合成生物学 ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (4): 806-828.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-043
高黏性蛋白材料的合成生物学及应用
李全飞1,2, 陈乾1,2, 刘浩1,2, 贺坤东1,2, 潘亮1,2, 雷鹏1,2, 谷益安1,2, 孙良1,2, 李莎1,2, 邱益彬1,2, 王瑞1,2, 徐虹1,2
- 1.南京工业大学食品与轻工学院,江苏 南京 210009
2.材料化学工程全国重点实验室,江苏 南京 210009
-
收稿日期:2025-05-08修回日期:2025-07-02出版日期:2025-08-31发布日期:2025-09-03 -
通讯作者:王瑞 -
作者简介:李全飞 (1998—),男,博士研究生。研究方向为高黏性蛋白的生物合成及分离纯化。E-mail:202462218257@njtech.edu.cn王瑞 (1987—),男,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为高性能蛋白材料合成生物学与应用。E-mail:ruiwang2013@njtech.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金面上项目(22478185);江苏省合成生物学基础研究中心项目(BK20233003);南京工业大学材料化学工程全国重点实验室项目(KL-MCE-22A05);南京工业大学材料化学工程全国重点实验室项目(SKL-MCE-23A17)
Synthetic biology and applications of high-adhesion protein materials
LI Quanfei1,2, CHEN Qian1,2, LIU Hao1,2, HE Kundong1,2, PAN Liang1,2, LEI Peng1,2, GU Yi’an1,2, SUN Liang1,2, LI Sha1,2, QIU Yibin1,2, WANG Rui1,2, XU Hong1,2
- 1.College of Food Science and Light Industry,Nanjing University of Technology,Nanjing 210009,Jiangsu,China
2.State Key Laboratory of Materials-oriented Chemical Engineering,Nanjing 210009,Jiangsu,China
-
Received:2025-05-08Revised:2025-07-02Online:2025-08-31Published:2025-09-03 -
Contact:WANG Rui
摘要:
高黏性蛋白材料因其卓越的生物黏附性和潜在的生物相容性,在生物医用材料和黏合剂领域展现出巨大的应用潜力。然而,传统方式获取的高黏蛋白材料面临诸多挑战,如产量低、结构复杂、难以规模化生产等。合成生物学作为新兴的交叉学科,为解决这些瓶颈提供了创新策略。本综述系统总结了近年来高黏性蛋白材料的生物合成、改性及应用进展,重点突出了合成生物学在解决高黏性蛋白材料产量、可控性以及功能多样性等方面的优势。全面梳理了基因工程实现对贻贝黏蛋白、藤壶胶蛋白和扇贝足丝蛋白等黏附蛋白的精确设计和高效表达,从而克服高黏蛋白材料在产量和可控性方面的限制。同时,综述了这些蛋白材料在生物黏合剂和医用功能涂层方面的独特优势,如贻贝蛋白的湿面黏附性、藤壶胶蛋白的强黏附性以及类弹性蛋白的可调控性。通过合成生物学方法,可以突破高黏蛋白材料在产量、性能和功能方面的限制,加速其在组织工程、表界面改性等领域的应用。最后,总结了当前合成生物学在高黏蛋白材料领域的最新进展和创新点,并展望了其未来的发展方向,为开发高性能、多功能的高黏蛋白材料提供了新的思路和策略。
中图分类号:
引用本文
李全飞, 陈乾, 刘浩, 贺坤东, 潘亮, 雷鹏, 谷益安, 孙良, 李莎, 邱益彬, 王瑞, 徐虹. 高黏性蛋白材料的合成生物学及应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(4): 806-828.
LI Quanfei, CHEN Qian, LIU Hao, HE Kundong, PAN Liang, LEI Peng, GU Yi’an, SUN Liang, LI Sha, QIU Yibin, WANG Rui, XU Hong. Synthetic biology and applications of high-adhesion protein materials[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 806-828.
| 宿主细胞 | 优点 | 缺点 | 适用性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 大肠杆菌 | 生长快速,培养成本低廉,遗传背景清晰,易于基因操作 | 缺乏真核细胞的翻译后修饰机制,容易形成包涵体,可能导致蛋白活性降低 | 适用于表达结构简单、不需要复杂翻译后修饰的蛋白 |
| 枯草芽孢杆菌 | 分泌表达能力强,有利于蛋白的正确折叠,无内毒素污染 | 蛋白酶含量高,可能导致目的蛋白降解 | 适用于表达分泌蛋白 |
| 酿酒酵母/毕赤酵母 | 真核表达系统,能够进行一些简单的翻译后修饰,分泌表达能力较强 | 糖基化修饰可能与人源蛋白不同 | 适用于表达高分子量的、需要糖基化的蛋白 |
| 动物细胞 | 能够进行完整的翻译后修饰,保证蛋白的正确折叠和生物活性 | 生长速度较慢,培养成本很高,容易受到病毒污染 | 适用于表达需要复杂糖基化修饰的蛋白,例如抗体和治疗性蛋白 |
| 植物细胞 | 培养成本低廉,易于大规模培养,安全性高 | 翻译后修饰能力有限,表达水平相对较低 | 适用于表达一些结构简单的蛋白,或者用于大规模生产 |
表1 重组蛋白表达常用宿主细胞比较
Table 1 Comparison of common host cells for recombinant protein production
| 宿主细胞 | 优点 | 缺点 | 适用性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 大肠杆菌 | 生长快速,培养成本低廉,遗传背景清晰,易于基因操作 | 缺乏真核细胞的翻译后修饰机制,容易形成包涵体,可能导致蛋白活性降低 | 适用于表达结构简单、不需要复杂翻译后修饰的蛋白 |
| 枯草芽孢杆菌 | 分泌表达能力强,有利于蛋白的正确折叠,无内毒素污染 | 蛋白酶含量高,可能导致目的蛋白降解 | 适用于表达分泌蛋白 |
| 酿酒酵母/毕赤酵母 | 真核表达系统,能够进行一些简单的翻译后修饰,分泌表达能力较强 | 糖基化修饰可能与人源蛋白不同 | 适用于表达高分子量的、需要糖基化的蛋白 |
| 动物细胞 | 能够进行完整的翻译后修饰,保证蛋白的正确折叠和生物活性 | 生长速度较慢,培养成本很高,容易受到病毒污染 | 适用于表达需要复杂糖基化修饰的蛋白,例如抗体和治疗性蛋白 |
| 植物细胞 | 培养成本低廉,易于大规模培养,安全性高 | 翻译后修饰能力有限,表达水平相对较低 | 适用于表达一些结构简单的蛋白,或者用于大规模生产 |
| 纯化方法 | 原理 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 亲和色谱 | 基于目标蛋白与特定配体(如抗体、金属离子、辅酶等)之间的高特异性结合 | 高特异性、高纯度、操作简便 | 可能需要添加标签,洗脱条件可能较为苛刻,某些配体价格昂贵 |
| 离子交换色谱 | 基于目标蛋白与固定化的带电基团之间的静电相互作用 | 适用于大规模纯化,成本较低 | 特异性不如亲和色谱,需要优化洗脱条件 |
| 凝胶过滤色谱 | 基于目标蛋白的分子大小进行分离 | 操作简便,可以确定蛋白的分子量 | 分辨率较低,不适用于分离分子量相近的蛋白 |
| 疏水相互作用色谱 | 基于目标蛋白表面的疏水性与固定化的疏水基团之间的相互作用 | 适用于分离疏水性蛋白 | 需要优化盐浓度和洗脱条件 |
| 超滤/透析 | 利用半透膜对分子大小的截留作用 | 操作简便,适用于大规模处理 | 不能分离分子大小相近的蛋白 |
| 沉淀法 | 通过改变溶液的条件(如盐浓度、pH 值、温度等),使目标蛋白溶解度降低,从而沉淀析出 | 成本低廉,适用于大规模初步纯化 | 特异性较低,可能需要后续的精细纯化 |
表2 常见蛋白纯化方法的对比
Table 2 Comparison of characteristics of common protein purification methods
| 纯化方法 | 原理 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 亲和色谱 | 基于目标蛋白与特定配体(如抗体、金属离子、辅酶等)之间的高特异性结合 | 高特异性、高纯度、操作简便 | 可能需要添加标签,洗脱条件可能较为苛刻,某些配体价格昂贵 |
| 离子交换色谱 | 基于目标蛋白与固定化的带电基团之间的静电相互作用 | 适用于大规模纯化,成本较低 | 特异性不如亲和色谱,需要优化洗脱条件 |
| 凝胶过滤色谱 | 基于目标蛋白的分子大小进行分离 | 操作简便,可以确定蛋白的分子量 | 分辨率较低,不适用于分离分子量相近的蛋白 |
| 疏水相互作用色谱 | 基于目标蛋白表面的疏水性与固定化的疏水基团之间的相互作用 | 适用于分离疏水性蛋白 | 需要优化盐浓度和洗脱条件 |
| 超滤/透析 | 利用半透膜对分子大小的截留作用 | 操作简便,适用于大规模处理 | 不能分离分子大小相近的蛋白 |
