Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (1): 67-85.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-047
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Optimization and development of CRISPR/Cas9 systems for genome editing
TENG Xiaolong, SHI Shuobo
- Beijing Advanced Innovation Center of Soft Matter Science and Engineering,Beijing University of Chemical Technology,Beijing 100029,China
-
Received:2022-09-01Revised:2022-10-28Online:2023-03-07Published:2023-02-28 -
Contact:SHI Shuobo
CRISPR/Cas9系统在基因组编辑中的优化与发展
滕小龙, 史硕博
- 北京化工大学,北京软物质科学与工程高精尖创新中心,北京 100029
-
通讯作者:史硕博 -
作者简介:滕小龙 (1996—),男,硕士研究生。研究方向为CRISPR/Cas9工具的开发与应用。E-mail:2020210871@mail.buct.edu.cn史硕博 (1981—),男,教授。研究方向为代谢工程与合成生物学的基础与应用性研究,构建和改造微生物使其能够直接用于高效生产有用的化学品、植物天然产物等生物制品等。E-mail:shishuobo@mail.buct.edu.cn
第一联系人:滕小龙(1996—),男,硕士研究生。研究方向为CRISPR/Cas9工具的开发与应用。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(21878013)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
TENG Xiaolong, SHI Shuobo. Optimization and development of CRISPR/Cas9 systems for genome editing[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 67-85.
滕小龙, 史硕博. CRISPR/Cas9系统在基因组编辑中的优化与发展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 67-85.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2022-047
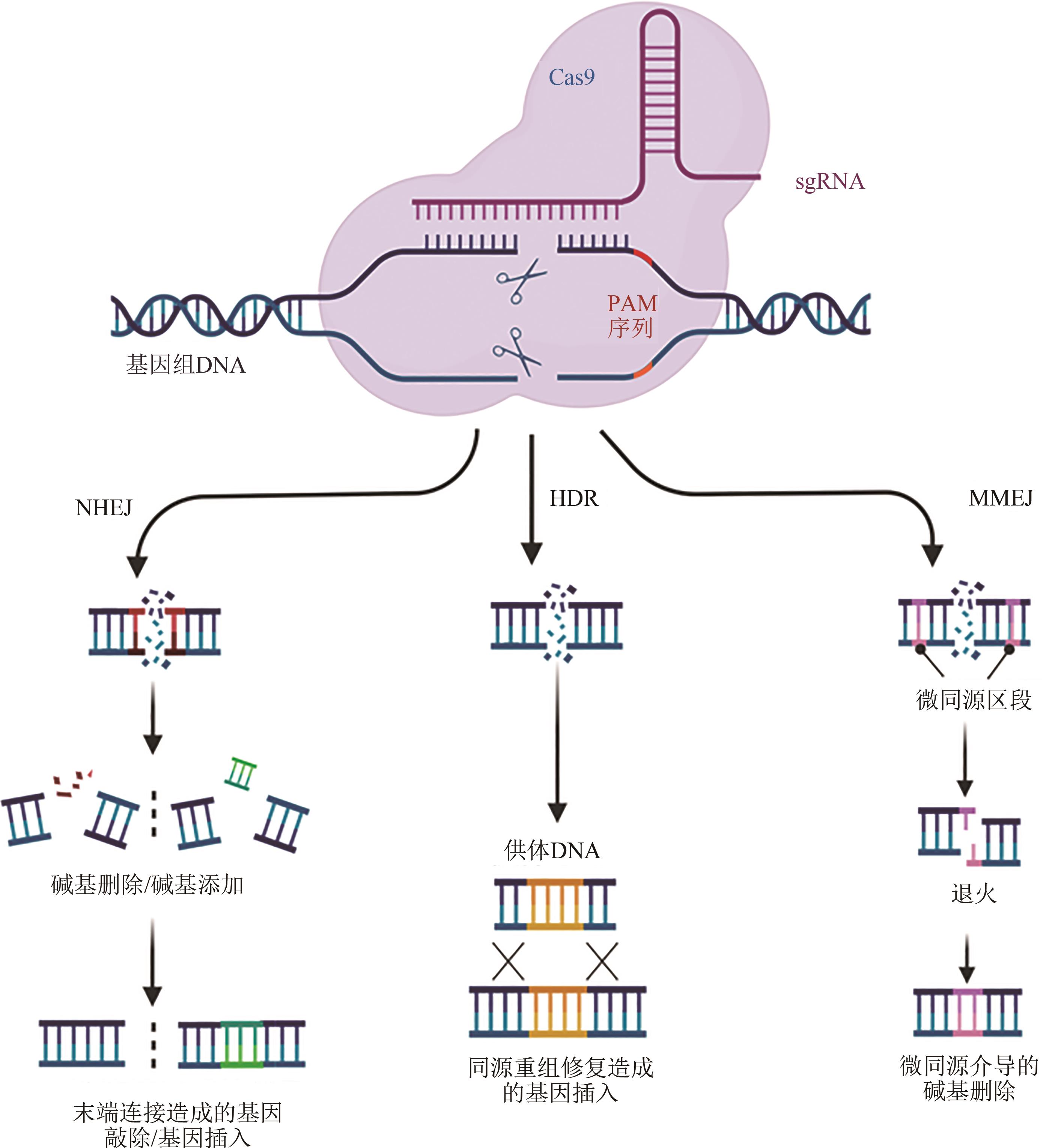
Fig. 1 Gene editing mechanism of CRISPR/Cas9 systems(NHEJ-mediated fragment deletion/insertion, HDR-mediated gene editing and MMEJ-mediated gene editing are shown diagrammatically from left and middle to right)
| 变体及直系同源 | 改造位点或方式 | PAM | 特性 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SpCas9 | 原生酿脓链球菌Cas9 | NGG | 1368个氨基酸 | [ |
| dCas9 | D10A,H840A | NGG | 核酸酶活性失活 | [ |
| nCas9(D10A) | D10A | NGG | 切口酶,非靶向链切割活性失活 | [ |
| nCas9(H840A) | H840A | NGG | 切口酶,靶向链切割活性失活 | [ |
| SpCas9NG | R1335V,L1111R,D1135V,G1218R,E1219F,A1322R,T1337R | NG | PAM改变;通过Cas9理性设计获得 | [ |
| VRERSpCas9 | D1135A,G1218R,R1335E,T1337R | NGCG | PAM改变;通过细菌选择性定向进化获得 | [ |
| VQRSpCas9 | D1135V,R1335Q,T1337R | NGAN,NGNG | PAM改变;通过细菌选择性定向进化获得 | [ |
| EQRSpCas9 | D1335E,R1335Q,T1337R | NGAG | PAM改变;通过细菌选择性定向进化获得 | [ |
| xCas9 | A262T,R324L,S409I,E480K,E543D,M694I,E1219V | NG,GAA,GAT | PAM改变;通过噬菌体辅助持续进化获得 | [ |
| SpG | D1135L,S1136W,G1218K,E1219Q,R1335Q,T1337R | NGN | PAM改变;通过SpCas9理性设计获得 | [ |
| SpRY | SpG,A61R,L1111R,A1322R,N1317R,R1333P | NRN,NYN | PAM改变;通过对SpG进一步理性设计获得 | [ |
| evoCas9 | M495V, Y515N, K526E, R661Q | NGG | 保真性提高,编辑效率接近天然SpCas9 | [ |
| fCas9 | SpdCas9与FokI融合 | NGG | 保真性提高;通过将FokI核酸酶与dCas9融合获得 | [ |
| StCas9 | 原生嗜热链球菌Cas9 | NNAGAAW | 1121个氨基酸 | [ |
| NmCas9 | 原生脑膜炎奈瑟菌Cas9 | NNNNGATT | 1082个氨基酸 | [ |
| SaCas9 | 原生金黄色葡萄球菌Cas9 | NNGRRT | 1053个氨基酸;基因组编辑效率与SpCas9相当 | [ |
| CjCas9 | 原生曲状杆菌Cas9 | NNNVRYM | 984个氨基酸 | [ |
Table 1 Major Cas9 variants and orthologues as well as their features
| 变体及直系同源 | 改造位点或方式 | PAM | 特性 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SpCas9 | 原生酿脓链球菌Cas9 | NGG | 1368个氨基酸 | [ |
| dCas9 | D10A,H840A | NGG | 核酸酶活性失活 | [ |
| nCas9(D10A) | D10A | NGG | 切口酶,非靶向链切割活性失活 | [ |
| nCas9(H840A) | H840A | NGG | 切口酶,靶向链切割活性失活 | [ |
| SpCas9NG | R1335V,L1111R,D1135V,G1218R,E1219F,A1322R,T1337R | NG | PAM改变;通过Cas9理性设计获得 | [ |
| VRERSpCas9 | D1135A,G1218R,R1335E,T1337R | NGCG | PAM改变;通过细菌选择性定向进化获得 | [ |
| VQRSpCas9 | D1135V,R1335Q,T1337R | NGAN,NGNG | PAM改变;通过细菌选择性定向进化获得 | [ |
| EQRSpCas9 | D1335E,R1335Q,T1337R | NGAG | PAM改变;通过细菌选择性定向进化获得 | [ |
| xCas9 | A262T,R324L,S409I,E480K,E543D,M694I,E1219V | NG,GAA,GAT | PAM改变;通过噬菌体辅助持续进化获得 | [ |
| SpG | D1135L,S1136W,G1218K,E1219Q,R1335Q,T1337R | NGN | PAM改变;通过SpCas9理性设计获得 | [ |
| SpRY | SpG,A61R,L1111R,A1322R,N1317R,R1333P | NRN,NYN | PAM改变;通过对SpG进一步理性设计获得 | [ |
| evoCas9 | M495V, Y515N, K526E, R661Q | NGG | 保真性提高,编辑效率接近天然SpCas9 | [ |
| fCas9 | SpdCas9与FokI融合 | NGG | 保真性提高;通过将FokI核酸酶与dCas9融合获得 | [ |
| StCas9 | 原生嗜热链球菌Cas9 | NNAGAAW | 1121个氨基酸 | [ |
| NmCas9 | 原生脑膜炎奈瑟菌Cas9 | NNNNGATT | 1082个氨基酸 | [ |
| SaCas9 | 原生金黄色葡萄球菌Cas9 | NNGRRT | 1053个氨基酸;基因组编辑效率与SpCas9相当 | [ |
| CjCas9 | 原生曲状杆菌Cas9 | NNNVRYM | 984个氨基酸 | [ |
| 功能 | 效应蛋白或gRNA工程 | 系统 | 特征 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 表达调控 | 无 | dCas9 | 原核生物基因抑制表达,真核生物基因抑制效率低 | [ |
| KRAB,MXI1,TUP1抑制结构域 | dCas9 | 可在真核生物中抑制基因表达 | [ | |
| KRAB-MeCP1融合抑制结构域 | dCas9 | 在哺乳动物细胞中高效抑制目的基因表达 | [ | |
| p65,VP64激活结构域 | dCas9 | 激活基因表达,效率较低 | [ | |
| VP64-p65-Rta(VPR)融合激活结构域 | dCas9 | 与VP64相比提高了22~320倍;多重基因激活表达;刺激iPSCs神经元分化 | [ | |
| gRNA工程;gRNA上携带携带两个MS2发夹二级结构 | dCas9 | 每个发夹结构招募一个MS2-p65-HSF1融合激活蛋白;与VP64相比,使10个靶基因上调2倍以上 | [ | |
| SPY系统(包括SpyTag和SpyCatcher)和Med2激活结构域 | dCas9 | 招募多拷贝SpyCatcher和Med2融合蛋白使酿酒酵母目的基因表达提高34.9倍 | [ | |
