合成生物学 ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (4): 846-872.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-029
植物源疫苗研究进展
宋心雨1, 潘炜松1, 吴泰茹2, 潘家豪2, 吴川3, 李伟展4
- 1.湖南农业大学生物科学技术学院,湖南 长沙 410125
2.湖南诺合新生物科技有限公司,湖南 长沙 410001
3.中南大学冶金与环境学院,湖南 长沙 410083
4.香港教育大学科学及环境学系,香港 999077
-
收稿日期:2025-03-26修回日期:2025-06-09出版日期:2025-08-31发布日期:2025-09-03 -
通讯作者:潘炜松 -
作者简介:宋心雨 (2001—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为水稻生物反应器遗传转化。E-mail:2171613731@qq.com潘炜松 (1981—),男,副教授,硕士生导师。研究方向主要集中于分子农业领域,包括创制具有人源化翻译后修饰系统的植物反应器,开发合成生物学相关的生物技术工具,利用遗传工程与合成生物学手段开发创新型植物产品,在环境-生物学交叉学科领域,综合运用分子生物学、反向遗传学、细胞力学等技术手段研究水稻重金属砷的吸收、转运与调控机理。 E-mail:497609872@qq.com -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(31670955)
Research progress in plant-derived vaccines
SONG Xinyu1, PAN Weisong1, WU Tairu2, PAN Jiahao2, WU Chuan3, LI Waichin4
- 1.School of Bioscience and Biotechnology,Hunan Agricultural University,Changsha 410125,Hunan,China
2.Hunan Novomore Biotechnology Corporation,Changsha 410001,Hunan,China
3.School of Metallurgical and Environmental Engineering,Central South University,Changsha 410083,Hunan,China
4.Department of Science and Environmental Studies,The Education University of Hong Kong,Hongkong 999077,China
-
Received:2025-03-26Revised:2025-06-09Online:2025-08-31Published:2025-09-03 -
Contact:PAN Weisong
摘要:
在当今全球公共卫生领域,疫苗作为预防和控制传染病的关键手段,其研发和生产技术的创新备受瞩目。植物源疫苗作为一种新兴的疫苗生产技术,凭借其独特的优势逐渐崭露头角。与传统疫苗生产方式相比,植物源疫苗具有显著优势,在分子生物学技术的加持下,能够在较短时间内实现大规模生产,有效应对传染病的大规模爆发。本文首先介绍了植物源疫苗的基本概念,阐述了植物源疫苗的发展历程,同时对植物源疫苗的不同分类方法进行了系统梳理,此外还探讨了植物源疫苗的表达平台和表达体系,比较了不同平台和体系如稳定表达和瞬时表达体系的优缺点,总结了提高疫苗效力和安全性的策略和优化方法,系统探讨了国内外植物源疫苗的开发进展。植物源疫苗作为一种具有巨大潜力的新兴疫苗技术,有望在未来的公共卫生事业中发挥更加重要的作用。
中图分类号:
引用本文
宋心雨, 潘炜松, 吴泰茹, 潘家豪, 吴川, 李伟展. 植物源疫苗研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(4): 846-872.
SONG Xinyu, PAN Weisong, WU Tairu, PAN Jiahao, WU Chuan, LI Waichin. Research progress in plant-derived vaccines[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 846-872.
| 疫苗种类 | 目标抗原 | 受体植物 | 表达体系 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病毒疫苗 | 人乙型肝炎病毒表面抗原(HBsAg)蛋白 | 番茄 | 稳定表达体系 | |
| HIV中和人单克隆抗体2G 12 | 烟草 | 瞬时表达体系 | ||
| SARS-CoV-2刺突蛋白的受体结合结构域 | 烟草 | 瞬时表达体系 | ||
| 人乳头状瘤病毒(HPV)疫苗 | 本氏烟草 | 瞬时表达体系 | ||
| 埃博拉病毒疫苗 | 烟草 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| 猪繁殖与呼吸综合征(PRRS)的亚单位疫苗 | 烟草 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| 禽流感病毒血凝素 | 马铃薯 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| 非洲猪瘟P30重组蛋白 | 本氏烟草 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| 诺瓦病毒VLP | 生菜 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| 埃博拉病毒和西尼罗河病毒的治疗性单克隆抗体mAb | 生菜 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| HPV疫苗 | 生菜 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| 牛瘤病毒(BPV)病毒样颗粒 | 烟草 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| 人源轮状病毒VP7蛋白 | 花生 | 稳定表达系统 | ||
| 狂犬病病毒G蛋白 | 水稻 | 稳定表达系统 | ||
| 猪瘟E2融合蛋白 | 烟草 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| 癌胚抗原的单链Fv抗体 | 小麦 | 稳定表达系统 | ||
| 日本脑炎病毒(JEV)包膜蛋白(E) | 水稻胚乳 | 稳定表达系统 | ||
| ErbB2酪氨酸激酶受体 | 烟草 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| 高尔基病疫苗 | α-L-艾杜糖苷酶 | 玉米种子胚乳 | 稳定表达系统 | |
| 细菌疫苗 | LTB-ST | 烟草 | 瞬时表达系统 | |
| 幽门螺旋杆菌ureB抗原 | 水稻胚乳 | 稳定表达系统 | ||
| 寄生虫疫苗 | 抗轮虫保护性抗原As16 | 水稻胚乳 | 稳定表达系统 | |
| 房尘螨(HDM)过敏原Der p 1 | 水稻胚乳 | 稳定表达系统 | ||
| 利什曼虫的前鞭毛体表面抗原(PSA) | 本氏烟草 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| 阿尔茨海默病疫苗 | 淀粉样β肽Aβ 42 | 水稻胚乳 | 稳定表达系统 |
表1 一些已投入临床或动物实验的植物外源物质及其表达方式
Table 1 Plant-derived foreign substances that have been put into clinical or animal experiments and their expression methods
| 疫苗种类 | 目标抗原 | 受体植物 | 表达体系 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病毒疫苗 | 人乙型肝炎病毒表面抗原(HBsAg)蛋白 | 番茄 | 稳定表达体系 | |
