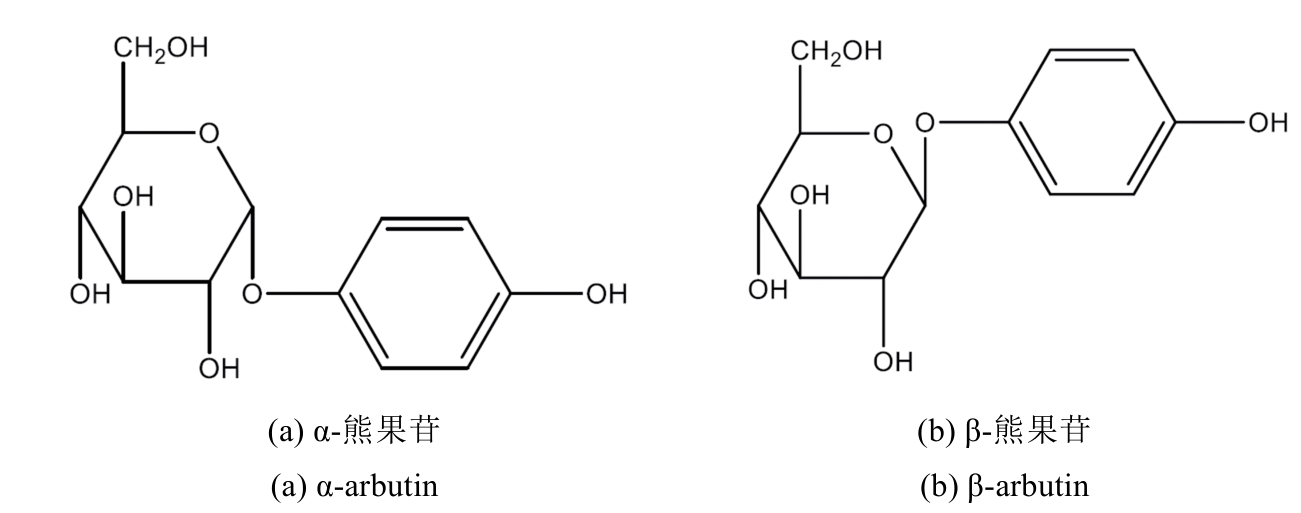
合成生物学 ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (1): 118-135.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-054
生物合成法生产α-熊果苷的研究进展
仲泉周1,2, 单依怡1,2, 裴清云1,2, 金艳芸1,2, 王艺涵1,2, 孟璐远1, 王歆韵1, 张雨鑫1, 刘坤媛1, 王慧中1,2, 冯尚国1,2
- 1.杭州师范大学生命与环境科学学院,浙江 杭州 311121
2.浙江省药用植物种质改良和质量监控重点实验室,浙江 杭州 311121
-
收稿日期:2024-07-18修回日期:2024-11-08出版日期:2025-02-28发布日期:2025-03-12 -
通讯作者:冯尚国 -
作者简介:仲泉周 (1999—),男,硕士研究生。研究方向为酶定向催化、天然产物生物合成。E-mail:2023112010028@stu.hznu.edu.cn冯尚国 (1980—),男,博士,高级实验师,硕士生导师。研究方向为药用种质资源评价、酶定向催化及天然产物生物合成。 E-mail:fengsg@hznu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(31970346);浙江省自然科学基金(LY20H280012);广东省科技计划(2023B1212060046);杭州市科技基金(20191203B02);杭州师范大学生命与环境科学学院教学改革项目
Research progress in the production of α-arbutin through biosynthesis
ZHONG Quanzhou1,2, SHAN Yiyi1,2, PEI Qingyun1,2, JIN Yanyun1,2, WANG Yihan1,2, MENG Luyuan1, WANG Xinyun1, ZHANG Yuxin1, LIU Kunyuan1, WANG Huizhong1,2, FENG Shangguo1,2
- 1.College of Life and Environmental Science,Hangzhou Normal University,Hangzhou 311121,Zhejiang,China
2.Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory for Genetic Improvement and Quality Control of Medicinal Plants,Hangzhou 311121,Zhejiang,China
-
Received:2024-07-18Revised:2024-11-08Online:2025-02-28Published:2025-03-12 -
Contact:FENG Shangguo
摘要:
熊果苷(arbutin)是一种天然的糖苷类化合物,广泛存在于自然界中。α-熊果苷(α-arbutin)是其一种异构体,由于其高效安全的美白作用和许多优秀的药理作用,受到越来越多的市场关注。研究发现,生物合成法生产α-熊果苷相较于自然提取法和化学合成法有着更高的产量、更安全的环境、更有竞争力的价格等优势,已经成为主流生产方式。本文介绍了常用于α-熊果苷生产的七种酶类的相关研究,分别为α-淀粉酶、蔗糖磷酸化酶、环糊精糖基转移酶、α-葡萄糖基酶、葡聚糖蔗糖酶、淀粉蔗糖酶和蔗糖异构酶。另外对全细胞催化法、微生物发酵法生产α-熊果苷的研究进展进行综述,对α-熊果苷生产过程中存在的问题进行了剖析并提出在工业化发展上的建议,最后对α-熊果苷合成的未来方向进行了展望,以期能够为实现更高效、更低成本的α-熊果苷生产提供新思路。
中图分类号:
引用本文
仲泉周, 单依怡, 裴清云, 金艳芸, 王艺涵, 孟璐远, 王歆韵, 张雨鑫, 刘坤媛, 王慧中, 冯尚国. 生物合成法生产α-熊果苷的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 118-135.
ZHONG Quanzhou, SHAN Yiyi, PEI Qingyun, JIN Yanyun, WANG Yihan, MENG Luyuan, WANG Xinyun, ZHANG Yuxin, LIU Kunyuan, WANG Huizhong, FENG Shangguo. Research progress in the production of α-arbutin through biosynthesis[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 118-135.
