Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (5): 833-846.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-042
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Biological carbon fixation: from natural to synthetic
XIAO Lu1,2, LI Yin1
- 1.CAS Key Laboratory of Microbial Physiological and Metabolic Engineering,State Key Laboratory of Microbial Resources,Institute of Microbiology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100101,China
2.Institute of Synthetic Biology,Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academey of Science,Shenzhen 518055,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2022-08-03Revised:2022-09-19Online:2022-11-16Published:2022-10-31 -
Contact:LI Yin
生物固碳:从自然生物到人工合成
肖璐1,2, 李寅1
- 1.中国科学院微生物研究所 中国科学院微生物生理与代谢工程重点实验室 微生物资源前期开发国家重点实验室,北京 100101
2.中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院合成生物学研究所,广东,深圳 518055
-
通讯作者:李寅 -
作者简介:肖璐 (1994—),女,博士后。研究方向为生物固碳与酶工程。E-mail:xiaolu314@126.com李寅 (1974—),男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为微生物分子生理学与系统生物技术。E-mail:yli@im.ac.cn -
基金资助:中国科学院B类先导科技专项培育项目(XDPB18)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
XIAO Lu, LI Yin. Biological carbon fixation: from natural to synthetic[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(5): 833-846.
肖璐, 李寅. 生物固碳:从自然生物到人工合成[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(5): 833-846.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2022-042
| 途径 | 厌氧/ 好氧 | 反应数 | 产物 | 固碳酶 | ATP/CO2/(mol/mol) | NAD(P)H/CO2/(mol/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 卡尔文循环[ | 好氧 | 11 | 3-PGA | Rubisco | 3 | 2 |
| 还原性TCA 循环[ | 厌氧 | 9 | 乙酰辅酶A | 2-oxoglutarate synthase and isocitrate dehydrogenase | 1 | 2 |
| WL途径[ | 厌氧 | 8 | 乙酰辅酶A | Formate dehydrogenase and CO dehydrogenate/ Acetyl-CoA synthase | 0.5 | 2 |
| 3-羟基丙酸双循环[ | 好氧 | 16 | 丙酮酸 | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase and propionyl-CoA carboxylase | 1.67 | 1.67 |
| 3-羟基丙酸/4-羟基丁酸循环[ | 好氧 | 16 | 乙酰辅酶A | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase and propionyl-CoA carboxylase | 2 | 2 |
| 二羧酸/4-羟基丁酸循环[ | 厌氧 | 14 | 乙酰辅酶A | Pyruvate synthase and Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase | 1.5 | 2 |
Tab. 1 Comparison of six natural carbon fixation pathways
| 途径 | 厌氧/ 好氧 | 反应数 | 产物 | 固碳酶 | ATP/CO2/(mol/mol) | NAD(P)H/CO2/(mol/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 卡尔文循环[ | 好氧 | 11 | 3-PGA | Rubisco | 3 | 2 |
| 还原性TCA 循环[ | 厌氧 | 9 | 乙酰辅酶A | 2-oxoglutarate synthase and isocitrate dehydrogenase | 1 | 2 |
| WL途径[ | 厌氧 | 8 | 乙酰辅酶A | Formate dehydrogenase and CO dehydrogenate/ Acetyl-CoA synthase | 0.5 | 2 |
| 3-羟基丙酸双循环[ | 好氧 | 16 | 丙酮酸 | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase and propionyl-CoA carboxylase | 1.67 | 1.67 |
| 3-羟基丙酸/4-羟基丁酸循环[ | 好氧 | 16 | 乙酰辅酶A | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase and propionyl-CoA carboxylase | 2 | 2 |
| 二羧酸/4-羟基丁酸循环[ | 厌氧 | 14 | 乙酰辅酶A | Pyruvate synthase and Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase | 1.5 | 2 |
| Strain | Fermentation time | Fermentation mode | Product | Titer or productivity | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clostridium ljungdahlii | 560 h | Cell recycle in the CSTR | Ethanol | 48 g/L | [ |
| Acetobacterium woodii | 11 d | A batch-operated stirred-tank bioreactor | Acetate | 44 g/L | [ |
| Acetobacterium woodii | - | Continuous fermentation | Acetone | 26.4 mg/(L·h) | [ |
| Clostridium sp. MTButOH365 | 6 d | Single-stage continuous fermentation | Butanol | 21.98 g/L | [ |
| Clostridium sp. MAceT113 | 5 d | Single-stage continuous fermentation | Acetone | 104 g/L | [ |
| Clostridium sp. MT1802 | 25 d | Single-stage continuous fermentation | 2,3-butanediol | 9.18 g/L | [ |
