合成生物学 ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (1): 107-125.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-015
酶催化杂Diels-Alder反应
王翠珍1, 陈窕1, 王健博1,2
- 1.湖南师范大学化学化工学院,化学生物学及中药分析教育部重点实验室,植化单体开发与利用湖南省重点实验室,湖南 长沙 410081
2.浙江大学基础医学院药物生物技术研究所,浙江大学医学院附属第二医院综合ICU科室,浙江 杭州 310030
-
收稿日期:2023-02-21修回日期:2023-05-29出版日期:2024-02-29发布日期:2024-03-20 -
通讯作者:王健博 -
作者简介:王翠珍 (1998—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为酶催化碳氟键断裂以及活化。 E-mail:wangcuizhen1998@163.com陈窕 (2000—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为糖基转移酶催化机理的研究。 E-mail:chentiao1208@163.com王健博 (1982—),男,博士,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为酶的催化机理以及按需定制。 E-mail:jwang2023@zju.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(22077029);湖南省自然科学基金杰出青年项目(2021JJ10034)
Enzyme-catalyzed Hetero-Diels-Alder reactions
WANG Cuizhen1, CHEN Tiao1, WANG Jianbo1,2
- 1.Key Laboratory of Chemical Biology and Traditional Chinese Medicine Research (Ministry of Education),Key Laboratory of Phytochemical R & D of Human Province,College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Hunan Normal University,Changsha 410081,Hunan,China
2.Institute of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Zhejiang University and Department of Integrated ICU,The Second Hospital Affiliated to Zhejiang University School of Medicine,Hangzhou 310030,Zhejiang,China
-
Received:2023-02-21Revised:2023-05-29Online:2024-02-29Published:2024-03-20 -
Contact:WANG Jianbo
摘要:
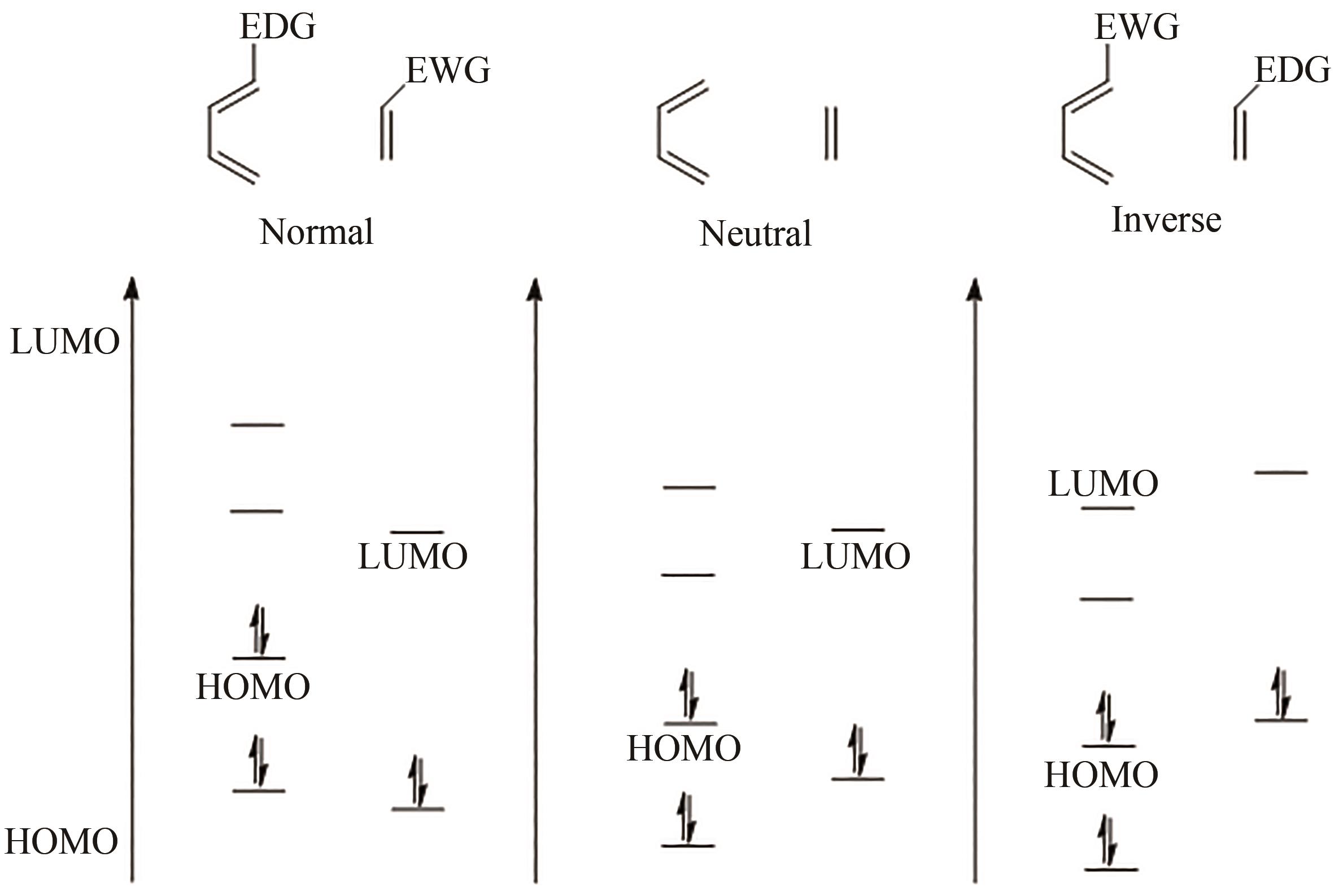
Diels-Alder反应被认为是合成复杂天然产物的最有效的方法之一,一直以来都深受化学家的关注。而杂原子参与的HDA(Hetero-Diels-Alder)反应是合成各种天然杂环的重要工具,其中以氧杂DA反应和氮杂DA反应最为常见。酶催化HDA反应以其绿色温和、高效、高选择性等优势受到人们广泛关注。随着杂环天然产物中酶催化HDA反应的不断发现,对HDA相关酶的立体选择性、底物特异性的研究也不断深入,有效促进了人们对这一类酶序列与功能关系的了解,为其挖掘和改造奠定了基础。本文集中对目前已知的酶催化HDA反应合成杂环天然产物的成果进行概述,主要包括吡喃类化合物和吲哚生物碱生物合成中涉及的酶促HDA反应,以期通过对途径和催化机理的分析,为发展新的相关生物催化剂用于合成非天然的杂环产物提供思路。
中图分类号:
引用本文
王翠珍, 陈窕, 王健博. 酶催化杂Diels-Alder反应[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 107-125.
