Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (5): 932-946.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-035
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of automated high-throughput technology in natural product biosynthesis
HU Zhehui1,2, XU Juan2, BIAN Guangkai1
- 1.Insititute of Syntheitc Biology,Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenzhen 518055,Guangdong,China
2.National Key Laboeratory for Germplasm Innovation & Utilization of Horticultural Crops,College of Horticulture and Forestry,Huazhong Agricultural University,Wuhan 430071,Hubei,China
-
Received:2023-05-06Revised:2023-07-24Online:2023-11-15Published:2023-10-31 -
Contact:BIAN Guangkai
自动化高通量技术在天然产物生物合成中的应用
胡哲辉1,2, 徐娟2, 卞光凯1
- 1.中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院合成生物学研究所,广东 深圳 518055
2.华中农业大学园艺林学学院,果蔬园艺作物种质创新与利用全国重点实验室,湖北 武汉 430071
-
通讯作者:卞光凯 -
作者简介:胡哲辉 (1998—),男,博士研究生。研究方向为植物来源萜类天然产物生物合成。E-mail:zh.hu2@siat.ac.cn卞光凯 (1986—),男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为天然产物生物合成及高值天然产物高效合成;利用合成生物学手段改造丝状真菌生产高性能生物材料。E-mail:gk.bian@siat.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划“绿色生物制造”重点专项(2022YFC2106100);国家自然科学基金面上项目(32070063)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
HU Zhehui, XU Juan, BIAN Guangkai. Application of automated high-throughput technology in natural product biosynthesis[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(5): 932-946.
胡哲辉, 徐娟, 卞光凯. 自动化高通量技术在天然产物生物合成中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 932-946.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2023-035
| 应用领域 | 传统方法 | 自动化高通量方法 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 方式 | 特点 | 方式 | 特点 | |
| 天然产物的挖掘 | 直接分离 同源激活 异源表达 | 生物样本单一 局限于单个基因的异源表达 产物丰度低、筛选通量低 | 打造特定微生物高产底盘 基于海量数据库批量挖掘 高通量工作站自动化验证 | 不受限于特定的生物样本 充分释放酶的产物合成潜力 规模化、自动化 |
| 天然产物高效合成 | 突变体文库平板筛选 关键酶的定点诱变 人工改造代谢通路 | 突变体间微小差异分辨率低 试错过程需要消耗大量劳动力 无法完全释放酶的催化潜力 | 基于auto-HTP对突变体文库高效筛选 自动化改造底盘细胞 限速酶定向进化 微生物适应性进化 | 自动化实现海量试错 多维度改造底盘细胞 缩短菌株改造研发周期 |
| 天然产物的快速检测 | 气相色谱、质谱 液相色谱、质谱 核磁共振 基于紫外/可见光谱检测 | 耗时长、通量低 对目标产物的产量和纯度要求高 | 基于荧光光谱检测 基于生物传感器的荧光检测 基于先进光谱技术的检测 | 便捷、高效、省时 对目标产物的动态、实时、自动化检测 |
Table 1 A comparison of automated high-throughput and traditional methods in natural product biosynthesis
| 应用领域 | 传统方法 | 自动化高通量方法 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 方式 | 特点 | 方式 | 特点 | |
| 天然产物的挖掘 | 直接分离 同源激活 异源表达 | 生物样本单一 局限于单个基因的异源表达 产物丰度低、筛选通量低 | 打造特定微生物高产底盘 基于海量数据库批量挖掘 高通量工作站自动化验证 | 不受限于特定的生物样本 充分释放酶的产物合成潜力 规模化、自动化 |
| 天然产物高效合成 | 突变体文库平板筛选 关键酶的定点诱变 人工改造代谢通路 | 突变体间微小差异分辨率低 试错过程需要消耗大量劳动力 无法完全释放酶的催化潜力 | 基于auto-HTP对突变体文库高效筛选 自动化改造底盘细胞 限速酶定向进化 微生物适应性进化 | 自动化实现海量试错 多维度改造底盘细胞 缩短菌株改造研发周期 |
| 天然产物的快速检测 | 气相色谱、质谱 液相色谱、质谱 核磁共振 基于紫外/可见光谱检测 | 耗时长、通量低 对目标产物的产量和纯度要求高 | 基于荧光光谱检测 基于生物传感器的荧光检测 基于先进光谱技术的检测 | 便捷、高效、省时 对目标产物的动态、实时、自动化检测 |
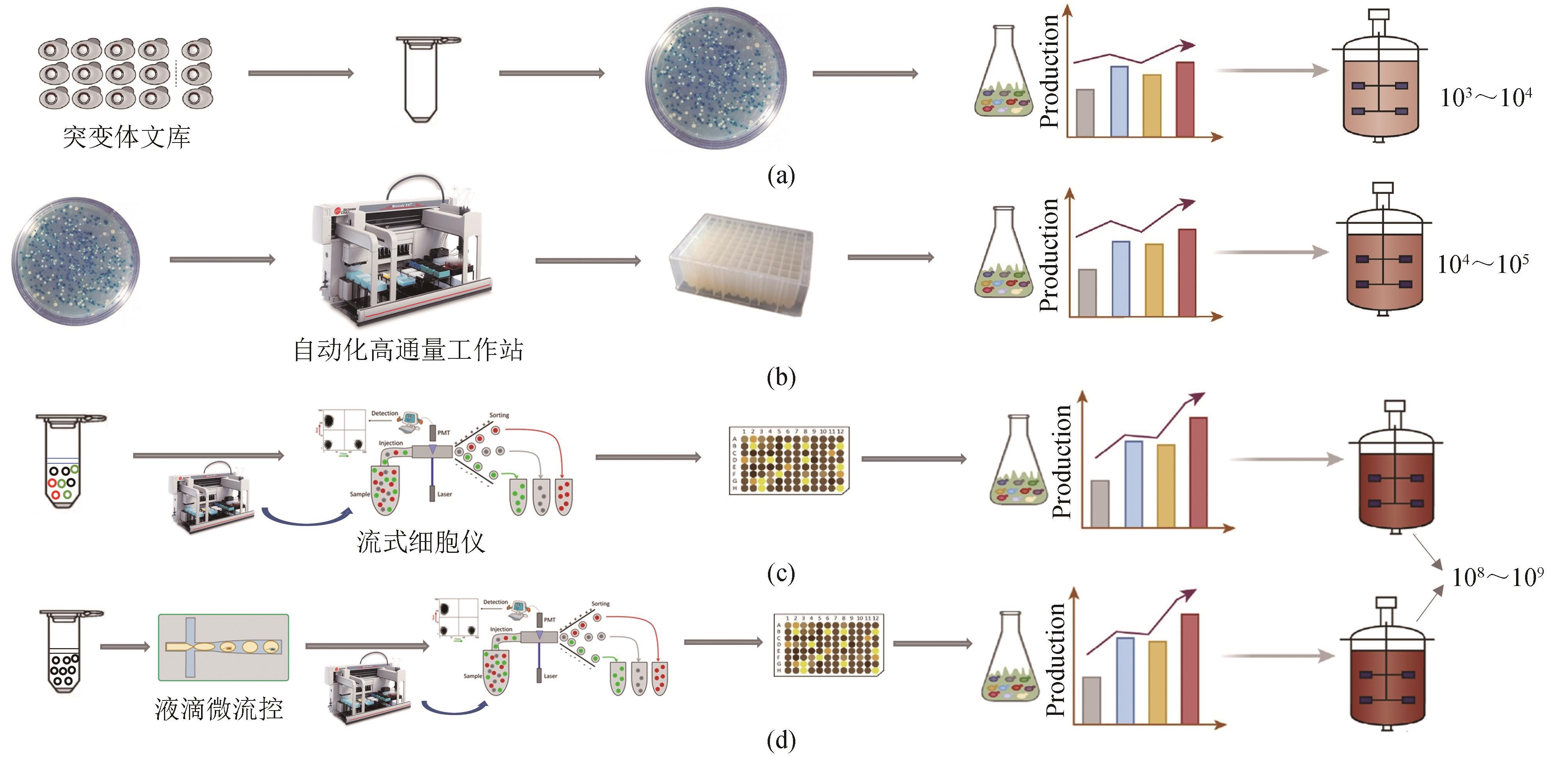
Fig. 1 A comparison of different screening methods[41-42](a) Traditional screening method based on agar plates, with a screening throughput of 103~104; (b) Microplate screening method based on automation equipment, with a screening throughput of 104~105; (c) Fluorescence activated cell sorting, with a screening throughput of 108~109; (d) Droplet-based microfluidic sorting, with a screening throughput of 108~109
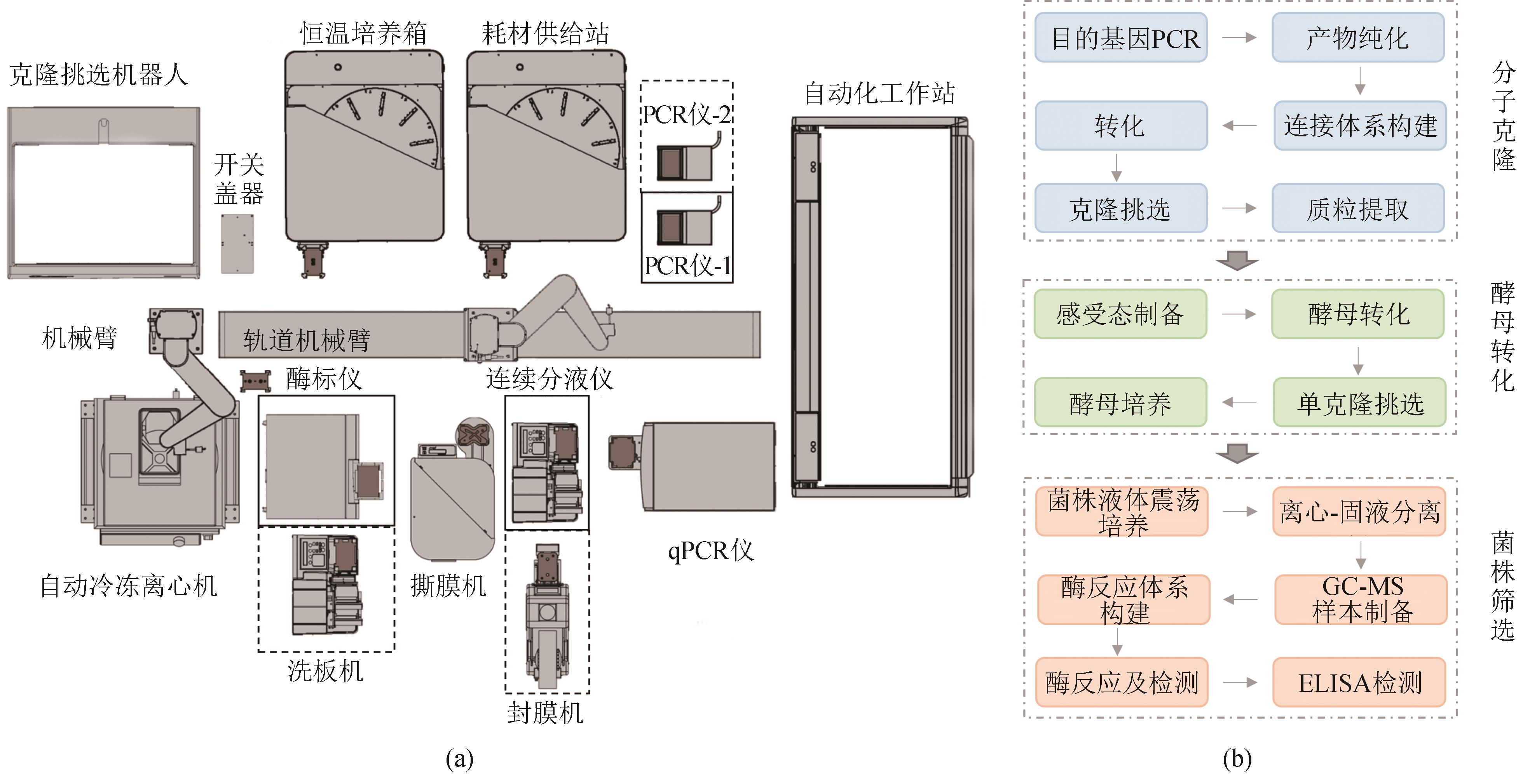
Fig. 2 Automated high-throughput workstation(a) Schematic diagram of the automated high-throughput workstation; (b) A representative workflow of automated high-throughput process, with yeast engineering shown as an example
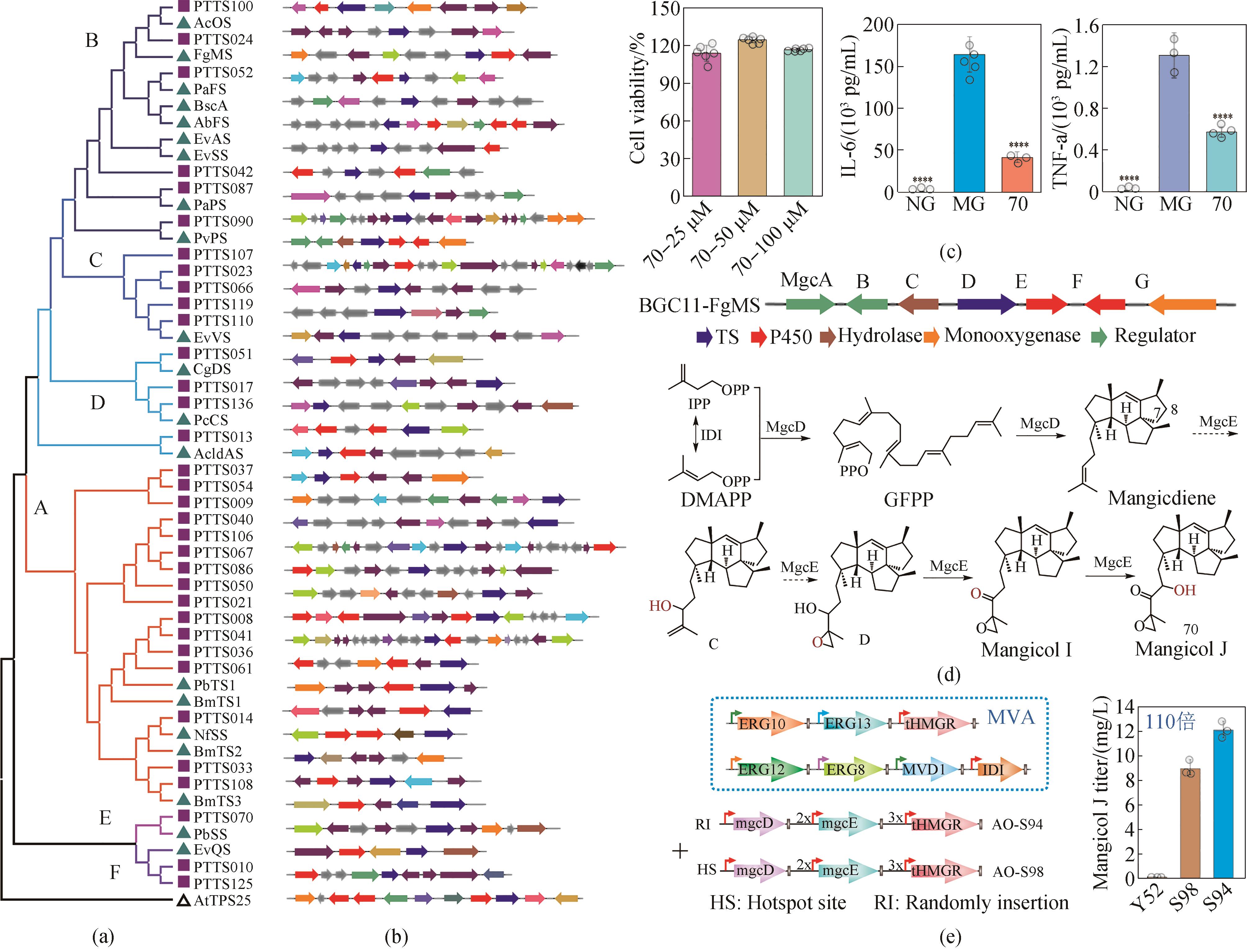
