合成生物学 ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (2): 290-305.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-068
L-精氨酸的微生物合成研究进展
王倩1,2, 果士婷2, 辛波1, 钟成1, 王钰2
- 1.天津科技大学生物工程学院,天津 300222
2.中国科学院天津工业生物技术研究所,低碳合成工程生物学重点实验室,天津 300308
-
收稿日期:2024-08-28修回日期:2024-10-31出版日期:2025-04-30发布日期:2025-05-20 -
通讯作者:钟成,王钰 -
作者简介:王倩 (1998—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为甲醇合成氨基酸菌种选育和合成调控机制。E-mail:wangqian23@tib.cas.cn钟成 (1979—),男,博士,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为微生物发酵合成生物纳米材料,纤维素的生物合成代谢与降解,固体废弃物资源综合利用等。E-mail:czhong@tust.edu.cn王钰 (1987—),男,博士,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为工业微生物的基因编辑育种和一碳原料的生物转化利用研究。E-mail:wang_y@tib.cas.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2023YFD1300700)
Advances in biosynthesis of L-arginine using engineered microorganisms
WANG Qian1,2, GUO Shiting2, XIN Bo1, ZHONG Cheng1, WANG Yu2
- 1.College of Biotechnology,Tianjin University of Science and Technology,Tianjin 300222,China
2.Key Laboratory of Engineering Biology for Low-Carbon Manufacturing,Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Tianjin 300308,China
-
Received:2024-08-28Revised:2024-10-31Online:2025-04-30Published:2025-05-20 -
Contact:ZHONG Cheng, WANG Yu
摘要:
L-精氨酸是一种碱性氨基酸,是护肤产品中常用的中和剂、保湿剂和抗氧化剂,此外,L-精氨酸还广泛应用于饲料、医药、食品等领域。以工程化的谷氨酸棒杆菌和大肠杆菌等微生物为催化剂,以可再生的淀粉糖为原料,通过微生物发酵的方法生产L-精氨酸是目前该产品最主要的生产方法。为创制高效的工程微生物菌种,早期研究者通常采用诱变筛选的方法,但由于突变的不确定性和非定向性,育种效率较低。随着合成生物技术的发展,人工设计L-精氨酸的合成途径和调控机制,并通过基因编辑理性创制工程微生物菌种成为研究的主流。本文综述了不同微生物中发现的L-精氨酸合成途径及调控机制,以谷氨酸棒杆菌和大肠杆菌为主,介绍了设计创制L-精氨酸高产菌种的合成生物学代谢改造策略,以及基于生物传感器的高通量筛选在L-精氨酸高产菌种筛选中的应用。最后,展望了进一步提高L-精氨酸生物合成水平的潜在策略,以及一碳原料等新型非粮碳资源在未来L-精氨酸生产中的应用前景。
中图分类号:
引用本文
王倩, 果士婷, 辛波, 钟成, 王钰. L-精氨酸的微生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(2): 290-305.
WANG Qian, GUO Shiting, XIN Bo, ZHONG Cheng, WANG Yu. Advances in biosynthesis of L-arginine using engineered microorganisms[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 290-305.
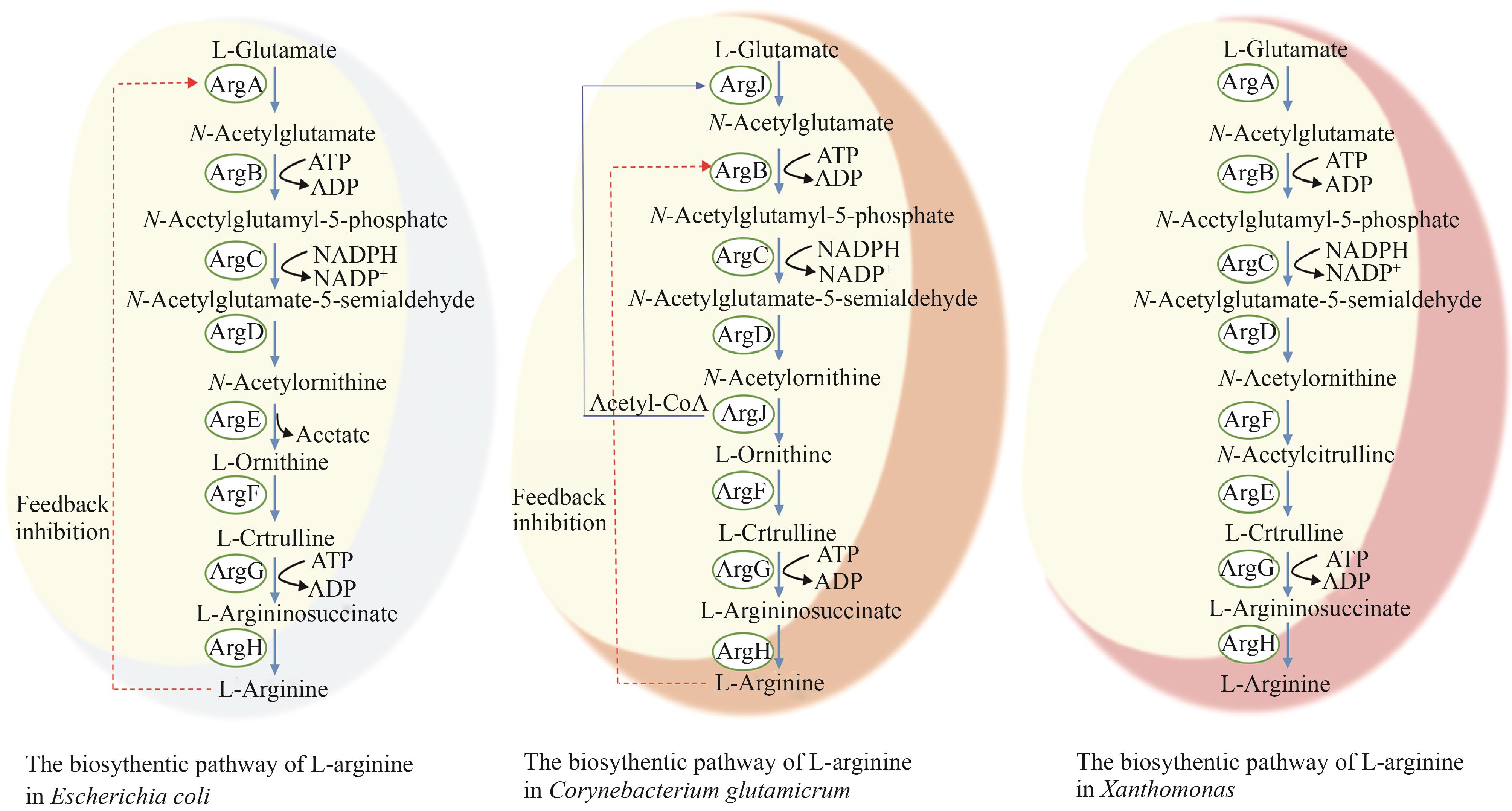
图1 微生物中L-精氨酸生物合成途径(ArgA—乙酰谷氨酸合成酶;ArgB—乙酰谷氨酸激酶;ArgC—乙酰谷氨酰磷酸还原酶;ArgD—乙酰鸟氨酸转氨酶;ArgE—乙酰鸟氨酸脱乙酰基酶;ArgF—鸟氨酸氨甲酰转移酶;ArgG—精氨酸琥珀酸合成酶;ArgH—精氨酸琥珀酸裂解酶;ArgF`—乙酰鸟氨酸氨甲酰转移酶;ArgJ—鸟氨酸乙酰转移酶)
Fig. 1 Biosynthetic pathways of ʟ-arginine in microorganisms(ArgA—acetylglutamate synthase; ArgB—acetylglutamate kinase; ArgC—acetyl-glutamyl-phosphate reductase; ArgD—acetylornithine aminotransferase; ArgE—acetylornithine deacetylase; ArgF—ornithine carbamoyltransferase; ArgG—argininosuccinate synthase; ArgH—argininosuccinate lyase; ArgF`—acetylornithine carbamoyltransferase; ArgJ—ornithine acetyltransferase)
| 菌种 | 代谢改造策略 | 原料 | 产量 /(g/L) | 转化率 /(g/g) | 生产强度 /[g/(L·h)] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 谷氨酸棒杆菌 | 增强辅因子NADPH的供应:过表达pntAB和ppnk;解除阻遏蛋白对L | 葡萄糖 | 67.01 | 0.35 | 0.89 | 补料分批发酵 | [ |
| 谷氨酸棒杆菌 | 诱变育种;增强辅因子NADPH的供应:下调pgi的表达,过表达tkt、tal、zwf、opcA、pgl;强化L-精氨酸合成途径:过表达argGH、carAB;解除阻遏蛋白对L-精氨酸操纵子的转录抑制:敲除argR和farR;增强前体物质L-谷氨酸的供应:敲除ncgl1221 | 葡萄糖; 蔗糖 | 92.50 | 0.40 | 1.28 | 补料分批发酵 | [ |
| 钝齿棒杆菌 | 解除终产物对L-精氨酸合成关键酶的反馈抑制:定点突变ArgBE19Y/I74V/F91H/K234T | 葡萄糖 | 61.20 | 0.43 | 0.64 | 补料分批发酵 | [ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 解除阻遏蛋白对L-精氨酸操纵子的转录抑制:敲除argR;解除终产物对L-精氨酸合成关键酶的反馈抑制:外源表达argJ;强化L-精氨酸合成途径:外源表达argCJBDF | 葡萄糖 | 70.10 | 0.33 | 1.17 | 补料分批发酵 | [ |
| 钝齿棒杆菌 | 增强前体物质L-谷氨酸的供应:过表达iolT1、ptsG、ppgk、pyc、gltA、gdh,下调odhA的表达;强化L-精氨酸合成途径:过表达argCJBDF、argGH;阻断副产物合成途径:敲除proB,下调lysC的表达;增强辅因子NADPH的供应:下调pgi的表达 | 葡萄糖 | 87.30 | 0.43 | 1.21 | 补料分批发酵 | [ |
| 钝齿棒杆菌 | 增强辅因子ATP的供应:过表达pyk、pgk,敲除frd12、nox、amn | 葡萄糖 | 57.30 | 0.33 | 0.58 | 补料分批发酵 | [ |
| 钝齿棒杆菌 | 阻断副产物合成途径:敲除proB;解除终产物对L-精氨酸合成关键酶的反馈抑制:定点突变ArgBE19R,H26E,D311,D312R | 葡萄糖 | 16.50 | 0.39 | 0.15 | 摇瓶发酵 | [ |
| 钝齿棒杆菌 | 增强前体物质L-谷氨酸的供应:敲除putP、pta、ncg12310、ncgl1221;增强L-精氨酸转运:过表达lysE | 葡萄糖 | 24.85 | 0.57 | 0.23 | 摇瓶发酵 | [ |
| 钝齿棒杆菌 | 增强氮源供应:过表达glnA、aspA、gdh | 葡萄糖 | 53.20 | 0.32 | 0.55 | 补料分批发酵 | [ |
| 钝齿棒杆菌 | 增强氮源供应:敲除amtR,过表达amtB2 | 葡萄糖 | 60.90 | 0.36 | 0.63 | 补料分批发酵 | [ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 阻断L-精氨酸降解途径:敲除adiA、speC、speF;解除阻遏蛋白对L-精氨酸操纵子的转录抑制:敲除argR;解除终产物对L-精氨酸合成关键酶的反馈抑制:过表达ArgAH15Y;增强L-精氨酸转运:过表达argO | 葡萄糖 | 11.64 | 1.18 | 0.24 | 补料分批发酵 | [ |
| 钝齿棒杆菌 | 增强L-精氨酸转运:过表达lysE | 葡萄糖 | 35.91 | — | 0.37 | 摇瓶发酵 | [ |
| 钝齿棒杆菌 | 解除终产物对L-精氨酸合成关键酶的反馈抑制:过表达glnK | 49.98 | 0.34 | 0.52 | 补料分批发酵 | [ | |