| HIV中和人单克隆抗体2G 12 | 烟草 | 瞬时表达体系 | ||
| SARS-CoV-2刺突蛋白的受体结合结构域 | 烟草 | 瞬时表达体系 | ||
| 人乳头状瘤病毒(HPV)疫苗 | 本氏烟草 | 瞬时表达体系 | ||
| 埃博拉病毒疫苗 | 烟草 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| 猪繁殖与呼吸综合征(PRRS)的亚单位疫苗 | 烟草 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| 禽流感病毒血凝素 | 马铃薯 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| 非洲猪瘟P30重组蛋白 | 本氏烟草 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| 诺瓦病毒VLP | 生菜 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| 埃博拉病毒和西尼罗河病毒的治疗性单克隆抗体mAb | 生菜 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| HPV疫苗 | 生菜 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| 牛瘤病毒(BPV)病毒样颗粒 | 烟草 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| 人源轮状病毒VP7蛋白 | 花生 | 稳定表达系统 | ||
| 狂犬病病毒G蛋白 | 水稻 | 稳定表达系统 | ||
| 猪瘟E2融合蛋白 | 烟草 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| 癌胚抗原的单链Fv抗体 | 小麦 | 稳定表达系统 | ||
| 日本脑炎病毒(JEV)包膜蛋白(E) | 水稻胚乳 | 稳定表达系统 | ||
| ErbB2酪氨酸激酶受体 | 烟草 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| 高尔基病疫苗 | α-L-艾杜糖苷酶 | 玉米种子胚乳 | 稳定表达系统 | |
| 细菌疫苗 | LTB-ST | 烟草 | 瞬时表达系统 | |
| 幽门螺旋杆菌ureB抗原 | 水稻胚乳 | 稳定表达系统 | ||
| 寄生虫疫苗 | 抗轮虫保护性抗原As16 | 水稻胚乳 | 稳定表达系统 | |
| 房尘螨(HDM)过敏原Der p 1 | 水稻胚乳 | 稳定表达系统 | ||
| 利什曼虫的前鞭毛体表面抗原(PSA) | 本氏烟草 | 瞬时表达系统 | ||
| 阿尔茨海默病疫苗 | 淀粉样β肽Aβ 42 | 水稻胚乳 | 稳定表达系统 |
| 抗原 | 表达系统 | 宿主 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 猪O型口蹄疫病毒(FMDV)抗原表位融合结构蛋白VP1 | 瞬时表达 | 本氏烟草 | |
| 呼吸道合胞病毒(RSV)F蛋白 | 瞬时表达 | 本氏烟草 | |
| 霍乱毒素B亚基(CTB) | 瞬时表达 | 本氏烟草 | |
| 中东呼吸综合征冠状病毒刺突蛋白S1亚基抗原 | 瞬时表达 | 本氏烟草 |
表2 植物来源的一些抗原实例
Table 2 Plant-derived antigen examples
| 抗原 | 表达系统 | 宿主 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 猪O型口蹄疫病毒(FMDV)抗原表位融合结构蛋白VP1 | 瞬时表达 | 本氏烟草 | |
| 呼吸道合胞病毒(RSV)F蛋白 | 瞬时表达 | 本氏烟草 | |
| 霍乱毒素B亚基(CTB) | 瞬时表达 | 本氏烟草 | |
| 中东呼吸综合征冠状病毒刺突蛋白S1亚基抗原 | 瞬时表达 | 本氏烟草 |
| 抗原 | 表达系统 | 植物宿主 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Influenza A H5N1 HA | 用质体蓝素表达载体瞬时表达 | 本氏烟草N. benthamiana | [ |
| HBsAg L protein | 稳定的转基因植物 | 烟草Tobacco | [ |
| Dengue-3 capsid, prM/M and E | 稳定的转质体叶绿体表达 | 莴苣Lettuce | [ |
| HBsAg VLP displaying HIV-1 ENV and GAG epitopes | 稳定的转基因植物 | 番茄Tomato | [ |
| HBsAg VLP displaying HIV-1 polyepitope | 稳定的转基因植物 | 烟草Tobacco 拟南芥Arabidopsis | [ |
| HBsAg VLP displaying HBV preS1 epitope | 稳定的转基因植物 | 水稻Rice | [ |
| HBsAg VLP displaying full-length GFP | 用非病毒载体瞬时表达 | 本氏烟草N. benthamiana | [ |
| HIV-1Gag VLP displaying gp41 | MagnICON“解构”病毒载体的瞬时表达 | 本氏烟草N. benthamiana | [ |
表3 植物来源的一些包膜VLP的实例
Table 3 Examples of some plant-derived enveloped VLPs
| 抗原 | 表达系统 | 植物宿主 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Influenza A H5N1 HA | 用质体蓝素表达载体瞬时表达 | 本氏烟草N. benthamiana | [ |
| HBsAg L protein | 稳定的转基因植物 | 烟草Tobacco | [ |
| Dengue-3 capsid, prM/M and E | 稳定的转质体叶绿体表达 | 莴苣Lettuce | [ |
| HBsAg VLP displaying HIV-1 ENV and GAG epitopes | 稳定的转基因植物 | 番茄Tomato | [ |
| HBsAg VLP displaying HIV-1 polyepitope | 稳定的转基因植物 | 烟草Tobacco 拟南芥Arabidopsis | [ |
| HBsAg VLP displaying HBV preS1 epitope | 稳定的转基因植物 | 水稻Rice | [ |
| HBsAg VLP displaying full-length GFP | 用非病毒载体瞬时表达 | 本氏烟草N. benthamiana | [ |
| HIV-1Gag VLP displaying gp41 | MagnICON“解构”病毒载体的瞬时表达 | 本氏烟草N. benthamiana | [ |
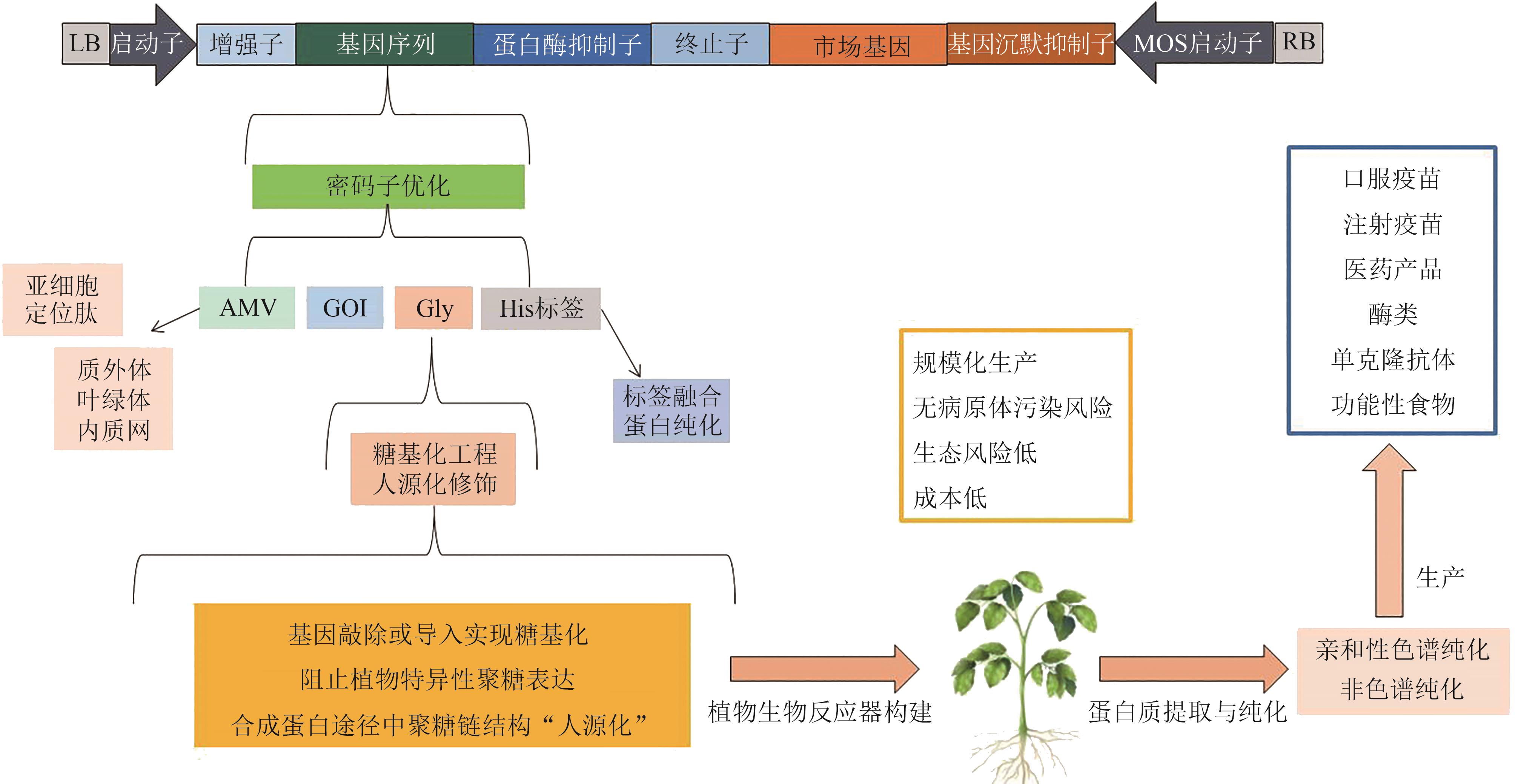
图1 植物源疫苗的生产流程[5](基因设计构建质粒载体,将载体通过适当的方法导入宿主植物,让目的基因在宿主植物体内表达,收集表达目标蛋白的植物组织,研磨后提取蛋白,纯化后得到产品)
Fig. 1 The production process of plant-derived vaccines[5](Design and construct the plasmid vector for the gene. Introduce the vector into the host plant using appropriate methods. Allow the target gene to be expressed within the host plant. Collect the plant tissues that express the target protein. Grind the tissues to extract the protein. Purify the protein to obtain the final product.)