WANG Cuizhen, CHEN Tiao, WANG Jianbo. Enzyme-catalyzed Hetero-Diels-Alder reactions[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(1): 107-125.
| HDA酶基因簇 | 来源 | HDA产物 | 晶体结构 | 催化机理 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| lep | Aspergillus flavus | 1, 2 | [ | [ |
| eupf | Penicillium janthinellum | 3, 4, 5 | - | [ |
| pyc | Leptobacillium sp. | 6, 36 | - | [ |
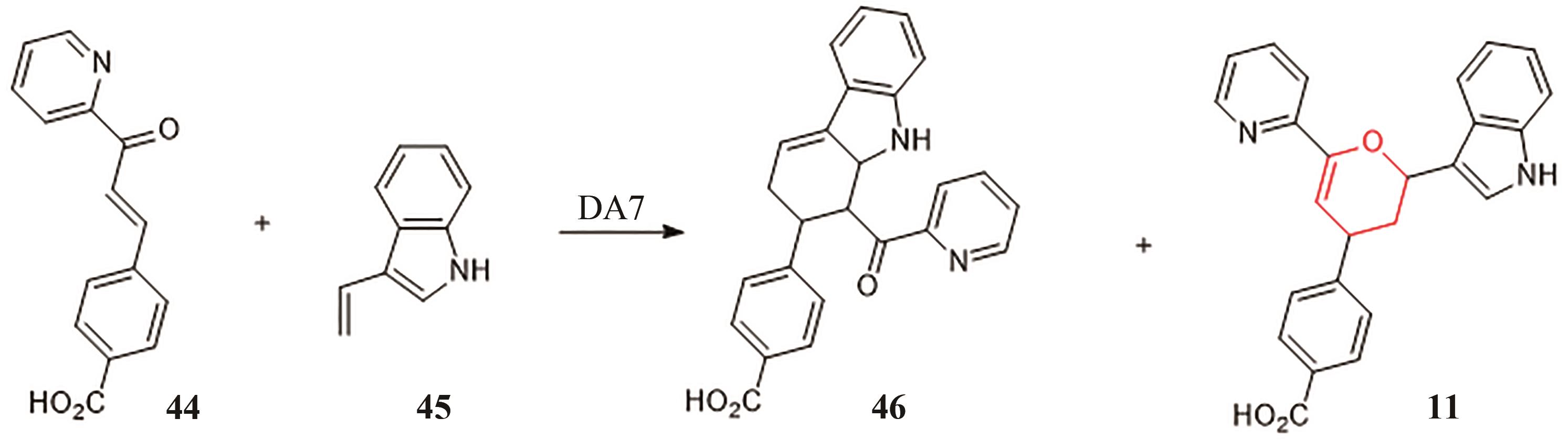
| epi | Epicoccum sorghinum FT1062[ | 9, 10, 41 | - | - |
| upi | Uncinocarpus reesii[ | 9, 10, 41 | - | - |
| hpi | Hymenoscyphus scutula[ | 9, 10, 41 | [ | [ |
| tsn | Streptomyces longisporoflavus | 13 | [ | [ |
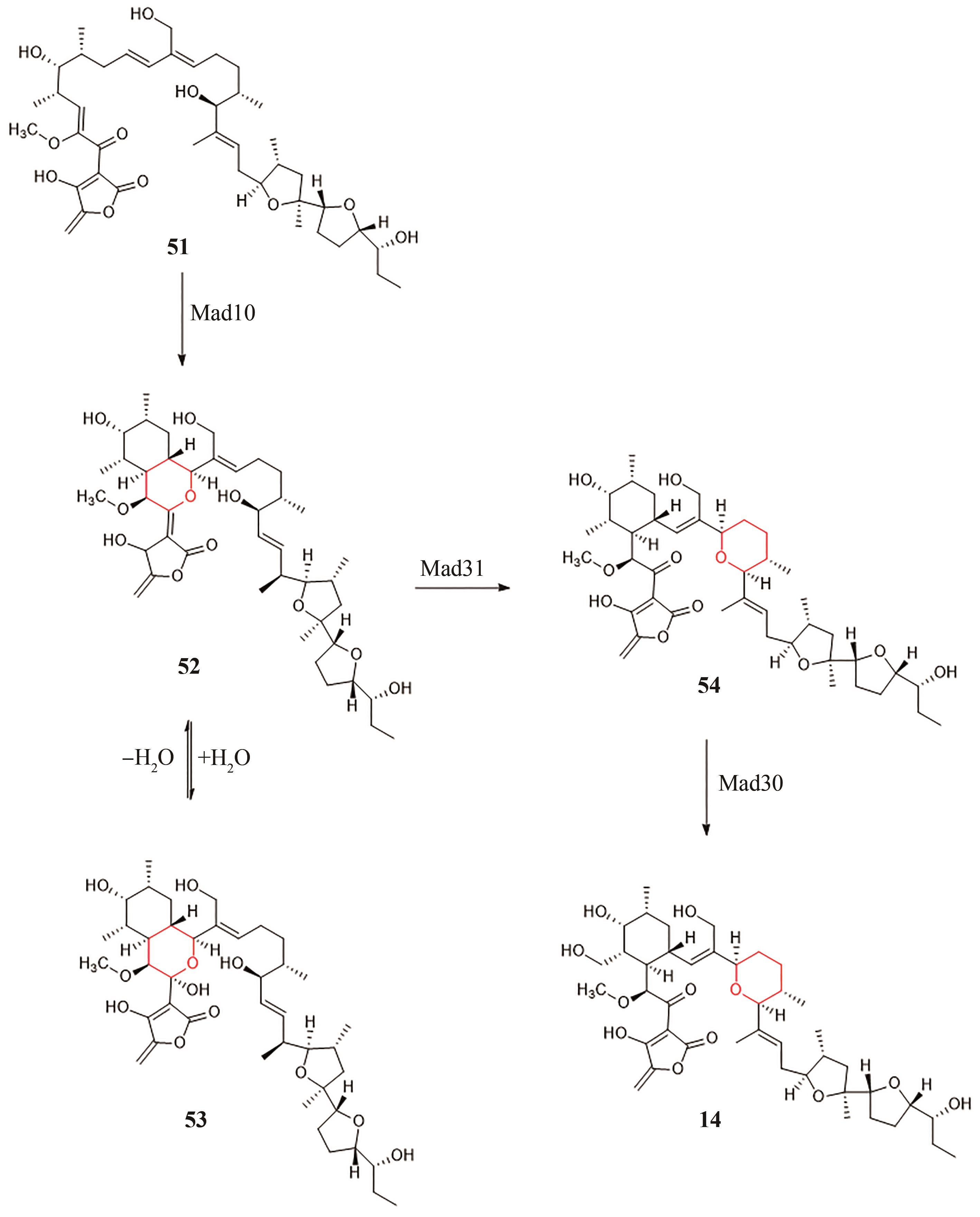
| mad | Actinomadura verrucosospora[ | 14 | - | - |
| mal | Malbranchea aurantiaca[ | 17, 18 | [ | [ |
| ctd | Penicillium citrinum ATCC 9849[ | 19, 20 | [ | [ |
表1 HDA酶及其产物
Table 1 HDA enzymes and products
| HDA酶基因簇 | 来源 | HDA产物 | 晶体结构 | 催化机理 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| lep | Aspergillus flavus | 1, 2 | [ | [ |
| eupf | Penicillium janthinellum | 3, 4, 5 | - | [ |
| pyc | Leptobacillium sp. | 6, 36 | - | [ |
| epi | Epicoccum sorghinum FT1062[ | 9, 10, 41 | - | - |
| upi | Uncinocarpus reesii[ | 9, 10, 41 | - | - |
| hpi | Hymenoscyphus scutula[ | 9, 10, 41 | [ | [ |
| tsn | Streptomyces longisporoflavus | 13 | [ | [ |
| mad | Actinomadura verrucosospora[ | 14 | - | - |
| mal | Malbranchea aurantiaca[ | 17, 18 | [ | [ |
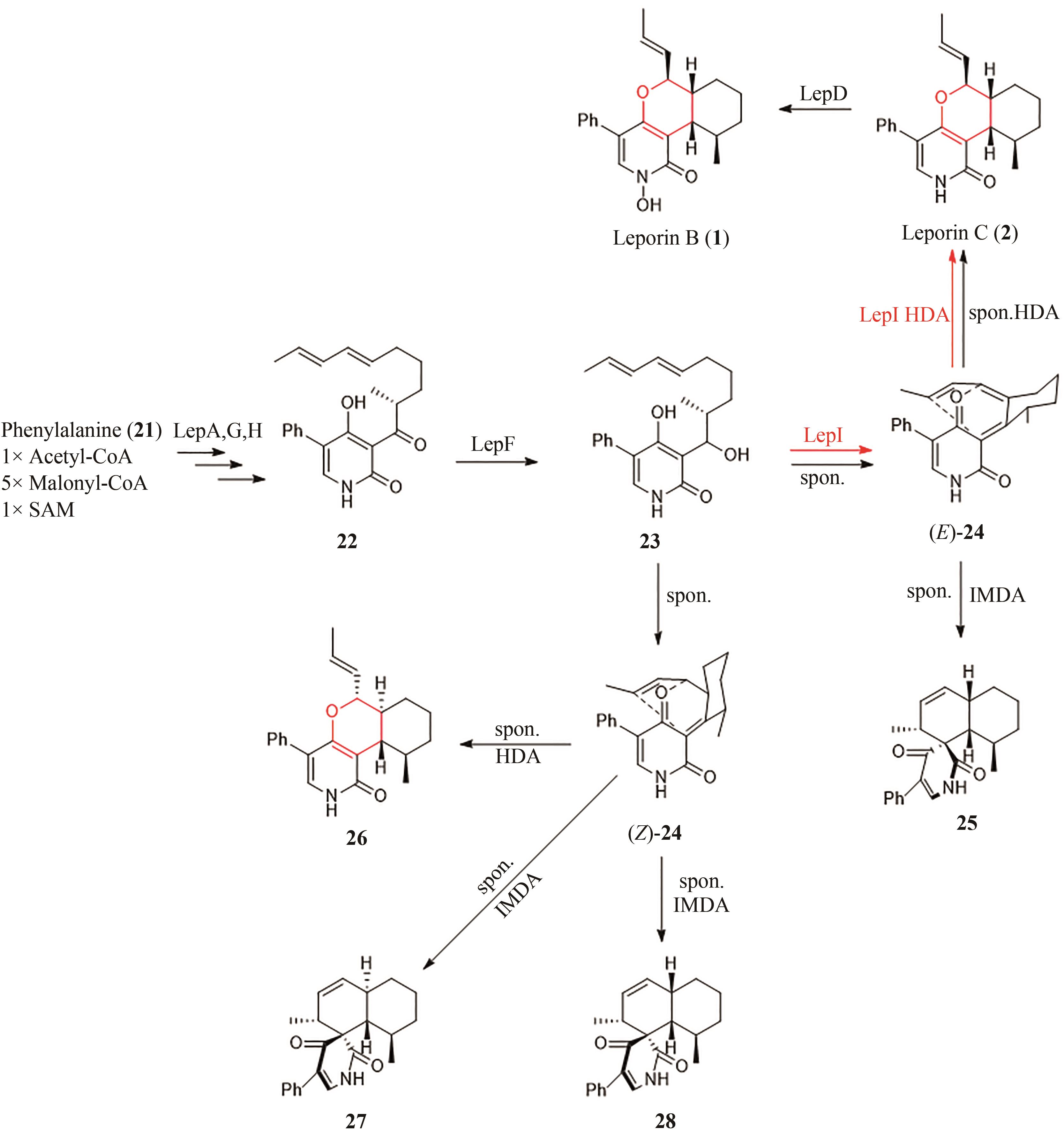
| ctd | Penicillium citrinum ATCC 9849[ | 19, 20 | [ | [ |
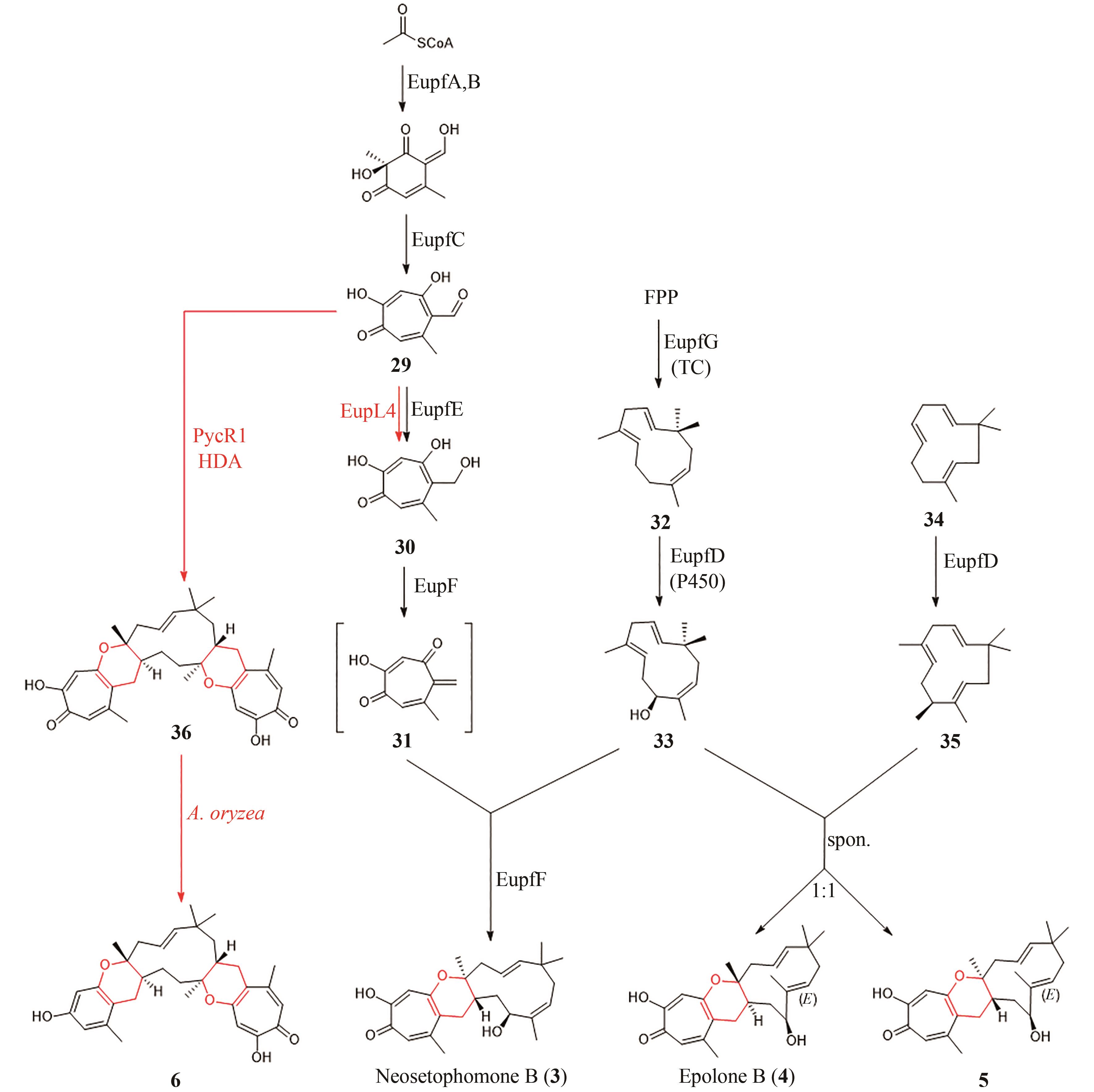
| 1 | DHAMBRI S, MOHAMMAD S, VAN BUU O N, et al. Recent advances in the synthesis of natural multifunctionalized decalins[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2015, 32(6): 841-864. |
| 2 | STOCKING E M, WILLIAMS R M. Chemistry and biology of biosynthetic Diels-Alder reactions[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2003, 42(27): 3078-3115. |
| 3 | VERMEEREN P, HAMLIN T A, BICKELHAUPT F M. Origin of asynchronicity in Diels-Alder reactions[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2021, 23(36): 20095-20106. |
| 4 | JIANG B, LIANG Q J, HAN Y, et al. Copper-catalyzed dehydrogenative Diels-Alder reaction[J]. Organic Letters, 2018, 20(11): 3215-3219. |
| 5 | DIELS O, ALDER K. Synthesen in der hydroaromatischen Reihe[J/OL]. Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, 1928, 460(1): 98-122[2023-02-01]. . |
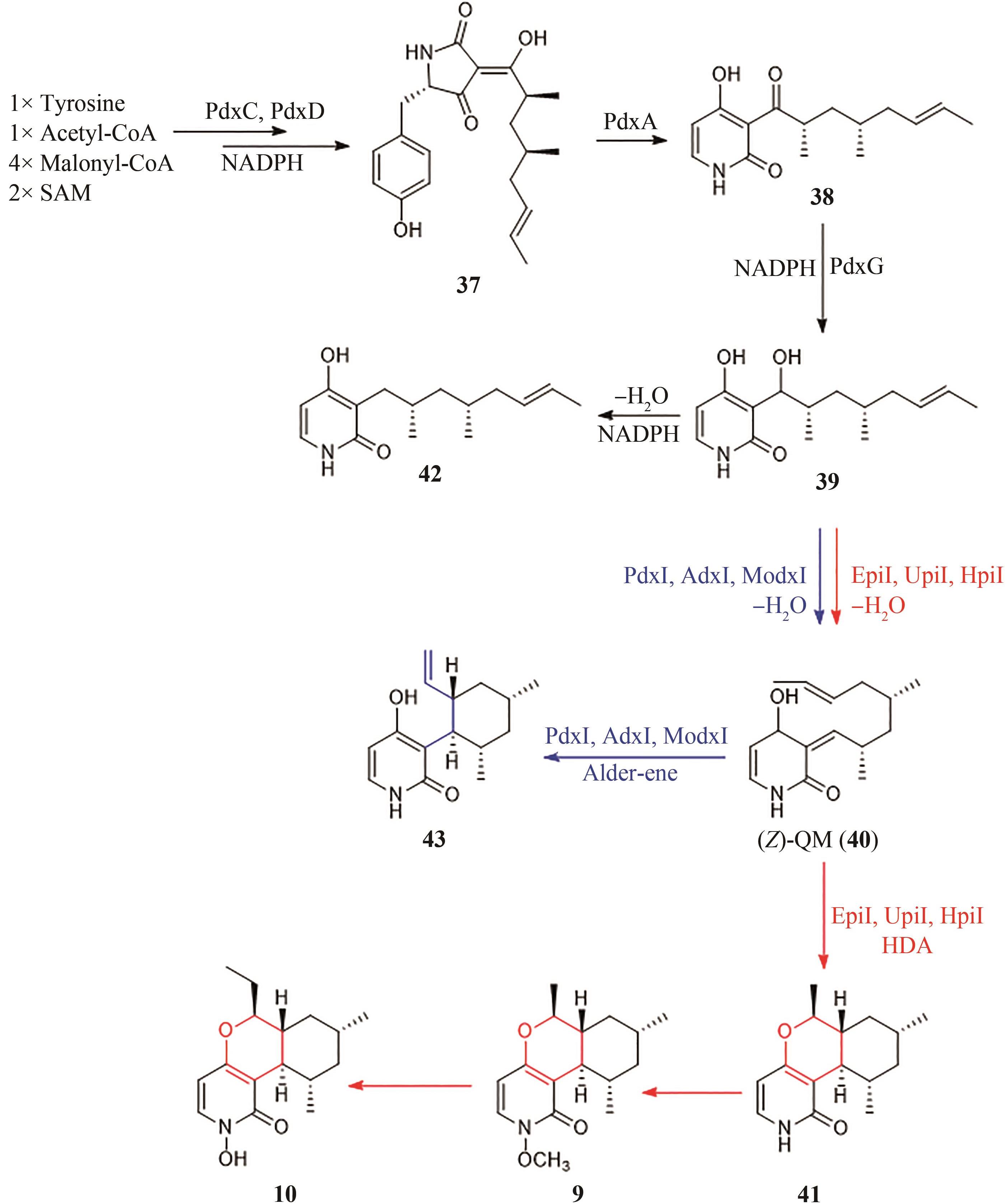
| 6 | MIKAMI K, SHIMIZU M. Asymmetric ene reactions in organic synthesis[J]. Chemical Reviews, 1992, 92(5): 1021-1050. |
| 7 | VERMEEREN P, HAMLIN T A, FERNÁNDEZ I, et al. How Lewis acids catalyze Diels-Alder reactions[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 132(15): 6260-6265. |
| 8 | PING Y J, ZHOU Y M, WU L L, et al. Fe-BPsalan complex catalyzed highly enantioselective Diels-Alder reaction of alkylidene β-ketoesters[J]. Organic Chemistry Frontiers, 2021, 8(9): 1910-1917. |
| 9 | COLE C J F, FUENTES L, SNYDER S A. Asymmetric pyrone Diels-Alder reactions enabled by dienamine catalysis[J]. Chemical Science, 2019, 11(8): 2175-2180. |
| 10 | HILVERT D, HILL K W, NARED K D, et al. Antibody catalysis of the Diels-Alder reaction[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1989, 111(26): 9261-9262. |
| 11 | TARASOW T M, TARASOW S L, EATON B E. RNA-catalysed carbon-carbon bond formation[J]. Nature, 1997, 389(6646): 54-57. |
