合成生物学 ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (3): 516-529.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-054
亚胺还原酶在手性胺合成中的应用
杨璐, 瞿旭东
- 上海交通大学生命科学技术学院,微生物代谢国家重点实验室,教育部代谢与发育科学国际合作联合实验室,上海 200240
-
收稿日期:2021-05-01修回日期:2021-07-27出版日期:2022-06-30发布日期:2022-07-13 -
通讯作者:瞿旭东 -
作者简介:杨璐 (1993—),女,博士研究生。研究方向为杂环类生物碱的生物合成研究及酶工程改造。E-mail:yl2020@sjtu.edu.cn瞿旭东 (1980—),男,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为生物合成与生物催化。E-mail:quxd19@sjtu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(31970054);国家重点研发计划(2018YFC1706200)
Application of imine reductase in the synthesis of chiral amines
YANG Lu, QU Xudong
- State Key Laboratory of Microbial Metabolism,School of Life Sciences and Biotechnology,Shanghai Jiao Tong University,Shanghai 200240,China
-
Received:2021-05-01Revised:2021-07-27Online:2022-06-30Published:2022-07-13 -
Contact:QU Xudong
摘要:
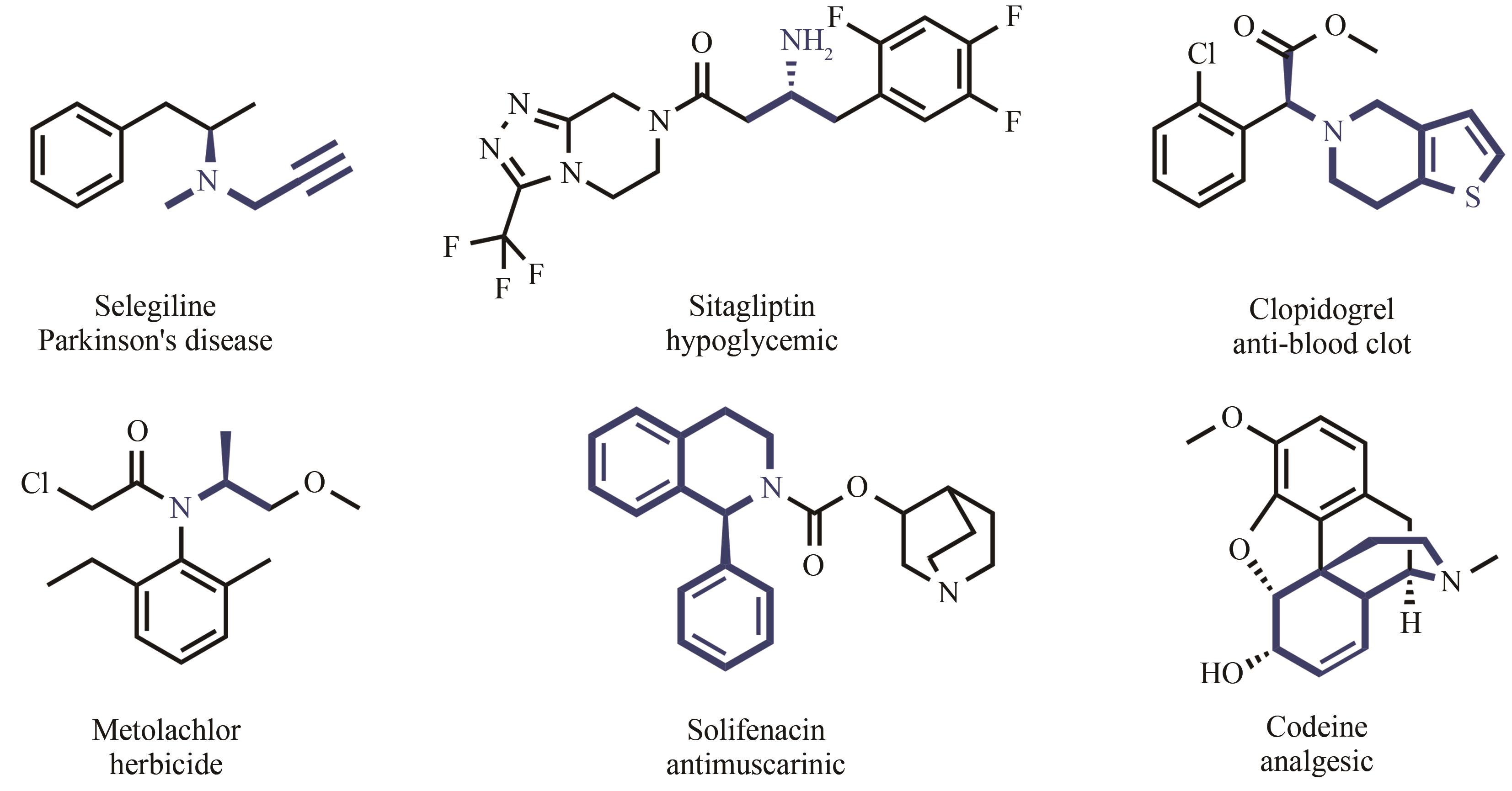
手性胺存在于许多生物活性物质中,是重要的手性助剂,同时也是合成天然产物及手性药物的关键中间体。2019年零售额前200名的药物中,含有手性胺结构的药物超过三成,因此发展高效、便捷合成手性胺化合物的方法是研究的重要方向。通过酶催化方法制备手性胺化合物,因具有高效性、环境友好性、经济效率高等优点,获得了学术界及工业界的广泛关注。本文所综述的亚胺还原酶(IREDs)是一类NAD(P)H依赖的氧化还原酶,可催化亚胺的不对称还原合成手性胺。IREDs具有催化效率高、区域及立体选择性强等优异的特性,在众多合成手性胺方法中脱颖而出,吸引了科研工作者的研究目光。近年来,随着生物信息学、结构生物学、高通量筛选方法的飞速发展和数据库的不断扩充,鉴定了许多不同功能的IRED,并在IRED的发现、分子改造、底物谱扩展和多酶级联应用等方面均取得了显著的成果,其中不乏一些具有工业应用价值。本文概述了IRED的结构特征及作用机理,着重介绍了IRED的分子改造和在多酶串联反应中的应用,以及在不对称催化手性胺生物合成中遇到的瓶颈、获得的突破和进展。此外还对酶法合成手性胺化合物实现工业化生产所面临的挑战及巨大潜力,以及新颖的人工生物合成途径设计对克服这些挑战的重要性进行了展望。
中图分类号:
引用本文
杨璐, 瞿旭东. 亚胺还原酶在手性胺合成中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(3): 516-529.
