合成生物学 ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (5): 716-733.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-058
苄基异喹啉类生物碱的微生物合成研究进展及挑战
林芝, 胡致伟, 瞿旭东, 林双君
- 上海交通大学生命科学技术学院,微生物代谢国家重点实验室,教育部代谢与发育科学国际合作联合实验室,上海 200240
-
收稿日期:2021-05-07修回日期:2021-06-10出版日期:2021-10-31发布日期:2021-11-19 -
通讯作者:林双君 -
作者简介:林芝 (1989—),女,博士,助理研究员。研究方向为重要手性化合物的绿色制造,活性天然产物的生物合成和合成生物学等。E-mail:linz@sjtu.edu.cn林双君 (1972—),男,博士,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为生物活性天然产物的发现及结构鉴定,天然产物的生物合成与组合生物合成,酶催化反应的机理及应用等。E-mail:linsj@sjtu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(21632007);国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0901900);上海交通大学新进教师启动计划(21X010500698)
Advances and challenges in microbial production of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids
LIN Zhi, HU Zhiwei, QU Xudong, LIN Shuangjun
- State Key Laboratory of Microbial Metabolism,School of Life Science and Biotechnology & Joint International Research Laboratory of Metabolic and Developmental Sciences,Shanghai Jiao Tong University,Shanghai 200240,China
-
Received:2021-05-07Revised:2021-06-10Online:2021-10-31Published:2021-11-19 -
Contact:LIN Shuangjun
摘要:
微生物发酵是一种经济高效、可持续的生产方式,可替代植物种植和化学合成来生产多种植物来源的药物。苄基异喹啉类生物碱作为植物来源生物碱的典型代表,具有多种重要的生理活性,已成为极具吸引力的微生物合成研究的靶标分子。随着该类生物碱天然生物合成途径逐渐被阐明以及多种酶学元件的发现,使得通过大肠杆菌和酿酒酵母等微生物宿主合成苄基异喹啉类生物碱的研究取得了重大进展。本综述着重介绍了这些进展中的突破性成果,包括苄基异喹啉类生物碱微生物合成过程中瓶颈反应的突破以及合成途径中相关酶的催化特性对代谢流的影响等,指出了微生物生产苄基异喹啉类生物碱走向工业化应用所面临的挑战,以及酶工程和新人工微生物合成途径的设计开发对克服这些挑战的重要性。
中图分类号:
引用本文
林芝, 胡致伟, 瞿旭东, 林双君. 苄基异喹啉类生物碱的微生物合成研究进展及挑战[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(5): 716-733.
LIN Zhi, HU Zhiwei, QU Xudong, LIN Shuangjun. Advances and challenges in microbial production of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(5): 716-733.
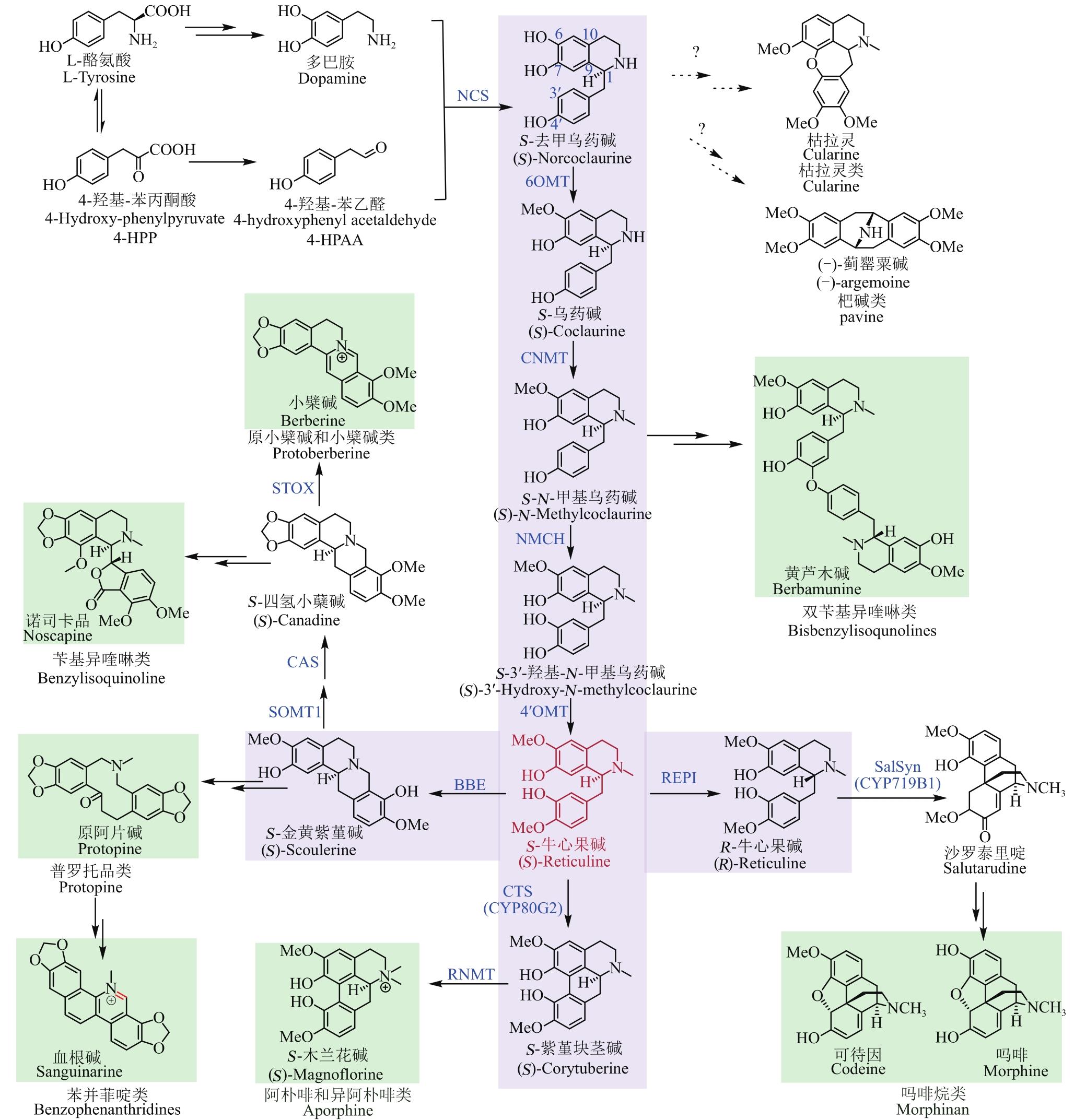
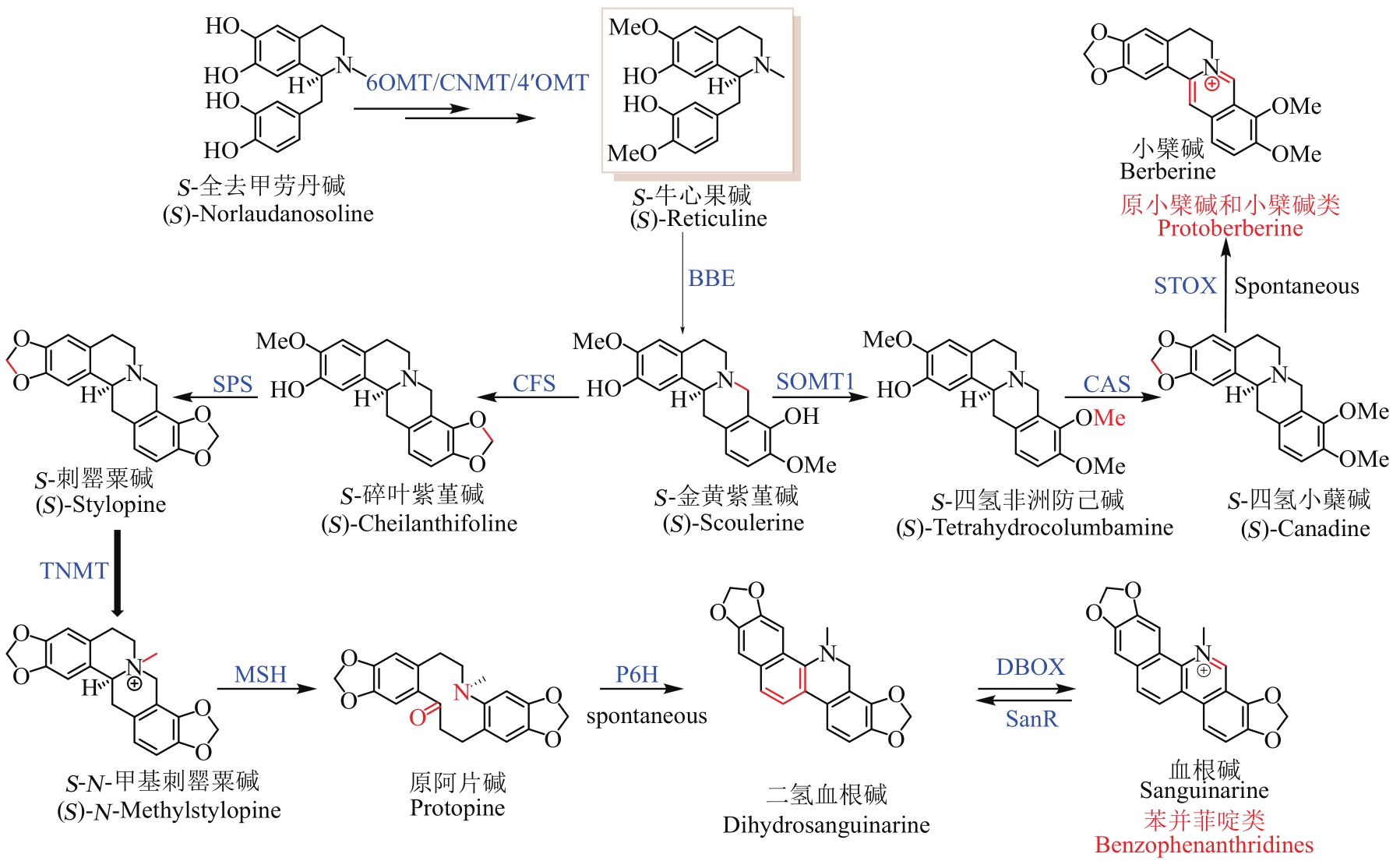
图1 BIA的骨架类型及其生物合成途径(绿色框为BIA的7大骨架类型,紫色框内为BIA上游共性化合成途径及关键的分支点,红色表示关键中间体S-牛心果碱;实线表示生物合成途径已知,虚线表示生物合成途径未知)
Fig. 1 Skeletons of BIAs and the proposed pathways for their biosynthesis(The green box represents the seven skeletons of BIAs, and the purple box represents the shared-upstream synthetic pathway and key branch points for synthesizing BIAs. Red color indicates the key intermediate (S)-Reticuline. The solid and dashed lines show known and unknown pathways for the synthesis of BIAs, respectively)

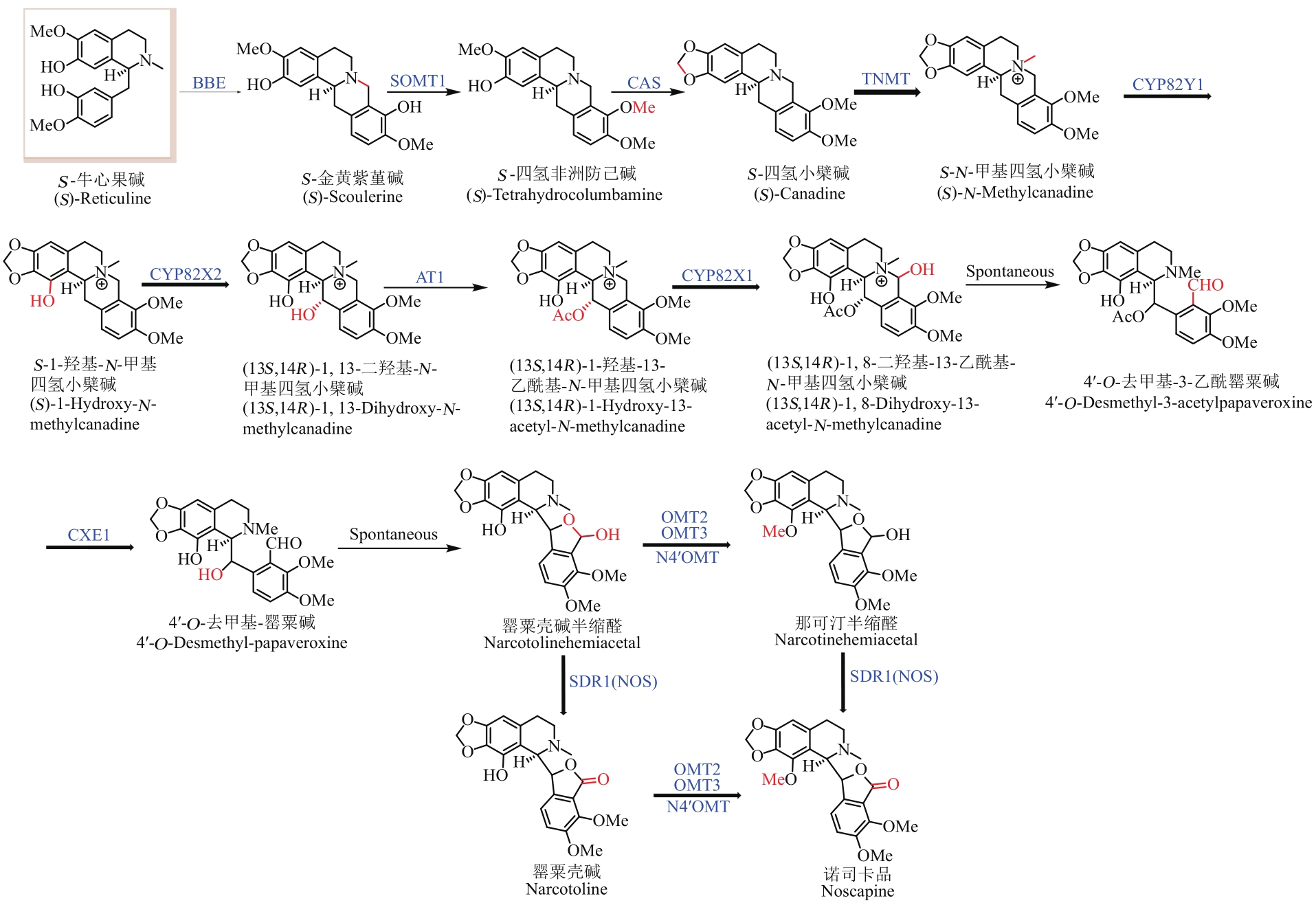
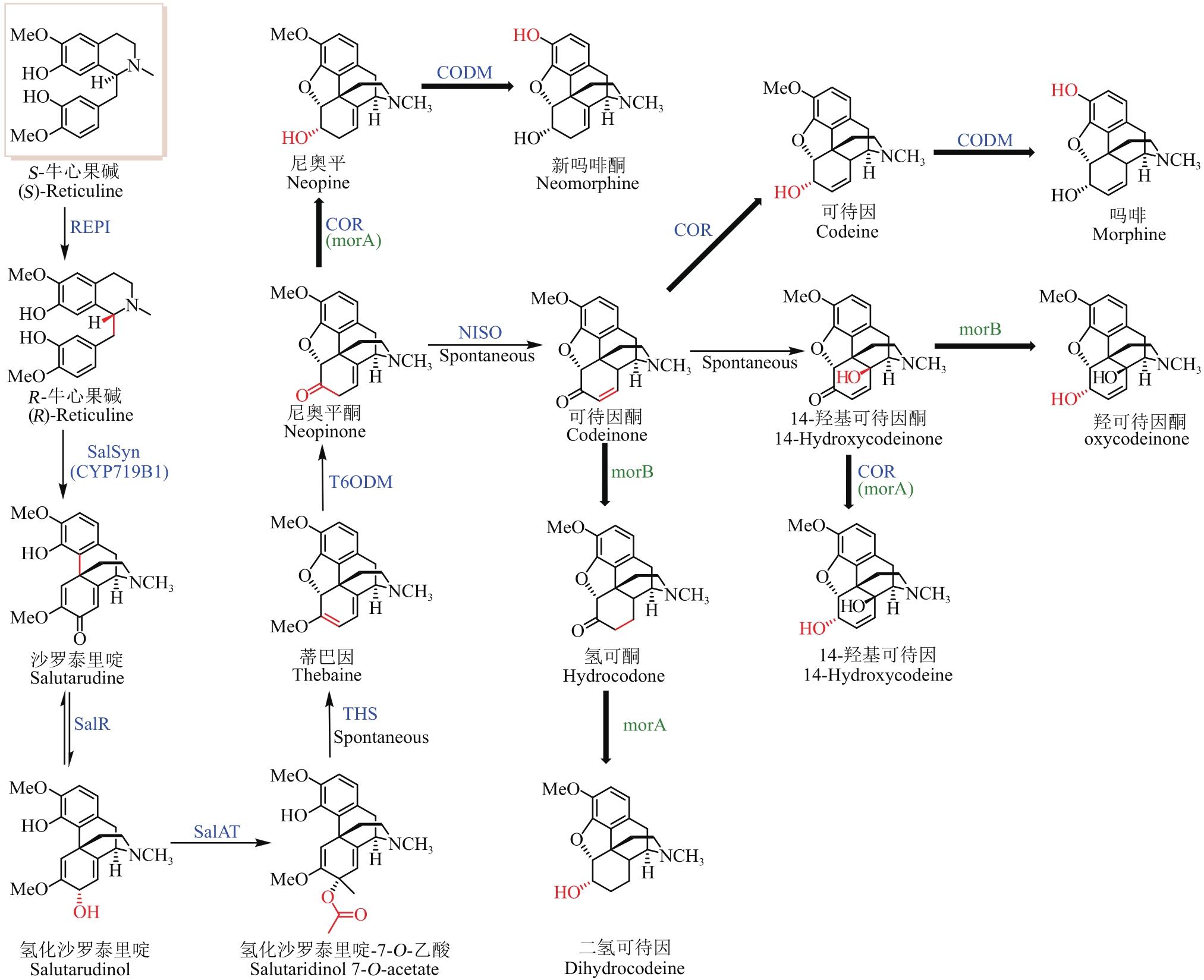
图2 S-牛心果碱的微生物合成途径总结及代谢流示意图(蓝色酶表示模拟天然生物合成途径的微生物合成BIA途径,红色酶和羟基代表人工设计的微生物合成BIA途径。加粗的箭头表示该步反应酶的底物识别较为宽泛;细箭头表示底物识别较为单一,下文同此)
Fig. 2 Pathway for the microbial synthesis of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids(The microbial synthesis pathway of BIAs with enzymes highlighted by blue color is a mimic of the natural biosynthetic pathway, while enzymes and hydroxyl highlighted with red color represent the artificially designed pathway for microbial synthesis of BIAs. The bold and thin arrows indicate that the substrate recognition of the enzyme is relatively broad and specific, respectively)
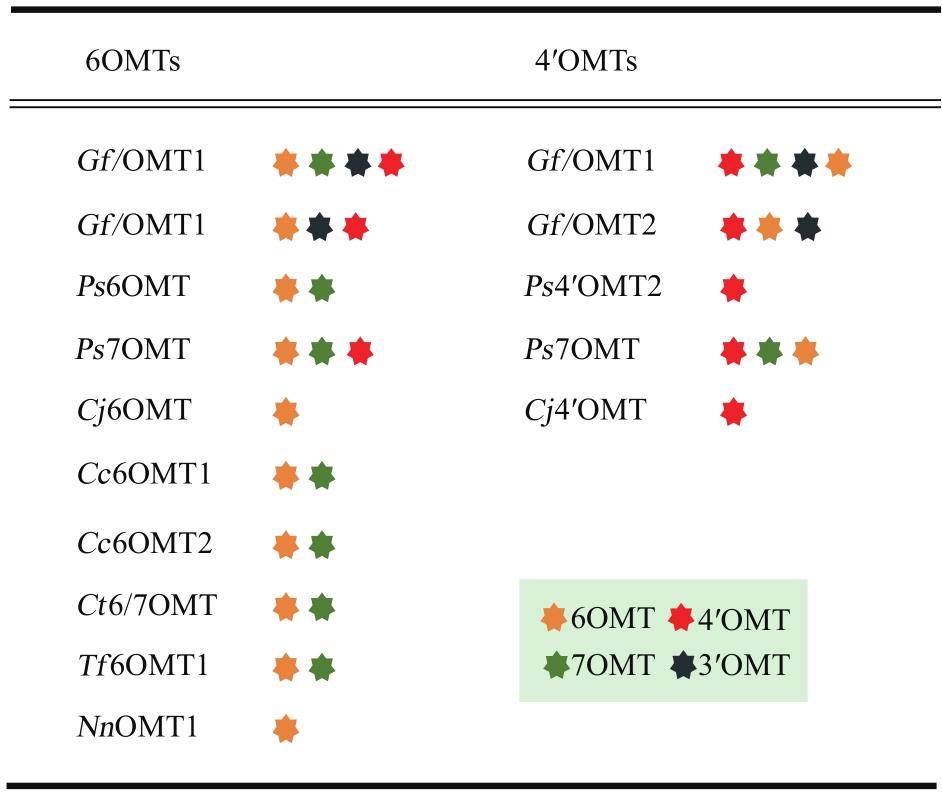
图3 代表性的6OMT和4′OMT对3′、4′、6以及7位羟基的交叉区域选择性(不同颜色的星点代表不同位置的甲基化功能)
Fig. 3 Cross-regioselectivity of 6OMT and 4′OMT to 3′, 4′, 6 and 7 hydroxyl groups(The stars with different colors represent the methylation function at different positions)
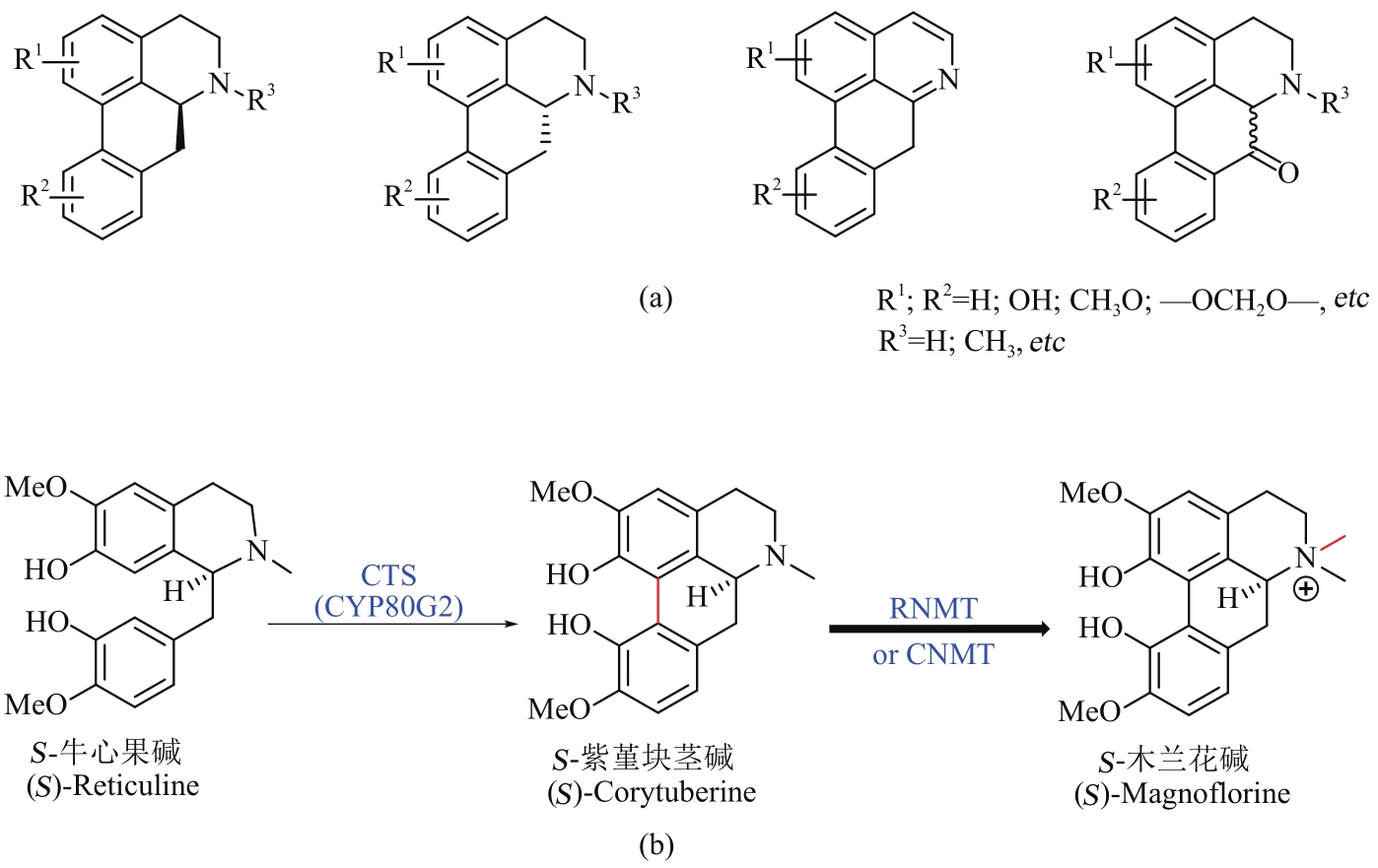
图4 阿朴啡类生物碱的代表性骨架结构(a)和微生物合成途径(b)(化合物上的红色表示每步酶反应生成的键,下文同此)
Fig. 4 Skeletons of aporphines (a) and their microbial synthesis (b)(The red color on the compound indicates the bond formed in each step of the enzyme reaction)
