合成生物学 ›› 2020, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (6): 722-731.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-020
达托霉素生物合成过程的调控机制研究进展
方教乐1,2, 吕中原1,2, 孙晨番1,2, 刘一帆1,2, 徐炜锋1,2, 毛旭明1,2, 李永泉1,2
- 1.浙江大学药物生物技术研究所,浙江 杭州 310058
2.浙江省微生物生化与代谢工程重点实验室,浙江 杭州 310058
-
收稿日期:2020-03-10修回日期:2020-11-05出版日期:2020-12-31发布日期:2021-01-15 -
通讯作者:毛旭明,李永泉 -
作者简介:方教乐(1991—),男,博士研究生,研究方向为微生物次级代谢产物调控,链霉菌隐性基因簇激活,表观遗传学研究。E-mail:fjl20@live.cn
毛旭明(1978—),男,博士,教授,研究方向为基于合成生物学的微生物药物开发、微生物药物生物合成的调控机制研究、基于多组学的新活性和新结构微生物天然产物挖掘、微生物天然产物生物合成的酶学机制和化学机制研究。E-mail:xmmao@zju.edu.cn
李永泉(1962—),男,博士,求是特聘教授,研究方向为微生物合成生物学、微生物次级代谢调控和微生物制药。E-mail:lyq@zju.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家新药创制重大专项(2018ZX09711001-006-013);国家自然科学基金(3173002)
An overview on regulatory mechanism of daptomycin biosynthesis
FANG Jiaole1,2, LYU Zhongyuan1,2, SUN Chenfan1,2, LIU Yifan1,2, XU Weifeng1,2, MAO Xuming1,2, LI Yongquan1,2
- 1.Institute of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou 310058,Zhejiang,China
2.Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory for Microbial Biochemistry and Metabolic Engineering,Hangzhou 310058,Zhejiang,China
-
Received:2020-03-10Revised:2020-11-05Online:2020-12-31Published:2021-01-15 -
Contact:MAO Xuming, LI Yongquan
摘要:
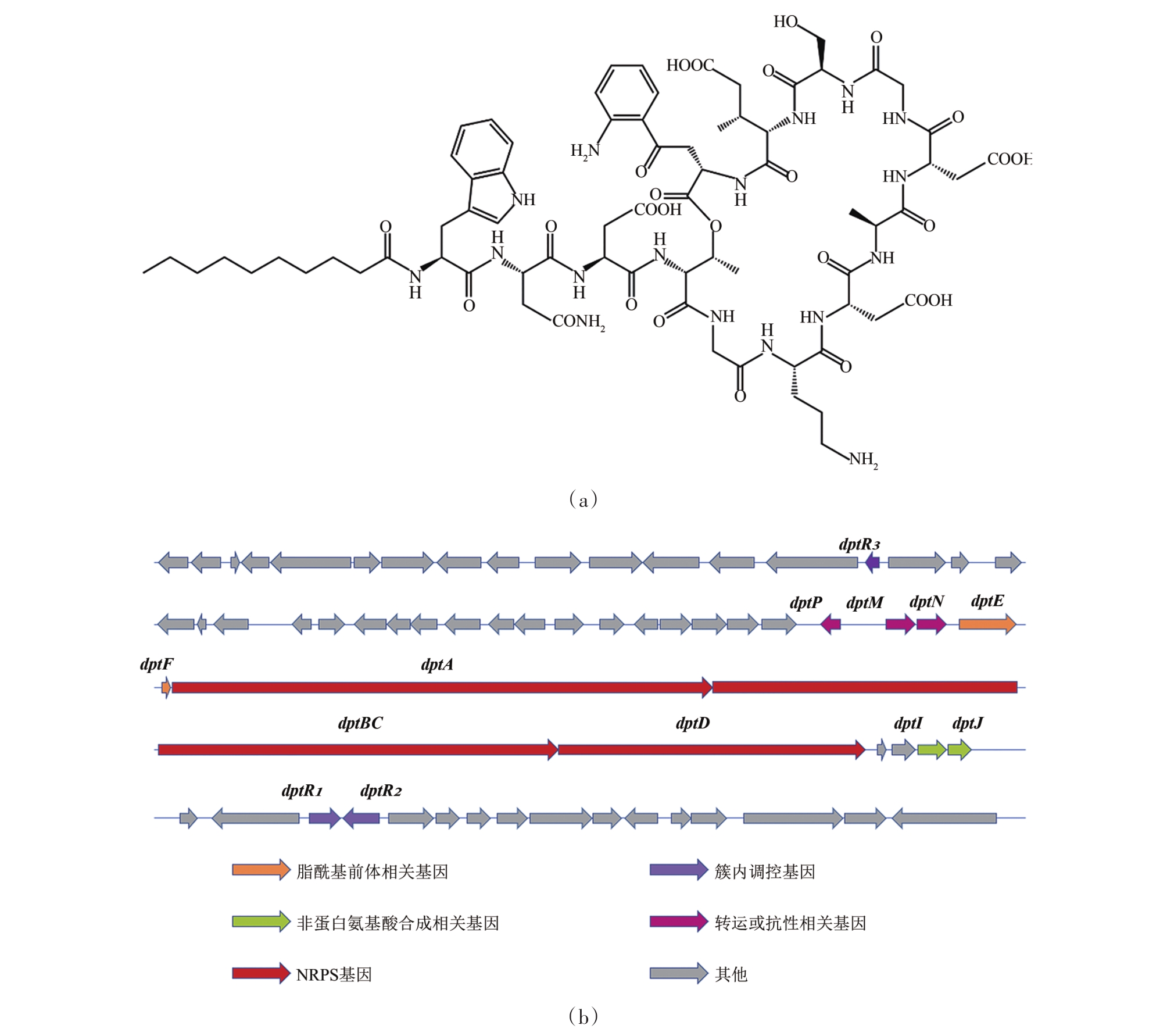
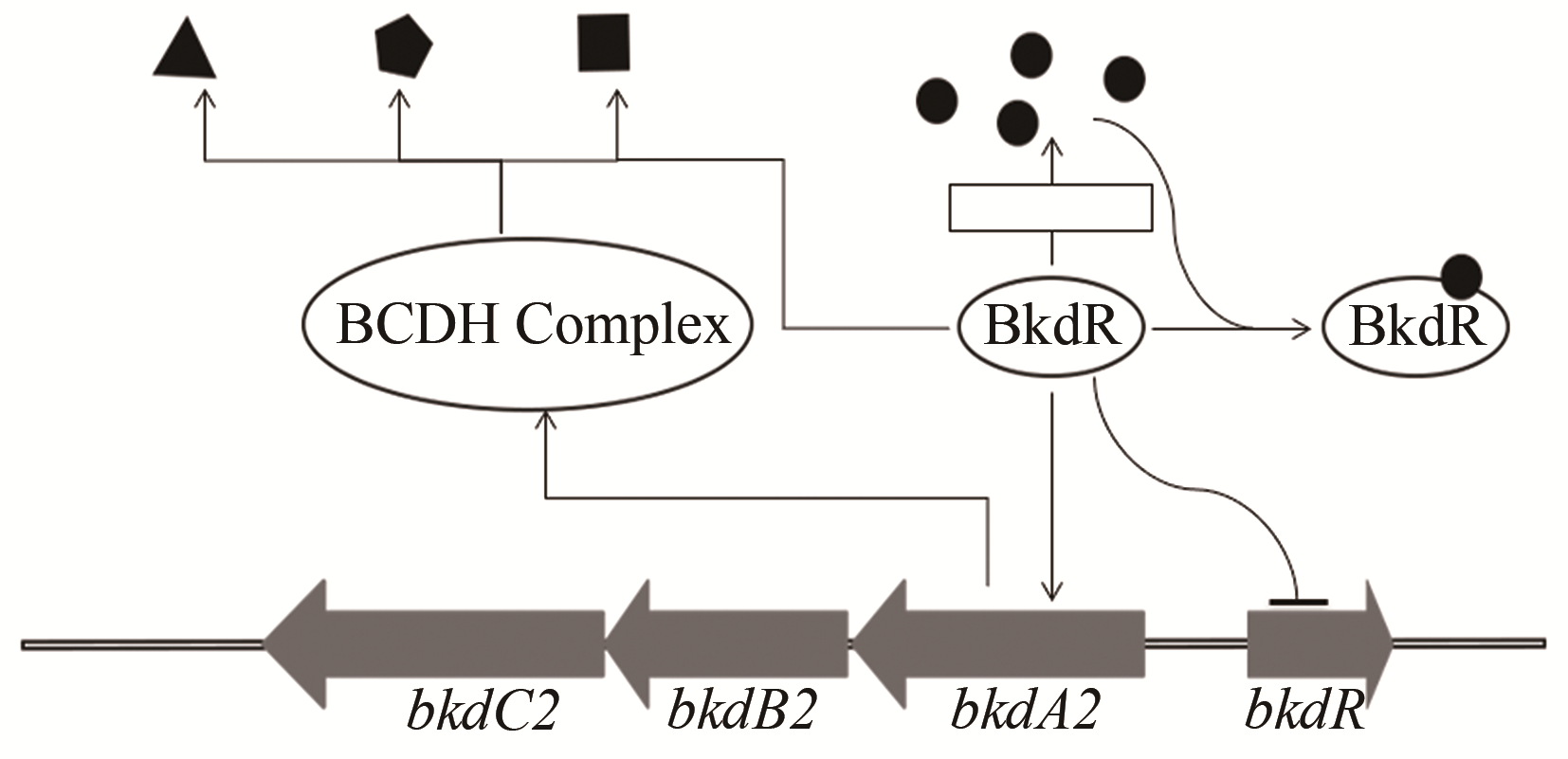
微生物是天然产物类药物的重要来源之一,其中许多链霉菌来源的抗生素类药物一直活跃在对付细菌感染的前沿阵地。然而随着“超级细菌”的陆续发现,以及新药研发速度的滞缓,人类尚缺乏“超级细菌”的最终治疗手段。达托霉素是由玫瑰孢链霉菌(Streptomyces roseosporus)经发酵产生的一种新型环脂肽类抗生素,由于其独特的结构及特殊的药物机制,被视为多重耐药革兰阳性细菌引起的重症感染的最后一道防线。然而在工业发酵过程中,达托霉素的生物合成水平很低,有极高的提升潜力。本文总结了近年来国内外相关达托霉素合成的调控机制研究,包括调控蛋白的挖掘、途径特异性调控机制、级联调控途径、脂酰前体合成途径、GBL信号途径与磷酸双组分系统及其协同调控机制等,揭示了次级代谢调控网络的复杂性,并阐述了通过调控通路重构实现达托霉素优质高产的策略。
中图分类号:
引用本文
方教乐, 吕中原, 孙晨番, 刘一帆, 徐炜锋, 毛旭明, 李永泉. 达托霉素生物合成过程的调控机制研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(6): 722-731.
FANG Jiaole, LYU Zhongyuan, SUN Chenfan, LIU Yifan, XU Weifeng, MAO Xuming, LI Yongquan. An overview on regulatory mechanism of daptomycin biosynthesis[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(6): 722-731.
