• 特约评述 •
基于基因线路的合成生物传感器设计与应用
邓稼轩1, 陈升言1,2, 王宝俊1,2
- 1.浙江大学化学工程与生物工程学院,浙江 杭州 310058
2.浙江大学杭州国际科创中心,浙江 杭州 311215
-
收稿日期:2025-04-02修回日期:2025-05-28出版日期:2025-05-29 -
通讯作者:王宝俊 -
作者简介:邓稼轩 (2002—),男,博士研究生。研究方向为基于基因线路的合成生物传感器设计与肿瘤诊疗应用。 E-mail:jiaxuan.deng@zju.edu.cn王宝俊 (1982—),男,浙江大学求是讲席教授,教育部“长江学者奖励计划”讲席学者。研究方向为合成生物学和生物工程,长期从事合成生物使能技术、基因线路设计研究及其在生物传感、智能诊疗和生物制造等领域的创新应用。 E-mail:baojun.wang@zju.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2023YFF1204500);国家自然科学基金委(32320103001);浙江省“尖兵”“领雁”研发攻关计划(2024C03011)
Genetic circuit-enabled synthetic biosensors: design and applications
DENG Jiaxuan1, CHEN Shengyan1,2, WANG Baojun1,2
- 1.College of Chemical and Biological Engineering,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou 310058,Zhejiang,China
2.ZJU-Hangzhou Global Scientific and Technological Innovation Center,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou 311215,Zhejiang,China
-
Received:2025-04-02Revised:2025-05-28Online:2025-05-29 -
Contact:WANG Baojun
摘要:
合成生物传感器利用基因编码的生物识别元件特异性识别靶标并将其转换成可量化的生物信号,然后通过基因线路介导的功能器件实现生物信号的定制化处理与多模态信号输出,具有生物相容性高、成本低、环境友好等优势,已在环境监测、生物制造过程监控、精准医学诊疗等领域展现出重要应用潜力。合成生物学方法和前沿技术的突破性进展,特别是模块化的工程设计原理、基因线路的可编程动态调控策略和人工智能辅助的生物元件挖掘与从头设计,为合成生物传感器的开发提供了前所未有的助力。然而,当前合成生物传感器的产业化应用仍在多个性能指标方面面临制约:即敏感性(Sensitivity)、特异性(Specificity)、响应速度(Speed)、稳定性(Stability)和安全性(Biosafety)——简称5S挑战。本文系统梳理了基于基因线路的合成生物传感器信号识别机制与设计范式,深入剖析了各类型合成生物传感器的技术优势与应用瓶颈,并归纳了代表性的基因线路传感功能扩展模块与应用案例。最后,本文还介绍了合成生物传感器的关键特征以及典型优化方法,探讨了未来加速推进合成生物传感器实现广泛实际应用的挑战与机遇。
中图分类号:
引用本文
邓稼轩, 陈升言, 王宝俊. 基于基因线路的合成生物传感器设计与应用[J]. 合成生物学, DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-031.
DENG Jiaxuan, CHEN Shengyan, WANG Baojun. Genetic circuit-enabled synthetic biosensors: design and applications[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-031.
| 领域 | 具体应用 | 检测靶标 | 传感基因线路元件 | 检测限 | 工作范围 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 环境 监测 | 重金属离子 | As3+ | 转录因子ArsR、转录信号放大器 | 0.1 ppb | 0.1-5 ppb | [ |
| Cd2+ | 转录因子CadR | 0.39 μg/L | 0-60 μg/L | [ | ||
| As3+ | II型CRISPR系统 | 0-32 μM | [ | |||
| U6+ | 双组分系统UzcRS-UrpRS、AND gate、天然系统活性放大器 | 1 μM | 1-5.2 μM | [ | ||
| Hg2+ | toehold开关、转录因子MerR | 5 nM | 5-7.5 nM | [ | ||
| Au3+ | 转录因子HspR、重组酶系统 | 5 μM | 5-100 μM | [ | ||
| Cu2+ | P CopA 启动子 | 0-50 mM | [ | |||
| 爆炸残留物 | 2,4-DNT | yqjF启动子 | 4.8 mg/L | 4.8-25 mg/L | [ | |
| TNT | TNT核糖开关,记忆开关 | 25 μM | [ | |||
| 农药 | 2-苯基苯酚 | 转录因子HbpR、转录信号放大器 | 1 μM | 1-50 μM | [ | |
| 有机污染物 | 单环芳烃 | 双组分系统TodTS | 0.04 mg/L | 0.04-1 mg/L | [ | |
| 甲醇 | 双组分系统MxcQZ-OmpR | 0-0.05% | [ | |||
| 环境病原 细菌 | AHL | 转录因子QscR | 0.01 μM | 0.01-5 μM | [ | |
| 医学 诊疗 | 监测体液 物质 | 孕酮 | 从头设计转录因子DLA | 0.16 μg/L | 0.16- 60 μg/L | [ |
| 人血清中 的锌 | 转录因子ZntR、Zur | 0-20 μM | [ | |||
| 大麻素类 化合物 | 基于CB2受体的酵母GPCR | 1 nM | [ | |||
| 检测疾病标志物以诊断疾病 | 转化生长 因子-β | 双组分系统Smad | 0.024 ng/mL | 0.024- 6.25 ng/mL | [ | |
| 胆盐 | 人工跨膜转录因子CadC-TcpP | 28.3 μM | 28.3- 58.99 μM | [ | ||
| 血红素 | 转录因子HrtR,拨动开关 | 0.12 ppm | [ | |||
| 肠炎标志物NO | 转录因子NorR,重组酶记忆模块 | 30 μM | [ | |||
| RNA | CRISPR-Cas13a/C2c2系统 | [ | ||||
| DNA | CRISPR-Cas12a系统 | [ | ||||
| 传感并治疗疾病 | 血液脂肪酸 | 人工转录因子LSR | 5 μM | 5-100 μM | [ | |
| 霍乱弧菌群体感应信号CAI-1 | 人工转录因子HR | 细胞密度108 CFU/ml | [ | |||
| 原儿茶酸 | 转录因子 PcaV | 0-1000 μM | [ | |||
| 硫代硫酸盐 | 双组分系统 ThsRS | 0.016 mM | 0.016-1 mM | [ | ||
| 阿司匹林 | 复合转录因子Myr-NPR1/NPR4-VanR-VP16 | 10-250 μM | [ | |||
| 硝酸甘油 | 级联生化反应和转录因子CREB | 75 µM | [ | |||
| 调节肠道 生态 | 鼠李糖、硫酸软骨素、IPTG | 转录因子RhaR和LacI、双组分系统BT3334- BT0267、 CRISPR记忆模块 | 0.3 mM; 0.01 mM; 6 μM | [ | ||
| 生物 制造 | 检测目标产物产量辅助菌株筛选 | L-赖氨酸 | 转录因子LysG | 40 mM | 40-320 mM | [ |
| L-半胱氨酸 | 转录因子CcdR | 0-50 mM | [ | |||
| 苹果酸 | 转录因子MalR | 5 g/L | 5-15 g/L | [ | ||
| 代谢动态 调控 | 半乳糖醛酸 | 转录因子ExuR | 1-100 mg/L | [ | ||
| 葡萄糖 | 转录因子Mlc | [ | ||||
| L-赖氨酸 | 转录因子LysG | 0.05-8 mM | [ | |||
| 长链脂肪酸 | 转录因子FadR、TetR | [ | ||||
| 优化发酵 参数 | L-乳酸、D-乳酸 | 转录因子EcLldR、PfPdhR | 15-200 mM;0-50 mM | [ | ||
| 辅助酶的定向进化 | 乳果糖 | 转录因子LacI-L5 | 5 μM | 10-500 μM | [ | |
| 茶碱 | 茶碱核糖开关 | 10 μM | 10-1000 μM | [ | ||
| 生物碱 | 转录因子RamR | 1-100 μM | [ | |||
| 4'-O-甲基去甲酰胺 | 转录因子RamR | 2.5 μM | 2.5-100 μM | [ | ||
| 食品 安全 | 检测食物毒性物质 | 腐胺 | 转录因子PuuR | 5.37 mM | [ | |
| 毒素黄素 | 转录因子ToxR | 50 nM | 50-500 nM | [ | ||
| 组胺 | 转录因子HinK | 0.39 ppm | 0.28-18 ppm | [ | ||
| 四环素 | 转录因子TetR、聚合酶链回收(PSR)放大线路 | 12 ppb | [ | |||
| 食品质量 控制 | 柚皮素 | 柚皮素核糖开关 | 0-0.6 mM | [ | ||
| 细胞 调控 | 调控细胞 分裂与运动 | 光照 | 转录因子LexRO、基因逻辑门 | 0.059 mW/cm2 | [ |
