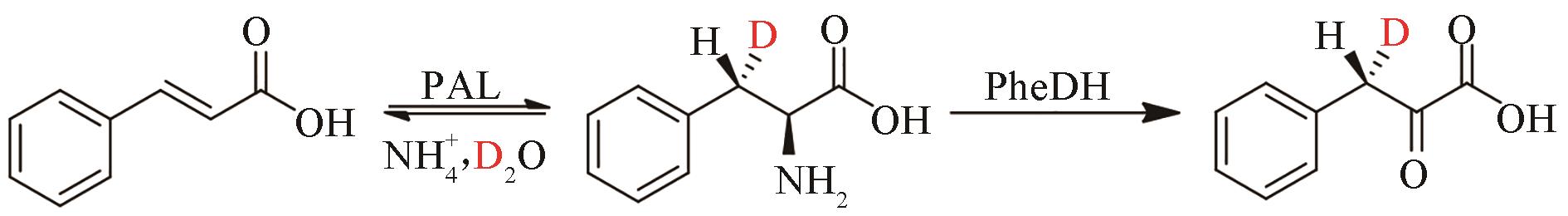
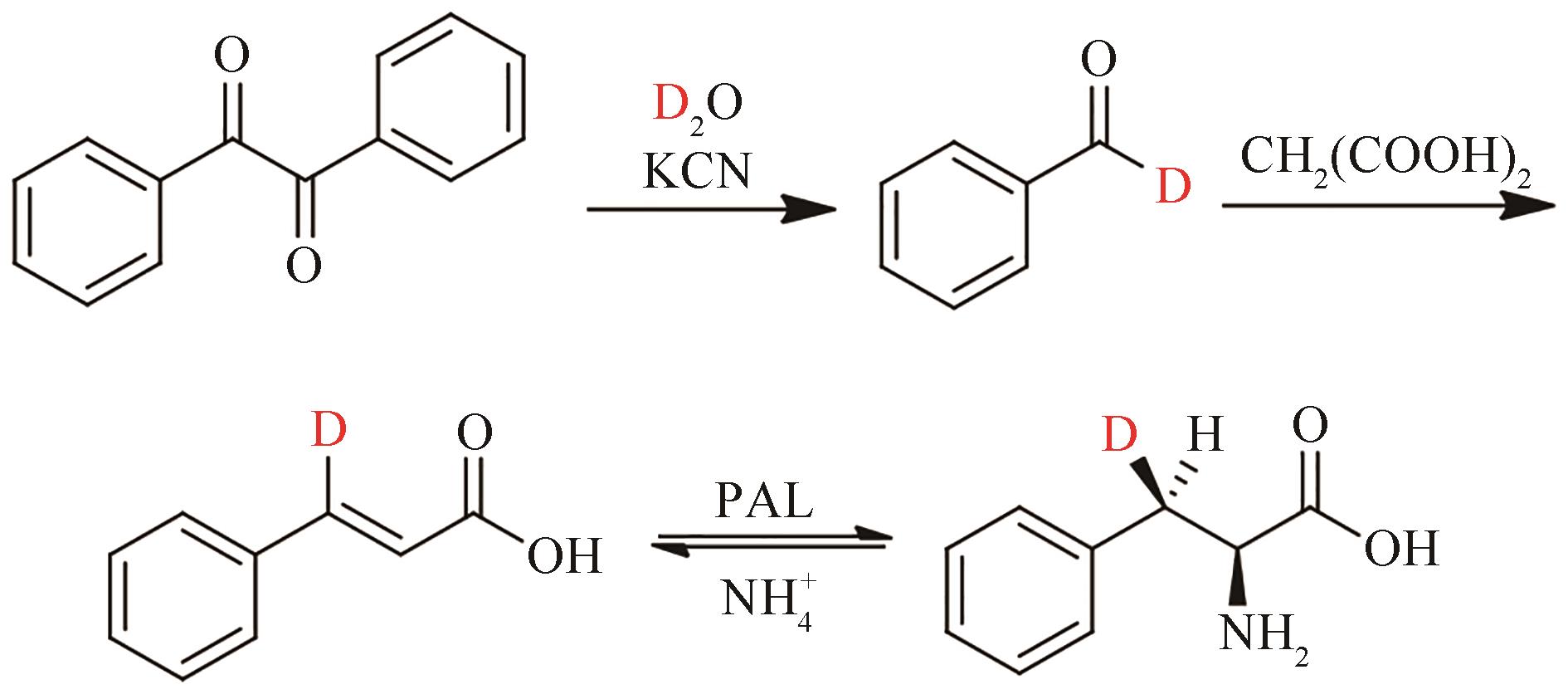
合成生物学 ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (3): 530-544.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-067
生物催化惰性碳氢键的氘代反应研究进展
楼玉姣1, 徐鉴2, 吴起1
- 1.浙江大学化学系,浙江 杭州 310027
2.浙江工业大学生物工程学院,浙江 杭州 310014
-
收稿日期:2021-06-18修回日期:2021-11-10出版日期:2022-06-30发布日期:2022-07-13 -
通讯作者:徐鉴,吴起 -
作者简介:楼玉姣 (1995—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为酶定向进化与催化新功能。E-mail: 2560753069@qq.com徐鉴 (1989—),男,教授。研究方向为酶定向进化,合成生物学,酶催化多功能性,手性生物催化等。E-mail: jianxu@zjut.edu.cn。吴起 (1976—),男,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为酶定向进化,合成生物学,手性生物催化,生物聚合等。E-mail: wuqi1000@163.com。 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2021YFC2102000);国家自然科学基金(91956128);浙江省自然科学基金(LY19B020014)
Progress of biocatalytic deuteration of inert carbon-hydrogen bonds
LOU Yujiao1, XU Jian2, WU Qi1
- 1.Department of Chemistry,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou 310027,Zhejiang,China
2.College of Biotechnology and Bioengineering,Zhejiang University of Technology,Hangzhou 310014,Zhejiang,China
-
Received:2021-06-18Revised:2021-11-10Online:2022-06-30Published:2022-07-13 -
Contact:XU Jian, WU Qi
摘要:
氘代化合物在代谢组学、蛋白质组学以及合成化学中的机理研究等方面都有重要的应用。由于C—D键比C—H键更稳定,可以显著提高氘代药物的体内代谢稳定性和生物半衰期,而随着2017年第1个氘代药物丁苯那嗪上市,氘代化合物的重要性进一步被人们关注,国内外许多研究机构都开启了氘代药的研究。氘代化合物的合成方法通常有化学法和生物法两种,由于生物酶与传统的化学催化剂相比具有绿色、低毒、节约成本等优势,并且具有突出的立体选择性,生物催化方法受到了越来越多的关注。本文重点综述了目前已报道的合成氘代化合物的生物催化方法,主要包括生物催化氢氘交换、还原氘代、脱羧氘代等3类反应,这些反应的基本模式都是从氘代水溶剂中汲取氘代质子转移到惰性碳氢键的特定氢原子上。虽然生物酶法制备氘代化合物的研究才刚刚起步,鉴于氘代分子在医药、化学中的重要地位,生物催化氘代反应在未来将会得到越来越广泛的应用。
中图分类号:
引用本文
楼玉姣, 徐鉴, 吴起. 生物催化惰性碳氢键的氘代反应研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(3): 530-544.
LOU Yujiao, XU Jian, WU Qi. Progress of biocatalytic deuteration of inert carbon-hydrogen bonds[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(3): 530-544.