| 活性 | 模型 | 培养时间 | 材料 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 祛痰平喘 | 体内 | 3天 | 动物实验-小鼠 | [ |
| 拮抗H2O2损伤 | 体外 | 36时 | 人脐静脉内皮细胞 | [ |
| 低温保护 | 体外 | 2~3月 | 人胫骨细胞 | [ |
| 放射防护 | 体内 | 7天 | 动物实验-小鼠 | [ |
| 伤口愈合 | 体外 | 48时 | 人真皮成纤维细胞 | [ |
| 治疗多发性硬化症 | 体内 | 14天 | 动物实验-大鼠 | [ |
| 降低前列腺癌 | 体外 | 5天 | LNCaP细胞系 | [ |
| 治疗心肌梗死 | 体内 | 25天 | 动物实验-大鼠 | [ |
| 降低肝癌 | 体内 | 3周 | 动物实验-大鼠 | [ |
| 美白 | 体内 | 4天 | 3D黑色素皮肤模型 | [ |
| 神经保护 | 体内 | 21天 | 动物实验-大鼠 | [ |
| 改善肝纤维化 | 体内 | 6周 | 动物实验-小鼠 | [ |
表1 α-熊果苷的药理作用及生物活性
Table 1 Pharmacological effect and biological activity of α-arbutin
| 活性 | 模型 | 培养时间 | 材料 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 祛痰平喘 | 体内 | 3天 | 动物实验-小鼠 | [ |
| 拮抗H2O2损伤 | 体外 | 36时 | 人脐静脉内皮细胞 | [ |
| 低温保护 | 体外 | 2~3月 | 人胫骨细胞 | [ |
| 放射防护 | 体内 | 7天 | 动物实验-小鼠 | [ |
| 伤口愈合 | 体外 | 48时 | 人真皮成纤维细胞 | [ |
| 治疗多发性硬化症 | 体内 | 14天 | 动物实验-大鼠 | [ |
| 降低前列腺癌 | 体外 | 5天 | LNCaP细胞系 | [ |
| 治疗心肌梗死 | 体内 | 25天 | 动物实验-大鼠 | [ |
| 降低肝癌 | 体内 | 3周 | 动物实验-大鼠 | [ |
| 美白 | 体内 | 4天 | 3D黑色素皮肤模型 | [ |
| 神经保护 | 体内 | 21天 | 动物实验-大鼠 | [ |
| 改善肝纤维化 | 体内 | 6周 | 动物实验-小鼠 | [ |
| 来源 | 所用试剂 | 提取方法 | 定量方法 | 产率 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 日本梨树(枝条) | 10%甲醇 | 超声均质 | 液相色谱/质谱(LC/MS) | 12.8 mg/g | [ |
| 玉露香(果皮) | 色谱级甲醇 | 超声过滤 | 高效液相色谱(HPLC) | 0.872 mg/g | [ |
| 鸭梨(果肉) | 色谱级甲醇 | 超声过滤 | 高效液相色谱(HPLC) | 0.012 mg/g | [ |
| 鸭梨(果心) | 色谱级甲醇 | 超声过滤 | 高效液相色谱(HPLC) | 0.268 mg/g | [ |
| 红景天 | 60%乙醇 | 超声过滤 | 高效液相色谱(HPLC) | 3.2 mg/g | [ |
| 皇冠梨(果皮) | 无水乙醇 | 超声辅助 | 高效液相色谱(HPLC) | 0.229 mg/g | [ |
表2 天然植物中提取熊果苷的研究
Table 2 Studies on extracting arbutin from natural plants
| 来源 | 所用试剂 | 提取方法 | 定量方法 | 产率 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 日本梨树(枝条) | 10%甲醇 | 超声均质 | 液相色谱/质谱(LC/MS) | 12.8 mg/g | [ |
| 玉露香(果皮) | 色谱级甲醇 | 超声过滤 | 高效液相色谱(HPLC) | 0.872 mg/g | [ |
| 鸭梨(果肉) | 色谱级甲醇 | 超声过滤 | 高效液相色谱(HPLC) | 0.012 mg/g | [ |
| 鸭梨(果心) | 色谱级甲醇 | 超声过滤 | 高效液相色谱(HPLC) | 0.268 mg/g | [ |
| 红景天 | 60%乙醇 | 超声过滤 | 高效液相色谱(HPLC) | 3.2 mg/g | [ |
| 皇冠梨(果皮) | 无水乙醇 | 超声辅助 | 高效液相色谱(HPLC) | 0.229 mg/g | [ |
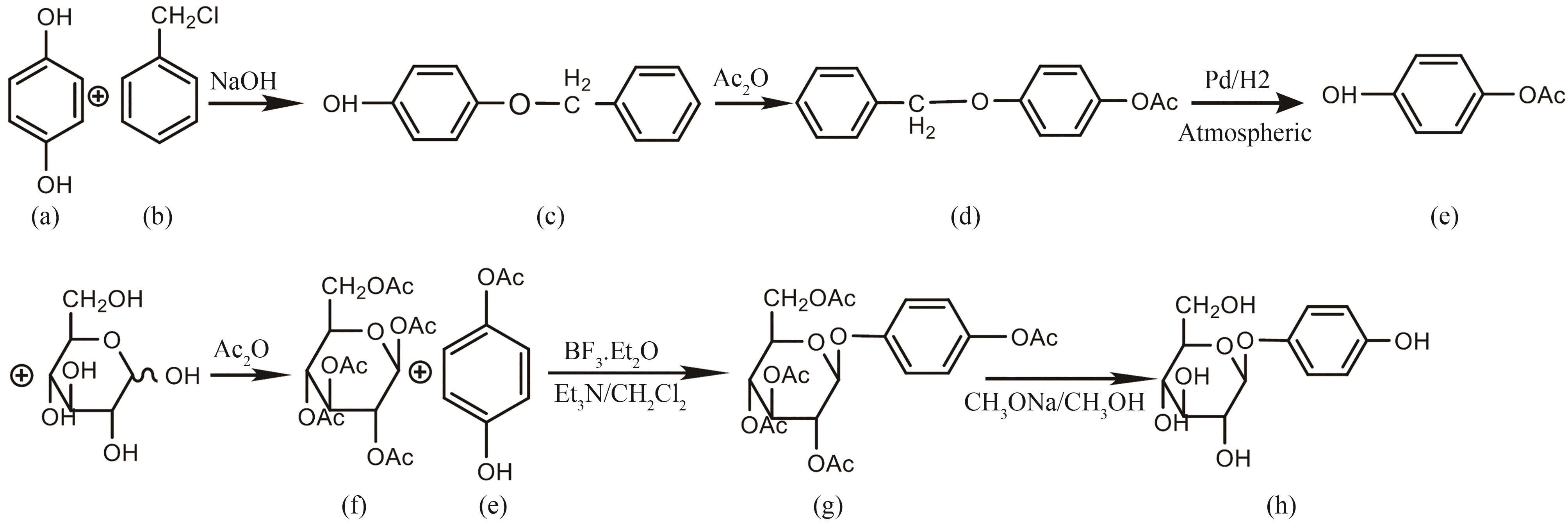
图2 熊果苷合成路线(a)1,4-苯二酚;(b)氯苄;(c)4-苄氧基苯酚;(d)4-苄氧基苯酚乙酸酯;(e)4-乙酰氧基苯酚;(f)全乙酰葡萄糖;(g)全乙酰熊果苷;(h)β-熊果苷
Fig. 2 Synthesis routes for various arbutins(a)1,4-Benzenediol; (b) Chlorobenzyl; (c) 4-Benzyloxyphenol; (d) 4-Benzyloxyphenol acetate; (e) 4-Acetoxyphenol; (f) Acetylated glucose; (g) Acetylated arbutin; (h) β-Arbutin
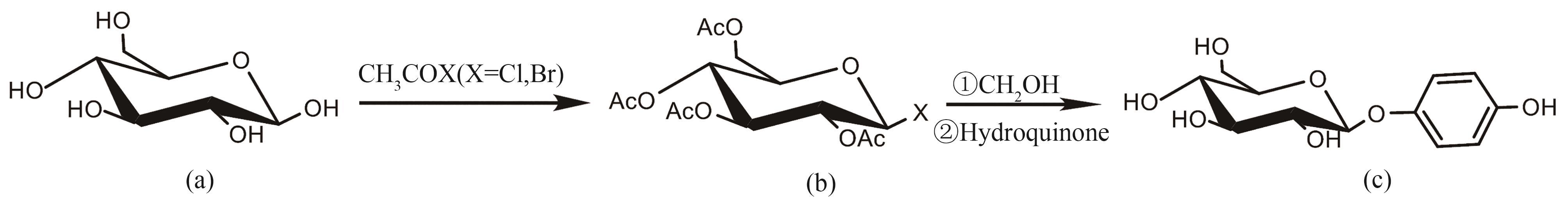
图3 两步法合成熊果苷合成路线(a)葡萄糖;(b)2,3,4,6-四-O-乙酰基-α-D-葡萄糖酰氯化物或溴化物;(c)β-熊果苷
Fig. 3 Route for the two-step synthesis of arbutin(a) glucose; (b) 2,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-α-D-glucosyl chloride or bromide; (c) β-Arbutin
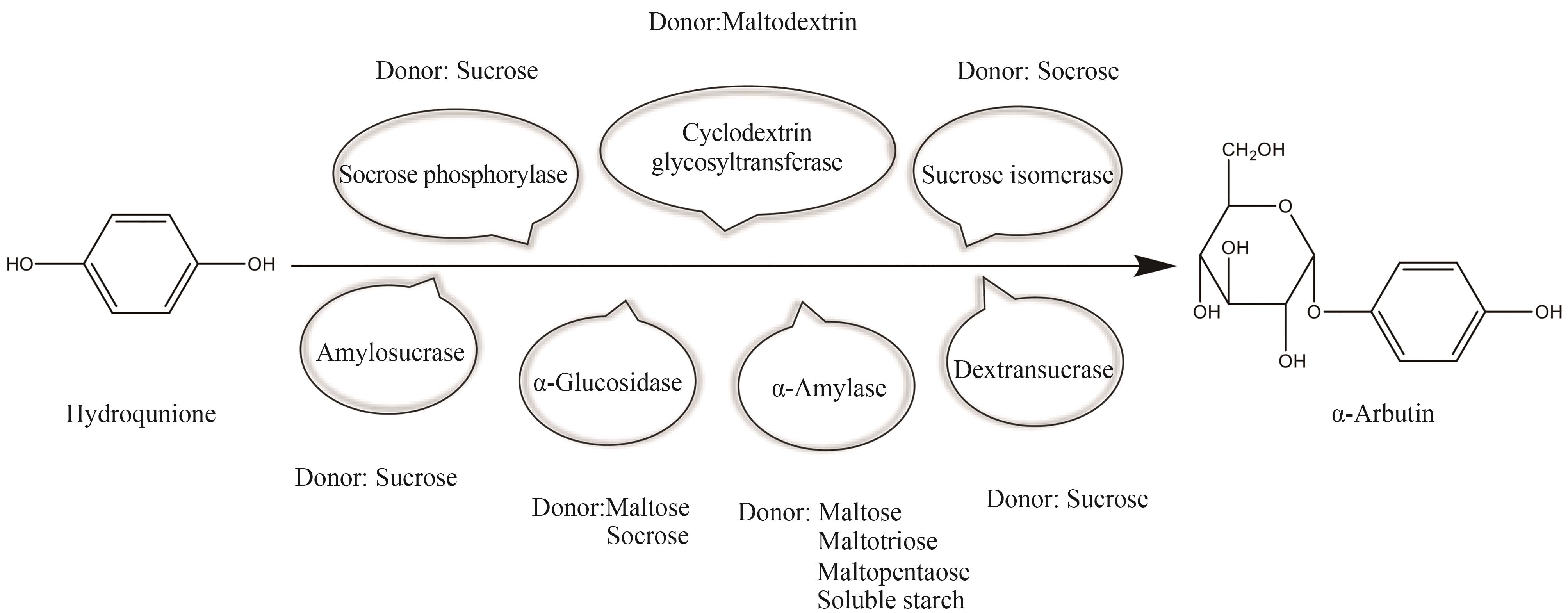
| 酶类 | 来源 | 供体 | 供体/氢醌 | 转化率 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sucrose phosphorylase | Streptococcus mutans UA159 | Sucrose | 2∶1 | 72.4% | [ |
| Sucrose phosphorylase | Bacillus velezensis | Sucrose | 4∶1 | 44.09% | [ |
| Sucrose phosphorylase | Leuconostoc mesenteroides ATCC 12291 | Sucrose | 5∶1 | 99% | [ |
| Sucrose phosphorylase | Paenibacillus elgii | Sucrose | 5∶1 | 60.9% | [ |
| Sucrose phosphorylase | Lactobacillus mesenteroides | Sucrose | 20∶1 | 95.3% | [ |
| Sucrose phosphorylase | Streptococcus mutans | Sucrose | 6∶1 | 80.15% | [ |
| α-Amylase | bacillus subtilis X-23 | Maltose | 2∶1 | 9% | [ |
| α-Amylase | bacillus subtilis X-23 | Maltotriose | 2∶1 | 22.4% | [ |
| α-Amylase | bacillus subtilis X-23 | Maltopentaose | 2∶1 | 24.8% | [ |
| α-Amylase | bacillus subtilis X-23 | Soluble starch | 2∶1 | 32.4% | [ |
| α-Amylase | Thermus thermophilus ATCC 33923 | Cassava starch | — | 83%① | [ |
| Amylosucrase | Deinococcus geothermalis | Sucrose | 10∶1 | 90% | [ |
| Amylosucrase | Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris 8004 | Sucrose | 80∶1 | 95% | [ |
| Amylosucrase | Thermal spring metagenome | Sucrose | 5∶1 | 75% | [ |
| Cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase | Thermoanaerobacter sp. | Maltodextrin | — | 61% | [ |
| Cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase | Anaerobranca gottschalkii | Maltodextrin | 6∶1 | 25% | [ |
| Cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase | Paenibacillus macerans | Maltodextrin | 6∶1 | 20% | [ |
| Cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase | Bacillus stearothermophilus NO2 | Maltodextrin | 6∶1 | 14% | [ |
| Cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase | Bacillus circulans 251 | Maltodextrin | 6∶1 | 11% | [ |
| Cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase | Anaerobranca gottschalkii | Maltodextrin | 6∶1 | 63% | [ |
| α-Glucosidase | Xanthomonas campestris | Maltose | — | 72% | [ |
| α-Glucosidase | Xanthomonas campestris | Sucrose | 9∶1 | 94% | [ |
| Dextransucrase | Leuconostoc mesenteroides B-1299 | Sucrose | — | 0.4% | [ |
| Sucrose isomerase | Erwinia rhapontici | Sucrose | 50∶1 | 33.2% | [ |