| 沉淀法 | 通过改变溶液的条件(如盐浓度、pH 值、温度等),使目标蛋白溶解度降低,从而沉淀析出 | 成本低廉,适用于大规模初步纯化 | 特异性较低,可能需要后续的精细纯化 |
| [12] | HWANG D S, GIM Y, CHA H J. Expression of functional recombinant mussel adhesive protein type 3A in Escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2005, 21(3): 965-970. |
| [13] | 郝东, 魏文培, 周浩, 等. 重组贻贝粘蛋白Mfp-3P的制备及促进伤口愈合的作用[J]. 生物工程学报, 2024, 40(5): 1498-1508. |
| HAO D, WEI W P, ZHOU H, et al. Preparation of recombinant mussel mucin Mfp-3P and its promotion of wound healing[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2024, 40(5): 1498-1508. | |
| [14] | HWANG D S, KIM K R, LIM S H, et al. Recombinant mussel adhesive protein as a gene delivery material[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2009, 102(2): 616-623. |
| [15] | QI H S, ZHENG W W, ZHANG C, et al. Novel mussel-inspired universal surface functionalization strategy: protein-based coating with residue-specific post-translational modification in vivo [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(13): 12846-12853. |
| [16] | JO Y K, KIM H J, JEONG Y, et al. Biomimetic surface engineering of biomaterials by using recombinant mussel adhesive proteins[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2018, 5(9): 1800068. |
| [17] | XUE R, ZHANG M, ZHANG C X, et al. Molecular simulations guiding recombinant mussel protein with enhanced applicable properties for adhesive materials[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2025, 307: 141988. |
| [18] | FICHMAN G, ADLER-ABRAMOVICH L, MANOHAR S, et al. Seamless metallic coating and surface adhesion of self-assembled bioinspired nanostructures based on di-(3,4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine) peptide motif[J]. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(7): 7220-7228. |
| [19] | CUI M K, WANG X Y, AN B L, et al. Exploiting mammalian low-complexity domains for liquid-liquid phase separation-driven underwater adhesive coatings[J]. Science Advances, 2019, 5(8): eaax3155. |
| [20] | WANG X, LIANG Q Y, LUO Y X, et al. Engineering the next generation of theranostic biomaterials with synthetic biology[J]. Bioactive Materials, 2024, 32: 514-529. |
| [21] | YU Y, LIU Z M, CHEN M, et al. Enhancing the expression of recombinant κ-carrageenase in Pichia pastoris using dual promoters, co-expressing chaperones and transcription factors[J]. Biocatalysis and Biotransformation, 2020, 38(2): 104-113. |
| [22] | PAPAMICHAIL D, LIU H M, MACHADO V, et al. Codon context optimization in synthetic gene design[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 2018, 15(2): 452-459. |
| [23] | YAO L, WANG X Y, XUE R, et al. Comparative analysis of mussel foot protein 3B co-expressed with tyrosinases provides a potential adhesive biomaterial[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2022, 195: 229-236. |
| [24] | WEI W, KIM J M, MEDINA D, et al. GeneOptimizer program-assisted cDNA reengineering enhances sRAGE autologous expression in Chinese hamster ovary cells[J]. Protein Expression and Purification, 2014, 95: 143-148. |
| [25] | ZHANG M Y, SONG J, XIAO J, et al. Engineered multiple translation initiation sites: a novel tool to enhance protein production in Bacillus licheniformis and other industrially relevant bacteria[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2022, 50(20): 11979-11990. |
| [26] | LIU J, XU L M, JIN Y, et al. Cell-targeting cationic gene delivery system based on a modular design rationale[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(22): 14200-14210. |
| [27] | CUI M K, QI Q, GURRY T, et al. Modular genetic design of multi-domain functional amyloids: insights into self-assembly and functional properties[J]. Chemical Science, 2019, 10(14): 4004-4014. |
| [28] | ZHOU X M, SHIMANOVICH U, HERLING T W, et al. Enzymatically active microgels from self-assembling protein nanofibrils for microflow chemistry[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(6): 5772-5781. |
| [29] | ALJABALI A A A, EL-TANANI M, TAMBUWALA M M. Principles of CRISPR-Cas9 technology: advancements in genome editing and emerging trends in drug delivery[J]. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 2024, 92: 105338. |
| [30] | GARAY-NOVILLO J N, RUIZ-MASÓ J Á, DEL SOLAR G, et al. Easy-curing and pH-regulated CRISPR-Cas9 plasmids for gene editing and plasmid curing in Lactococcus cremoris [J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 2024, 17(12): e70060. |