| 1 | LI J W, VEDERAS J C. Drug discovery and natural products: end of an era or an endless frontier?[J]. Science, 2009, 325(5937):161-165. |
| 2 | HARVEY A L. Natural products as a screening resource[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2007, 11(5):480-484. |
| 3 | LEONARD E, RUNGUPHAN W, O′CONNOR S, et al. Opportunities in metabolic engineering to facilitate scalable alkaloid production[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2009, 5(5):292-300. |
| 4 | PADDON C J, KEASLING J D. Semi-synthetic artemisinin: a model for the use of synthetic biology in pharmaceutical development[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2014, 12(5):355-367. |
| 5 | WEBER C, OPATZ T. Bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids[J]. The Alkaloids: Chemistry and Biology, 2019, 81:1-114. |
| 6 | HAGEL J M, FACCHINI P J. Benzylisoquinoline alkaloid metabolism: a century of discovery and a brave new world[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2013, 54(5):647-672. |
| 7 | QING Z X, HUANG J L, YANG X Y, et al. Anticancer and reversing multidrug resistance activities of natural isoquinoline alkaloids and their structure-activity relationship[J]. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 2018, 25(38):5088-5114. |
| 8 | MOHAMED S M, HASSAN E M, IBRAHIM N A. Cytotoxic and antiviral activities of aporphine alkaloids of Magnolia grandiflora L[J]. Natural Product Research, 2010, 24(15):1395-1402. |
| 9 | MUÑOZ V, SAUVAIN M, MOLLINEDO P, et al. Antimalarial activity and cytotoxicity of (-)-roemrefidine isolated from the stem bark of Sparattanthelium amazonum [J]. Planta Medica, 1999, 65(5):448-449. |
| 10 | GUO Y G, DING Y H, WU G J, et al. Three new alkaloids from Xylopia vielana and their antiinflammatory activities[J]. Fitoterapia, 2018, 127:96-100. |
| 11 | CHIA Y C, CHEN K S, CHANG Y L, et al. Antiplatelet actions of aporphinoids from Formosan plants[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 1999, 9(23):3295-3300. |
| 12 | CHEN K S, KO F N, TENG C M, et al. Antiplatelet and vasorelaxing actions of some aporphinoids[J]. Planta Medica, 1996, 62(2):133-136. |
| 13 | DASTMALCHI M, PARK M R, MORRIS J S, et al. Family portraits: the enzymes behind benzylisoquinoline alkaloid diversity[J]. Phytochemistry Reviews, 2018, 17(2):249-277. |
| 14 | NARCROSS L, FOSSATI E, BOURGEOIS L, et al. Microbial factories for the production of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2016, 34(3):228-241. |
| 15 | FUJII N, INUI T, IWASA K, et al. Knockdown of berberine bridge enzyme by RNAi accumulates (S)-reticuline and activates a silent pathway in cultured California poppy cells[J]. Transgenic Research, 2007, 16(3):363-375. |
| 16 | LISCOMBE D K, FACCHINI P J. Molecular cloning and characterization of tetrahydroprotoberberine cis-N-methyltransferase, an enzyme involved in alkaloid biosynthesis in opium poppy[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2007, 282(20):14741-14751. |
| 17 | TAKEMURA T, IKEZAWA N, IWASA K, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cytochrome P450 in sanguinarine biosynthesis from Eschscholzia californica cells[J]. Phytochemistry, 2013, 91:100-108. |
| 18 | WINKLER A, LYSKOWSKI A, RIEDL S, et al. A concerted mechanism for berberine bridge enzyme[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2008, 4(12):739-741. |