| 植物蛋白酶抑制剂PI | 参考文献 |
|---|---|
| 半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂PhyCys家族 | |
| 丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂家族 | |
| α-淀粉酶/胰蛋白酶抑制剂家族 | |
| 南瓜胰蛋白酶抑制剂家族 | |
| 芥菜胰蛋白酶抑制剂家族 | |
| 天冬氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂家族 | |
| 金属羧肽酶抑制剂家族 | |
| Bowman-Birk Ser蛋白酶抑制剂 | |
| 烟草丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂Ⅱ基因的胰蛋白酶(C1)和胰凝乳蛋白酶(T1)抑制域 | |
| 水稻半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂oryzacystatin-I | |
| 番茄组织蛋白酶D抑制剂(SlCDI) | |
| 番茄半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂SlCYS 8 | |
| CaPR 4c | |
| NbPot1 | |
| HsTIMP靶向基质金属蛋白酶 |
表 4 一些常用植物蛋白酶抑制剂
Table 4 Some commonly used plant protease inhibitors
| 植物蛋白酶抑制剂PI | 参考文献 |
|---|---|
| 半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂PhyCys家族 | |
| 丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂家族 | |
| α-淀粉酶/胰蛋白酶抑制剂家族 | |
| 南瓜胰蛋白酶抑制剂家族 | |
| 芥菜胰蛋白酶抑制剂家族 | |
| 天冬氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂家族 | |
| 金属羧肽酶抑制剂家族 | |
| Bowman-Birk Ser蛋白酶抑制剂 | |
| 烟草丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂Ⅱ基因的胰蛋白酶(C1)和胰凝乳蛋白酶(T1)抑制域 | |
| 水稻半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂oryzacystatin-I | |
| 番茄组织蛋白酶D抑制剂(SlCDI) | |
| 番茄半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂SlCYS 8 | |
| CaPR 4c | |
| NbPot1 | |
| HsTIMP靶向基质金属蛋白酶 |
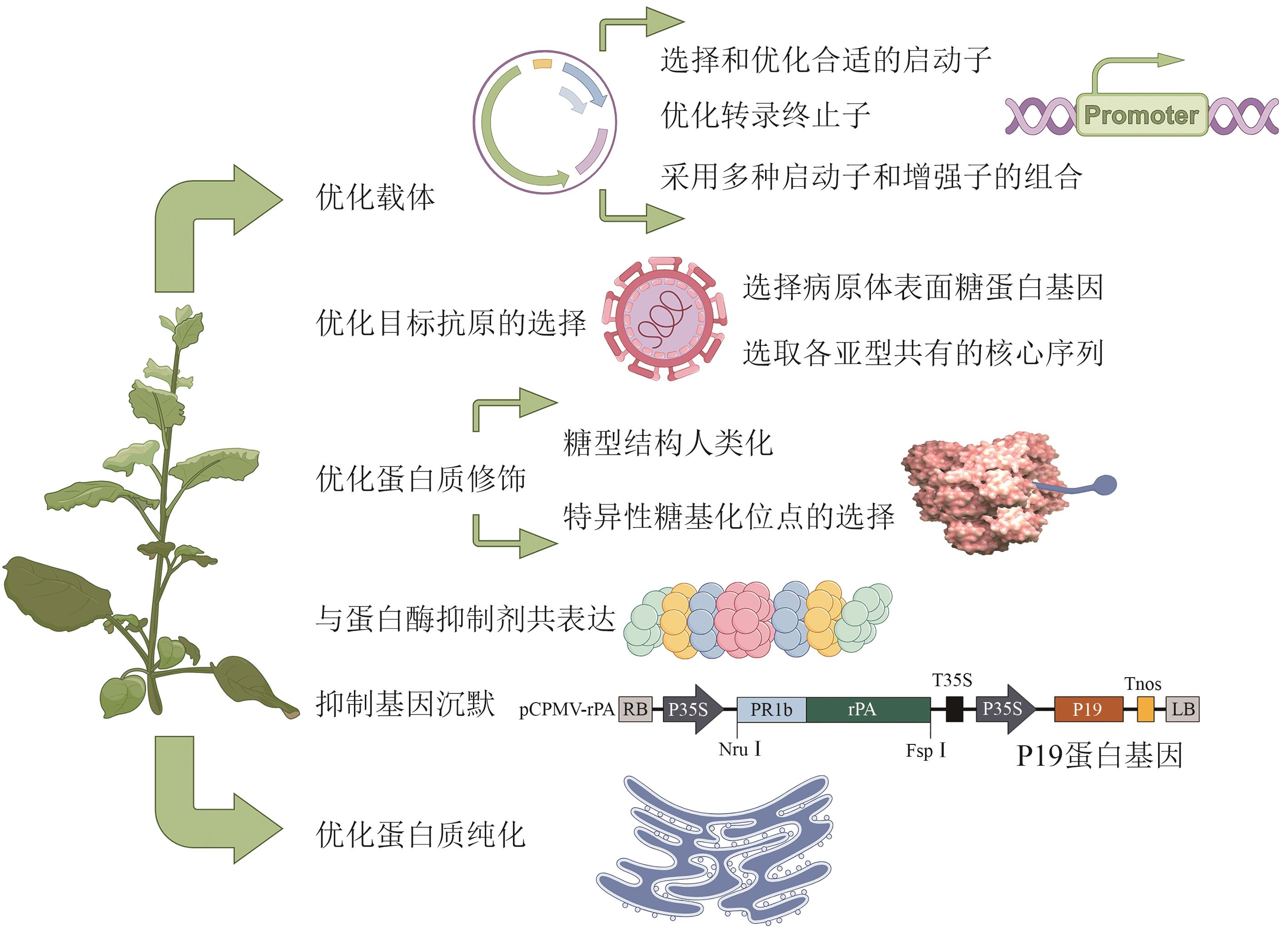
图2 植物源疫苗的优化(植物源疫苗的优化可以通过优化载体,优化目标抗原的选择,优化蛋白质修饰,让目的基因与蛋白酶抑制剂基因和沉默抑制基因共表达,优化纯化过程来达成。图中P19蛋白基因共表达参考Ma等[155]的研究。本图由Figdraw绘制)
Fig. 2 Optimization of plant-derived vaccines(The optimization of plant-derived vaccines can be achieved through the optimization of vectors, the selection of target antigens, the modification of proteins, co-expression of the target gene with protease inhibitor genes and silencing suppressor genes, and the optimization of the purification process. The co-expression of the P19 protein gene in the figure refers to the study by Ma et al[155]. This figure was created by Figdraw.)
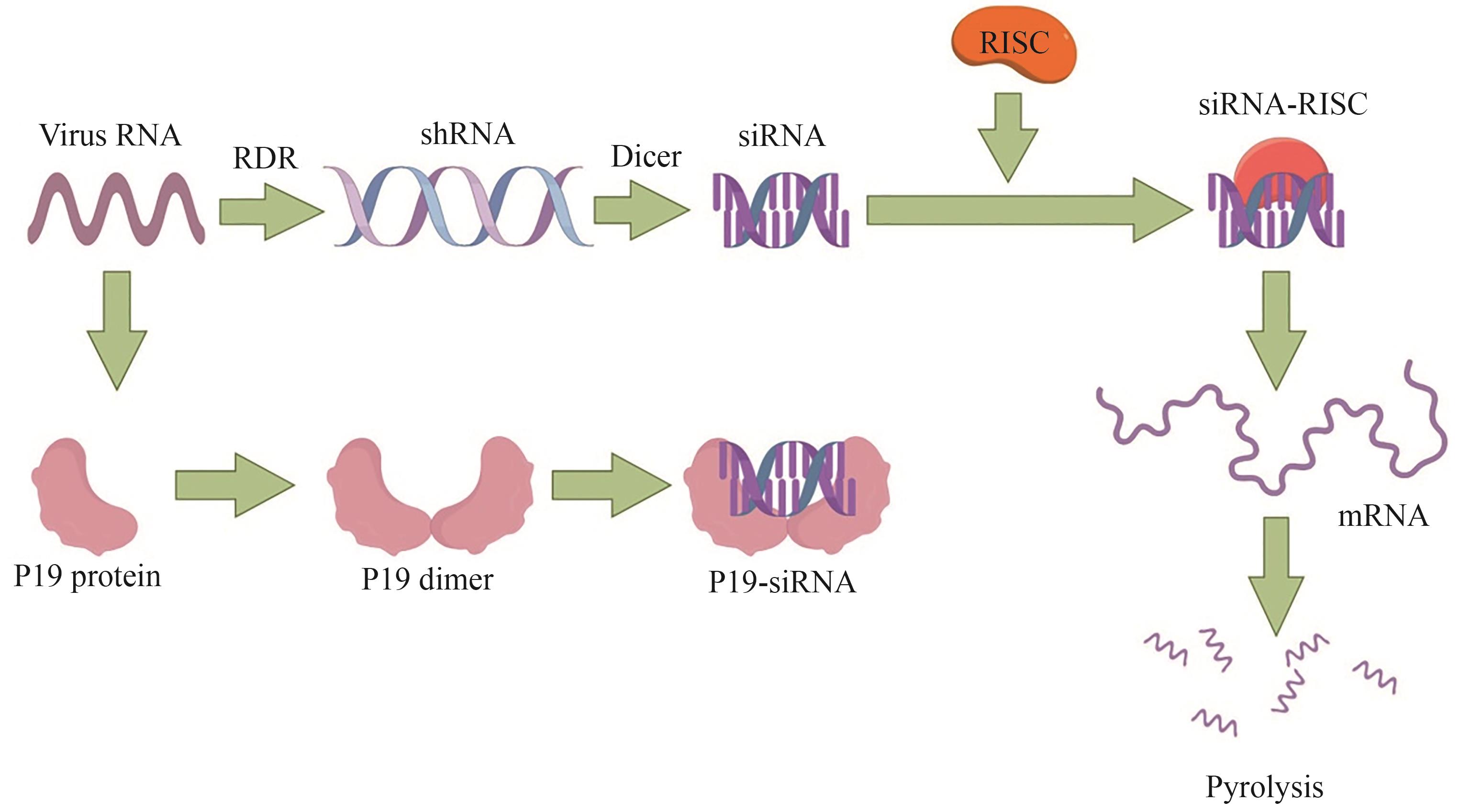
图3 P19蛋白作用原理(侵入植物体的病毒RNA会组装成双链shRNA,被Dicer酶切成21~23 bp的siRNA,与RISC组合成siRNA-RISC复合体,并结合至同源的mRNA上使其裂解。而当P19蛋白被表达后,它会组装成二聚体结合siRNA,使siRNA无法结合RISC,从而使沉默过程无法进行。本图由Figdraw绘制)
Fig. 3 The mechanism of action of P19 protein(The viral RNA that invades the plant body is assembled into double-stranded shRNA, which is cut into 21-23 base pair siRNAs by the Dicer enzyme. These siRNAs form a siRNA-RISC complex and bind to the homologous mRNA, causing it to be cleaved. However, when the P19 protein is expressed, it assembles into a dimer that binds to the siRNA, preventing the siRNA from binding to RISC, and thus the silencing process cannot proceed. This figure was created by Figdraw.)