表3 不同酶类催化对苯二酚生产熊果苷
Table 3 Arbutin production from hydroquinone catalyzed by different enzymes
| 酶类 | 来源 | 供体 | 供体/氢醌 | 转化率 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sucrose phosphorylase | Streptococcus mutans UA159 | Sucrose | 2∶1 | 72.4% | [ |
| Sucrose phosphorylase | Bacillus velezensis | Sucrose | 4∶1 | 44.09% | [ |
| Sucrose phosphorylase | Leuconostoc mesenteroides ATCC 12291 | Sucrose | 5∶1 | 99% | [ |
| Sucrose phosphorylase | Paenibacillus elgii | Sucrose | 5∶1 | 60.9% | [ |
| Sucrose phosphorylase | Lactobacillus mesenteroides | Sucrose | 20∶1 | 95.3% | [ |
| Sucrose phosphorylase | Streptococcus mutans | Sucrose | 6∶1 | 80.15% | [ |
| α-Amylase | bacillus subtilis X-23 | Maltose | 2∶1 | 9% | [ |
| α-Amylase | bacillus subtilis X-23 | Maltotriose | 2∶1 | 22.4% | [ |
| α-Amylase | bacillus subtilis X-23 | Maltopentaose | 2∶1 | 24.8% | [ |
| α-Amylase | bacillus subtilis X-23 | Soluble starch | 2∶1 | 32.4% | [ |
| α-Amylase | Thermus thermophilus ATCC 33923 | Cassava starch | — | 83%① | [ |
| Amylosucrase | Deinococcus geothermalis | Sucrose | 10∶1 | 90% | [ |
| Amylosucrase | Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris 8004 | Sucrose | 80∶1 | 95% | [ |
| Amylosucrase | Thermal spring metagenome | Sucrose | 5∶1 | 75% | [ |
| Cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase | Thermoanaerobacter sp. | Maltodextrin | — | 61% | [ |
| Cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase | Anaerobranca gottschalkii | Maltodextrin | 6∶1 | 25% | [ |
| Cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase | Paenibacillus macerans | Maltodextrin | 6∶1 | 20% | [ |
| Cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase | Bacillus stearothermophilus NO2 | Maltodextrin | 6∶1 | 14% | [ |
| Cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase | Bacillus circulans 251 | Maltodextrin | 6∶1 | 11% | [ |
| Cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase | Anaerobranca gottschalkii | Maltodextrin | 6∶1 | 63% | [ |
| α-Glucosidase | Xanthomonas campestris | Maltose | — | 72% | [ |
| α-Glucosidase | Xanthomonas campestris | Sucrose | 9∶1 | 94% | [ |
| Dextransucrase | Leuconostoc mesenteroides B-1299 | Sucrose | — | 0.4% | [ |
| Sucrose isomerase | Erwinia rhapontici | Sucrose | 50∶1 | 33.2% | [ |
| 1 | 孙雷, 姚德立, 姚德坤, 等. α-熊果苷的研究进展[J]. 中国林副特产, 2016(3): 87-90. |
| SUN L, YAO D L, YAO D K, et al. Research progress of alpha arbutin[J]. Forest By-Product and Speciality in China, 2016(3): 87-90. | |
| 2 | 李晓娇, 刘忆明. α-熊果苷合成研究进展[J]. 保山学院学报, 2014, 33(2): 18-21. |
| LI X J, LIU Y M. Development in synthesis of α-arbutin[J]. Journal of Baoshan University, 2014, 33(2): 18-21. | |
| 3 | 刘晓婷, 王鑫璇. 熊果苷的药理作用及机制研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2022, 48(2): 309-316. |
| LIU X T, WANG X X. Research progress on the pharmacological action and mechanism of arbutin[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2022, 48(2): 309-316. | |
| 4 | KARI F W, BUCHER J, EUSTIS S L, et al. Toxicity and carcinogenicity of hydroquinone in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 1992, 30(9): 737-747. |
| 5 | 张凤兰, 吴景, 王钢力, 等. α-熊果苷和脱氧熊果苷美白作用机制及安全性评价研究进展[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2018, 35(4): 370-375. |
| ZHANG F L, WU J, WANG G L, et al. Whitening effect of α-arbutin and deoxyarbutin and safety evaluation: a review of recent studies[J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 2018, 35(4): 370-375. | |
| 6 | 李岗, 钏定泽. 常用祛斑美白剂作用机理研究[J]. 精细与专用化学品, 2024, 32(7): 11-21. |
| LI G, CHUAN D Z. Summary of mechanism action of common freckle whitening agents[J]. Fine and Specialty Chemicals, 2024, 32(7): 11-21. | |
| 7 | 张凤兰, 苏哲, 吴景, 等. β-熊果苷和氢醌安全性评价及化妆品法规管理现状[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2017, 34(11): 1017-1021. |
| ZHANG F L, SU Z, WU J, et al. Safety evaluation of β-arbutin and hydroquinone and regulatory status of cosmetics[J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 2017, 34(11): 1017-1021. | |
| 8 | 王晓芊. 熊果苷的潮起潮落: 解析美白成分熊果苷[J]. 中国化妆品, 2019(10): 85-87. |
| WANG X Q. Analysis arbutin whitening ingredients[J]. China Cosmetics Review, 2019(10): 85-87. | |
| 9 | 唐婕妤, 彭菲. 熊果苷的药理作用与资源获取途径研究进展[J]. 今日药学, 2015, 25(9): 673-677. |
| TANG J Y, PENG F. Research progress of pharmacological effects and ways of obtaining resources of arbutin[J]. Pharmacy Today, 2015, 25(9): 673-677. | |
| 10 | PARK J J, HWANG S J, KANG Y S, et al. Synthesis of arbutin-gold nanoparticle complexes and their enhanced performance for whitening[J]. Archives of Pharmacal Research, 2019, 42(11): 977-989. |
| 11 | 杨小玉, 刘金俊, 刘蕾, 等. 黑色素的生成代谢机制及研究方法进展[J]. 日用化学工业(中英文), 2023, 53(10): 1194-1203. |
| YANG X Y, LIU J J, LIU L, et al. Progress in metabolic mechanism and research methods of melanin production[J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2023, 53(10): 1194-1203. | |