| 大肠杆菌 | 解除终产物对L-精氨酸合成关键酶的反馈抑制:敲除argA;阻断副产物合成途径:敲除pflB(编码丙酮酸-甲酸裂解酶)、ldhA(编码乳酸脱氢酶)、poxB(编码丙酮酸氧化酶)、adhE(编码乙醇脱氢酶)、aceE(编码丙酮酸脱氢酶)、speF;阻断L-精氨酸降解途径:敲除speB、astA;解除阻遏蛋白对L-精氨酸操纵子的转录抑制:敲除argR;强化L-精氨酸合成途径:过表达argCBI、argD、argG、argH、carAB | 葡萄糖; 乙酰谷氨酸 | 4.00 | — | — | 摇瓶发酵 | [ |
表1 代谢改造微生物合成L-精氨酸
Table 1 Production of L-arginine by metabolically engineered microorganisms
| 菌种 | 代谢改造策略 | 原料 | 产量 /(g/L) | 转化率 /(g/g) | 生产强度 /[g/(L·h)] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 谷氨酸棒杆菌 | 增强辅因子NADPH的供应:过表达pntAB和ppnk;解除阻遏蛋白对L | 葡萄糖 | 67.01 | 0.35 | 0.89 | 补料分批发酵 | [ |
| 谷氨酸棒杆菌 | 诱变育种;增强辅因子NADPH的供应:下调pgi的表达,过表达tkt、tal、zwf、opcA、pgl;强化L-精氨酸合成途径:过表达argGH、carAB;解除阻遏蛋白对L-精氨酸操纵子的转录抑制:敲除argR和farR;增强前体物质L-谷氨酸的供应:敲除ncgl1221 | 葡萄糖; 蔗糖 | 92.50 | 0.40 | 1.28 | 补料分批发酵 | [ |
| 钝齿棒杆菌 | 解除终产物对L-精氨酸合成关键酶的反馈抑制:定点突变ArgBE19Y/I74V/F91H/K234T | 葡萄糖 | 61.20 | 0.43 | 0.64 | 补料分批发酵 | [ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 解除阻遏蛋白对L-精氨酸操纵子的转录抑制:敲除argR;解除终产物对L-精氨酸合成关键酶的反馈抑制:外源表达argJ;强化L-精氨酸合成途径:外源表达argCJBDF | 葡萄糖 | 70.10 | 0.33 | 1.17 | 补料分批发酵 | [ |
| 钝齿棒杆菌 | 增强前体物质L-谷氨酸的供应:过表达iolT1、ptsG、ppgk、pyc、gltA、gdh,下调odhA的表达;强化L-精氨酸合成途径:过表达argCJBDF、argGH;阻断副产物合成途径:敲除proB,下调lysC的表达;增强辅因子NADPH的供应:下调pgi的表达 | 葡萄糖 | 87.30 | 0.43 | 1.21 | 补料分批发酵 | [ |
| 钝齿棒杆菌 | 增强辅因子ATP的供应:过表达pyk、pgk,敲除frd12、nox、amn | 葡萄糖 | 57.30 | 0.33 | 0.58 | 补料分批发酵 | [ |
| 钝齿棒杆菌 | 阻断副产物合成途径:敲除proB;解除终产物对L-精氨酸合成关键酶的反馈抑制:定点突变ArgBE19R,H26E,D311,D312R | 葡萄糖 | 16.50 | 0.39 | 0.15 | 摇瓶发酵 | [ |
| 钝齿棒杆菌 | 增强前体物质L-谷氨酸的供应:敲除putP、pta、ncg12310、ncgl1221;增强L-精氨酸转运:过表达lysE | 葡萄糖 | 24.85 | 0.57 | 0.23 | 摇瓶发酵 | [ |
| 钝齿棒杆菌 | 增强氮源供应:过表达glnA、aspA、gdh | 葡萄糖 | 53.20 | 0.32 | 0.55 | 补料分批发酵 | [ |
| 钝齿棒杆菌 | 增强氮源供应:敲除amtR,过表达amtB2 | 葡萄糖 | 60.90 | 0.36 | 0.63 | 补料分批发酵 | [ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 阻断L-精氨酸降解途径:敲除adiA、speC、speF;解除阻遏蛋白对L-精氨酸操纵子的转录抑制:敲除argR;解除终产物对L-精氨酸合成关键酶的反馈抑制:过表达ArgAH15Y;增强L-精氨酸转运:过表达argO | 葡萄糖 | 11.64 | 1.18 | 0.24 | 补料分批发酵 | [ |
| 钝齿棒杆菌 | 增强L-精氨酸转运:过表达lysE | 葡萄糖 | 35.91 | — | 0.37 | 摇瓶发酵 | [ |
| 钝齿棒杆菌 | 解除终产物对L-精氨酸合成关键酶的反馈抑制:过表达glnK | 49.98 | 0.34 | 0.52 | 补料分批发酵 | [ | |
| 大肠杆菌 | 解除终产物对L-精氨酸合成关键酶的反馈抑制:敲除argA;阻断副产物合成途径:敲除pflB(编码丙酮酸-甲酸裂解酶)、ldhA(编码乳酸脱氢酶)、poxB(编码丙酮酸氧化酶)、adhE(编码乙醇脱氢酶)、aceE(编码丙酮酸脱氢酶)、speF;阻断L-精氨酸降解途径:敲除speB、astA;解除阻遏蛋白对L-精氨酸操纵子的转录抑制:敲除argR;强化L-精氨酸合成途径:过表达argCBI、argD、argG、argH、carAB | 葡萄糖; 乙酰谷氨酸 | 4.00 | — | — | 摇瓶发酵 | [ |
| 1 | 范玉洁. 精氨酸水平对离乳期梅花鹿生长性能、瘤胃发酵和菌群结构的影响[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2021. |
| FAN Y J. Effects of arginine level on growth performance, rumen fermentation and flora structure of sika deer during weaning period[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2021. | |
| 2 | 宁诚. 三种外源性氨基酸对乳化香肠色泽影响的研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2019. |
| NING C. Study on the effect of three exogenous amino acids onthe color of emulsion sausage[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2019. | |
| 3 | 张豪. 基于辅因子及全局转录因子代谢工程改造钝齿棒杆菌对产L-精氨酸影响[D]. 南昌: 江西师范大学, 2023. |
| ZHANG H. Effects of cofactor and global transcription factor metabolic engineering modified Corynebacterium crenatum onL-arginine production[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Normal University, 2023. | |
| 4 | 李宜静. 孕妇血和脐血L-精氨酸水平与婴儿体格发育关系的前瞻性研究[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2019. |
| LI Y J. Maternal and cord bloodL-arginine level in relation to the body size in infants in the first year of life: a prospective study[D]. Guangzhou: Southern Medical University, 2019. | |
| 5 | 温伟红, 崔龙生. 一种精氨酸在化妆品中的研究应用[J]. 广东化工, 2019, 46(3): 51-52. |
| WEN W H, CUI L S. The application research of the arginine in cosmetics[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2019, 46(3): 51-52. | |
| 6 | WU M M, XIAO H, SHAO F Y, et al. Arginine accelerates intestinal health through cytokines and intestinal microbiota[J]. International Immunopharmacology, 2020, 81: 106029. |
| 7 | 刘晓华, 曹郁生, 陈燕. 精氨酸-共轭亚油酸抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2008, 36(8): 69-71. |
| LIU X H, CAO Y S, CHEN Y. Antioxidant activity of arginine-conjugated linoleic acid complex [J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2008, 36(8): 69-71. | |
| 8 | 王霞, 陶文沂, 孙志浩, 等. L-精氨酸发酵研究进展[J]. 工业微生物, 2000, 30(4): 50-54. |