| 19 | HAGEL J M, BEAUDOIN G A, FOSSATI E, et al. Characterization of a flavoprotein oxidase from opium poppy catalyzing the final steps in sanguinarine and papaverine biosynthesis[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2012, 287(51):42972-42983. |
| 20 | AMANN M, NAGAKURA N, ZENK M H. Purification and properties of (S)-tetrahydroprotoberberine oxidase from suspension-cultured cells of Berberis wilsoniae [J]. European Journal of Biochemistry, 1988, 175(1):17-25. |
| 21 | GALANIE S, THODEY K, TRENCHARD I J, et al. Complete biosynthesis of opioids in yeast[J]. Science, 2015, 349(6252):1095-1100. |
| 22 | WINZER T, KERN M, KING A J, et al. Plant science. Morphinan biosynthesis in opium poppy requires a P450-oxidoreductase fusion protein[J]. Science, 2015, 349(6245):309-312. |
| 23 | FARROW S C, HAGEL J M, BEAUDOIN G A, et al. Stereochemical inversion of (S)-reticuline by a cytochrome P450 fusion in opium poppy[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2015, 11(9):728-732. |
| 24 | HAGEL J M, FACCHINI P J. Dioxygenases catalyze the O-demethylation steps of morphine biosynthesis in opium poppy[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2010, 6(4):273-275. |
| 25 | IKEZAWA N, IWASA K, SATO F. Molecular cloning and characterization of CYP80G2, a cytochrome P450 that catalyzes an intramolecular C-C phenol coupling of (S)-reticuline in magnoflorine biosynthesis, from cultured Coptis japonica cells[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2008, 283(14):8810-8821. |
| 26 | MINAMI H, KIM J S, IKEZAWA N, et al. Microbial production of plant benzylisoquinoline alkaloids[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2008, 105(21):7393-7398. |
| 27 | KIM J S, NAKAGAWA A, YAMAZAKI Y, et al. Improvement of reticuline productivity from dopamine by using engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2013, 77(10):2166-2168. |
| 28 | NAKAGAWA A, MINAMI H, KIM J S, et al. A bacterial platform for fermentative production of plant alkaloids[J]. Nature Communications, 2011, 2:326. |
| 29 | NAKAGAWA A, MATSUZAKI C, MATSUMURA E, et al. (R,S)-tetrahydropapaveroline production by stepwise fermentation using engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4:6695. |
| 30 | LÜTKE-EVERSLOH T, STEPHANOPOULOS G. L-Tyrosine production by deregulated strains of Escherichia coli [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2007, 75(1):103-110. |
| 31 | LICHMAN B R, GERSHATER M C, LAMMING E D, et al. "Dopamine-first" mechanism enables the rational engineering of the norcoclaurine synthase aldehyde activity profile[J]. The FEBS Journal, 2015, 282(6):1137-1151. |
| 32 | HAWKINS K M, SMOLKE C D. Production of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2008, 4(9):564-573. |
| 33 | FOSSATI E, EKINS A, NARCROSS L, et al. Reconstitution of a 10-gene pathway for synthesis of the plant alkaloid dihydrosanguinarine in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5:3283. |
| 34 | FITZPATRICK P F. Tetrahydropterin-dependent amino acid hydroxylases[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 1999, 68:355-381. |
| 35 | CLAUS H, DECKER H. Bacterial tyrosinases[J]. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 2006, 29(1):3-14. |
| 36 | HALAOULI S, ASTHER M, SIGOILLOT J C, et al. Fungal tyrosinases: new prospects in molecular characteristics, bioengineering and biotechnological applications[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2006, 100(2):219-232. |