| 12 | OHBAYASHI N, FUKUDA M. Recent advances in understanding the molecular basis of melanogenesis in melanocytes[J]. F1000Research, 2020, 9(F1000 Faculty Rev): 608. |
| 13 | 叶希韵, 朱萍亚. 黑色素的合成与美白产品的研究进展[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2016(2): 1-8. |
| YE X Y, ZHU P Y. A review of the studies on melanin synthesis and whitening products[J]. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), 2016(2): 1-8. | |
| 14 | 彭海月, 汪婷, 李国瑞, 等. 黑色素的合成及小分子对其功能的调控[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(11): 3357-3366. |
| PENG H Y, WANG T, LI G R, et al. Synthesis of melanin and its function regulation by small molecules[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3357-3366. | |
| 15 | MAEDA K, FUKUDA M. Arbutin: mechanism of its depigmenting action in human melanocyte culture[J]. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 1996, 276(2): 765-769. |
| 16 | BOO Y C. Arbutin as a skin depigmenting agent with antimelanogenic and antioxidant properties[J]. Antioxidants, 2021, 10(7): 1129. |
| 17 | 王亚芳, 周宇辉, 张建军. 熊果苷镇咳、祛痰及平喘的药效学研究[J]. 中草药, 2003, 34(8): 739-741. |
| WANG Y F, ZHOU Y H, ZHANG J J. Pharmacodynamics of arbutin on relieving cough, dispelling phlegm and preventing asthma[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2003, 34(8): 739-741. | |
| 18 | 董钦, 张春晶, 周宏博, 等. 熊果苷拮抗H2O2损伤的研究[J]. 哈尔滨医科大学学报, 2005, 39(2): 142-144. |
| DONG Q, ZHANG C J, ZHOU H B, et al. The study of arbutin against the damage caused by H2O2 in ECV-304 cells[J]. Journal of Harbin Medical University, 2005, 39(2): 142-144. | |
| 19 | ROSA S C, GONÇALVES J, JUDAS F, et al. Assessment of strategies to increase chondrocyte viability in cryopreserved human osteochondral allografts: evaluation of the glycosylated hydroquinone, arbutin[J]. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 2009, 17(12): 1657-1661. |
| 20 | NADI S, ELAHI M, MORADI S, et al. Radioprotective effect of arbutin in megavoltage therapeutic X-irradiated mice using liver enzymes assessment[J]. Journal of Biomedical Physics & Engineering, 2019, 9(5): 533-540. |
| 21 | POLOULIAKH N, LUDWIG V, MEGURO A, et al. Alpha-arbutin promotes wound healing by lowering ROS and upregulating insulin/IGF-1 pathway in human dermal fibroblast[J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2020, 11: 586843. |
| 22 | EBRAHIM-TABAR F, NAZARI A, POURAMIR M, et al. Arbutin improves functional recovery and attenuates glial activation in lysolecethin-induced demyelination model in rat optic chiasm[J]. Molecular Neurobiology, 2020, 57(7): 3228-3242. |
| 23 | SAFARI H, ZABIHI E, POURAMIR M, et al. Decrease of intracellular ROS by arbutin is associated with apoptosis induction and downregulation of IL-1β and TNF-α in LNCaP; prostate cancer[J]. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 2020, 44(9): e13360. |
| 24 | SIVASANGARI S, ASAIKUMAR L, VENNILA L. Arbutin prevents alterations in mitochondrial and lysosomal enzymes in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction: an in vivo study[J]. Human & Experimental Toxicology, 2021, 40(1): 100-112. |
| 25 | ZENG X T, LIU H P, HUANG Z P, et al. Anticancer effect of arbutin on diethylnitrosamine-induced liver carcinoma in rats via the GRP and GADD pathway[J]. Journal of Environmental Pathology, Toxicology and Oncology, 2022, 41(1): 15-26. |
| 26 | 江漪, 李光先, 廖娜, 等. 采用3D黑素皮肤模型评价α-熊果苷的美白功效[J]. 日用化学品科学, 2023, 46(7): 34-36. |
| JIANG Y, LI G X, LIAO N, et al. Evaluation of the whitening efficacy of α-arbutin by 3D melanin skin model[J]. Detergent & Cosmetics, 2023, 46(7): 34-36. | |
| 27 | 王晓静, 敖雪, 张宏燕, 等. 熊果苷调节Gas6/Axl信号通路对缺氧缺血性脑损伤新生大鼠的神经保护作用[J]. 中国优生与遗传杂志, 2024, 32(2): 261-266. |
| WANG X J, AO X, ZHANG H Y, et al. Neuroprotective effect of arbutin on neonatal rats with hypoxic ischemic brain damage by regulating the Gas6/Axl signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Birth Health & Heredity, 2024, 32(2): 261-266. | |
| 28 | 曹家樊, 孙跃, 丁鑫, 等. 熊果苷通过抑制巨噬细胞募集并调控Akt/NF-κB和Smad信号通路改善小鼠肝纤维化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 652-659. |
| CAO J F, SUN Y, DING X, et al. Arbutin ameliorates liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting macrophage recruitment and regulating the Akt/NF-κB and Smad signaling pathways[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(4): 652-659. | |
| 29 | 张明光, 胡立松, 王石发. 熊果苷的合成方法及其检测研究进展[J]. 化工时刊, 2006, 20(12): 61-64. |
| ZHANG M G, HU L S, WANG S F. Development of arbutin synthesis and its determination[J]. Chemical Industry Times, 2006, 20(12): 61-64. | |
| 30 | ZHU X T, TIAN Y Q, ZHANG W L, et al. Recent progress on biological production of α-arbutin[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(19): 8145-8152. |