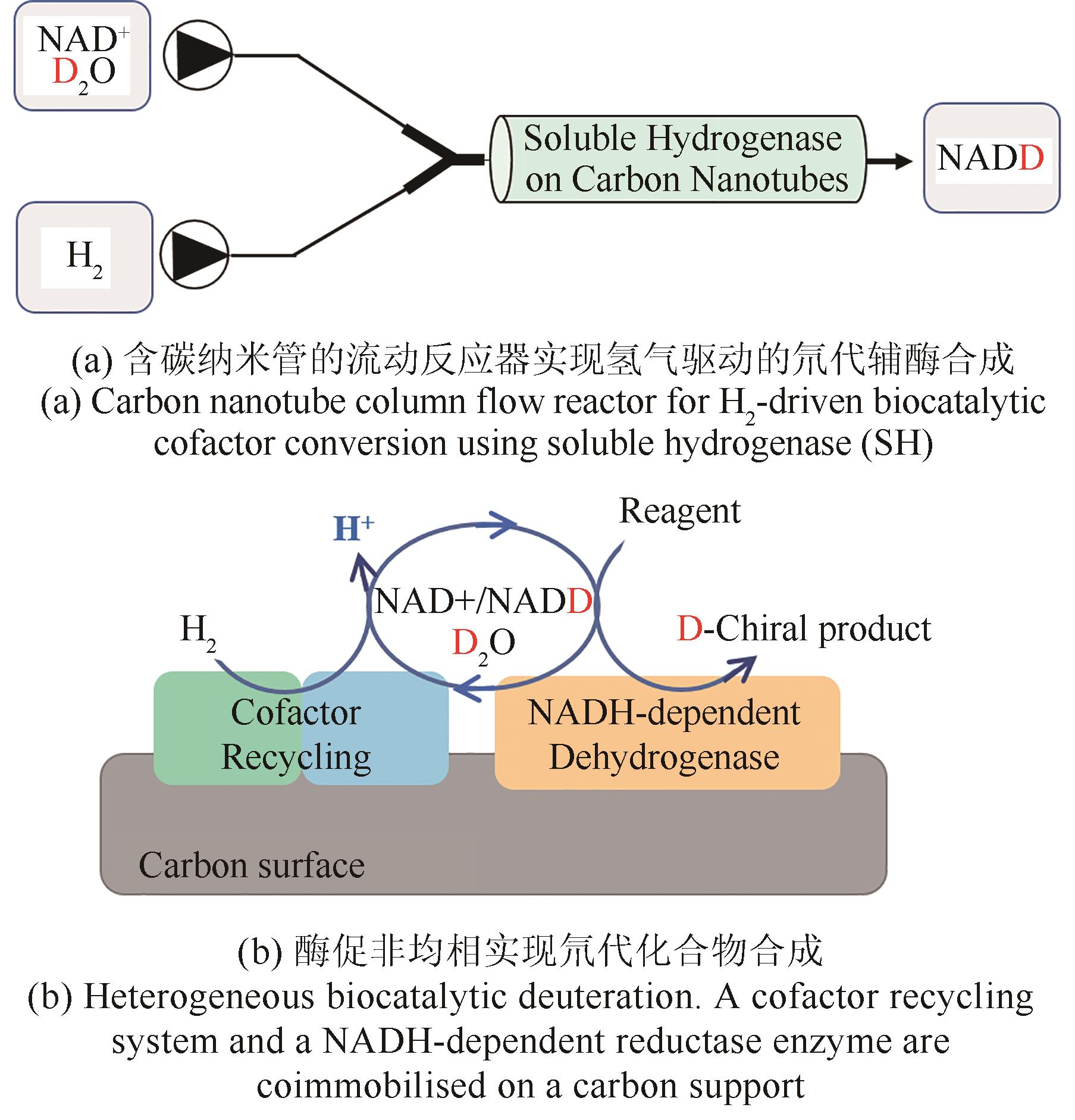
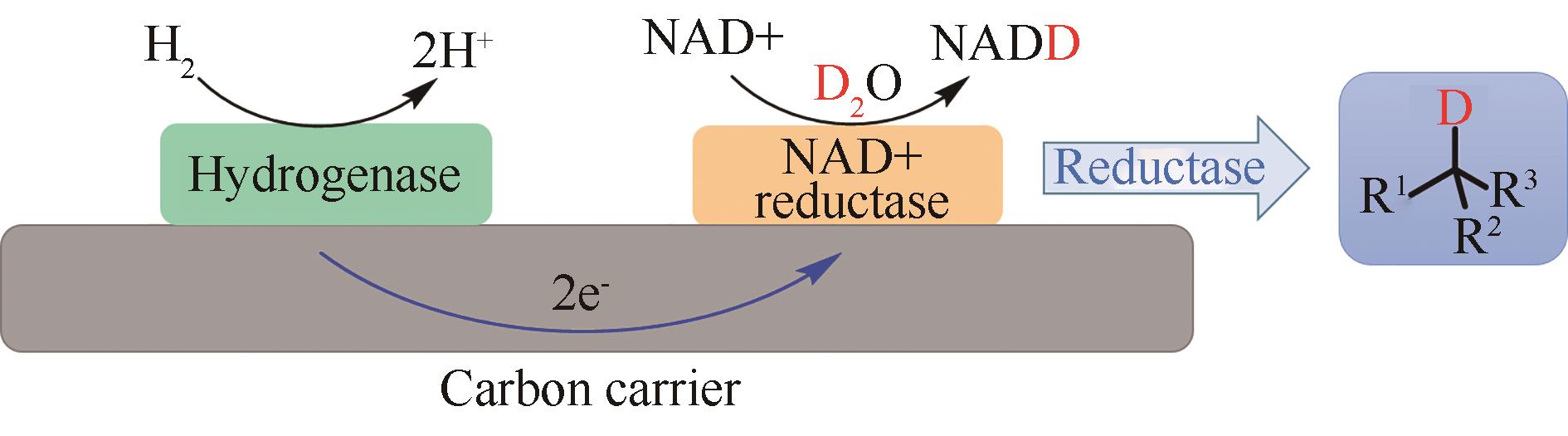
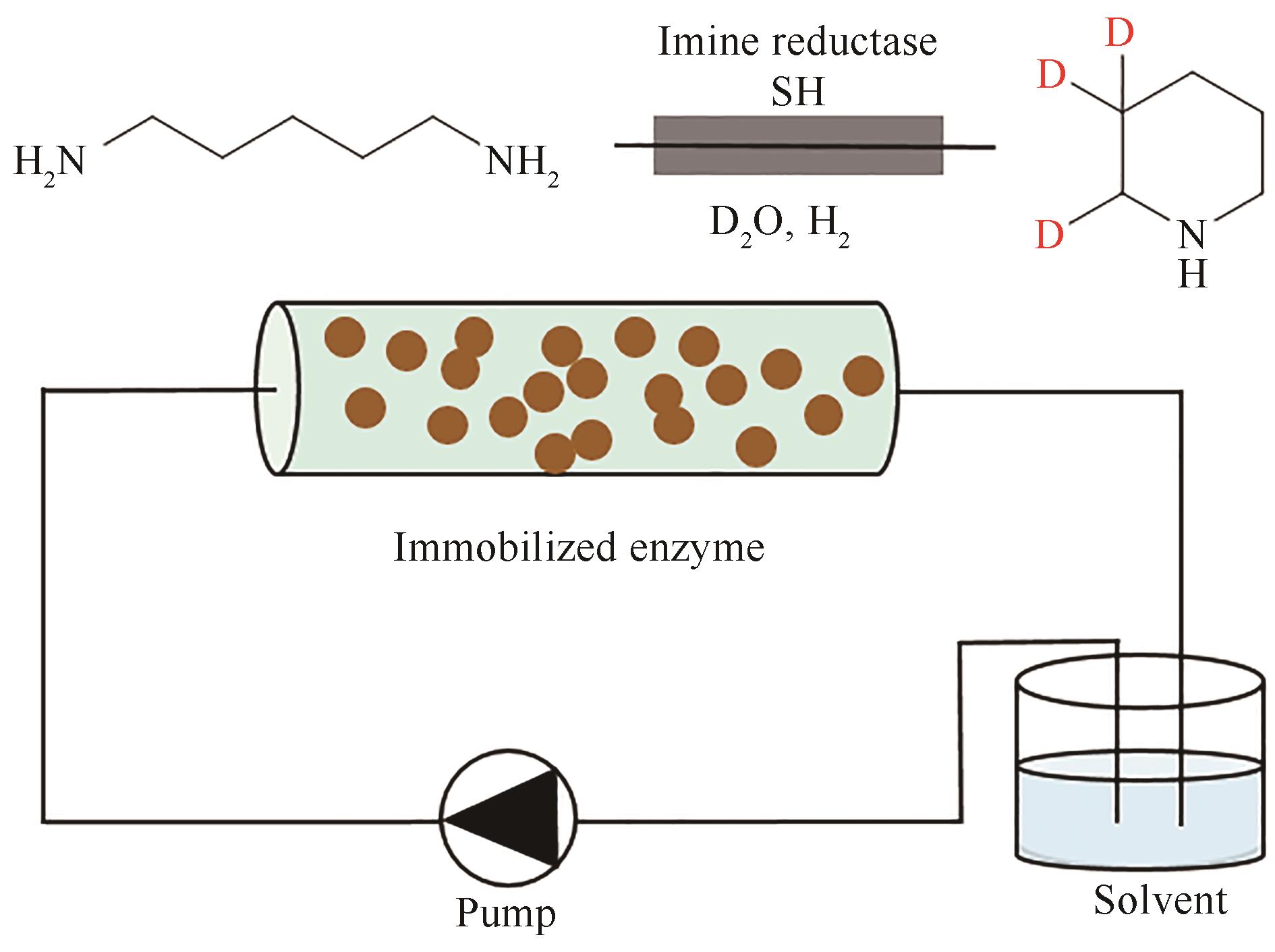
图10 碳表面固定化酶的流动反应器实现氢气驱动的氘代化合物合成
Fig. 10 Heterogeneous biocatalytic deuteration driven by H2 in a flow reactor containing carbon support-immobilized enzymes.