| [1] | HUEBBERS J W, BUYEL J F. On the verge of the market- plant factories for the automated and standardized production of biopharmaceuticals[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2021, 46: 107681. |
| [2] | CHAN J C N, CHAN A T C. Biologics and biosimilars what, why and how[J]. ESMO Open, 2017, 2(1): e000180. |
| [3] | CHUNG Y H, CHURCH D, KOELLHOFFER E C, et al. Integrating plant molecular farming and materials research for next-generation vaccines[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2021, 7(5): 372-388. |
| [4] | GUREVICH E V, GUREVICH V V. Beyond traditional pharmacology: new tools and approaches[J]. British Journal of Pharmacology, 2015, 172(13): 3229-3241. |
| [5] | 邹奇, 潘炜松, 邱健, 等. 植物生物反应器优化策略与最新应用[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 2023, 43(1): 71-86. |
| ZOU Q, PAN W S, QIU J, et al. Recent advances in optimization strategies and applications of plant bioreactors[J]. China Biotechnology, 2023, 43(1): 71-86. | |
| [6] | WARD B J, MAKARKOV A, SÉGUIN A, et al. Efficacy, immunogenicity, and safety of a plant-derived, quadrivalent, virus-like particle influenza vaccine in adults (18-64 years) and older adults (≥65 years): two multicentre, randomised phase 3 trials[J]. The Lancet, 2020, 396(10261): 1491-1503. |
| [7] | RYBICKI E P. Plant molecular farming of virus-like nanoparticles as vaccines and reagents[J]. WIREs Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology, 2020, 12(2): e1587. |
| [8] | 蔡静波. 成纤维细胞生长因子9在红花中的表达、活性及药效学初步研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2018. |
| CAI J B. Expression, biological activity and pharmacodynamics preliminary study of fibroblast growth factor 9 in safflower[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| [9] | 李校堃, 马吉胜. 植物反应器: 生产FGF的“植物工厂”[J]. 生命世界, 2019(11): 16-17. |
| LI X K, MA J S. Plant bioreactors: the “Plant Factories” for FGF production[J]. Life World, 2019(11): 16-17. | |
| [10] | 杨香芳, 刘召明, 申茂欣, 等. 基因工程疫苗在动物疾病防治中的前景[J]. 中国动物保健, 2024, 26(2): 5-6. |
| YANG X F, LIU Z M, SHEN M X, et al. Prospects of genetically engineered vaccines in the prevention and control of animal diseases[J]. China Animal Health, 2024, 26(2): 5-6. | |
| [11] | FAUSTHER-BOVENDO H, KOBINGER G. Plant-made vaccines and therapeutics[J]. Science, 2021, 373(6556): 740-741. |
| [12] | 吴建祥, 周继勇, 于翠. 转基因植物生产基因工程疫苗技术[J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2001, 23(2): 157-159. |
| WU J X, ZHOU J Y, YU C. The technology of develop gene enginering vaccine by trangenic plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2001, 23(2): 157-159. | |
| [13] | MASON H S, LAM D M, ARNTZEN C J. Expression of hepatitis B surface antigen in transgenic plants[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1992, 89(24): 11745-11749. |
| [14] | LIU Y L, WANG J F, QIU B S, et al. Expression of human hepatitis B virus surface antigen gene in transgenic tobacco[J]. Science in China Series B, Chemistry, Life Sciences & Earth Sciences, 1994, 37(1): 37-41. |
| [15] | MATIĆ S, QUAGLINO E, ARATA L, et al. The rat ErbB2 tyrosine kinase receptor produced in plants is immunogenic in mice and confers protective immunity against ErbB2+ mammary cancer[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2016, 14(1): 153-159. |
| [16] | NAUPU P N, VAN ZYL A R, RYBICKI E P, et al. Immunogenicity of plant-produced human papillomavirus (HPV) virus-like particles (VLPs)[J]. Vaccines, 2020, 8(4): 740. |
| [17] | MAHARJAN P M, CHEON J, JUNG J, et al. Plant-expressed receptor binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein elicits humoral immunity in mice[J]. Vaccines, 2021, 9(9): 978. |
| [18] | XU Q R, MA F S, YANG D C, et al. Rice-produced classical swine fever virus glycoprotein E2 with herringbone-dimer design to enhance immune responses[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2023, 21(12): 2546-2559. |
| [19] | YUSIBOV V, STREATFIELD S J, KUSHNIR N. Clinical development of plant-produced recombinant pharmaceuticals: vaccines, antibodies and beyond[J]. Human Vaccines, 2011, 7(3): 313-321. |
| [20] | ALEXANDER J, WARD S, MENDY J, et al. Pre-clinical evaluation of a replication-competent recombinant adenovirus serotype 4 vaccine expressing influenza H5 hemagglutinin[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(2): e31177. |
| [21] | CUMMINGS J F, GUERRERO M L, MOON J E, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a plant-produced recombinant monomer hemagglutinin-based influenza vaccine derived from influenza A (H1N1) pdm09 virus: a Phase 1 dose-escalation study in healthy adults[J]. Vaccine, 2014, 32(19): 2251-2259. |
| [22] | KHANTASUP K, CHANTIMA W, SANGMA C, et al. Design and generation of humanized single-chain Fv derived from mouse hybridoma for potential targeting application[J]. Monoclonal Antibodies in Immunodiagnosis and Immunotherapy, 2015, 34(6): 404-417. |
| [23] | MA J K, DROSSARD J, LEWIS D, et al. Regulatory approval and a first-in-human phase Ⅰ clinical trial of a monoclonal antibody produced in transgenic tobacco plants[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2015, 13(8): 1106-1120. |
| [24] | Merck’s ERVEBO® [ebola zaire vaccine (rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP) live] |
| granted conditional approval in the European Union[EB/OL]. (2019-11-11)[2025-06-01]. . | |
| [25] | MAHARJAN P M, CHOE S. Plant-based COVID-19 vaccines: current status, design, and development strategies of candidate vaccines[J]. Vaccines, 2021, 9(9): 992. |
| [26] | WARD B J, GOBEIL P, SÉGUIN A, et al. Phase 1 randomized trial of a plant-derived virus-like particle vaccine for COVID-19[J]. Nature Medicine, 2021, 27(6): 1071-1078. |
| [27] | SU H, VAN EERDE A, RIMSTAD E, et al. Plant-made vaccines against viral diseases in humans and farm animals[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2023, 14: 1170815. |
| [28] | 王跃驹, 王海军, 庞小静. 生菜作为宿主在表达人乳头瘤病毒蛋白或制备人宫颈癌疫苗中的应用: CN111393511A [P]. 2020-07-10. |
| WANG Y J, WANG H J, PANG X J. Application of lettuce as a host in expressing human papillomavirus proteins or preparing human cervical cancer vaccines: CN111393511A[P]. 2020-07-10. | |
| [29] | LAI H F, HE J Y, ENGLE M, et al. Robust production of virus-like particles and monoclonal antibodies with geminiviral replicon vectors in lettuce[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2012, 10(1): 95-104. |
| [30] | VANDERBURGT J T, HARPER O, GARNHAM C P, et al. Plant production of a virus-like particle-based vaccine candidate against porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2023, 14: 1044675. |
| [31] | 宋长征, SMASON Hugh. 禽流感病毒血凝素疫苗在转基因马铃薯中的表达[J]. 生物技术, 2001, 11(5): 3-4. |
| SONG C Z, SMASON H. Expression hemagglutinin vaccine of avian influenza virus in transgenic potato[J]. Biotechnology, 2001, 11(5): 3-4. | |
| [32] | 刘悦. 马铃薯Y病毒介导的非洲猪瘟病毒p30蛋白在本氏烟草中的表达[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2023. |
| LIU Y. Expression of p30 protein of African swine fever virus mediated by potato virus Y in Nicotiana benthamiana [D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2023. | |
| [33] | PINEO C B, HITZEROTH I I, RYBICKI E P. Immunogenic assessment of plant-produced human papillomavirus type 16 L1/L2 chimaeras[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2013, 11(8): 964-975. |
| [34] | RYBICKI E P. Plant molecular farming of virus-like nanoparticles as vaccines and reagents[J]. WIREs Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology, 2020, 12(2): e1587. |
| [35] | 贾宇臣, 赵凯, 薛昕, 等. 轮状病毒抗原蛋白G3VP7基因在花生中遗传转化的研究[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2012, 29(2): 328-331. |
| JIA Y C, ZHAO K, XUE X, et al. Study on genetic transformation of antigen G3VP7 gene of human rotavirus in peanut[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2012, 29(2): 328-331. | |
| [36] | 申雪静, 张二芹, 许倩茹, 等. 狂犬病病毒G蛋白在水稻中的表达及遗传稳定性鉴定[J]. 农业生物技术学报, 2019, 27(2): 204-211. |
| SHEN X J, ZHANG E Q, XU Q R, et al. Expression of rabies virus G protein in rice (Oryza sativa) and identification of its genetic stability[J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2019, 27(2): 204-211. | |
| [37] | KIM S Y, JUNG B K, PARK G N, et al. Histopathological evaluation of the efficacy for plant-produced E2 protein vaccine against classical swine fever virus (CSFV) in piglets[J]. Journal of Bacteriology and Virology, 2019, 49(3): 133. |
| [38] | WANG Y Y, DENG H Q, ZHANG X B, et al. Generation and immunogenicity of Japanese encephalitis virus envelope protein expressed in transgenic rice[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2009, 380(2): 292-297. |