| SunTag系统(包括GCN4肽和抗GCN4抗体的单链可变片段scFv)和MIG1抑制结构域 | dCpf1 | 招募多拷贝ScFv与MIG1融合蛋白使酿酒酵母目的基因受到95%的抑制 | [ | |
| 表观基因组编辑 | KRAB-DNA甲基化酶催化结构域融合蛋白 | dCas9 | 融合抑制因子和甲基化酶;造成目的基因78%的稳定沉默 | [ |
| 两侧分别融合KRAB和Dnmt3A-Dnmt3L融合DNA甲基化酶结构域 | dCas9 | 在干细胞分裂分化为神经细胞后仍维持DNA甲基化和基因抑制 | [ | |
| TET1甲基胞嘧啶双加氧酶1催化结构域 | dCas9 | dCas9- TET1靶向至BRCA1基因启动子后成功地上调其表达水平 | [ | |
| 人类组蛋白乙酰基转移酶p300催化核心 | dCas9 | 催化组蛋白H3 第27位赖氨酸残基的乙酰基化;基因表达上调 | [ | |
| 单碱基编辑 | 胞嘧啶脱氨酶,腺嘌呤脱氨酶 | nCas9 | 在不造成DNA双链断裂的条件下使目的碱基产生C:G与T:A或A:T与G:C的碱基对替换 | [ |
| CBE-UGI融合蛋白 | nCas9 | UGI能够防止胞嘧啶C脱氨后的尿嘧啶U被切除,从而显著提高了CBEs的编辑效率 | [ | |
| 单链DNA结合结构域ssDBD融合到胞嘧啶脱氨酶与nCas9之间 | nCas9 | 通过延长ssDNA的暴露时间极大地提高CBEs的编辑效率;使CBEs的编辑窗口范围得到了提高 | [ | |
| 组合nCas9、胞嘧啶脱氨酶和尿嘧啶-DNA糖基化酶 | nCas9 | 首次实现大肠杆菌中C到A 87.2%和哺乳动物细胞C到G 5.3%至53.0%的编辑效率 | [ | |
| 先导编辑 | 通过gRNA工程改造的pegRNA;与逆转录酶融合 | nCas9 | 改变pegRNA可实现精确的碱基替换、基因敲除和插入 | [ |
| 通过gRNA工程改造的pegRNA;与逆转录酶和Rad51融合 | nCas9 | 融合单链DNA结合蛋白Rad51使PE2的编辑效率最高提升2.6倍 | [ |
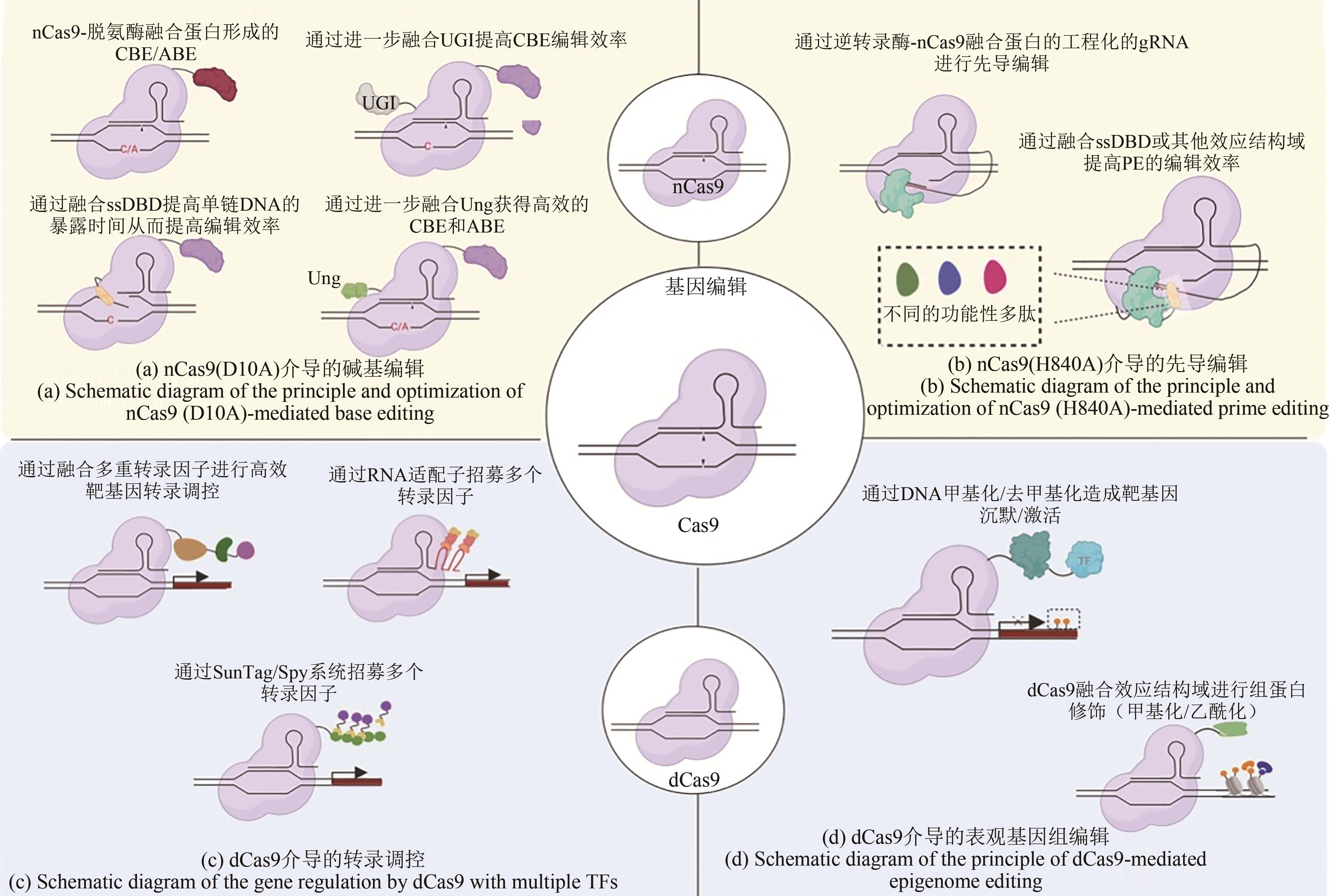
Table 2 Functional optimization through fusion expression of effector proteins with CRISPR/Cas9 system
| 功能 | 效应蛋白或gRNA工程 | 系统 | 特征 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 表达调控 | 无 | dCas9 | 原核生物基因抑制表达,真核生物基因抑制效率低 | [ |
| KRAB,MXI1,TUP1抑制结构域 | dCas9 | 可在真核生物中抑制基因表达 | [ | |
| KRAB-MeCP1融合抑制结构域 | dCas9 | 在哺乳动物细胞中高效抑制目的基因表达 | [ | |
| p65,VP64激活结构域 | dCas9 | 激活基因表达,效率较低 | [ | |
| VP64-p65-Rta(VPR)融合激活结构域 | dCas9 | 与VP64相比提高了22~320倍;多重基因激活表达;刺激iPSCs神经元分化 | [ | |
| gRNA工程;gRNA上携带携带两个MS2发夹二级结构 | dCas9 | 每个发夹结构招募一个MS2-p65-HSF1融合激活蛋白;与VP64相比,使10个靶基因上调2倍以上 | [ | |
| SPY系统(包括SpyTag和SpyCatcher)和Med2激活结构域 | dCas9 | 招募多拷贝SpyCatcher和Med2融合蛋白使酿酒酵母目的基因表达提高34.9倍 | [ | |
| SunTag系统(包括GCN4肽和抗GCN4抗体的单链可变片段scFv)和MIG1抑制结构域 | dCpf1 | 招募多拷贝ScFv与MIG1融合蛋白使酿酒酵母目的基因受到95%的抑制 | [ | |
| 表观基因组编辑 | KRAB-DNA甲基化酶催化结构域融合蛋白 | dCas9 | 融合抑制因子和甲基化酶;造成目的基因78%的稳定沉默 | [ |
| 两侧分别融合KRAB和Dnmt3A-Dnmt3L融合DNA甲基化酶结构域 | dCas9 | 在干细胞分裂分化为神经细胞后仍维持DNA甲基化和基因抑制 | [ | |
| TET1甲基胞嘧啶双加氧酶1催化结构域 | dCas9 | dCas9- TET1靶向至BRCA1基因启动子后成功地上调其表达水平 | [ | |
| 人类组蛋白乙酰基转移酶p300催化核心 | dCas9 | 催化组蛋白H3 第27位赖氨酸残基的乙酰基化;基因表达上调 | [ | |
| 单碱基编辑 | 胞嘧啶脱氨酶,腺嘌呤脱氨酶 | nCas9 | 在不造成DNA双链断裂的条件下使目的碱基产生C:G与T:A或A:T与G:C的碱基对替换 | [ |
| CBE-UGI融合蛋白 | nCas9 | UGI能够防止胞嘧啶C脱氨后的尿嘧啶U被切除,从而显著提高了CBEs的编辑效率 | [ | |
| 单链DNA结合结构域ssDBD融合到胞嘧啶脱氨酶与nCas9之间 | nCas9 | 通过延长ssDNA的暴露时间极大地提高CBEs的编辑效率;使CBEs的编辑窗口范围得到了提高 | [ | |
| 组合nCas9、胞嘧啶脱氨酶和尿嘧啶-DNA糖基化酶 | nCas9 | 首次实现大肠杆菌中C到A 87.2%和哺乳动物细胞C到G 5.3%至53.0%的编辑效率 | [ | |
| 先导编辑 | 通过gRNA工程改造的pegRNA;与逆转录酶融合 | nCas9 | 改变pegRNA可实现精确的碱基替换、基因敲除和插入 | [ |
| 通过gRNA工程改造的pegRNA;与逆转录酶和Rad51融合 | nCas9 | 融合单链DNA结合蛋白Rad51使PE2的编辑效率最高提升2.6倍 | [ |
| 宿主细胞 | 多重CRISPR策略 | 靶向目标数量 | 应用/概念验证 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 哺乳动物细胞 | 2个间隔区通过天然CRISPR序列自我加工 | 2个靶标(1个基因) | 对1个靶基因敲除,效率为1.6% | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | Casy4核酸酶加工 | 3个基因 | 同时对3个不同启动子进行激活,使得3个报告基因荧光强度提升了2倍 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 基于Csy4核酸酶加工的多gRNA快速组装 | 12个靶标(3个基因) | 通过12个gRNA靶向使得3个报告基因荧光强度分别被抑制了92%、81%和95% | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 基于tRNA转录本切割机制的多gRNA表达系统 | 8个基因 | 通过两轮8个基因的敲除获得了30倍的游离脂肪酸产量 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 多个gRNA表达盒通过pol Ⅲ启动子启动 | 3个基因 | 将适配子与gRNA融合进行多基因调控,获得了不同的紫罗兰素生物合成产物 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 基于Csy4核酸酶加工的多gRNA快速组装策略及多Cas9正交组合调控 | 3个基因 | 通过组合调控使两个报告基因表达分别被抑制和激活5倍,同时以95%的效率敲除第三个基因 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 通过质粒表达多个gRNA表达盒以及截短gRNA用于调控 | 3个基因 | 通过对三个基因分别进行编辑、激活和抑制获得了α-檀香烯2.66倍的产量 | [ |
| 马克思克鲁维酵母(Kluyveromyces marxianus) | 基于tRNA转录本切割机制的多gRNA表达系统 | 6个靶标(4个基因) | 通过对4个基因进行调控,使乙酸乙酯的产量提升了3.8倍 | [ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 多个gRNA表达盒通过质粒表达 | 3个基因 | 通过对3个基因进行组合调控得到了2.3倍苹果酸产量菌株 | [ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 多个gRNA表达盒通过质粒表达 | 3个基因 | 对苹果酸合成途径基因进行组合调控后获得了2.3倍苹果酸产量菌株 | [ |
| 枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis) | 多个gRNA表达盒整合至基因组 | 3个基因 | 通过多基因动态组合调控提高了N-乙酰葡糖胺产量 | [ |
| 天蓝色链霉菌(Streptomyces coelicolor) | 多个gRNA表达盒与dCas9在质粒上表达 | 4个基因 | 通过对4个靶基因同时进行抑制,使其mRNA表达量降为对照的2%~32% | [ |
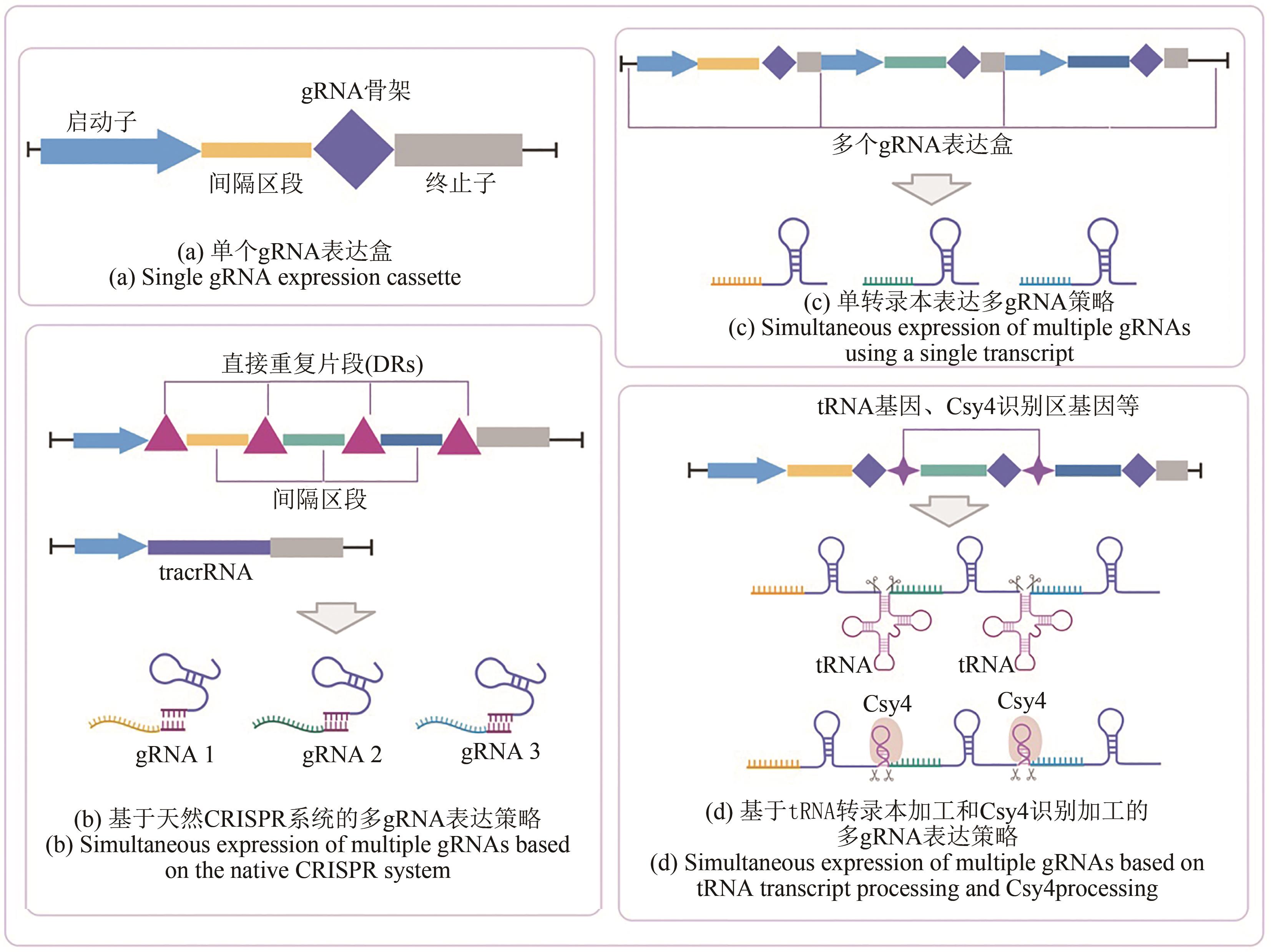
Table 3 Research on the applications of the multiplexed CRISPR/Cas9 system