| Clostridium sp. MT1424 | 25 d | Single-stage continuous fermentation | Methanol | 70.4 g/L | [ |
| Clostridium sp. MT1424 | 25 d | Single-stage continuous fermentation | Formate | 4.3 g/L | [ |
| Clostridium sp. MT1243 | 25 d | Single-stage continuous fermentation | Mevalonate | 97 mmol/L | [ |
Tab. 2 Production of chemicals from syngas fermentation using microorganisms equipped with the WL pathway
| Strain | Fermentation time | Fermentation mode | Product | Titer or productivity | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clostridium ljungdahlii | 560 h | Cell recycle in the CSTR | Ethanol | 48 g/L | [ |
| Acetobacterium woodii | 11 d | A batch-operated stirred-tank bioreactor | Acetate | 44 g/L | [ |
| Acetobacterium woodii | - | Continuous fermentation | Acetone | 26.4 mg/(L·h) | [ |
| Clostridium sp. MTButOH365 | 6 d | Single-stage continuous fermentation | Butanol | 21.98 g/L | [ |
| Clostridium sp. MAceT113 | 5 d | Single-stage continuous fermentation | Acetone | 104 g/L | [ |
| Clostridium sp. MT1802 | 25 d | Single-stage continuous fermentation | 2,3-butanediol | 9.18 g/L | [ |
| Clostridium sp. MT1424 | 25 d | Single-stage continuous fermentation | Methanol | 70.4 g/L | [ |
| Clostridium sp. MT1424 | 25 d | Single-stage continuous fermentation | Formate | 4.3 g/L | [ |
| Clostridium sp. MT1243 | 25 d | Single-stage continuous fermentation | Mevalonate | 97 mmol/L | [ |
| 途径 | 体内/体外 | 反应 数 | 底物 | 产物 | 固碳酶 | 固碳速率 /[nmol C/(min·mg总酶量)] | ATP/CO2/(mol/mol) | NAD(P)H /CO2/(mol/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCG途径 | 体内 | 8 | CO2、PEP | 乙酰辅酶A | Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase | — | 3 | 3 |
| CETCH循环 | 体外 | 12 | CO2 | 乙醛酸 | Enoyl-CoA carboxylases/ reductases | 3.87 [5 nmol C/(min·mg核心酶)] | 1 | 1 |
| SACA途径 | 体外 | 3 | 甲醛 | 乙酰辅酶A | — | — | — | — |
| POAP循环 | 体外 | 4 | CO2 | 草酸 | Pyruvate synthase and pyruvate carboxylase | 6.8 | 1 | 0.5 |
| ASAP途径 | 体外 | 11 | CO2 | 淀粉 | Formolase | 17.2 | 0.5 | 2 |
Tab. 3 Comparison of artificial carbon fixation pathways
| 途径 | 体内/体外 | 反应 数 | 底物 | 产物 | 固碳酶 | 固碳速率 /[nmol C/(min·mg总酶量)] | ATP/CO2/(mol/mol) | NAD(P)H /CO2/(mol/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCG途径 | 体内 | 8 | CO2、PEP | 乙酰辅酶A | Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase | — | 3 | 3 |
| CETCH循环 | 体外 | 12 | CO2 | 乙醛酸 | Enoyl-CoA carboxylases/ reductases | 3.87 [5 nmol C/(min·mg核心酶)] | 1 | 1 |
| SACA途径 | 体外 | 3 | 甲醛 | 乙酰辅酶A | — | — | — | — |
| POAP循环 | 体外 | 4 | CO2 | 草酸 | Pyruvate synthase and pyruvate carboxylase | 6.8 | 1 | 0.5 |
| ASAP途径 | 体外 | 11 | CO2 | 淀粉 | Formolase | 17.2 | 0.5 | 2 |
| 1 | BERG I A. Ecological aspects of the distribution of different autotrophic CO2 fixation pathways[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 77(6): 1925-1936. |
| 2 | GAO Z X, ZHAO H, LI Z M, et al. Photosynthetic production of ethanol from carbon dioxide in genetically engineered cyanobacteria[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5: 9857-9865. |
| 3 | VARMAN A M, YU Y, YOU L, et al. Photoautotrophic production of D-lactic acid in an engineered cyanobacterium[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2013, 12: 117. |
| 4 | GAO X Y, SUN T, PEI G S, et al. Cyanobacterial chassis engineering for enhancing production of biofuels and chemicals[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2016, 100(8): 3401-3413. |
| 5 | GONG F Y, CAI Z, LI Y. Synthetic biology for CO2 fixation[J]. Science China Life Sciences, 2016, 59: 1106-1114. |
| 6 | GONG F Y, ZHU H W, ZHANG Y P, et al. Biological carbon fixation: From natural to synthetic[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2018, 28: 221-227. |