| WANG X, TAO W Y, SUN Z H, et al. The progress of L-arginine fermentation[J]. Industrial Microbiology, 2000, 30(4): 50-54. | |
| 9 | 尹刚明, 李冰, 蔡妙颜, 等. 从头发中提取L-精氨酸的研究[J]. 现代食品科技, 2008, 24(9): 921-923, 906. |
| YIN G M, LI B, CAI M Y, et al. Extraction of L-arginine from human hair[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2008, 24(9): 921-923, 906. | |
| 10 | UTAGAWA T. Production of arginine by fermentation[J]. The Journal of Nutrition, 2004, 134(10): 2854S-2857S. |
| 11 | 龙梦飞, 徐美娟, 张显, 等. 合成生物学与代谢工程在谷氨酸棒杆菌产氨基酸中的应用[J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2019, 49(5): 541-552. |
| LONG M F, XU M J, ZHANG X, et al. Synthetic biology and metabolic engineering for amino acid production in Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 2019, 49(5): 541-552. | |
| 12 | CHENG G, XU J Z, XIA X H, et al. Breeding L-arginine-producing strains by a novel mutagenesis method: atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP)[J]. Preparative Biochemistry & Biotechnology, 2016, 46(5): 509-516. |
| 13 | 雷庆子, 王博, 堵国成, 等. 诱变育种提高嗜盐四联球菌精氨酸和瓜氨酸利用能力[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2018, 44(6): 30-36. |
| LEI Q Z, WANG B, DU G C, et al. Enhancement of arginine and citrulline utilization ability of Tetragenococcus halophilus by mutation breeding[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2018, 44(6): 30-36. | |
| 14 | LU C D. Pathways and regulation of bacterial arginine metabolism and perspectives for obtaining arginine overproducing strains[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2006, 70(3): 261-272. |
| 15 | JIANG Y, SHENG Q, WU X Y, et al. L-arginine production in Corynebacterium glutamicum: manipulation and optimization of the metabolic process[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2021, 41(2): 172-185. |
| 16 | JORGE J M P, NGUYEN A Q D, PÉREZ-GARCÍA F, et al. Improved fermentative production of gamma-aminobutyric acid via the putrescine route: systems metabolic engineering for production from glucose, amino sugars, and xylose[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2017, 114(4): 862-873. |
| 17 | MEISWINKEL T M, RITTMANN D, LINDNER S N, et al. Crude glycerol-based production of amino acids and putrescine by Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 145: 254-258. |
| 18 | ZHANG B, YU M, ZHOU Y, et al. Improvement of L-ornithine production by attenuation of argF in engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum S9114[J]. AMB Express, 2018, 8(1): 26. |
| 19 | BECKER J, WITTMANN C. A field of dreams: lignin valorization into chemicals, materials, fuels, and health-care products[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2019, 37(6): 107360. |
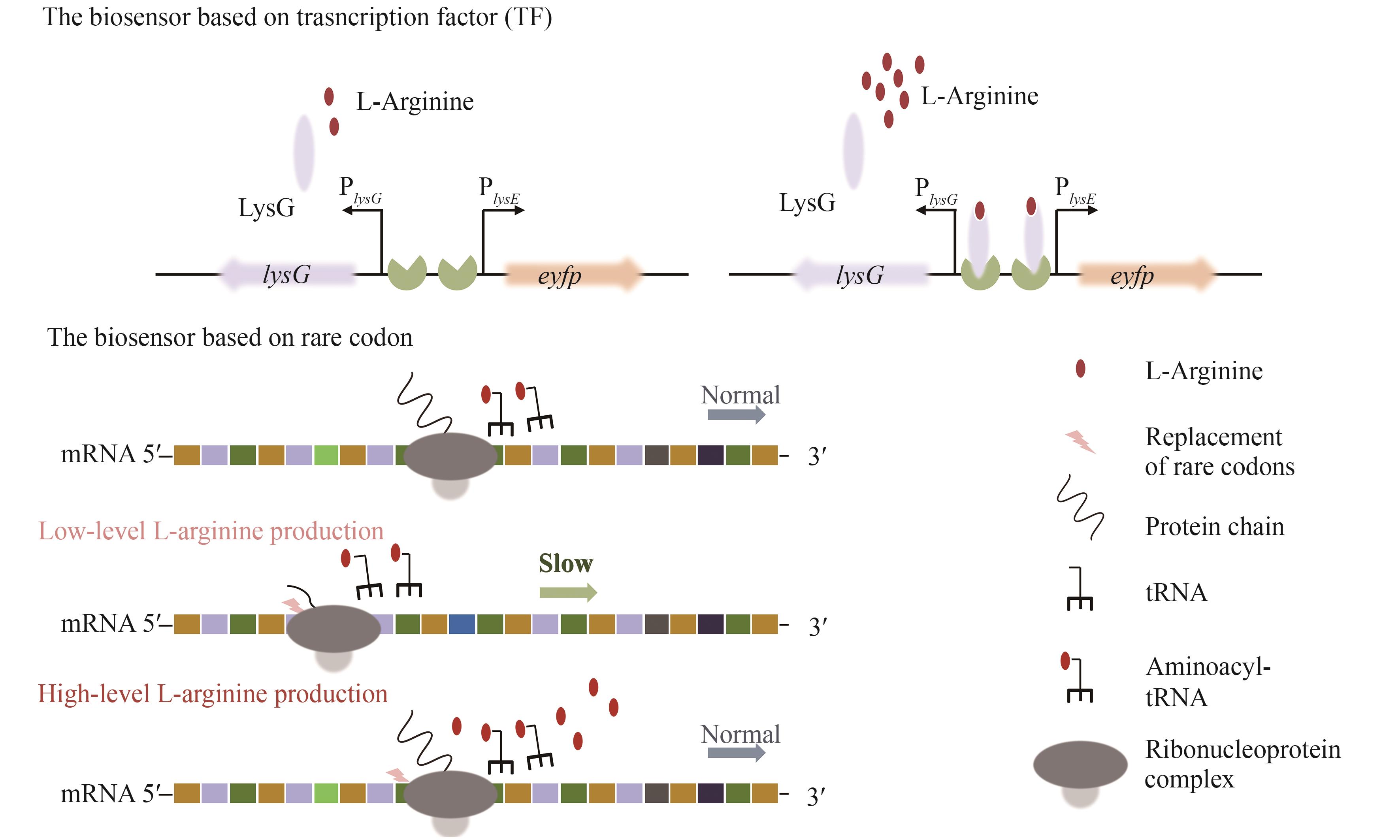
| 20 | JEANDET P, SOBARZO-SÁNCHEZ E, CLÉMENT C, et al. Engineering stilbene metabolic pathways in microbial cells[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2018, 36(8): 2264-2283. |
| 21 | KIM H T, KHANG T U, BARITUGO K A, et al. Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for the production of glutaric acid, a C5 dicarboxylic acid platform chemical[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 51: 99-109. |
| 22 | DUPERRAY F, JEZEQUEL D, GHAZI A, et al. Excretion of glutamate from Corynebacterium glutamicum triggered by amine surfactants[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)- Biomembranes, 1992, 1103(2): 250-258. |
| 23 | SCHNEIDER J, NIERMANN K, WENDISCH V F. Production of the amino acids L-glutamate, L-lysine, L-ornithine and L-arginine from arabinose by recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2011, 154(2/3): 191-198. |
| 24 | WANG H D, LIU S, WANG B B, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for efficient production of L-arginine[M/OL]// Advances in applied microbiology, 2023, 122: 127-150 [2024-03-01]. . |
| 25 | SGOBBA E, STUMPF A K, VORTMANN M, et al. Synthetic Escherichia coli-Corynebacterium glutamicum consortia for L-lysine production from starch and sucrose[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 260: 302-310. |
| 26 | 孙聪, 陈鑫, 上官春雨, 等. 钝齿棒杆菌黄素血红蛋白Hmp在L-精氨酸合成中的作用[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2022, 28(3): 561-568. |