| 31 | JURICA K, GOBIN I, KREMER D, et al. Arbutin and its metabolite hydroquinone as the main factors in the antimicrobial effect of strawberry tree (Arbutus unedo L.) leaves[J]. Journal of Herbal Medicine, 2017, 8: 17-23. |
| 32 | SASAKI C, ICHITANI M, KUNIMOTO K K, et al. Extraction of arbutin and its comparative content in branches, leaves, stems, and fruits of Japanese pear Pyrus pyrifolia cv. Kousui[J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2014, 78(5): 874-877. |
| 33 | 李凡, 罗嘉亮, 李六林, 等. 梨果不同部位中熊果苷的差异分布规律[J]. 经济林研究, 2020, 38(2): 154-160, 168. |
| LI F, LUO J L, LI L L, et al. Distribution regularity of arbutin in different parts of pear fruits[J]. Non-wood Forest Research, 2020, 38(2): 154-160, 168. | |
| 34 | 胡英婕. 红景天中熊果苷的提取和含量测定[J]. 上海化工, 2021, 46(1): 16-18. |
| HU Y J. Extraction and determination of arbutin in Rhodiola [J]. Shanghai Chemical Industry, 2021, 46(1): 16-18. | |
| 35 | 张乐乐, 楚艳艳, 杨欧, 等. 皇冠梨渣中熊果苷的纯化工艺[J]. 许昌学院学报, 2023, 42(5): 70-74. |
| ZHANG L L, CHU Y Y, YANG O, et al. Optimization of purification process of arbutin from Huangguan pear pomace[J]. Journal of Xuchang University, 2023, 42(5): 70-74. | |
| 36 | 徐超. 熊果苷的合成与产业化研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2018. |
| XU C. Study on the synthesis and industrialization of arbutin [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2018. | |
| 37 | 陈方达, 陈耀笼, 张洋. β-熊果苷合成新方法[J]. 浙江化工, 2016, 47(9): 29-31. |
| CHEN F D, CHEN Y L, ZHANG Y. Preparation method of β-arbutin[J]. Zhejiang Chemical Industry, 2016, 47(9): 29-31. | |
| 38 | 孙竞阳, 冯中华, 侯熙彦, 等. 熊果苷类似物的合成、表征及美白活性[J]. 中国药物化学杂志, 2017, 27(4): 267-273. |
| SUN J Y, FENG Z H, HOU X Y, et al. Synthesis, characterization and whitening activity of arbutin analogues[J]. Chinese Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2017, 27(4): 267-273. | |
| 39 | HUANG S L, ZHU Y L, PAN Y J, et al. Synthesis of arbutin by two-step reaction from glucose[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University Science, 2004, 5(12): 1509-1511. |
| 40 | ZHOU H Y, ZHAO J, LI A T, et al. Chemical and biocatalytic routes to arbutin [J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(18): 3303. |
| 41 | 张雨捷, 石曈, 王佳, 等. 熊果苷的生物合成研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2024, 40(8): 2457-2472. |
| ZHANG Y J, SHI T, WANG J, et al. Research progress in biosynthesis of arbutin[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2024, 40(8): 2457-2472. | |
| 42 | ZHANG B, GOU K X, XU K X, et al. De novo biosynthesis of β-arbutin in Corynebacterium glutamicum via pathway engineering and process optimization[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels and Bioproducts, 2024, 17(1): 88. |
| 43 | 沈洋, 吕雪芹, 林璐, 等. 蔗糖磷酸化酶的半理性设计及生产α-熊果苷的条件优化[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2020, 46(13): 1-9. |
| SHEN Y, LYU X Q, LIN L, et al. Semi-rational design of sucrose phosphorylase and optimization of conditions for α-arbutin production[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(13): 1-9. | |
| 44 | 陈显玲, 宋连萍, 周燕妮, 等. 蔗糖磷酸化酶产生菌的筛选及其催化合成α-熊果苷条件优化[J]. 中国酿造, 2022, 41(3): 117-124. |
| CHEN X L, SONG L P, ZHOU Y N, et al. Screening of sucrose phosphorylase producing strain and enzymatic synthesis conditions optimization of α-arbutin[J]. China Brewing, 2022, 41(3): 117-124. | |
| 45 | 李晓玉, 夏媛媛, 沈微, 等. 肠膜明串珠菌蔗糖磷酸化酶的酶学表征及在催化合成α-熊果苷中的应用[J]. 生物工程学报, 2020, 36(8): 1546-1555. |
| LI X Y, XIA Y Y, SHEN W, et al. Characterization of a sucrose phosphorylase from Leuconostoc mesenteroides for the synthesis of α-arbutin[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2020, 36(8): 1546-1555. | |
| 46 | SU R Y, ZHENG W, LI A Q, et al. Characterization of a novel sucrose phosphorylase from Paenibacillus elgii and its use in biosynthesis of α-arbutin[J]. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2023, 40(1): 24. |
| 47 | AO J W, PAN X W, WANG Q, et al. Efficient whole-cell biotransformation for α-arbutin production through the engineering of sucrose phosphorylase combined with engineered cell modification[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2023, 71(5): 2438-2445. |
| 48 | 周祺, 吕雪芹, 柴雪莹, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌全细胞催化高效合成α-熊果苷[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2021, 47(22): 1-7. |
| ZHOU Q, LYU X Q, CHAI X Y, et al. Highly efficient synthesis of α-arbutin by whole-cell catalysis of Bacillus subtilis [J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2021, 47(22): 1-7. | |
| 49 | NISHIMURA T, KOMETANI T, TAKII H, et al. Purification and some properties of α-amylase from Bacillus subtilis X-23 that glucosylates phenolic compounds such as hydroquinone[J]. Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering, 1994, 78(1): 31-36. |
| 50 | RUDEEKULTHAMRONG P, KAULPIBOON J. Optimization of amylomaltase for the synthesis of α-arbutin derivatives as tyrosinase inhibitors[J]. Carbohydrate Research, 2020, 494: 108078. |