| 7 | SANTOS CORREA S, SCHULTZ J, LAUERSEN K J, et al. Natural carbon fixation and advances in synthetic engineering for redesigning and creating new fixation pathways[J]. Journal of Advanced Research, 2022. |
| 8 | CALVIN M, BENSON A A. The path of carbon in photosynthesis[J]. Science, 1948, 107(2784): 476-480. |
| 9 | EVANS M C, BUCHANAN B B, ARNON D I. A new ferredoxin-dependent carbon reduction cycle in a photosynthetic bacterium[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1966, 55(4): 928-934. |
| 10 | RAGSDALE S W. The Eastern and Western branches of the Wood/Ljungdahl pathway: How the East and West were won[J]. BioFactors, 1997, 6(1): 3-11. |
| 11 | STRAUSS G, FUCHS G. Enzymes of a novel autotrophic CO2 fixation pathway in the phototrophic bacterium Chloroflexus aurantiacus, the 3-hydroxypropionate cycle[J]. European Journal of Biochemistry, 1993, 215(3): 633-643. |
| 12 | BERG I A, KOCKELKORN D, BUCKEL W, et al. A 3-hydroxypropionate/4-hydroxybutyrate autotrophic carbon dioxide assimilation pathway in Archaea[J]. Science, 2007, 318(5857): 1782-1786. |
| 13 | HUBER H, GALLENBERGER M, JAHN U, et al. A dicarboxylate/4-hydroxybutyrate autotrophic carbon assimilation cycle in the hyperthermophilic Archaeum Ignicoccus hospitalis [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2008, 105(22): 7851-7856. |
| 14 | FUCHS G. Alternative pathways of carbon dioxide fixation: insights into the early evolution of life?[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 2011, 65: 631-658. |
| 15 | ANTONOVSKY N, GLEIZER S, NOOR E, et al. Sugar synthesis from CO2 in Escherichia coli [J]. Cell, 2016, 166(1): 115-125. |
| 16 | ZHUANG Z Y, LI S Y. Rubisco-based engineered Escherichia coli for in situ carbon dioxide recycling[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 150: 79-88. |
| 17 | GUADALUPE-MEDINA V, WISSELINK H W, LUTTIK M A, et al. Carbon dioxide fixation by Calvin-Cycle enzymes improves ethanol yield in yeast[J]. Biotechnolology Biofuels, 2013, 6(1): 125. |
| 18 | WHITNEY S M, HOUTZ R L, ALONSO H. Advancing our understanding and capacity to engineer nature's CO2-sequestering enzyme, rubisco[J]. Plant Physiology, 2011, 155(1): 27-35. |
| 19 | TCHERKEZ G G B, FARQUHAR G D, ANDREWS T J. Despite slow catalysis and confused substrate specificity, all ribulose bisphosphate carboxylases may be nearly perfectly optimized[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(19): 7246-7251. |
| 20 | ANDERSSON I. Catalysis and regulation in rubisco[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2008, 59(7): 1555-1568. |
| 21 | CAI Z, LIU G X, ZHANG J L, et al. Development of an activity-directed selection system enabled significant improvement of the carboxylation efficiency of Rubisco[J]. Protein & Cell, 2014, 5(7): 552-562. |
| 22 | GENKOV T, MEYER M, GRIFFITHS H, et al. Functional hybrid rubisco enzymes with plant small subunits and algal large subunits: engineered rbcS cDNA for expression in chlamydomonas [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2010, 285(26): 19833-19841. |
| 23 | ISHIKAWA C, HATANAKA T, MISOO S, et al. Functional incorporation of sorghum small subunit increases the catalytic turnover rate of Rubisco in transgenic rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2011, 156(3): 1603-1611. |
| 24 | DUCAT D C, SILVER P A. Improving carbon fixation pathways[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2012, 16(3/4): 337-344. |
| 25 | LIANG F Y, ENGLUND E, LINDBERG P, et al. Engineered cyanobacteria with enhanced growth show increased ethanol production and higher biofuel to biomass ratio[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 46: 51-59. |