| [39] | HE X, HASELHORST T, VON ITZSTEIN M, et al. Production of α-L-iduronidase in maize for the potential treatment of a human lysosomal storage disease[J]. Nature Communications, 2012, 3: 1062. |
| [40] | ROSALES-MENDOZA S, ALPUCHE-SOLÍS Á G, SORIA-GUERRA R E, et al. Expression of an Escherichia coli antigenic fusion protein comprising the heat labile toxin B subunit and the heat stable toxin, and its assembly as a functional oligomer in transplastomic tobacco plants[J]. The Plant Journal, 2009, 57(1): 45-54. |
| [41] | GU Q, HAN N, LIU J Y, et al. Expression of Helicobacter pylori urease subunit B gene in transgenic rice[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2006, 28(20): 1661-1666. |
| [42] | MATSUMOTO Y, SUZUKI S, NOZOYE T, et al. Oral immunogenicity and protective efficacy in mice of transgenic rice plants producing a vaccine candidate antigen (As16) of Ascaris suum fused with cholera toxin B subunit[J]. Transgenic Research, 2009, 18(2): 185-192. |
| [43] | YANG L J, KAJIURA H, SUZUKI K, et al. Generation of a transgenic rice seed-based edible vaccine against house dust mite allergy[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2008, 365(2): 334-339. |
| [44] | LACOMBE S, BANGRATZ M, BRIZARD J P, et al. Optimized transitory ectopic expression of promastigote surface antigen protein in Nicotiana benthamiana, a potential anti-leishmaniasis vaccine candidate[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2018, 125(1): 116-123. |
| [45] | YOSHIDA T, KIMURA E, KOIKE S, et al. Transgenic rice expressing amyloid β-peptide for oral immunization[J]. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 2011, 7(3): 301-307. |
| [46] | 任兆钧, 刘勇, 郭云生, 等. 烟草表达口蹄疫植物基因工程疫苗及其制备方法: CN1820784[P]. 2006-08-23. |
| REN Z J, LIU Y, GUO Y S, et al. Tobacco-expressed FMD plant genetic engineering vaccine and its preparation method: CN1820784[P]. 2006-08-23. | |
| [47] | BUETOW D E, KORBAN S S, SANDHU J, et al. Plant-derived vaccines against respiratory syncytial virus: WO0068392[P]. 2020-05-10. |
| [48] | LANGRIDGE W H R, ARAKAWA T, CHONG D, et al. Expression of cholera toxin B subunit in transgenic plants and efficacy thereof in oralvaccines: WO9918225 [P]. 1998-10-07. |
| [49] | SOHRAB S S, ASHAR E I A, ELKAFRAWY, SHERIF A A, et al. Development of an edible vaccine: WO2021161028A1 [P]. 2021-08-21. |
| [50] | 王跃驹, 马磊, 王海军. 生菜作为宿主在表达乙肝疫苗中的应用: CN110229847A[P]. 2019-09-13. |
| WANG Y J, MA L, WANG H J. Application of lettuce as a host in expressing hepatitis B vaccine: CN110229847A[P]. 2019-09-13. | |
| [51] | 刘地, 李博, 毕成, 等. 具备定点偶联功能的HBc-VLPs的制备与性质鉴定[J]. 生物工程学报, 2020, 36(7): 1440-1449. |
| LIU D, LI B, BI C, et al. Preparation and characterization of HBc virus like particles with site-directed coupling function[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2020, 36(7): 1440-1449. | |
| [52] | CHO K N, OUH I O, PARK Y M, et al. A plant-produced porcine parvovirus 1-82 VP2 subunit vaccine protects pregnant sows against challenge with a genetically heterologous PPV1 strain[J]. Vaccines, 2023, 11(1): 54. |
| [53] | D’AOUST M A, LAVOIE P O, COUTURE M M J, et al. Influenza virus-like particles produced by transient expression in Nicotiana benthamiana induce a protective immune response against a lethal viral challenge in mice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2008, 6(9): 930-940. |
| [54] | D’AOUST M A, COUTURE M M J, CHARLAND N, et al. The production of hemagglutinin-based virus-like particles in plants: a rapid, efficient and safe response to pandemic influenza[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2010, 8(5): 607-619. |
| [55] | POTERA C. Vaccine manufacturing gets boost from tobacco plants: canada-based medicago opens U.S. facility to exploit its influenza vaccine production method[J]. Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News, 2012, 13(6): 8-10. |
| [56] | LOU X M, YAO Q H, ZHANG Z, et al. Expression of the human hepatitis B virus large surface antigen gene in transgenic tomato plants[J]. Clinical and Vaccine Immunology, 2007, 14(4): 464-469. |
| [57] | PNIEWSKI T, KAPUSTA J, BOCIĄG P, et al. Plant expression, lyophilisation and storage of HBV medium and large surface antigens for a prototype oral vaccine formulation[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2012, 31(3): 585-595. |
| [58] | KANAGARAJ A P, VERMA D, DANIELL H. Expression of dengue-3 premembrane and envelope polyprotein in lettuce chloroplasts[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2011, 76(3): 323-333. |
| [59] | SHCHELKUNOV S N, SALYAEV R K, POZDNYAKOV S G, et al. Immunogenicity of a novel, bivalent, plant-based oral vaccine against hepatitis B and human immunodeficiency viruses[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2006, 28(13): 959-967. |
| [60] | GRECO R, MICHEL M, GUETARD D, et al. Production of recombinant HIV-1/HBV virus-like particles in Nicotiana tabacum and Arabidopsis thaliana plants for a bivalent plant-based vaccine[J]. Vaccine, 2007, 25(49): 8228-8240. |
| [61] | GUETARD D, GRECO R, CERVANTES GONZALEZ M, et al. Immunogenicity and tolerance following HIV-1/HBV plant-based oral vaccine administration[J]. Vaccine, 2008, 26(35): 4477-4485. |
| [62] | 马燕斌, 李换丽, 文晋, 等. 转基因抗草甘膦棉花R1-3株系的分子特征鉴定[J]. 中国农业科学, 2023, 56(17): 3277-3284. |
| MA Y B, LI H L, WEN J, et al. Identification of molecular characterizations for transgenic cotton R1-3 line of glyphosate tolerance[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2023, 56(17): 3277-3284. | |
| [63] | QIAN B J, SHEN H F, LIANG W Q, et al. Immunogenicity of recombinant hepatitis B virus surface antigen fused with preS1 epitopes expressed in rice seeds[J]. Transgenic Research, 2008, 17(4): 621-631. |
| [64] | HUANG Z, MASON H S. Conformational analysis of hepatitis B surface antigen fusions in an Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression system[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2004, 2(3): 241-249. |
| [65] | KESSANS S A, FRATER J, MATOBA N, et al. P02-10. Plant expression of chimeric Gag/gp41 virus-like particles as a mucosally-targeted subunit vaccine against HIV-1[J]. Retrovirology, 2009, 6(3): P15. |
| [66] | 河北大学科学与技术创新研究院. 为什么接种疫苗时总是选择上臂,而不是其他部位[EB/OL]. (2021-06-11)[2025-06-01]. . |
| Hebei University Institute of Science and Technology Innovation. Why is the upper arm always chosen for vaccination instead of other sites[EB/OL]. (2021-06-11)[2025-06-01]. . | |
| [67] | Inc Medicago. Quebec-based Medicago is transforming the use of plant-based technologies to rapidly develop and produce novel vaccines and therapeutic proteins[EB/OL]. [2025-06-01]. . |
| [68] | 张玉满, 谢传淼, 方荣祥,等. 利用枸杞作为烟草花叶病毒瞬时表达外源蛋白的生物反应器:CN114634948A[P]. 2022-06-17. |
| ZHANG Y M, XIE C M, FANG R X, et al. Utilization of wolfberry as a bioreactor for transient expression of foreign proteins via tobacco mosaic virus CN 114634948A[P]. 2022-06-17. | |
| [69] | LEI L. Lettuce-manufactured pharmaceuticals[J]. Nature Plants, 2019, 5(7): 646. |
| [70] | KEHAGIA E, PAPAKYRIAKOPOULOU P, VALSAMI G. Advances in intranasal vaccine delivery: a promising non-invasive route of immunization[J]. Vaccine, 2023, 41(24): 3589-3603. |
| [71] | CHEN X J, FAN X D, LI F Z. Development and evaluation of a novel diammonium glycyrrhizinate phytosome for nasal vaccination[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2022, 14(10): 2000. |
| [72] | GAOBOTSE G, VENKATARAMAN S, MMEREKE K M, et al. Recent progress on vaccines produced in transgenic plants[J]. Vaccines, 2022, 10(11): 1861. |
| [73] | KUMAR M, KUMARI N, THAKUR N, et al. A comprehensive overview on the production of vaccines in plant-based expression systems and the scope of plant biotechnology to combat against SARS-CoV-2 virus pandemics[J]. Plants, 2021, 10(6): 1213. |
| [74] | SMITH C M, FRY S C, GOUGH K C, et al. Recombinant plants provide a new approach to the production of bacterial polysaccharide for vaccines[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(2): e88144. |
| [75] | 周丹丹, 俞嘉宁. 植物细胞中瞬时表达系统的建立及研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2013, 29(24): 151-156. |
| ZHOU D D, YU J N. The progress of establishing transient expression system in plant cell[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2013, 29(24): 151-156. | |
| [76] | WIGDOROVITZ A, CARRILLO C, SANTOS M J DUS, et al. Induction of a protective antibody response to foot and mouth disease virus in mice following oral or parenteral immunization with alfalfa transgenic plants expressing the viral structural proteinVP1[J]. Virology, 1999,255(2):347-353. |