| 1 | HUBER F M, PIEPER R L, TIETZ A J. The synthesis of A21978C analogs by Streptomyces roseosporus cultivated under carbon limitation and fed fatty acids [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 1990, 7: 283-292. |
| 2 | DOEKEL S, COËFFET-LE GAL M F, GU Jianqiao, et al. Non-ribosomal peptide synthetase module fusions to produce derivatives of daptomycin in Streptomyces roseosporus [J]. Microbiology, 2008, 154(9): 2872-2880. |
| 3 | SAUERMANN R, ROTHENBURGER M, GRANINGER W, et al. Daptomycin: a review 4 years after first approval [J]. Pharmacology, 2008, 81: 79-91. |
| 4 | SMITH J R, CLAEYS K C, ZASOWSKI E J, et al. Daptomycin resistance [M]// MAYERS D L, SOBEL J D, OUELLETTE M, et al. Antimicrobial drug resistance: mechanisms of drug resistance. Springer International Publishing; 2017: 307-317. |
| 5 | PERSECHINI A, MONCRIEF N D, KRETSINGER R H. The EF-hand family of calcium-modulated proteins [J]. Trends in Neurosciences, 1989, 12(11): 462-467. |
| 6 | ROBBEL L, MARAHIEL M A. Daptomycin, a bacterial lipopeptide synthesized by a nonribosomal machinery [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2010, 285(36): 27501-27508. |
| 7 | ROMERO-RODRÍGUEZ A, ROBLEDO-CASADOS I, SÁNCHEZ S. An overview on transcriptional regulators in Streptomyces [J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Gene Regulatory Mechanisms, 2015, 1849(8): 1017-1039. |
| 8 | LIU Gang, CHATER K F, CHANDRA G, et al. Molecular regulation of antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces [J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 2013, 77(12): 112-143. |
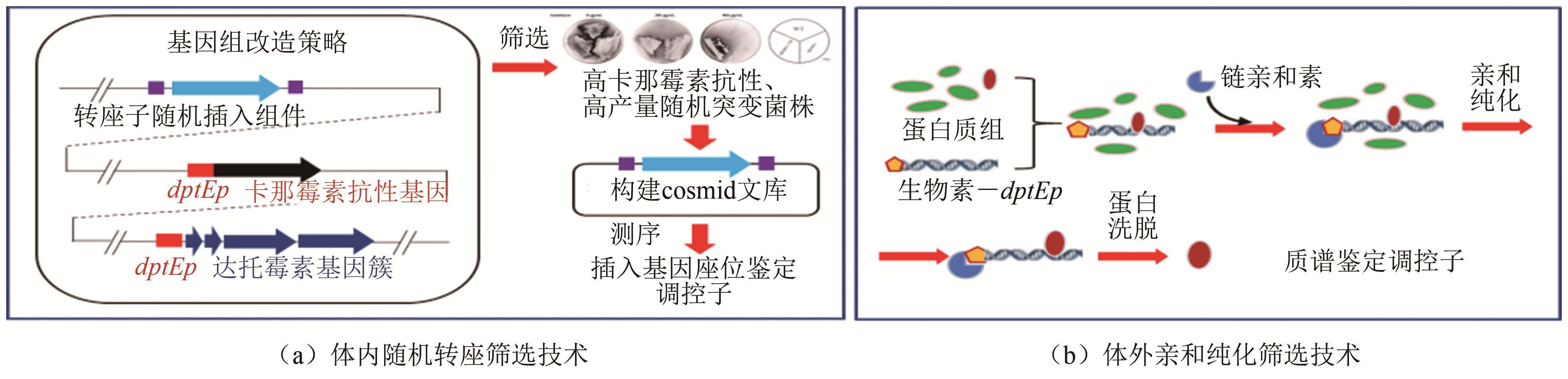
| 9 | LUO Shuai, CHEN Xin'ai, MAO Xuming, et a. Transposon-based identification of a negative regulator for the antibiotic hyper-production in Streptomyces [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(15): 6581-6592. |