YANG Lu, QU Xudong. Application of imine reductase in the synthesis of chiral amines[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(3): 516-529.
| Entry | Enzyme | Source | Substrate | Products | ee/% | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IR2 | Actinomaduramadurae | 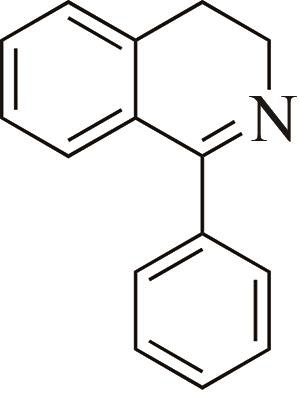 | 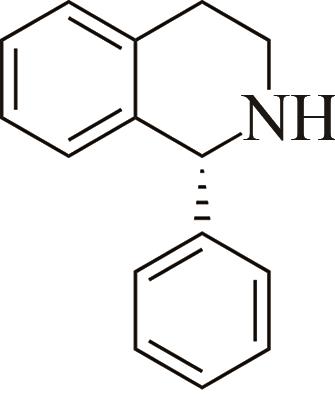 | 99 R | [ |
| 2 | IR45 | Streptomyces aurantiacus | 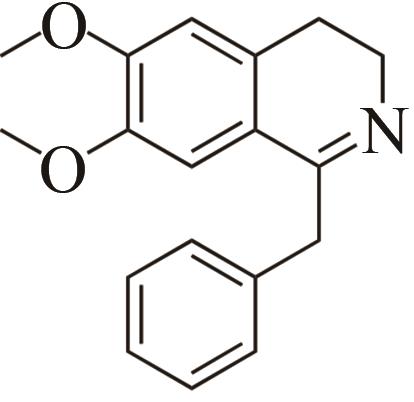 | 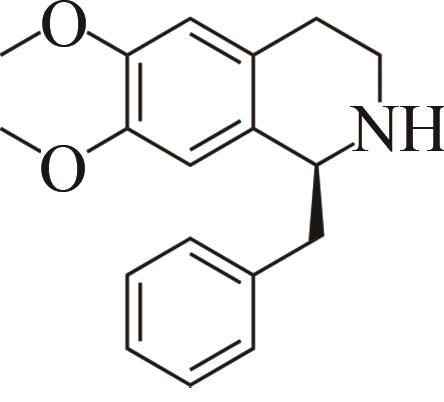 | 99 S | [ |
| 3 | IR46 | Saccharothrixespanaensis | 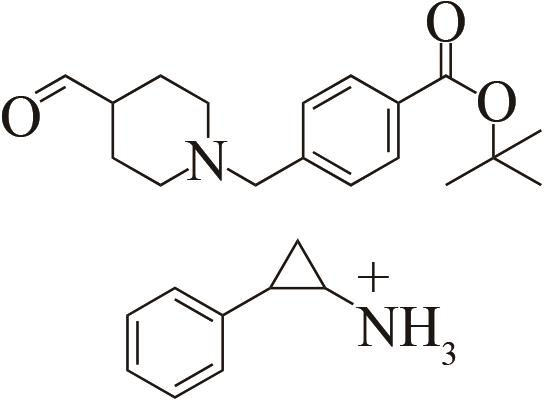 | 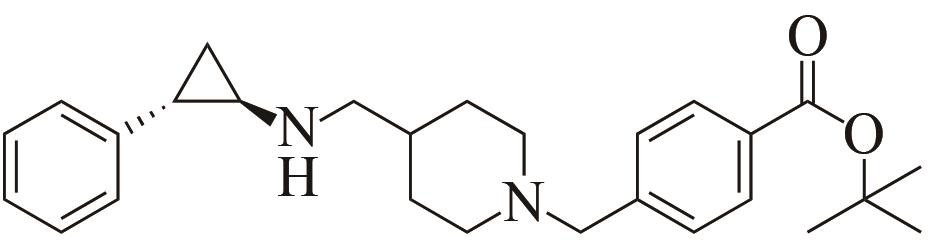 | 99 R | [ |
| 4 | IR1 | Leishmania major | 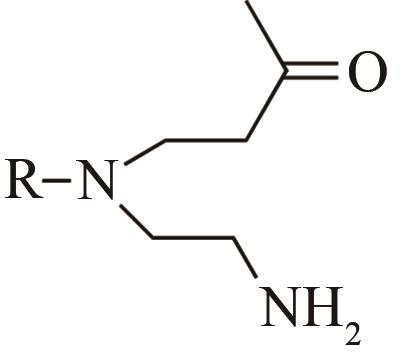 | 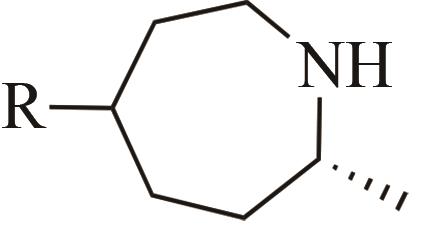 | 99 R | [ |
| 5 | AoIRED | Amycolatopsisorientalis | 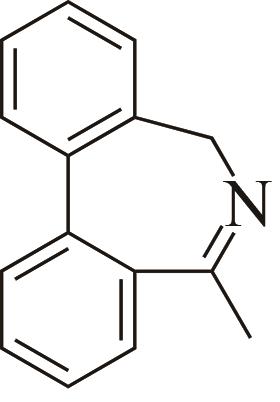 | 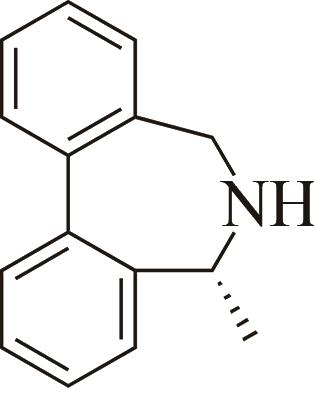 | 40 R | [ |
表1 亚胺还原酶改造实例
Tab. 1 Examples of imine reductase modifications
| Entry | Enzyme | Source | Substrate | Products | ee/% | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IR2 | Actinomaduramadurae |  |  | 99 R | [ |
| 2 | IR45 | Streptomyces aurantiacus |  |  | 99 S | [ |
| 3 | IR46 | Saccharothrixespanaensis |  |  | 99 R | [ |
| 4 | IR1 | Leishmania major |  |  | 99 R | [ |
| 5 | AoIRED | Amycolatopsisorientalis |  |  | 40 R | [ |
| 1 | GHISLIERI D, TURNER N J. Biocatalytic approaches to the synthesis of enantiomerically pure chiral amines[J]. Topics in Catalysis, 2014, 57(5):284-300. |
| 2 | SCHRITTWIESER J H, VELIKOGNE S, KROUTIL W. Biocatalytic imine reduction and reductive amination of ketones[J]. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 2015, 357(8):1655-1685. |
| 3 | GUO F, BERGLUND P. Transaminase biocatalysis: optimization and application[J]. Green Chemistry, 2017, 19(2):333-360. |
| 4 | MATHEW S, YUN H. ω-Transaminases for the production of optically pure amines and unnatural amino acids[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2012, 2(6):993-1001. |
| 5 | KOHLS H, STEFFEN-MUNSBERG F, HÖHNE M. Recent achievements in developing the biocatalytic toolbox for chiral amine synthesis[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2014, 19: 180-192. |
| 6 | JIANG J J, CHEN X, ZHANG D L, et al. Characterization of (R)-selective amine transaminases identified by in silico motif sequence blast[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 99(6):2613-2621. |
| 7 | JIANG J J, CHEN X, FENG J H, et al. Substrate profile of an ω-transaminase from Burkholderia vietnamiensis and its potential for the production of optically pure amines and unnatural amino acids[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 2014, 100: 32-39. |
| 8 | YANG L, ZHU J M, SUN C H, et al. Biosynthesis of plant tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids through an imine reductase route[J]. Chemical Science, 2019, 11(2): 364-371. |
| 9 | KIM Y, PARK J, KIM M J. Dynamic kinetic resolution of amines and amino acids by enzyme-metal cocatalysis[J]. ChemCatChem, 2011, 3(2):271-277. |