Fig. 3 The application of biocasting in efficient mining of new functional terpenoid genes (gene clusters) and the biosynthesis of mangicol J, a new anti-inflammatory molecule[51, 56](a) The batch mining of 34 new chimeric terpenoid synthases (PTTC); (b) The reconstruction of 39 terpenoid gene clusters into 208 mutants; (c) High-throughput screening of 185 terpenoids leading to the isolation of compound 70 (mangicol J) with high anti-inflammatory activity; (d) The elucidation of the biosynthetic pathway of mangicol J; (e) The construction of a general Aspergillus oryzae chassis for efficient biosynthesis of mangicol J
| 1 | RODRIGUES T, REKER D, SCHNEIDER P, et al. Counting on natural products for drug design[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2016, 8(6): 531-541. |
| 2 | ATANASOV A G, WALTENBERGER B, PFERSCHY-WENZIG E M, et al. Discovery and resupply of pharmacologically active plant-derived natural products: a review[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2015, 33(8): 1582-1614. |
| 3 | HARVEY A L, EDRADA-EBEL R, QUINN R J. The re-emergence of natural products for drug discovery in the genomics era[J]. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2015, 14(2): 111-129. |
| 4 | BIAN G K, HAN Y C, HOU A W, et al. Releasing the potential power of terpene synthases by a robust precursor supply platform[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 42: 1-8. |
| 5 | BIAN G K, DENG Z X, LIU T G. Strategies for terpenoid overproduction and new terpenoid discovery[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2017, 48: 234-241. |
| 6 | GAO J C, JIANG L H, LIAN J Z. Development of synthetic biology tools to engineer Pichia pastoris as a chassis for the production of natural products[J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2021, 6(2): 110-119. |
| 7 | MORRISON K C, HERGENROTHER P J. Natural products as starting points for the synthesis of complex and diverse compounds[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2014, 31(1): 6-14. |
| 8 | SMANSKI M J, ZHOU H, CLAESEN J, et al. Synthetic biology to access and expand nature's chemical diversity[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2016, 14(3): 135-149. |
| 9 | PYNE M E, NARCROSS L, MARTIN V J J. Engineering plant secondary metabolism in microbial systems[J]. Plant Physiology, 2019, 179(3): 844-861. |
| 10 | ZHU F Y, ZHONG X F, HU M Z, et al. In vitro reconstitution of mevalonate pathway and targeted engineering of farnesene overproduction in Escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2014, 111(7): 1396-1405. |
| 11 | PADDON C J, WESTFALL P J, PITERA D J, et al. High-level semi-synthetic production of the potent antimalarial artemisinin[J]. Nature, 2013, 496(7446): 528-532. |
| 12 | RO D K, PARADISE E M, OUELLET M, et al. Production of the antimalarial drug precursor artemisinic acid in engineered yeast[J]. Nature, 2006, 440(7086): 940-943. |
| 13 | BIAN G K, YUAN Y J, TAO H, et al. Production of taxadiene by engineering of mevalonate pathway in Escherichia coli and endophytic fungus Alternaria alternata TPF6 [J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 12(4): 1600697. |
| 14 | SAGWAN-BARKDOLL L, ANTEROLA A M. Taxadiene-5α-ol is a minor product of CYP725A4 when expressed in Escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 2018, 65(3): 294-305. |
| 15 | ZHU C Y, YOU X, WU T, et al. Efficient utilization of carbon to produce aromatic valencene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using mannitol as the substrate[J]. Green Chemistry, 2022, 24(11): 4614-4627. |