| 12 | KIM H J, RUSZCZYCKY M W, CHOI S H, et al. Enzyme-catalysed [4+2] cycloaddition is a key step in the biosynthesis of spinosyn A[J]. Nature, 2011, 473(7345): 109-112. |
| 13 | FAGE C D, ISIORHO E A, LIU Y, et al. The structure of SpnF, a standalone enzyme that catalyzes [4+2] cycloaddition[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2015, 11(4): 256-258. |
| 14 | YANG Z Y, YANG S, YU P Y, et al. Influence of water and enzyme SpnF on the dynamics and energetics of the ambimodal[6+4]/[4+2] cycloaddition[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(5): E848-E855. |
| 15 | HASHIMOTO T, KUZUYAMA T. Mechanistic insights into Diels-Alder reactions in natural product biosynthesis[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2016, 35: 117-123. |
| 16 | SIEGEL J B, ZANGHELLINI A, LOVICK H M, et al. Computational design of an enzyme catalyst for a stereoselective bimolecular Diels-Alder reaction[J]. Science, 2010, 329(5989): 309-313. |
| 17 | MLOSTOŃ G, GRZELAK P, HEIMGARTNER H. Hetero-Diels-Alder reactions of hetaryl thiochalcones with acetylenic dienophiles[J]. Journal of Sulfur Chemistry, 2017, 38(1): 1-10. |
| 18 | PERTSCHI R, WAGNER P, GHOSH N, et al. Gold(I)- catalyzed synthesis of furopyrans: insight into hetero-Diels-Alder reactions[J]. Organic Letters, 2019, 21(15): 6084-6088. |
| 19 | LI T Z, GENG C A, YIN X J, et al. Catalytic asymmetric total synthesis of (+)- and (-)-paeoveitol via a hetero-Diels-Alder reaction[J]. Organic Letters, 2017, 19(3): 429-431. |
| 20 | LIANG D, RAO L, XIAO C, et al. Intermolecular hetero-Diels-Alder reactions of photogenerated aza-ortho-quinone methides with aldehydes[J]. Organic Letters, 2019, 21(21): 8783-8788. |
| 21 | RUDY H K A, WANNER K T. Accessing tricyclic imines comprising a 2-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octane scaffold by intramolecular hetero-Diels-Alder reaction of 4-alkenyl-substituted N-silyl-1, 4-dihydropyridines[J]. Synthesis, 2019, 51(22): 4296-4310. |
| 22 | HEJMANOWSKA J, JASIŃSKI M, WOJCIECHOWSKI J, et al. The first organocatalytic, ortho-regioselective inverse-electron-demand hetero-Diels-Alder reaction[J]. Chemical Communications, 2017, 53(83): 11472-11475. |
| 23 | ZHANG K K, ZHANG Q Y, WEI D H, et al. Hetero-Diels-Alder reactions of 2H-phospholes with allenes: synthesis and functionalization of 6-methylene-1-phosphanorbornenes[J]. Organic Chemistry Frontiers, 2021, 8(14): 3740-3745. |
| 24 | GUO X Y, WANG Q R, TAO F G. Synthesis of 2-acyl-2H-1,2,3-diazaphospholes and their Diels-Alder reaction with cyclopentadiene[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemistry, 2010, 22(9): 1003-1007. |
| 25 | ALI-ASGARI S, NIA J I, ZALI S. Regioselectivity in the hetero-Diels-Alder reactions of styrenes with 2-aza-1,3-butadiene: a DFT study[J]. Journal of Chemical Sciences, 2017, 129(8): 1319-1325. |
| 26 | XIE M S, LIN L L, FENG X M. Catalytic asymmetric inverse-electron-demand hetero-Diels-Alder reactions[J]. The Chemical Record, 2017, 17(12): 1184-1202. |
| 27 | OHASHI M, LIU F, HAI Y, et al. SAM-dependent enzyme-catalysed pericyclic reactions in natural product biosynthesis[J]. Nature, 2017, 549(7673): 502-506. |
| 28 | CHEN Q B, GAO J, JAMIESON C, et al. Enzymatic intermolecular hetero-Diels-Alder reaction in the biosynthesis of tropolonic sesquiterpenes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(36): 14052-14056. |