| 51 | SEO D H, JUNG J H, HA S J, et al. High-yield enzymatic bioconversion of hydroquinone to α-arbutin, a powerful skin lightening agent, by amylosucrase[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2012, 94(5): 1189-1197. |
| 52 | ZHU L J, JIANG D, ZHOU Y Y, et al. Batch-feeding whole-cell catalytic synthesis of α-arbutin by amylosucrase from Xanthomonas campestris [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2019, 46(6): 759-767. |
| 53 | AGARWAL N, RAI A K, SINGH S P. Biotransformation of hydroquinone into α-arbutin by transglucosylation activity of a metagenomic amylosucrase[J]. 3 Biotech, 2021, 11(8): 362. |
| 54 | ZHAO S W, ZHOU Q, LONG N B, et al. Preparation and characterization of a novel 3D polymer support for the immobilization of cyclodextrin glucanotransferase and efficient biocatalytic synthesis of α-arbutin[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 185: 108519. |
| 55 | 张文蕾, 宿玲恰, 陶秀梅, 等. 环糊精葡萄糖基转移酶生产α-熊果苷的反应条件优化及分子改造[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2017, 43(6): 49-53. |
| ZHANG W L, SU L Q, TAO X M, et al. Optimization of conditions for production of α-arbutin by cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase and its molecular modification[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2017, 43(6): 49-53. | |
| 56 | 刘嘉琦, 谭明, 董钧, 等. 环糊精葡萄糖基转移酶的分子改造及其在合成α-熊果苷中的应用[J]. 生物工程学报, 2024, 40(6): 1845-1855. |
| LIU J Q, TAN M, DONG J, et al. Molecular modification of cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase and its application in the synthesis of α-arbutin[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2024, 40(6): 1845-1855. | |
| 57 | WU Y Q, YU X J, ZHOU H Y, et al. Revealing the critical role of Leucine145 of α-glucosidase AglA for enhancing α-arbutin production[J]. Molecular Catalysis, 2023, 537: 112943. |
| 58 | 陆跃乐,陈小龙,范永仙,等.一种含α-糖苷酶基因的重组大肠杆菌及其应用: CN201710655841.X[P]. 2020-10-09. |
| LU Y L, CHEN X L, FAN Y X, et al. Recombinant Escherichia coli containing α-glycosidase gene and its application:CN201710655841.X[P]. 2020-10-09. | |
| 59 | SEO E S, KANG J, LEE J H, et al. Synthesis and characterization of hydroquinone glucoside using Leuconostoc mesenteroides dextransucrase[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2009, 45(5): 355-360. |
| 60 | ZHOU X, ZHENG Y T, WEI X M, et al. Sucrose isomerase and its mutants from Erwinia rhapontici can synthesise α-arbutin[J]. Protein and Peptide Letters, 2011, 18(10): 1028-1034. |
| 61 | STAM M R, DANCHIN E G J, RANCUREL C, et al. Dividing the large glycoside hydrolase family 13 into subfamilies: towards improved functional annotations of alpha-amylase-related proteins[J]. Protein Engineering, Design & Selection, 2006, 19(12): 555-562. |
| 62 | 姚栋. 蔗糖磷酸化酶的高效表达及合成α-熊果苷的研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2020. |
| YAO D. Efficient expression of sucrose phosphorylase and synthesis of α-arbutin[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2020. | |
| 63 | 李晓玉. 重组蔗糖磷酸化酶酶学性质表征、应用及热稳定性改造[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2020. |
| LI X Y. Characterization, application and thermostability engineering of recombinant sucrose phosphorylase[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2020. | |
| 64 | ZUBER P, HEALY J M, LOSICK R. Effects of plasmid propagation of a sporulation promoter on promoter utilization and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1987, 169(2): 461-469. |
| 65 | 姜黎黎,张淼,李平顺.一种米曲霉菌株及其液态发酵生产真菌α-淀粉酶的方法: CN201210524063.8[P]. 2013-5-15. |
| JIANG L L, ZHANG M, LI P S. The invention relates to a method for producing fungal α-amylase by liquid fermentation of Aspergillus oryzae strain and the strain thereof:CN201210524063.8[P]. 2013-5-15. | |
| 66 | 白静, 王君, 李末, 等. 细菌α-淀粉酶活性提升研究进展[J]. 饲料研究, 2023, 46(15): 158-162. |
| BAI J, WANG J, LI M, et al. Research progress on enhancement of bacterial α-amylase activity[J]. Feed Research, 2023, 46(15): 158-162. | |
| 67 | MACGREGOR E A, JANEČEK Š, SVENSSON B. Relationship of sequence and structure to specificity in the α-amylase family of enzymes[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology, 2001, 1546(1): 1-20. |
| 68 | JUNG J H, SEO D H, HA S J, et al. Enzymatic synthesis of salicin glycosides through transglycosylation catalyzed by amylosucrases from Deinococcus geothermalis and Neisseria polysaccharea [J]. Carbohydrate Research, 2009, 344(13): 1612-1619. |
| 69 | MACKENZIE C R, MCDONALD I J, JOHNSON K G. Glycogen metabolism in the genus Neisseria: synthesis from sucrose by amylosucrase[J]. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 1978, 24(4): 357-362. |
| 70 | SKOV L K, MIRZA O, HENRIKSEN A, et al. Amylosucrase, a glucan-synthesizing enzyme from the alpha-amylase family[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2001, 276(27): 25273-25278. |
