, 2019(5): 25-26. | |
| [41] | BAJGUZ A, CHMUR M, GRUSZKA D. Comprehensive overview of the brassinosteroid biosynthesis pathways: substrates, products, inhibitors, and connections[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 1034. |
| [42] | MÜSSIG C. Brassinosteroid-promoted growth[J]. Plant Biology, 2005, 7(2): 110-117. |
| [43] | JIANG H X, WANG J, ZHOU L, et al. Coenzyme Q biosynthesis in the biopesticide Shenqinmycin-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain M18[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2019, 46(7): 1025-1038. |
| [44] | ZHAO X Z, CHEN Z, YU L, et al. Investigating the antifungal activity and mechanism of a microbial pesticide Shenqinmycin against Phoma sp[J]. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 2018, 147: 46-50. |
| [45] | TANG J T, LI Y K, ZHANG L L, et al. Biosynthetic pathways and functions of indole-3-acetic acid in microorganisms[J]. Microorganisms, 2023, 11(8): 2077. |
| [46] | FU S F, WEI J Y, CHEN H W, et al. Indole-3-acetic acid: a widespread physiological code in interactions of fungi with other organisms[J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2015, 10(8): e1048052. |
| [47] | GENG X Q, JIN L, SHIMADA M, et al. The phytotoxin coronatine is a multifunctional component of the virulence armament of Pseudomonas syringae [J]. Planta, 2014, 240(6): 1149-1165. |
| [48] | YOUNG S A, PARK S K, RODGERS C, et al. Physical and functional characterization of the gene cluster encoding the polyketide phytotoxin coronatine in Pseudomonas syringae pv. glycinea[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1992, 174(6): 1837-1843. |
| [49] | GAO M, ZHANG C, LU H. Coronatine is more potent than jasmonates in regulating Arabidopsis circadian clock[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 12862. |
| [50] | HODOȘAN C, GÎRD C E, GHICA M V, et al. Pyrethrins and pyrethroids: a comprehensive review of natural occurring compounds and their synthetic derivatives[J]. Plants, 2023, 12(23): 4022. |
| [51] | VALENTINE W M. Pyrethrin and pyrethroid insecticides[J]. Veterinary Clinics of North America: Small Animal Practice, 1990, 20(2): 375-382. |
| [52] | YU L, ZHOU W T, SHE Y X, et al. Efficient biosynthesis of nucleoside cytokinin angustmycin A containing an unusual sugar system[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 6633. |
| [53] | MITANI T, HEINZE J E, FREESE E. Induction of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis by decoyinine or hadacidin[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 1977, 77(3): 1118-1125. |
| [54] | 王龙, 刘悦, 邹子玉, 等. 1%谷维菌素可溶液剂对水稻生长和产量的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2023, 51(14): 83-89. |
| WANG L, LIU Y, ZOU Z Y, et al. Effects of guvermectin 1% SL on growth and yield of rice[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 51(14): 83-89. | |
| [55] | PATIL P B, PATEL J K. Chemopreventive aspects, investigational anticancer applications and current perspectives on allyl isothiocyanate (AITC): a review[J]. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 2023, 478(12): 2763-2777. |
| [56] | DENG Y P, HO C T, LAN Y Q, et al. Bioavailability, health benefits, and delivery systems of allicin: a review[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2023, 71(49): 19207-19220. |
| [57] | CHOO S, CHIN V K, WONG E H, et al. Review: antimicrobial properties of allicin used alone or in combination with other medications[J]. Folia Microbiologica, 2020, 65(3): 451-465. |
| [58] | YANG X, BAI S, WU J M, et al. Antifungal activity and potential action mechanism of allicin against Trichosporon asahii [J]. Microbiology Spectrum, 2023, 11(3): e00907-23. |
| [59] | YI J S, KIM J M, BAN Y H, et al. Modular polyketide synthase-derived insecticidal agents: from biosynthesis and metabolic engineering to combinatorial biosynthesis for their production[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2023, 40(5): 972-987. |