| 29 | DAN Q Y, NEWMISTER S A, KLAS K R, et al. Fungal indole alkaloid biogenesis through evolution of a bifunctional reductase/Diels-Alderase[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2019, 11(11): 972-980. |
| 30 | JIANG X X, WANG R. Recent developments in catalytic asymmetric inverse-electron-demand Diels-Alder reaction[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2013, 113(7): 5515-5546. |
| 31 | HANDULA M, CHEN K T, SEIMBILLE Y. IEDDA: an attractive bioorthogonal reaction for biomedical applications[J]. Molecules, 2021, 26(15): 4640. |
| 32 | SAUER J, SUSTMANN R. Mechanistic aspects of Diels-Alder reactions: a critical survey[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English, 1980, 19(10): 779-807. |
| 33 | GOUVERNEUR V, REITER M. Biocatalytic approaches to hetero-Diels-Alder adducts of carbonyl compounds[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2005, 11(20): 5806-5815. |
| 34 | TARASOW T M, EATON B E. The Diels-Alder reaction and biopolymer catalysis[J].Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences CMLS, 1999, 55(11): 1463-1472. |
| 35 | KLAS K, TSUKAMOTO S, SHERMAN D H, et al. Natural Diels-Alderases: elusive and irresistable[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2015, 80(23): 11672-11685. |
| 36 | HATANO M, SAKAMOTO T, MOCHIZUKI T, et al. Tris(pentafluorophenyl)borane-assisted chiral phosphoric acid catalysts for enantioselective inverse-electron-demand hetero-Diels-Alder reaction of α,β-substituted acroleins[J]. Asian Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2019, 8(7): 1061-1066. |
| 37 | WANG X C, LI Z Y, DOYLE M P. Barriers to enantiocontrol in Lewis acid catalyzed hetero-Diels-Alder reactions[J]. Chemical Communications, 2009(37): 5612-5614. |
| 38 | JIN M, TANG C Y, LI Y Y, et al. Enantioselective access to tricyclic tetrahydropyran derivatives by a remote hydrogen bonding mediated intramolecular IEDHDA reaction[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 7188. |
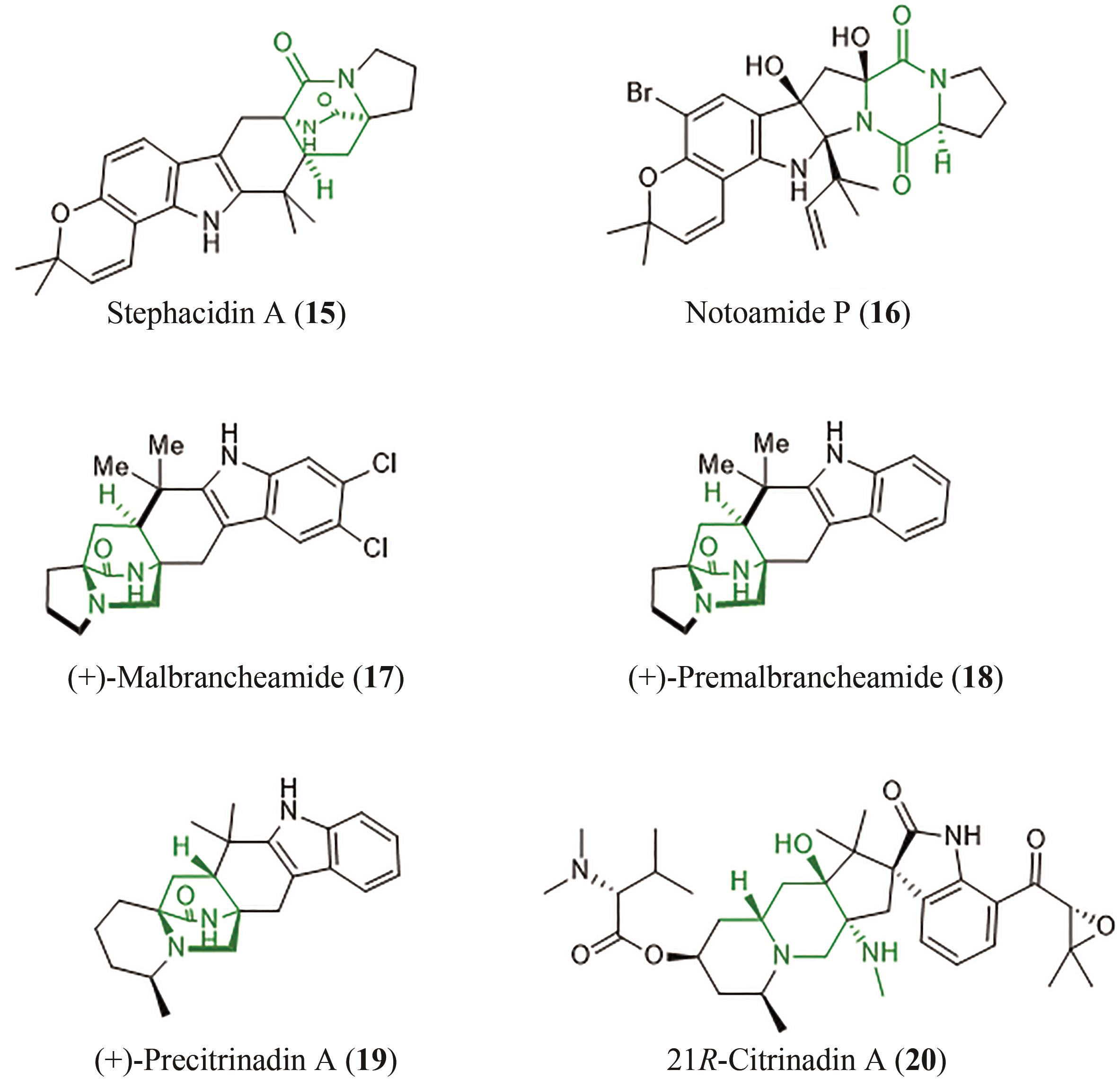
| 39 | LAINA-MARTÍN V, FERNÁNDEZ-SALAS J A, ALEMÁN J. Organocatalytic strategies for the development of the enantioselective inverse-electron-demand hetero-Diels-Alder reaction[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2021, 27(49): 12509-12520. |
| 40 | BLACK K, LIU P, XU L, et al. Dynamics, transition states, and timing of bond formation in Diels-Alder reactions[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(32): 12860-12865. |
| 41 | LI B, GUAN X Y, YANG S, et al. Mechanism of the stereoselective catalysis of Diels-Alderase PyrE3 involved in pyrroindomycin biosynthesis[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2022, 144(11): 5099-5107. |
| 42 | SATO M, YAGISHITA F, MINO T, et al. Involvement of lipocalin-like CghA in decalin-forming stereoselective intramolecular [4+2] cycloaddition[J]. Chembiochem, 2015, 16(16): 2294-2298. |
| 43 | LI L, YU P Y, TANG M C, et al. Biochemical characterization of a eukaryotic decalin-forming Diels-Alderase[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(49): 15837-15840. |
| 44 | ZHANG Z, JAMIESON C S, ZHAO Y L, et al. Enzyme-catalyzed inverse-electron demand Diels-Alder reaction in the biosynthesis of antifungal ilicicolin H[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(14): 5659-5663. |
| 45 | LIU Z W, RIVERA S, NEWMISTER S A, et al. An NmrA-like enzyme-catalysed redox-mediated Diels-Alder cycloaddition with anti-selectivity[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2023, 15(4): 526-534. |