| 26 | ROSENTHAL D M, LOCKE A M, KHOZAEI M, et al. Over-expressing the C3 photosynthesis cycle enzyme Sedoheptulose-1-7 bisphosphatase improves photosynthetic carbon gain and yield under fully open air CO2 fumigation (FACE)[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2011, 11: 123. |
| 27 | KÖPKE M, HELD C, HUJER S, et al. Clostridium ljungdahlii represents a microbial production platform based on syngas[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(29): 13087-13092. |
| 28 | MUNASINGHE P C, KHANAL S K. Biomass-derived syngas fermentation into biofuels: opportunities and challenges[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(13): 5013-5022. |
| 29 | BENGELSDORF F R, STRAUB M, DÜRRE P. Bacterial synthesis gas (syngas) fermentation[J]. Environmental Technology, 2013, 34(13/14): 1639-1651. |
| 30 | MUNASINGHE P C, KHANAL S K. Syngas fermentation to biofuel: evaluation of carbon monoxide mass transfer coefficient (kLa) in different reactor configurations[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2010, 26(6): 1616-1621. |
| 31 | LIU K, ATIYEH H K, STEVENSON B S, et al. Mixed culture syngas fermentation and conversion of carboxylic acids into alcohols[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 152: 337-346. |
| 32 | BERZIN V, KIRIUKHIN M, TYURIN M. Selective production of acetone during continuous synthesis gas fermentation by engineered biocatalyst Clostridium sp. MAceT113[J]. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 2012, 55(2): 149-154. |
| 33 | KLASSON K T, ACKERSON M D, CLAUSEN E C, et al. Biological conversion of coal and coal-derived synthesis gas[J]. Fuel, 1993, 72(12): 1673-1678. |
| 34 | DEMLER M, WEUSTER-BOTZ D. Reaction engineering analysis of hydrogenotrophic production of acetic acid by Acetobacterium woodii [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2011, 108(2): 470-474. |
| 35 | HOFFMEISTER S, GERDOM M, BENGELSDORF F R, et al. Acetone production with metabolically engineered strains of Acetobacterium woodii [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2016, 36: 37-47. |
| 36 | BERZIN V, TYURIN M, KIRIUKHIN M. Selective n-butanol production by Clostridium sp. MTButOH1365 during continuous synthesis gas fermentation due to expression of synthetic thiolase, 3-hydroxy butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase, crotonase, butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase, butyraldehyde dehydrogenase, and NAD-dependent butanol dehydrogenase[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2013, 169(3): 950-959. |
| 37 | TYURIN M, KIRIUKHIN M. Synthetic 2,3-butanediol pathway integrated using Tn7-tool and powered via elimination of sporulation and acetate production in acetogen biocatalyst[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2013, 170(6): 1503-1524. |
| 38 | TYURIN M, KIRIUKHIN M. Selective methanol or formate production during continuous CO₂ fermentation by the acetogen biocatalysts engineered via integration of synthetic pathways using Tn7-tool[J]. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2013, 29(9): 1611-1623. |
| 39 | KIRIUKHIN M, TYURIN M. Mevalonate production by engineered acetogen biocatalyst during continuous fermentation of syngas or CO₂/H₂ blend[J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2014, 37(2): 245-260. |
| 40 | ALBER B, OLINGER M, RIEDER A, et al. Malonyl-coenzyme A reductase in the modified 3-hydroxypropionate cycle for autotrophic carbon fixation in archaeal Metallosphaera and Sulfolobus spp.[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2006, 188(24): 8551-8559. |