表1 基于基因线路的合成生物传感器设计与典型应用
Table 1 Typical genetic circuit-enabled synthetic biosensors and applications
| 领域 | 具体应用 | 检测靶标 | 传感基因线路元件 | 检测限 | 工作范围 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 环境 监测 | 重金属离子 | As3+ | 转录因子ArsR、转录信号放大器 | 0.1 ppb | 0.1-5 ppb | [ |
| Cd2+ | 转录因子CadR | 0.39 μg/L | 0-60 μg/L | [ | ||
| As3+ | II型CRISPR系统 | 0-32 μM | [ | |||
| U6+ | 双组分系统UzcRS-UrpRS、AND gate、天然系统活性放大器 | 1 μM | 1-5.2 μM | [ | ||
| Hg2+ | toehold开关、转录因子MerR | 5 nM | 5-7.5 nM | [ | ||
| Au3+ | 转录因子HspR、重组酶系统 | 5 μM | 5-100 μM | [ | ||
| Cu2+ | P CopA 启动子 | 0-50 mM | [ | |||
| 爆炸残留物 | 2,4-DNT | yqjF启动子 | 4.8 mg/L | 4.8-25 mg/L | [ | |
| TNT | TNT核糖开关,记忆开关 | 25 μM | [ | |||
| 农药 | 2-苯基苯酚 | 转录因子HbpR、转录信号放大器 | 1 μM | 1-50 μM | [ | |
| 有机污染物 | 单环芳烃 | 双组分系统TodTS | 0.04 mg/L | 0.04-1 mg/L | [ | |
| 甲醇 | 双组分系统MxcQZ-OmpR | 0-0.05% | [ | |||
| 环境病原 细菌 | AHL | 转录因子QscR | 0.01 μM | 0.01-5 μM | [ | |
| 医学 诊疗 | 监测体液 物质 | 孕酮 | 从头设计转录因子DLA | 0.16 μg/L | 0.16- 60 μg/L | [ |
| 人血清中 的锌 | 转录因子ZntR、Zur | 0-20 μM | [ | |||
| 大麻素类 化合物 | 基于CB2受体的酵母GPCR | 1 nM | [ | |||
| 检测疾病标志物以诊断疾病 | 转化生长 因子-β | 双组分系统Smad | 0.024 ng/mL | 0.024- 6.25 ng/mL | [ | |
| 胆盐 | 人工跨膜转录因子CadC-TcpP | 28.3 μM | 28.3- 58.99 μM | [ | ||
| 血红素 | 转录因子HrtR,拨动开关 | 0.12 ppm | [ | |||
| 肠炎标志物NO | 转录因子NorR,重组酶记忆模块 | 30 μM | [ | |||
| RNA | CRISPR-Cas13a/C2c2系统 | [ | ||||
| DNA | CRISPR-Cas12a系统 | [ | ||||
| 传感并治疗疾病 | 血液脂肪酸 | 人工转录因子LSR | 5 μM | 5-100 μM | [ | |
| 霍乱弧菌群体感应信号CAI-1 | 人工转录因子HR | 细胞密度108 CFU/ml | [ | |||
| 原儿茶酸 | 转录因子 PcaV | 0-1000 μM | [ | |||
| 硫代硫酸盐 | 双组分系统 ThsRS | 0.016 mM | 0.016-1 mM | [ | ||
| 阿司匹林 | 复合转录因子Myr-NPR1/NPR4-VanR-VP16 | 10-250 μM | [ | |||
| 硝酸甘油 | 级联生化反应和转录因子CREB | 75 µM | [ | |||
| 调节肠道 生态 | 鼠李糖、硫酸软骨素、IPTG | 转录因子RhaR和LacI、双组分系统BT3334- BT0267、 CRISPR记忆模块 | 0.3 mM; 0.01 mM; 6 μM | [ | ||
| 生物 制造 | 检测目标产物产量辅助菌株筛选 | L-赖氨酸 | 转录因子LysG | 40 mM | 40-320 mM | [ |
| L-半胱氨酸 | 转录因子CcdR | 0-50 mM | [ | |||
| 苹果酸 | 转录因子MalR | 5 g/L | 5-15 g/L | [ | ||
| 代谢动态 调控 | 半乳糖醛酸 | 转录因子ExuR | 1-100 mg/L | [ | ||
| 葡萄糖 | 转录因子Mlc | [ | ||||
| L-赖氨酸 | 转录因子LysG | 0.05-8 mM | [ | |||
| 长链脂肪酸 | 转录因子FadR、TetR | [ | ||||
| 优化发酵 参数 | L-乳酸、D-乳酸 | 转录因子EcLldR、PfPdhR | 15-200 mM;0-50 mM | [ | ||
| 辅助酶的定向进化 | 乳果糖 | 转录因子LacI-L5 | 5 μM | 10-500 μM | [ | |
| 茶碱 | 茶碱核糖开关 | 10 μM | 10-1000 μM | [ | ||
| 生物碱 | 转录因子RamR | 1-100 μM | [ | |||
| 4'-O-甲基去甲酰胺 | 转录因子RamR | 2.5 μM | 2.5-100 μM | [ | ||
| 食品 安全 | 检测食物毒性物质 | 腐胺 | 转录因子PuuR | 5.37 mM | [ | |
| 毒素黄素 | 转录因子ToxR | 50 nM | 50-500 nM | [ | ||
| 组胺 | 转录因子HinK | 0.39 ppm | 0.28-18 ppm | [ | ||
| 四环素 | 转录因子TetR、聚合酶链回收(PSR)放大线路 | 12 ppb | [ | |||
| 食品质量 控制 | 柚皮素 | 柚皮素核糖开关 | 0-0.6 mM | [ | ||
| 细胞 调控 | 调控细胞 分裂与运动 | 光照 | 转录因子LexRO、基因逻辑门 | 0.059 mW/cm2 | [ |
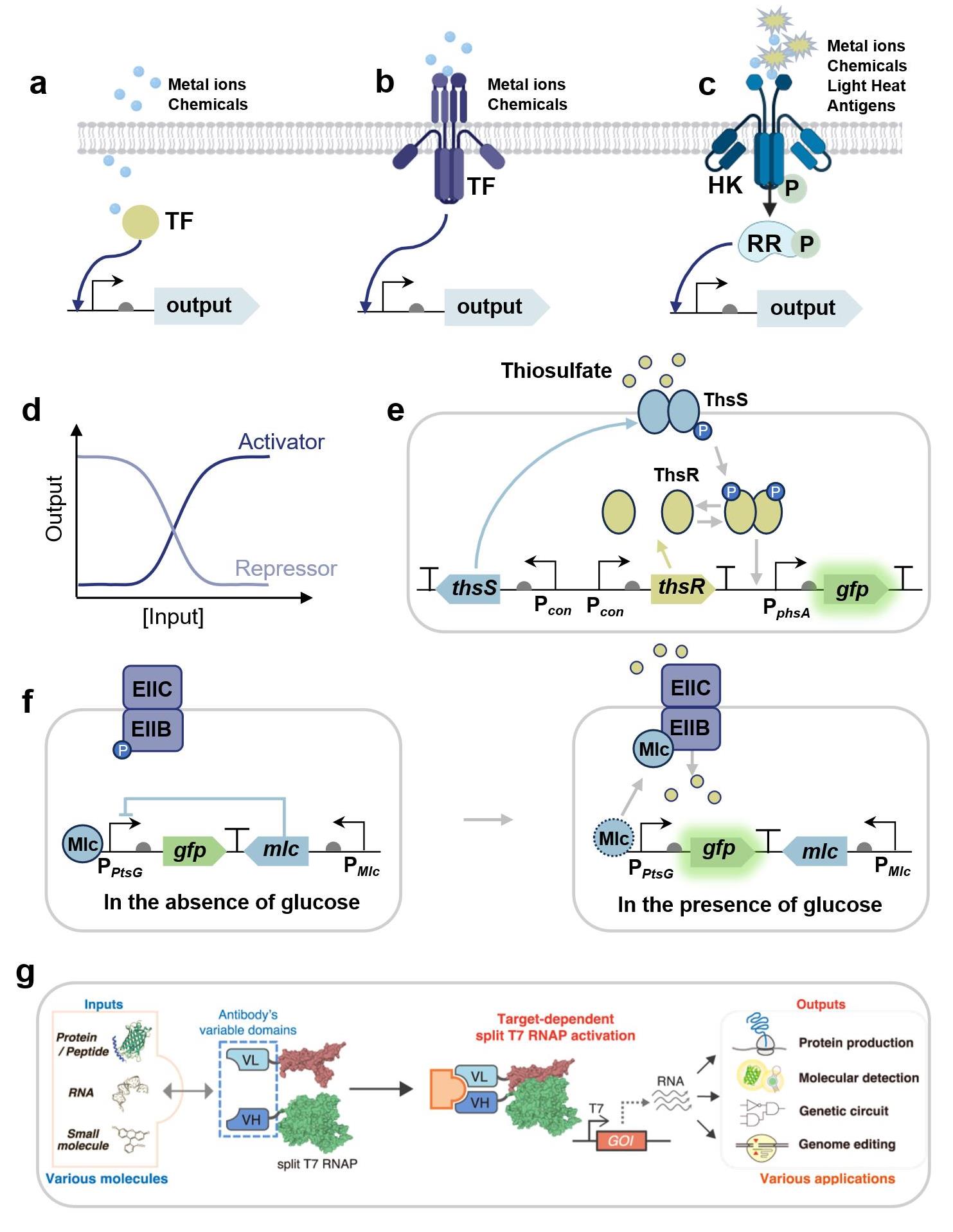
图1 基于转录调控蛋白的合成生物传感器信号识别机制与应用(a-c) 基于变构转录因子、跨膜转录因子和双组分系统的传感器信号识别机制;(d) 激活和抑制型转录因子传感器的响应曲线 (e) 感应硫代硫酸盐的双组分系统ThsRS传感器基因线路示意图[54];(f) 监测葡萄糖摄取率的转录因子生物传感器基因线路示意图[14];(g) 基于靶标依赖性拆分T7 RNA聚合酶的生物传感器基因线路示意图[95]。(TF: Transcriptional factor; HK: Histidine kinase; RR: Response regulator; GOI: Gene of interest.)
Fig. 1 Mechanisms and applications of transcriptional regulatory protein-enabled synthetic biosensors(a-c) Mechanisms of allosteric transcription factors, transmembrane transcription factors, and two-component systems-enabled biosensors; (d) Response curves of biosensors based on activation-type and repression-type transcription factor; (e) Gene circuit of a thiosulfate-sensing sensor based on the two-component system ThsRS[54]; (f) Gene circuit of a transcription factor-enabled biosensor for monitoring glucose uptake[14]; (g) Gene circuit of a target-dependent RNA polymerase-enabled biosensor[95].
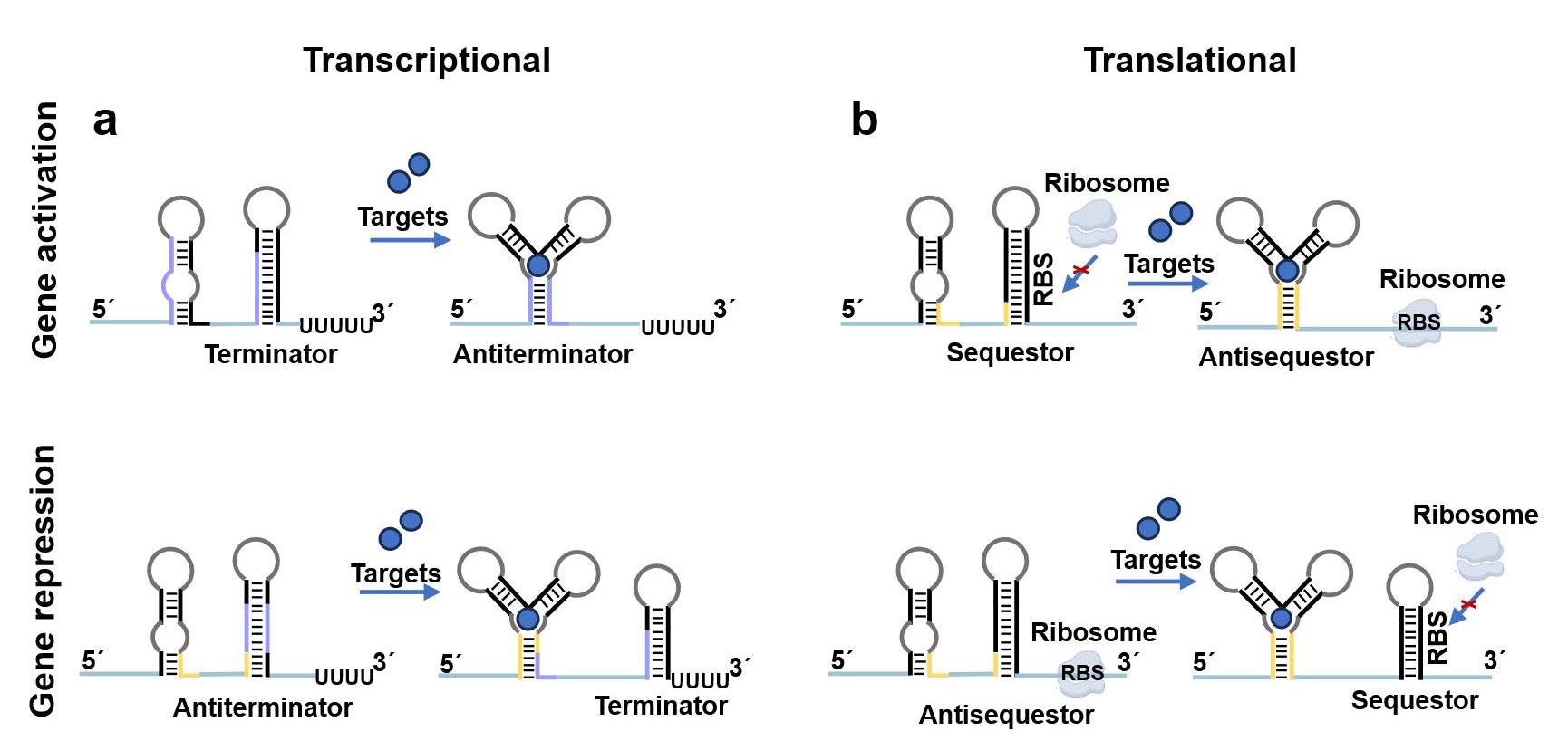
图2 基于核糖开关的合成生物传感器信号识别机制(a) 转录激活型和转录抑制型核糖开关传感器信号识别机制;(b) 翻译激活型和翻译抑制型核糖开关传感器信号识别机制。
Fig. 2 Mechanisms of riboswitches-enabled synthetic biosensors(a) Riboswitch-enabled sensors based on transcriptional activation and transcriptional repression.(b) Riboswitch-enabled sensors based on translational activation and translational repression..
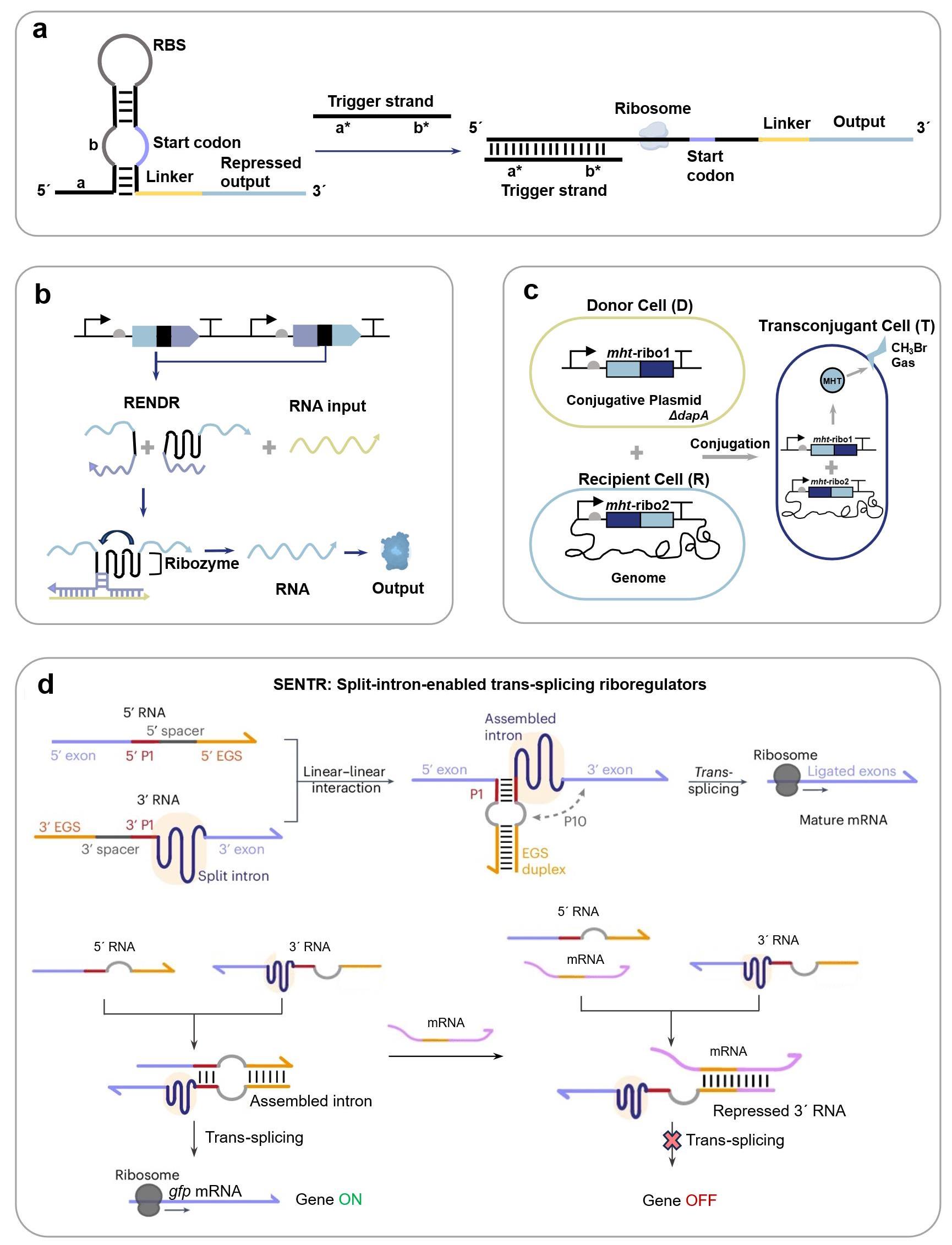
图3 基于核糖核酸调节子的合成生物传感器信号识别机制与应用(a) toehold开关信号识别机制[124];(b) 核酶传感平台RENDR的基因线路示意图[125];(c) 利用分裂核酶报告土壤中细菌DNA转移的基因线路示意图[133];(d) I型断裂内含子反式剪接系统SENTR的信号识别机制以及传感细胞内目标mRNA分子的原理示意图[122]。(RENDER: Ribozyme-ENabled Detection of RNA;SENTR: Split-intron-enabled trans-splicing riboregulators.)