| 宿主细胞 | 多重CRISPR策略 | 靶向目标数量 | 应用/概念验证 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 哺乳动物细胞 | 2个间隔区通过天然CRISPR序列自我加工 | 2个靶标(1个基因) | 对1个靶基因敲除,效率为1.6% | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | Casy4核酸酶加工 | 3个基因 | 同时对3个不同启动子进行激活,使得3个报告基因荧光强度提升了2倍 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 基于Csy4核酸酶加工的多gRNA快速组装 | 12个靶标(3个基因) | 通过12个gRNA靶向使得3个报告基因荧光强度分别被抑制了92%、81%和95% | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 基于tRNA转录本切割机制的多gRNA表达系统 | 8个基因 | 通过两轮8个基因的敲除获得了30倍的游离脂肪酸产量 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 多个gRNA表达盒通过pol Ⅲ启动子启动 | 3个基因 | 将适配子与gRNA融合进行多基因调控,获得了不同的紫罗兰素生物合成产物 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 基于Csy4核酸酶加工的多gRNA快速组装策略及多Cas9正交组合调控 | 3个基因 | 通过组合调控使两个报告基因表达分别被抑制和激活5倍,同时以95%的效率敲除第三个基因 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 通过质粒表达多个gRNA表达盒以及截短gRNA用于调控 | 3个基因 | 通过对三个基因分别进行编辑、激活和抑制获得了α-檀香烯2.66倍的产量 | [ |
| 马克思克鲁维酵母(Kluyveromyces marxianus) | 基于tRNA转录本切割机制的多gRNA表达系统 | 6个靶标(4个基因) | 通过对4个基因进行调控,使乙酸乙酯的产量提升了3.8倍 | [ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 多个gRNA表达盒通过质粒表达 | 3个基因 | 通过对3个基因进行组合调控得到了2.3倍苹果酸产量菌株 | [ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 多个gRNA表达盒通过质粒表达 | 3个基因 | 对苹果酸合成途径基因进行组合调控后获得了2.3倍苹果酸产量菌株 | [ |
| 枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis) | 多个gRNA表达盒整合至基因组 | 3个基因 | 通过多基因动态组合调控提高了N-乙酰葡糖胺产量 | [ |
| 天蓝色链霉菌(Streptomyces coelicolor) | 多个gRNA表达盒与dCas9在质粒上表达 | 4个基因 | 通过对4个靶基因同时进行抑制,使其mRNA表达量降为对照的2%~32% | [ |
| 1 | ISHINO Y, SHINAGAWA H, MAKINO K, et al. Nucleotide sequence of the iap gene, responsible for alkaline phosphatase isozyme conversion in Escherichia coli, and identification of the gene product[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1987, 169(12): 5429-5433. |
| 2 | JANSEN R, VAN EMBDEN J D A, GAASTRA W, et al. Identification of genes that are associated with DNA repeats in prokaryotes[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2002, 43(6): 1565-1575. |
| 3 | BROUNS S J J, JORE M M, LUNDGREN M, et al. Small CRISPR RNAs guide antiviral defense in prokaryotes[J]. Science, 2008, 321(5891): 960-964. |
| 4 | CONG L, RAN F A, COX D, et al. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems[J]. Science, 2013, 339(6121): 819-823. |
| 5 | BARRANGOU R. CRISPR-Cas systems and RNA-guided interference[J]. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: RNA, 2013, 4(3): 267-278. |
| 6 | SHMAKOV S, ABUDAYYEH O O, MAKAROVA K S, et al. Discovery and functional characterization of diverse class 2 CRISPR-cas systems[J]. Molecular Cell, 2015, 60(3): 385-397. |
| 7 | CHANDRASEGARAN S, CARROLL D. Origins of programmable nucleases for genome engineering[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2016, 428(5): 963-989. |
| 8 | PORTEUS M H, CARROLL D. Gene targeting using zinc finger nucleases[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2005, 23(8): 967-973. |
| 9 | JOUNG J K, SANDER J D. TALENs: a widely applicable technology for targeted genome editing[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2013, 14(1): 49-55. |
| 10 | WYMAN C, KANAAR R. DNA double-strand break repair: all's well that ends well[J]. Annual Review of Genetics, 2006, 40: 363-383. |
| 11 | GAO C X. Genome engineering for crop improvement and future agriculture[J]. Cell, 2021, 184(6): 1621-1635. |
| 12 | CHANG H H Y, PANNUNZIO N R, ADACHI N, et al. Non-homologous DNA end joining and alternative pathways to double-strand break repair[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2017, 18(8): 495-506. |
| 13 | RAN F A, HSU P D, LIN C Y, et al. Double nicking by RNA-guided CRISPR Cas9 for enhanced genome editing specificity[J]. Cell, 2013, 154(6): 1380-1389. |
| 14 | RAN F A, HSU P D, WRIGHT J, et al. Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system[J]. Nature Protocols, 2013, 8(11): 2281-2308. |
| 15 | ZHU S Y, LI W, LIU J Z, et al. Genome-scale deletion screening of human long non-coding RNAs using a paired-guide RNA CRISPR-Cas9 library[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2016, 34(12): 1279-1286. |
| 16 | PAQUET D, KWART D, CHEN A, et al. Efficient introduction of specific homozygous and heterozygous mutations using CRISPR/Cas9[J]. Nature, 2016, 533(7601): 125-129. |
| 17 | REIDER APEL A, D'ESPAUX L, WEHRS M, et al. A Cas9-based toolkit to program gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2016, 45(1): 496-508. |
| 18 | MORENO A M, FU X, ZHU J, et al. In situ gene therapy via AAV-CRISPR-Cas9-mediated targeted gene regulation[J]. Mol Ther, 2018, 26(7): 1818-1827. |
| 19 | KLEINSTIVER B P, PREW M S, TSAI S Q, et al. Engineered CRISPR-Cas9 nucleases with altered PAM specificities[J]. Nature, 2015, 523(7561): 481-485. |
| 20 | HU J H, MILLER S M, GEURTS M H, et al. Evolved Cas9 variants with broad PAM compatibility and high DNA specificity[J]. Nature, 2018, 556(7699): 57-63. |