| 10 | NUGENT T C, EL-SHAZLY M. Chiral amine synthesis-recent developments and trends for enamide reduction, reductive amination, and imine reduction[J]. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 2010, 352(5):753-819. |
| 11 | CHENG F, ZHU L L, SCHWANEBERG U. Directed evolution 2.0: improving and deciphering enzyme properties[J]. Chemical Communications, 2015, 51(48):9760-9772. |
| 12 | RAMSDEN J I, HEATH R S, DERRINGTON S R, et al. Biocatalytic N-alkylation of amines using either primary alcohols or carboxylic acids via reductive aminase cascades[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(3):1201-1206. |
| 13 | CHENG F, CHEN X L, XIANG C, et al. Fluorescence-based high-throughput screening system for R-ω-transaminase engineering and its substrate scope extension[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2020, 104(7): 2999-3009. |
| 14 | BALKENHOHL F, DITRICH K, HAUER B, et al. Optically active amines via lipase-catalyzed methoxyacetylation[J]. Journal Fur Praktische Chemie-Chemiker-Zeitung, 1997, 339(4):381-384. |
| 15 | AHN Y, KO S B, KIM M J, et al. Racemization catalysts for the dynamic kinetic resolution of alcohols and amines[J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2008, 252(5/6/7): 647-658. |
| 16 | SAVILE C K, JANEY J M, MUNDORFF E C, et al. Biocatalytic asymmetric synthesis of chiral amines from ketones applied to sitagliptin manufacture[J]. Science, 2010, 329(5989):305-309. |
| 17 | KELLY S A, POHLE S, WHARRY S, et al. Application of ω-transaminases in the pharmaceutical industry[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(1):349-367. |
| 18 | MUTTI F G, FUCHS C S, PRESSNITZ D, et al. Stereoselectivity of four (R)-selective transaminases for the asymmetric amination of ketones[J]. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 2011, 353(17):3227-3233. |
| 19 | GOMM A, O'REILLY E. Transaminases for chiral amine synthesis[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2018, 43: 106-112. |
| 20 | ALEXEEVA M, ENRIGHT A, DAWSON M J, et al. Deracemization of α-methylbenzylamine using an enzyme obtained by in vitro evolution[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2002, 41(17):3177-3180. |
| 21 | CARR R, ALEXEEVA M, ENRIGHT A, et al. Directed evolution of an amine oxidase possessing both broad substrate specificity and high enantioselectivity[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2003, 42(39):4807-4810. |
| 22 | MUTTI F G, KNAUS T, SCRUTTON N S, et al. Conversion of alcohols to enantiopure amines through dual-enzyme hydrogen-borrowing cascades[J]. Science, 2015, 349(6255):1525-1529. |
| 23 | ALEKU G A, FRANCE S P, MAN H, et al. A reductive aminase from Aspergillus oryzae [J]. Nature Chemistry, 2017, 9(10):961-969. |
| 24 | ZHU J M, TAN H Q, YANG L, et al. Enantioselective synthesis of 1-aryl-substituted tetrahydroisoquinolines employing imine reductase[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(10): 7003-7007. |
| 25 | MANGAS-SANCHEZ J, FRANCE S P, MONTGOMERY S L, et al. Imine reductases (IREDs)[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2017, 37:19-25. |