Fig. 3 Mechanisms and applications of riboregulator-enabled synthetic biosensors(a) Mechanism of the toehold switch[124]; (b) A ribozyme-based sensing platform RENDR[125]; (c) Gene circuit of a sensor for reporting bacterial DNA transfer in soil using split ribozymes[133]; (d) Mechanism of the group I intron-enabled RNA trans-splicing system SENTR and its application for intracellular mRNA detection [122].
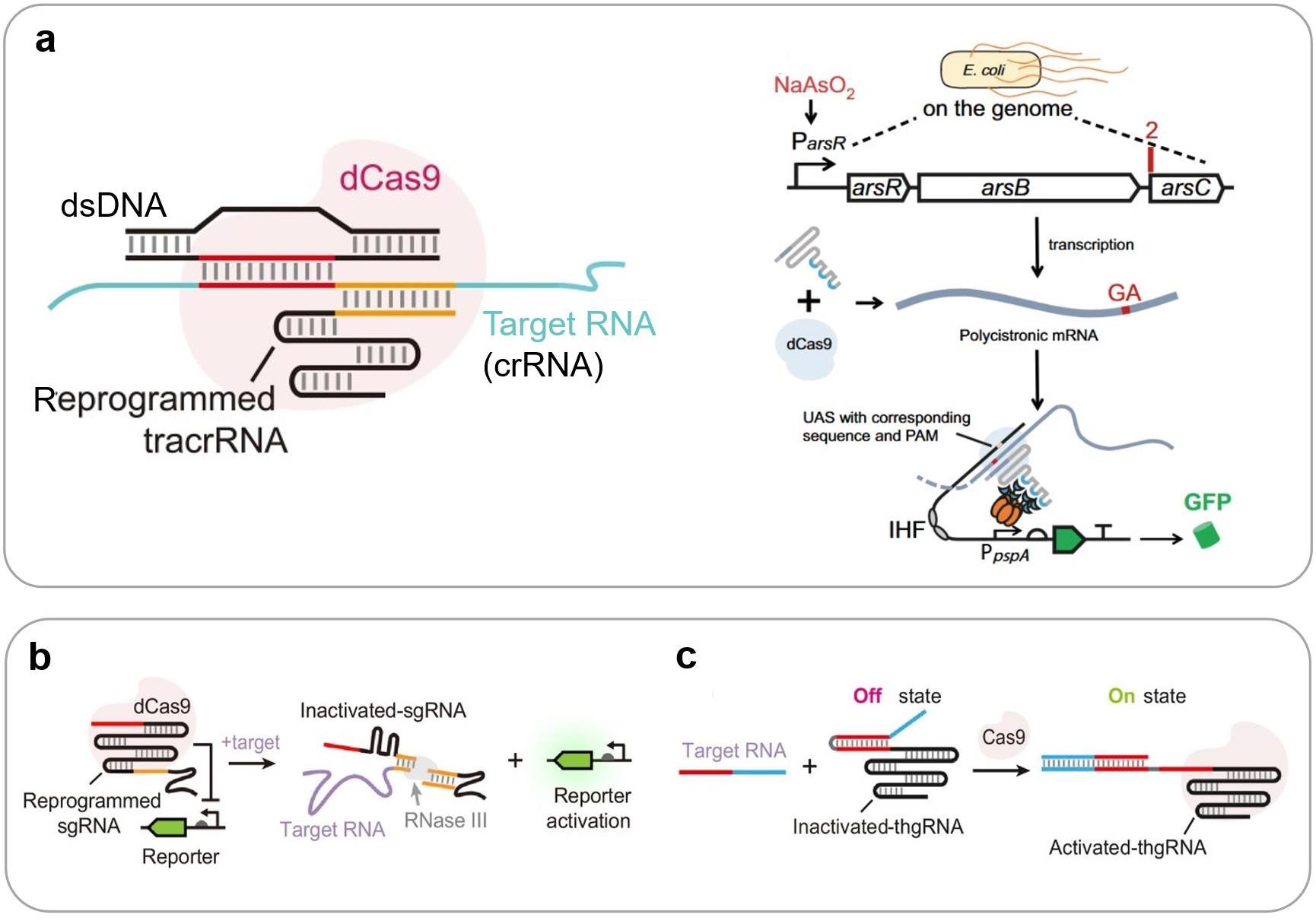
图4 基于CRISPR技术的合成生物传感器信号识别机制(a) 基于II型CRISPR系统重编程tracrRNA的细胞内RNA传感原理与应用案例[17];(b) 基于RNA触发RNA加工的传感系统[142];(c) 基于链置换反应的RNA传感[143]。(UAS: Upstream activating sequence; PAM: Protospacer adjacent motif; IHF: Integration host factor)
Fig. 4 Mechanisms of CRISPR-enabled synthetic biosensors(a) RNA sensing enabled by reprogrammed tracrRNA in type II CRISPR system[17]; (b) RNA sensing enabled by RNA-triggered RNA processing[142]; (c) RNA sensing enabled by strand displacement reactions[143].
| 信号识别机制 | 优势 | 劣势 |
|---|---|---|
| 变构转录因子 | 信号识别元件和工程化优化改造手段丰富,调控机制简单,可监测胞内代谢物 | 细胞代谢负担大,响应速度慢,天然元件性能低下依赖人工优化 |
| 原核生物双组分系统 | 检测信号广谱,可响应细胞外环境 | 工程化改造困难,信号转导依赖胞内环境,元件串扰大特异性较低,宿主兼容性差 |
| 核糖开关 | 可编程性高,细胞代谢负担低,响应快速,特异性高 | 受胞内环境干扰较大,开关比率低,优化手段较少,检测靶标类型有限 |
| 核糖核酸调节子 | 可编程性与正交性高,跨体系适配性优异,设计与优化便捷,响应快速,细胞代谢负担低 | 全细胞环境中敏感性、稳定性低,检测靶标单一 |
| CRISPR系统 | 可编程性与正交性高,特异性高,传感功能丰富 | 泄漏水平较高,检测内源mRNA案例少,存在脱靶效应与细胞毒性 |
表2 基于基因线路的合成生物传感器不同信号识别机制与优劣势
Table 2 Advantages and limitations of genetic circuit-enabled synthetic biosensors based on different signal recognition mechanisms
| 信号识别机制 | 优势 | 劣势 |
|---|---|---|
| 变构转录因子 | 信号识别元件和工程化优化改造手段丰富,调控机制简单,可监测胞内代谢物 | 细胞代谢负担大,响应速度慢,天然元件性能低下依赖人工优化 |
| 原核生物双组分系统 | 检测信号广谱,可响应细胞外环境 | 工程化改造困难,信号转导依赖胞内环境,元件串扰大特异性较低,宿主兼容性差 |
| 核糖开关 | 可编程性高,细胞代谢负担低,响应快速,特异性高 | 受胞内环境干扰较大,开关比率低,优化手段较少,检测靶标类型有限 |
| 核糖核酸调节子 | 可编程性与正交性高,跨体系适配性优异,设计与优化便捷,响应快速,细胞代谢负担低 | 全细胞环境中敏感性、稳定性低,检测靶标单一 |
| CRISPR系统 | 可编程性与正交性高,特异性高,传感功能丰富 | 泄漏水平较高,检测内源mRNA案例少,存在脱靶效应与细胞毒性 |
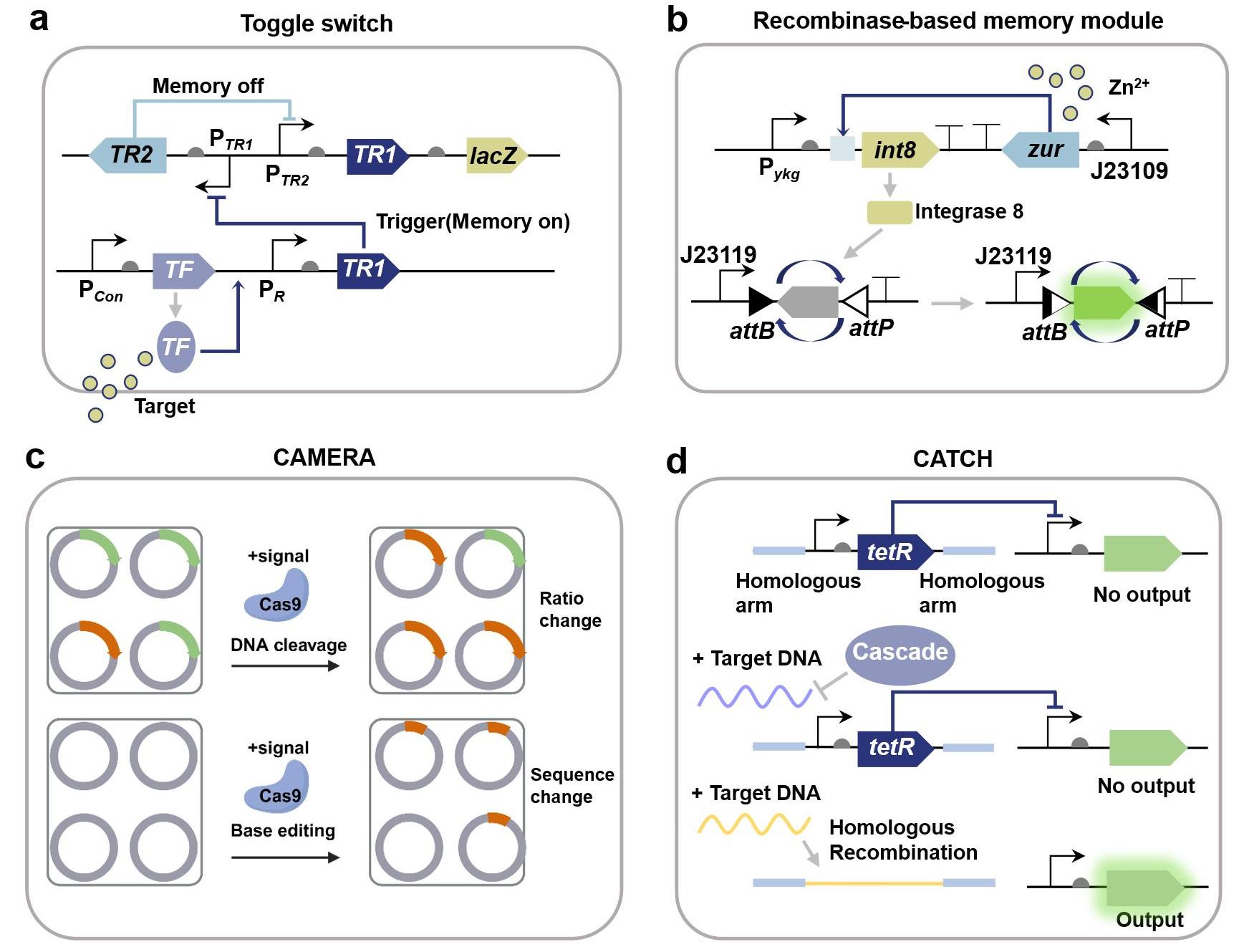
图5 典型合成生物传感信号记忆模块的设计原理(a) 基于拨动开关的生物记忆模块基因线路示意图;(b) 基于重组酶翻转机制的锌离子记忆模块基因线路示意图[153];(c) 基于CRISPR/Cas的CAMERA细胞环境信号记录系统原理示意图[158];(d) 基于CRISPR/Cas的DNA感知记录模块(CATCH)基因线路示意图[159]。(TF: Transcriptional factor; TR: Transcriptional repressor.)
Fig. 5 Typical biomemory modules for recording biosensing signals(a) Gene circuit for a biomemory module based on toggle switch; (b) Gene circuit of a zinc ion memory module based on the recombinase flip mechanism[153]; (c) Principle of the CAMERA recording system based on CRISPR/Cas[158]; (d) Gene circuit of the DNA sensing and recording module (CATCH) based on CRISPR/Cas[159].