| 1 | SCHMIDT C. First deuterated drug approved[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2017, 35(6): 493-494. |
| 2 | ELMORE C S, BRAGG R A. Isotope chemistry; a useful tool in the drug discovery arsenal[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2015, 25(2): 167-171. |
| 3 | ELMORE C S. Chapter 25 the use of isotopically labeled compounds in drug discovery[M]// Annual reports in medicinal chemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2009: 515-534. |
| 4 | GANT T G. Using deuterium in drug discovery: leaving the label in the drug[J]. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2014, 57(9): 3595-3611. |
| 5 | ISIN E M, ELMORE C S, NILSSON G N, et al. Use of radiolabeled compounds in drug metabolism and pharmacokinetic studies[J]. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 2012, 25(3): 532-542. |
| 6 | JUNK T, CATALLO W J. Hydrogen isotope exchange reactions involving C–H (D, T) bonds[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 1997, 26(5): 401-406. |
| 7 | ATZRODT J, DERDAU V, FEY T, et al. The renaissance of H/D exchange[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2007, 46(41): 7744-7765. |
| 8 | VALERO M, DERDAU V. Highlights of aliphatic C(sp3)-H hydrogen isotope exchange reactions[J]. Journal of Labelled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals, 2020, 63(6): 266-280. |
| 9 | ATZRODT J, DERDAU V, KERR W J, et al. C-H functionalisation for hydrogen isotope exchange[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(12): 3022-3047. |
| 10 | YANG H F, ZARATE C, PALMER W N, et al. Site-selective nickel-catalyzed hydrogen isotope exchange in N-heterocycles and its application to the tritiation of pharmaceuticals[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(11): 10210-10218. |
| 11 | ZARATE C, YANG H F, BEZDEK M J, et al. Ni(I)-X complexes bearing a bulky α-diimine ligand: synthesis, structure, and superior catalytic performance in the hydrogen isotope exchange in pharmaceuticals[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(12): 5034-5044. |
| 12 | PALMER W N, CHIRIK P J. Cobalt-catalyzed stereoretentive hydrogen isotope exchange of C(sp3)-H bonds[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(9): 5674-5678. |
| 13 | MA S, VILLA G, THUY-BOUN P S, et al. Palladium-catalyzed ortho-selective C-H deuteration of arenes: evidence for superior reactivity of weakly coordinated palladacycles[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53(3): 734-737. |
| 14 | ITO N, ESAKI H, MAESAWA T, et al. Efficient and selective Pt/C-catalyzed H-D exchange reaction of aromatic rings[J]. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 2008, 81(2): 278-286. |
| 15 | MAEGAWA T, FUJIWARA Y, INAGAKI Y, et al. Mild and efficient H/D exchange of alkanes based on C-H activation catalyzed by rhodium on charcoal[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2008, 47(29): 5394-5397. |
| 16 | ESAKI H, OHTAKI R, MAEGAWA T, et al. Novel Pd/C-catalyzed redox reactions between aliphatic secondary alcohols and ketones under hydrogenation conditions: application to H-D exchange reaction and the mechanistic study[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2007, 72(6): 2143-2150. |
| 17 | KURIMOTO A, SHERBO R S, CAO Y, et al. Electrolytic deuteration of unsaturated bonds without using D2 [J]. Nature Catalysis, 2020, 3(9): 719-726. |
| 18 | WU Y M, LIU C B, WANG C H, et al. Selective transfer semihydrogenation of alkynes with H2O (D2O) as the H (D) source over a Pd-P cathode[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(47): 21170-21175. |
| 19 | LIU X, LIU R Y, QIU J X, et al. Chemical-reductant-free electrochemical deuteration reaction using deuterium oxide[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(33): 13962-13967. |
| 20 | HONG H L, ZOU Z R, LIANG G, et al. Direct electrochemical reductive amination between aldehydes and amines with a H/D-donor solvent[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2020, 18(30): 5832-5837. |
| 21 | LOH Y Y, NAGAO K, HOOVER A J, et al. Photoredox-catalyzed deuteration and tritiation of pharmaceutical compounds[J]. Science, 2017, 358(6367): 1182-1187. |