| 37 | DELOACHE W C, RUSS Z N, NARCROSS L, et al. An enzyme-coupled biosensor enables (S)-reticuline production in yeast from glucose[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2015, 11(7):465-471. |
| 38 | PYNE M E, KEVVAI K, GREWAL P S, et al. A yeast platform for high-level synthesis of tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1):3337. |
| 39 | BOURGEOIS L, PYNE M E, MARTIN V J J. A highly characterized synthetic landing pad system for precise multicopy gene integration in yeast[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(11):2675-2685. |
| 40 | LI Y, LI S, THODEY K, et al. Complete biosynthesis of noscapine and halogenated alkaloids in yeast[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(17):E3922-E3931. |
| 41 | NISHIHACHIJO M, HIRAI Y, KAWANO S, et al. Asymmetric synthesis of tetrahydroisoquinolines by enzymatic Pictet-Spengler reaction[J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2014, 78(4):701-707. |
| 42 | PESNOT T, GERSHATER M C, WARD J M, et al. The catalytic potential of Coptis japonica NCS2 revealed-development and utilisation of a fluorescamine-based assay[J]. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 2012, 354(16):2997-3008. |
| 43 | MINAMI H, DUBOUZET E, IWASA K, et al. Functional analysis of norcoclaurine synthase in Coptis japonica [J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2007, 282(9):6274-6282. |
| 44 | RODDAN R, WARD J M, KEEP N H, et al. Pictet-Spenglerases in alkaloid biosynthesis: future applications in biocatalysis[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2020, 55:69-76. |
| 45 | ILARI A, FRANCESCHINI S, BONAMORE A, et al. Structural basis of enzymatic (S)-norcoclaurine biosynthesis[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2009, 284(2):897-904. |
| 46 | ZHAO J X, MÉNDEZ-SÁNCHEZ D, RODDAN R, et al. Norcoclaurine synthase-mediated stereoselective synthesis of 1,1′-disubstituted, spiro- and bis-tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2021, 11(1):131-138. |
| 47 | BONAMORE A, CALISTI L, CALCATERRA A, et al. A novel enzymatic strategy for the synthesis of substituted tetrahydroisoquinolines[J]. Chemistry Select, 2016, 1(8):1525-1528. |
| 48 | LICHMAN B R, LAMMING E D, PESNOT T, et al. One-pot triangular chemoenzymatic cascades for the syntheses of chiral alkaloids from dopamine[J]. Green Chemistry, 2015, 17(2):852-855. |
| 49 | RODDAN R, GYGLI G, SULA A, et al. Acceptance and kinetic resolution of α-methyl-substituted aldehydes by norcoclaurine synthases[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(10):9640-9649. |
| 50 | LICHMAN B R, ZHAO J, HAILES H C, et al. Enzyme catalysed Pictet-Spengler formation of chiral 1,1'-disubstituted- and spiro-tetrahydroisoquinolines[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8:14883. |
| 51 | ZHAO J, LICHMAN B R, WARD J M, et al. One-pot chemoenzymatic synthesis of trolline and tetrahydroisoquinoline analogues[J]. Chemical Communications, 2018, 54(11):1323-1326. |
| 52 | GREWAL P S, SAMSON J A, BAKER J J, et al. Peroxisome compartmentalization of a toxic enzyme improves alkaloid production[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2021, 17(1):96-103. |
| 53 | MORRIS J S, FACCHINI P J. Molecular origins of functional diversity in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid methyltransferases[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10:1058. |