| [31] | ZHENG R X, ZHANG L X, PARVIN R, et al. Progress and perspective of CRISPR-Cas9 technology in translational medicine[J]. Advanced Science, 2023, 10(25): 2300195. |
| [32] | KIM S, SUNG B H, KIM S C, et al. Genetic incorporation of L-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) biosynthesized by a tyrosine phenol-lyase[J]. Chemical Communications, 2018, 54(24): 3002-3005. |
| [33] | ASENJO J A, PARRADO J, ANDREWS B A. Rational design of purification processes for recombinant proteins[J]. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1991, 646(1): 334-356. |
| [34] | BEYGMORADI A, HOMAEI A, HEMMATI R, et al. Recombinant protein expression: challenges in production and folding related matters[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2023, 233: 123407. |
| [35] | RESTREPO-PINEDA S, PÉREZ N O, VALDEZ-CRUZ N A, et al. Thermoinducible expression system for producing recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli: advances and insights[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2021, 45(6): fuab023. |
| [36] | NAKAMURA T, KOMA D, OSHIMA M, et al. Application of chromosomal gene insertion into Escherichia coli for expression of recombinant proteins[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2018, 126(2): 266-272. |
| [37] | DE MARCO A, DEUERLING E, MOGK A, et al. Chaperone-based procedure to increase yields of soluble recombinant proteins produced in E. coli [J]. BMC Biotechnology, 2007, 7: 32. |
| [38] | WANG X Y, FENG X X, XUE R, et al. Promoting soluble expression of hybrid mussel foot proteins by SUMO-TrxA tags for production of mussel glue[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2023, 225: 840-847. |
| [39] | WU P P, TAO Q, LIU Y X, et al. Efficient secretion of mussel adhesion proteins using a chaperone protein Spy as fusion tag in Bacillus subtilis [J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2023, 18(10): 2200582. |
| [40] | URUSHIDA Y, NAKANO M, MATSUDA S, et al. Identification and functional characterization of a novel barnacle cement protein[J]. The FEBS Journal, 2007, 274(16): 4336-4346. |
| [41] | MORI Y, URUSHIDA Y, NAKANO M, et al. Calcite-specific coupling protein in barnacle underwater cement[J]. The FEBS Journal, 2007, 274(24): 6436-6446. |
| [42] | BILL R M. Recombinant protein subunit vaccine synthesis in microbes: a role for yeast?[J]. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 2015, 67(3): 319-328. |
| [43] | MISSOUM A. Recombinant protein production and purification using eukaryotic cell factories[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2021, 2290: 215-228. |
| [44] | 李楠楠, 王智平, 鲁涛, 等. 厚壳贻贝足丝盘黏附蛋白mcofp-3的重组真核表达[J]. 生物技术通报, 2010, 26(12): 148-153. |
| LI N N, WANG Z P, LU T, et al. Recombinant expression of mcofp-3 from Mytilus coruscus plaque[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2010, 26(12): 148-153. | |
| [45] | 王绪霞, 张龙雨, 王磊, 等. 藤壶附着机理及其粘胶蛋白的研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2022, 38(12): 4449-4461. |
| [1] | LIU A P, APPEL E A, ASHBY P D, et al. The living interface between synthetic biology and biomaterial design[J]. Nature Materials, 2022, 21(4): 390-397. |
| [2] | ZHANG X Y, WANG J X, ZHANG Y, et al. Synthesizing biomaterials in living organisms[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2023, 52(23): 8126-8164. |
| [3] | MALCI K, LI I S, KISSEROUDIS N, et al. Modulating microbial materials-engineering bacterial cellulose with synthetic biology[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2024, 13(12): 3857-3875. |
| [4] | ZHAO H M. Synthetic biology continues to grow[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2024, 13(1): 1-2. |
| [5] | LEI Q, ZHAO Y F, LIU S Y, et al. Nanomaterials boost the biomedical application of synthetic biology[J]. Science China Materials, 2024, 67(7): 2051-2066. |
| [6] | YAN X, LIU X, ZHAO C H, et al. Applications of synthetic biology in medical and pharmaceutical fields[J]. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 2023, 8: 199. |
| [7] | XU T, HUANG X Y, DAO J W, et al. Synthetic biology for medical biomaterials[J]. Interdisciplinary Medicine, 2025: e20240087. |