| 26 | HEBERLING M M, WU B, BARTSCH S, et al. Priming ammonia lyases and aminomutases for industrial and therapeutic applications[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2013, 17(2):250-260. |
| 27 | LOVELOCK S L, LLOYD R C, TURNER N J. Phenylalanine ammonia lyase catalyzed synthesis of amino acids by an MIO- cofactor independent pathway[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53(18):4652-4656. |
| 28 | GROGAN G, TURNER N J. InspIRED by nature: NADPH-dependent imine reductases (IREDs) as catalysts for the preparation of chiral amines[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2016, 22(6):1900-1907. |
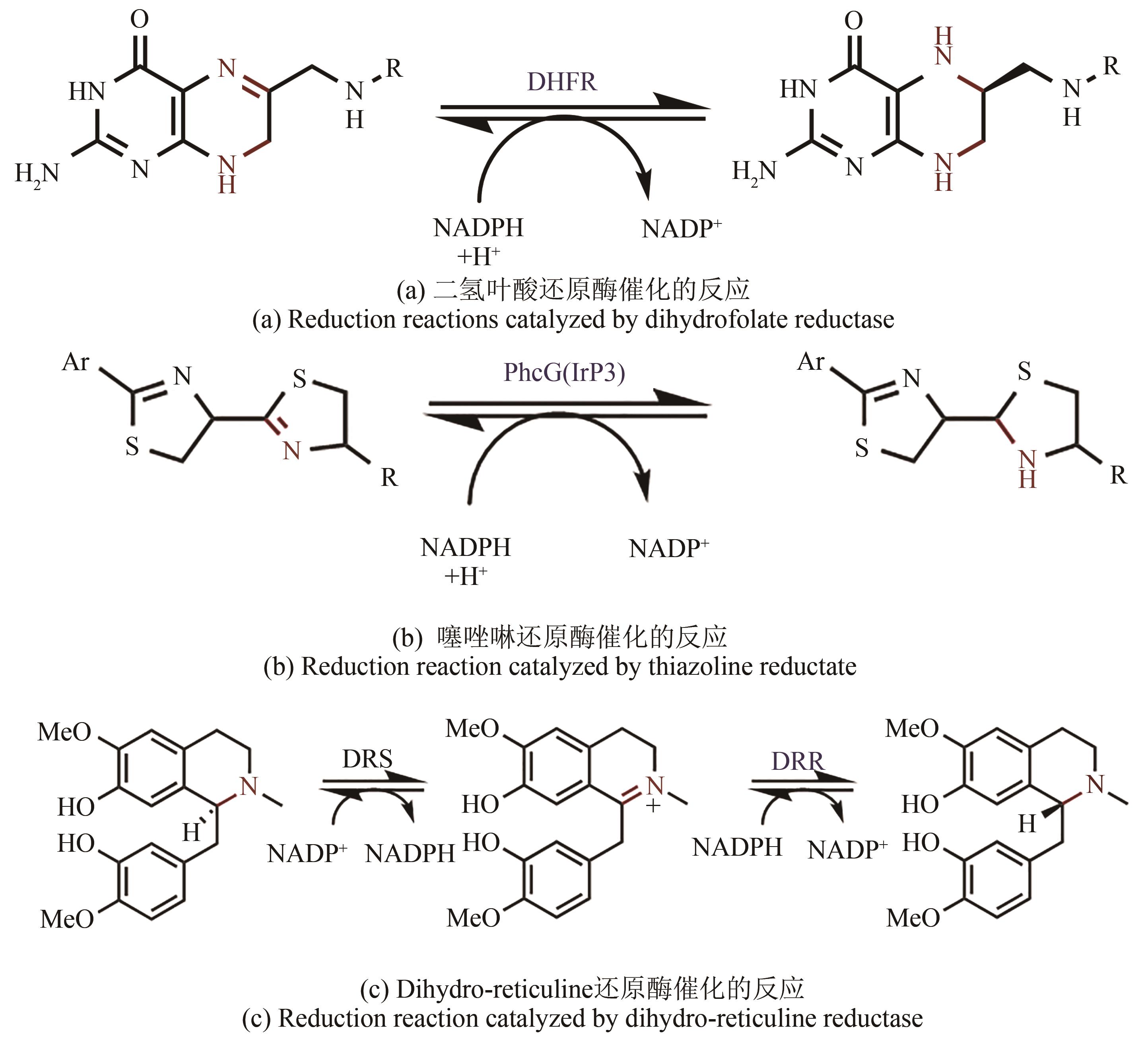
| 29 | POSNER B A, LI L Y, BETHELL R, et al. Engineering specificity for folate into dihydrofolate reductase from Escherichia coli [J]. Biochemistry, 1996, 35(5):1653-1663. |
| 30 | MENEELY K M, LAMB A L. Two structures of a thiazolinyl imine reductase from Yersinia enterocolitica provide insight into catalysis and binding to the nonribosomal peptide synthetase module of HMWP1 [J]. Biochemistry, 2012, 51(44):9002-9013. |
| 31 | MENEELY K M, RONNEBAUM T A, RILEY A P, et al. Holo structure and steady state kinetics of the thiazolinyl imine reductases for siderophore biosynthesis[J]. Biochemistry, 2016, 55(38):5423-5433. |
| 32 | WINZER T, KERN M, KING A J, et al. Morphinan biosynthesis in opium poppy requires a P450-oxidoreductase fusion protein[J]. Science, 2015, 349(6245):309-312. |
| 33 | FARROW S C, HAGEL J M, BEAUDOIN G A W, et al. Stereochemical inversion of (S)-reticuline by a cytochrome P450 fusion in opium poppy[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2015, 11(9): 728-732. |
| 34 | NARDINI M, RICCI G, CACCURI A M, et al. Purification and characterization of a ketimine-reducing enzyme[J]. European Journal of Biochemistry, 1988, 173(3): 689-694. |
| 35 | NARDINI M, RICCI G, VESCI L, et al. Bovine brain ketimine reductase[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1988, 957(2): 286-292. |
| 36 | HALLEN A, COOPER A J L, JAMIE J F, et al. Mammalian forebrain ketimine reductase identified as μ-crystallin; potential regulation by thyroid hormones[J]. Journal of Neurochemistry, 2011, 118(3): 379-387. |
| 37 | LI H, WILLIAMS P, MICKLEFIELD J, et al. A dynamic combinatorial screen for novel imine reductase activity[J]. Tetrahedron, 2004, 60(3): 753-758. |
| 38 | MURAMATSU H, MIHARA H, KAKUTANI R, et al. Enzymatic synthesis of N-methyl-L-phenylalanine by a novel enzyme, N-methyl-L-amino acid dehydrogenase, from Pseudomonas putida [J]. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 2004, 15(18): 2841-2843. |
| 39 | MURAMATSU H, MIHARA H, KAKUTANI R, et al. The putative malate/lactate dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida is an NADPH-dependent Δ¹-piperideine-2-carboxylate/Δ¹-pyrroline-2-carboxylate reductase involved in the catabolism of D-lysine and D-proline[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2005, 280(7):5329-5335. |
| 40 | MURAMATSU H, MIHARA H, GOTO M, et al. A new family of NAD(P)H-dependent oxidoreductases distinct from conventional Rossmann-fold proteins[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2005, 99(6):541-547. |