| 54 | MORISHIGE T, TSUJITA T, YAMADA Y, et al. Molecular characterization of the S-adenosyl-L-methionine:3′-hydroxy-N-methylcoclaurine 4′-O-methyltransferase involved in isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis in Coptis japonica [J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2000, 275(30):23398-23405. |
| 55 | OUNAROON A, DECKER G, SCHMIDT J, et al. (R,S)-Reticuline 7-O-methyltransferase and (R,S)-norcoclaurine 6-O-methyltransferase of Papaver somniferum-cDNA cloning and characterization of methyl transfer enzymes of alkaloid biosynthesis in opium poppy[J]. The Plant Journal, 2003, 36(6):808-819. |
| 56 | FACCHINI P J, PARK S U. Developmental and inducible accumulation of gene transcripts involved in alkaloid biosynthesis in opium poppy[J]. Phytochemistry, 2003, 64(1):177-186. |
| 57 | SAMANANI N, PARK S U, FACCHINI P J. Cell type-specific localization of transcripts encoding nine consecutive enzymes involved in protoberberine alkaloid biosynthesis[J]. The Plant Cell, 2005, 17(3):915-926. |
| 58 | INUI T, TAMURA K, FUJII N, et al. Overexpression of Coptis japonica norcoclaurine 6-O-methyltransferase overcomes the rate-limiting step in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis in cultured Eschscholzia californica [J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2007, 48(2):252-262. |
| 59 | DESGAGNÉ-PENIX I, FACCHINI P J. Systematic silencing of benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthetic genes reveals the major route to papaverine in opium poppy[J]. The Plant Journal, 2012, 72(2):331-344. |
| 60 | CHANG L M, HAGEL J M, FACCHINI P J. Isolation and characterization of O-methyltransferases involved in the biosynthesis of glaucine in Glaucium flavum [J]. Plant Physiology, 2015, 169(2):1127-1140. |
| 61 | ROBIN A Y, GIUSTINI C, GRAINDORGE M, et al. Crystal structure of norcoclaurine-6-O-methyltransferase, a key rate-limiting step in the synthesis of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids[J]. The Plant Journal, 2016, 87(6):641-653. |
| 62 | GUO L, WINZER T, YANG X, et al. The opium poppy genome and morphinan production[J]. Science, 2018, 362(6412):343-347. |
| 63 | MENÉNDEZ-PERDOMO I M, FACCHINI P J. Isolation and characterization of two O-methyltransferases involved in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis in sacred lotus (Nelumbo nucifera)[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2020, 295(6): 1598-1612. |
| 64 | CHOI K B, MORISHIGE T, SHITAN N, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of coclaurine N-methyltransferase from cultured cells of Coptis japonica [J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2002, 277(1):830-835. |
| 65 | LISCOMBE D K, ZIEGLER J, SCHMIDT J, et al. Targeted metabolite and transcript profiling for elucidating enzyme function: isolation of novel N-methyltransferases from three benzylisoquinoline alkaloid-producing species[J]. The Plant Journal, 2009, 60(4):729-743. |
| 66 | HAGEL J M, MORRIS J S, LEE E J, et al. Transcriptome analysis of 20 taxonomically related benzylisoquinoline alkaloid-producing plants[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2015, 15(1):227. |
| 67 | ZIEGLER J, DIAZ-CHÁVEZ M L, KRAMELL R, et al. Comparative macroarray analysis of morphine containing Papaver somniferum and eight morphine free Papaver species identifies an O-methyltransferase involved in benzylisoquinoline biosynthesis[J]. Planta, 2005, 222(3):458-471. |
| 68 | PAULI H H, KUTCHAN T M. Molecular cloning and functional heterologous expression of two alleles encoding (S)-N-methylcoclaurine 3'-hydroxylase (CYP80B1), a new methyl jasmonate-inducible cytochrome P-450-dependent mono-oxygenase of benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis[J]. The Plant Journal, 1998, 13(6):793-801. |