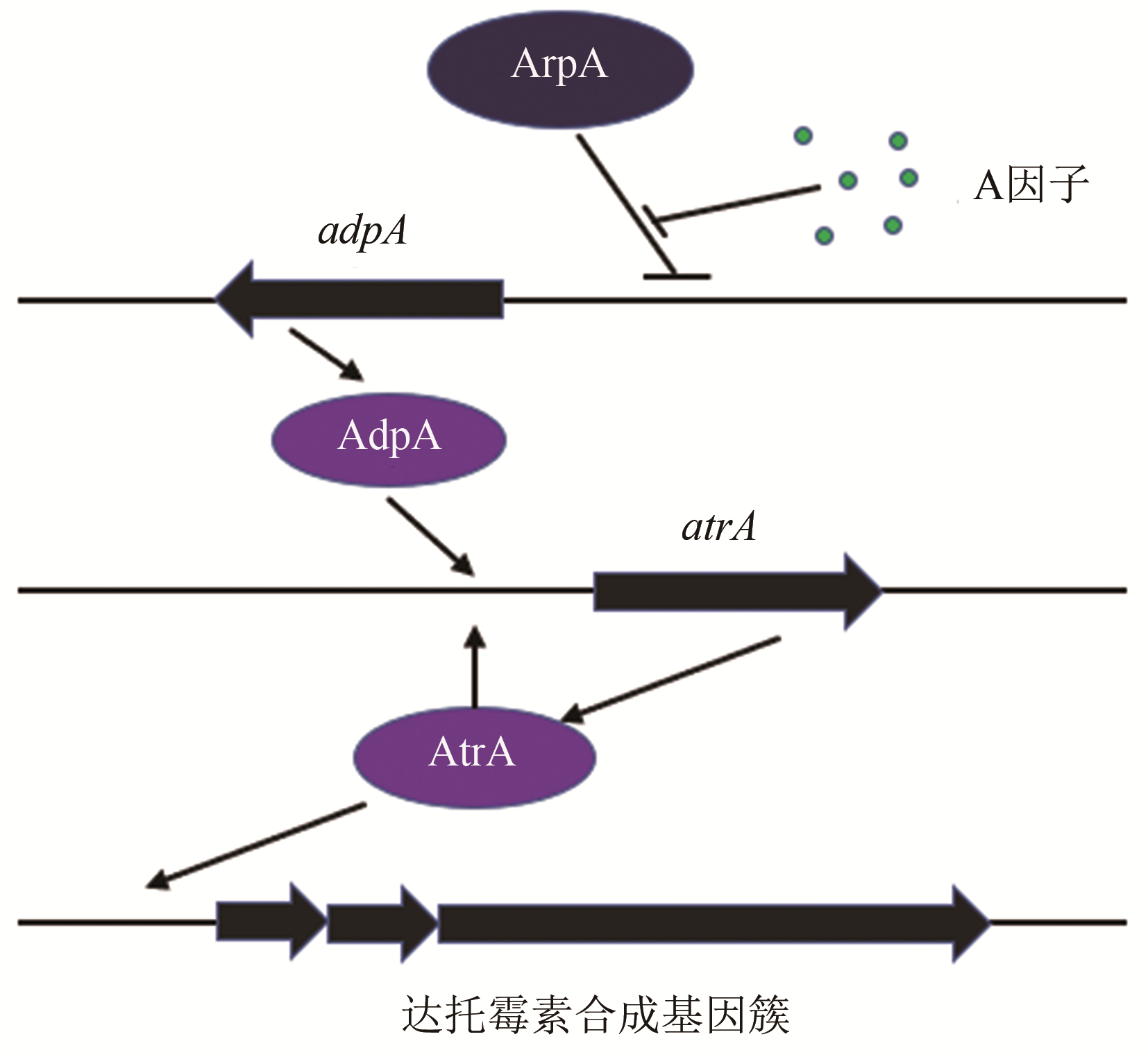
| 10 | MAO Xuming, LUO Shuai, ZHOU Richeng, et al. Transcriptional regulation of the daptomycin gene cluster in Streptomyces roseosporus by an autoregulator, AtrA [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2015, 290(12): 7992-8001. |
| 11 | YUAN Penghui, ZHOU Richeng, CHEN Xuepeng, et a. DepR1, a TetR family transcriptional regulator, positively regulates daptomycin production in an industrial producer, Streptomyces roseosporus SW0702 [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2016, 82(6): 03002. |
| 12 | MAO Xuming, LUO Shuai, LI Yongquan. Negative regulation of daptomycin production by DepR2, an ArsR-family transcriptional factor [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2017, 44(6): 1653-1658. |
| 13 | RAMOS J L, MARTÍNEZ-BUENO M, MOLINA-HENARES A J, et al. The TetR family of transcriptional repressors [J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 2005, 69(2): 326-356. |
| 14 | XU Delin, SEGHEZZI N, ESNAULT C, et al. Repression of antibiotic production and sporulation in Streptomyces coelicolor by overexpression of a TetR family transcriptional regulator [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2010, 76(23): 7741-7753. |
| 15 | LIU Wenshuai, ZHANG Qinling, GUO Jia, et al. Increasing avermectin production in Streptomyces avermitilis by manipulating the expression of a novel TetR-family regulator and its target gene product [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 81(15): 5157-5173. |
| 16 | WEI Junhong, TIAN Yuqing, NIU Guoqing, et al. GouR, a TetR family transcriptional regulator, coordinates the biosynthesis and export of gougerotin in Streptomyces graminearus [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2014, 80(2): 714-722. |
| 17 | BUSENLEHNER L S, PENNELLA M A, GIEDROC D P. The SmtB/ArsR family of metalloregulatory transcriptional repressors: structural insights into prokaryotic metal resistance [J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2003, 27(23): 131-143. |