| 41 | VAIJAYANTHI T, CHADHA A. Asymmetric reduction of aryl imines using Candida parapsilosis ATCC 7330[J]. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 2008, 19(1): 93-96. |
| 42 | ESPINOZA-MORAGA M, PETTA T, VASQUEZ-VASQUEZ M, et al. Bioreduction of β-carboline imines to amines employing Saccharomyces bayanus [J]. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 2010, 21(16): 1988-1992. |
| 43 | MITSUKURA K, SUZUKI M, TADA K, et al. Asymmetric synthesis of chiral cyclic amine from cyclic imine by bacterial whole-cell catalyst of enantioselective imine reductase[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2010, 8(20):4533-4535. |
| 44 | MITSUKURA K, SUZUKI M, SHINODA S, et al. Purification and characterization of a novel (R)-imine reductase from Streptomyces sp. GF3587 [J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2011, 75(9): 1778-1782. |
| 45 | SLABU I, GALMAN J L, WEISE N J, et al. Putrescine transaminases for the synthesis of saturated nitrogen heterocycles from polyamines[J]. ChemCatChem, 2016, 8(6):1038-1042. |
| 46 | HUSSAIN S, LEIPOLD F, MAN H, et al. An (R)-imine reductase biocatalyst for the asymmetric reduction of cyclic imines[J]. ChemCatChem, 2015, 7(4):579-583. |
| 47 | LEIPOLD F, HUSSAIN S, GHISLIERI D, et al. Asymmetric reduction of cyclic imines catalyzed by a whole-cell biocatalyst containing an (S)-imine reductase[J]. ChemCatChem, 2013, 5(12): 3505-3508. |
| 48 | SCHELLER P N, FADEMRECHT S, HOFELZER S, et al. Enzyme toolbox: novel enantiocomplementary imine reductases[J]. ChemBioChem, 2014, 15(15):2201-2204. |
| 49 | FADEMRECHT S, SCHELLER P N, NESTL B M, et al. Identification of imine reductase-specific sequence motifs[J]. Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics, 2016, 84(5): 600-610. |
| 50 | LENZ M, SCHELLER P N, RICHTER S M, et al. Cultivation and purification of two stereoselective imine reductases from Streptosporangium roseum and Paenibacillus elgii [J]. Protein Expression and Purification, 2017, 133:199-204. |
| 51 | MITSUKURA K, KURAMOTO T, YOSHIDA T, et al. A NADPH-dependent (S)-imine reductase (SIR) from Streptomyces sp. GF3546 for asymmetric synthesis of optically active amines: purification, characterization, gene cloning, and expression[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2013, 97(18): 8079-8086. |
| 52 | LENZ M, BORLINGHAUS N, WEINMANN L, et al. Recent advances in imine reductase-catalyzed reactions[J]. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2017, 33(11): 199. |
| 53 | MIRABAL-GALLARDO Y, SORIANO M D P C, SANTOS L S. Stereoselective bioreduction of β-carboline imines through cell-free extracts from earthworms (Eisenia foetida)[J]. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 2013, 24(8): 440-443. |
| 54 | PENG H D, WEI E M, WANG J L, et al. Deciphering piperidine formation in polyketide-derived indolizidines reveals a thioester reduction, transamination, and unusual imine reduction process[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2016, 11(12):3278-3283. |
| 55 | LI H, ZHANG G X, LI L M, et al. A novel (R)-imine reductase from Paenibacillus lactis for asymmetric reduction of 3H-indoles[J]. ChemCatChem, 2016, 8(4): 724-727. |