| 21 | KOCAK D D, JOSEPHS E A, BHANDARKAR V, et al. Increasing the specificity of CRISPR systems with engineered RNA secondary structures[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2019, 37(6): 657-666. |
| 22 | QI L S, LARSON M H, GILBERT L A, et al. Repurposing CRISPR as an RNA-guided platform for sequence-specific control of gene expression[J]. Cell, 2013, 152(5): 1173-1183. |
| 23 | PEREZ-PINERA P, KOCAK D D, VOCKLEY C M, et al. RNA-guided gene activation by CRISPR-Cas9-based transcription factors[J]. Nature Methods, 2013, 10(10): 973-976. |
| 24 | MAEDER M L, LINDER S J, CASCIO V M, et al. CRISPR RNA-guided activation of endogenous human genes[J]. Nature Methods, 2013, 10(10): 977-979. |
| 25 | NAKAMURA M, GAO Y C, DOMINGUEZ A A, et al. CRISPR technologies for precise epigenome editing[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2021, 23(1): 11-22. |
| 26 | ANZALONE A V, KOBLAN L W, LIU D R. Genome editing with CRISPR-Cas nucleases, base editors, transposases and prime editors[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(7): 824-844. |
| 27 | ANZALONE A V, RANDOLPH P B, DAVIS J R, et al. Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand breaks or donor DNA[J]. Nature, 2019, 576(7785): 149-157. |
| 28 | LIU G W, LIN Q P, JIN S, et al. The CRISPR-Cas toolbox and gene editing technologies[J]. Molecular Cell, 2022, 82(2): 333-347. |
| 29 | THAKORE P I, BLACK J B, HILTON I B, et al. Editing the epigenome: technologies for programmable transcription and epigenetic modulation[J]. Nature Methods, 2016, 13(2): 127-137. |
| 30 | KOMOR A C, KIM Y B, PACKER M S, et al. Programmable editing of a target base in genomic DNA without double-stranded DNA cleavage[J]. Nature, 2016, 533(7603): 420-424. |
| 31 | NISHIMASU H, SHI X, ISHIGURO S, et al. Engineered CRISPR-Cas9 nuclease with expanded targeting space[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6408): 1259-1262. |
| 32 | WALTON R T, CHRISTIE K A, WHITTAKER M N, et al. Unconstrained genome targeting with near-PAMless engineered CRISPR-Cas9 variants[J]. Science, 2020, 368(6488): 290-296. |
| 33 | CASINI A, OLIVIERI M, PETRIS G, et al. A highly specific SpCas9 variant is identified by in vivo screening in yeast[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(3): 265-271. |
| 34 | GUILINGER J P, THOMPSON D B, LIU D R. Fusion of catalytically inactive Cas9 to FokI nuclease improves the specificity of genome modification[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2014, 32(6): 577-582. |
| 35 | DEVEAU H, BARRANGOU R, GARNEAU J E, et al. Phage response to CRISPR-encoded resistance in Streptococcus thermophilus [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2008, 190(4): 1390-1400. |
| 36 | ESVELT K M, MALI P, BRAFF J L, et al. Orthogonal Cas9 proteins for RNA-guided gene regulation and editing[J]. Nature Methods, 2013, 10(11): 1116-1121. |
| 37 | RAN F A, CONG L, YAN W X, et al. In vivo genome editing using Staphylococcus aureus Cas9[J]. Nature, 2015, 520(7546): 186-191. |
| 38 | KIM E, KOO T, PARK S W, et al. In vivo genome editing with a small Cas9 orthologue derived from Campylobacter jejuni[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 14500. |
| 39 | JINEK M, CHYLINSKI K, FONFARA I, et al. A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity[J]. Science, 2012, 337(6096): 816-821. |
| 40 | MALI P, YANG L H, ESVELT K M, et al. RNA-guided human genome engineering via Cas9[J]. Science, 2013, 339(6121): 823-826. |
| 41 | DELTCHEVA E, CHYLINSKI K, SHARMA C M, et al. CRISPR RNA maturation by trans-encoded small RNA and host factor RNase III[J]. Nature, 2011, 471(7340): 602-607. |
| 42 | GASIUNAS G, BARRANGOU R, HORVATH P, et al. Cas9-crRNA ribonucleoprotein complex mediates specific DNA cleavage for adaptive immunity in bacteria[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(39): E2579-E2586. |
| 43 | DONG C, JIANG L H, XU S J, et al. A single Cas9-VPR nuclease for simultaneous gene activation, repression, and editing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(9): 2252-2257. |
| 44 | FU Y F, SANDER J D, REYON D, et al. Improving CRISPR-Cas nuclease specificity using truncated guide RNAs[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2014, 32(3): 279-284. |
| 45 | CHO S W, KIM S, KIM Y, et al. Analysis of off-target effects of CRISPR/Cas-derived RNA-guided endonucleases and nickases[J]. Genome Research, 2014, 24(1): 132-141. |
| 46 | NØDVIG C S, NIELSEN J B, KOGLE M E, et al. A CRISPR-Cas9 system for genetic engineering of filamentous fungi[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(7): e0133085. |