| 41 | FAST A G, PAPOUTSAKIS E T. Stoichiometric and energetic analyses of non-photosynthetic CO2-fixation pathways to support synthetic biology strategies for production of fuels and chemicals[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering, 2012, 1(4): 380-395. |
| 42 | LIU Y W, JIANG H F. Directed evolution of propionyl-CoA carboxylase for succinate biosynthesis[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2021, 39(4): 330-331. |
| 43 | BAR-EVEN A. Does acetogenesis really require especially low reduction potential?[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics, 2013, 1827(3): 395-400. |
| 44 | LI B, ELLIOTT S J The Catalytic Bias of 2 -Oxoacid:Ferredoxin Oxidoreductase in CO2: evolution and reduction through a ferredoxin-mediated electrocatalytic assay[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 199: 349-356. |
| 45 | FURDUI C, RAGSDALE S W. The role of pyruvate ferredoxin oxidoreductase in pyruvate synthesis during autotrophic growth by the Wood-Ljungdahl pathway[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2000, 275(37): 28494-28499. |
| 46 | WITT A, POZZI R, DIESCH S, et al. New light on ancient enzymes-in vitro CO2 Fixation by Pyruvate Synthase of Desulfovibrio africanus and Sulfolobus acidocaldarius [J]. The FEBS Journal, 2019, 286(22): 4494-4508. |
| 47 | XIAO L, LIU G X, GONG F Y, et al. The reductive carboxylation activity of heterotetrameric pyruvate synthases from hyperthermophilic Archaea[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2021, 572: 151-156. |
| 48 | BAR-EVEN A, NOOR E, LEWIS N E, et al. Design and analysis of synthetic carbon fixation pathways[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(19): 8889-8894. |
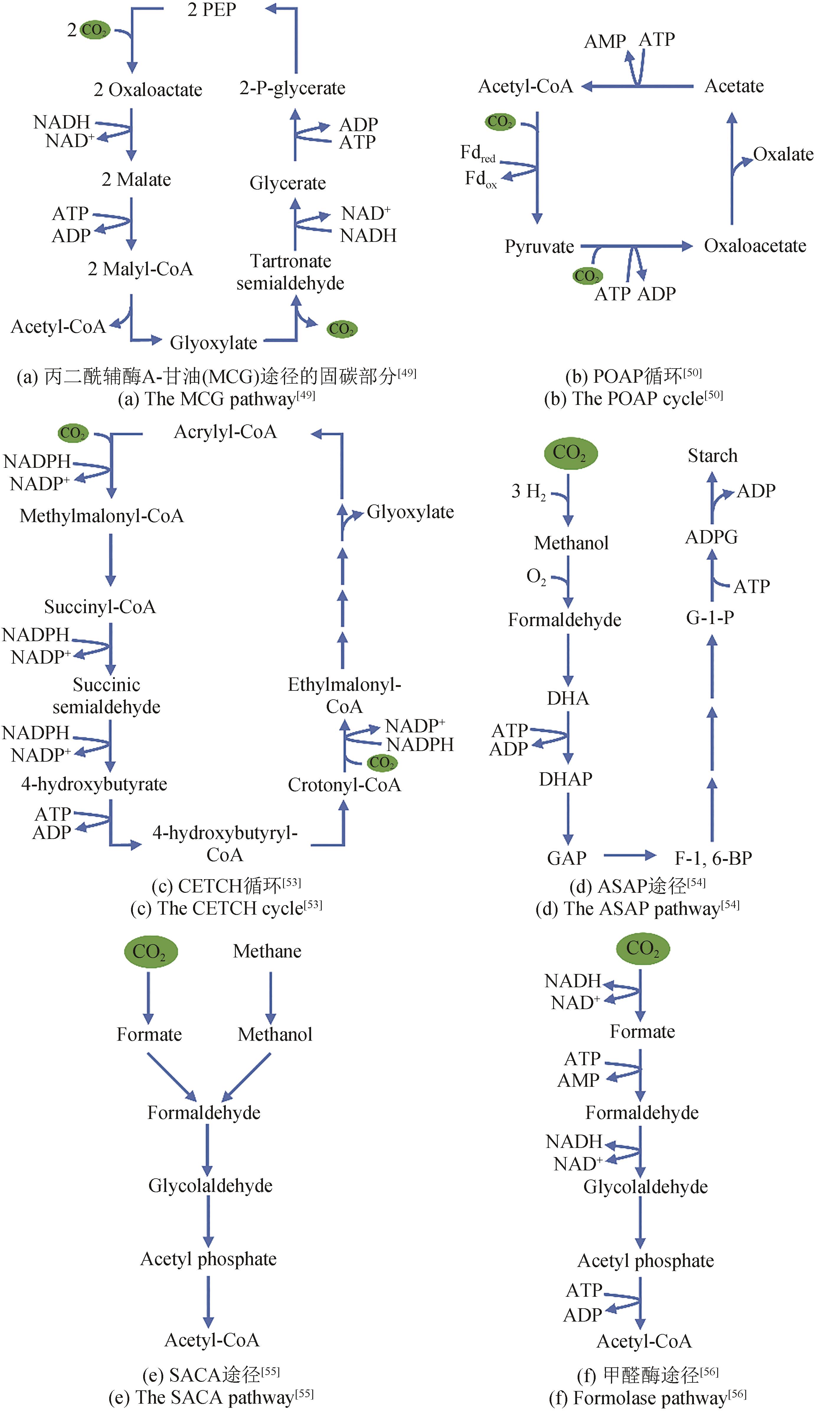
| 49 | YU H, LI X Q, DUCHOUD F, et al. Augmenting the Calvin-Benson-Bassham cycle by a synthetic malyl-CoA-glycerate carbon fixation pathway[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 2008. |
| 50 | XIAO L, LIU G X, GONG F Y, et al. A minimized synthetic carbon fixation cycle[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2022, 12(1): 799-808. |
| 51 | FURDUI C, RAGSDALE S W. The roles of coenzyme A in the pyruvate: ferredoxin oxidoreductase reaction mechanism: rate enhancement of electron transfer from a radical intermediate to an iron-sulfur cluster[J]. Biochemistry, 2002, 41(31): 9921-9937. |
| 52 | RAGSDALE S W. Pyruvate ferredoxin oxidoreductase and its radical intermediate[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2003, 103(6): 2333-2346. |
| 53 | SCHWANDER T, VON BORZYSKOWSKI L S, BURGENER S, et al. A synthetic pathway for the fixation of carbon dioxide in vitro [J]. Science, 2016, 354(6314): 900-904. |
| 54 | CAI T, SUN H B, QIAO J, et al. Cell-free chemoenzymatic starch synthesis from carbon dioxide[J]. Science, 2021, 373(6562): 1523-1527. |
| 55 | LU X Y, LIU Y W, YANG Y Q, et al. Constructing a synthetic pathway for acetyl-coenzyme A from one-carbon through enzyme design[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 1378. |
| 56 | SIEGEL J B, SMITH A L, POUST S, et al. Computational protein design enables a novel one-carbon assimilation pathway[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(12): 3704-3709. |
| 57 | ERB T J, BERG I A, BRECHT V, et al. Synthesis of C5-dicarboxylic acids from C2-units involving crotonyl-CoA carboxylase/reductase: the ethylmalonyl-CoA pathway[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2007, 104(25): 10631-10636. |
| 58 | ERB T J, BRECHT V, FUCHS G, et al. Carboxylation mechanism and stereochemistry of crotonyl-CoA carboxylase/reductase, a carboxylating enoyl-thioester reductase[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(22): 8871-8876. |