| SUN C, CHEN X, SHANGGUAN C Y, et al. Role of Corynebacterium crenatum flavohemoglobin Hmp in the synthesis of L-arginine[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2022, 28(3): 561-568. | |
| 27 | 宋卓琳. 改造钝齿棒杆菌糖代谢途径提高L-精氨酸的产量[D]. 南昌: 江西师范大学, 2023. |
| SONG Z L. Modifying the glycometabolic pathway of Corynabacterium crenatum to increase L-arginine production[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Normal University, 2023. | |
| 28 | BECKER J, WITTMANN C. Bio-based production of chemicals, materials and fuels-Corynebacterium glutamicum as versatile cell factory[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2012, 23(4): 631-640. |
| 29 | SHIN J H, LEE S Y. Metabolic engineering of microorganisms for the production of L-arginine and its derivatives[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2014, 13: 166. |
| 30 | LI Y, CONG H, LIU B N, et al. Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for methionine production by removing feedback inhibition and increasing NADPH level[J]. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 2016, 109(9): 1185-1197. |
| 31 | MORIZONO H, CABRERA-LUQUE J, SHI D S, et al. Acetylornithine transcarbamylase: a novel enzyme in arginine biosynthesis[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2006, 188(8): 2974-2982. |
| 32 | CUNIN R, GLANSDORFF N, PIÉRARD A, et al. Biosynthesis and metabolism of arginine in bacteria[J]. Microbiological Reviews, 1986, 50(3): 314-352. |
| 33 | PIETTE J, CUNIN R, VAN VLIET F, et al. Homologous control sites and DNA transcription starts in the related argF and argI genes of Escherichia coli K12[J]. The EMBO Journal, 1982, 1(7): 853-857. |
| 34 | SAKANYAN V, PETROSYAN P, LECOCQ M, et al. Genes and enzymes of the acetyl cycle of arginine biosynthesis in Corynebacterium glutamicum: enzyme evolution in the early steps of the arginine pathway[J]. Microbiology, 1996, 142(Pt 1): 99-108. |
| 35 | HUANG Y Y, ZHANG H, TIAN H M, et al. Mutational analysis to identify the residues essential for the inhibition of N-acetyl glutamate kinase of Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 99(18): 7527-7537. |
| 36 | RAMÓN-MAIQUES S, FERNÁNDEZ-MURGA M L, GIL-ORTIZ F, et al. Structural bases of feed-back control of arginine biosynthesis, revealed by the structures of two hexameric N-acetylglutamate kinases, from Thermotoga maritima and Pseudomonas aeruginosa [J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2006, 356(3): 695-713. |
| 37 | SHENG Q, WU X Y, XU X Y, et al. Production of L-glutamate family amino acids in Corynebacterium glutamicum: physiological mechanism, genetic modulation, and prospects[J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2021, 6(4): 302-325. |
| 38 | ZHAN M L, KAN B J, DONG J J, et al. Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for improved L-arginine synthesis by enhancing NADPH supply[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2019, 46(1): 45-54. |
| 39 | PARK S H, KIM H U, KIM T Y, et al. Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for L-arginine production[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 4618. |
| 40 | ZHANG J J, XU M J, GE X X, et al. Reengineering of the feedback-inhibition enzyme N-acetyl-L-glutamate kinase to enhance L-arginine production in Corynebacterium crenatum [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2017, 44(2): 271-283. |
| 41 | WANG H D, XU J Z, ZHANG W G. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for efficient production of L-arginine[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2022, 106(17): 5603-5613. |
| 42 | MAN Z W, XU M J, RAO Z M, et al. Systems pathway engineering of Corynebacterium crenatum for improved L-arginine production[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 28629. |
| 43 | MAN Z W, RAO Z M, XU M J, et al. Improvement of the intracellular environment for enhancing L-arginine production of Corynebacterium glutamicum by inactivation of H2O2-forming flavin reductases and optimization of ATP supply[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2016, 38: 310-321. |
| 44 | ZHANG B, WAN F, QIU Y L, et al. Increased L-arginine production by site-directed mutagenesis of N-acetyl-L-glutamate kinase and proB gene deletion in Corynebacterium crenatum [J]. Biomedical and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 28(12): 864-874. |