| 16 | YE Z L, HUANG Y L, SHI B, et al. Coupling cell growth and biochemical pathway induction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for production of (+)-valencene and its chemical conversion to (+)-nootkatone[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2022, 72: 107-115. |
| 17 | VELÁZQUEZ J E, SADAÑOSKI M A, ZAPATA P D, et al. Bioproduction of α-terpineol and R-(+)-limonene derivatives by terpene-tolerant ascomycete fungus as a potential contribution to the citrus value chain[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2021, 130(1): 76-89. |
| 18 | TAO H, LAUTERBACH L, BIAN G K, et al. Discovery of non-squalene triterpenes[J]. Nature, 2022, 606(7913): 414-419. |
| 19 | ZHU X X, LIU X N, LIU T, et al. Synthetic biology of plant natural products: from pathway elucidation to engineered biosynthesis in plant cells[J]. Plant Communications, 2021, 2(5): 100229. |
| 20 | LV X M, GU J L, WANG F, et al. Combinatorial pathway optimization in Escherichia coli by directed co-evolution of rate-limiting enzymes and modular pathway engineering[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2016, 113(12): 2661-2669. |
| 21 | MARKEL U, ESSANI K D, BESIRLIOGLU V, et al. Advances in ultrahigh-throughput screening for directed enzyme evolution[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(1): 233-262. |
| 22 | SILVERMAN L, CAMPBELL R, BROACH J R. New assay technologies for high-throughput screening[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 1998, 2(3): 397-403. |
| 23 | SHAO F C, LEE P W, LI H, et al. Emerging platforms for high-throughput enzymatic bioassays[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2023, 41(1): 120-133. |
| 24 | CLARKE L J, KITNEY R I. Synthetic biology in the UK - an outline of plans and progress[J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2016, 1(4): 243-257. |
| 25 | APPLETON E, MADSEN C, ROEHNER N, et al. Design automation in synthetic biology[J]. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 2017, 9(4): a023978. |
| 26 | 饶聪, 云轩, 虞沂, 等. 微生物药物的合成生物学研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(1): 92-102. |
| RAO C, YUN X, YU Y, et al. Research progress in synthetic biology of microbial drugs [J]. Synthetic Biology, 2020, 1(1): 92-102. | |
| 27 | HERTZBERG R P, POPE A J. High-throughput screening: new technology for the 21st century[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2000, 4(4): 445-451. |
| 28 | DÖRR M, FIBINGER M P C, LAST D, et al. Fully automatized high-throughput enzyme library screening using a robotic platform[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2016, 113(7): 1421-1432. |
| 29 | DU G S, FANG Q, DEN TOONDER J M J. Microfluidics for cell-based high throughput screening platforms—a review[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2016, 903: 36-50. |
| 30 | LUO Z S, ZENG W Z, DU G C, et al. A high-throughput screening procedure for enhancing pyruvate production in Candida glabrata by random mutagenesis[J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2017, 40(5): 693-701. |
| 31 | MACHILLOT P, QUINTAL C, DALONNEAU F, et al. Automated buildup of biomimetic films in cell culture microplates for high-throughput screening of cellular behaviors[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(27): 1801097. |
| 32 | CAO X M, LUO Z S, ZENG W Z, et al. Enhanced avermectin production by Streptomyces avermitilis ATCC 31267 using high-throughput screening aided by fluorescence-activated cell sorting[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(2): 703-712. |
| 33 | FENG W Q, UEDA E, LEVKIN P A. Droplet microarrays: from surface patterning to high-throughput applications[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(20): 1706111. |