| 71 | KURKOV S V, LOFTSSON T. Cyclodextrins[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2013, 453(1): 167-180. |
| 72 | SHIEH W J, HEDGES A R. Properties and applications of cyclodextrins[J]. Journal of Macromolecular Science, Part A, 1996, 33(5): 673-683. |
| 73 | 李兆丰, 顾正彪, 堵国成, 等. 环糊精葡萄糖基转移酶的结构特征与催化机理[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 2010, 30(6): 144-150. |
| LI Z F, GU Z B, DU G C, et al. Structural characteristics and catalytic mechanisms of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase[J]. China Biotechnology, 2010, 30(6): 144-150. | |
| 74 | RIMPHANITCHAYAKIT V, TONOZUKA T, SAKANO Y. Construction of chimeric cyclodextrin glucanotransferases from Bacillus circulans A11 and Paenibacillus macerans IAM1243 and analysis of their product specificity[J]. Carbohydrate Research, 2005, 340(14): 2279-2289. |
| 75 | PENNINGA D, VAN DER VEEN B A, KNEGTEL R M, et al. The raw starch binding domain of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase from Bacillus circulans strain 251[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1996, 271(51): 32777-32784. |
| 76 | PARDHI D S, RABADIYA K J, PANCHAL R R, et al. Cyclodextrin glucanotransferase: fundamentals and biotechnological implications[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2023, 107(19): 5899-5907. |
| 77 | RUDEEKULTHAMRONG P, SAWASDEE K, KAULPIBOON J. Production of long-chain isomaltooligosaccharides from maltotriose using the thermostable amylomaltase and transglucosidase enzymes[J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 2013, 18(4): 778-786. |
| 78 | ZHOU C, XUE Y F, MA Y H. Enhancing the thermostability of α-glucosidase from Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis MB4 by single proline substitution[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2010, 110(1): 12-17. |
| 79 | YAMAMOTO T, UNNO T, WATANABE Y, et al. Purification and characterization of Acremonium implicatum alpha-glucosidase having regioselectivity for alpha-1,3-glucosidic linkage[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2004, 1700(2): 189-198. |
| 80 | 李林波, 王宝石, 张明霞, 等. α-葡萄糖苷酶高效合成低聚异麦芽糖的策略分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2021, 47(21): 275-281. |
| LI L B, WANG B S, ZHANG M X, et al. Strategical analysis of high-efficient synthesis of isomalto-oligosaccharides by α-glucosidase[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2021, 47(21): 275-281. | |
| 81 | AUIEWIRIYANUKUL W, SABURI W, KATO K, et al. Function and structure of GH13_31 α-glucosidase with high α-(1→4)-glucosidic linkage specificity and transglucosylation activity[J]. FEBS Letters, 2018, 592(13): 2268-2281. |
| 82 | LOMBARD V, GOLACONDA RAMULU H, DRULA E, et al. The carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy) in 2013[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2014, 42(Database issue): D490-D495. |
| 83 | OKUYAMA M, SABURI W, MORI H, et al. α-Glucosidases and α-1,4-glucan lyases: structures, functions, and physiological actions[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2016, 73(14): 2727-2751. |
| 84 | WU P H, GIRIDHAR R, WU W T. Surface display of transglucosidase on Escherichia coli by using the ice nucleation protein of Xanthomonas campestris and its application in glucosylation of hydroquinone[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2006, 95(6): 1138-1147. |
| 85 | SHI Q, JUVONEN M, HOU Y X, et al. Lactose- and cellobiose-derived branched trisaccharides and a sucrose-containing trisaccharide produced by acceptor reactions of Weissella confusa dextransucrase[J]. Food Chemistry, 2016, 190: 226-236. |
| 86 | 刘丽娜, 姜静, 赵丹. 微生物葡聚糖蔗糖酶的研究进展[J]. 生物技术, 2020, 30(5): 504-510. |
| LIU L N, JIANG J, ZHAO D. Research progress of microbial glucansucrase[J]. Biotechnology, 2020, 30(5): 504-510. | |
| 87 | PIJNING T, VUJIČIĆ-ŽAGAR A, KRALJ S, et al. Structure of the α-1,6/α-1,4-specific glucansucrase GTFA from Lactobacillus reuteri 121[J]. Acta Crystallographica Section F, Structural Biology and Crystallization Communications, 2012, 68(Pt 12): 1448-1454. |
| 88 | MENG X F, GANGOITI J, BAI Y X, et al. Structure-function relationships of family GH70 glucansucrase and 4,6-α- glucanotransferase enzymes, and their evolutionary relationships with family GH13 enzymes[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2016, 73(14): 2681-2706. |
| 89 | 黎志德, 刘桂云, 常国炜, 等. 葡聚糖蔗糖酶及其家族在结构与功能上的研究进展[J]. 现代食品科技, 2023, 39(12): 336-344. |
| LI Z D, LIU G Y, CHANG G W, et al. Research advances in structural and functional properties of glucansucrases and their families[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2023, 39(12): 336-344. | |
| 90 | WU L T, LIU Y, CHI B, et al. An innovative method for immobilizing sucrose isomerase on ε-poly-L-lysine modified mesoporous TiO2 [J]. Food Chemistry, 2015, 187: 182-188. |