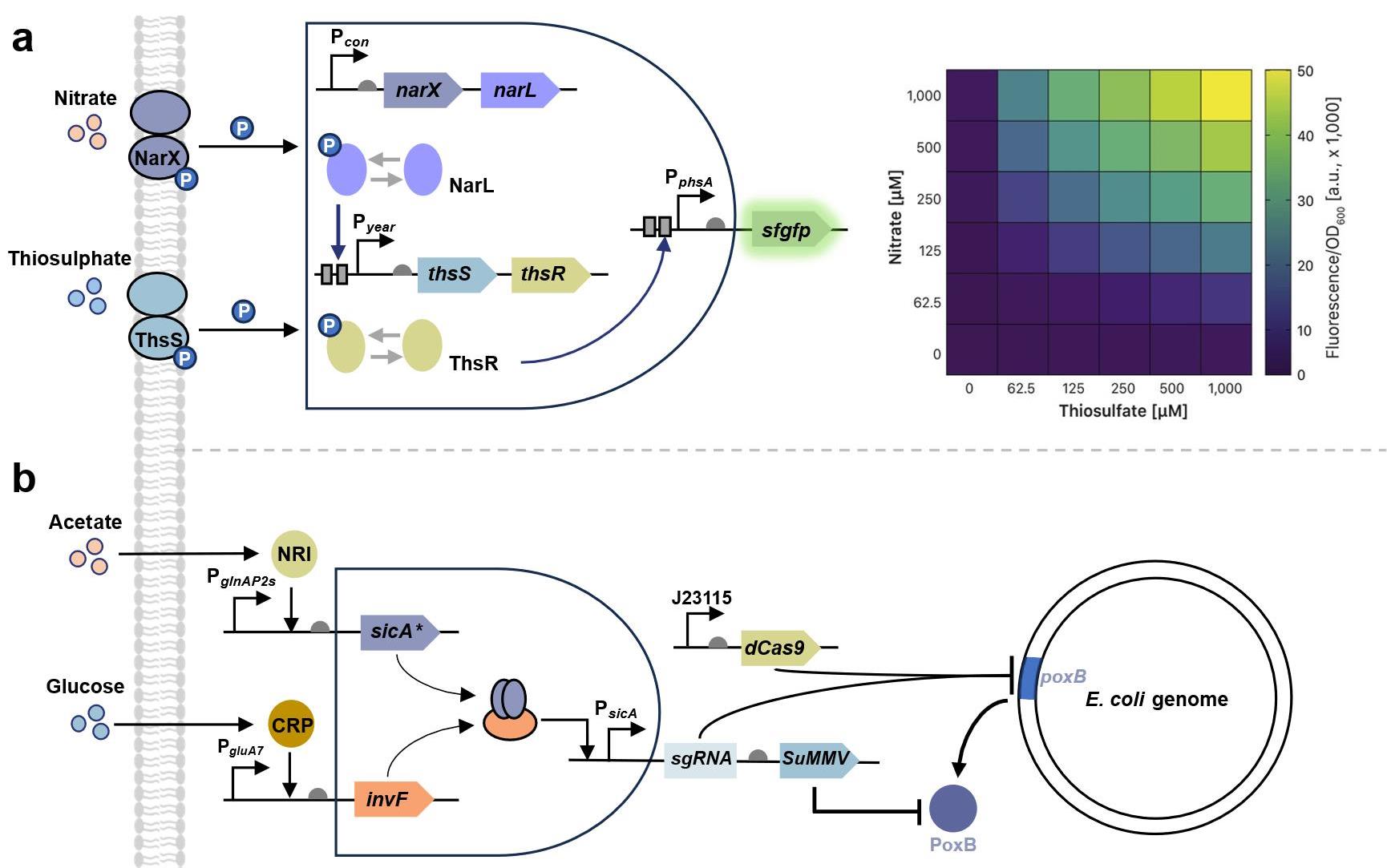
图6 基于多层次生物计算模块的生物传感基因线路设计与应用(a) 基于AND逻辑门构建的双输入生物传感器基因线路示意图及其响应热图[104](b) 整合多靶标输入的代谢调控传感器基因线路示意图[163]。
Fig. 6 Circuit designs and applications of multilayered biocomputing modules(a) Gene circuit of a dual-parameter biosensor based on an AND logic gate and its response heatmap[104]; (b) Gene circuit of a metabolic control sensor integrating a multi-input genetic logic circuit [163];
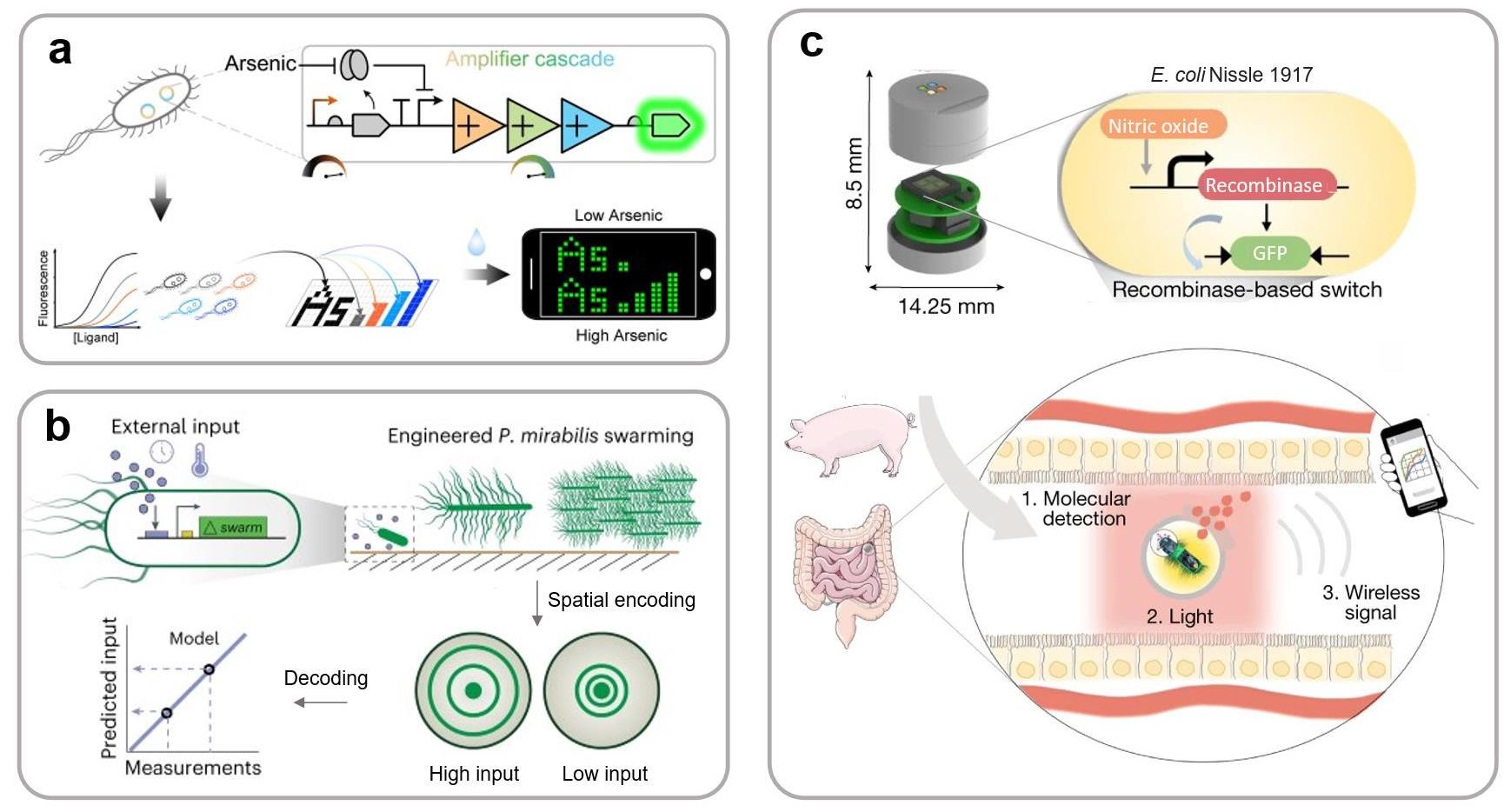
图7 与多种检测平台耦合的多模态输出合成生物传感系统设计(a) 琼脂糖水凝胶封装砷离子传感器阵列,实现砷污染检测智能手机平台可视化阵列显示[32];(b) 通过细菌空间运动图案实现生物传感信号的可视化输出[36];(c) 荧光传感器与光电芯片耦合,将光信号转为无线信号输出[48]。
Fig. 7 Synthetic biosensing systems with multimodal outputs for integration with various detection platforms(a) A agarose hydrogel-encapsulated arsenic ion sensor for visual array display on a smartphone platform[32]; (b) A sensor that visualizes biosensing signals through the formation of bacterial spatial motility patterns[36]; (c) A sensing system coupling a fluorescent sensor with a photoelectric chip to convert optical signals into wireless signals[48].
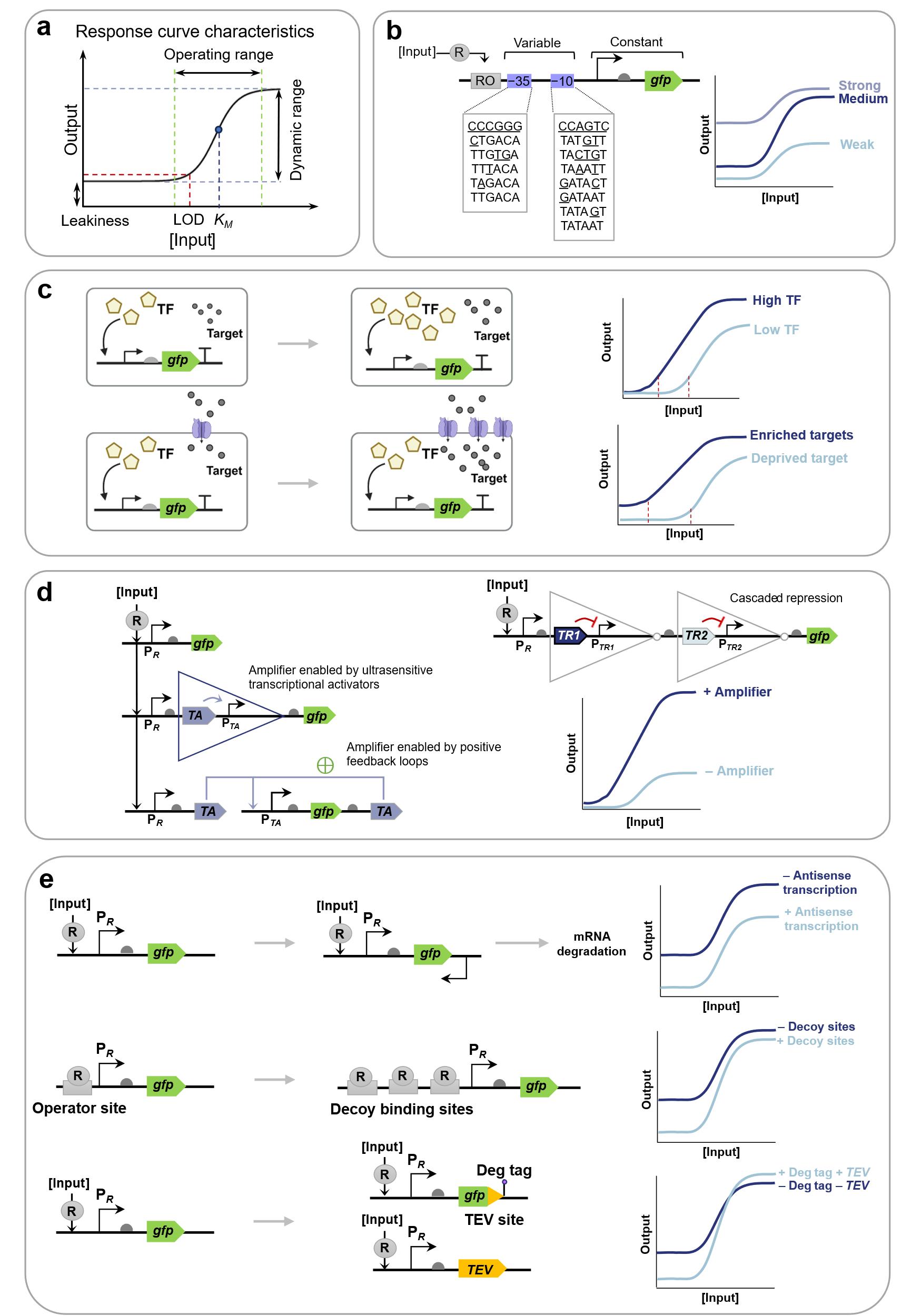
图8 合成生物传感器的敏感性优化策略(a) 基于基因线路的合成生物传感器的典型响应曲线和特征;(b) 基于启动子工程的动态范围优化机制;(c) 通过生物识别元件浓度梯度调节与靶标富集技术降低检测限;(d) 利用基于激活转录因子、正反馈回路和双抑制因子的传感信号放大器优化动态范围[7];(e) 利用反义RNA转录介导的翻译阻断、诱饵DNA结合位点竞争性抑制、引入输出蛋白降解标签减少传感器泄漏[1]。(R: Regulator; OR: Operator site for regulator; TF: Transcriptional factor; TA: Transcriptional activator; TR: Transcriptional repressor.)
Fig. 8 Strategies for increasing the sensitivity of genetic circuit-enabled synthetic biosensors(a) Typical response curves and characteristics of genetic circuit-enabled synthetic biosensors.; (b) Dynamic range optimization based on promoter engineering; (c) Limit of detection optimization by gradient regulation of biorecognition components concentration and target enrichment technology; (d) Dynamic range optimization using sensing signal amplifiers based on activator transcription factors, positive feedback loops and cascade repressors [7]; (e) Leakage optimization utilizing antisense RNA-mediated translation blocking, decoy DNA binding site competitive inhibition, and output protein degradation tags[1].