| 47 | CHOI K R, LEE S Y. CRISPR technologies for bacterial systems: current achievements and future directions[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2016, 34(7): 1180-1209. |
| 48 | FRIEDLAND A E, TZUR Y B, ESVELT K M, et al. Heritable genome editing in C. elegans via a CRISPR-Cas9 system[J]. Nature Methods, 2013, 10(8): 741-743. |
| 49 | SHEN B, ZHANG J, WU H Y, et al. Generation of gene-modified mice via Cas9/RNA-mediated gene targeting[J]. Cell Research, 2013, 23(5): 720-723. |
| 50 | HWANG W Y, FU Y F, REYON D, et al. Efficient genome editing in zebrafish using a CRISPR-Cas system[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2013, 31(3): 227-229. |
| 51 | JIANG W Z, ZHOU H B, BI H H, et al. Demonstration of CRISPR/Cas9/sgRNA-mediated targeted gene modification in Arabidopsis, tobacco, sorghum and rice[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2013, 41(20): e188. |
| 52 | HSU P D, LANDER E S, ZHANG F. Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering[J]. Cell, 2014, 157(6): 1262-1278. |
| 53 | FU Y F, FODEN J A, KHAYTER C, et al. High-frequency off-target mutagenesis induced by CRISPR-Cas nucleases in human cells[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2013, 31(9): 822-826. |
| 54 | MILLER S M, WANG T N, RANDOLPH P B, et al. Continuous evolution of SpCas9 variants compatible with non-G PAMs[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(4): 471-481. |
| 55 | SLAYMAKER I M, GAO L Y, ZETSCHE B, et al. Rationally engineered Cas9 nucleases with improved specificity[J]. Science, 2016, 351(6268): 84-88. |
| 56 | KLEINSTIVER B P, PATTANAYAK V, PREW M S, et al. High-fidelity CRISPR-Cas9 nucleases with no detectable genome-wide off-target effects[J]. Nature, 2016, 529(7587): 490-495. |
| 57 | CHEN J S, DAGDAS Y S, KLEINSTIVER B P, et al. Enhanced proofreading governs CRISPR-Cas9 targeting accuracy[J]. Nature, 2017, 550(7676): 407-410. |
| 58 | VAKULSKAS C A, DEVER D P, RETTIG G R, et al. A high-fidelity Cas9 mutant delivered as a ribonucleoprotein complex enables efficient gene editing in human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells[J]. Nature Medicine, 2018, 24(8): 1216-1224. |
| 59 | ROSE J C, POPP N A, RICHARDSON C D, et al. Suppression of unwanted CRISPR-Cas9 editing by co-administration of catalytically inactivating truncated guide RNAs[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 2697. |
| 60 | ZHANG Y, HEIDRICH N, AMPATTU B J, et al. Processing-independent CRISPR RNAs limit natural transformation in Neisseria meningitidis [J]. Molecular Cell, 2013, 50(4): 488-503. |
| 61 | HOU Z, ZHANG Y, PROPSON N E, et al. Efficient genome engineering in human pluripotent stem cells using Cas9 from Neisseria meningitidis [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(39): 15644-15649. |
| 62 | GILBERT L A, LARSON M H, MORSUT L, et al. CRISPR-mediated modular RNA-guided regulation of transcription in eukaryotes[J]. Cell, 2013, 154(2): 442-451. |
| 63 | EDMONDSON D G, SMITH M M, ROTH S Y. Repression domain of the yeast global repressor Tup1 interacts directly with histones H3 and H4[J]. Genes & Development, 1996, 10(10): 1247-1259. |
| 64 | YEO N C, CHAVEZ A, LANCE-BYRNE A, et al. An enhanced CRISPR repressor for targeted mammalian gene regulation[J]. Nature Methods, 2018, 15(8): 611-616. |
| 65 | FARZADFARD F, PERLI S D, LU T K. Tunable and multifunctional eukaryotic transcription factors based on CRISPR/Cas[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2013, 2(10): 604-613. |
| 66 | XU X S, QI L S. A CRISPR-dCas toolbox for genetic engineering and synthetic biology[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2019, 431(1): 34-47. |
| 67 | CHAVEZ A, SCHEIMAN J, VORA S, et al. Highly efficient Cas9-mediated transcriptional programming[J]. Nature Methods, 2015, 12(4): 326-328. |
| 68 | KONERMANN S, BRIGHAM M D, TREVINO A E, et al. Genome-scale transcriptional activation by an engineered CRISPR-Cas9 complex[J]. Nature, 2015, 517(7536): 583-588. |
| 69 | ZHAI H T, CUI L, XIONG Z, et al. CRISPR-mediated protein-tagging signal amplification systems for efficient transcriptional activation and repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2022, 50(10): 5988-6000. |
| 70 | AMABILE A, MIGLIARA A, CAPASSO P, et al. Inheritable silencing of endogenous genes by hit-and-run targeted epigenetic editing[J]. Cell, 2016, 167(1): 219-232.e14. |
| 71 | NUÑEZ J K, CHEN J, POMMIER G C, et al. Genome-wide programmable transcriptional memory by CRISPR-based epigenome editing[J]. Cell, 2021, 184(9): 2503-2519.e17. |