| [60] | HUANG K X, XIA L Q, ZHANG Y M, et al. Recent advances in the biochemistry of spinosyns[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2009, 82(1): 13-23. |
| [61] | KIM H J, PONGDEE R, WU Q Q, et al. The biosynthesis of spinosyn in Saccharopolyspora spinosa: synthesis of the cross-bridging precursor and identification of the function of SpnJ[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2007, 129(47): 14582-14584. |
| [62] | GORDEEV E G, ANANIKOV V P. Computational study of a model system of enzyme-mediated [4+2] cycloaddition reaction[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(4): e0119984. |
| [63] | ISIORHO E A, LIU H W, KEATINGE-CLAY A T. Structural studies of the spinosyn rhamnosyltransferase, SpnG[J]. Biochemistry, 2012, 51(6): 1213-1222. |
| [64] | BANERJEE A, SHARKEY T D. Methylerythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) pathway metabolic regulation[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2014, 31(8): 1043-1055. |
| [65] | RODRı́GUEZ-CONCEPCIÓN M, BORONAT A. Elucidation of the methylerythritol phosphate pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis in bacteria and plastids. a metabolic milestone achieved through genomics[J]. Plant Physiology, 2002, 130(3): 1079-1089. |
| [66] | MIZIORKO H M. Enzymes of the mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2011, 505(2): 131-143. |
| [67] | CROTEAU R, ALONSO W R, KOEPP A E, et al. Biosynthesis of monoterpenes: partial purification, characterization, and mechanism of action of 1,8-cineole synthase[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 1994, 309(1): 184-192. |
| [68] | LÜCKER J, TAMER M K EL, SCHWAB W, et al. Monoterpene biosynthesis in lemon (Citrus limon)[J]. European Journal of Biochemistry, 2002, 269(13): 3160-3171. |
| [69] | JONGEDIJK E, CANKAR K, BUCHHAUPT M, et al. Biotechnological production of limonene in microorganisms[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2016, 100(7): 2927-2938. |
| [70] | KRAUSE S T, LIAO P, CROCOLL C, et al. The biosynthesis of thymol, carvacrol, and thymohydroquinone in Lamiaceae proceeds via cytochrome P450s and a short-chain dehydrogenase[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2021, 118(52): e2110092118. |
| [71] | LI Q A, MAVRODI D V, THOMASHOW L S, et al. Ligand binding induces an ammonia channel in 2-amino-2-desoxyisochorismate (ADIC) synthase PhzE[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2011, 286(20): 18213-18221. |
| [72] | PARSONS J F, CALABRESE K, EISENSTEIN E, et al. Structure and mechanism of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PhzD, an isochorismatase from the phenazine biosynthetic pathway[J]. Biochemistry, 2003, 42(19): 5684-5693. |
| [73] | BLANKENFELDT W, KUZIN A P, SKARINA T, et al. Structure and function of the phenazine biosynthetic protein PhzF from Pseudomonas fluorescens [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101(47): 16431-16436. |
| [74] | AHUJA E G, JANNING P, MENTEL M, et al. PhzA/B catalyzes the formation of the tricycle in phenazine biosynthesis[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008, 130(50): 17053-17061. |
| [75] | XU N N, AHUJA E G, JANNING P, et al. Trapped intermediates in crystals of the FMN-dependent oxidase PhzG provide insight into the final steps of phenazine biosynthesis[J]. Acta Crystallographica Section D, Biological Crystallography, 2013, 69(Pt 8): 1403-1413. |
| [76] | SAMANANI N, FACCHINI P J. Purification and characterization of norcoclaurine synthase. The first committed enzyme in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis in plants[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2002, 277(37): 33878-33883. |
| [77] | MINAMI H, KIM J S, IKEZAWA N. Microbial production of plant benzylisoquinoline alkaloids[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2008, 105(21): 7393-7398. |