| 34 | POPOVIC A, TCHIGVINTSEV A, TRAN H, et al. Metagenomics as a tool for enzyme discovery: hydrolytic enzymes from marine-related metagenomes[M/OL]//Advances in experimental medicine and biology: prokaryotic systems biology. Cham: Springer, 2015, 883: 1-20 [2023-04-10]. . |
| 35 | 杨建花, 苏晓岚, 朱蕾蕾. 高通量筛选系统在定向改造中的新进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2021, 37(7): 2197-2210. |
| YANG J H, SU X L, ZHU L L. Advances of high-throughput screening system in reengineering of biological entities[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2021, 37(7): 2197-2210. | |
| 36 | LONGWELL C K, LABANIEH L, COCHRAN J R. High-throughput screening technologies for enzyme engineering[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2017, 48: 196-202. |
| 37 | LEEMHUIS H, KELLY R M, DIJKHUIZEN L. Directed evolution of enzymes: library screening strategies[J]. IUBMB Life, 2009, 61(3): 222-228. |
| 38 | XIAO H, BAO Z H, ZHAO H M. High throughput screening and selection methods for directed enzyme evolution[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2015, 54(16): 4011-4020. |
| 39 | YANG G Y, WITHERS S G. Ultrahigh-throughput FACS-based screening for directed enzyme evolution[J]. ChemBioChem, 2009, 10(17): 2704-2715. |
| 40 | MEWIS K, TAUPP M, HALLAM S J. A high throughput screen for biomining cellulase activity from metagenomic libraries[J]. Journal of Visualized Experiments, 2011(48): e2461. |
| 41 | QIN Y L, WU L, WANG J G, et al. A fluorescence-activated single-droplet dispenser for high accuracy single-droplet and single-cell sorting and dispensing[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(10): 6815-6819. |
| 42 | ZENG W Z, GUO L K, XU S, et al. High-throughput screening technology in industrial biotechnology[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2020, 38(8): 888-906. |
| 43 | 唐婷, 付立豪, 郭二鹏, 等. 自动化合成生物技术与工程化设施平台[J]. 科学通报, 2021, 66(3): 300-309. |
| TANG T, FU L H, GUO E P, et al. Automation in synthetic biology using biological foundries[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2021, 66(3): 300-309. | |
| 44 | HILLSON N, CADDICK M, CAI Y Z, et al. Building a global alliance of biofoundries[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 2040. |
| 45 | 崔金明, 张炳照, 马迎飞, 等. 合成生物学研究的工程化平台[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2018, 33(11): 1249-1257. |
| CUI J M, ZHANG B Z, MA Y F, et al. Engineering platforms for synthetic biology research[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 33(11): 1249-1257. | |
| 46 | YEOH J W, SWAINSTON N, VEGH P, et al. SynBiopython: an open-source software library for Synthetic Biology[J]. Synthetic Biology, 2021, 6(1): ysab001. |
| 47 | 张亭, 冷梦甜, 金帆, 等. 合成生物研究重大科技基础设施概述[J]. 合成生物学, 2022(1): 184-194. |
| ZHANG T, LENG M T, JIN F, et al. Overview on platform for synthetic biology research at Shenzhen[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022(1): 184-194. | |
| 48 | CHAO R, LIANG J, TASAN I, et al. Fully automated one-step synthesis of single-transcript TALEN pairs using a biological foundry[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(4): 678-685. |
| 49 | SI T, CHAO R, MIN Y H, et al. Automated multiplex genome-scale engineering in yeast[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 15187. |
| 50 | WANI M C, TAYLOR H L, WALL M E, et al. Plant antitumor agents. Ⅵ. The isolation and structure of taxol, a novel antileukemic and antitumor agent from Taxus brevifolia [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1971, 93(9): 2325-2327. |