| 72 | CHOUDHURY S R, CUI Y, LUBECKA K, et al. CRISPR-dCas9 mediated TET1 targeting for selective DNA demethylation at BRCA1 promoter[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(29): 46545-46556. |
| 73 | HILTON I B, D'IPPOLITO A M, VOCKLEY C M, et al. Epigenome editing by a CRISPR-Cas9-based acetyltransferase activates genes from promoters and enhancers[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2015, 33(5): 510-517. |
| 74 | HESS G T, FRÉSARD L, HAN K, et al. Directed evolution using dCas9-targeted somatic hypermutation in mammalian cells[J]. Nature Methods, 2016, 13(12): 1036-1042. |
| 75 | GAUDELLI N M, KOMOR A C, REES H A, et al. Programmable base editing of A·T to G·C in genomic DNA without DNA cleavage[J]. Nature, 2017, 551(7681): 464-471. |
| 76 | ZHANG X H, CHEN L, ZHU B Y, et al. Increasing the efficiency and targeting range of cytidine base editors through fusion of a single-stranded DNA-binding protein domain[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2020, 22(6): 740-750. |
| 77 | ZHAO D D, LI J, LI S W, et al. Glycosylase base editors enable C-to-A and C-to-G base changes[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2021, 39(1): 35-40. |
| 78 | SONG M, LIM J M, MIN S, et al. Generation of a more efficient prime editor 2 by addition of the Rad51 DNA-binding domain[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 5617. |
| 79 | LATCHMAN D S. Transcription factors: an overview[J]. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 1997, 29(12): 1305-1312. |
| 80 | KARIN M. Too many transcription factors: positive and negative interactions[J]. The New Biologist, 1990, 2(2): 126-131. |
| 81 | DEUSCHLE U, MEYER W K, THIESEN H J. Tetracycline-reversible silencing of eukaryotic promoters[J]. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 1995, 15(4): 1907-1914. |
| 82 | GOSSEN M, BUJARD H. Tight control of gene expression in mammalian cells by tetracycline-responsive promoters[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1992, 89(12): 5547-5551. |
| 83 | SADOWSKI I, MA J, TRIEZENBERG S, et al. GAL4-VP16 is an unusually potent transcriptional activator[J]. Nature, 1988, 335(6190): 563-564. |
| 84 | ZHANG L, SPRATT S K, LIU Q, et al. Synthetic zinc finger transcription factor action at an endogenous chromosomal site: activation of the human erythropoietin gene[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2000, 275(43): 33850-33860. |
| 85 | CONG L, ZHOU R H, KUO Y C, et al. Comprehensive interrogation of natural TALE DNA-binding modules and transcriptional repressor domains[J]. Nature Communications, 2012, 3: 968. |
| 86 | MAEDER M L, LINDER S J, REYON D, et al. Robust, synergistic regulation of human gene expression using TALE activators[J]. Nature Methods, 2013, 10(3): 243-245. |
| 87 | PEREZ-PINERA P, OUSTEROUT D G, BRUNGER J M, et al. Synergistic and tunable human gene activation by combinations of synthetic transcription factors[J]. Nature Methods, 2013, 10(3): 239-242. |
| 88 | GILBERT L A, HORLBECK M A, ADAMSON B, et al. Genome-scale CRISPR-mediated control of gene repression and activation[J]. Cell, 2014, 159(3): 647-661. |
| 89 | LARSON M H, GILBERT L A, WANG X W, et al. CRISPR interference (CRISPRi) for sequence-specific control of gene expression[J]. Nature Protocols, 2013, 8(11): 2180-2196. |
| 90 | SUN M Y, JU J, DING Y, et al. The signaling pathways regulated by KRAB zinc-finger proteins in cancer[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Reviews on Cancer, 2022, 1877(3): 188731. |
| 91 | KEARNS N A, GENGA R M J, ENUAMEH M S, et al. Cas9 effector-mediated regulation of transcription and differentiation in human pluripotent stem cells[J]. Development, 2014, 141(1): 219-223. |
| 92 | GAO X F, TSANG J C H, GABA F, et al. Comparison of TALE designer transcription factors and the CRISPR/dCas9 in regulation of gene expression by targeting enhancers[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2014, 42(20): e155. |
| 93 | KEARNS N A, PHAM H, TABAK B, et al. Functional annotation of native enhancers with a Cas9-histone demethylase fusion[J]. Nature Methods, 2015, 12(5): 401-403. |
| 94 | THAKORE P I, D'IPPOLITO A M, SONG L Y, et al. Highly specific epigenome editing by CRISPR-Cas9 repressors for silencing of distal regulatory elements[J]. Nature Methods, 2015, 12(12): 1143-1149. |
| 95 | TANENBAUM M E, GILBERT L A, QI L S, et al. A protein-tagging system for signal amplification in gene expression and fluorescence imaging[J]. Cell, 2014, 159(3): 635-646. |