| 22 | ZHANG M L, YUAN X G, ZHU C J, et al. Deoxygenative deuteration of carboxylic acids with D2O[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(1): 312-316. |
| 23 | DONG Y Y, SU Y L, DU L L, et al. Plasmon-enhanced deuteration under visible-light irradiation[J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(9): 10754-10760. |
| 24 | LANG Y T, PENG X J, LI C J, et al. Photoinduced catalyst-free deborylation-deuteration of arylboronic acids with D2O[J]. Green Chemistry, 2020, 22(19): 6323-6327. |
| 25 | ZHANG Y T, JI P, DONG Y, et al. Deuteration of formyl groups via a catalytic radical H/D exchange approach[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(3): 2226-2230. |
| 26 | DONG J Y, WANG X C, WANG Z, et al. Formyl-selective deuteration of aldehydes with D2O via synergistic organic and photoredox catalysis[J]. Chemical Science, 2020, 11(4): 1026-1031. |
| 27 | NILSSON G N, KERR W J. The development and use of novel iridium complexes as catalysts for ortho-directed hydrogen isotope exchange reactions[J]. Journal of Labelled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals, 2010, 53(11/12): 662-667. |
| 28 | PONY YU R, HESK D, RIVERA N, et al. Iron-catalysed tritiation of pharmaceuticals[J]. Nature, 2016, 529(7585): 195-199. |
| 29 | LIU C B, CHEN Z X, SU C L, et al. Controllable deuteration of halogenated compounds by photocatalytic D2O splitting[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 80. |
| 30 | TAGLANG C, MARTÍNEZ-PRIETO L M, DEL ROSAL I, et al. Enantiospecific C-H activation using ruthenium nanocatalysts[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(36): 10474-10477. |
| 31 | HALE L V A, SZYMCZAK N K. Stereoretentive deuteration of α-chiral amines with D2O[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(41): 13489-13492. |
| 32 | BROWN J A, COCHRANE A R, IRVINE S, et al. The synthesis of highly active iridium(I) complexes and their application in catalytic hydrogen isotope exchange[J]. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 2014, 356(17): 3551-3562. |
| 33 | KERR W J, REID M, TUTTLE T. Iridium-catalyzed formyl-selective deuteration of aldehydes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(27): 7808-7812. |
| 34 | ARNOLD F H. Innovation by evolution: bringing new chemistry to life (Nobel lecture)[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(41): 14420-14426. |
| 35 | ZEYMER C, HILVERT D. Directed evolution of protein catalysts[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2018, 87: 131-157. |
| 36 | DEVINE P N, HOWARD R M, KUMAR R, et al. Extending the application of biocatalysis to meet the challenges of drug development[J]. Nature Reviews Chemistry, 2018, 2(12): 409-421. |
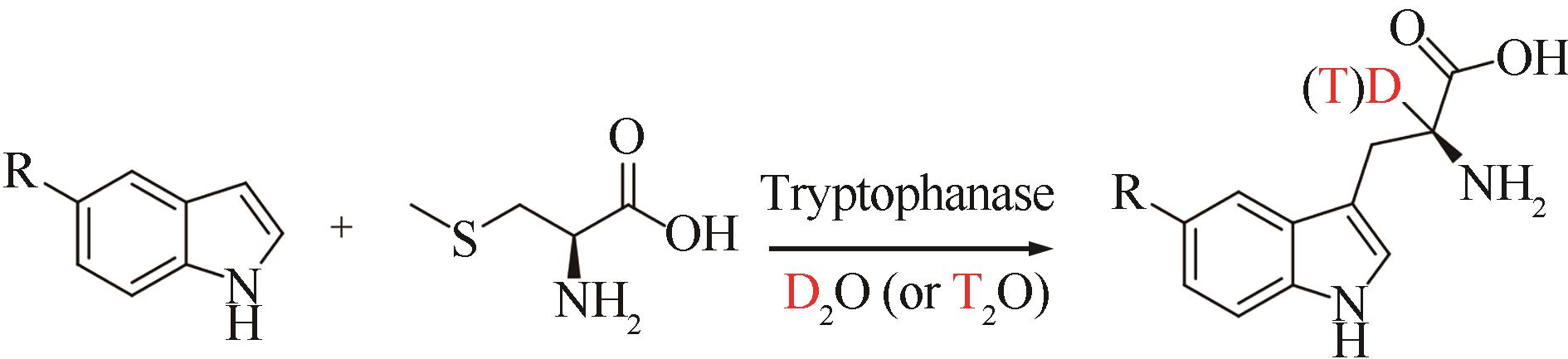
| 37 | QU G, LI A T, ACEVEDO-ROCHA C G, et al. The crucial role of methodology development in directed evolution of selective enzymes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(32): 13204-13231. |
| 38 | BORNSCHEUER U T, HUISMAN G W, KAZLAUSKAS R J, et al. Engineering the third wave of biocatalysis[J]. Nature, 2012, 485(7397): 185-194. |
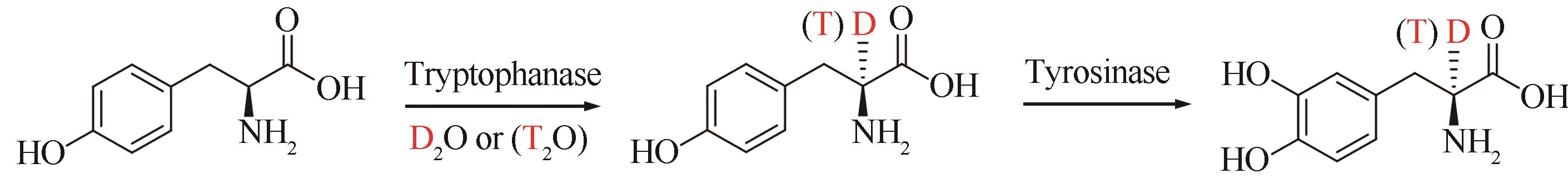
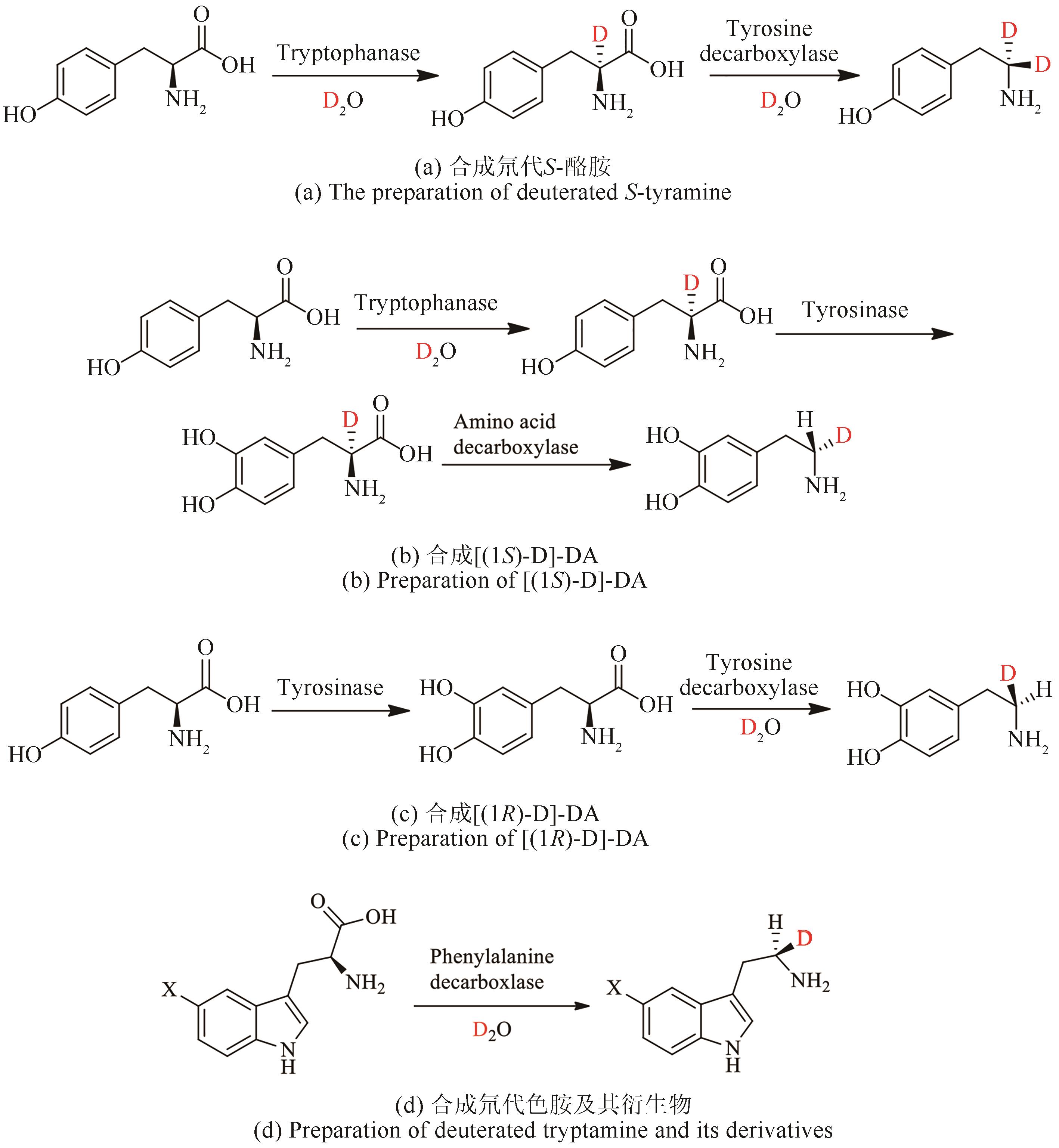
| 39 | CUI Y L, WANG Y H, TIAN W Y, et al. Development of a versatile and efficient C—N lyase platform for asymmetric hydroamination via computational enzyme redesign[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2021, 4(5): 364-373. |
| 40 | PAYNE K A P, WHITE M D, FISHER K, et al. New cofactor supports α,β-unsaturated acid decarboxylation via 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition[J]. Nature, 2015, 522(7557): 497-501. |
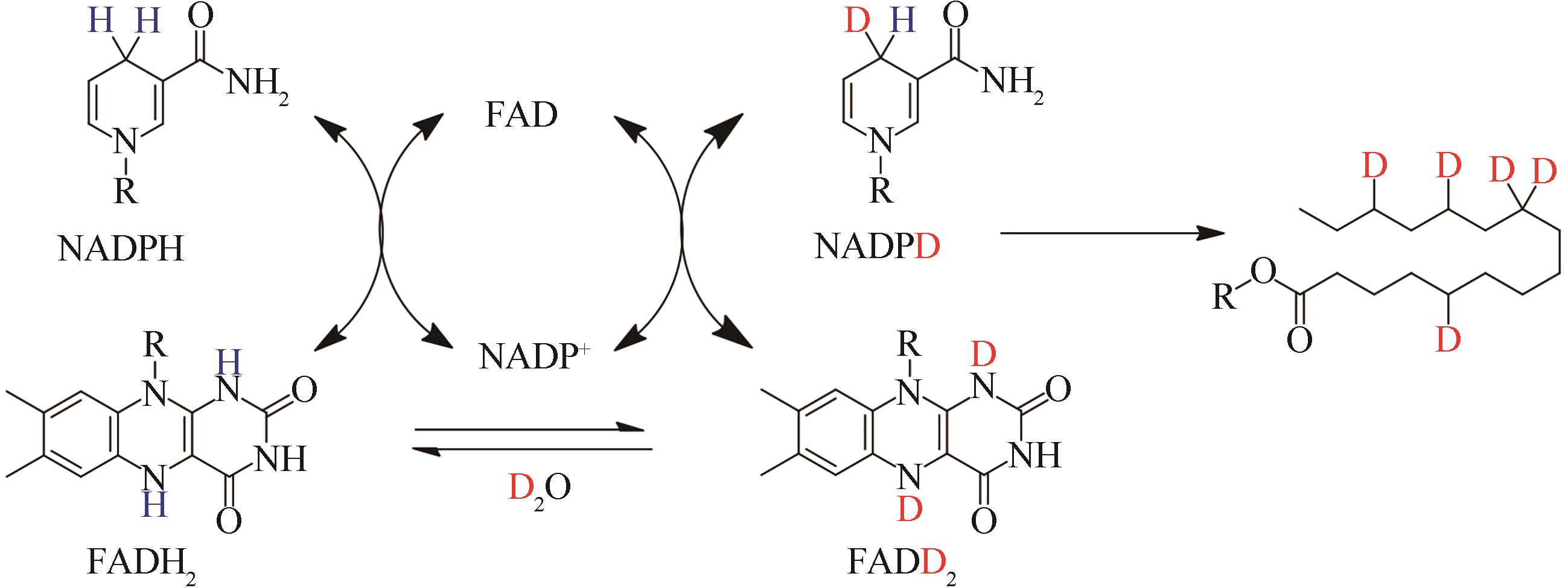
| 41 | PAYER S E, MARSHALL S A, BÄRLAND N, et al. Regioselective para-carboxylation of catechols with a prenylated flavin dependent decarboxylase[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(44): 13893-13897. |
| 42 | HERNÁNDEZ K, PARELLA T, PETRILLO G, et al. Intramolecular benzoin reaction catalyzed by benzaldehyde lyase from pseudomonas fluorescens biovar I[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(19): 5304-5307. |