| 45 | HUANG M Z, ZHAO Y, LI R, et al. Improvement of L-arginine production by in silico genome-scale metabolic network model guided genetic engineering[J]. 3 Biotech, 2020, 10(3): 126. |
| 46 | GUO J, MAN Z W, RAO Z M, et al. Improvement of the ammonia assimilation for enhancing L-arginine production of Corynebacterium crenatum [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2017, 44(3): 443-451. |
| 47 | XU M J, LI J, SHU Q F, et al. Enhancement of L-arginine production by increasing ammonium uptake in an AmtR-deficient Corynebacterium crenatum mutant[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2019, 46(8): 1155-1166. |
| 48 | GINESY M, BELOTSERKOVSKY J, ENMAN J, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for enhanced arginine biosynthesis[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2015, 14: 29. |
| 49 | XU M J, RAO Z M, YANG J, et al. The effect of a LYSE exporter overexpression on L-arginine production in Corynebacterium crenatum [J]. Current Microbiology, 2013, 67(3): 271-278. |
| 50 | XU M J, TANG M, CHEN J M, et al. PII signal transduction protein GlnK alleviates feedback inhibition of N-acetyl-L-glutamate kinase by L-arginine in Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2020, 86(8): e00039-20. |
| 51 | NIE M Z, WANG J Y, ZHANG K C. A novel strategy for L-arginine production in engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2023, 22(1): 138. |
| 52 | YIM S H, JUNG S, LEE S K, et al. Purification and characterization of an arginine regulatory protein, ArgR, in Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2011, 38(12): 1911-1920. |
| 53 | XU M J, RAO Z M, DOU W F, et al. The role of ARGR repressor regulation on L-arginine production in Corynebacterium crenatum [J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2013, 170(3): 587-597. |
| 54 | HÄNSSLER E, MÜLLER T, JESSBERGER N, et al. FarR, a putative regulator of amino acid metabolism in Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2007, 76(3): 625-632. |
| 55 | LEE S Y, PARK J M, LEE J H, et al. Interaction of transcriptional repressor ArgR with transcriptional regulator FarR at the argB promoter region in Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 77(3): 711-718. |
| 56 | CHEN X L, ZHANG B, TANG L, et al. Expression and characterization of ArgR, an arginine regulatory protein in Corynebacterium crenatum [J]. Biomedical and Environmental Sciences, 2014, 27(6): 436-443. |
| 57 | CHEN S H, MERICAN A F, SHERRATT D J. DNA binding of Escherichia coli arginine repressor mutants altered in oligomeric state[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 1997, 24(6): 1143-1156. |
| 58 | IKEDA M, MITSUHASHI S, TANAKA K, et al. Reengineering of a Corynebacterium glutamicum L-arginine and L-citrulline producer[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2009, 75(6): 1635-1641. |
| 59 | XU J Z, YANG H K, ZHANG W G. NADPH metabolism: a survey of its theoretical characteristics and manipulation strategies in amino acid biosynthesis[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2018, 38(7): 1061-1076. |
| 60 | CHEMLER J A, FOWLER Z L, MCHUGH K P, et al. Improving NADPH availability for natural product biosynthesis in Escherichia coli by metabolic engineering[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2010, 12(2): 96-104. |
| 61 | BECKER J, ZELDER O, HÄFNER S, et al. From zero to hero-design-based systems metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for L-lysine production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2011, 13(2): 159-168. |
| 62 | TAKENO S, MURATA R, KOBAYASHI R, et al. Engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum with an NADPH-generating glycolytic pathway for L-lysine production[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2010, 76(21): 7154-7160. |
| 63 | YUAN L, QIN Y L, ZOU Z C, et al. Enhancing intracellular NADPH bioavailability through improving pentose phosphate pathway flux and its application in biocatalysis asymmetric reduction reaction[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2022, 134(6): 528-533. |