| 59 | GONG F Y, LI Y. Fixing carbon, unnaturally[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6314): 830-831. |
| 60 | KIM S, LINDNER S N, ASLAN S, et al. Growth of E. coli on formate and methanol via the reductive glycine pathway[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2020, 16(5): 538-545. |
| 61 | SHERWIN E D. Electrofuel synthesis from variable renewable electricity: an optimization-based techno-economic analysis[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(11): 7583-7594. |
| 62 | SZIMA S, C-C CORMOS. Improving methanol synthesis from carbon-free H2 and captured CO2: a techno-economic and environmental evaluation[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2018, 24: 555-563. |
| 63 | GLEIZER S, BEN-NISSAN R, BAR-ON Y M, et al. Conversion of Escherichia coli to generate all biomass carbon from CO2 [J]. Cell, 2019, 179(6): 1255-1263.e12. |
| 64 | CHEN C T, CHEN F Y H, BOGORAD I W, et al. Synthetic methanol auxotrophy of Escherichia coli for methanol-dependent growth and production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 49: 257-266. |
| 65 | CHEN F Y H, JUNG H W, TSUEI C Y, et al. Converting Escherichia coli to a synthetic methylotroph growing solely on methanol[J]. Cell, 2020, 182(4): 933-946.e14. |
| 66 | REYSENBACH A L, SHOCK E. Merging genomes with geochemistry in hydrothermal ecosystems[J]. Science, 2002, 296(5570): 1077-1082. |
| 67 | NAKAGAWA S, TAKAI K. Deep-sea vent chemoautotrophs: diversity, biochemistry and ecological significance[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2008, 65(1): 1-14. |
| 68 | CAMPBELL D, HURRY V, CLARKE A K, et al. Chlorophyll fluorescence analysis of cyanobacterial photosynthesis and acclimation[J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 1998, 62(3): 667-683. |
| 69 | STANIER R Y, COHEN-BAZIRE G. Phototrophic prokaryotes: the cyanobacteria[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 1977, 31: 225-274. |
| 70 | YAMAMOTO M, TAKAI K. Sulfur metabolisms in epsilon- and gamma-proteobacteria in deep-sea hydrothermal fields[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2011, 2: 192. |
| 71 | SCHUCHMANN K, MÜLLER V. Autotrophy at the thermodynamic limit of life: a model for energy conservation in acetogenic bacteria[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2014, 12(12): 809-821. |
| 72 | WANG S N, HUANG H Y, MOLL J, et al. NADP+ reduction with reduced ferredoxin and NADP+ reduction with NADH are coupled via an electron-bifurcating enzyme complex in Clostridium kluyveri [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2010, 192(19): 5115-5123. |
| 73 | HUANG H Y, WANG S N, MOLL J, et al. Electron bifurcation involved in the energy metabolism of the acetogenic bacterium Moorella thermoacetica growing on glucose or H2 plus CO2 [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2012, 194(14): 3689-3699. |
| 74 | KLETZIN A, URICH T, MüLLER F, et al. Dissimilatory oxidation and reduction of elemental sulfur in thermophilic archaea[J]. Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes, 2004, 36(1): 77-91. |
| 75 | NAKAGAWA S, TAKAKI Y, SHIMAMURA S, et al. Deep-sea vent epsilon-proteobacterial genomes provide insights into emergence of pathogens[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2007, 104(29): 12146-12150. |
| 76 | MENG H K, ZHANG W, ZHU H W, et al. Over-expression of an electron transport protein OmcS provides sufficient NADH for D-lactate production in cyanobacterium[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2021, 14(1): 109. |