| 56 | LI H, TIAN P, XU J H, et al. Identification of an imine reductase for asymmetric reduction of bulky dihydroisoquinolines[J]. Organic Letters, 2017, 19(12):3151-3154. |
| 57 | ZHANG Y H, CHEN F F, LI B B, et al. Stereocomplementary synthesis of pharmaceutically relevant chiral 2-aryl-substituted pyrrolidines using imine reductases[J]. Organic Letters, 2020, 22(9):3367-3372. |
| 58 | RODRÍGUEZ-MATA M, FRANK A, WELLS E, et al. Structure and activity of NADPH-dependent reductase Q1EQE0 from Streptomyces kanamyceticus, which catalyses the R-selective reduction of an imine substrate[J]. ChemBioChem, 2013, 14(11): 1372-1379. |
| 59 | LOKANATH N K, OHSHIMA N, TAKIO K, et al. Crystal structure of novel NADP-dependent 3-hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase from Thermus thermophilus HB8[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2005, 352(4): 905-917. |
| 60 | HUBER T, SCHNEIDER L, PRÄG A, et al. Direct reductive amination of ketones: structure and activity of S-selective imine reductases from Streptomyces [J]. ChemCatChem, 2014, 6(8): 2248-2252. |
| 61 | MAN H, WELLS E, HUSSAIN S, et al. Structure, activity and stereoselectivity of NADPH-dependent oxidoreductases catalysing the S-selective reduction of the imine substrate 2-methylpyrroline[J]. ChemBioChem, 2015, 16(7):1052-1059. |
| 62 | ALEKU G A, MAN H, FRANCE S P, et al. Stereoselectivity and structural characterization of an imine reductase (IRED) from Amycolatopsis orientalis [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2016, 6(6): 3880-3889. |
| 63 | MEYER T, ZUMBRÄGEL N, GEERDS C, et al. Structural characterization of an S-enantioselective imine reductase from Mycobacterium smegmatis [J]. Biomolecules, 2020, 10(8):1130-1142. |
| 64 | REETZ M T, KAHAKEAW D, LOHMER R. Addressing the numbers problem in directed evolution[J]. ChemBioChem, 2008, 9(11):1797-1804. |
| 65 | CURRIN A, SWAINSTON N, DAY P J, et al. Synthetic biology for the directed evolution of protein biocatalysts: navigating sequence space intelligently[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(5):1172-1239. |
| 66 | SCHOBER M, MACDERMAID C, OLLIS A A, et al. Chiral synthesis of LSD1 inhibitor GSK2879552 enabled by directed evolution of an imine reductase[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2019, 2(10):909-915. |
| 67 | XU Z F, YAO P Y, SHENG X, et al. Biocatalytic access to 1,4-diazepanes via imine reductase-catalyzed intramolecular asymmetric reductive amination[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(15):8780-8787. |
| 68 | FRANCE S P, ALEKU G A, SHARMA M, et al. Biocatalytic routes to enantiomerically enriched dibenz[c,e]azepines[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(49): 15589-15593. |
| 69 | RENATA H, WANG Z J, ARNOLD F H. Expanding the enzyme universe: accessing non-natural reactions by mechanism-guided directed evolution[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(11):3351-3367. |
| 70 | PORTER J L, RUSLI R A, OLLIS D L. Directed evolution of enzymes for industrial biocatalysis[J]. ChemBioChem, 2016, 17(3):197-203. |