| [77] | VENKATARAMAN S, KHAN I, HABIBI P, et al. Recent advances in expression and purification strategies for plant made vaccines[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2023, 14: 1273958. |
| [78] | NURZIJAH I, ELBOHY O A, KANYUKA K, et al. Development of plant-based vaccines for prevention of avian influenza and Newcastle disease in poultry[J]. Vaccines, 2022, 10(3): 478. |
| [79] | 陈亚波. 新城疫病毒HN蛋白与F蛋白结构域共表达对细胞融合的影响[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2006. |
| CHEN Y B. Cell fusion as affected by co-expression of structural domains of hemagglutinin-neuraminidase and fusion protein of Newcastle disease virus[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2006. | |
| [80] | SU Y L, LARZÁBAL M, SONG H, et al. Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157: H7 antigens produced in transgenic lettuce effective as an oral vaccine in mice[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2023, 136(10): 214. |
| [81] | IMANI J, LORENZ H, KOGEL K H, et al. Transgenic carrots: potential source of edible vaccines[J]. Journal Für Verbraucherschutz und Lebensmittelsicherheit, 2007, 2(): 105. |
| [82] | 张丹凤, 余自青, 吴锁伟, 等. 植物生物反应器在分子医药农业中的应用[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 2016, 36(1): 86-94. |
| ZHANG D F, YU Z Q, WU S W, et al. Progress of plant as bioreactor in molecular pharming[J]. China Biotechnology, 2016, 36(1): 86-94. | |
| [83] | 俞瑶, 程华, 陈素梅, 等. 基于农杆菌真空渗透法的菊花瞬时表达系统的优化[J]. 农业生物技术学报, 2023, 31(12): 2654-2664. |
| YU Y, CHENG H, CHEN S M, et al. Optimization of transient expression system in Chrysanthemum morifolium based on Agrobacterium vacuum infiltration method[J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2023, 31(12): 2654-2664. | |
| [84] | 郎遥玲, 王倩, 陈彬, 等. 农杆菌介导注射法建立番茄子叶瞬时表达系统[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(34): 5462-5468. |
| LANG Y L, WANG Q, CHEN B, et al. Establishment of transient expression system of eggplant Cotyledon by Agrobacterium-mediated injection[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(34): 5462-5468. | |
| [85] | 黄爽, 范杰英, 韦正乙, 等. 烟草花叶病毒瞬时表达系统在医药蛋白生产中的应用[J]. 分子植物育种, 2019, 17(21): 7078-7086. |
| HUANG S, FAN J Y, WEI Z Y, et al. Application of tobacco mosaic virus-based transient expression system in pharmaceutical protein production[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2019, 17(21): 7078-7086. | |
| [86] | SHAHID N, DANIELL H. Plant-based oral vaccines against zoonotic and non-zoonotic diseases[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2016, 14(11): 2079-2099. |
| [87] | 蔡玉婷, 茹毅, 孙坤, 等. 植物中表达口蹄疫病毒抗原研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2023, 39(4): 1548-1561. |
| CAI Y T, RU Y, SUN K, et al. Expression of antigens of foot-and-mouth disease virus in plants: a review[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2023, 39(4): 1548-1561. | |
| [88] | DANIELL H. Chloroplasts engineered to express pharmaceutical proteins in edible plants: US 20090022705[P]. 2009-01-22. |
| [89] | SETHI L, KUMARI K, DEY N. Engineering of plants for efficient production of therapeutics[J]. Molecular Biotechnology, 2021, 63(12): 1125-1137. |
| [90] | 林优红, 程霞英, 杨东风, 等. 高等植物叶绿体表达重组蛋白研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2018, 34(5): 631-643. |
| LIN Y H, CHENG X Y, YANG D F, et al. Advances in chloroplast expression of recombinant proteins in higher plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2018, 34(5): 631-643. | |
| [91] | 郝宇娉, 陆琳, 杨志红. 转基因植物疫苗的研究进展[J]. 核农学报, 2020, 34(12): 2708-2724. |
| HAO Y P, LU L, YANG Z H. Progress on transgenic plants vaccines[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 34(12): 2708-2724. | |
| [92] | NOCHI T, TAKAGI H, YUKI Y, et al. Rice-based mucosal vaccine as a global strategy for cold-chain- and needle-free vaccination[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2007, 104(26): 10986-10991. |
| [93] | YUKI Y, MEJIMA M, KUROKAWA S, et al. Induction of toxin-specific neutralizing immunity by molecularly uniform rice-based oral cholera toxin B subunit vaccine without plant-associated sugar modification[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2013, 11(7): 799-808. |
| [94] | SUZUKI K, KAMINUMA O, YANG L J, et al. Prevention of allergic asthma by vaccination with transgenic rice seed expressing mite allergen: induction of allergen-specific oral tolerance without bystander suppression[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2011, 9(9): 982-990. |
| [95] | 鲜彬, 徐翔铭, 吴清华, 等. 农杆菌和基因枪介导的瞬时表达方法研究综述[J]. 中药与临床, 2022, 13(5): 110-117. |
| XIAN B, XU X M, WU Q H, et al. A review of the methods of transient expression mediated by Agrobacterium and particle bombardment[J]. Pharmacy and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica, 2022, 13(5): 110-117. | |
| [96] | 唐琳, 徐莺, 赵婷婷, 等. 番红花组织基因枪转化瞬时表达检测[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2004, 26(4): 35-38. |
| TANG L, XU Y, ZHAO T T, et al. Transient expression of gus gene via particle bombardment in Crocus sativus L[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2004, 26(4): 35-38. | |
| [97] | 张馨悦. 萱草花粉的离体萌发、贮存及遗传转化研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2020. |
| ZHANG X Y. In vitro germination, storage, and genetic transformation of Hemerocallis pollen[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| [98] | 高璐, 薛永来. 农杆菌介导的水稻快速高效基因转化系统[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(4): 39-42. |
| GAO L, XUE Y L. Agrobacterium-mediated rapid and efficient gene transformation system in rice[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(4): 39-42. | |
| [99] | 肖军, 张云霄, 刘伯峰. 烟草的组织培养技术研究[J]. 泰山学院学报, 2009, 31(6): 94-98. |
| XIAO J, ZHANG Y X, LIU B F. Study on tissue culture technique of Nicotiana tabacum [J]. Journal of Taishan University, 2009, 31(6): 94-98. | |
| [100] | 莫倩珍, 麦荣嘉, 杨志晓, 等. 快速高效植物瞬时表达的实验室烟草无土栽培体系的构建[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2012, 32(6): 772-777. |
| MO Q Z, MAI R J, YANG Z X, et al. A hydroponic cultivation system for rapid high-yield transient protein expressioin in Nicotiana plants under laboratory conditions[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2012, 32(6): 772-777. | |
| [101] | 刘晓丽, 向欢, 杨兴有, 等. 光照强度对烟草生长发育及产量和质量的影响研究进展[J]. 现代农业科技, 2022(5): 14-17, 27. |
| LIU X L, XIANG H, YANG X Y, et al. Research progress on the influence of light intensity on tobacco growth, yield and quality[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022(5): 14-17, 27. | |
| [102] | YANG M, SUN H Y, LAI H F, et al. Plant-produced Zika virus envelope protein elicits neutralizing immune responses that correlate with protective immunity against Zika virus in mice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2018, 16(2): 572-580. |
| [103] | PYRSKI M, RUGOWSKA A, WIERZBIŃSKI K R, et al. HBcAg produced in transgenic tobacco triggers Th1 and Th2 response when intramuscularly delivered[J]. Vaccine, 2017, 35(42): 5714-5721. |
| [104] | MENZEL S, HOLLAND T, BOES A, et al. Downstream processing of a plant-derived malaria transmission-blocking vaccine candidate[J]. Protein Expression and Purification, 2018, 152: 122-130. |
| [105] | 李宏. 植物组织RNA提取的难点及对策[J]. 生物技术通报, 1999, 15(1): 36-39. |
| LI H. The difficulties in the isolation of RNA from plant tissues and their resolving strategies[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 1999, 15(1): 36-39. | |
| [106] | LEE D, COAKER G. Purification and detection of ubiquitinated plant proteins using tandem ubiquitin binding entities[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2023, 2581: 245-254. |
| [107] | MATSUSHIMA A, MATSUO K. Removal of plant endogenous proteins from tobacco leaf extract by freeze–thaw treatment for purification of recombinant proteins[J]. Plant Science, 2024, 339: 111953. |
| [108] | 李颖, 张悦婧, 王馨, 等. 农杆菌菌株及其侵染浓度和时间对基于菜豆黄矮病毒表达载体瞬时表达外源基因的影响[J]. 植物科学学报, 2021, 39(3): 297-305. |
| LI Y, ZHANG Y J, WANG X, et al. Effects of Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain and its infection time and concentration on transient expression of foreign genes based on expression vector of bean yellow dwarf virus[J]. Plant Science Journal, 2021, 39(3): 297-305. | |
| [109] | ROSENTHAL S H. Improving expression vectors for recombinant protein production in plants [D]. Tempe: Arizona State University, 2012. |
| [110] | 喻文聪, 袁玉辉, 李湘, 等. 芥菜型油菜BjuA03.TTG2基因启动子克隆及表达载体构建[J]. 作物研究, 2023, 37(1): 55-61. |