| 64 | LINDNER S N, NIEDERHOLTMEYER H, SCHMITZ K, et al. Polyphosphate/ATP-dependent NAD kinase of Corynebacterium glutamicum: biochemical properties and impact of ppnK overexpression on lysine production[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2010, 87(2): 583-593. |
| 65 | SHAFEY H M EL, GHANEM S, MERKAMM M, et al. Corynebacterium glutamicum superoxide dismutase is a manganese-strict non-cambialistic enzyme in vitro [J]. Microbiological Research, 2008, 163(1): 80-86. |
| 66 | ELLIS R J. Macromolecular crowding: an important but neglected aspect of the intracellular environment[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2001, 11(1): 114-119. |
| 67 | ZHOU J W, LIU L M, SHI Z P, et al. ATP in current biotechnology: regulation, applications and perspectives[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2009, 27(1): 94-101. |
| 68 | HARA K Y, KONDO A. ATP regulation in bioproduction[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2015, 14: 198. |
| 69 | LIU L M, LI Y, DU G C, et al. Increasing glycolytic flux in Torulopsis glabrata by redirecting ATP production from oxidative phosphorylation to substrate-level phosphorylation[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2006, 100(5): 1043-1053. |
| 70 | MAJUMDAR R, BARCHI B, TURLAPATI S A, et al. Glutamate, ornithine, arginine, proline, and polyamine metabolic interactions: the pathway is regulated at the post-transcriptional level[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 78. |
| 71 | LONG M F, XU M J, MA Z F, et al. Significantly enhancing production of trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline by integrated system engineering in Escherichia coli [J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(21): eaba2383. |
| 72 | LEE S Y, CHO J Y, LEE H J, et al. Enhancement of ornithine production in proline-supplemented Corynebacterium glutamicum by ornithine cyclodeaminase[J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2010, 20(1): 127-131. |
| 73 | WENDISCH V F, JORGE J M P, PÉREZ-GARCÍA F, et al. Updates on industrial production of amino acids using Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2016, 32(6): 105. |
| 74 | WANG Q, JIANG A, TANG J B, et al. Enhanced production of L-arginine by improving carbamoyl phosphate supply in metabolically engineered Corynebacterium crenatum [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2021, 105(8): 3265-3276. |
| 75 | CHARLIER D, BERVOETS I. Regulation of arginine biosynthesis, catabolism and transport in Escherichia coli [J]. Amino Acids, 2019, 51(8): 1103-1127. |
| 76 | APPLEBAUM D M, DUNLAP J C, MORRIS D R. Comparison of the biosynthetic and biodegradative ornithine decarboxylases of Escherichia coli [J]. Biochemistry, 1977, 16(8): 1580-1584. |
| 77 | SHIRAI H, MIZUGUCHI K. Prediction of the structure and function of AstA and AstB, the first two enzymes of the arginine succinyltransferase pathway of arginine catabolism[J]. FEBS Letters, 2003, 555(3): 505-510. |
| 78 | SANDER T, WANG C Y, GLATTER T, et al. CRISPRi-based downregulation of transcriptional feedback improves growth and metabolism of arginine overproducing E. coli [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(9): 1983-1990. |
| 79 | NAKAMURA J, HIRANO S, ITO H, et al. Mutations of the Corynebacterium glutamicum NCgl1221 gene, encoding a mechanosensitive channel homolog, induce L-glutamic acid production[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2007, 73(14): 4491-4498. |
| 80 | BOUVIER J, STRAGIER P, MORALES V, et al. Lysine represses transcription of the Escherichia coli dapB gene by preventing its activation by the ArgP activator[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2008, 190(15): 5224-5229. |
| 81 | CELIS R T. Repression and activation of arginine transport genes in Escherichia coli K12 by the ArgP protein[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 1999, 294(5): 1087-1095. |
| 82 | MARBANIANG C N, GOWRISHANKAR J. Transcriptional cross-regulation between Gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, demonstrated using ArgP-argO of Escherichia coli and LysG-lysE of Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2012, 194(20): 5657-5666. |