| [8] | HAO D Z, LI X C, YANG E F, et al. Barnacle inspired high-strength hydrogel for adhesive[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2023, 11: 1183799. |
| [9] | PAPOV V V, DIAMOND T V, BIEMANN K, et al. Hydroxyarginine-containing polyphenolic proteins in the adhesive plaques of the marine mussel Mytilus edulis [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1995, 270(34): 20183-20192. |
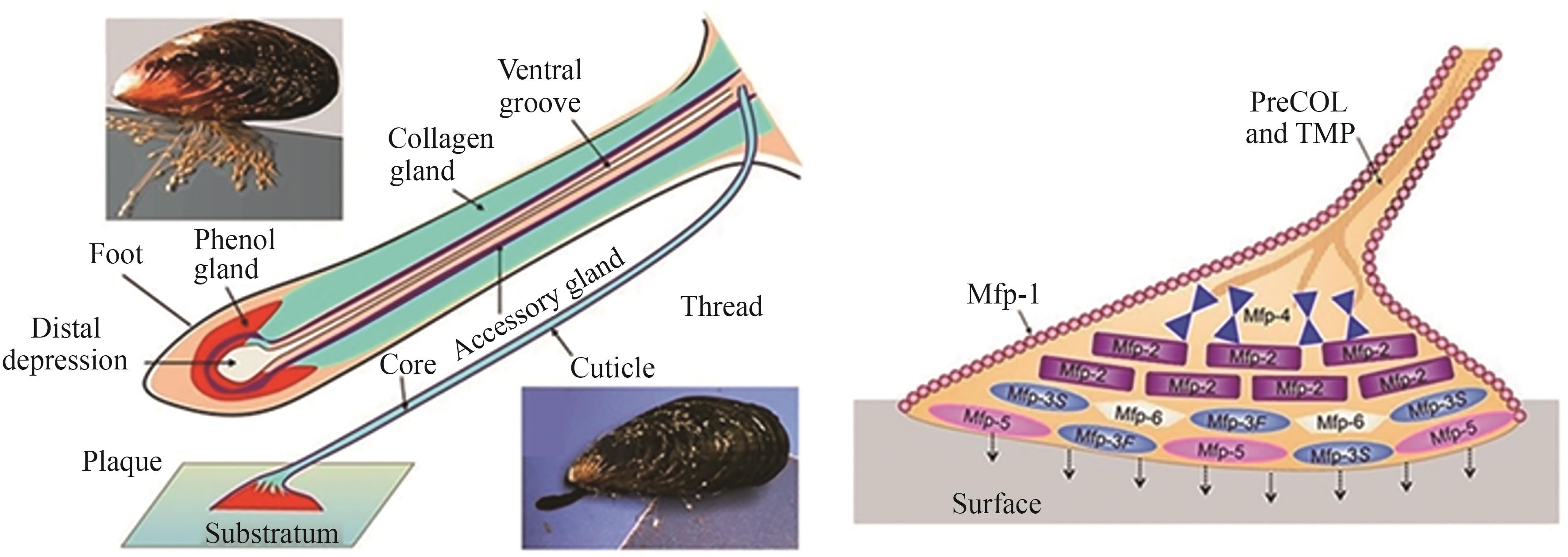
| [10] | WAITE J H. Mussel adhesion-essential footwork[J]. The Journal of Experimental Biology, 2017, 220(Pt 4): 517-530. |
| [11] | GIM Y S, HWANG D S, LIM S H, et al. Production of fusion mussel adhesive fp-353 in Escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2008, 24(6): 1272-1277. |
| [45] | WANG X X, ZHANG L Y, WANG L, et al. The adhesion mechanism of barnacle and its cement proteins: a review[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2022, 38(12): 4449-4461. |
| [46] | CARON A W, ARCHAMBAULT J, MASSIE B. High-level recombinant protein production in bioreactors using the baculovirus-insect cell expression system[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 1990, 36(11): 1133-1140. |
| [47] | THOMPSON C M, MONTES J, AUCOIN M G, et al. Recombinant protein production in large-scale agitated bioreactors using the baculovirus expression vector system[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2016, 1350: 241-261. |
| [48] | LIM S H, KIM K R, CHOI Y S, et al. In vivo post-translational modifications of recombinant mussel adhesive protein in insect cells[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2011, 27(5): 1390-1396. |
| [49] | RADEMACHER T, SACK M, BLESSING D, et al. Plant cell packs: a scalable platform for recombinant protein production and metabolic engineering[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 17(8): 1560-1566. |
| [50] | XU J F, KIELISZEWSKI M J. A novel plant cell bioproduction platform for high-yield secretion of recombinant proteins[M/OL]//Recombinant gene expression. Methods in molecular biology. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press, 2012, 824: 483-500. (2011-11-21)[2025-07-01]. . |
| [51] | 吕玉伟, 张雨靖, 吕亚维, 等. 贻贝粘蛋白Mgfp-5基因在烟草中的转化[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2016, 35(1): 172-182. |
| LV Y W, ZHANG Y J, LV Y W, et al. Transformation of Mytilus galloprovincialis foot protein type 5(Mgfp-5) gene in tobacco[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2016, 35(1): 172-182. | |
| [52] | 吕亚维. 贻贝粘合蛋白Mgfp-5基因在菊苣中的表达研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2018. |
| LÜ Y W. Expression study of mussel adhesive protein Mgfp-5 gene in Cichorium intybus [D]. Xi’an: Northwest University, 2018. | |
| [53] | PINA A S, LOWE C R, ROQUE A C A. Challenges and opportunities in the purification of recombinant tagged proteins[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2014, 32(2): 366-381. |
| [54] | MUWONGE K, YAMAN B, MÉSZÁROS A, et al. Improved expression of aggregation-prone tau proteins using a spidroin-derived solubility tag[J]. Separations, 2024, 11(7): 198. |
| [55] | TRIPATHI N K. Production and purification of recombinant proteins from Escherichia coli [J]. ChemBioEng Reviews, 2016, 3(3): 116-133. |
| [56] | JIANG R Z, YUAN S T, ZHOU Y L, et al. Strategies to overcome the challenges of low or no expression of heterologous proteins in Escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2024, 75: 108417. |
| [57] | LI G Y, XIAO Z Z, LU H P, et al. A simple method for recombinant protein purification using self-assembling peptide-tagged tobacco etch virus protease[J]. Protein Expression and Purification, 2016, 128: 86-92. |
| [58] | HWANG D S, GIM Y, YOO H J, et al. Practical recombinant hybrid mussel bioadhesive fp-151[J]. Biomaterials, 2007, 28(24): 3560-3568. |
| [59] | SAGERT J, SUN C J, WAITE J H. Chemical subtleties of mussel and polychaete holdfasts[M/OL]//Biological adhesives. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2006: 125-143 [2025-07-01]. . |
| [60] | ZHU Y J, HUANG S C, QIAN Z G, et al. Direct and efficient incorporation of DOPA into resilin-like proteins enables cross-linking into tunable hydrogels[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2023, 24(4): 1774-1783. |