| 43 | XU J, HU Y J, FAN J J, et al. Light-driven kinetic resolution of α-functionalized carboxylic acids enabled by an engineered fatty acid photodecarboxylase[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(25): 8474-8478. |
| 44 | ZHANG R K, CHEN K, HUANG X Y, et al. Enzymatic assembly of carbon-carbon bonds via iron-catalysed sp3 C–H functionalization[J]. Nature, 2019, 565(7737): 67-72. |
| 45 | KAN S B J, HUANG X Y, GUMULYA Y, et al. Genetically programmed chiral organoborane synthesis[J]. Nature, 2017, 552(7683): 132-136. |
| 46 | KAN S B J, LEWIS R D, CHEN K, et al. Directed evolution of cytochrome c for carbon-silicon bond formation: bringing silicon to life[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6315): 1048-1051. |
| 47 | HUANG X Q, WANG B J, WANG Y J, et al. Photoenzymatic enantioselective intermolecular radical hydroalkylation[J]. Nature, 2020, 584(7819): 69-74. |
| 48 | BIEGASIEWICZ K F, COOPER S J, GAO X, et al. Photoexcitation of flavoenzymes enables a stereoselective radical cyclization[J]. Science, 2019, 364(6446): 1166-1169. |
| 49 | ATZRODT J, DERDAU V, FEY T, et al. The renaissance of H/D exchange[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2007, 46 (41): 7744-7765. |
| 50 | LIU M, CHEN X, CHEN T Q, et al. A facile and general acid-catalyzed deuteration at methyl groups of N-heteroarylmethanes[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2017, 15(12): 2507-2511. |
| 51 | MOOZEH K, SO S M, CHIN J. Catalytic stereoinversion of L-alanine to deuterated D-alanine[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(32): 9381-9385. |
| 52 | ZHAN M, XU R X, TIAN Y, et al. A simple and cost-effective method for the regioselective deuteration of phenols[J]. European Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2015, 2015(15): 3370-3373. |
| 53 | YAMADA T, SAWAMA Y, SHIBATA K, et al. Multiple deuteration of alkanes synergistically-catalyzed by platinum and rhodium on carbon as a mixed catalytic system[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(18): 13727-13732. |
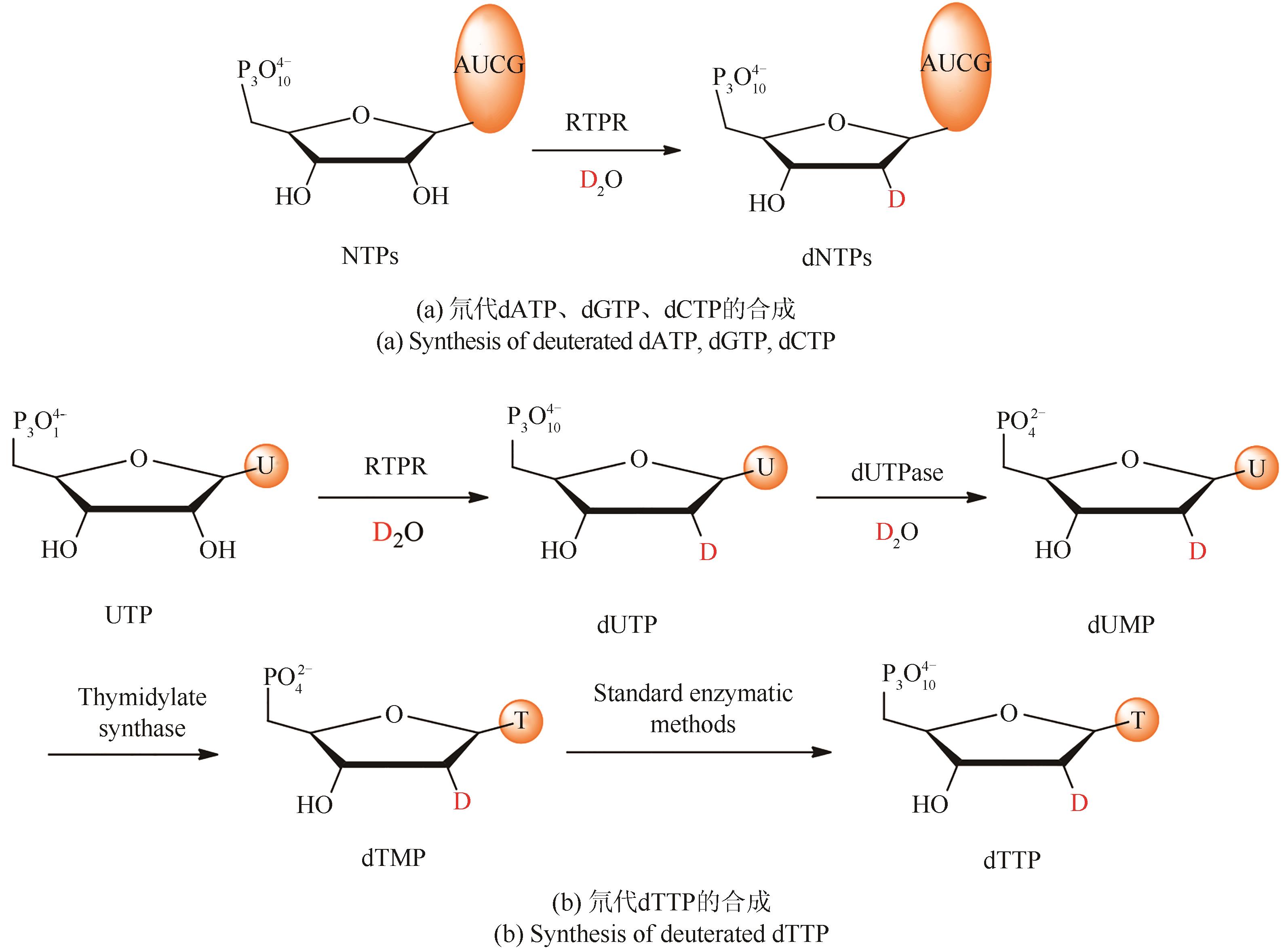
| 54 | VALERO M, KRUISSINK T, BLASS J, et al. C–H functionalization-prediction of selectivity in iridium(I)-catalyzed hydrogen isotope exchange competition reactions[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(14): 5626-5631. |
| 55 | KERR W J, MUDD R J, REID M, et al. Iridium-catalyzed C(sp3)—H activation for mild and selective hydrogen isotope exchange[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(11): 10895-10900. |
| 56 | AUGUSTYNIAK W, KAŃSKI R, KAŃSKA M. Synthesis of tritium labelled[2′,6′]-L-tyrosine[J]. Journal of Labelled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals, 2004, 47(13): 977-981. |
| 57 | WOOD W A, GUNSALUS I C, UMBREIT W W. Function of pyridoxal phosphate: resolution and purification of the tryptophanase enzyme of Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1947, 170(1): 313-321. |
| 58 | WATANABE T, SNELL E E. Reversibility of the tryptophanase reaction: synthesis of tryptophan from indole, pyruvate, and ammonia[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1972, 69(5): 1086-1090. |
| 59 | SNELL E E. Tryptophanase: structure, catalytic activities, and mechanism of action[J]. Advances in Enzymology and Related Areas of Molecular Biology, 1975, 42: 287-333. |
| 60 | KIICK D M, PHILLIPS R S. Mechanistic deductions from multiple kinetic and solvent deuterium isotope effects and pH studies of pyridoxal phosphate dependent carbon-carbon lyases: Escherichia coli tryptophan indole-lyase[J]. Biochemistry, 1988, 27(19): 7339-7344. |
| 61 | BORODA E, RAKOWSKA S, KAŃSKI R, et al. Enzymatic synthesis of L-tryptophan and 5prime-hydroxy-L-tryptophan labeled with deuterium and tritium at the α-carbon position[J]. Journal of Labelled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals, 2003, 46(8): 691-698. |
| 62 | KAWATA Y, TANI S, SATO M, et al. Preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of tryptophanase from Escherichia coli [J]. FEBS Letters, 1991, 284(2): 270-272. |
| 63 | PANUFNIK E, KAŃSKA M. Enzymatic synthesis of isotopomers of tyramine labeled with deuterium and tritium[J]. Journal of Labelled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals, 2007, 50(2): 85-89. |