| [78] | MUEMMLER S, RUEFFER M, NAGAKURA N, et al. S-adenosyl-L-methionine: (S)-scoulerine 9-O-methyltransferase, a highly stereo- and regio-specific enzyme in tetrahydroprotoberberine biosynthesis[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 1985, 4(1): 36-39. |
| [79] | IKEZAWA N, IWASA K, SATO F. CYP719A subfamily of cytochrome P450 oxygenases and isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis in Eschscholzia californica [J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2009, 28(1): 123-133. |
| [80] | MATSUDA K, KIKUTA Y, HABA A, et al. Biosynthesis of pyrethrin Ⅰ in seedlings of Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium [J]. Phytochemistry, 2005, 66(13): 1529-1535. |
| [81] | XU H Y, MOGHE G D, WIEGERT-RININGER K, et al. Coexpression analysis identifies two oxidoreductases involved in the biosynthesis of the monoterpene acid moiety of natural pyrethrin insecticides in Tanacetum cinerariifolium [J]. Plant Physiology, 2018, 176(1): 524-537. |
| [82] | XU H Y, LYBRAND D, BENNEWITZ S, et al. Production of trans-chrysanthemic acid, the monoterpene acid moiety of natural pyrethrin insecticides, in tomato fruit[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 47: 271-278. |
| [83] | XU H Y, LI W, SCHILMILLER A L, et al. Pyrethric acid of natural pyrethrin insecticide: complete pathway elucidation and reconstitution in Nicotiana benthamiana [J]. New Phytologist, 2019, 223(2): 751-765. |
| [84] | LI W, ZHOU F, PICHERSKY E. Jasmone hydroxylase, a key enzyme in the synthesis of the alcohol moiety of pyrethrin insecticides[J]. Plant Physiology, 2018, 177(4): 1498-1509. |
| [85] | LI W, LYBRAND D B, ZHOU F, et al. Pyrethrin biosynthesis: the cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase CYP82Q3 converts jasmolone to pyrethrolone[J]. Plant Physiology, 2019, 181(3): 934-944. |
| [86] | LYBRAND D B, XU H Y, LAST R L, et al. How plants synthesize pyrethrins: safe and biodegradable insecticides[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2020, 25(12): 1240-1251. |
| [87] | LIANG Y, LU W Y, WEN J P. Improvement of Saccharopolyspora spinosa and the kinetic analysis for spinosad production[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2009, 152(3): 440-448. |
| [88] | ZHANG X M, XUE C Y, ZHAO F L, et al. Suitable extracellular oxidoreduction potential inhibit rex regulation and effect central carbon and energy metabolism in Saccharopolyspora spinosa [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2014, 13: 98. |
| [89] | ZHAO F L, ZHANG C B, YIN J, et al. Coupling of spinosad fermentation and separation process via two-step macroporous resin adsorption method[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2015, 176(8): 2144-2156. |
| [90] | LAN Z, ZHAO C, GUO W Q, et al. Optimization of culture medium for maximal production of spinosad using an artificial neural network - genetic algorithm modeling[J]. Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 25(4): 253-261. |
| [91] | BAI Y, ZHOU P P, FAN P, et al. Four-stage dissolved oxygen strategy based on multi-scale analysis for improving spinosad yield by Saccharopolyspora spinosa ATCC49460[J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 2015, 8(3): 561-568. |
| [92] | WANG C, ZHANG X L, CHEN Z, et al. Strain construction for enhanced production of spinosad via intergeneric protoplast fusion[J]. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 2009, 55(9): 1070-1075. |
| [93] | JIN Z H, XU B, LIN S Z, et al. Enhanced production of spinosad in Saccharopolyspora spinosa by genome shuffling[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2009, 159(3): 655-663. |
| [94] | LUO Y S, KOU X X, DING X Z, et al. Promotion of spinosad biosynthesis by chromosomal integration of the Vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene in Saccharopolyspora spinosa [J]. Science China Life Sciences, 2012, 55(2): 172-180. |