| 91 | 陈宁, 张佳钰, 郑明强, 等. 蔗糖异构酶在异麦芽酮糖生产中的研究进展[J]. 食品与生物技术学报, 2023, 42(1): 55-65. |
| CHEN N, ZHANG J Y, ZHENG M Q, et al. Research progress of sucrose isomerase in isomaltulose production[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2023, 42(1): 55-65. | |
| 92 | PARK Y K, UEKANE R T, PUPIN A M. Conversion of sucrose to isomaltulose by microbial glucosyltransferase[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 1992, 14(7): 547-551. |
| 93 | ZHANG F, CHENG F, JIA D X, et al. Characterization of a recombinant sucrose isomerase and its application to enzymatic production of isomaltulose[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2021, 43(1): 261-269. |
| 94 | ZHANG D H, LI X Z, ZHANG L H. Isomaltulose synthase from Klebsiella sp. strain LX3 gene cloning and characterization and engineering of thermostability[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2002, 68(6): 2676-2682. |
| 95 | KUROSU J, SATO T, YOSHIDA K, et al. Enzymatic synthesis of alpha-arbutin by alpha-anomer-selective glucosylation of hydroquinone using lyophilized cells of Xanthomonas campestris WU-9701[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2002, 93(3): 328-330. |
| 96 | ZHU L J, XU M, LU C X, et al. Optimization of whole-cell biotransformation for scale-up production of α-arbutin from hydroquinone by the use of recombinant Escherichia coli [J]. AMB Express, 2019, 9(1): 94. |
| 97 | 敖巨葳. 肠膜明串珠菌蔗糖磷酸化酶的表达、分子改造及应用于合成α-熊果苷的研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2023. |
| AO J W. Expression, molecular modification and application of sucrose phosphorylase from Leuconostoc mesenteroides for the synthesis of α-arbutin[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2023. | |
| 98 | 吴涵, 毛银, 周胜虎, 等.大肠杆菌全细胞催化产α-熊果苷的研究[J].食品与发酵工业, 2025, 51(4): 131-138. |
| WU H, MAO Y, ZHOU S H, et al. Production of α-arbutin by Escherichia coli through whole-cell catalysis[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2025, 51(4): 131-138. | |
| 99 | 吴涛, 李一豪, 胡珀, 等. 具有催化熊果苷酰化反应能力的微生物全细胞培养条件的优化[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2024, 50(22): 137-142. |
| WU T, LI Y H, HU P, et al. Optimization of microbial whole cell culture conditions with catalytic activity for arbutin acylation[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2024, 50(22): 137-142. | |
| 100 | ZHOU Q, WU Y K, DENG J Y, et al. Combinatorial metabolic engineering enables high yield production of α-arbutin from sucrose by biocatalysis[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2023, 107(9): 2897-2910. |
| 101 | LIU C Q, DENG L, ZHANG P, et al. Screening of high α-arbutin producing strains and production of α-arbutin by fermentation[J]. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2013, 29(8): 1391-1398. |
| 102 | WEI M, REN Y, LIU C X, et al. Fermentation scale up for α-arbutin production by Xanthomonas BT-112[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2016, 233: 1-5. |
| 103 | 高磊. 两步法发酵联产α-熊果苷与黄原胶[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2017. |
| GAO L. Two-stop fermentation of α-arbutin and xanthan gum [D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2017. |
| [1] | 竺方欢, 岑雪聪, 陈振. 微生物合成二元醇研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1367-1385. |
| [2] | 刘益宁, 蒲伟, 杨金星, 王钰. ω-氨基酸与内酰胺的生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1350-1366. |
| [3] | 李庚, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 王佳, 袁其朋. 过氧化物酶的重组表达和应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1498-1517. |
| [4] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [5] | 程晓雷, 刘天罡, 陶慧. 萜类化合物的非常规生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1050-1071. |
| [6] | 刘子健, 穆柏杨, 段志强, 王璇, 陆晓杰. 与核酸兼容的化学反应开发进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1102-1124. |
| [7] | 张守祺, 王涛, 孔尧, 邹家胜, 刘元宁, 徐正仁. 天然产物的化学-酶法合成:方法与策略的演进[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 913-940. |
| [8] | 谢向前, 郭雯, 王欢, 李进. 含氨基乙烯半胱氨酸核糖体肽的生物合成与化学合成[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 981-996. |
| [9] | 汤志军, 胡友财, 刘文. 酶促4+2和2+2环加成反应:区域与立体选择性的理解与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 401-407. |
| [10] | 张俊, 金诗雪, 云倩, 瞿旭东. 聚酮化合物非天然延伸单元的生物合成与结构改造应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 561-570. |
| [11] | 陈锡玮, 张华然, 邹懿. 真菌源非核糖体肽类药物生物合成及代谢工程[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 571-592. |
| [12] | 冯金, 潘海学, 唐功利. 近十年天然产物药物的生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 408-446. |
| [13] | 奚萌宇, 胡逸灵, 顾玉诚, 戈惠明. 基因组挖掘指导天然药物分子的发现[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 447-473. |
| [14] | 施鑫杰, 杜艺岭. 双嵌入家族抗肿瘤非核糖体肽的生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 593-611. |
| [15] | 宋永相, 张秀凤, 李艳芹, 肖华, 闫岩. 自抗性基因导向的活性天然产物挖掘[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 474-491. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||