| 64 | PAJĄK M, KAŃSKA M. Synthesis of isotopomers of L-DOPA and dopamine labeled with hydrogen isotopes in the side chain[J]. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 2009, 281(3): 365-370. |
| 65 | ZHANG Z Y, CHEN L, LIU L, et al. Chemical basis for deuterium labeling of fat and NADPH[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(41): 14368-14371. |
| 66 | MACHEROUX P, GHISLA S, SANNER C, et al. Reduced flavin: NMR investigation of N5-H exchange mechanism, estimation of ionisation constants and assessment of properties as biological catalyst[J]. BMC Biochemistry, 2005, 6: 26. |
| 67 | BENSON T E, MARQUARDT J L, MARQUARDT A C, et al. Overexpression, purification, and mechanistic study of UDP-N-acetylenolpyruvylglucosamine reductase[J]. Biochemistry, 1993, 32(8): 2024-2030. |
| 68 | CHEN S, GUILLORY R J. The [4B-3H] NADH-H2O exchange-reaction of the mitochondrial NADH dehydrogenase[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 1985, 129(2): 584-590. |
| 69 | ESWARAMOORTHY S, BONANNO J B, BURLEY S K, et al. Mechanism of action of a flavin-containing monooxygenase[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(26): 9832-9837. |
| 70 | KRUEGER S K, WILLIAMS D E. Mammalian flavin-containing monooxygenases: structure/function, genetic polymorphisms and role in drug metabolism[J]. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 2005, 106(3): 357-387. |
| 71 | ALDERTON W K, COOPER C E, KNOWLES R G. Nitric oxide synthases: structure, function and inhibition[J]. The Biochemical Journal, 2001, 357(Pt 3): 593-615. |
| 72 | SUMNER J S, MATTHEWS R G. Stereochemistry and mechanism of hydrogen transfer between NADPH and methylenetetrahydrofolate in the reaction catalyzed by methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase from pig liver[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1992, 114(18): 6949-6956. |
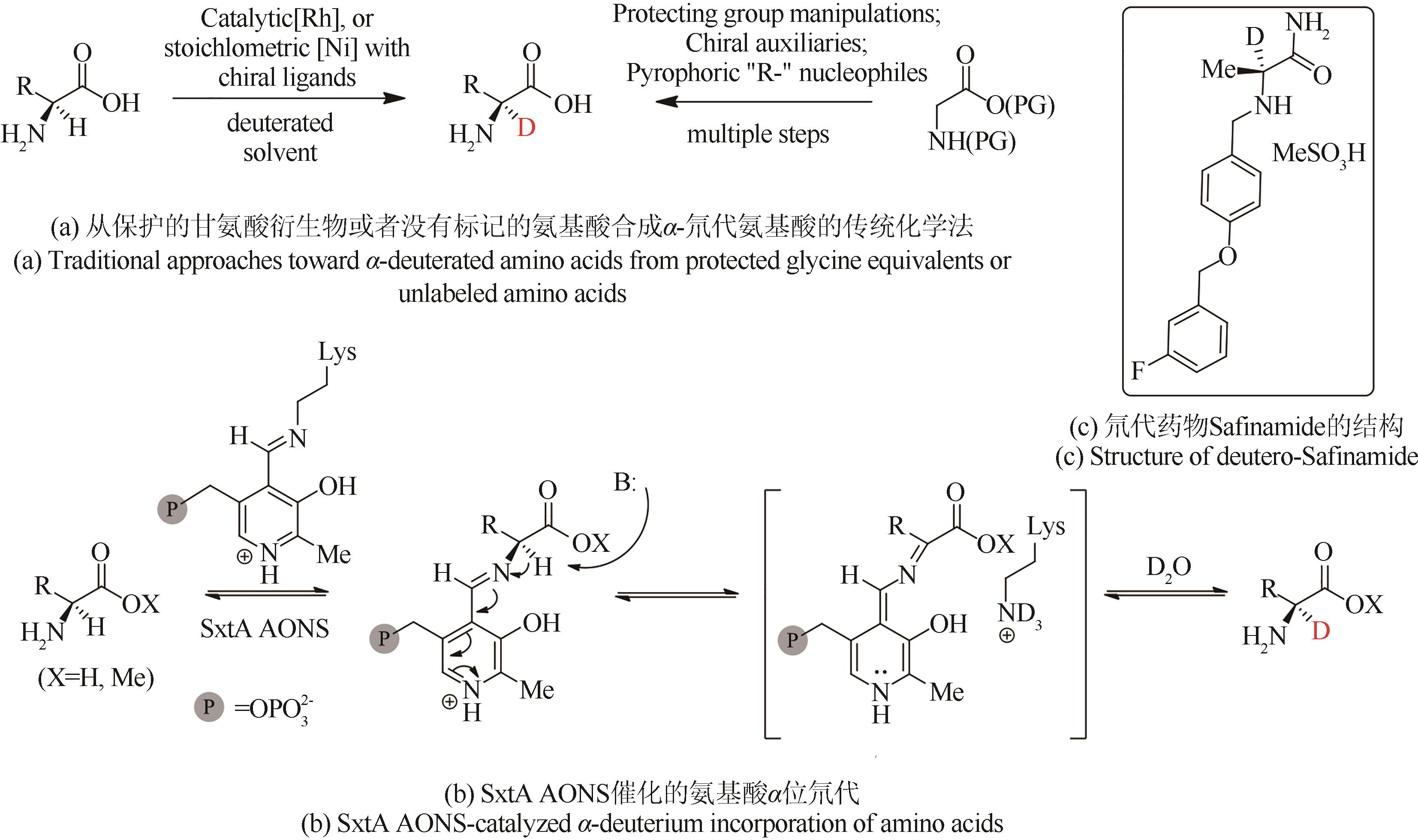
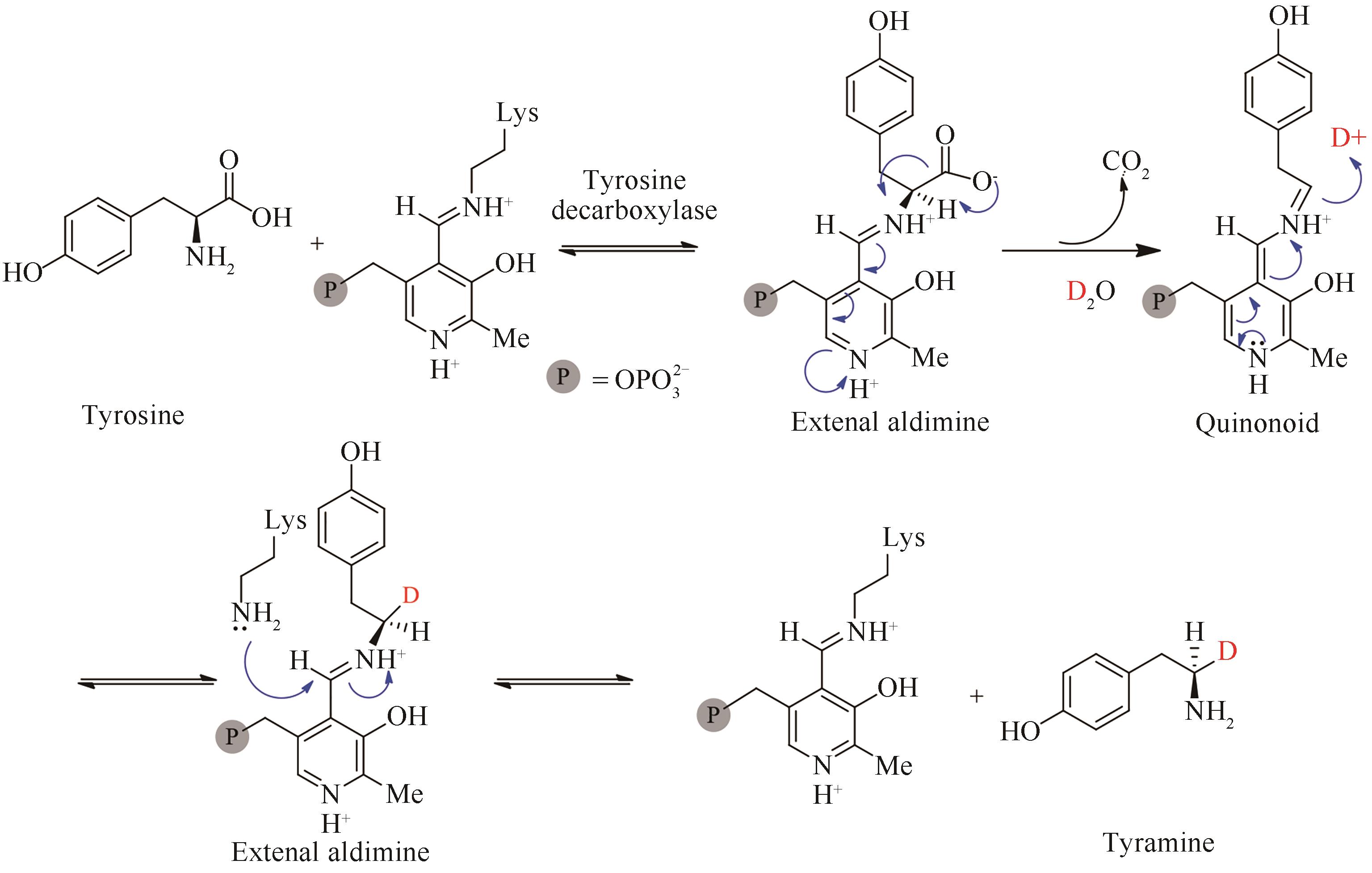
| 73 | CHUN S W, NARAYAN A R H. Biocatalytic, stereoselective deuteration of α-amino acids and methyl esters[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(13): 7413-7418. |
| 74 | ELEMES Y, RAGNARSSON U. Synthesis of enantiopure α-deuteriated Boc-L-amino acids[J]. Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 1, 1996(6): 537-540. |
| 75 | TAKEDA R, ABE H, SHIBATA N, et al. Asymmetric synthesis of α-deuterated α-amino acids[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2017, 15(33): 6978-6983. |
| 76 | CHATTERJEE B, KRISHNAKUMAR V, GUNANATHAN C. Selective α-deuteration of amines and amino acids using D2O[J]. Organic Letters, 2016, 18(22): 5892-5895. |
| 77 | XU J, LOU Y J, WANG L L, et al. Rational design of biocatalytic deuteration platform of aldehydes[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2021, 11(21): 13348-13354. |
| 78 | MACDONALD D, LU P. Determination of DNA structure in solution: enzymatic deuteration of the ribose 2' carbon[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2002, 124(33): 9722-9723. |
| 79 | ZIMMER D P, CROTHERS D M. NMR of enzymatically synthesized uniformly 13C 15N-labeled DNA oligonucleotides[J]. Proceeding of the National Acedemy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1995, 92(8): 3091-3095. |
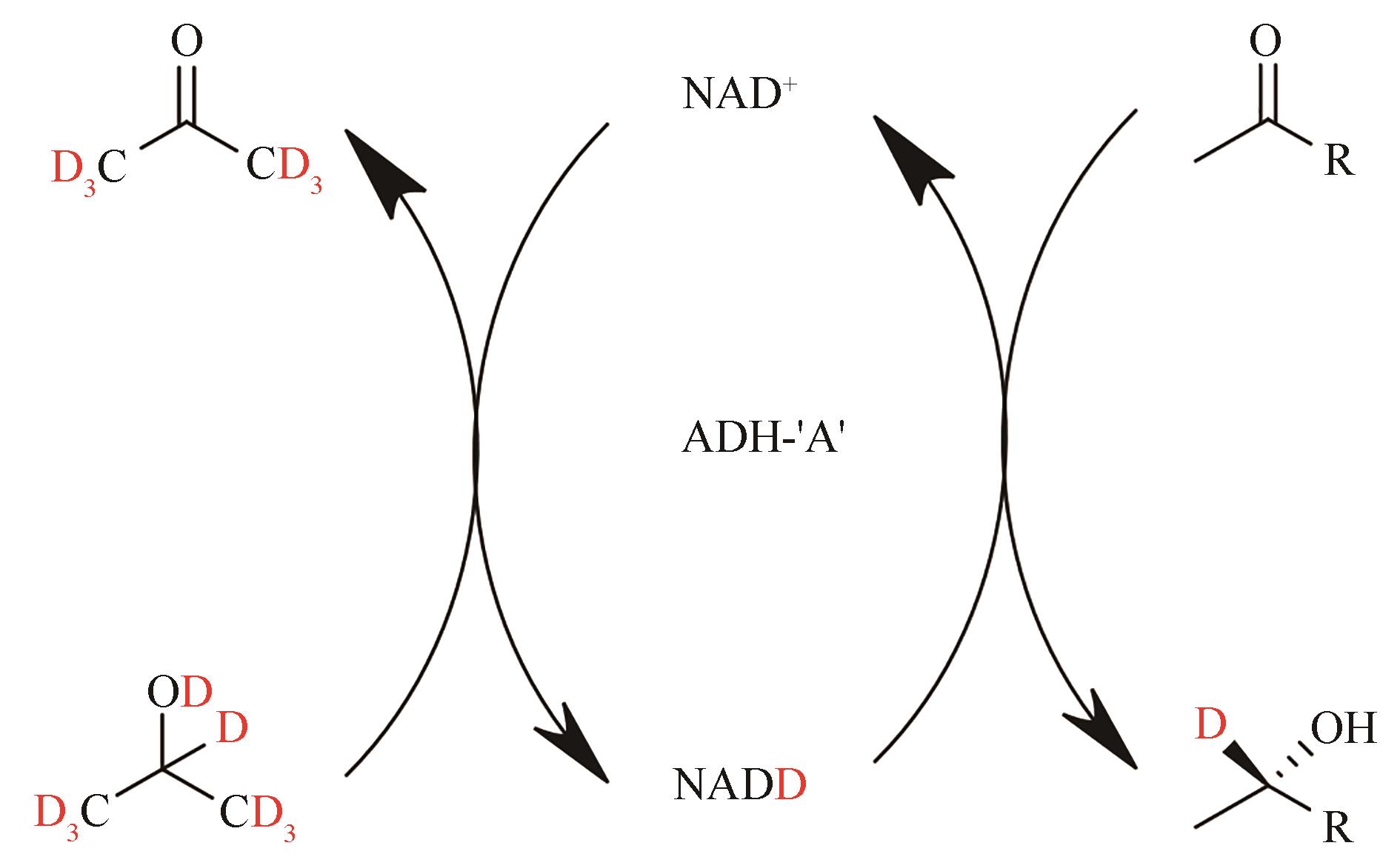
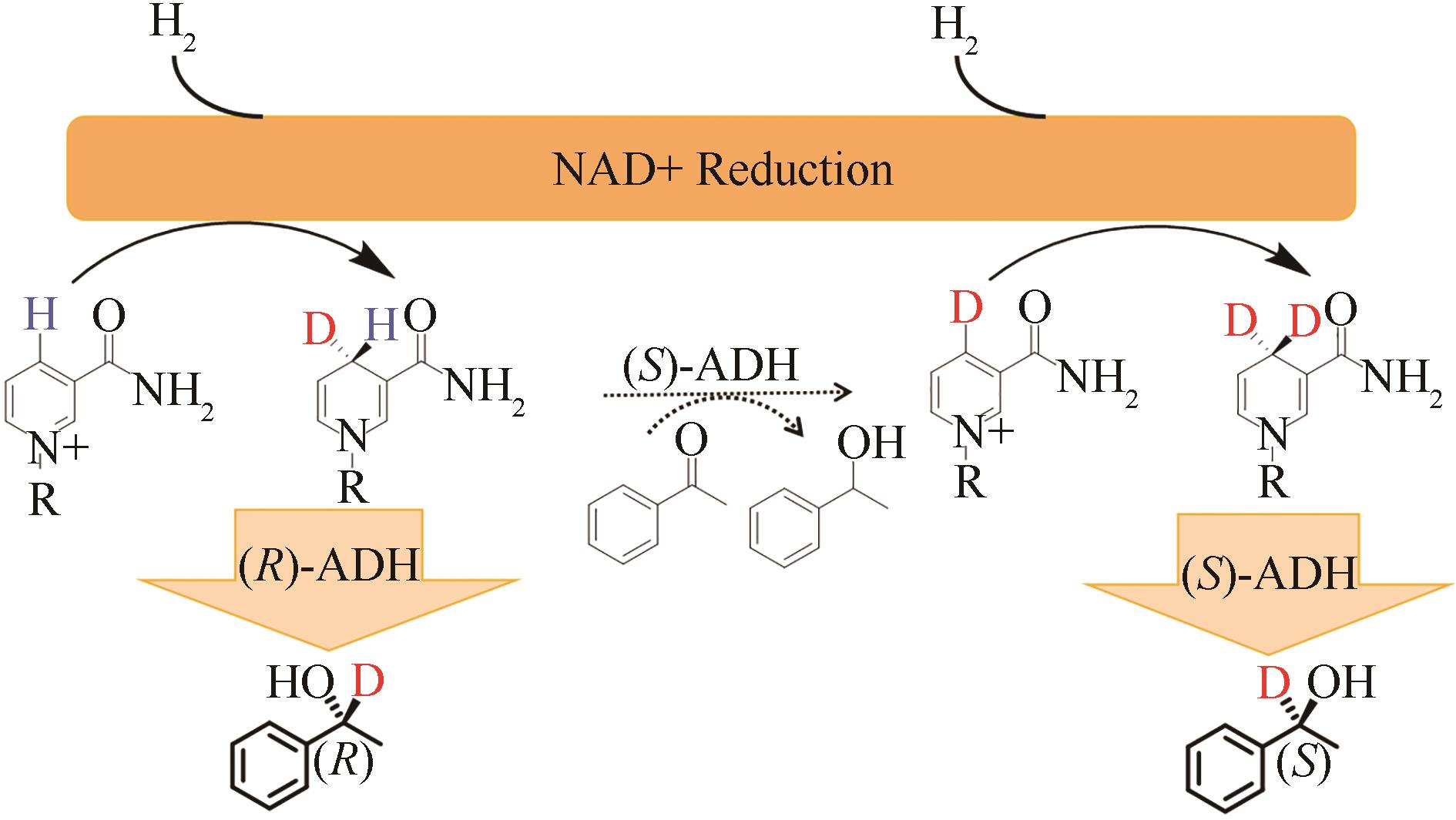
| 80 | EDEGGER K, GRUBER C C, POESSL T M, et al. Biocatalytic deuterium-and hydrogen-transfer using over-expressed ADH-' A': enhanced stereoselectivity and 2H-labeled chiral alcohols[J]. Chemical Communications, 2006(22): 2402-2404. |
| 81 | YAHASHIRI A, SEN A, KOHEN A. Microscale synthesis and kinetic isotope effect analysis of (4R)-[Ad-14C, 4-2H] NADPH and (4R)-[Ad-3H, 4-2H] NADPH[J]. Journal of Labelled Compounds & Radiopharmaceuticals, 2009, 52(11): 463-466. |
| 82 | WONG C H, WHITESIDES G M. Enzyme-catalyzed organic synthesis: regeneration of deuterated nicotinamide cofactors for use in large-scale enzymatic synthesis of deuterated substances[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1983, 105(15): 5012-5014. |
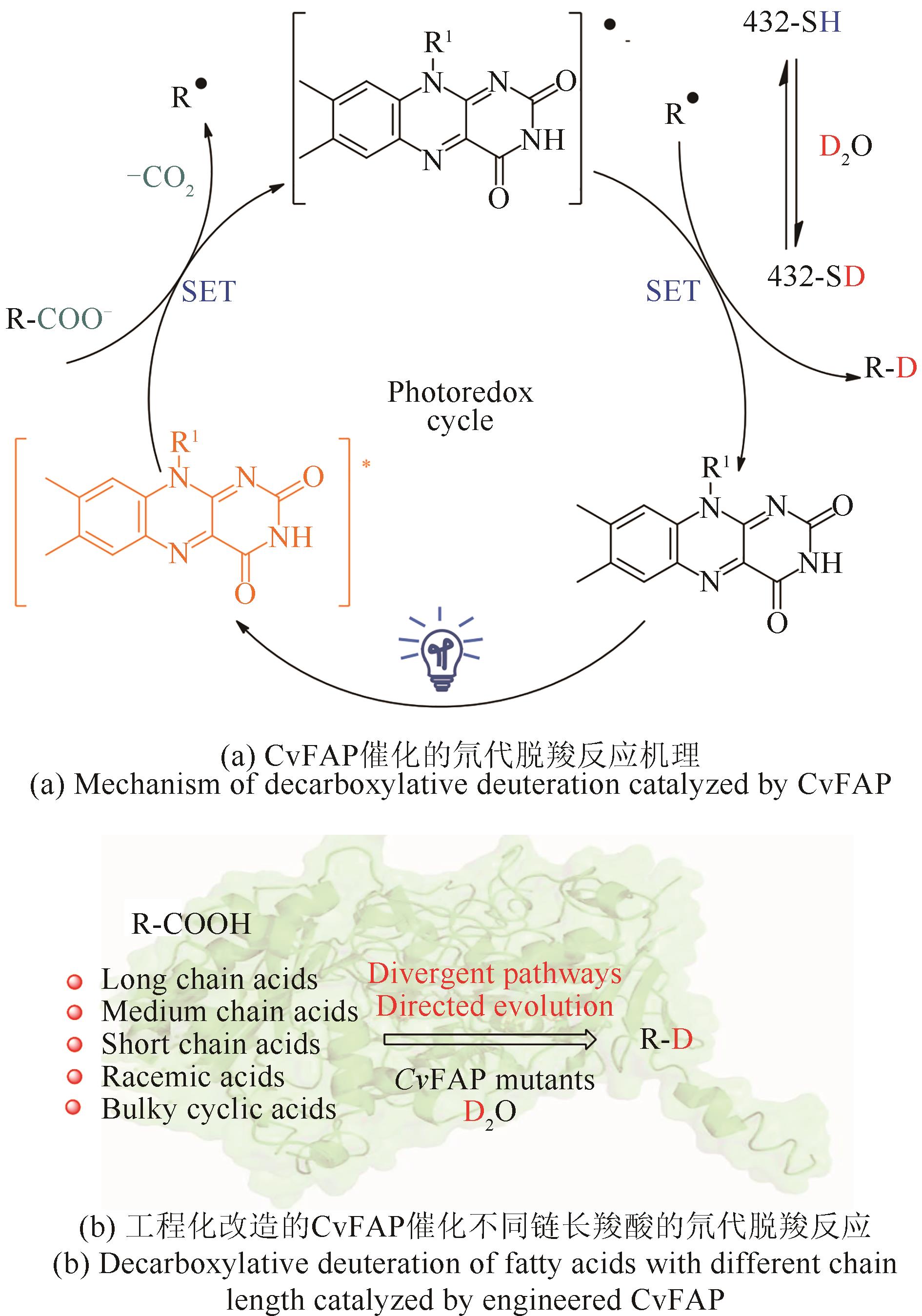