| [95] | PAN H X, LI J, HE N J, et al. Improvement of spinosad production by overexpression of gtt and gdh controlled by promoter PermE* in Saccharopolyspora spinosa SIPI-A2090[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2011, 33(4): 733-739. |
| [96] | JHA A K, POKHREL A R, CHAUDHARY A K, et al. Metabolic engineering of rational screened Saccharopolyspora spinosa for the enhancement of spinosyns A and D production[J]. Molecules and Cells, 2014, 37(10): 727-733. |
| [97] | WANG X Y, ZHANG C B, WANG M L, et al. Genome-scale metabolic network reconstruction of Saccharopolyspora spinosa for spinosad production improvement[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2014, 13(1): 41. |
| [98] | AN Z H, TAO H, WANG Y, et al. Increasing the heterologous production of spinosad in Streptomyces albus J1074 by regulating biosynthesis of its polyketide skeleton[J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2021, 6(4): 292-301. |
| [99] | HUANG J, YU Z, LI M H, et al. High level of spinosad production in the heterologous host Saccharopolyspora erythraea [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2016, 82(18): 5603-5611. |
| [100] | LI J, MU X, DONG W Y, et al. A non-carboxylative route for the efficient synthesis of central metabolite malonyl-CoA and its derived products[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2024, 7(4): 361-374. |
| [101] | KALLSCHEUER N, VOGT M, STENZEL A, et al. Construction of a Corynebacterium glutamicum platform strain for the production of stilbenes and (2S)-flavanones[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2016, 38: 47-55. |
| [102] | BRAGA A, OLIVEIRA J, SILVA R, et al. Impact of the cultivation strategy on resveratrol production from glucose in engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2018, 265: 70-75. |
| [103] | ZHANG M Y, GAO Q D, LIU Y J, et al. Metabolic engineering of Rhodotorula toruloides for resveratrol production[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2022, 21(1): 270. |
| [104] | SHRESTHA A, PANDEY R P, POKHREL A R, et al. Modular pathway engineering for resveratrol and piceatannol production in engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(22): 9691-9706. |
| [105] | LIM C G, FOWLER Z L, HUELLER T, et al. High-yield resveratrol production in engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 77(10): 3451-3460. |
| [106] | MENG L J, DIAO M X, WANG Q Y, et al. Efficient biosynthesis of resveratrol via combining phenylalanine and tyrosine pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2023, 22(1): 46. |
| [107] | SÁEZ-SÁEZ J, WANG G K, MARELLA E R, et al. Engineering the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica for high-level resveratrol production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 62: 51-61. |
| [108] | TRANCHIDA P Q, ZOCCALI M, BONACCORSI I, et al. The off-line combination of high performance liquid chromatography and comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-mass spectrometry: a powerful approach for highly detailed essential oil analysis[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2013, 1305: 276-284. |
| [109] | NICHKOVA M, FU X, YANG Z, et al. Immunochemical screening of pesticides (simazine and cypermethrin) in orange oil[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2009, 57(13): 5673-5679. |
| [110] | DUNLOP M J, DOSSANI Z Y, SZMIDT H L, et al. Engineering microbial biofuel tolerance and export using efflux pumps[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2011, 7: 487. |
| [111] | ALONSO-GUTIERREZ J, CHAN R, BATTH T S, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for limonene and perillyl alcohol production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2013, 19: 33-41. |