| 96 | JIANG W, FENG S J, HUANG S S, et al. BE-PLUS: a new base editing tool with broadened editing window and enhanced fidelity[J]. Cell Research, 2018, 28(8): 855-861. |
| 97 | GALLEGO-BARTOLOMÉ J, GARDINER J, LIU W L, et al. Targeted DNA demethylation of the Arabidopsis genome using the human TET1 catalytic domain[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(9): E2125-E2134. |
| 98 | MORITA S, NOGUCHI H, HORII T, et al. Targeted DNA demethylation in vivo using dCas9-peptide repeat and scFv-TET1 catalytic domain fusions[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2016, 34(10): 1060-1065. |
| 99 | HUANG Y H, SU J Z, LEI Y, et al. DNA epigenome editing using CRISPR-Cas suntag-directed DNMT3A[J]. Genome Biology, 2017, 18: 176. |
| 100 | ZHANG X, WANG W, SHAN L, et al. Gene activation in human cells using CRISPR/Cpf1-p300 and CRISPR/Cpf1-SunTag systems[J]. Protein & Cell, 2018, 9(4): 380-383. |
| 101 | ZHUO C Y, ZHANG J B, LEE J H, et al. Spatiotemporal control of CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing[J]. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 2021, 6: 238. |
| 102 | CHEN J J, HAN M Y, GONG T, et al. Epigenetic modification enhances ergot alkaloid production of Claviceps purpurea [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2019, 41(12): 1439-1449. |
| 103 | HOFACKER D, BROCHE J, LAISTNER L, et al. Engineering of effector domains for targeted DNA methylation with reduced off-target effects[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(2): 502. |
| 104 | GLOBAL BURDEN OF DISEASE STUDY 2013 Collaborators. Global, regional, and incidence national, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013[J]. The Lancet, 2015, 386(9995): 743-800. |
| 105 | HAAPANIEMI E, BOTLA S, PERSSON J, et al. CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing induces a p53-mediated DNA damage response[J]. Nature Medicine, 2018, 24(7): 927-930. |
| 106 | IHRY R J, WORRINGER K A, SALICK M R, et al. p53 inhibits CRISPR-Cas9 engineering in human pluripotent stem cells[J]. Nature Medicine, 2018, 24(7): 939-946. |
| 107 | 李广栋, 张鲁, 富俊才, 等. 单碱基编辑工具—腺嘌呤碱基编辑器ABE的研究进展[J]. 农业生物技术学报, 2019, 27(10): 1831-1839. |
| LI G D, ZHANG L, FU J C, et al. Advances in research on single base editing tool—adenine base editor ABE[J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2019, 27(10): 1831-1839. | |
| 108 | KIM Y B, KOMOR A C, LEVY J M, et al. Increasing the genome-targeting scope and precision of base editing with engineered Cas9-cytidine deaminase fusions[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2017, 35(4): 371-376. |
| 109 | KOBLAN L W, DOMAN J L, WILSON C, et al. Improving cytidine and adenine base editors by expression optimization and ancestral reconstruction[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(9): 843-846. |
| 110 | DAVIS J R, WANG X, WITTE I P, et al. Efficient in vivo base editing via single adeno-associated viruses with size-optimized genomes encoding compact adenine base editors[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2022, 6(11): 1272-1283. |
| 111 | CHEN S Y, LIU Z Q, XIE W H, et al. Compact Cje3Cas9 for efficient in vivo genome editing and adenine base editing[J]. The CRISPR Journal, 2022, 5(3): 472-486. |
| 112 | VELIMIROVIC M, ZANETTI L C, SHEN M W, et al. Peptide fusion improves prime editing efficiency[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 3512. |
| 113 | FERREIRA R, SKREKAS C, NIELSEN J, et al. Multiplexed CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing and gene regulation using Csy4 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(1): 10-15. |
| 114 | MCCARTY N S, SHAW W M, ELLIS T, et al. Rapid assembly of gRNA arrays via modular cloning in yeast[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(4): 906-910. |
| 115 | ZHANG Y P, WANG J, WANG Z B, et al. A gRNA-tRNA array for CRISPR-Cas9 based rapid multiplexed genome editing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 1053. |
| 116 | MCCARTY N S, GRAHAM A E, STUDENÁ L, et al. Multiplexed CRISPR technologies for gene editing and transcriptional regulation[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 1281. |
| 117 | JIANG W Y, BIKARD D, COX D, et al. RNA-guided editing of bacterial genomes using CRISPR-Cas systems[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2013, 31(3): 233-239. |
| 118 | ZALATAN J G, LEE M E, ALMEIDA R, et al. Engineering complex synthetic transcriptional programs with CRISPR RNA scaffolds[J]. Cell, 2015, 160(1/2): 339-350. |