| 18 | KIM Hae Mi, Bo-Eun AHN, Ju-Hyung LEE, et al. Regulation of a nickel-cobalt efflux system and nickel homeostasis in a soil actinobacterium Streptomyces coelicolor [J]. Metallomics, 2015, 7(4): 702-709. |
| 19 | ZMIJEWSKI M J, BRIGGS B, OCCOLOWITZ J. Role of branched chain fatty acid precursors in regulating factor profile in the biosynthesis of A21978C complex [J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 1986, 39(10): 1483-1485. |
| 20 | TARDU M, BULUT S, KAVAKLI I H. MerR and ChrR mediate blue light induced photo-oxidative stress response at the transcriptional level in Vibrio cholerae [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 40817. |
| 21 | BROWN N L, STOYANOV J V, KIDD S P, et al. The MerR family of transcriptional regulators [J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2003, 27(2): 145-163. |
| 22 | SCHUMACHER M A, HENGST C D DEN, BUSH M J, et al. The MerR-like protein BldC binds DNA direct repeats as cooperative multimers to regulate Streptomyces development [J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1139. |
| 23 | MIAO V, COËFFET-LE GAL M F, BRIAN P, et al. Daptomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces roseosporus: cloning and analysis of the gene cluster and revision of peptide stereochemistry [J]. Microbiology, 2005, 151(5): 1507-1523. |
| 24 | 靳旭, 魏维, 饶敏, 等. 链霉菌HCCB10043中调控基因dptR1、dptR2及dptR3对A21978C合成的影响[J]. 中国抗生素杂志, 2014, 39(7): 490-493. |
| JIN Xu, WEI Wei, RAO Min, et al. Influence of regulatory genes dptR1, dptR2 and dptR3 on A21978C production in Streptomyces sp. HCCB10043 [J]. Chinese Journal of Antibiotics, 2014, 39(7): 490-493. | |
| 25 | ULANOVA D, KITANI S, FUKUSAKI E, et al. SdrA, a new DeoR family regulator involved in Streptomyces avermitilis morphological development and antibiotic production [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2013, 79(24): 7916-7921. |