| 51 | YUAN Y J, CHENG S, BIAN G K, et al. Efficient exploration of terpenoid biosynthetic gene clusters in filamentous fungi[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2022, 5(4): 277-287. |
| 52 | CHEVRETTE M G, GUTIÉRREZ-GARCÍA K, SELEM-MOJICA N, et al. Evolutionary dynamics of natural product biosynthesis in bacteria[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2020, 37(4): 566-599. |
| 53 | CHEVRETTE M G, GAVRILIDOU A, MANTRI S, et al. The confluence of big data and evolutionary genome mining for the discovery of natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2021, 38(11): 2024-2040. |
| 54 | CHEN S C, ZHANG C, ZHANG L H. Investigation of the molecular landscape of bacterial aromatic polyketides by global analysis of type Ⅱ polyketide synthases[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(24): e202202286. |
| 55 | ZIEMERT N, ALANJARY M, WEBER T. The evolution of genome mining in microbes - a review[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2016, 33(8): 988-1005. |
| 56 | CHEN R, JIA Q D, MU X, et al. Systematic mining of fungal chimeric terpene synthases using an efficient precursor-providing yeast chassis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2021, 118(29): e2023247118. |
| 57 | NARITA K, SATO H, MINAMI A, et al. Focused genome mining of structurally related sesterterpenes: enzymatic formation of enantiomeric and diastereomeric products[J]. Organic Letters, 2017, 19(24): 6696-6699. |
| 58 | 范震, 潘海学, 唐功利. 工程酵母助力真菌嵌合萜类合酶的快速系统挖掘[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(5): 666-673. |
| FAN Z, PAN H X, TANG G L. Engineered yeast facilitates rapid and systematic mining of fungal chimeric terpene synthases[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(5): 666-673. | |
| 59 | 涂然, 李世新, 李昊霓, 等. 液滴微流控技术在微生物工程菌株选育中的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 165-184. |
| TU R, LI S X, LI H N, et al. Advances and applications of droplet-based microfluidics in evolution and screening of engineered microbial strains[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 165-184. | |
| 60 | MA F Q, CHUNG M T, YAO Y, et al. Efficient molecular evolution to generate enantioselective enzymes using a dual-channel microfluidic droplet screening platform[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 1030. |
| 61 | LEAVELL M D, SINGH A H, KAUFMANN-MALAGA B B. High-throughput screening for improved microbial cell factories, perspective and promise[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2020, 62: 22-28. |
| 62 | MEADOWS A L, HAWKINS K M, TSEGAYE Y, et al. Rewriting yeast central carbon metabolism for industrial isoprenoid production[J]. Nature, 2016, 537(7622): 694-697. |
| 63 | LEVISSON M, ARAYA-CLOUTIER C, DE BRUIJN W J C, et al. Toward developing a yeast cell factory for the production of prenylated flavonoids[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2019, 67(49): 13478-13486. |
| 64 | LAUCHLI R, RABE K S, KALBARCZYK K Z, et al. High-throughput screening for terpene-synthase-cyclization activity and directed evolution of a terpene synthase[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(21): 5571-5574. |
| 65 | FURUBAYASHI M, IKEZUMI M, KAJIWARA J, et al. A high-throughput colorimetric screening assay for terpene synthase activity based on substrate consumption[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(3): e93317. |
| 66 | ZHOU S H, LIU P R, CHEN J, et al. Characterization of mutants of a tyrosine ammonia-lyase from Rhodotorula glutinis [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2016, 100(24): 10443-10452. |