| 83 | NANDINENI M R, GOWRISHANKAR J. Evidence for an arginine exporter encoded by yggA (argO) that is regulated by the LysR-type transcriptional regulator ArgP in Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2004, 186(11): 3539-3546. |
| 84 | PATHANIA A, SARDESAI A A. Distinct paths for basic amino acid export in Escherichia coli: YbjE (LysO) mediates export of L-lysine[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2015, 197(12): 2036-2047. |
| 85 | PATHANIA A, GUPTA A K, DUBEY S, et al. The topology of the L-arginine exporter ArgO conforms to an Nin-Cout configuration in Escherichia coli: requirement for the cytoplasmic N-terminal domain, functional helical interactions, and an aspartate pair for ArgO function[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2016, 198(23): 3186-3199. |
| 86 | JIANG S, WANG D H, WANG R R, et al. Reconstructing a recycling and nonauxotroph biosynthetic pathway in Escherichia coli toward highly efficient production of L-citrulline[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2021, 68: 220-231. |
| 87 | CHEN M L, CHEN X L, WAN F, et al. Effect of Tween 40 and DtsR1 on L-arginine overproduction in Corynebacterium crenatum [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2015, 14: 119. |
| 88 | NARESH V, LEE N. A review on biosensors and recent development of nanostructured materials-enabled biosensors[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(4): 1109. |
| 89 | LIN J L, WAGNER J M, ALPER H S. Enabling tools for high-throughput detection of metabolites: Metabolic engineering and directed evolution applications[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2017, 35(8): 950-970. |
| 90 | 蒲伟, 陈久洲, 王钰, 等. 氨基酸生物传感器的开发及应用研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2023, 39(6): 2485-2501. |
| PU W, CHEN J Z, WANG Y, et al. Advances of development and application amino acid biosensors[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2023, 39(6): 2485-2501. | |
| 91 | XU M J, LIU P P, CHEN J M, et al. Development of a novel biosensor-driven mutation and selection system via in situ growth of Corynebacterium crenatum for the production of L-arginine[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2020, 8: 175. |
| 92 | TUO J K, NAWAB S, MA X Y, et al. Recent advances in screening amino acid overproducers[J]. Engineering Microbiology, 2023, 3(1): 100066. |
| 93 | BELLMANN A, VRLJIĆ M, PÁTEK M, et al. Expression control and specificity of the basic amino acid exporter LysE of Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Microbiology, 2001, 147(Pt 7): 1765-1774. |
| 94 | BINDER S, SCHENDZIELORZ G, STÄBLER N, et al. A high-throughput approach to identify genomic variants of bacterial metabolite producers at the single-cell level[J]. Genome Biology, 2012, 13(5): R40. |
| 95 | SCHENDZIELORZ G, DIPPONG M, GRÜNBERGER A, et al. Taking control over control: use of product sensing in single cells to remove flux control at key enzymes in biosynthesis pathways[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2014, 3(1): 21-29. |
| 96 | STELLA R G, BAUMANN P, LORKE S, et al. Biosensor-based isolation of amino acid-producing Vibrio natriegens strains[J]. Metabolic Engineering Communications, 2021, 13: e00187. |
| 97 | JIANG S, WANG R R, WANG D H, et al. Metabolic reprogramming and biosensor-assisted mutagenesis screening for high-level production of L-arginine in Escherichia coli [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2023, 76: 146-157. |
| 98 | ZHENG B, MA X Y, WANG N, et al. Utilization of rare codon-rich markers for screening amino acid overproducers[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 3616. |
| 99 | 周文娟, 付刚, 齐显尼, 等. 发酵工业菌种的迭代创制[J]. 生物工程学报, 2022, 38(11): 4200-4218. |
| ZHOU W J, FU G, QI X N, et al. Upgrading microbial strains for fermentation industry[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2022, 38(11): 4200-4218. | |
| 100 | LIU J, OU Y, XU J Z, et al. L-lysine production by systems metabolic engineering of an NADPH auto-regulated Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 387: 129701. |
| 101 | LI Y J, WEI H B, WANG T, et al. Current status on metabolic engineering for the production of L-aspartate family amino acids and derivatives[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 245(Pt B): 1588-1602. |