| [61] | OHKAWA K, NISHIDA A, YAMAMOTO H, et al. A glycosylated byssal precursor protein from the green mussel Perna viridis with modified Dopa side-chains[J]. Biofouling, 2004, 20(2): 101-115. |
| [62] | ZHAO H, SAGERT J, HWANG D S, et al. Glycosylated hydroxytryptophan in a mussel adhesive protein from Perna viridis [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2009, 284(35): 23344-23352. |
| [63] | HENNEBERT E, MALDONADO B, LADURNER P, et al. Experimental strategies for the identification and characterization of adhesive proteins in animals: a review[J]. Interface Focus, 2015, 5(1): 20140064. |
| [64] | BRITTAIN W D G, LLOYD C M, COBB S L. Synthesis of complex unnatural fluorine-containing amino acids[J]. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 2020, 239: 109630. |
| [65] | ADHIKARI A, BHATTARAI B R, ARYAL A, et al. Reprogramming natural proteins using unnatural amino acids[J]. RSC Advances, 2021, 11(60): 38126-38145. |
| [66] | ZHOU J L, LIU Y Q, SUN Z K. LADA strategy for the synthesis of unnatural amino acids and direct modifications of peptides[J]. Science China Chemistry, 2023, 66(6): 1788-1794. |
| [67] | SAAL K A, RICHTER F, REHLING P, et al. Combined use of unnatural amino acids enables dual-color super-resolution imaging of proteins via click chemistry[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(12): 12247-12254. |
| [68] | LI Y R, CHAMPION J A. Photocrosslinked, tunable protein vesicles for drug delivery applications[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2021, 10(15): 2001810. |
| [69] | DESHMUKH M, SINGH S, GEYER A. Synthetic adhesive oligopeptides with rigid polyhydroxylated amino acids[J]. Biopolymers, 2013, 99(5): 273-281. |
| [70] | PRIEMEL T, PALIA G, FÖRSTE F, et al. Microfluidic-like fabrication of metal ion-cured bioadhesives by mussels[J]. Science, 2021, 374(6564): 206-211. |
| [71] | FAN X M, FANG Y, ZHOU W K, et al. Mussel foot protein inspired tough tissue-selective underwater adhesive hydrogel[J]. Materials Horizons, 2021, 8(3): 997-1007. |
| [72] | KROGSGAARD M, NUE V, BIRKEDAL H. Mussel-inspired materials: self-healing through coordination chemistry[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2016, 22(3): 844-857. |
| [73] | WEI W, YU J, BROOMELL C, et al. Hydrophobic enhancement of Dopa-mediated adhesion in a mussel foot protein[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(1): 377-383. |
| [74] | LU Q Y, DANNER E, WAITE J H, et al. Adhesion of mussel foot proteins to different substrate surfaces[J]. Journal of the Royal Society, Interface, 2013, 10(79): 20120759. |
| [75] | YANG B S, JIN S L, PARK Y J, et al. Coacervation of interfacial adhesive proteins for initial mussel adhesion to a wet surface[J]. Small, 2018, 14(52): 1803377. |
| [76] | SHIN M, YOON T, YANG B, et al. Thiol-rich fp-6 controls the tautomer equilibrium of oxidized Dopa in interfacial mussel foot proteins[J]. Langmuir, 2022, 38(11): 3446-3452. |
| [77] | CHOI Y S, YANG Y J, YANG B, et al. In vivo modification of tyrosine residues in recombinant mussel adhesive protein by tyrosinase co-expression in Escherichia coli [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2012, 11: 139. |
| [78] | LEE S J, HAN Y H, NAM B H, et al. A novel expression system for recombinant marine mussel adhesive protein Mefp1 using a truncated OmpA signal peptide[J]. Molecules and Cells, 2008, 26(1): 34-40. |
| [79] | BASHIR Z, YU W T, XU Z Y, et al. Engineering bio-adhesives based on protein-polysaccharide phase separation[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(17): 9987. |
| [80] | ZHANG H, BRÉ L P, ZHAO T Y, et al. Mussel-inspired hyperbranched poly(amino ester) polymer as strong wet tissue adhesive[J]. Biomaterials, 2014, 35(2): 711-719. |
| [81] | KIM H J, HWANG B H, LIM S, et al. Mussel adhesion-employed water-immiscible fluid bioadhesive for urinary fistula sealing[J]. Biomaterials, 2015, 72: 104-111. |
| [82] | CUI C Y, LIU W G. Recent advances in wet adhesives: adhesion mechanism, design principle and applications[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2021, 116: 101388. |
| [83] | ZHANG F, LIU S W, ZHANG Y, et al. Underwater bonding strength of marine mussel-inspired polymers containing DOPA-like units with amino groups[J]. RSC Advances, 2012, 2(24): 8919-8921. |
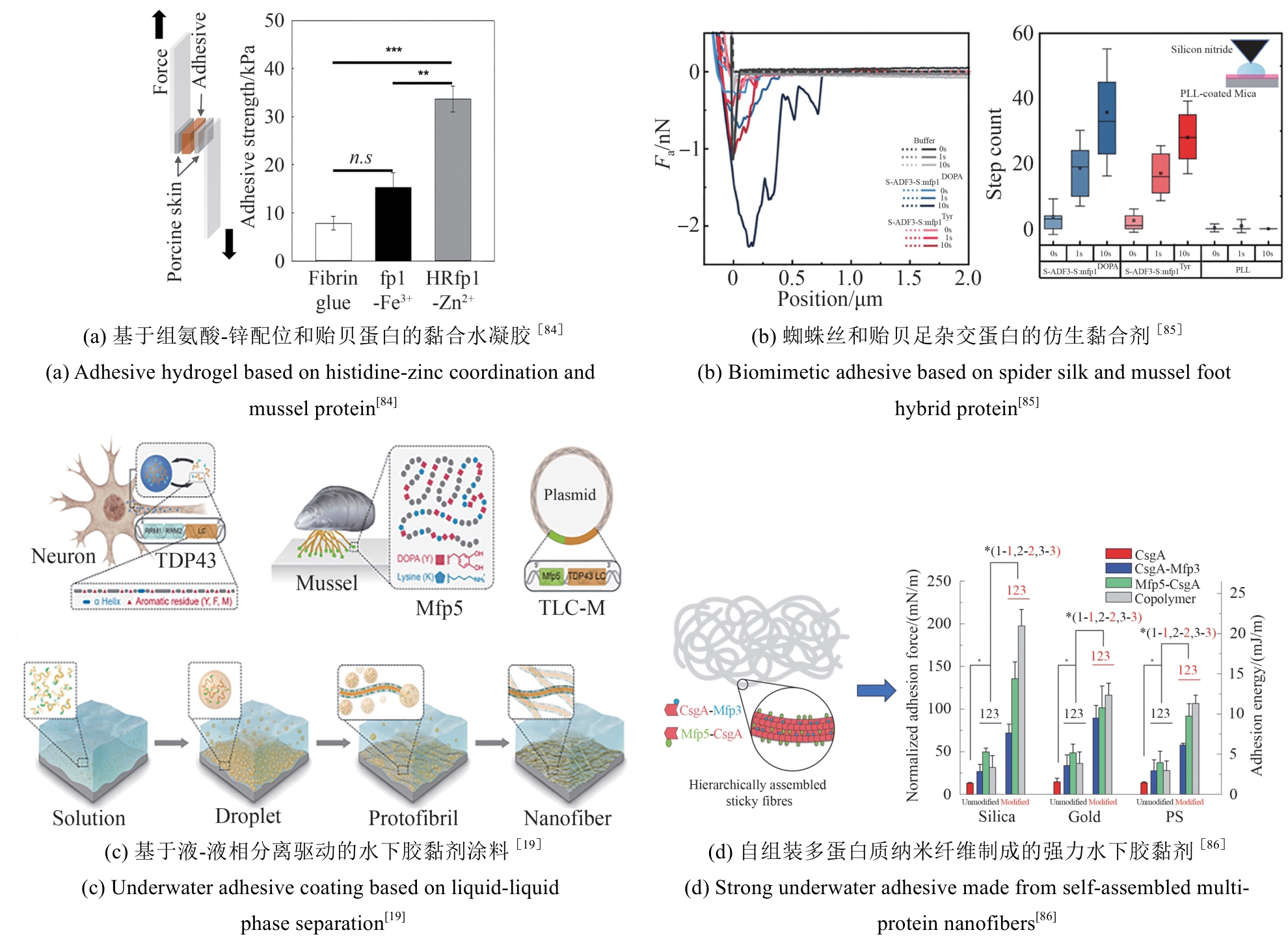