| 83 | REEVE H A, LAUTERBACH L, LENZ O, et al. Enzyme-modified particles for selective biocatalytic hydrogenation by hydrogen-driven NADH recycling[J]. ChemCatChem, 2015, 7(21): 3480-3487. |
| 84 | ROWBOTHAM J S, RAMIREZ M A, LENZ O, et al. Bringing biocatalytic deuteration into the toolbox of asymmetric isotopic labelling techniques[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 1454. |
| 85 | ROWBOTHAM J S, REEVE H A, VINCENT K A. Hybrid chemo-, bio-, and electrocatalysis for atom-efficient deuteration of cofactors in heavy water[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2021, 11(5): 2596-2604. |
| 86 | WANG X D, YIU H H P. Heterogeneous catalysis mediated cofactor NADH regeneration for enzymatic reduction[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2016, 6(3): 1880-1886. |
| 87 | WANG X D, SABA T, YIU H H P, et al. Cofactor NAD(P)H regeneration inspired by heterogeneous pathways[J]. Chem, 2017, 2(5): 621-654. |
| 88 | SABA T, BURNETT J W H, LI J W, et al. A facile analytical method for reliable selectivity examination in cofactor NADH regeneration[J]. Chemical Communications, 2020, 56(8): 1231-1234. |
| 89 | BAUMANN M, BAXENDALE I R. The synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) using continuous flow chemistry[J]. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2015, 11: 1194-1219. |
| 90 | BOGDAN A R, DOMBROWSKI A W. Emerging trends in flow chemistry and applications to the pharmaceutical industry[J]. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2019, 62(14): 6422-6468. |
| 91 | THOMPSON L A, ROWBOTHAM J S, NICHOLSON J H, et al. Rapid, heterogeneous biocatalytic hydrogenation and deuteration in a continuous flow reactor[J]. ChemCatChem, 2020, 12(15): 3913-3918. |
| 92 | AL-SHAMERI A, PETRICH M C, JUNGE PURING K, et al. Powering artificial enzymatic cascades with electrical energy[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(27): 10929-10933. |
| 93 | GOOßEN L, RUDZKI M, ALCALDE-ARAGONÉS A, et al. Selective copper-or silver-catalyzed decarboxylative deuteration of aromatic carboxylic acids[J]. Synthesis, 2012, 2012(2): 184-193. |
| 94 | GRAINGER R, NIKMAL A, CORNELLA J, et al. Selective deuteration of (hetero)aromatic compounds via deutero-decarboxylation of carboxylic acids[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2012, 10(16): 3172-3174. |
| 95 | BHADRA S, DZIK W I, GOOSSEN L J. Decarboxylative etherification of aromatic carboxylic acids[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(24): 9938-9941. |
| 96 | PATRA T, MUKHERJEE S, MA J J, et al. Visible-light-photosensitized aryl and alkyl decarboxylative functionalization reactions[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(31): 10514-10520. |
| 97 | BELLEAU B, BURBA J. The stereochemistry of the enzymic decarboxylation of amino acids[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1960, 82(21): 5751-5752. |
| 98 | ZHANG K, NI Y. Tyrosine decarboxylase from Lactobacillus brevis: soluble expression and characterization[J]. Protein Expression and Purification, 2014, 94: 33-39. |
| 99 | THOMAS B, BEAL M F. Parkinson's disease[J]. Human Molecular Genetics, 2007, 16(R2): R183-R194. |
| 100 | SIEVER L J, DAVIS K L. The pathophysiology of schizophrenia disorders: perspectives from the spectrum[J]. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 2004, 161(3): 398-413. |
| 101 | CERAVOLO R, VOLTERRANI D, GAMBACCINI G, et al. Presynaptic nigro-striatal function in a group of Alzheimer's disease patients with Parkinsonism: evidence from a dopamine transporter imaging study[J]. Journal of Neural Transmission, 2004, 111(8): 1065-1073. |
| 102 | LI J, ZHU M, MANNING-BOG A B, et al. Dopamine and L-DOPA disaggregate amyloid fibrils: implications for Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease[J]. FASEB Journal, 2004, 18(9): 962-964. |
| 103 | DUNATHAN H C. Stereochemical aspects of pyridoxal phosphate catalysis[M]// Advances in enzymology-and related areas of molecular biology. Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2006: 79-134. |
| 104 | VEDERAS J C, REINGOLD I D, SELLERS H W. Stereospecificity of sodium borohydride reduction of tyrosine decarboxylase from Streptococcus faecalis [J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1979, 254(12): 5053-5057. |