| 102 | ZHAO Z Q, CAI M M, LIU Y R, et al. Genomics and transcriptomics-guided metabolic engineering Corynebacterium glutamicum for L-arginine production[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 364: 128054. |
| 103 | WEN J B, XIAO Y Q, LIU T, et al. Rich biotin content in lignocellulose biomass plays the key role in determining cellulosic glutamic acid accumulation by Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2018, 11: 132. |
| 104 | WITTHOFF S, SCHMITZ K, NIEDENFÜHR S, et al. Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for methanol metabolism[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 81(6): 2215-2225. |
| 105 | WHITAKER W B, JONES J A, BENNETT R K, et al. Engineering the biological conversion of methanol to specialty chemicals in Escherichia coli [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 39: 49-59. |
| 106 | BENNETT R K, GONZALEZ J E, WHITAKER W B, et al. Expression of heterologous non-oxidative pentose phosphate pathway from Bacillus methanolicus and phosphoglucose isomerase deletion improves methanol assimilation and metabolite production by a synthetic Escherichia coli methylotroph[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 45: 75-85. |
| 107 | CHEN F Y H, JUNG H W, TSUEI C Y, et al. Converting Escherichia coli to a synthetic methylotroph growing solely on methanol[J]. Cell, 2020, 182(4): 933-946. e14. |
| 108 | REITER M A, BRADLEY T, BÜCHEL L A, et al. A synthetic methylotrophic Escherichia coli as a chassis for bioproduction from methanol[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2024, 7(5): 560-573. |
| 109 | TUYISHIME P, WANG Y, FAN L W, et al. Engineering Corynebacterium glutamicum for methanol-dependent growth and glutamate production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 49: 220-231. |
| 110 | GREGORY G J, BENNETT R K, PAPOUTSAKIS E T. Recent advances toward the bioconversion of methane and methanol in synthetic methylotrophs[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2022, 71: 99-116. |
| 111 | BRAUTASET T, JAKOBSEN Ø M, JOSEFSEN K D, et al. Bacillus methanolicus: a candidate for industrial production of amino acids from methanol at 50 ℃[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2007, 74(1): 22-34. |
| 112 | BRAUTASET T, JAKOBSEN Ø M, DEGNES K F, et al. Bacillus methanolicus pyruvate carboxylase and homoserine dehydrogenaseⅠand Ⅱ and their roles for L-lysine production from methanol at 50 ℃[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2010, 87(3): 951-964. |
| [1] | 吴柯, 罗家豪, 李斐然. 机器学习驱动的基因组规模代谢模型构建与优化[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(3): 566-584. |
| [2] | 田晓军, 张日新. 合成基因回路面临的细胞“经济学窘境”[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(3): 532-546. |
| [3] | 李永珠, 陈禹. 酵母基因组规模模型进展及发展趋势[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(3): 585-602. |
| [4] | 章益蜻, 刘高雯. 合成生物学视角下的基因功能探索与酵母工程菌株文库构建[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(3): 685-700. |
| [5] | 黄怡, 司同, 陆安静. 生物制造标准体系建设的现状、问题与建议[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(3): 701-714. |
| [6] | 宋成治, 林一瀚. AI+定向进化赋能蛋白改造及优化[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(3): 617-635. |
| [7] | 高琪, 肖文海. 酵母合成单萜类化合物的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(2): 357-372. |
| [8] | 张梦瑶, 蔡鹏, 周雍进. 合成生物学助力萜类香精香料可持续生产[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(2): 334-356. |
| [9] | 张璐鸥, 徐丽, 胡晓旭, 杨滢. 合成生物学助力化妆品走进生物制造新时代[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(2): 479-491. |
| [10] | 伊进行, 唐宇琳, 李春雨, 吴鹤云, 马倩, 谢希贤. 氨基酸衍生物在化妆品中的应用及其生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(2): 254-289. |
| [11] | 韦灵珍, 王佳, 孙新晓, 袁其朋, 申晓林. 黄酮类化合物生物合成及其在化妆品中应用的研究[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(2): 373-390. |
| [12] | 肖森, 胡立涛, 石智诚, 王发银, 余思婷, 堵国成, 陈坚, 康振. 可控分子量透明质酸的生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(2): 445-460. |
| [13] | 左一萌, 张姣姣, 连佳长. 酿酒酵母使能技术在化妆品原料合成中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(2): 233-253. |
| [14] | 汤传根, 王璟, 张烁, 张昊宁, 康振. 功能肽合成和挖掘策略研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(2): 461-478. |
| [15] | 郭婷婷, 韩湘凝, 黄熙婷, 张婷婷, 孔健. 乳酸菌的合成生物学工具及在合成益肤因子中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(2): 320-333. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||