| 26 | GE Beibei, LIU Yan, LIU Binghua, et al. Characterization of novel DeoR-family member from the Streptomyces ahygroscopicus strain CK-15 that acts as a repressor of morphological development [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2016, 100(20): 8819-8828. |
| 27 | JEON Jong-Min, CHOI Tae-Rim, Bo-Rahm LEE, et al. Decreased growth and antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) by deletion of a highly conserved DeoR family regulator, SCO1463 [J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering 2019, 24(4): 613-621. |
| 28 | WANG Feng, REN Nini, LUO Shuai, et al. DptR2, a DeoR-type auto-regulator, is required for daptomycin production in Streptomyces roseosporus [J]. Gene, 2014, 544(2): 208-215. |
| 29 | MARTIN R G, ROSNER J L. Binding of purified multiple antibiotic-resistance repressor protein (MarR) to mar operator sequences [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1995, 92(12): 5456-5460. |
| 30 | INOKA C P, GROVE A. Molecular mechanisms of ligand-mediated attenuation of DNA binding by MarR family transcriptional regulators [J]. Journal of Molecular Cell Biology, 2010, 2(5): 243-254 |
| 31 | GROVE A. Regulation of metabolic pathways by MarR family transcription factors [J]. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 15: 366-371. |
| 32 | So-Young OH, SHIN Jung-Ho, Jung-Hye ROE. Dual role of OhrR as a repressor and an activator in response to organic hydroperoxides in Streptomyces coelicolor [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2007, 189(17): 6284-6292. |
| 33 | HUANG Hao, GROVE A. The transcriptional regulator TamR from Streptomyces coelicolor controls a key step in central metabolism during oxidative stress [J]. Mol. Microbiol., 2013, 87(6): 1151-1166. |
| 34 | ZHANG Qinling, CHEN Qiong, ZHUANG Shuai, et al. A MarR family transcriptional regulator, DptR3, activates daptomycin biosynthesis and morphological differentiation in Streptomyces roseosporus [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 81(11): 3753-3765. |