| 71 | HESTERICOVÁ M, HEINISCH T, ALONSO-COTCHICO L, et al. Directed evolution of an artificial imine reductase[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(7): 1863-1868. |
| 72 | NEWTON C R, GRAHAM A, HEPTINSTALL L E, et al. Analysis of any point mutation in DNA. The amplification refractory mutation system (ARMS)[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1989, 17(7): 2503-2516. |
| 73 | MORLEY K L, KAZLAUSKAS R J. Improving enzyme properties: when are closer mutations better?[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2005, 23(5):231-237. |
| 74 | MINDT M, HANNIBAL S, HEUSER M, et al. Fermentative production of N-alkylated glycine derivatives by recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum using a mutant of imine reductase DpkA from Pseudomonas putida [J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2019, 7: 232. |
| 75 | PAVLIDIS I V, WEIß M S, GENZ M, et al. Identification of (S)-selective transaminases for the asymmetric synthesis of bulky chiral amines[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2016, 8(11): 1076-1082. |
| 76 | TANIHARA H, INOUE T, YAMAMOTO T, et al. Intra-ocular pressure-lowering effects of a Rho kinase inhibitor, ripasudil (K-115), over 24 hours in primary open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension: a randomized, open-label, crossover study[J]. Acta Ophthalmologica, 2015, 93(4): e254-e260. |
| 77 | GARWEG G, REHREN D V, HINTZE U. L-pipecolate formation in the mammalian brain. Regional distribution of Δ1-Pyrroline-2-carboxylate reductase activity[J]. Journal of Neurochemistry, 1980, 35(3): 616-621. |
| 78 | GAND M, THÖLE C, MÜLLER H, et al. A NADH-accepting imine reductase variant: immobilization and cofactor regeneration by oxidative deamination[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2016, 230: 11-18. |
| 79 | BORLINGHAUS N, NESTL B M. Switching the cofactor specificity of an imine reductase[J]. ChemCatChem, 2018, 10(1):183-187. |
| 80 | HEATH R S, PONTINI M, HUSSAIN S, et al. Combined imine reductase and amine oxidase catalyzed deracemization of nitrogen heterocycles[J]. ChemCatChem, 2016, 8(1):117-120. |
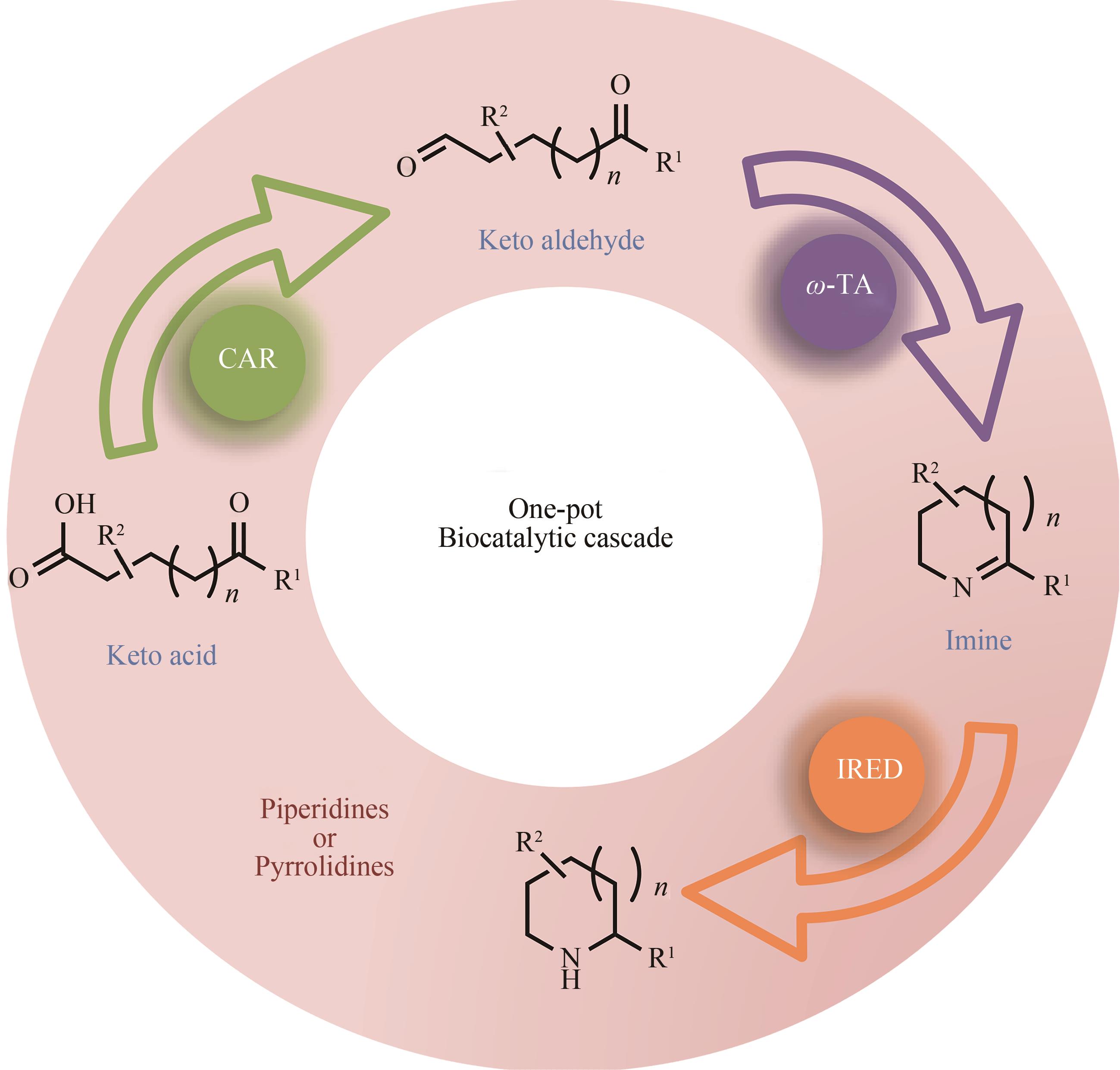
| 81 | FRANCE S P, HUSSAIN S, HILL A M, et al. One-pot cascade synthesis of mono- and disubstituted piperidines and pyrrolidines using carboxylic acid reductase (CAR), ω-transaminase (ω-TA), and imine reductase (IRED) biocatalysts[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2016, 6(6):3753-3759. |
| 82 | HEPWORTH L J, FRANCE S P, HUSSAIN S, et al. Enzyme cascades in whole cells for the synthesis of chiral cyclic amines[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(4):2920-2925. |
| 83 | MONTGOMERY S L, MANGAS-SANCHEZ J, THOMPSON M P, et al. Direct alkylation of amines with primary and secondary alcohols through biocatalytic hydrogen borrowing[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(35): 10491-10494. |
| 84 | FORD G J, KRESS N, MATTEY A P, et al. Synthesis of protected 3-aminopiperidine and 3-aminoazepane derivatives using enzyme cascades[J]. Chemical Communications, 2020, 56(57):7949-7952. |