| YU W C, YUAN Y H, LI X, et al. Clonging of BjuA03.TTG2 gene promoter from Brassica juncea and construction of its plant expression vectors[J]. Crop Research, 2023, 37(1): 55-61. | |
| [111] | TAKITA E, YOSHIDA K, HANANO S, et al. Development of the binary vector pTACAtg1 for stable gene expression in plant: reduction of gene silencing in transgenic plants carrying the target gene with long flanking sequences[J]. Plant Biotechnology, 2021, 38(4): 391-400. |
| [112] | 郭金洁, 张丹, 张伟, 等. CaMV 35S 增强子调节玉米基因表达的机制研究[J]. 农业生物技术学报, 2023, 31(5): 914-926. |
| GUO J J, ZHANG D, ZHANG W, et al. Study on the mechanism of CaMV 35S enhancer regulating gene expression in maize (Zea mays)[J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2023, 31(5): 914-926. | |
| [113] | 贾小明, 张焕玲, 樊军锋. 热激启动子控制的FT基因诱导杨树早期开花体系的优化[J]. 林业科学, 2011, 47(11): 37-43. |
| JIA X M, ZHANG H L, FAN J F. System optimization of precociously flowering of poplar induced by FT gene controlled by a heat shock promoter[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2011, 47(11): 37-43. | |
| [114] | 熊雨飞, 徐娅, 成烨, 等. 一种水稻种子胚乳优势表达启动子pNFYA2、制备方法及应用: CN118345074A[P]. 2024-07-16. |
| XIONG Y F, XU Y, CHENG Y, et al. Rice seed endosperm dominant expression promoter pNFYA 2, preparation method and application: CN118345074A[P]. 2024-07-16. | |
| [115] | 魏祥进, 胡培松, 李港, 等. 一种水稻胚乳特异性表达启动子pEnd2及其应用: CN114854749A[P]. 2022-08-05. |
| WEI X J, HU P S, LI G, et al. Rice endosperm specific expression promoter pEnd2 and application thereof: CN114854749A[P]. 2022-08-05. | |
| [116] | 宋任涛, 张伟, 田忠瑞, 等. 玉米胚乳特异表达启动子PMAP启动子、其克隆方法及其应用: CN105316338A[P]. 2016-02-10. |
| SONG R T, ZHANG W, TIAN Z R, et al. Corn endosperm specific expression promoter PMAP promoter and cloning method and application thereof: CN105316338A[P]. 2016-02-10. | |
| [117] | 武兆云, 张倩, 郭玉鸽, 等. 基于植物重组蛋白产量提高的研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2022, 38(8): 2784-2797. |
| WU Z Y, ZHANG Q, GUO Y G, et al. Improving the production of plant-based recombinant protein: a review[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2022, 38(8): 2784-2797. | |
| [118] | ROSENTHAL S H, DIAMOS A G, MASON H S. An intronless form of the tobacco extensin gene terminator strongly enhances transient gene expression in plant leaves[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2018, 96(4): 429-443. |
| [119] | HAGER K J, PÉREZ MARC G, GOBEIL P, et al. Efficacy and safety of a recombinant plant-based adjuvanted COVID-19 vaccine[J]. New England Journal of Medicine, 2022, 386(22): 2084-2096. |
| [120] | OH S W, SHAO J F, MITRA J, et al. Enhancer release and retargeting activates disease-susceptibility genes[J]. Nature, 2021, 595(7869): 735-740. |
| [121] | MA F S, XU Q R, WANG A P, et al. A universal design of restructured dimer antigens: development of a superior vaccine against the paramyxovirus in transgenic rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America, 2024, 121(4): e2305745121. |
| [122] | 赵连三, 秦山. 可高效安全表达的新型核酸疫苗: CN1367020[P]. 2002-09-04. |
| ZHAO L S, QIN S. A new type of nucleic acid vaccine for efficient and safe expression: CN1367020[P]. 2002-09-04 | |
| [123] | 杨柳, 秦文, 王丽媛, 等. 利用血清筛选和模拟胃肠液消化稳定性试验评价植物源重组人血清白蛋白潜在致敏性[J]. 中国食品卫生杂志, 2022, 34(1): 34-38. |
| YANG L, QIN W, WANG L Y, et al. Evaluation of the potential allergenicity of Oryza sativa recombinant human serum albumin by serum screening and simulated gastrointestinal fluid digestion stability test[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene, 2022, 34(1): 34-38. | |
| [124] | FAUSTHER-BOVENDO H, KOBINGER G. Plant-made vaccines and therapeutics[J]. Science, 2021, 373(6556): 740-741. |
| [125] | 区永祥, 苏韵琳. 一种利用表达O157: H7抗原的转基因生菜研制的口服疫苗: CN117003886A[P]. 2023-11-07. |
| OU Y X, SU Y L. Oral vaccine developed by using transgenic lettuce expressing O157: H7 antigen: CN117003886A[P]. 2023-11-07. | |
| [126] | 赖强, 倪能能, 钟泽民, 等. 一种猪圆环病毒2型重组植物乳杆菌口服疫苗的制备方法及应用: CN106520817A[P]. 2017-03-22. |
| LAI Q, NI N N, ZHONG Z M, et al. Preparation method and applications of porcine circovirus type Ⅱ recombinant Lactobacillus plantarum oral vaccine: CN106520817A[P]. 2017-03-22. | |
| [127] | NEWBY M L, ALLEN J D, CRISPIN M. Influence of glycosylation on the immunogenicity and antigenicity of viral immunogens[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2024, 70: 108283. |
| [128] | STRASSER R. Plant glycoengineering for designing next-generation vaccines and therapeutic proteins[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2023, 67: 108197. |
| [129] | OLSZEWSKI N E, WEST C M, SASSI S O, et al. O-GlcNAc protein modification in plants: evolution and function[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2010, 1800(2): 49-56. |
| [130] | WU J, ZHU W T, SHAN X T, et al. Glycoside-specific metabolomics combined with precursor isotopic labeling for characterizing plant glycosyltransferases[J]. Molecular Plant, 2022, 15(10): 1517-1532. |
| [131] | DICKEY LYNN F, KEVIN M COX, PEELE CHARLES G, et al. Compositions and methods for humanization and optimization of N-glycans in plants: WO2007084926[P]. 2007-01-17. |
| [132] | HANANIA U, ARIEL T, TEKOAH Y, et al. Establishment of a tobacco BY2 cell line devoid of plant-specific xylose and fucose as a platform for the production of biotherapeutic proteins[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 15(9): 1120-1129. |
| [133] | 尹恒, 赵小明, 王文霞, 等. 植物糖生物学与糖链植物疫苗[J]. 生命科学, 2011, 23(6): 598-604. |
| YIN H, ZHAO X M, WANG W X, et al. Plant glycobiology and carbohydrate-based plant disease vaccines[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2011, 23(6): 598-604. | |
| [134] | KIM T G, LEE H J, JANG Y S, et al. Co-expression of proteinase inhibitor enhances recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor production in transgenic rice cell suspension culture[J]. Protein Expression and Purification, 2008, 61(2): 117-121. |
| [135] | GROSSE-HOLZ F, MADEIRA L, ZAHID M A, et al. Three unrelated protease inhibitors enhance accumulation of pharmaceutical recombinant proteins in Nicotiana benthamiana [J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2018, 16(10): 1797-1810. |
| [136] | 冯玮. 植物蛋白酶抑制剂研究进展概述[J]. 生物学教学, 2020, 45(12): 61-63. |
| FENG W. Overview of research progress on plant protease inhibitors[J]. Biology Teaching, 2020, 45(12): 61-63. | |
| [137] | VOLPICELLA M, LEONI C, COSTANZA A, et al. Cystatins, serpins and other families of protease inhibitors in plants[J]. Current Protein & Peptide Science, 2011, 12(5): 386-398. |
| [138] | PATSTON P A, GETTINS P G. Significance of secondary structure predictions on the reactive center loop region of serpins: a model for the folding of serpins into a metastable state[J]. FEBS Letters, 1996, 383(1-2): 87-92. |
| [139] | AHN J W, ATWELL B J, ROBERTS T H. Serpin genes AtSRP2 and AtSRP3 are required for normal growth sensitivity to a DNA alkylating agent in Arabidopsis [J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2009, 9: 52. |
| [140] | SALES P M, SOUZA P M, SIMEONI L A, et al. α-Amylase inhibitors: a review of raw material and isolated compounds from plant source[J]. Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2012, 15(1): 141-183. |
| [141] | HATAKEYAMA T, HIRAOKA M, FUNATSU G. Amino acid sequences of the two smallest trypsin inhibitors from sponge gourd seeds[J]. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 1991, 55(10): 2641-2642. |
| [142] | RAWLINGS N D, BARRETT A J, THOMAS P D, et al. The MEROPS database of proteolytic enzymes, their substrates and inhibitors in 2017 and a comparison with peptidases in the PANTHER database[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 46(D1): D624-D632. |
| [143] | DÍEZ-DÍAZ M, CONEJERO V, RODRIGO I, et al. Isolation and characterization of wound-inducible carboxypeptidase inhibitor from tomato leaves[J]. Phytochemistry, 2004, 65(13): 1919-1924. |
| [144] | KOMARNYTSKY S, BORISJUK N, YAKOBY N, et al. Cosecretion of protease inhibitor stabilizes antibodies produced by plant roots[J]. Plant Physiology, 2006, 141(4): 1185-1193. |
| [145] | PILLAY P, KIBIDO T, DU PLESSIS M, et al. Use of transgenic oryzacystatin-Ⅰ-expressing plants enhances recombinant protein production[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2012, 168(6): 1608-1620. |
| [146] | GOULET C, BENCHABANE M, ANGUENOT R, et al. A companion protease inhibitor for the protection of cytosol-targeted recombinant proteins in plants[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2010, 8(2): 142-154. |
| [147] | JUTRAS P V, MARUSIC C, LONOCE C, et al. An accessory protease inhibitor to increase the yield and quality of a tumour-targeting mAb in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(11): e0167086. |