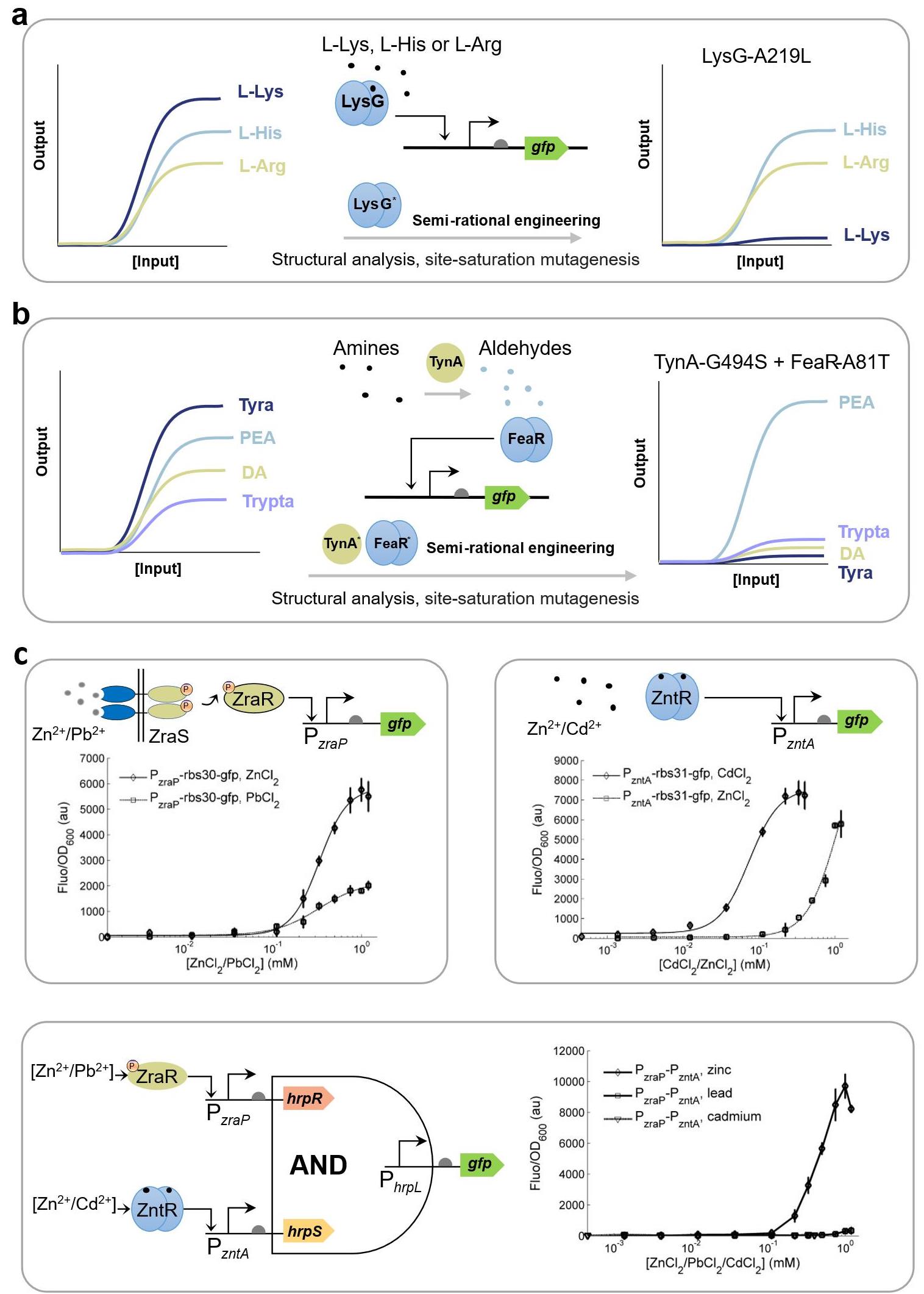
图9 合成生物传感器的特异性优化策略(a) 对转录因子LysG进行半理性设计与饱和突变,使其不结合L-赖氨酸(L-Lys),同时保持其L-组氨酸(L-His)和L-精氨酸(L-Arg)结合能力[191];(b) 对TynA-FeaR传感系统进行半理性设计与饱和突变,使其特异性检测苯乙胺。(DA:多巴胺;PEA:苯乙胺;Tyra:酪胺;Trypta:色胺)[192];(c) 将转录因子ZraR、ZntR通过AND gate耦合后特异性响应Zn2+[7,21]。
Fig. 9 Strategies for increasing the specificity of genetic circuit-enabled synthetic biosensors(a) Semi-rational design and saturation mutagenesis of the transcription factor LysG to prevent its binding to L-lysine (L-Lys) while retaining its ability to bind L-arginine (L-Arg) and L-histidine (L-His)[191]; (b) Semi-rational design and saturation mutagenesis of the TynA-FeaR sensing system for specific detection of phenylethylamine. (DA: dopamine; PEA: phenylethylamine; Tyra: tyramine; Trypta: tryptamine)[192]; (c) Coupling transcription factors ZraR and ZntR through an AND gate for specific respond to Zn²⁺[7,21].
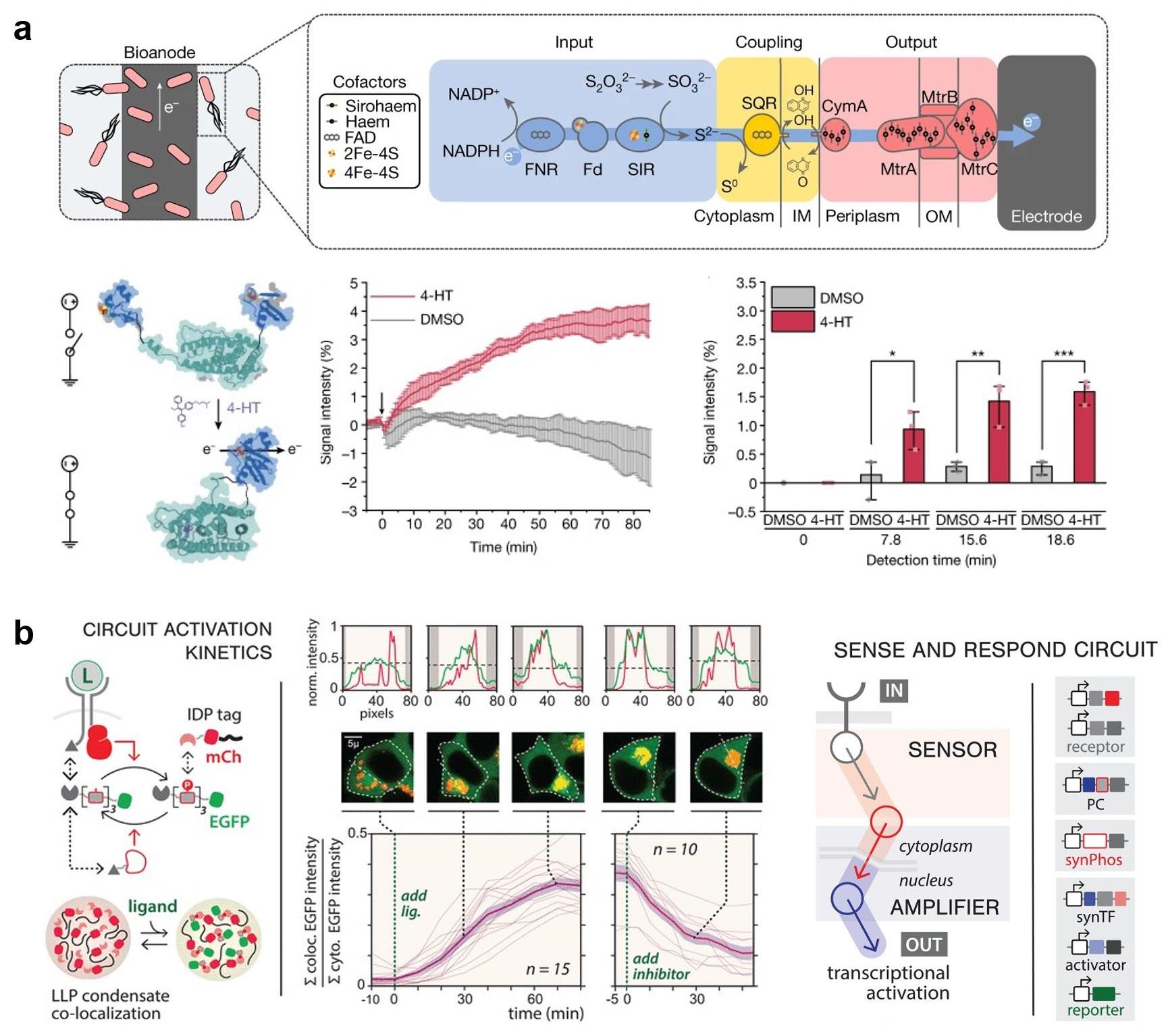
图10 合成生物传感器的响应速度优化示例(a) 基于大肠杆菌合成电子传递链的传感器设计,通过控制蛋白导电开关快速检测内分泌干扰素4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-HT)[6];(b) 快速激活和失活的蛋白质磷酸化信号转导网络的可逆性响应动力学曲线以及传感机制[197]。(IM: Inner membrane; OM: Outer membrane; PC: Phospho-couple)
Fig. 10 Examples of improving the response speed of genetic circuit-enabled synthetic biosensors(a) An E. coli-based sensor with a synthetic electron transfer chain that express an electrical protein switch enable rapid detection of an endocrine disruptor 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-HT)[6]; (b) Reversible response kinetics curve and sensing mechanism of a protein phosphorylation signaling network with rapid activation and deactivation[197].
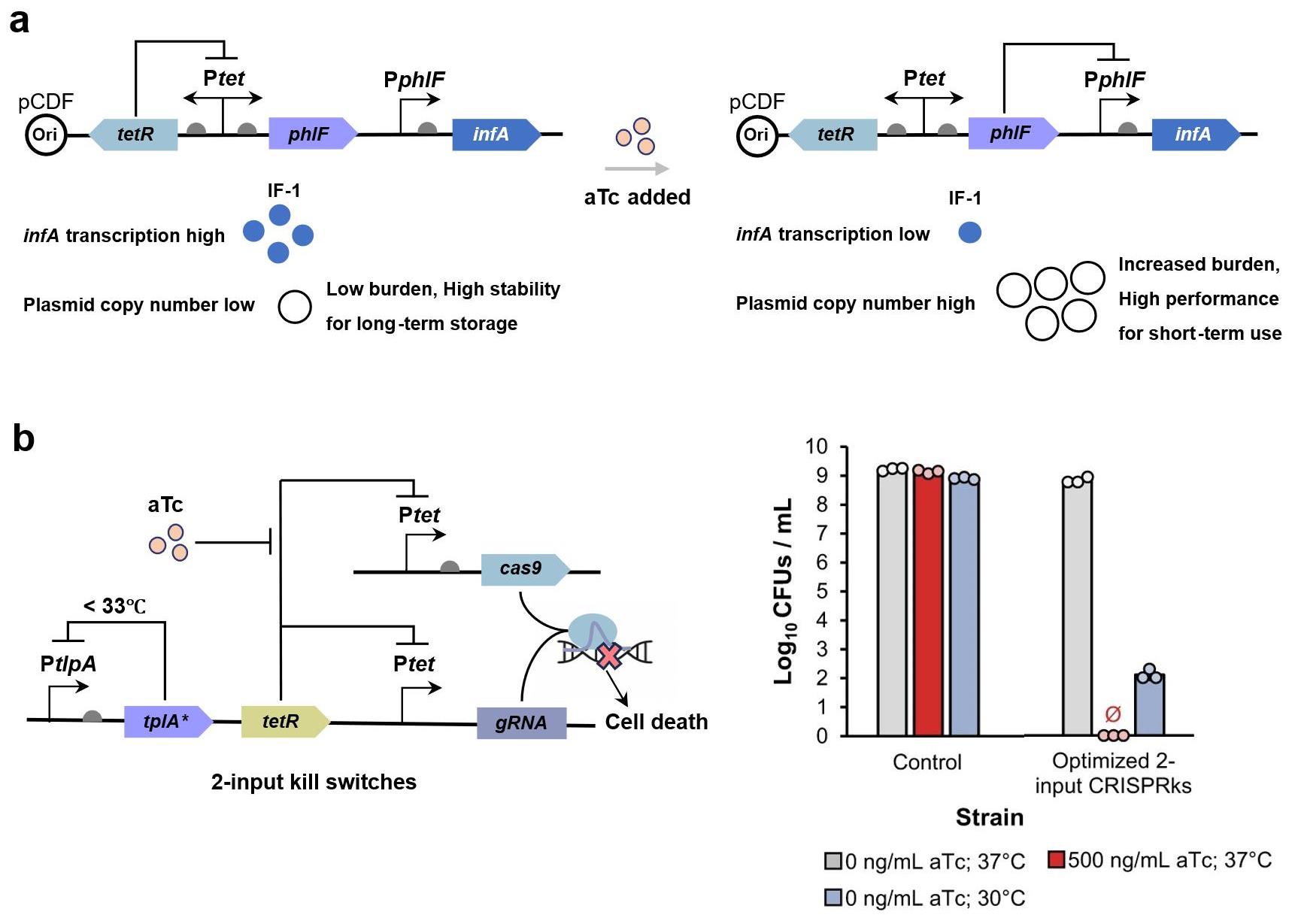
图11 基于基因线路的合成生物传感器稳定性和生物安全性优化示例(a) 一种基于翻译起始因子动态调控的大肠杆菌质粒拷贝数控制及遗传稳定性提升方法[204];(b) 一种响应化学诱导剂无水四环素(aTc)和温度变化的CRISPR-Cas9大肠杆菌双模态杀伤开关设计(CRISPRks)[212]。
Fig. 11 Examples of stability and biosafety optimization for genetic circuit-enabled synthetic biosensors(a) A plasmid copy number control platform in Escherichia coli based on dynamic regulation of translation initiation factors[204]; (b) A biocontaining CRISPR-Cas9 dual-modal kill switch (CRISPRks) for E. coli under the dual control of chemical inducer anhydrotetracycline (aTc) and temperature changes[212].