| [84] | MAENG S W, PARK T Y, PARK Y J, et al. Self-healable adhesive hydrogel with a preserved underwater adhesive ability based on histidine-zinc coordination and a bioengineered hybrid mussel protein[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2024, 25(1): 379-387. |
| [85] | YIN Y, ROAS-ESCALONA N, LINDER M B. Molecular engineering of a spider silk and mussel foot hybrid protein gives a strong and tough biomimetic adhesive[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2024, 11(8): 2300934. |
| [86] | ZHONG C, GURRY T, CHENG A A, et al. Strong underwater adhesives made by self-assembling multi-protein nanofibres[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2014, 9(10): 858-866. |
| [87] | BARROS N R, CHEN Y, HOSSEINI V, et al. Recent developments in mussel-inspired materials for biomedical applications[J]. Biomaterials Science, 2021, 9(20): 6653-6672. |
| [88] | LEE H, HA Y M, LEE S H, et al. Spontaneously restored electrical conductivity of bioactive gel comprising mussel adhesive protein-coated carbon nanotubes[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(90): 87044-87048. |
| [89] | KIM D Y, OH Y B, PARK J S, et al. Anti-microbial activities of mussel-derived recombinant proteins against gram-negative bacteria[J]. Antibiotics, 2024, 13(3): 239. |
| [90] | HU Y B, QIAO Y Z, LEI P, et al. Dual network hydrogel coatings based on recombinant mussel protein with enhanced antibacterial and super-lubrication properties for urinary catheter applications[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 474: 145502. |
| [91] | LEE J Y, KIM E J, KIM K J, et al. Protective topical dual-sided nanofibrous hemostatic dressing using mussel and silk proteins with multifunctionality of hemostasis and anti-bacterial infiltration[J]. Small, 2024, 20(18): 2308833. |
| [92] | CHEONG H Y, KIM J M, KIM B J, et al. Multi-dimensional bioinspired tactics using an engineered mussel protein glue-based nanofiber conduit for accelerated functional nerve regeneration[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2019, 90: 87-99. |
| [93] | DICKINSON G H, YANG X, WU F H, et al. Localization of phosphoproteins within the barnacle adhesive interface[J]. Biological Bulletin, 2016, 230(3): 233-242. |
| [94] | XU Z Z, LIU Z C, ZHANG C, et al. Advance in barnacle cement with high underwater adhesion[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2022, 139(37): e52894. |
| [95] | TILBURY M A, MCCARTHY S, DOMAGALSKA M, et al. The expression and characterization of recombinant cp19k barnacle cement protein from Pollicipes pollicipes [J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B, Biological Sciences, 2019, 374(1784): 20190205. |
| [96] | LI F, YE L N, ZHANG L Y, et al. Design of a genetically programmed barnacle-curli inspired living-cell bioadhesive[J]. Materials Today Bio, 2022, 14: 100256. |
| [97] | LIANG C, LI Y Q, LIU Z M, et al. Protein aggregation formed by recombinant cp19k homologue of Balanus albicostatus combined with an 18 kDa N-terminus encoded by pET-32a(+) plasmid having adhesion strength comparable to several commercial glues[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(8): e0136493. |
| [98] | LIU X P, LIANG C, ZHANG X K, et al. Amyloid fibril aggregation: an insight into the underwater adhesion of barnacle cement[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2017, 493(1): 654-659. |
| [99] | JIA L, YU Y B, ZHENG J Y, et al. Self-assembling bioadhesive inspired by the fourth repetitive sequence of Balanus albicostatus cement protein 20kDa (Balcp-20k)[J]. Marine Biotechnology, 2022, 24(6): 1148-1157. |
| [100] | 李婧. 藤壶粘胶蛋白Mrcp20K在毕赤酵母中的高效表达[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2021. |
| LI J. High-level expression of barnacle adhesive protein Mrcp20K in Pichia pastoris [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2021. | |
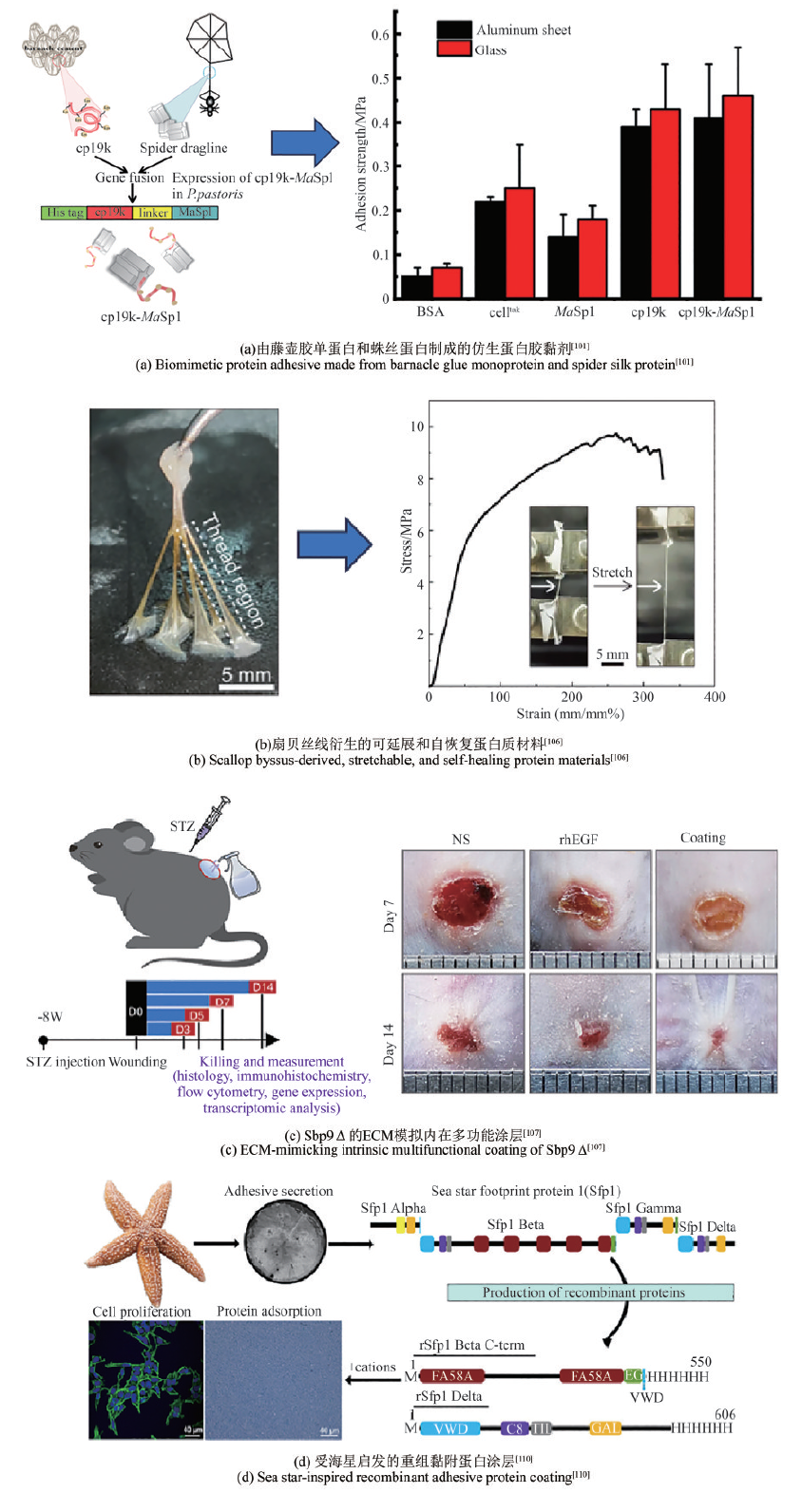
| [101] | YE L N, LIU X X, LI K, et al. A bioinspired synthetic fused protein adhesive from barnacle cement and spider dragline for potential biomedical materials[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2023, 253: 127125. |
| [102] | SHI Y X, XU Y, ZHANG L Y, et al. Genetically programmed temperature-responsive barnacle-derived protein with an enhanced adhesion ability[J]. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 2024, 7(7): 4573-4579. |