| 69 | HUANG F C, KUTCHAN T M. Distribution of morphinan and benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloid gene transcript accumulation in Papaver somniferum [J]. Phytochemistry, 2000, 53(5):555-564. |
| 70 | GUINAUDEAU H, LEBŒUF M, CAVÉ A. Aporphinoid alkaloids, V[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 1994, 57(8):1033-1135. |
| 71 | MORRIS J S, FACCHINI P J. Isolation and characterization of reticuline N-methyltransferase involved in biosynthesis of the aporphine alkaloid magnoflorine in opium poppy[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2016, 291(45):23416-23427. |
| 72 | GRYCOVÁ L, DOSTÁL J, MAREK R. Quaternary protoberberine alkaloids[J]. Phytochemistry, 2007, 68(2):150-175. |
| 73 | WINKLER A, HARTNER F, KUTCHAN T M, et al. Biochemical evidence that berberine bridge enzyme belongs to a novel family of flavoproteins containing a bi-covalently attached FAD cofactor[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2006, 281(30):21276-21285. |
| 74 | KUTCHAN T M, DITTRICH H. Characterization and mechanism of the berberine bridge enzyme, a covalently flavinylated oxidase of benzophenanthridine alkaloid biosynthesis in plants[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1995, 270(41):24475-24481. |
| 75 | WINKLER A, PUHL M, WEBER H, et al. Berberine bridge enzyme catalyzes the six electron oxidation of (S)-reticuline to dehydroscoulerine[J]. Phytochemistry, 2009, 70(9):1092-1097. |
| 76 | DANG T-T T, FACCHINI P J. Characterization of three O-methyltransferases involved in noscapine biosynthesis in opium poppy[J]. Plant Physiology, 2012, 159(2):618-631. |
| 77 | IKEZAWA N, TANAKA M, NAGAYOSHI M, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of CYP719, a methylenedioxy bridge-forming enzyme that belongs to a novel P450 family, from cultured Coptis japonica cells[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2003, 278(40):38557-38565. |
| 78 | DÍAZ CHÁVEZ M L, ROLF M, GESELL A, et al. Characterization of two methylenedioxy bridge-forming cytochrome P450-dependent enzymes of alkaloid formation in the Mexican prickly poppy Argemone mexicana[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2011, 507(1):186-193. |
| 79 | GESELL A, DÍAZ CHÁVEZ M L, KRAMELL R, et al. Heterologous expression of two FAD-dependent oxidases with (S)-tetrahydroprotoberberine oxidase activity from Arge mone mexicana and Berberis wilsoniae in insect cells[J]. Planta, 2011, 233(6):1185-1197. |
| 80 | BEAUDOIN G A, FACCHINI P J. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding (S)-cis-N-methylstylopine 14-hydroxylase from opium poppy, a key enzyme in sanguinarine biosynthesis[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Reserach Communications, 2013, 431(3):597-603. |
| 81 | GALANIE S, SMOLKE C D. Optimization of yeast-based production of medicinal protoberberine alkaloids[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2015, 14:144. |
| 82 | TRENCHARD I J, SMOLKE C D. Engineering strategies for the fermentative production of plant alkaloids in yeast[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2015, 30:96-104. |
| 83 | HORI K, OKANO S, SATO F. Efficient microbial production of stylopine using a Pichia pastoris expression system[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6:22201. |