| 1 | HICKS M, BACHMANN T T, WANG B. Synthetic biology enables programmable cell-based biosensors[J]. ChemPhysChem, 2020, 21(2): 132-144. |
| 2 | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6, 45-64. DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-096 |
| 3 | SEDLMAYER F, AUBEL D, FUSSENEGGER M. Synthetic gene circuits for the detection, elimination and prevention of disease[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 2(6): 399-415. |
| 4 | VAN DER MEER J R, BELKIN S. Where microbiology meets microengineering: design and applications of reporter bacteria[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2010, 8(7): 511-522. |
| 5 | WANG B, KITNEY R I, JOLY N, et al. Engineering modular and orthogonal genetic logic gates for robust digital-like synthetic biology[J]. Nature Communications, 2011, 2, 508. |
| 6 | ATKINSON J T, SU L, ZHANG X, et al. Real-time bioelectronic sensing of environmental contaminants[J]. Nature, 2022, 611(7936): 548-553. |
| 7 | WAN X, HO T Y H, WANG B. Engineering prokaryote synthetic biology biosensors[M]//THOUAND G. Handbook of Cell Biosensors. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2022: 283-318. |
| 8 | VELUSAMY K, PERIYASAMY S, KUMAR P S, et al. Biosensor for heavy metals detection in wastewater: A review[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2022, 168: 113307. |
| 9 | LI J, CUI M, ZHAO J, et al. A self-amplifying plasmid based ultrasensitive biosensor for the detection of As(Ⅲ) in water[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2023, 221: 114937. |
| 10 | ZHANG T, ZHU K, ZHANG X, et al. Development of CadR-based cadmium whole cell biosensor for visual detection of environmental Cd2+ [J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2024, 1330: 343299. |
| 11 | WANG S H, WANG J W, ZHAO L T, et al. Soil microbial fuel cell based self-powered cathodic biosensor for sensitive detection of heavy metals[J]. Biosensors, 2023, 13, 145. |
| 12 | LIU J, XU J Z, RAO Z M, et al. An enzymatic colorimetric whole-cell biosensor for high-throughput identification of lysine overproducers[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2022, 216: 114681. |
| 13 | AUGUSTINIENE E, JONUSKIENE I, KAILIUVIENE J, et al. Application of whole-cell biosensors for analysis and improvement of L- and D-lactic acid fermentation by Lactobacillus spp. from the waste of glucose syrup production[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2023, 22, 223. |
| 14 | DING D, ZHU Y, BAI D, et al. Monitoring and dynamically controlling glucose uptake rate and central metabolism[J]. Nature Chemical Engineering, 2025, 2, 50-62. |
| 15 | RUAN Q, LIN X, WANG L, et al. An engineered (CAGA)12-EGFP cell-based biosensor for high-content and accurate detection of active TGF-β[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2023, 220: 114884. |
| 16 | HO C L, TAN H Q, CHUA K J, et al. Engineered commensal microbes for diet-mediated colorectal-cancer chemoprevention[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 2, 27-37. |
| 17 | LIU Y, PINTO F, WAN X, et al. Reprogrammed tracrRNAs enable repurposing of RNAs as crRNAs and sequence-specific RNA biosensors[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13, 1937. |
| 18 | 毛瑞超, 王宝俊. 合成生物元件与线路的智能设计[J]. 生物工程学报, 2025, 41(3): 1023-1051. DOI: 10.13345/j.cjb.240605 |
| 19 | BUSON F, GAO Y, WANG B. Genetic parts and enabling tools for biocircuit design[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2024, 13(3): 697-713. |
| 20 | GAO Y, WANG L, WANG B. Customizing cellular signal processing by synthetic multi-level regulatory circuits[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14, 8415. |
| 21 | WANG B, BARAHONA M, BUCK M. A modular cell-based biosensor using engineered genetic logic circuits to detect and integrate multiple environmental signals[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2013, 40, 368-376. |
| 22 | MERULLA D, VAN DER MEER J R. Regulatable and modulable background expression control in prokaryotic synthetic circuits by auxiliary repressor binding sites[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2016, 5, 36-45. |
| 23 | CHEMLA Y, SWEENEY C J, WOZNIAK C A, et al. Design and regulation of engineered bacteria for environmental release[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2025, 10(2): 281-300. |
| 24 | NAKAMURA H, KARUBE I. Current research activity in biosensors[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2003, 377(3): 446-468. |
| 25 | ZHANG H, LIN M, SHI H, et al. Programming a Pavlovian-like conditioning circuit in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5, 3102. |
| 26 | BERNARD E, WANG B. Synthetic cell-based sensors with programmed selectivity and sensitivity[M]//PRICKRIL B, RASOOLY A. Biosensors and Biodetection:Vol. 1572. YorkNew, NY: Springer New York, 2017: 349-363. |
| 27 | KIM H J, JEONG H, LEE S J. Synthetic biology for microbial heavy metal biosensors[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2018, 410(4): 1191-1203. |
| 28 | BRADLEY R W, WANG B. Designer cell signal processing circuits for biotechnology[J]. New Biotechnology, 2015, 32(6): 635-643. |
| 29 | WANG B, BUCK M. Customizing cell signaling using engineered genetic logic circuits[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 2012, 20(8): 376-384. |
| 30 | DE PAEPE B, DE MEY M. Biological switches: past and future milestones of transcription factor-based biosensors[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2025, 14, 72-86. |
| 31 | JOSHI S H N, JENKINS C, ULAETO D, et al. Accelerating genetic sensor development, scale-up, and deployment using synthetic biology[J]. BioDesign Research, 2024, 6: 0037. |
| 32 | WAN X, VOLPETTI F, PETROVA E, et al. Cascaded amplifying circuits enable ultrasensitive cellular sensors for toxic metals[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2019, 15(5): 540-548. |
| 33 | PARK D M, TAFFET M J. Combinatorial sensor design in caulobacter crescentus for selective environmental uranium detection[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(4): 807-817. |
| 34 | ZHANG Q, WEI Z, JIA X. Controllable detection threshold achieved through the toehold switch system in a mercury ion whole-cell biosensor[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2024, 256: 116283. |
| 35 | SALTEPE B, BOZKURT E U, GÜNGEN M A, et al. Genetic circuits combined with machine learning provides fast responding living sensors[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2021, 178: 113028. |
| 36 | DOSHI A, SHAW M, TONEA R, et al. Engineered bacterial swarm patterns as spatial records of environmental inputs[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2023, 19(7): 878-886. |
| 37 | YAGUR-KROLL S, AMIEL E, ROSEN R, et al. Detection of 2,4-dinitrotoluene and 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene by an Escherichia coli bioreporter: performance enhancement by directed evolution[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 99(17): 7177-7188. |
| 38 | ESSINGTON E A, VEZEAU G E, CETNAR D P, et al. An autonomous microbial sensor enables long-term detection of TNT explosive in natural soil[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15, 10471. |
| 39 | LUISI B, HEGAB R, PERSON C, et al. Engineered biosensors in an encapsulated and deployable system for environmental chemical detection[J]. ACS Sensors, 2022, 7(9): 2589-2596. |
| 40 | HERNÁNDEZ‐SÁNCHEZ V, MOLINA L, RAMOS J L, et al. New family of biosensors for monitoring BTX in aquatic and edaphic environments[J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 2016, 9(6): 858-867. |
| 41 | SELVAMANI V, MARUTHAMUTHU M K, ARULSAMY K, et al. Construction of methanol sensing Escherichia coli by the introduction of novel chimeric MxcQZ/OmpR two-component system from Methylobacterium organophilum XX[J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2017, 34(6): 1734-1739. |
| 42 | WU Y, WANG C W, WANG D, et al. A whole-cell biosensor for point-of-care detection of waterborne bacterial pathogens[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2021, 10(2): 333-344. |
| 43 | LIU K, ZHANG Y, LIU K, et al. De novo design of a transcription factor for a progesterone biosensor[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2022, 203: 113897. |
| 44 | WATSTEIN D M, STYCZYNSKI M P. Development of a pigment-based whole-cell zinc biosensor for human serum[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7, 267-275. |
| 45 | MIETTINEN K, LEELAHAKORN N, ALMEIDA A, et al. A GPCR-based yeast biosensor for biomedical, biotechnological, and point-of-use cannabinoid determination[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13, 3664. |
| 46 | CHANG H J, ZÚÑIGA A, CONEJERO I, et al. Programmable receptors enable bacterial biosensors to detect pathological biomarkers in clinical samples[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12, 5216. |
| 47 | ZOU Z P, YANG Y, WANG J, et al. Coupling split-lux cassette with a toggle switch in bacteria for ultrasensitive blood markers detection in feces and urine[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2022, 214: 114520. |
| 48 | INDA-WEBB M E, JIMENEZ M, LIU Q, et al. Sub-1.4 cm3 capsule for detecting labile inflammatory biomarkers in situ[J]. Nature, 2023, 620(7973): 386-392. |
| 49 | GOOTENBERG J S, ABUDAYYEH O O, LEE J W, et al. Nucleic acid detection with CRISPR-Cas13a/C2c2[J]. Science, 2017, 356(6336): 438-442. |
| 50 | CHEN J S, MA E, HARRINGTON L B, et al. CRISPR-Cas12a target binding unleashes indiscriminate single-stranded DNase activity[J]. Science, 2018, 360(6387): 436-439. |
| 51 | RÖSSGER K, CHARPIN-EL-HAMRI G, FUSSENEGGER M. A closed-loop synthetic gene circuit for the treatment of diet-induced obesity in mice[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4, 2825. |
| 52 | MAO N, CUBILLOS-RUIZ A, CAMERON D E, et al. Probiotic strains detect and suppress cholera in mice[J]. Science Translational Medicine, 2018, 10(445): eaao2586. |
| 53 | JIANG S, CHEN H, CHEN S, et al. Genetically encoded biosensors for constrained biological functions in probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2025, 14, 296-303. |
| 54 | ZOU Z P, DU Y, FANG T T, et al. Biomarker-responsive engineered probiotic diagnoses, records, and ameliorates inflammatory bowel disease in mice[J]. Cell Host & Microbe, 2023, 31(2): 199-212.e5. |
| 55 | HUANG J, TEIXEIRA A P, GAO T, et al. Aspirin-responsive gene switch regulating therapeutic protein expression[J]. Nature Communications, 2025, 16, 2028. |
| 56 | MAHAMEED M, XUE S, DANUSER B, et al. Nitroglycerin-responsive gene switch for the on-demand production of therapeutic proteins[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2025. |
| 57 | MIMEE M, TUCKER A C, VOIGT C A, et al. Programming a human commensal bacterium, bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, to sense and respond to stimuli in the murine gut microbiota[J]. Cell Systems, 2016, 2(3): 214. |
| 58 | GAO J, DU M, ZHAO J, et al. Design of a genetically encoded biosensor to establish a high-throughput screening platform for L-cysteine overproduction[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2022, 73: 144-157. |
| 59 | ZHANG Y, LI Y, XIAO F, et al. Engineering of a biosensor in response to malate in Bacillus licheniformis [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2021, 10(7): 1775-1784. |
| 60 | NI C, FOX K J, PRATHER K L J. Substrate-activated expression of a biosynthetic pathway in Escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2022, 17(3): 2000433. |
| 61 | PU W, CHEN J, LIU P, et al. Directed evolution of linker helix as an efficient strategy for engineering LysR-type transcriptional regulators as whole-cell biosensors[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2023, 222: 115004. |
| 62 | MANNAN A A, BATES D G. Designing an irreversible metabolic switch for scalable induction of microbial chemical production[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12, 3419. |
| 63 | WU J, JIANG P, CHEN W, et al. Design and application of a lactulose biosensor[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7, 45994. |
| 64 | MICHENER J K, SMOLKE C D. High-throughput enzyme evolution in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using a synthetic RNA switch[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2012, 14(4): 306-316. |
| 65 | D'OELSNITZ S, KIM W, BURKHOLDER N T, et al. Using fungible biosensors to evolve improved alkaloid biosyntheses[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2022, 18(9): 981-989. |
| 66 | D'OELSNITZ S, DIAZ D J, KIM W, et al. Biosensor and machine learning-aided engineering of an amaryllidaceae enzyme[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15, 2084. |
| 67 | SELIM A S, PERRY J M, NASR M A, et al. A synthetic biosensor for detecting putrescine in beef samples[J]. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 2022, 5(11): 5487-5496. |
| 68 | CHOI O, LEE Y, HAN I, et al. A simple and sensitive biosensor strain for detecting toxoflavin using β-galactosidase activity[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2013, 50: 256-261. |
| 69 | BHATT A, JAIN S, NAVANI N K. Rapid, sensitive, and specific microbial whole-cell biosensor for the detection of histamine: a potential food toxin[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024, 72(49): 27466-27478. |
| 70 | LI Y, LUCCI T, VILLARRUEL DUJOVNE M, et al. A cell-free biosensor signal amplification circuit with polymerase strand recycling[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2025. |
| 71 | LI X, ZHANG C, XU X, et al. A single-component light sensor system allows highly tunable and direct activation of gene expression in bacterial cells[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 48(6): e33-e33. |
| 72 | XIU Y, JANG S, JONES J A, et al. Naringenin-responsive riboswitch‐based fluorescent biosensor module for Escherichia coli co-cultures[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2017, 114(10): 2235-2244. |
| 73 | LIU C C, JEWETT M C, CHIN J W, et al. Toward an orthogonal central dogma[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2018, 14(2): 103-106. |