| 77 | WANG M M, HU L, FAN L H, et al. Enhanced 1-butanol production in engineered Klebsiella pneumoniae by NADH regeneration[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2015, 29: 1823-1829. |
| 78 | XU Z N, JING K J, LIU Y, et al. High-level expression of recombinant glucose dehydrogenase and its application in NADPH regeneration[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2007, 34(1): 83-90. |
| 79 | MÜLLER V, CHOWDHURY N P, BASEN M. Electron bifurcation: a long-hidden energy-coupling mechanism[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 2018, 72: 331-353. |
| 80 | THAUER R K, KASTER A K, SEEDORF H, et al. Methanogenic Archaea: ecologically relevant differences in energy conservation[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2008, 6(8): 579-591. |
| 81 | KASTER A K, MOLL J, PAREY K, et al. Coupling of ferredoxin and heterodisulfide reduction via electron bifurcation in hydrogenotrophic methanogenic archaea[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108(7): 2981-2986. |
| 82 | BUCKEL W, THAUER R K. Energy conservation via electron bifurcating ferredoxin reduction and proton/Na+ translocating ferredoxin oxidation[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics, 2013, 1827(2): 94-113. |
| 83 | ATKINSON J T, CAMPBELL I, BENNETT G N, et al. Cellular assays for ferredoxins: a strategy for understanding electron flow through protein carriers that link metabolic pathways[J]. Biochemistry, 2016, 55(51): 7047-7064. |
| 84 | IKEDA T, NAKAMURA M, ARAI H, et al. Ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase from the thermophilic hydrogen-oxidizing bacterium, Hydrogenobacter thermophilus TK-6[J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2009, 297(1): 124-130. |
| 85 | AGAPAKIS C M, SILVER P A. Modular electron transfer circuits for synthetic biology: insulation of an engineered biohydrogen pathway[J]. Bioengineered Bugs, 2010, 1(6): 413-418. |
| 86 | BAR-EVEN A, FLAMHOLZ A, NOOR E, et al. Thermodynamic constraints shape the structure of carbon fixation pathways[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics, 2012, 1817(9): 1646-1659. |
| 87 | ZHAO T X, LI Y, ZHANG Y P. Biological carbon fixation: a thermodynamic perspective[J]. Green Chemistry, 2021, 23(20): 7852-7864. |
| 88 | MAN Z W, GUO J, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Regulation of intracellular ATP supply and its application in industrial biotechnology[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2020, 40(8): 1151-1162. |
| 89 | ZHANG X L, JANTAMA K, MOORE J C, et al. Metabolic evolution of energy-conserving pathways for succinate production in Escherichia coli [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(48): 20180-20185. |
| 90 | YAMANAKA K, KITO N, IMOKAWA Y, et al. Mechanism of epsilon-poly-L-lysine production and accumulation revealed by identification and analysis of an epsilon-poly-L-lysine-degrading enzyme[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2010, 76(17): 5669-5675. |
| 91 | WANG D, YU X, WEI G Y. Pullulan production and physiological characteristics of Aureobasidium pullulans under acid stress[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2013, 97(18): 8069-8077. |
| 92 | XU R Y, WANG D D, WANG C L, et al. Improved S-adenosylmethionine and glutathione biosynthesis by heterologous expression of an ATP6 gene in Candida utilis [J]. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 2018, 58(10): 875-882. |
| 93 | ZHANG X X, LIU S K, TAKANO T. Overexpression of a mitochondrial ATP synthase small subunit gene (AtMtATP6) confers tolerance to several abiotic stresses in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2008, 30(7): 1289-1294. |
