|
||
|
Research progress and development trends in the biosynthesis of neutral core human milk oligosaccharides
Synthetic Biology Journal
2025, 6 (5):
1126-1144.
DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-083
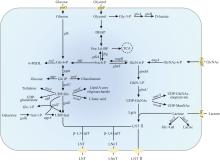
Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) are essentially functional and nutritional components found in human milk. They can be primarily classified into fucosylated, neutral core, and sialylated HMOs. Lacto-N-triose Ⅱ (LNT Ⅱ), lacto-N-neotetraose (LNnT), and lacto-N-tetraose (LNT) are common neutral core human milk oligosaccharides (ncHMOs), which can be extended to form longer-chain HMOs and play important roles in intestinal health. In recent years, the biosynthesis of ncHMOs has developed rapidly, and industrial-scale production is from theoretical possibility to practical reality. The synthesis approaches for ncHMOs include chemical synthesis, enzymatic synthesis, and microbial cell synthesis. As the rapid development in biotechnology, enzymatic and microbial cell synthesis have emerged as prominent methods in ncHMOs biosynthesis. Enzymatic synthesis is highly efficient, regioselective, and stereoselective. Currently, glycosyltransferases and glycoside hydrolases represent the two major types of enzymes used for biosynthesizing ncHMOs. Glycosidase-based enzymatic synthesis has demonstrated high conversion rates for LNT Ⅱ and LNnT production. However, the enzymatic synthesis of LNT is less efficient and requires further improvement. Notably, the production of LNnT and LNT typically relies on LNT Ⅱ as a key precursor, requiring a multi-step synthetic strategy. Microbial cell synthesis employs metabolic engineering to construct continuously synthetic pathways in microbial cells such as Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. Knocking out genes in competitive pathway, optimizing genes expression, regenerating cofactors have significantly enhanced the yields of ncHMOs. The biosynthesis of ncHMOs faces several critical challenges, including the low activity and poor substrate specificity of key glycosyltransferases, such as β-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase and β-1,3-galactosyltransferase. Additionally, the transporters of LNT Ⅱ and LNnT are not clear in microbial cell. Furthermore, the yields of LNT Ⅱ should be substantially improved for industrial-scale production. Thus, it is important to overcome the interconnected limitations in enzyme engineering (particularly glycosyltransferase specificity and activity), microbial cell modification (focusing on metabolic compatibility and pathway design), and bioprocess optimization (through rational pathway redesign) via an integrated synthetic biology and fermentation engineering approach in the future. These strategies are essential for achieving efficient, cost-effective biosynthesis of ncHMO at industrial scale.

Fig. 1
The structures (a) and functions (b) of LNT Ⅱ and their derivatives
Extracts from the Article
HMO由D-葡萄糖、D-半乳糖、L-岩藻糖、N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖和N-乙酰神经氨酸等5种单糖通过不同糖苷键连接而成,结构多样、丰度跨度大,存在众多异构体[4]。随着糖组学的发展,特别是生物质谱在表征聚糖方面的突破,现已发现大约200种结构不同的HMO,并表征了160种低聚糖结构[5-7]。HMO的还原末端都带有乳糖,乳糖可通过添加β-1, 3-连接的Galβ 1, 3GlcNAc或β-1, 4-连接的Galβ1, 4GlcNAc进行延伸。添加Galβ1, 3GlcNAc形成Ⅰ型链(Ⅰ型寡糖),如乳糖-N-四糖(lacto-N-tetraose,LNT),LNT可进一步经岩藻糖基化修饰形成乳糖-N-岩藻五糖Ⅰ(LNFP Ⅰ)[8]、乳糖-N-双岩藻糖基六糖Ⅱ(LNDFH Ⅱ)[9],经唾液酸化修饰形成双唾液酸乳糖-N-四糖(DSLNT)[10]。添加的Galβ1, 4GlcNAc则会形成Ⅱ型链(Ⅱ型寡糖),如乳糖-N-新四糖(lacto-N-neotetraose,LNnT),LNnT可进一步经岩藻糖基化修饰形成乳糖-N-岩藻乳糖Ⅲ(LNFP Ⅲ)[11]、乳糖-N-新双岩藻糖基六糖Ⅱ(LNnDFH Ⅱ)[12],经唾液酸化修饰形成唾液酸乳糖-N-四糖c(LSTc)[13]、唾液酸乳糖-N-四糖d(LSTd)[14][图1(a)]。此外,乳糖或延伸后的寡糖链可通过添加岩藻糖(α-1,2、α-1,3或α-1,4-连接)形成如2′-岩藻糖基乳糖、3-岩藻糖基乳糖和二岩藻糖基乳糖等HMO,和/或通过添加唾液酸(α-2,3或α-2,6-连接)形成3′-唾液酸乳糖和6′-唾液酸乳糖等HMO[15-17]。基于这些结构修饰,HMO可分为三大类:岩藻糖基化HMO、中性核心HMO和唾液酸化HMO[18-19]。以乳糖-N-三糖Ⅱ(lacto-N-triose Ⅱ,LNT Ⅱ)为核心骨架的LNnT和LNT是常见的ncHMO,其含量在人初乳中浓度分别可达0.4 g/L和0.59 g/L[17,20](表1)。
ncHMO作为HMO的重要成分和其他关键功能性HMO的核心骨架结构,其生理功能正被逐步揭示[图1(b)]。LNT Ⅱ为三糖,易被益生菌代谢或直接与宿主受体结合,能够上调肠道免疫因子DEFB1表达,对上皮细胞表面进行糖基化修饰,促进益生菌植物乳杆菌WCFS1肠道黏附与增殖[21]。LNnT能够促进肠道干细胞增殖分化,巩固肠道屏障,效果优于低聚半乳糖[22]。LNnT还能显著调节健康成年人的肠道菌群,特别是促进青春型双歧杆菌Bifidobacterium adolescentis的增殖。LNT能促进两歧双歧杆菌B. bifidum的增殖,并提高肠道乙酸含量[23]。轮状病毒是导致婴幼儿患胃肠炎的主要病原体,其感染依赖于表面蛋白VP4的VP8*结构域与宿主细胞表面聚糖的特异性结合[24]。研究表明,LNT通过氢键和疏水相互作用与VP8*稳定结合,在缓解胃肠炎方面发挥作用[25]。LNT及LNT Ⅱ衍生糖(LNFP Ⅰ、LNFP Ⅱ、LNFP Ⅲ和DSLNT)通过黏附于致病性大肠杆菌和霍乱弧菌产生的不同外毒素而显示出抗病原活性[26]。随着母乳寡糖制备技术的提高,ncHMO衍生糖的研究也日益受到关注。LNFP Ⅲ能够激活小鼠骨髓树突状细胞,以TLR4依赖的方式引发Th2免疫应答[27]。LSTc可以减少肺炎链球菌的定植和黏附,预防肺炎链球菌感染[28]。ncHMO还可与其他HMO联用通过脑-肠轴促进大脑神经发育和认知功能完善[29]。
Other Images/Table from this Article
|