| 74 | JOHNS N I, GOMES A L C, YIM S S, et al. Metagenomic mining of regulatory elements enables programmable species-selective gene expression[J]. Nature Methods, 2018, 15(5): 323-329. |
| 75 | XUE H, SHI H, YU Z, et al. Design, construction, and characterization of a set of biosensors for aromatic compounds[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2014, 3(12): 1011-1014. |
| 76 | LI S, LI Z, TAN G Y, et al. In vitro allosteric transcription factor-based biosensing[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2023, 41(8): 1080-1095. |
| 77 | GRAZON C, BAER R C, KUZMANOVIĆ U, et al. A progesterone biosensor derived from microbial screening[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11, 1276. |
| 78 | SHEN W K, CHEN S Y, GAN Z Q, et al. AnimalTFDB 4.0: a comprehensive animal transcription factor database updated with variation and expression annotations[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2023, 51(D1): D39-D45. |
| 79 | RAULUSEVICIUTE I, RIUDAVETS-PUIG R, BLANC-MATHIEU R, et al. JASPAR 2024: 20th anniversary of the open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2024, 52(D1): D174-D182. |
| 80 | D'OELSNITZ S, LOVE J D, DIAZ D J, et al. GroovDB: A database of ligand-inducible transcription factors[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2022, 11(10): 3534-3537. |
| 81 | NISHIKAWA K K, CHEN J, ACHESON J F, et al. Highly multiplexed design of an allosteric transcription factor to sense new ligands[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15, 10001. |
| 82 | MITCHLER M M, GARCIA J M, MONTERO N E, et al. Transcription factor-based biosensors: a molecular-guided approach for natural product engineering[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2021, 69: 172-181. |
| 83 | HASKETT T L, PARAMASIVAN P, MENDES M D, et al. Engineered plant control of associative nitrogen fixation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2022, 119(16): e2117465119. |
| 84 | DING N, YUAN Z, MA Z, et al. AI-assisted rational design and activity prediction of biological elements for optimizing transcription-factor-based biosensors[J]. Molecules, 2024, 29(15): 3512. |
| 85 | TELLECHEA-LUZARDO J, MARTÍN LÁZARO H, MORENO LÓPEZ R, et al. Sensbio: an online server for biosensor design[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2023, 24, 71. |
| 86 | JUNG K, FABIANI F, HOYER E, et al. Bacterial transmembrane signalling systems and their engineering for biosensing[J]. Open Biology, 2018, 8(4): 180023. |
| 87 | ULRICH L E, KOONIN E V, ZHULIN I B. One-component systems dominate signal transduction in prokaryotes[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 2005, 13(2): 52-56. |
| 88 | GUBENSÄK N, SAGMEISTER T, BUHLHELLER C, et al. Vibrio cholerae's ToxRS bile sensing system[J]. eLife, 2023, 12: e88721. |
| 89 | DELL C L, NEELY M N, OLSON E R. Altered pH lysine signalling mutants of cadC, a gene encoding a membrane-bound transcriptional activator of the Escherichia coli cadBA operon[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 1994, 14, 7-16. |
| 90 | EICHINGER A, HANEBURGER I, KOLLER C, et al. Crystal structure of the sensory domain of Escherichia coli CadC, a member of the ToxR‐like protein family[J]. Protein Science, 2011, 20(4): 656-669. |
| 91 | FRITZ G, KOLLER C, BURDACK K, et al. Induction kinetics of a conditional pH stress response system in Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2009, 393(2): 272-286. |
| 92 | CHANG H J, MAYONOVE P, ZAVALA A, et al. A modular receptor platform to expand the sensing repertoire of bacteria[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7, 166-175. |
| 93 | SHEN L, CHEN Y, HU L, et al. Development of a highly sensitive, visual platform for the detection of cadmium in actual wastewater based on evolved whole-cell biosensors[J]. ACS Sensors, 2024, 9(2): 654-661. |
| 94 | LI Q, CHEN S, WANG H, et al. Decoding wheat contamination through self-assembled whole-cell biosensor combined with linear and non-linear machine learning algorithms[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2025, 267: 116869. |
| 95 | KOMATSU S, OHNO H, SAITO H. Target-dependent RNA polymerase as universal platform for gene expression control in response to intracellular molecules[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14, 7256. |
| 96 | CAO W, HUANG C, ZHOU X, et al. Engineering two-component systems for advanced biosensing: From architecture to applications in biotechnology[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2024, 75: 108404. |
| 97 | SADOTRA S, LOU Y C, TANG H C, et al. Structural basis for promoter DNA recognition by the response regulator OmpR[J]. Journal of Structural Biology, 2021, 213, 107638. |
| 98 | ALVAREZ A F, GEORGELLIS D. Environmental adaptation and diversification of bacterial two-component systems[J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2023, 76: 102399. |
| 99 | GALPERIN M Y. Diversity of structure and function of response regulator output domains[J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2010, 13(2): 150-159. |
| 100 | ISHII E, EGUCHI Y. Diversity in sensing and signaling of bacterial sensor histidine kinases[J]. Biomolecules, 2021, 11(10): 1524. |
| 101 | BHATE M P, MOLNAR K S, GOULIAN M, et al. Signal transduction in histidine kinases: insights from new structures[J]. Structure, 2015, 23(6): 981-994. |
| 102 | ZHOU S, ALPER H S, ZHOU J, et al. Intracellular biosensor-based dynamic regulation to manipulate gene expression at the spatiotemporal level[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2023, 43(4): 646-663. |
| 103 | LIU C, YU H, ZHANG B, et al. Engineering whole-cell microbial biosensors: Design principles and applications in monitoring and treatment of heavy metals and organic pollutants[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2022, 60: 108019. |
| 104 | WOO S G, MOON S J, KIM S K, et al. A designed whole-cell biosensor for live diagnosis of gut inflammation through nitrate sensing[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2020, 168: 112523. |
| 105 | ZHANG J, XU J, YIN J, et al. Design and optimization of a two-component TorRST-based biosensor for detection and degradation of trimethylamine N-oxide[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2025, 14(2): 553-563. . |
| 106 | RAMAKRISHNAN P, TABOR J J. Repurposing Synechocystis PCC6803 UirS-UirR as a UV-violet/green photoreversible transcriptional regulatory tool in E. coli [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2016, 5(7): 733-740. |
| 107 | SCHMIDL S R, EKNESS F, SOFJAN K, et al. Rewiring bacterial two-component systems by modular DNA-binding domain swapping[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2019, 15(7): 690-698. |
| 108 | SUN L, ZHANG Q, KONG X, et al. Highly efficient neutralizer-free l-malic acid production using engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 370: 128580. |
| 109 | WU Y, ZHU L, LI S, et al. High content design of riboswitch biosensors: All-around rational module-by-module design[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2023, 220: 114887. |
| 110 | DOUAKI A, GAROLI D, INAM A K M S, et al. Smart approach for the design of highly selective aptamer-based biosensors[J]. Biosensors, 2022, 12(8): 574. |
| 111 | LEE M, SHIN S, KIM S, et al. Recent advances in biological applications of aptamer-based fluorescent biosensors[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(21): 7327. |
| 112 | WANG X, WEI W, ZHAO J. Using a riboswitch sensor to detect Co2+/Ni2+ transport in E. coli [J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2021, 9: 631909. |
| 113 | MCNERNEY M P, PIORINO F, MICHEL C L, et al. Active analyte import improves the dynamic range and sensitivity of a vitamin B12 Biosensor[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(2): 402-411. |
| 114 | QIN P P, CHEN P R, TAN L, et al. Programming ADAR-recruiting hairpin RNA sensor to detect endogenous molecules[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2025, 53, gkae1146. |
| 115 | MCCOWN P J, CORBINO K A, STAV S, et al. Riboswitch diversity and distribution[J]. RNA, 2017, 23(7): 995-1011. |
| 116 | GAN Z, ROSLAN M A M, SHUKOR M Y ABD, et al. Advances in aptamer-based biosensors and cell-internalizing SELEX technology for diagnostic and therapeutic application[J]. Biosensors, 2022, 12(11): 922. |
| 117 | GUO M, HUANG K, XU W. Third generation whole-cell sensing systems: synthetic biology inside, nanomaterial outside[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2021, 39(6): 550-559. |
| 118 | YOSHIKAWA A M, RANGEL A E, ZHENG L, et al. A massively parallel screening platform for converting aptamers into molecular switches[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14, 2336. |
| 119 | MURANAKA N, SHARMA V, NOMURA Y, et al. Efficient design strategy for whole-cell and cell-free biosensors based on engineered riboswitches[J]. Analytical Letters, 2009, 42, 108-122. |
| 120 | COPELAND C E, LANGLOIS A, KIM J, et al. The cell-free system: A new apparatus for affordable, sensitive, and portable healthcare[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 175: 108124. |
| 121 | NGUYEN P Q, SOENKSEN L R, DONGHIA N M, et al. Wearable materials with embedded synthetic biology sensors for biomolecule detection[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2021, 39(11): 1366-1374. |
| 122 | GAO Y, MARDIAN R, MA J, et al. Programmable trans-splicing riboregulators for complex cellular logic computation[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2025. |
| 123 | GREEN A A, SILVER P A, COLLINS J J, et al. Toehold switches: de-novo-designed regulators of gene expression[J]. Cell, 2014, 159(4): 925-939. |
| 124 | YARRA S S, ASHOK G, MOHAN U. "Toehold switches; a foothold for synthetic biology"[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2023, 120(4): 932-952. |
| 125 | GAMBILL L, STAUBUS A, MO K W, et al. A split ribozyme that links detection of a native RNA to orthogonal protein outputs[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14, 543. |
| 126 | MA D, LI Y, WU K, et al. Multi-arm RNA junctions encoding molecular logic unconstrained by input sequence for versatile cell-free diagnostics[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2022, 6(3): 298-309. |
| 127 | KIM J, ZHOU Y, CARLSON P D, et al. De novo-designed translation-repressing riboregulators for multi-input cellular logic[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2019, 15(12): 1173-1182. |
| 128 | CHAPPELL J, WESTBROOK A, VEROSLOFF M, et al. Computational design of small transcription activating RNAs for versatile and dynamic gene regulation[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8, 1051. |
| 129 | KÖKSALDI İ Ç, KÖSE S, AHAN R E, et al. SARS-CoV-2 detection with de novo-designed synthetic riboregulators[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 93(28): 9719-9727. |
| 130 | CHEN Y, XIA W, PAN Z, et al. Development of a cell-free, toehold switch-based biosensor for rapid and sensitive zika virus detection[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2025, 97(6): 3486-3494. |
| 131 | CISNEROS A F, ROULEAU F D, BAUTISTA C, et al. Toeholder: a software for automated design and in silico validation of toehold riboswitches[A]. Bioinformatics, 2021. |
| 132 | VALERI J A, COLLINS K M, RAMESH P, et al. Sequence-to-function deep learning frameworks for engineered riboregulators[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11, 5058. |
| 133 | SELINIDIS M A, CORLISS A C, CHAPPELL J, et al. Ribozyme-mediated gene-fragment complementation for nondestructive reporting of DNA transfer within soil[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2024, 13(11): 3539-3547. |
| 134 | JINEK M, EAST A, CHENG A, et al. RNA-programmed genome editing in human cells[J]. eLife, 2013, 2: e00471. |
| 135 | JIANG G, GAO Y, ZHOU N, et al. CRISPR-powered RNA sensing in vivo[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2024, 42(12): 1601-1614. |
| 136 | DÍAZ-GALICIA E, GRÜNBERG R, AROLD S T. How to find the right RNA-sensing CRISPR-Cas system for an in vitro application[J]. Biosensors, 2022, 12(2): 53. |
| 137 | JINEK M, CHYLINSKI K, FONFARA I, et al. A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity[J]. Science, 2012, 337(6096): 816-821. |
| 138 | JIAO C, RECKSTADT C, KÖNIG F, et al. RNA recording in single bacterial cells using reprogrammed tracrRNAs[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2023, 41(8): 1107-1116. |
| 139 | JIAO C, SHARMA S, DUGAR G, et al. Noncanonical crRNAs derived from host transcripts enable multiplexable RNA detection by Cas9[J]. Science, 2021, 372(6545): 941-948. |
| 140 | LIU Y, WAN X, WANG B. Engineered CRISPRa enables programmable eukaryote-like gene activation in bacteria[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10, 3693. |
| 141 | BIKARD D, JIANG W, SAMAI P, et al. Programmable repression and activation of bacterial gene expression using an engineered CRISPR-Cas system[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2013, 41(15): 7429-7437. |
| 142 | LEE Y J, HOYNES-O'CONNOR A, LEONG M C, et al. Programmable control of bacterial gene expression with the combined CRISPR and antisense RNA system[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2016, 44(5): 2462-2473. |
| 143 | SIU K H, CHEN W. Riboregulated toehold-gated gRNA for programmable CRISPR-Cas9 function[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2019, 15(3): 217-220. |
| 144 | FU Y, FODEN J A, KHAYTER C, et al. High-frequency off-target mutagenesis induced by CRISPR-Cas nucleases in human cells[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2013, 31(9): 822-826. |
| 145 | GOOTENBERG J S, ABUDAYYEH O O, KELLNER M J, et al. Multiplexed and portable nucleic acid detection platform with Cas13, Cas12a, and Csm6[J]. Science, 2018, 360(6387): 439-444. |
| 146 | CHIANG A J, HASTY J. Design of synthetic bacterial biosensors[J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2023, 76: 102380. |
| 147 | COURBET A, ENDY D, RENARD E, et al. Detection of pathological biomarkers in human clinical samples via amplifying genetic switches and logic gates[J]. Science Translational Medicine, 2015, 7(289). |