| 105 | DRAGULSKA S, KAŃSKA M. Enzymatic synthesis of tryptamine and its halogen derivatives selectively labeled with hydrogen isotopes[J]. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 2014, 299(1): 759-763. |
| 106 | PANUFNIK E, KAŃSKI R, KAŃSKA M. Enzymatic synthesis of tritium-labelled isotopomers of histamine[J]. Journal of Labelled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals, 2005, 48(1): 45-50. |
| 107 | XU J, FAN J J, LOU Y J, et al. Light-driven decarboxylative deuteration enabled by a divergently engineered photodecarboxylase[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 3983. |
| 108 | SORIGUÉ D, LÉGERET B, CUINÉ S, et al. An algal photoenzyme converts fatty acids to hydrocarbons[J]. Science, 2017, 357(6354): 903-907. |
| 109 | SORIGUÉ D, HADJIDEMETRIOU K, BLANGY S, et al. Mechanism and dynamics of fatty acid photodecarboxylase[J]. Science, 2021, 372(6538): eabd5687. |
| 110 | HAVIR E A, HANSON K R. L-Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (II): Mechanism and kinetic properties of the enzyme from potato tubers[J]. Biochemistry, 1968, 7(5): 1904-1914. |
| 111 | HAVIR E A, HANSON K R. L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (maize, potato, and Rhodotorula glutinis). Studies of the prosthetic group with nitromethane[J]. Biochemistry, 1975, 14(8): 1620-1626. |
| 112 | HODGINS D S. Yeast phenylalanine ammonia-lyase[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1971, 246(9): 2977-2985. |
| 113 | SCHUSTER B, RÉTEY J. The mechanism of action of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase: the role of prosthetic dehydroalanine[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1995, 92(18): 8433-8437. |
| 114 | GLOGE A, LANGER B, POPPE L, et al. The behavior of substrate analogues and secondary deuterium isotope effects in the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase reaction[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 1998, 359(1): 1-7. |
| 115 | LEWANDOWICZ A, JEMIELITY J, KAŃSKA M, et al. Tritium secondary kinetic isotope effect on phenylalanine ammonia-lyase-catalyzed reaction[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 1999, 370(2): 216-221. |
| 116 | JEMIELITY J, KANSKI R, KANSKA M. Synthesis of tritium labeled[3R-3H]-, and[3S-3H]-L-phenylalanine[J]. Journal of Labelled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals, 2001, 44(4): 295-304. |
| 117 | GULYÁS B, HALLDIN C. New PET radiopharmaceuticals beyond FDG for brain tumor imaging[J]. The Quarterly Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, 2012, 56(2): 173-190. |
| [1] | 温艳华, 刘合栋, 曹春来, 巫瑞波. 蛋白质工程在医药产业中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 65-86. |
| [2] | 程峰, 邹树平, 徐建妙, 汤恒, 薛亚平, 郑裕国. 生物高纯精草:高光学纯L-草铵膦生物制造的创新与发展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1404-1418. |
| [3] | 张守祺, 王涛, 孔尧, 邹家胜, 刘元宁, 徐正仁. 天然产物的化学-酶法合成:方法与策略的演进[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 913-940. |
| [4] | 郑梦梦, 刘犇犇, 林芝, 瞿旭东. 重要甾体化合物的化学酶法合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 941-959. |
| [5] | 付雨, 钟芳锐. 化学原理驱动的光生物不对称催化研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1021-1049. |
| [6] | 祁延萍, 朱晋, 张凯, 刘彤, 王雅婕. 定向进化在蛋白质工程中的应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(6): 1081-1108. |
| [7] | 王汇滨, 车昌丽, 游松. Fe/α-酮戊二酸依赖型卤化酶在绿色卤化反应中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(3): 545-566. |
| [8] | 杨璐, 瞿旭东. 亚胺还原酶在手性胺合成中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(3): 516-529. |
| [9] | 熊亮斌, 宋璐, 赵云秋, 刘坤, 刘勇军, 王风清, 魏东芝. 甾体化合物绿色生物制造:从生物转化到微生物从头合成[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(6): 942-963. |
| [10] | 张发光, 曲戈, 孙周通, 马军安. 从化学合成到生物合成——天然产物全合成新趋势[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(5): 674-696. |
| [11] | 汤恒, 韩鑫, 邹树平, 郑裕国. 多酶催化体系在医药化学品合成中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(4): 559-576. |
| [12] | 吴淑可, 周颐, 王文, 张巍, 高鹏飞, 李智. 从单酶催化到多酶级联催化——从王义翘教授在酶技术领域的贡献说开去[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(4): 543-558. |
| [13] | 王俊婷, 郭潇佳, 李青, 万里, 赵宗保. 创制非天然辅酶偏好型甲醇脱氢酶[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(4): 651-661. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||