| 67 | HEMMERICH J, NOACK S, WIECHERT W, et al. Microbioreactor systems for accelerated bioprocess development[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2018, 13(4): 1700141. |
| 68 | WONG B G, MANCUSO C P, KIRIAKOV S, et al. Precise, automated control of conditions for high-throughput growth of yeast and bacteria with eVOLVER[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(7): 614-623. |
| 69 | JIAN X J, GUO X J, WANG J, et al. Microbial microdroplet culture system (MMC): an integrated platform for automated, high-throughput microbial cultivation and adaptive evolution[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2020, 117(6): 1724-1737. |
| 70 | OWENS R J. Structural proteomics: high-throughput methods. preface[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2015, 1261: v. |
| 71 | JIAN X J, GUO X J, WANG J, et al. Automated microbial cultivation and adaptive evolution using microbial microdroplet culture system (MMC)[J]. Journal of Visualized Experiments, 2022(180): e62800. |
| 72 | LEE K S, BOCCAZZI P, SINSKEY A J, et al. Microfluidic chemostat and turbidostat with flow rate, oxygen, and temperature control for dynamic continuous culture[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2011, 11(10): 1730-1739. |
| 73 | BENEYTON T, THOMAS S, GRIFFITHS A D, et al. Droplet-based microfluidic high-throughput screening of heterologous enzymes secreted by the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [J].Microbial Cell Factories, 2017, 16(1): 18. |
| 74 | GRÜNBERGER A, WIECHERT W, KOHLHEYER D. Single-cell microfluidics: opportunity for bioprocess development[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2014, 29: 15-23. |
| 75 | PICARD L P, PROSSER R S. Advances in the study of GPCRs by 19F NMR[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2021, 69: 169-176. |
| 76 | WANG Q, FENG L R, WEI L, et al. Mutation breeding of lycopene-producing strain Blakeslea trispora by a novel atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP)[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2014, 174(1): 452-460. |
| 77 | TAN J, CHU J, HAO Y Y, et al. High-throughput system for screening of cephalosporin C high-yield strain by 48-deep-well microtiter plates[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2013, 169(5): 1683-1695. |
| 78 | ZENG W Z, DU G C, CHEN J, et al. A high-throughput screening procedure for enhancing α-ketoglutaric acid production in Yarrowia lipolytica by random mutagenesis[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2015, 50(10): 1516-1522. |
| 79 | GUO C X, HU Y L, YANG C Y, et al. Developing a colorimetric assay for Fe(Ⅱ)/2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 2018, 548: 109-114. |
| 80 | HAMEDIRAD M, CHAO R, WEISBERG S, et al. Towards a fully automated algorithm driven platform for biosystems design[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 5150. |
| 81 | GAO F, HAO Z Z, SUN X H, et al. A versatile system for fast screening and isolation of Trichoderma reesei cellulase hyperproducers based on DsRed and fluorescence-assisted cell sorting[J].Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2018, 11(1): 261. |
| 82 | LI H Q, LI T F, ZUO H, et al. A novel rhodamine-based fluorescent pH probe for high-throughput screening of high-yield polymalic acid strains from random mutant libraries[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(97): 94756-94762. |
| 83 | LIU Y, XUE Z L, CHEN S P, et al. A high-throughput screening strategy for accurate quantification of menaquinone based on fluorescence-activated cell sorting[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2016, 43(6): 751-760. |