| 148 | RIGLAR D T, GIESSEN T W, BAYM M, et al. Engineered bacteria can function in the mammalian gut long-term as live diagnostics of inflammation[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2017, 35(7): 653-658. |
| 149 | GARDNER T S, CANTOR C R, COLLINS J J. Construction of a genetic toggle switch in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6767): 339-342. |
| 150 | OLORUNNIJI F J, ROSSER S J, STARK W M. Site-specific recombinases: molecular machines for the Genetic Revolution[J]. Biochemical Journal, 2016, 473(6): 673-684. |
| 151 | WANG Y, YAU Y Y, PERKINS-BALDING D, et al. Recombinase technology: applications and possibilities[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2011, 30(3): 267-285. |
| 152 | BONNET J, YIN P, ORTIZ M E, et al. Amplifying genetic logic gates[J]. Science, 2013, 340(6132): 599-603. |
| 153 | ZHU D, GALLEY J, PIZZINI J, et al. Microbial biosensor for sensing and treatment of intestinal inflammation[A]. Synthetic Biology, 2023. |
| 154 | ABEDI M H, YAO M S, MITTELSTEIN D R, et al. Ultrasound-controllable engineered bacteria for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13, 1585. |
| 155 | NOVÁK B, TYSON J J. Design principles of biochemical oscillators[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2008, 9(12): 981-991. |
| 156 | GUO L, LIU M, BI Y, et al. Using a synthetic machinery to improve carbon yield with acetylphosphate as the core[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14, 5286. |
| 157 | DIN M O, DANINO T, PRINDLE A, et al. Synchronized cycles of bacterial lysis for in vivo delivery[J]. Nature, 2016, 536(7614): 81-85. |
| 158 | TANG W, LIU D R. Rewritable multi-event analog recording in bacterial and mammalian cells[J]. Science, 2018, 360(6385): eaap8992. |
| 159 | COOPER R M, WRIGHT J A, NG J Q, et al. Engineered bacteria detect tumor DNA[J]. Science, 2023, 381(6658): 682-686. |
| 160 | KALVAPALLE P B, STAUBUS A, DYSART M J, et al. Information storage across a microbial community using universal RNA barcoding[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2025. |
| 161 | BROPHY J A N, VOIGT C A. Principles of genetic circuit design[J]. Nature Methods, 2014, 11(5): 508-520. |
| 162 | CHIEN T, HARIMOTO T, KEPECS B, et al. Enhancing the tropism of bacteria via genetically programmed biosensors[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2021, 6, 94-104. |
| 163 | MOSER F, ESPAH BORUJENI A, GHODASARA A N, et al. Dynamic control of endogenous metabolism with combinatorial logic circuits[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2018, 14(11): e8605. |
| 164 | DIDOVYK A, TONOOKA T, TSIMRING L, et al. Rapid and scalable preparation of bacterial lysates for cell-free gene expression[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(12): 2198-2208. |
| 165 | ZEVALLOS-ALIAGA D, DE GRAEVE S, OBANDO-CHÁVEZ P, et al. Highly sensitive whole-cell mercury biosensors for environmental monitoring[J]. Biosensors, 2024, 14(5): 246. |
| 166 | MIMEE M, NADEAU P, HAYWARD A, et al. An ingestible bacterial-electronic system to monitor gastrointestinal health[J]. Science, 2018, 360(6391): 915-918. |
| 167 | HUANG Z, GUSTAVE W, BAI S, et al. Challenges and opportunities in commercializing whole-cell bioreporters in environmental application[J]. Environmental Research, 2024, 262: 119801. |
| 168 | PHAM C, STOGIOS P J, SAVCHENKO A, et al. Advances in engineering and optimization of transcription factor-based biosensors for plug-and-play small molecule detection[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2022, 76: 102753. |
| 169 | MEYER A J, SEGALL-SHAPIRO T H, GLASSEY E, et al. Escherichia coli "Marionette" strains with 12 highly optimized small-molecule sensors[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2019, 15(2): 196-204. |
| 170 | NASR M A, MARTIN V J J, KWAN D H. Divergent directed evolution of a TetR-type repressor towards aromatic molecules[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2023, 51(14): 7675-7690. |
| 171 | LIU Y, ZHOU Z, WU Y, et al. Engineered transcription factor-binding diversed functional nucleic acid-based synthetic biosensor[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2024, 77: 108463. |
| 172 | KASEY C M, ZERRAD M, LI Y, et al. Development of transcription factor-based designer macrolide biosensors for metabolic engineering and synthetic biology[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7, 227-239. |
| 173 | LANDRY B P, PALANKI R, DYULGYAROV N, et al. Phosphatase activity tunes two-component system sensor detection threshold[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9, 1433. |
| 174 | WANG B, BARAHONA M, BUCK M. Amplification of small molecule-inducible gene expression via tuning of intracellular receptor densities[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2015, 43(3): 1955-1964. |
| 175 | CAYRON J, PRUDENT E, ESCOFFIER C, et al. Pushing the limits of nickel detection to nanomolar range using a set of engineered bioluminescent Escherichia coli [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24, 4-14. |
| 176 | YAN H, WEN Y, TIAN Z, et al. A one-pot isothermal Cas12-based assay for the sensitive detection of microRNAs[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2023, 7(12): 1583-1601. |
| 177 | MOON J, LIU C. Asymmetric CRISPR enabling cascade signal amplification for nucleic acid detection by competitive crRNA[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14, 7504. |
| 178 | LOPRESIDE A, WAN X, MICHELINI E, et al. Comprehensive profiling of diverse genetic reporters with application to whole-cell and cell-free biosensors[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(23): 15284-15292. |
| 179 | CHEN S Y, ZHANG Y, LI R, et al. De novo design of the ArsR regulated Pars promoter enables a highly sensitive whole-cell biosensor for arsenic contamination[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 94(20): 7210-7218. |
| 180 | CHEN Y, HO J M L, SHIS D L, et al. Tuning the dynamic range of bacterial promoters regulated by ligand-inducible transcription factors[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9, 64. |
| 181 | WANG B, BARAHONA M, BUCK M. Engineering modular and tunable genetic amplifiers for scaling transcriptional signals in cascaded gene networks[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2014, 42(14): 9484-9492. |
| 182 | LIU L, ZHANG L, WANG J, et al. Copper-inducible expression system for metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2023, 134(6): lxad109. |
| 183 | SON H I, HAMRICK G S, SHENDE A R, et al. Population-level amplification of gene regulation by programmable gene transfer[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2025. |
| 184 | BROPHY J A, VOIGT C A. Antisense transcription as a tool to tune gene expression[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2016, 12, 854. |
| 185 | HO T Y H, SHAO A, LU Z, et al. A systematic approach to inserting split inteins for Boolean logic gate engineering and basal activity reduction[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12, 2200. |
| 186 | WAN X, PINTO F, YU L, et al. Synthetic protein-binding DNA sponge as a tool to tune gene expression and mitigate protein toxicity[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11, 5961. |
| 187 | LEE T, MAHESHRI N. A regulatory role for repeated decoy transcription factor binding sites in target gene expression[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2012, 8, 576. |
| 188 | COX R S, SURETTE M G, ELOWITZ M B. Programming gene expression with combinatorial promoters[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2007, 3, 145. |
| 189 | HAO N, KRISHNA S, AHLGREN-BERG A, et al. Road rules for traffic on DNA—systematic analysis of transcriptional roadblocking in vivo[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2014, 42(14): 8861-8872. |
| 190 | GRECO F V, PANDI A, ERB T J, et al. Harnessing the central dogma for stringent multi-level control of gene expression[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12, 1738. |
| 191 | DELLA CORTE D, VAN BEEK H L, SYBERG F, et al. Engineering and application of a biosensor with focused ligand specificity[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11, 4851. |
| 192 | ROTTINGHAUS A G, XI C, AMROFELL M B, et al. Engineering ligand-specific biosensors for aromatic amino acids and neurochemicals[J]. Cell Systems, 2022, 13(3): 204-214.e4. |
| 193 | BOSE D, SU Y, MARCUS A, et al. An RNA-based fluorescent biosensor for high-throughput analysis of the cGAS-cGAMP-STING pathway[J]. Cell Chemical Biology, 2016, 23(12): 1539-1549. |
| 194 | LIU Q, SCHUMACHER J, WAN X, et al. Orthogonality and burdens of heterologous AND gate gene circuits in E. coli [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(2): 553-564. |
| 195 | SCHAERLI Y, GILI M, ISALAN M. A split intein T7 RNA polymerase for transcriptional AND-logic[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2014, 42(19): 12322-12328. |
| 196 | THOMPSON I A P, ZHENG L, EISENSTEIN M, et al. Rational design of aptamer switches with programmable pH response[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11, 2946. |
| 197 | YANG X, ROCKS J W, JIANG K, et al. Engineering synthetic phosphorylation signaling networks in human cells[J]. Science, 2025, 387(6729): 74-81. |
| 198 | WANG X, KANG L, KONG D, et al. A programmable protease-based protein secretion platform for therapeutic applications[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2024, 20(4): 432-442. |
| 199 | VÁZQUEZ TORRES S, LEUNG P J Y, VENKATESH P, et al. De novo design of high-affinity binders of bioactive helical peptides[J]. Nature, 2024, 626(7998): 435-442. |
| 200 | HELLWEG L, EDENHOFER A, BARCK L, et al. A general method for the development of multicolor biosensors with large dynamic ranges[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2023, 19(9): 1147-1157. |
| 201 | TELLECHEA-LUZARDO J, STIEBRITZ M T, CARBONELL P. Transcription factor-based biosensors for screening and dynamic regulation[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2023, 11: 1118702. |
| 202 | SEGALL-SHAPIRO T H, SONTAG E D, VOIGT C A. Engineered promoters enable constant gene expression at any copy number in bacteria[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(4): 352-358. |
| 203 | SHAO B, RAMMOHAN J, ANDERSON D A, et al. Single-cell measurement of plasmid copy number and promoter activity[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12, 1475. |
| 204 | PARK G, YANG J, SEO S W. Dynamic control of the plasmid copy number maintained without antibiotics in Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Biological Engineering, 2024, 18, 71. |
| 205 | NAHER L, QUARIN S M, VANG D, et al. Lyophilizing SERS biosensors to enable translation into an easy-to-use assay[J]. Analytical Methods, 2024, 16(44): 7613-7623. |
| 206 | GOEL P, VISHWESWARAIAH R H, KUMAR N. Spore-based innovative paper-strip biosensor for the rapid detection of ß-lactam group in milk[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12, 21965. |
| 207 | VOLPETTI F, PETROVA E, MAERKL S J. A microfluidic biodisplay[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(11): 1979-1987. |
| 208 | WRIGHT O, DELMANS M, STAN G B, et al. GeneGuard: A modular plasmid system designed for biosafety[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2015, 4(3): 307-316. |
| 209 | ELLIS T, WANG X, COLLINS J J. Diversity-based, model-guided construction of synthetic gene networks with predicted functions[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2009, 27(5): 465-471. |
| 210 | CALLURA J M, DWYER D J, ISAACS F J, et al. Tracking, tuning, and terminating microbial physiology using synthetic riboregulators[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2010, 107(36): 15898-15903. |
| 211 | PINHEIRO V B, TAYLOR A I, COZENS C, et al. Synthetic genetic polymers capable of heredity and evolution[J]. Science, 2012, 336(6079): 341-344. |
| 212 | ROTTINGHAUS A G, FERREIRO A, FISHBEIN S R S, et al. Genetically stable CRISPR-based kill switches for engineered microbes[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13, 672. |
| 213 | HAYASHI N, LAI Y, FUERTE-STONE J, et al. Cas9-assisted biological containment of a genetically engineered human commensal bacterium and genetic elements[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15, 2096. |
| 214 | SUN S, CHEN J. Recent advances in hydrogel-based biosensors for cancer detection[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024, 16(36): 46988-47002. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 董颖, 马孟丹, 黄卫人. CRISPR-Cas系统的小型化研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 105-117. |
| [3] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [4] | 陈盈盈, 刘扬, 史俊杰, 马俊英, 鞠建华. CRISPR/Cas基因编辑及其新兴技术在丝状真菌研究中的系统应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 672-693. |
| [5] | 惠真, 唐啸宇. CRISPR/Cas9编辑系统在微生物天然产物研究中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 658-671. |
| [6] | 杜瑶, 高宏丹, 刘家坤, 刘孝荣, 邢志浩, 张涛, 马东礼. CRISPR-Cas系统在病原核酸检测中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 202-216. |
| [7] | 赵静宇, 张健, 祁庆生, 王倩. 基于细菌双组分系统的生物传感器的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 38-52. |
| [8] | 孟倩, 尹聪, 黄卫人. 肿瘤类器官及其在合成生物学中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 191-201. |
| [9] | 许志锰, 谢震. 引导编辑研究进展及其应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 1-15. |
| [10] | 陈雅如, 曹英秀, 宋浩. 电活性微生物基因编辑与转录调控技术进展与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(6): 1281-1299. |
| [11] | 马孟丹, 尚梦宇, 刘宇辰. CRISPR-Cas9系统在肿瘤生物学中的应用及前景[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(4): 703-719. |
| [12] | 王甜甜, 朱虹, 杨琛. 蓝细菌CRISPRa系统的开发及其代谢工程应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(4): 824-839. |
| [13] | 林继聪, 邹根, 刘宏民, 魏勇军. CRISPR/Cas基因组编辑技术在丝状真菌次级代谢产物合成中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(4): 738-755. |
| [14] | 马孟丹, 刘宇辰. 合成生物学在疾病信息记录与实时监测中的应用潜力[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(2): 301-317. |
| [15] | 梁丽亚, 刘嵘明. 靶向DNA的Ⅱ类CRISPR/Cas系统的蛋白工程化改造[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 86-101. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