| 46 | GHINI A A, BUMOUF C, LOPEZ J C, et al. Intramolecular Diels-Alder reactions on pyranose trienes. Stereoselective access to bis-annulated pyranosides[J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 1990, 31(16): 2301-2304. |
| 47 | HUANG G H, KOUKLOVSKY C, DE LA TORRE A. Inverse-electron-demand Diels-Alder reactions of 2-pyrones: bridged lactones and beyond[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2021, 27(15): 4760-4788. |
| 48 | ZHANG C W, JIN L, MONDIE B, et al. Leporin B: a novel hexokinase II gene inducing agent from an unidentified fungus[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2003, 13(8): 1433-1435. |
| 49 | MAYERL F, GAO Q, HUANG S, et al. Eupenifeldin, a novel cytotoxic bistropolone from eupenicillium brefeldianum[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 1993, 46(7): 1082-1088. |
| 50 | CAI P, SMITH D, CUNNINGHAM B, et al. Epolones: novel sesquiterpene-tropolones from fungus OS-F69284 that induce erythropoietin in human cells[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 1998, 61(6): 791-795. |
| 51 | QIAO Y B, XU Q Q, FENG W Y, et al. Asperpyridone A: an unusual pyridone alkaloid exerts hypoglycemic activity through the insulin signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2019, 82(10): 2925-2930. |
| 52 | CARY J W, UKA V, HAN Z, et al. An Aspergillus flavus secondary metabolic gene cluster containing a hybrid PKS-NRPS is necessary for synthesis of the 2-pyridones, leporins[J]. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 2015, 81: 88-97. |
| 53 | HALO L M, HENEGHAN M N, YAKASAI A A, et al. Late stage oxidations during the biosynthesis of the 2-pyridone tenellin in the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008, 130(52): 17988-17996. |
| 54 | GLÖCKLE A, GULDER T A M. A pericyclic reaction cascade in leporin biosynthesis[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(11): 2754-2756. |
| 55 | ESS D H, WHEELER S E, IAFE R G, et al. Bifurcations on potential energy surfaces of organic reactions[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2008, 47(40): 7592-7601. |
| 56 | CHANG Z Y, ANSBACHER T, ZHANG L L, et al. Crystal structure of LepI, a multifunctional SAM-dependent enzyme which catalyzes pericyclic reactions in leporin biosynthesis[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2019, 17(8): 2070-2076. |
| 57 | CAI Y J, HAI Y, OHASHI M, et al. Structural basis for stereoselective dehydration and hydrogen-bonding catalysis by the SAM-dependent pericyclase LepI[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2019, 11(9): 812-820. |
| 58 | CHANG M, ZHOU Y, WANG H, et al. Crystal structure of the multifunctional SAM-dependent enzyme LepI provides insights into its catalytic mechanism[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2019, 515(2): 255-260. |
| 59 | SUN Q, HU Y H, GU Y J, et al. Deciphering the regulatory and catalytic mechanisms of an unusual SAM-dependent enzyme[J]. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 2019, 4: 17. |
| 60 | LIAO L J, ZHOU Y Z, PENG T, et al. Crystal structure of a S-adenosyl-L-methionine-dependent O-methyltransferase-like enzyme from Aspergillus flavus [J]. Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics, 2021, 89(2): 185-192. |
| 61 | YAN D J, CHEN Q B, GAO J, et al. Complexity and diversity generation in the biosynthesis of fumiquinazoline-related peptidyl alkaloids[J]. Organic Letters, 2019, 21(5): 1475-1479. |