| [112] | WU J H, CHENG S, CAO J Y, et al. Systematic optimization of limonene production in engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2019, 67(25): 7087-7097. |
| [113] | ROLF J, JULSING M K, ROSENTHAL K, et al. A gram-scale limonene production process with engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Molecules, 2020, 25(8): 1881. |
| [114] | ZHANG X, LIU X, MENG Y H, et al. Combinatorial engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for improving limonene production[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 176: 108155. |
| [115] | 王靖楠, 庞建, 秦磊, 等. 丁烯基多杀菌素高产菌株的选育和改造策略[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 566-576. |
| WANG J N, PANG J, QIN L, et al. Breeding and modification strategies of butenyl-spinosyn high-yield strains[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(2): 566-576. | |
| [116] | 徐周钦, 郭超, 李金萍, 等. 60Co-NTG复合诱变选育丁烯基多杀菌素高产菌株及其杀虫活性[J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2024, 40(2): 299-309. |
| XU Z Q, GUO C, LI J P, et al. Breeding of butenyl-spinosyns high yielding strain by 60Co-NTG compound mutation and its insecticidal activity[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2024, 40(2): 299-309. | |
| [117] | 曹浩榄, 王立军, 冯颖赢, 等. 龟裂霉素新产生菌株的鉴定及其产量优化[J]. 微生物学通报, 2024, 51(8): 3133-3147. |
| CAO H L, WANG L J, FENG Y Y, et al. Identification and yield improvement of a new rimocidin-producing strain[J]. Microbiology China, 2024, 51(8): 3133-3147. | |
| [118] | WANG J Y, LI Z L, WANG W S, et al. Dynamic control strategy to produce riboflavin with lignocellulose hydrolysate in the thermophile Geobacillus thermoglucosidasius [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2022, 11(6): 2163-2174. |
| [119] | YIN M M, XIE L N, CHEN K, et al. Re-engineering fungal nonribosomal peptide synthetases by module dissection and duplicated thiolation domains[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(33): e202406360. |
| [1] | 于文文, 吕雪芹, 李兆丰, 刘龙. 植物合成生物学与母乳低聚糖生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(5): 992-997. |
| [2] | 颜钊涛, 周鹏飞, 汪阳忠, 张鑫, 谢雯燕, 田晨菲, 王勇. 植物合成生物学:植物细胞大规模培养的新机遇[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(5): 1107-1125. |
| [3] | 孙扬, 陈立超, 石艳云, 王珂, 吕丹丹, 徐秀美, 张立新. 作物光合作用合成生物学的策略与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(5): 1025-1040. |
| [4] | 赵欣雨, 盛琦, 刘开放, 刘佳, 刘立明. 天冬氨酸族饲用氨基酸微生物细胞工厂的创制[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(5): 1184-1202. |
| [5] | 何杨昱, 杨凯, 王玮琳, 黄茜, 丘梓樱, 宋涛, 何流赏, 姚金鑫, 甘露, 何玉池. 国际基因工程机器大赛中植物合成生物学主题的设计与实践[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(5): 1243-1254. |
| [6] | 张学博, 朱成姝, 陈睿雲, 金庆姿, 刘晓, 熊燕, 陈大明. 农业合成生物学:政策规划与产业发展协同推进[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(5): 1224-1242. |
| [7] | 刘婕, 郜钰, 马永硕, 尚轶. 合成生物学在农业中的进展及挑战[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(5): 998-1024. |
| [8] | 郑雷, 郑棋腾, 张天骄, 段鲲, 张瑞福. 构建根际合成微生物菌群促进作物养分高效吸收利用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(5): 1058-1071. |
| [9] | 李超, 张焕, 杨军, 王二涛. 固氮合成生物学研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(5): 1041-1057. |
| [10] | 刘丹, 王建宇, 江正强. 中性核心母乳寡糖生物合成的研究进展和发展趋势[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(5): 1126-1144. |
| [11] | 魏家秀, 嵇佩云, 节庆雨, 黄秋燕, 叶浩, 戴俊彪. 植物人工染色体的构建与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(5): 1093-1106. |
| [12] | 王明鹏, 陈蕾, 赵一冉, 张祎慜, 郑琪帆, 刘馨阳, 王毅学, 王钦宏. 卤化酶在生物催化中的应用:机制解析、定向进化和绿色制造的进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(4): 728-763. |
| [13] | 方馨仪, 孙丽超, 霍毅欣, 王颖, 岳海涛. 微生物合成高级醇的发展趋势与挑战[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(4): 873-898. |
| [14] | 朱欣悦, 陈恬恬, 邵恒煊, 唐曼玉, 华威, 程艳玲. 益生菌辅助防治恶性肿瘤的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(4): 899-919. |
| [15] | 吴晓燕, 宋琪, 许睿, 丁陈君, 陈方, 郭勍, 张波. 合成生物学研发竞争态势对比分析[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(4): 940-955. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||