| 94 | TAN X Y, NIELSEN J. The integration of bio-catalysis and electrocatalysis to produce fuels and chemicals from carbon dioxide[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2022, 51(11): 4763-4785. |
| 95 | CESTELLOS-BLANCO S, ZHANG H, KIM J M, et al. Photosynthetic semiconductor biohybrids for solar-driven biocatalysis[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2020, 3(3): 245-255. |
| 96 | SAKIMOTO K K, WONG A B, YANG P D. Self-photosensitization of nonphotosynthetic bacteria for solar-to-chemical production[J]. Science, 2016, 351(6268): 74-77. |
| 97 | ZHANG H, LIU H, TIAN Z Q, et al. Bacteria photosensitized by intracellular gold nanoclusters for solar fuel production[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2018, 13(10): 900-905. |
| 98 | WANG B, JIANG Z F, YU J C, et al. Enhanced CO2 reduction and valuable C2+ chemical production by a CdS-photosynthetic hybrid system[J]. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(19): 9296-9301. |
| 99 | YUAN M W, KUMMER M J, MINTEER S D. Strategies for boelectrochemical CO2 reduction[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2019, 25(63): 14258-14266. |
| 100 | MILLER M, ROBINSON W E, OLIVEIRA A R, et al. Interfacing formate dehydrogenase with metal oxides for the reversible electrocatalysis and solar-driven reduction of carbon dioxide[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(14): 4601-4605. |
| 101 | SCHLAGER S, HABERBAUER M, FUCHSBAUER A, et al. Bio-electrocatalytic application of microorganisms for carbon dioxide reduction to methane[J]. ChemSusChem, 2017, 10(1): 226-233. |
| 102 | LIU C M, YOUNG A L, STARLING-WINDHOF A, et al. Coupled chaperone action in folding and assembly of hexadecameric Rubisco[J]. Nature, 2010, 463(7278): 197-202. |
| [1] | GUO Shuyuan, ZHANG Qiannan, Gulikezi· MAIMAITIREXIATI, YANG Yiqun, YU Tao. Advances in microbial production of liquid biofuels [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 18-44. |
| [2] | XIAO Yan, LIU Yajun, FENG Yin′gang, CUI Qiu. Progress in synthetic biology research of Clostridium thermocellum for biomass energy applications [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(6): 1055-1081. |
| [3] | WEN Zhiqiong, LI Yuzhen, ZHANG Jin′gang, Wang Feifei, MA Xiaoqing, LI Fuli. Progress on bio-fixation and utilization of CO2 in acetogens driven by chemical energy [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(6): 1178-1190. |
| [4] | SUN Han, LIU Jin. Research progress and prospects in lipid metabolic engineering of eukaryotic microalgae [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(6): 1140-1160. |
| [5] | CHENG Zhenzhen, ZHANG Jian, GAO Cong, LIU Liming, CHEN Xiulai. Progress in metabolic engineering of microorganisms for the utilization of formate [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(4): 756-778. |
| [6] | Zhongliang SUN, Hui CHEN, Qiang WANG. From CO2 to value-added products—carbon neutral microalgal green biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(5): 953-965. |
| [7] | Jie REN, Anping ZENG. CO2 based biomanufacturing: from basic research to industrial application [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(6): 854-862. |
| [8] | Yu LIU, Huiling WEI, Jixiang LIU, Shaojie WANG, Haijia SU. Design and progress of synthetic consortia: a new frontier in synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(4): 635-650. |
| [9] | Kai WANG, Zihe LIU, Biqiang CHEN, Meng WANG, Yang ZHANG, Haoran BI, Yali ZHOU, Yiying HUO, Tianwei TAN. Microbial utilization of carbon dioxide to synthesize fuels and chemicals——third-generation biorefineries [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(1): 60-70. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||