| [103] | FUJII D, TAKASE K, TAKAGI A, et al. Design of RGDS peptide-immobilized self-assembling β-strand peptide from barnacle protein[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(3): 1240. |
| [104] | YE L N, YAN Y J, YAN J Y. Design and biofabrication of barnacle and spider silk protein decorated composite bacterial cellulose for diabetic wound healing[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2025, 354: 123301. |
| [105] | DAI X T, ZHU X, BAO L S, et al. Decoding the byssus fabrication by spatiotemporal secretome analysis of scallop foot[J]. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 2022, 20: 2713-2722. |
| [106] | ZHANG X K, CUI M K, WANG S S, et al. Extensible and self-recoverable proteinaceous materials derived from scallop byssal thread[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 2731. |
| [107] | WANG L L, XUE B, ZHANG X, et al. Extracellular matrix-mimetic intrinsic versatile coating derived from marine adhesive protein promotes diabetic wound healing through regulating the microenvironment[J]. ACS Nano, 2024, 18(22): 14726-14741. |
| [108] | STEWART R J. Protein-based underwater adhesives and the prospects for their biotechnological production[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2011, 89(1): 27-33. |
| [109] | BRUBAKER C E, MESSERSMITH P B. The present and future of biologically inspired adhesive interfaces and materials[J]. Langmuir, 2012, 28(4): 2200-2205. |
| [110] | LEFEVRE M, FLAMMANG P, ARANKO A S, et al. Sea star-inspired recombinant adhesive proteins self-assemble and adsorb on surfaces in aqueous environments to form cytocompatible coatings[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2020, 112: 62-74. |
| [111] | ZHANG D H, LIU J J, CHEN Q, et al. A sandcastle worm-inspired strategy to functionalize wet hydrogels[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 6331. |
| [112] | SU R, MA C, HAN B, et al. Proteins for hyperelastic materials[J]. Small, 2025, 21(9): e2406388. |
| [113] | ARIAS F J, SANTOS M, IBANEZ-FONSECA A, et al. Elastin-like recombinamers as smart drug delivery systems[J]. Current Drug Targets, 2018, 19(4): 360-379. |
| [114] | MISEREZ A, YU J, MOHAMMADI P. Protein-based biological materials: molecular design and artificial production[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2023, 123(5): 2049-2111. |
| [115] | VARANKO A K, SU J C, CHILKOTI A. Elastin-like polypeptides for biomedical applications[J]. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering, 2020, 22: 343-369. |
| [116] | GUO Y S, LIU S W, JING D, et al. The construction of elastin-like polypeptides and their applications in drug delivery system and tissue repair[J]. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2023, 21(1): 418. |
| [117] | LÓPEZ BARREIRO D, MINTEN I J, THIES J C, et al. Structure-property relationships of elastin-like polypeptides: a review of experimental and computational studies[J]. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 2023, 9(7): 3796-3809. |
| [118] | NETTLES D L, CHILKOTI A, SETTON L A. Applications of elastin-like polypeptides in tissue engineering[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2010, 62(15): 1479-1485. |
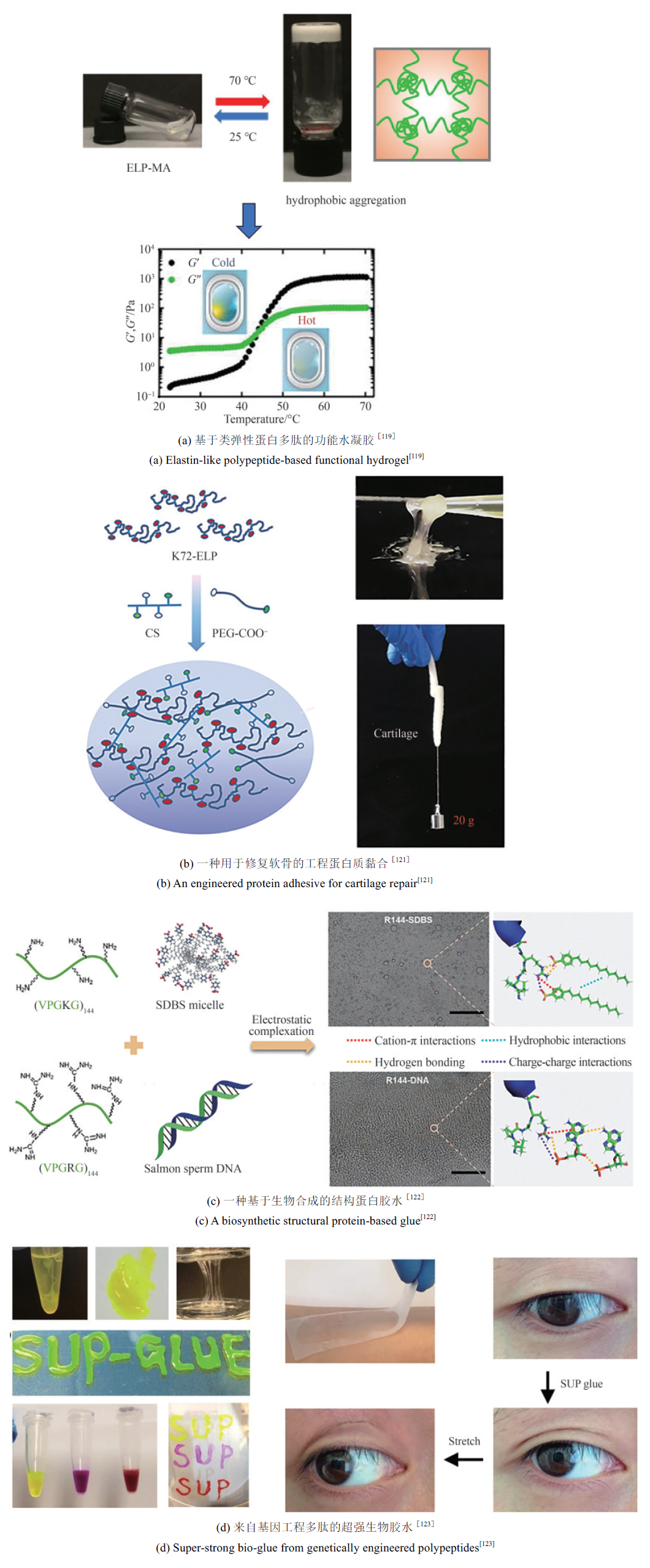
| [119] | GUO Z W, XU Y Y, DONG L N, et al. Design of functional hydrogels using smart polymer based on elastin-like polypeptides[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 435: 135155. |
| [120] | 李敬敬, 马超, 王帆, 等. 生物合成高性能蛋白及材料应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(4): 638-657. |
| LI J J, MA C, WANG F, et al. Biosynthesis of high-performance protein materials and their applications[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(4): 638-657. | |
| [121] | ZHANG J R, LI B, ZUO J L, et al. An engineered protein adhesive with properties of tissue integration and controlled release for efficient cartilage repair[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2021, 10(12): 2100109. |
| [122] | WANG Z L, GU X Q, LI B, et al. Molecularly engineered protein glues with superior adhesion performance[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(41): 2204590. |
| [123] | MA C, SUN J, LI B, et al. Ultra-strong bio-glue from genetically engineered polypeptides[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 3613. |