| [148] | KIM N H, HWANG B K. Pepper pathogenesis-related protein 4c is a plasma membrane-localized cysteine protease inhibitor that is required for plant cell death and defense signaling[J]. The Plant Journal, 2015, 81(1): 81-94. |
| [149] | GROSSE-HOLZ F, KELLY S, BLASKOWSKI S, et al. The transcriptome, extracellular proteome and active secretome of agroinfiltrated Nicotiana benthamiana uncover a large, diverse protease repertoire[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2018, 16(5): 1068-1084. |
| [150] | ARKADASH V, YOSEF G, SHIRIAN J, et al. Development of high affinity and high specificity inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinase 14 through computational design and directed evolution[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2017, 292(8): 3481-3495. |
| [151] | WINGFIELD P T, SAX J K, STAHL S J, et al. Biophysical and functional characterization of full-length, recombinant human tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 (TIMP-2) produced in Escherichia coli. Comparison of wild type and amino-terminal alanine appended variant with implications for the mechanism of TIMP functions[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1999, 274(30): 21362-21368. |
| [152] | HONG Q N, LIU J, WEI Y Q, et al. Application of baculovirus expression vector system (BEVS) in vaccine development[J]. Vaccines, 2023, 11(7): 1218. |
| [153] | 马婷, 张西倩, 丁向真, 等. 聚合酶Ⅱ转录的sRNA与RNA沉默抑制子对TMV病毒载体表达系统作用的比较[J]. 农业生物技术学报, 2016, 24(1): 1-9. |
| MA T, ZHANG X Q, DING X Z, et al. Comparison of effects of polⅡ-derived short RNA and RNA silencing suppressor on TMV-based expression vector system[J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2016, 24(1): 1-9. | |
| [154] | SCHOLTHOF H B. The tombusvirus-encoded P19: from irrelevance to elegance[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2006, 4(5): 405-411. |
| [155] | MA J X, DING X Z, LI Z Y, et al. Co-expression with replicating vector overcoming competitive effects derived by a companion protease inhibitor in plants[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 699442. |
| [156] | 李源源. 芸薹黄化病毒P0蛋白抑制RNA沉默的分子机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2015. |
| LI Y Y. Molecular mechanisms underlying suppression of RNA silencing by Brassica yellows virus P0 protein[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2015. | |
| [157] | 陈道, 张慧颖, 胡书明, 等. 小麦黄花叶病毒P1蛋白具有RNA沉默抑制活性促进病毒侵染小麦[C]//中国植物病理学会2023年学术年会论文集. 2023: 399. |
| CHEN D, ZHANG H Y, HU S M, et al. The P1 protein of wheat yellow mosaic virus exerts RNA silencing suppression activity to facilitate virus infection in wheat[C]//Proceedings of the 2023 Annual Conference of the Chinese Society of Plant Pathology. 2023: 399. | |
| [158] | 蒋铭轩, 李康, 罗亮, 等. 植物表达外源蛋白研究进展及展望[J]. 生物技术通报, 2023, 39(11): 110-122. |
| JIANG M X, LI K, LUO L, et al. Advances on the expressions of foreign proteins in plants[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2023, 39(11): 110-122. | |
| [159] | CHEN G F, WEI T Y, JU F R, et al. Protein quality control and aggregation in the endoplasmic reticulum: from basic to bedside[J]. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 2023, 11: 1156152. |
| [160] | XU F F, WANG L K. Deciphering ER stress-unfolded protein response relationship by visualizing unfolded proteins in the ER[J]. Cell Reports, 2024, 43(6): 114358. |
| [161] | WANG L, WANG C C. Oxidative protein folding fidelity and redoxtasis in the endoplasmic reticulum[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 2023, 48(1): 40-52. |
| [162] | 康跻耀, 翟松, 张志林. 一种植物蛋白纯化用研磨装置: CN216879518U[P]. 2022-07-05. |
| KANG J Y, ZHAI S, ZHANG Z L. Grinding device for purifying vegetable protein: CN216879518U[P]. 2022-07-05. | |
| [163] | 唐静秋, 丁惠, 王晗玉, 等. 一种植物蛋白纯化用固液分离装置: CN217258606U[P]. 2022-08-23. |
| TANG J Q, DING H, WANG H Y, et al. Solid-liquid separation device for purifying vegetable protein: CN217258606U[P]. 2022-08-23. | |
| [164] | DIAMOS A G, HUNTER J G L, PARDHE M D, et al. High level production of monoclonal antibodies using an optimized plant expression system[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2020, 17(7): 472. |
| [165] | SHANMUGARAJ B M, RAMALINGAM S. Plant expression platform for the production of recombinant pharmaceutical proteins[J]. Austin Journal of Biotechnology& Bioengineering, 2014: 1(6): 4. |
| [166] | STANDER J, MBEWANA S, MEYERS A E. Plant-derived human vaccines: recent developments[J]. BioDrugs, 2022, 36(5): 573-589. |
| [167] | CHEN Q, HE J Y, PHOOLCHAROEN W, et al. Geminiviral vectors based on bean yellow dwarf virus for production of vaccine antigens and monoclonal antibodies in plants[J]. Human Vaccines, 2011, 7(3): 331-338. |
| [168] | PEYRET H, LOMONOSSOFF G P. When plant virology met Agrobacterium: the rise of the deconstructed clones[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2015, 13(8): 1121-1135. |
| [169] | KLIMYUK V, POGUE G, HERZ S, et al. Production of recombinant antigens and antibodies in Nicotiana benthamiana using ‘magnifection’ technology: GMP-compliant facilities for small- and large-scale manufacturing[J]. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology, 2014, 375: 127-154. |
| [170] | POMATTO M A C, GAI C, NEGRO F, et al. Oral delivery of mRNA vaccine by plant-derived extracellular vesicle carriers[J]. Cells, 2023, 12(14): 1826. |
| [171] | RAMJEE L, LEMAY W, VURGUN N, et al. Projected impact of a plant-derived vaccine on the burden of seasonal influenza in Canada[J]. Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics, 2021, 17(10): 3643-3651. |
| [172] | UEDA H, OGAWA H. 植物糖タンパク質エピ トープの糖鎖生物学: 植物糖鎖エピトープの構造、免疫原性とアレルゲン性[J]. Trends in Glycoscience and Glycotechnology, 1999, 11(62): 413-428. |
| UEDA H, OGAWA H. Glycobiology of the plant glycoprotein epitope: structure, immunogenicity and allergenicity of plant glycotopes[J]. Trends in Glycoscience and Glycotechnology, 1999, 11(62): 413-428. | |
| [173] | SINGH S, SINGH P K, SACHAN K, et al. Recent progress and challenges in the development of edible vaccines produced by genetically modified plants[J]. Current Protein & Peptide Science, 2023, 24(9): 711-720. |
| [174] | KIM M Y, VERGARA E, TRAN A, et al. Marked enhancement of the immunogenicity of plant-expressed IgG-Fc fusion proteins by inclusion of cholera toxin non-toxic B subunit within the single polypeptide[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2024, 22(5): 1402-1416. |
| [175] | BHAR A. Is it possible to ensure COVID19 vaccine supply by using plants?[J]. The Nucleus, 2021, 64(2): 137-141. |
| [1] | 何杨昱, 杨凯, 王玮琳, 黄茜, 丘梓樱, 宋涛, 何流赏, 姚金鑫, 甘露, 何玉池. 国际基因工程机器大赛中植物合成生物学主题的设计与实践[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, (): 1-12. |
| [2] | 章益蜻, 刘高雯. 合成生物学视角下的基因功能探索与酵母工程菌株文库构建[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(3): 685-700. |
| [3] | 韦灵珍, 王佳, 孙新晓, 袁其朋, 申晓林. 黄酮类化合物生物合成及其在化妆品中应用的研究[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(2): 373-390. |
| [4] | 左一萌, 张姣姣, 连佳长. 酿酒酵母使能技术在化妆品原料合成中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(2): 233-253. |
| [5] | 孙扬, 陈立超, 石艳云, 王珂, 吕丹丹, 徐秀美, 张立新. 作物光合作用合成生物学的策略与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, (): 1-16. |
| [6] | 刘晓悦, 王盼娣, 吴刚, 刘芳. 基因工程辅助萝卜硫苷在十字花科作物中的高效生物合成[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 136-156. |
| [7] | 李庚, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 王佳, 袁其朋. 过氧化物酶的重组表达和应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1498-1517. |
| [8] | 竺方欢, 岑雪聪, 陈振. 微生物合成二元醇研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1367-1385. |
| [9] | 陈盈盈, 刘扬, 史俊杰, 马俊英, 鞠建华. CRISPR/Cas基因编辑及其新兴技术在丝状真菌研究中的系统应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 672-693. |
| [10] | 惠真, 唐啸宇. CRISPR/Cas9编辑系统在微生物天然产物研究中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 658-671. |
| [11] | 许志锰, 谢震. 引导编辑研究进展及其应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 1-15. |
| [12] | 陈雅如, 曹英秀, 宋浩. 电活性微生物基因编辑与转录调控技术进展与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(6): 1281-1299. |
| [13] | 肖艳, 刘亚君, 冯银刚, 崔球. 热纤梭菌在生物质能源开发中的合成生物学研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(6): 1055-1081. |
| [14] | 孙梦楚, 陆亮宇, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 王佳, 袁其朋. 基于荧光检测的高通量筛选技术和装备助力细胞工厂构建[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 947-965. |
| [15] | 林继聪, 邹根, 刘宏民, 魏勇军. CRISPR/Cas基因组编辑技术在丝状真菌次级代谢产物合成中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(4): 738-755. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