| 62 | SCHOR R, SCHOTTE C, WIBBERG D, et al. Three previously unrecognised classes of biosynthetic enzymes revealed during the production of xenovulene A[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 1963. |
| 63 | ZHAI Y N, LI Y M, ZHANG J Y, et al. Identification of the gene cluster for bistropolone-humulene meroterpenoid biosynthesis in Phoma sp.[J]. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 2019, 129: 7-15. |
| 64 | AYERS S, ZINK D L, POWELL J S, et al. Noreupenifeldin, a tropolone from an unidentified ascomycete[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2008, 71(3): 457-459. |
| 65 | SCHOTTE C, LI L, WIBBERG D, et al. Synthetic biology driven biosynthesis of unnatural tropolone sesquiterpenoids[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(52): 23870-23878. |
| 66 | LI C S, SAROTTI A, YANG B J, et al. A new N-methoxypyridone from the co-cultivation of Hawaiian endophytic fungi camporesia sambuci FT1061 and epicoccum sorghinum FT1062[J]. Molecules, 2017, 22(7): 1166. |
| 67 | SHIRATAKE S, NAKAHARA T, IWAHASHI H, et al. Rose myrtle (Rhodomyrtus tomentosa) extract and its component, piceatannol, enhance the activity of DNA polymeraseand suppress the inflammatory response elicitedby UVB-induced DNA damage in skin cells[J]. Molecular Medicine Reports, 2015, 12(4): 5857-5864. |
| 68 | OHASHI M, JAMIESON C S, CAI Y J, et al. An enzymatic Alder-ene reaction[J]. Nature, 2020, 586(7827): 64-69. |
| 69 | SINGH S, CHANG A, GOFF R D, et al. Structural characterization of the mitomycin 7-O-methyltransferase[J]. Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics, 2011, 79(7): 2181-2188. |
| 70 | BASLER S, STUDER S, ZOU Y K, et al. Efficient Lewis acid catalysis of an abiological reaction in a de novo protein scaffold[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2021, 13(3): 231-235. |
| 71 | KUMAR D, SHARMA P, SINGH H, et al. The value of pyrans as anticancer scaffolds in medicinal chemistry[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(59): 36977-36999. |
| 72 | SRIHARI P, KUMARASWAMY B, YADAV J S. A carbohydrate approach for the synthesis of tetrahydropyran containing C16-C29 fragment of sorangicin A[J]. Tetrahedron, 2009, 65(32): 6304-6309. |
| 73 | BOWEN J I, WANG L Y, CRUMP M P, et al. Ambruticins: tetrahydropyran ring formation and total synthesis[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2021, 19(28): 6210-6215. |
| 74 | TRENTADUE K, CHANG C F, NALIN A, et al. Enantioselective total synthesis of the putative biosynthetic intermediate Ambruticin J[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2021, 27(43): 11126-11131. |
| 75 | NEWBOLD C J, WALLACE R J, WATT N D, et al. Effect of the novel ionophore tetronasin (ICI 139603) on ruminal microorganisms[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1988, 54(2): 544-547. |
| 76 | HATSU M, SASAKI T, MIYADOH S, et al. SF2487, a new polyether antibiotic produced by Actinomadura[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 1990, 43(3): 259-266. |
| 77 | DEMYDCHUK Y, SUN Y H, HONG H, et al. Analysis of the tetronomycin gene cluster: insights into the biosynthesis of a polyether tetronate antibiotic[J]. ChemBioChem, 2008, 9(7): 1136-1145. |
| 78 | RIVA E, WILKENING I, GAZZOLA S, et al. Chemical probes for the functionalization of polyketide intermediates[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 126(44): 12138-12143. |