| 84 | KONZETT H, ROTHLIN E. [The effect of narcotine on cough reflex and on bronchial musculature[J]. Experientia, 1954, 10(11):472-473. |
| 85 | KARLSSON M O, DAHLSTRÖM B, ECKERNÄS S A, et al. Pharmacokinetics of oral noscapine[J]. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 1990, 39(3):275-279. |
| 86 | YE K, KE Y, KESHAVA N, et al. Opium alkaloid noscapine is an antitumor agent that arrests metaphase and induces apoptosis in dividing cells[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1998, 95(4):1601-1606. |
| 87 | KE Y, YE K Q, GROSSNIKLAUS H E, et al. Noscapine inhibits tumor growth with little toxicity to normal tissues or inhibition of immune responses[J]. Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy, 2000, 49(4/5):217-225. |
| 88 | ZHOU J, GUPTA K, YAO J, et al. Paclitaxel-resistant human ovarian cancer cells undergo c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-mediated apoptosis in response to noscapine[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2002, 277(42):39777-39785. |
| 89 | MAHMOUDIAN M, RAHIMI-MOGHADDAM P. The anti-cancer activity of noscapine: a review[J]. Recent Patents on Anti-Cancer Drug Discovery, 2009, 4(1):92-97. |
| 90 | WINZER T, GAZDA V, HE Z, et al. A Papaver somniferum 10-gene cluster for synthesis of the anticancer alkaloid noscapine[J]. Science, 2012, 336(6089):1704-1708. |
| 91 | DANG T T, CHEN X, FACCHINI P J. Acetylation serves as a protective group in noscapine biosynthesis in opium poppy[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2015, 11(2):104-106. |
| 92 | DANG T T, FACCHINI P J. CYP82Y1 is N-methylcanadine 1-hydroxylase, a key noscapine biosynthetic enzyme in opium poppy[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2014, 289(4):2013-2026. |
| 93 | LI Y, SMOLKE C D. Engineering biosynthesis of the anticancer alkaloid noscapine in yeast[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7:12137. |
| 94 | KIRBY G W. Biosynthesis of the morphine alkaloids[J]. Science, 1967, 155(3759):170-173. |
| 95 | THODEY K, GALANIE S, SMOLKE C D. A microbial biomanufacturing platform for natural and semisynthetic opioids[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2014, 10(10):837-844. |
| 96 | FOSSATI E, NARCROSS L, EKINS A, et al. Synthesis of morphinan alkaloids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(4):e0124459. |
| 97 | NAKAGAWA A, MATSUMURA E, KOYANAGI T, et al. Total biosynthesis of opiates by stepwise fermentation using engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7:10390. |
| 98 | GESELL A, ROLF M, ZIEGLER J, et al. CYP719B1 is salutaridine synthase, the C-C phenol-coupling enzyme of morphine biosynthesis in opium poppy[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2009, 284(36):24432-24442. |
| 99 | ZIEGLER J, VOIGTLÄNDER S, SCHMIDT J, et al. Comparative transcript and alkaloid profiling in Papaver species identifies a short chain dehydrogenase/reductase involved in morphine biosynthesis[J]. The Plant Journal, 2006, 48(2):177-192. |
| 100 | LENZ R, ZENK M H. Acetyl coenzyme A:salutaridinol-7-O-acetyltransferase from Papaver somniferum plant cell cultures. The enzyme catalyzing the formation of thebaine in morphine biosynthesis[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1995, 270(52):31091-31096. |
| 101 | GROTHE T, LENZ R, KUTCHAN T M. Molecular characterization of the salutaridinol 7-O-acetyltransferase involved in morphine biosynthesis in opium poppy Papaver somniferum [J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2001, 276(33):30717-30723. |