| 84 | ZHOU S H, LYU Y B, LI H Z, et al. Fine-tuning the (2 S)-naringenin synthetic pathway using an iterative high-throughput balancing strategy[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2019, 116(6): 1392-1404. |
| 85 | DEBON A, POTT M, OBEXER R, et al. Ultrahigh-throughput screening enables efficient single-round oxidase remodelling[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2019, 2(9): 740-747. |
| 86 | ZHOU S H, LYU Y B, LI H Z, et al. Fine-tuning the (2S)-naringenin synthetic pathway using an iterative high-throughput balancing strategy[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2019, 116(6): 1392-1404. |
| 87 | EGGELING L, BOTT M, MARIENHAGEN J. Novel screening methods—biosensors[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2015, 35: 30-36. |
| 88 | DEKKER L, POLIZZI K M. Sense and sensitivity in bioprocessing—detecting cellular metabolites with biosensors[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2017, 40: 31-36. |
| 89 | JUÁREZ J F, LECUBE-AZPEITIA B, BROWN S L, et al. Biosensor libraries harness large classes of binding domains for construction of allosteric transcriptional regulators[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 3101. |
| 90 | LIM H G, JANG S H, JANG S Y, et al. Design and optimization of genetically encoded biosensors for high-throughput screening of chemicals[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2018, 54: 18-25. |
| 91 | SUN H H, ZHAO H M, ANG E L. A new biosensor for stilbenes and a cannabinoid enabled by genome mining of a transcriptional regulator[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(4): 698-705. |
| 92 | CALERO P, VOLKE D C, LOWE P T, et al. A fluoride-responsive genetic circuit enables in vivo biofluorination in engineered Pseudomonas putida [J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 5045. |
| 93 | XIU Y, JANG S, JONES J A, et al. Naringenin-responsive riboswitch-based fluorescent biosensor module for Escherichia coli co-cultures[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2017, 114(10): 2235-2244. |
| 94 | SARNAIK A, LIU A, NIELSEN D, et al. High-throughput screening for efficient microbial biotechnology[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2020, 64: 141-150. |
| 95 | SHI S Y, XIE Y H, WANG G L, et al. Metabolite-based biosensors for natural product discovery and overproduction[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2022, 75: 102699. |
| 96 | WANG X X, REN L H, SU Y T, et al. Raman-activated droplet sorting (RADS) for label-free high-throughput screening of microalgal single-cells[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 89(22): 12569-12577. |
| 97 | 张凡忠, 相长君, 张骊駻. 进化与大数据导向生物信息学在天然产物研究中的发展及应用 [J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(4): |
| ZHANG F Z, XIANG C J, ZHANG L X. Advances and applications of evolutionary analysis and big-data guided bioinformatics in natural product research[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(4): | |
| 98 | GAVRIILIDOU A, KAUTSAR S A, ZABURANNYI N, et al. Compendium of specialized metabolite biosynthetic diversity encoded in bacterial genomes[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2022, 7(5): 726-735. |
| 99 | SMOLKE C D, SILVER P A. Informing biological design by integration of systems and synthetic biology[J]. Cell, 2011, 144(6): 855-859. |
| 100 | KHAMBHATI K, BHATTACHARJEE G, GOHIL N, et al. Exploring the potential of cell-free protein synthesis for extending the abilities of biological systems[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2019, 7: 248. |