| 79 | HASHIMOTO T, HASHIMOTO J, TERUYA K, et al. Biosynthesis of versipelostatin: identification of an enzyme-catalyzed [4+2]-cycloaddition required for macrocyclization of spirotetronate-containing polyketides[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(2): 572-575. |
| 80 | TIAN Z H, SUN P, YAN Y, et al. An enzymatic [4+2]cyclization cascade creates the pentacyclic core of pyrroindomycins[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2015, 11(4): 259-265. |
| 81 | BYRNE M J, LEES N R, HAN L C, et al. The catalytic mechanism of a natural Diels-Alderase revealed in molecular detail[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(19): 6095-6098. |
| 82 | ZHENG Q F, GUO Y J YANG L L, et al. Enzyme-dependent[4+2]cycloaddition depends on lid-like interaction of the N-terminal sequence with the catalytic core in PyrI4[J]. Cell Chemical Biology, 2016, 23(3): 352-360. |
| 83 | HOFMANN E, ZERBE P, SCHALLER F. The crystal structure of Arabidopsis thaliana allene oxide cyclase: insights into the oxylipin cyclization reaction[J]. The Plant Cell, 2006, 18(11): 3201-3217. |
| 84 | MARSH C O, LEES N R, HAN L C, et al. A natural Diels-Alder biocatalyst enables efficient [4+2] cycloaddition under harsh reaction conditions[J]. ChemCatChem, 2019, 11(20): 5027-5031. |
| 85 | LITTLE R, PAIVA F C R, JENKINS R, et al. Unexpected enzyme-catalysed [4+2] cycloaddition and rearrangement in polyether antibiotic biosynthesis[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2019, 2(11): 1045-1054. |
| 86 | LITTLE R F, SAMBORSKYY M, LEADLAY P F. The biosynthetic pathway to tetromadurin (SF2487/A80577), a polyether tetronate antibiotic[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(9): e0239054. |
| 87 | KLAS K R, KATO H, FRISVAD J C, et al. Structural and stereochemical diversity in prenylated indole alkaloids containing the bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane ring system from marine and terrestrial fungi[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2018, 35(6): 532-558. |
| 88 | MADARIAGA-MAZÓN A, HERNÁNDEZ-ABREU O, ESTRADA-SOTO S, et al. Insights on the vasorelaxant mode of action of malbrancheamide[J]. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 2015, 67(4): 551-558. |
| 89 | FIGUEROA M, DEL CARMEN GONZÁLEZ M, MATA R. Malbrancheamide B, a novel compound from the fungus Malbranchea aurantiaca [J]. Natural Product Research, 2008, 22(8): 709-714. |
| 90 | QIAN-CUTRONE J, HUANG S, SHU Y Z, et al. Stephacidin A and B: two structurally novel, selective inhibitors of the testosterone-dependent prostate LNCaP cells[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2002, 124(49): 14556-14557. |
| 91 | TSUKAMOTO S, UMAOKA H, YOSHIKAWA K, et al. Notoamide O, a structurally unprecedented prenylated indole alkaloid, and notoamides P-R from a marine-derived fungus, Aspergillus sp.[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2010, 73(8): 1438-1440. |
| 92 | MILLER K A, FIGUEROA M, VALENTE M W N, et al. Calmodulin inhibitory activity of the malbrancheamides and various analogs[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2008, 18(24): 6479-6481. |
| 93 | PORTER A E A, SAMMES P G. A Diels-Alder reaction of possible biosynthetic importance[J]. Journal of the Chemical Society D: Chemical Communications, 1970(17): 1103a. |