| 35 | BUSH M J, BIBB M J, CHANDRA G, et al. Genes required for aerial growth, cell division, and chromosome segregation are targets of WhiA before sporulation in Streptomyces venezuelae [J] mBio, 2013, 4(5): e00684-00613. |
| 36 | HUANG Xingwei, MA Tingmei, TIAN Jun, et al. wblA, a pleiotropic regulatory gene modulating morphogenesis and daptomycin production in Streptomyces roseosporus [J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2017, 123(3): 669-677. |
| 37 | NISHIDA H, OHNISHI Y, BEPPU T, et al. Evolution of γ-butyrolactone synthases and receptors in Streptomyces [J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2007, 9(8): 1986-1994. |
| 38 | OHNISHI Y, HORINOUCHI S. The A-factor regulatory cascade that leads to morphological development and secondary metabolism in Streptomyces [J]. Biofilms, 2004, 1(4): 319-328. |
| 39 | KIM Hyun Soo, NIHIRA T, TADA H, et al. Identification of binding protein of virginiae butanolide C, an autoregulator in virginiamycin production, from Streptomyces virginiae [J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 1989, 42(5): 769-778. |
| 40 | HASHIMOTO K, NIHIRA T, SAKUDA S, et al. IM-2, a butyrolactone autoregulator, induces production of several nucleoside antibiotics in Streptomyces sp. FRI-5 [J]. Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering, 1992, 73(6): 449-455. |
| 41 | OHNISHI Y, YAMAZAKI H, KATO J, et al. AdpA, a central transcriptional regulator in the A-factor regulatory cascade that leads to morphological development and secondary metabolism in Streptomyces griseus [J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2005, 69(3): 431-439. |
| 42 | RODRÍGUEZ H, RICO S, DÍAZ M, et al. Two-component systems in Streptomyces: key regulators of antibiotic complex pathways. [J] Microbial Cell Factories, 2013, 12(1): 127. |
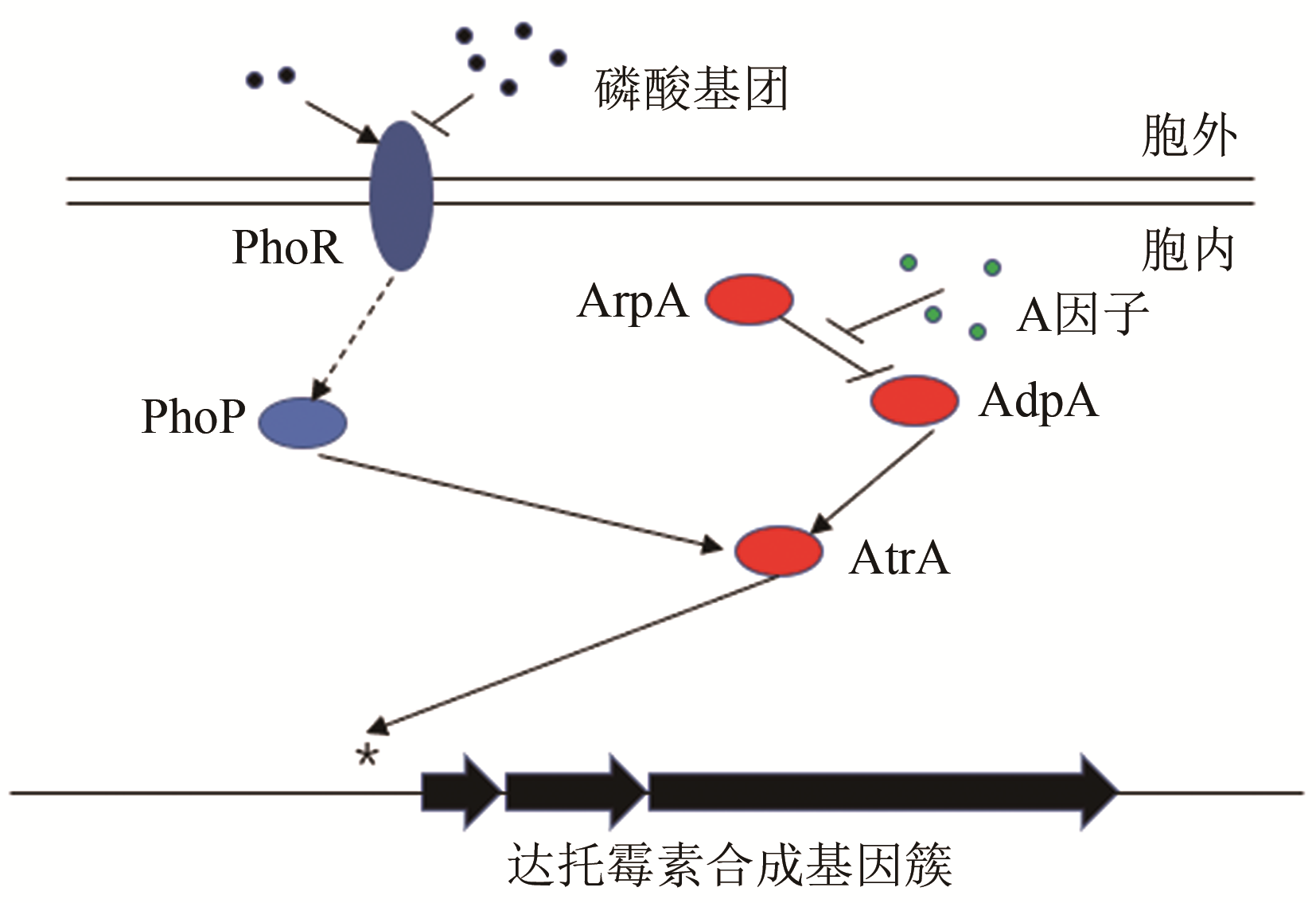