| 101 | YANG J H, TU R, YUAN H L, et al. Recent advances in droplet microfluidics for enzyme and cell factory engineering[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2021, 41(7): 1023-1045. |
| 102 | BOUZETOS E, GANAR K A, MASTROBATTISTA E, et al. (R)evolution-on-a-chip[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2022, 40(1): 60-76. |
| 103 | GIELEN F, HOURS R, EMOND S, et al. Ultrahigh-throughput-directed enzyme evolution by absorbance-activated droplet sorting (AADS)[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(47): E7383-E7389. |
| 104 | LIN G M, WARDEN-ROTHMAN R, VOIGT C A. Retrosynthetic design of metabolic pathways to chemicals not found in nature[J]. Current Opinion in Systems Biology, 2019, 14: 82-107. |
| [1] | GAO Ge, BIAN Qi, WANG Baojun. Synthetic genetic circuit engineering: principles, advances and prospects [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | LI Jiyuan, WU Guosheng. Two hypothesises for the origins of organisms from the synthetic biology perspective [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | JIAO Hongtao, QI Meng, SHAO Bin, JIANG Jinsong. Legal issues for the storage of DNA data [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | TANG Xinghua, LU Qianneng, HU Yilin. Philosophical reflections on synthetic biology in the Anthropocene [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | XU Huaisheng, SHI Xiaolong, LIU Xiaoguang, XU Miaomiao. Key technologies for DNA storage: encoding, error correction, random access, and security [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | SHI Ting, SONG Zhan, SONG Shiyi, ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job. In vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): a new frontier of industrial biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | CHAI Meng, WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi. Synthesis of organic acids from lignocellulose by biotransformation [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | SHAO Mingwei, SUN Simian, YANG Shimao, CHEN Guoqiang. Bioproduction based on extremophiles [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | CHEN Yu, ZHANG Kang, QIU Yijing, CHENG Caiyun, YIN Jingjing, SONG Tianshun, XIE Jingjing. Progress of microbial electrosynthesis for conversion of CO2 [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [10] | ZHENG Haotian, LI Chaofeng, LIU Liangxu, WANG Jiawei, LI Hengrun, NI Jun. Design, optimization and application of synthetic carbon-negative phototrophic community [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [11] | ZHENG Mengmeng, LIU Benben, LIN Zhi, QU Xudong. Recent advances in chemoenzymatic synthesis of important steroids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 941-959. |
| [12] | XIE Xiangqian, GUO Wen, WANG Huan, LI Jin. Biosynthesis and chemical synthesis of ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides containing aminovinyl cysteine [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 981-996. |
| [13] | CHEN Ziling, XIANG Yangfei. Integrated development of organoid technology and synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [14] | CAI Bingyu, TAN Xiangtian, LI Wei. Advances in synthetic biology for engineering stem cell [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [15] | ZHANG Jun, JIN Shixue, YUN Qian, QU Xudong. Biosynthesis of the unnatural extender units with polyketides and their structural modifications for applications in medicines [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 561-570. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||