| 94 | KAGIYAMA I, KATO H, NEHIRA T, et al. Taichunamides: prenylated indole alkaloids from Aspergillus taichungensis (IBT 19404)[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(3), 1128-1132. |
| 95 | FRALEY A E, GARCIA-BORRÀS M, TRIPATHI A, et al. Function and structure of MalA/MalA', iterative halogenases for late-stage C—H functionalization of indole alkaloids[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(34): 12060-12068. |
| 96 | SUNDERHAUS J D, SHERMAN D H, WILLIAMS R M. Studies on the biosynthesis of the stephacidin and notoamide natural products: a stereochemical and genetic conundrum[J]. Israel Journal of Chemistry, 2011, 51(3/4): 442-452. |
| 97 | LIU Z W, ZHAO F L, ZHAO B Y, et al. Structural basis of the stereoselective formation of the spirooxindole ring in the biosynthesis of citrinadins[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 4158. |
| 98 | LI S Y, SRINIVASAN K, TRAN H, et al. Comparative analysis of the biosynthetic systems for fungal bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane indole alkaloids: the (+)/(-)-notoamide, paraherquamide and malbrancheamide pathways[J]. MedChemComm, 2012, 3(8): 987-996. |
| 99 | JAMIESON C S, OHASHI M, LIU F, et al. The expanding world of biosynthetic pericyclases: cooperation of experiment and theory for discovery[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2019, 36(5): 698-713. |
| 100 | ROQUE J B, MERCADO-MARIN E V, RICHTER S C, et al. A unified strategy to reverse-prenylated indole alkaloids: total syntheses of preparaherquamide, premalbrancheamide, and (+)-VM-55599[J]. Chemical Science, 2020, 11(23): 5929-5934. |
| 101 | MILLER K A, WILLIAMS R M. Synthetic approaches to the bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane ring system common to the paraherquamides, stephacidins and related prenylated indole alkaloids[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2009, 38(11): 3160-3174. |
| [1] | 刘宽庆, 张以恒. 木质素的生物降解和生物利用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1264-1278. |
| [2] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [3] | 雷航彬, 何宁, 李斐煊, 董玲玲, 王世珍. 氢化酶固定化研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1485-1497. |
| [4] | 王子渊, 杨立荣, 吴坚平, 郑文隆. 酶促合成手性氨基酸的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1319-1349. |
| [5] | 董玲玲, 李斐煊, 雷航彬, 宋启迪, 王世珍. 仿生分区室固定化多酶体系[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1518-1529. |
| [6] | 李庚, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 王佳, 袁其朋. 过氧化物酶的重组表达和应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1498-1517. |
| [7] | 程峰, 邹树平, 徐建妙, 汤恒, 薛亚平, 郑裕国. 生物高纯精草:高光学纯L-草铵膦生物制造的创新与发展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1404-1418. |
| [8] | 张阿磊, 魏国光, 张弛, 陈磊, 周奚, 刘伟, 陈可泉. 几丁质资源生物降解和高值转化的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1279-1299. |
| [9] | 李怡霏, 陈艾, 孙俊松, 张以恒. 体外多酶分子机器产氢应用中的氢酶研究[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1461-1484. |
| [10] | 付雨, 钟芳锐. 化学原理驱动的光生物不对称催化研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1021-1049. |
| [11] | 郑梦梦, 刘犇犇, 林芝, 瞿旭东. 重要甾体化合物的化学酶法合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 941-959. |
| [12] | 程晓雷, 刘天罡, 陶慧. 萜类化合物的非常规生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1050-1071. |
| [13] | 杨皓然, 叶发荣, 黄平, 王平. 糖蛋白合成的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1072-1101. |
| [14] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [15] | 程中玉, 李付琸. 基于P450选择性氧化的天然产物化学-酶法合成进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 960-980. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||