| 43 | SOLALANDA A, MOURA R S, MARTIN J F. The two-component PhoR-PhoP system controls both primary metabolism and secondary metabolite biosynthesis in Streptomyces lividans [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2003, 100(10): 6133-6138. |
| 44 | BRIAN P, RIGGLE P, SANTOS R A, et al. Global negative regulation of Streptomyces coelicolor antibiotic synthesis mediated by an absA-encoded putative signal transduction system [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1996, 178(11): 3221-3231. |
| 45 | WANG Rui, MAST Y, WANG Jin, et al. Identification of two-component system AfsQ1/Q2 regulon and its cross-regulation with GlnR in Streptomyces coelicolor [J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2013, 87(1): 30-48. |
| 46 | UMEYAMA T, Ping-Chin LEE, UEDA K, et al. An AfsK/AfsR system involved in the response of aerial mycelium formation to glucose in Streptomyces griseus [J]. Microbiology, 1999, 145(9): 2281-2292. |
| 47 | MARTIN J F. Phosphate control of the biosynthesis of antibiotics and other secondary metabolites is mediated by the PhoR-PhoP system: an unfinished story [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2004, 186(16): 5197-5201. |
| 48 | ZHENG Yang, SUN Chenfan, FU Yu,et al. Dual regulation between the two-component system PhoRP and AdpA regulates antibiotic production in Streptomyces [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2019, 46(5): 725-737. |
| 49 | DEBONO M, BARNHART M, CARRELL C B, et al. A21978C, a complex of new acidic peptide antibiotics: isolation, chemistry, and mass spectral structure elucidation [J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 1987, 40(6): 761-777. |
| 50 | LUO Shuai, CHEN Xin'ai, MAO Xuming, et al. Regulatory and biosynthetic effects of the bkd gene clusters on the production of daptomycin and its analogs A21978C1-3 [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2018, 45(4): 271-279. |