| [124] | YANG M, ZHANG Z C, LIU Y, et al. Function and mechanism of RGD in bone and cartilage tissue engineering[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2021, 9: 773636. |
| [125] | TJONG W Y, LIN H H. The role of the RGD motif in CD97/ADGRE5-and EMR2/ADGRE2-modulated tumor angiogenesis[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2019, 520(2): 243-249. |
| [126] | CAO F Y, YIN W N, FAN J X, et al. Evaluating the effects of charged oligopeptide motifs coupled with RGD on osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(12): 6698-6705. |
| [127] | 邱凯, 陈馨, 李天全. 生物活性短肽RGD在骨组织诱导再生中的研究进展[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2003, 20(3): 546-549. |
| QIU K, CHEN X, LI T Q. The advance of bioactive peptide RGD in the research of bone regeneration[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2003, 20(3): 546-549. | |
| [128] | SANATI M, AFSHARI A R, AMINYAVARI S, et al. RGD-engineered nanoparticles as an innovative drug delivery system in cancer therapy[J]. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 2023, 84: 104562. |
| [129] | 杜学亮, 陈颖伟, 王连升, 等. 人工合成RGD小肽对肝星状细胞分泌细胞外基质的影响[J]. 放射免疫学杂志, 2004, 17(6): 433-435. |
| DU X L, CHEN Y W, WANG L S, et al. The effect of synthesized RGD peptide on the secretion of extracellular matrix (ECM) by the hepatic stallete cell[J]. Journal of Radioimmunology, 2004, 17(6): 433-435. | |
| [130] | NOIRI M, KUSHIRO K, TOGO S, et al. Influence of cell adhesive molecules attached onto PEG-lipid-modified fluid surfaces on cell adhesion[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B, Biointerfaces, 2019, 175: 375-383. |
| [131] | KANG Z, WANG Y N, XU J J, et al. An RGD-containing peptide derived from wild silkworm silk fibroin promotes cell adhesion and spreading[J]. Polymers, 2018, 10(11): 1193. |
| [132] | XU Q H, ZHANG Z, XIAO C S, et al. Injectable polypeptide hydrogel as biomimetic scaffolds with tunable bioactivity and controllable cell adhesion[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2017, 18(4): 1411-1418. |
| [133] | WAKU T, IMANISHI Y, YOSHINO Y, et al. Fusion of polymeric material-binding peptide to cell-adhesion artificial proteins enhances their biological function[J]. Biointerphases, 2017, 12(2): 021002. |
| [134] | WOHLRAB S, MÜLLER S, SCHMIDT A, et al. Cell adhesion and proliferation on RGD-modified recombinant spider silk proteins[J]. Biomaterials, 2012, 33(28): 6650-6659. |
| [1] | 方馨仪, 孙丽超, 霍毅欣, 王颖, 岳海涛. 微生物合成高级醇的发展趋势与挑战[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(4): 873-898. |
| [2] | 朱欣悦, 陈恬恬, 邵恒煊, 唐曼玉, 华威, 程艳玲. 益生菌辅助防治恶性肿瘤的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(4): 899-919. |
| [3] | 吴晓燕, 宋琪, 许睿, 丁陈君, 陈方, 郭勍, 张波. 合成生物学研发竞争态势对比分析[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(4): 940-955. |
| [4] | 张建康, 王文君, 郭洪菊, 白北辰, 张亚飞, 袁征, 李彦辉, 李航. 基于机器视觉的高通量微生物克隆挑选工作站研制及应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(4): 956-971. |
| [5] | 吴柯, 罗家豪, 李斐然. 机器学习驱动的基因组规模代谢模型构建与优化[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(3): 566-584. |
| [6] | 田晓军, 张日新. 合成基因回路面临的细胞“经济学窘境”[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(3): 532-546. |
| [7] | 章益蜻, 刘高雯. 合成生物学视角下的基因功能探索与酵母工程菌株文库构建[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(3): 685-700. |
| [8] | 黄怡, 司同, 陆安静. 生物制造标准体系建设的现状、问题与建议[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(3): 701-714. |
| [9] | 宋成治, 林一瀚. AI+定向进化赋能蛋白改造及优化[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(3): 617-635. |
| [10] | 张梦瑶, 蔡鹏, 周雍进. 合成生物学助力萜类香精香料可持续生产[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(2): 334-356. |
| [11] | 张璐鸥, 徐丽, 胡晓旭, 杨滢. 合成生物学助力化妆品走进生物制造新时代[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(2): 479-491. |
| [12] | 伊进行, 唐宇琳, 李春雨, 吴鹤云, 马倩, 谢希贤. 氨基酸衍生物在化妆品中的应用及其生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(2): 254-289. |
| [13] | 韦灵珍, 王佳, 孙新晓, 袁其朋, 申晓林. 黄酮类化合物生物合成及其在化妆品中应用的研究[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(2): 373-390. |
| [14] | 肖森, 胡立涛, 石智诚, 王发银, 余思婷, 堵国成, 陈坚, 康振. 可控分子量透明质酸的生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(2): 445-460. |
| [15] | 王倩, 果士婷, 辛波, 钟成, 王钰. L-精氨酸的微生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(2): 290-305. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||