| 119 | LIAN J Z, HAMEDIRAD M, HU S M, et al. Combinatorial metabolic engineering using an orthogonal tri-functional CRISPR system[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 1688. |
| 120 | LÖBS A K, SCHWARTZ C, THORWALL S, et al. Highly multiplexed CRISPRi repression of respiratory functions enhances mitochondrial localized ethyl acetate biosynthesis in Kluyveromyces marxianus [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(11): 2647-2655. |
| 121 | GAO C, WANG S H, HU G P, et al. Engineering Escherichia coli for malate production by integrating modular pathway characterization with CRISPRi-guided multiplexed metabolic tuning[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2018, 115(3): 661-672. |
| 122 | WU Y K, CHEN T C, LIU Y F, et al. CRISPRi allows optimal temporal control of N-acetylglucosamine bioproduction by a dynamic coordination of glucose and xylose metabolism in Bacillus subtilis [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 49: 232-241. |
| 123 | ZHAO Y W, LI L, ZHENG G S, et al. CRISPR/dCas9-mediated multiplex gene repression in streptomyces[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2018, 13(9): 1800121. |
| 124 | FAN R, CHAI Z Z, XING S N, et al. Shortening the sgRNA-DNA interface enables SpCas9 and eSpCas9(1.1) to nick the target DNA strand[J]. Science China Life Sciences, 2020, 63(11): 1619-1630. |
| 125 | LIU K I, RAMLI M N B, WOO C W A, et al. A chemical-inducible CRISPR-Cas9 system for rapid control of genome editing[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2016, 12(11): 980-987. |
| 126 | SHIN J, JIANG F G, LIU J J, et al. Disabling Cas9 by an anti-CRISPR DNA mimic[J]. Science Advances, 2017, 3(7): e1701620. |
| 127 | JAIN S, XUN G H, ABESTEH S, et al. Precise regulation of Cas9-mediated genome engineering by anti-CRISPR-based inducible CRISPR controllers[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2021, 10(6): 1320-1327. |
| 128 | YIN J H, LU R S, XIN C C, et al. Cas9 exo-endonuclease eliminates chromosomal translocations during genome editing[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 1204. |
| 129 | YEH W H, SHUBINA-OLEINIK O, LEVY J M, et al. In vivo base editing restores sensory transduction and transiently improves auditory function in a mouse model of recessive deafness[J]. Science Translational Medicine, 2020, 12(546): eaay9101. |
| 130 | WANG L R, LI L X, MA Y L, et al. Reactivation of γ-globin expression through Cas9 or base editor to treat β-hemoglobinopathies[J]. Cell Research, 2020, 30(3): 276-278. |
| [1] | REN Jiawei, ZHANG Jinpeng, XU Guoqiang, ZHANG Xiaomei, XU Zhenghong, ZHANG Xiaojuan. Effect of terminators on the downstream transcript unit with gene expression in Escherichiacoli [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 213-227. |
| [2] | HUI Zhen, TANG Xiaoyu. Applications of the CRISPR/Cas9 editing system in the study of microbial natural products [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 658-671. |
| [3] | YANG Yi, MAO Yufeng, YANG Chunhe, WANG Meng, LIAO Xiaoping, MA Hongwu. Recent progress in computational tools for designing editing sequences used in microbial genetic manipulations [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 30-46. |
| [4] | Qingzhuo WANG, Ping SONG, He HUANG. Synthetic biotechnology drives the development of natural eukaryotic lipid cell factories [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(6): 920-941. |
| [5] | Dan ZENG, Jianlin CHU, Yanru CHEN, Daidi FAN. Biological synthesis and applications of artificial protein functional materials [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(4): 528-542. |
| [6] | Qian LIU, Jingen LI, Chenyang ZHANG, Fangya LI, Chaoguang TIAN. Research progress of genome editing technologies for industrial filamentous fungi [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(2): 256-273. |
| [7] | Yong YU, Xinna ZHU, Xueli ZHANG. Construction and application of microbial cell factories for production of bulk chemicals [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(6): 674-684. |
| [8] | Hui WANG, Junbiao DAI, Zhouqing LUO. Reading, editing, and writing techniques for genome research [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(5): 503-515. |
| [9] | Zhongzheng CAO, Xinyi ZHANG, Yiyuan XU, Zhuo ZHOU, Wensheng WEI. Genome editing technology and its applications in synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(4): 413-426. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||