| 85 | COSGROVE S C, THOMPSON M P, AHMED S T, et al. One-pot synthesis of chiral N-arylamines by combining biocatalytic aminations with Buchwald-Hartwig N-arylation[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(41):18156-18160. |
| 86 | MARSHALL J R, YAO P Y, MONTGOMERY S L, et al. Screening and characterization of a diverse panel of metagenomic imine reductases for biocatalytic reductive amination[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2021, 13(2): 140-148. |
| 87 | HOPMANN K H, BAYER A. Enantioselective imine hydrogenation with iridium-catalysts: reactions, mechanisms and stereocontrol[J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2014, 268:59-82. |
| 88 | TANG W J, ZHANG X M. New chiral phosphorus ligands for enantioselective hydrogenation[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2003, 103(8): 3029-3070. |
| 89 | RIANT O, MOSTEFAÏ N, COURMARCEL J. Recent advances in the asymmetric hydrosilylation of ketones, imines and electrophilic double bonds[J]. Synthesis, 2004(18): 2943-2958. |
| 90 | VILAIVAN T, BHANTHUMNAVIN W, SRITANA-ANANT Y. Recent advances in catalytic asymmetric addition to imines and related C=N systems[J]. Current Organic Chemistry, 2005, 9(14):1315-1392. |
| 91 | MUSACCHIO A J, LAINHART B C, ZHANG X, et al. Catalytic intermolecular hydroaminations of unactivated olefins with secondary alkyl amines[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6326):727-730. |
| [1] | 温艳华, 刘合栋, 曹春来, 巫瑞波. 蛋白质工程在医药产业中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 65-86. |
| [2] | 仲泉周, 单依怡, 裴清云, 金艳芸, 王艺涵, 孟璐远, 王歆韵, 张雨鑫, 刘坤媛, 王慧中, 冯尚国. 生物合成法生产α-熊果苷的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 118-135. |
| [3] | 竺方欢, 岑雪聪, 陈振. 微生物合成二元醇研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1367-1385. |
| [4] | 刘益宁, 蒲伟, 杨金星, 王钰. ω-氨基酸与内酰胺的生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1350-1366. |
| [5] | 李庚, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 王佳, 袁其朋. 过氧化物酶的重组表达和应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1498-1517. |
| [6] | 程峰, 邹树平, 徐建妙, 汤恒, 薛亚平, 郑裕国. 生物高纯精草:高光学纯L-草铵膦生物制造的创新与发展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1404-1418. |
| [7] | 付雨, 钟芳锐. 化学原理驱动的光生物不对称催化研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1021-1049. |
| [8] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [9] | 程晓雷, 刘天罡, 陶慧. 萜类化合物的非常规生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1050-1071. |
| [10] | 刘子健, 穆柏杨, 段志强, 王璇, 陆晓杰. 与核酸兼容的化学反应开发进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1102-1124. |
| [11] | 张守祺, 王涛, 孔尧, 邹家胜, 刘元宁, 徐正仁. 天然产物的化学-酶法合成:方法与策略的演进[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 913-940. |
| [12] | 谢向前, 郭雯, 王欢, 李进. 含氨基乙烯半胱氨酸核糖体肽的生物合成与化学合成[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 981-996. |
| [13] | 汤志军, 胡友财, 刘文. 酶促4+2和2+2环加成反应:区域与立体选择性的理解与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 401-407. |
| [14] | 张俊, 金诗雪, 云倩, 瞿旭东. 聚酮化合物非天然延伸单元的生物合成与结构改造应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 561-570. |
| [15] | 陈锡玮, 张华然, 邹懿. 真菌源非核糖体肽类药物生物合成及代谢工程[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 571-592. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||