| 102 | THEUNS H G, B.M.LENTING H, A.SALEMINK C, et al. Neodihydrothebaine and bractazonine, two dibenz[d,f]azonine alkaloids of Papaver bracteatum [J]. Phytochemistry, 1984, 23:1929-1932. |
| 103 | CHEN X, HAGEL J M, CHANG L, et al. A pathogenesis-related 10 protein catalyzes the final step in thebaine biosynthesis[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2018, 14(7):738-743. |
| 104 | FARROW S C, FACCHINI P J. Dioxygenases catalyze O-demethylation and O,O-demethylenation with widespread roles in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid metabolism in opium poppy[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2013, 288(40):28997-29012. |
| 105 | UNTERLINNER B, LENZ R, KUTCHAN T M. Molecular cloning and functional expression of codeinone reductase: the penultimate enzyme in morphine biosynthesis in the opium poppy Papaver somniferum [J]. The Plant Journal, 1999, 18(5):465-475. |
| 106 | DASTMALCHI M, CHEN X, HAGEL J M, et al. Neopinone isomerase is involved in codeine and morphine biosynthesis in opium poppy[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2019, 15(4):384-390. |
| 107 | DASTMALCHI M, CHANG L, TORRES M A, et al. Codeinone reductase isoforms with differential stability, efficiency and product selectivity in opium poppy[J]. The Plant Journal, 2018. |
| 108 | ZHU J M, TAN H Q, YANG L, et al. Enantioselective synthesis of 1-aryl-substituted tetrahydroisoquinolines employing imine reductase[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(10):7003-7007. |
| 109 | YANG L, ZHU J, SUN C, et al. Biosynthesis of plant tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids through an imine reductase route[J]. Chemical Science, 2020, 11(2):364-371. |
| [1] | 郭姝媛, 张倩楠, 姑丽克孜·买买提热夏提, 杨一群, 于涛. 液体生物燃料合成与炼制的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 18-44. |
| [2] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [3] | 赵亮, 李振帅, 付丽平, 吕明, 王士安, 张全, 刘立成, 李福利, 刘自勇. 生物转化一碳化合物原料产油脂与单细胞蛋白研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1300-1318. |
| [4] | 竺方欢, 岑雪聪, 陈振. 微生物合成二元醇研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1367-1385. |
| [5] | 禹伟, 高教琪, 周雍进. 一碳生物转化合成有机酸的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1169-1188. |
| [6] | 陈锡玮, 张华然, 邹懿. 真菌源非核糖体肽类药物生物合成及代谢工程[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 571-592. |
| [7] | 谢皇, 郑义蕾, 苏依婷, 阮静怡, 李永泉. 放线菌聚酮类化合物生物合成体系重构研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| [8] | 惠真, 唐啸宇. CRISPR/Cas9编辑系统在微生物天然产物研究中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 658-671. |
| [9] | 赵静宇, 张健, 祁庆生, 王倩. 基于细菌双组分系统的生物传感器的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 38-52. |
| [10] | 孙绘梨, 崔金玉, 栾国栋, 吕雪峰. 面向高效光驱固碳产醇的蓝细菌合成生物技术研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(6): 1161-1177. |
| [11] | 晏雄鹰, 王振, 娄吉芸, 张皓瑜, 黄星宇, 王霞, 杨世辉. 生物燃料高效生产微生物细胞工厂构建研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(6): 1082-1121. |
| [12] | 程真真, 张健, 高聪, 刘立明, 陈修来. 代谢工程改造微生物利用甲酸研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(4): 756-778. |
| [13] | 刘家宇, 杨智晗, 杨蕾, 朱丽英, 朱政明, 江凌. 合成生物技术驱动酪丁酸梭菌细胞工厂开发的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(6): 1174-1200. |
| [14] | 郭姝媛, 吴良焕, 刘香健, 王博, 于涛. 微生物中一碳代谢网络构建的进展与挑战[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(1): 116-137. |
| [15] | 陈久洲, 王钰, 蒲伟, 郑平, 孙际宾. 5-氨基乙酰丙酸生物合成技术的发展及展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(6): 1000-1016. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||