| 51 | SPRUSANSKY O, STIRRETT K, SKINNER D D, et al. The bkdR gene of Streptomyces coelicolor is required for morphogenesis and antibiotic production and encodes a transcriptional regulator of a branched-chain amino acid dehydrogenase complex [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2005, 187(2): 664-671. |
| [1] | 仲泉周, 单依怡, 裴清云, 金艳芸, 王艺涵, 孟璐远, 王歆韵, 张雨鑫, 刘坤媛, 王慧中, 冯尚国. 生物合成法生产α-熊果苷的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 118-135. |
| [2] | 竺方欢, 岑雪聪, 陈振. 微生物合成二元醇研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1367-1385. |
| [3] | 刘益宁, 蒲伟, 杨金星, 王钰. ω-氨基酸与内酰胺的生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1350-1366. |
| [4] | 李庚, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 王佳, 袁其朋. 过氧化物酶的重组表达和应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1498-1517. |
| [5] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [6] | 程晓雷, 刘天罡, 陶慧. 萜类化合物的非常规生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1050-1071. |
| [7] | 刘子健, 穆柏杨, 段志强, 王璇, 陆晓杰. 与核酸兼容的化学反应开发进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1102-1124. |
| [8] | 张守祺, 王涛, 孔尧, 邹家胜, 刘元宁, 徐正仁. 天然产物的化学-酶法合成:方法与策略的演进[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 913-940. |
| [9] | 谢向前, 郭雯, 王欢, 李进. 含氨基乙烯半胱氨酸核糖体肽的生物合成与化学合成[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 981-996. |
| [10] | 汤志军, 胡友财, 刘文. 酶促4+2和2+2环加成反应:区域与立体选择性的理解与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 401-407. |
| [11] | 张俊, 金诗雪, 云倩, 瞿旭东. 聚酮化合物非天然延伸单元的生物合成与结构改造应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 561-570. |
| [12] | 陈锡玮, 张华然, 邹懿. 真菌源非核糖体肽类药物生物合成及代谢工程[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 571-592. |
| [13] | 冯金, 潘海学, 唐功利. 近十年天然产物药物的生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 408-446. |
| [14] | 奚萌宇, 胡逸灵, 顾玉诚, 戈惠明. 基因组挖掘指导天然药物分子的发现[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 447-473. |
| [15] | 施鑫杰, 杜艺岭. 双嵌入家族抗肿瘤非核糖体肽的生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 593-611. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||