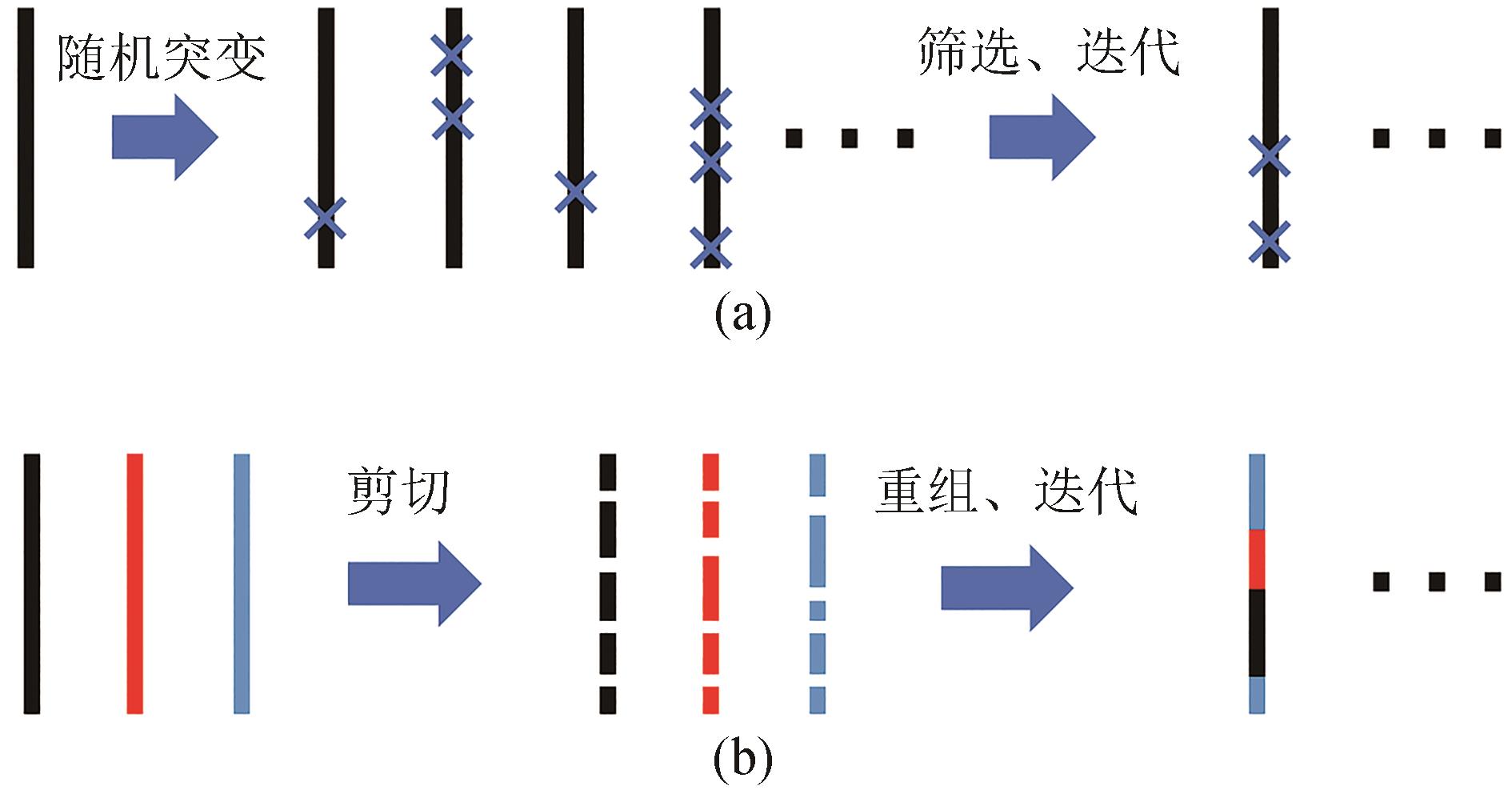
Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (3): 524-534.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-009
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Enzyme engineering in the age of artificial intelligence
KANG Liqi1,2, TAN Pan3, HONG Liang1,2
- 1.School of Physics and Astronomy,Shanghai Jiao Tong University,Shanghai 200240,China
2.Shanghai National Center for Applied Mathematics (SJTU Center),Institute of Natural Sciences,Shanghai Jiao Tong University,Shanghai 200240,China
3.Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory,Shanghai 200240,China
-
Received:2023-01-16Revised:2023-03-29Online:2023-07-05Published:2023-06-30 -
Contact:TAN Pan, HONG Liang
人工智能时代下的酶工程
康里奇1,2, 谈攀3, 洪亮1,2
- 1.上海交通大学物理与天文学院,上海 200240
2.上海交通大学自然科学研究院,上海国家应用数学中心(交大分中心),上海 200240
3.上海人工智能实验室,上海 200240
-
通讯作者:谈攀,洪亮 -
作者简介:康里奇 (1997—),男,博士研究生。研究方向为人工智能功能蛋白质设计。 E-mail:liqikang@sjtu.edu.cn谈攀 (1990—),男,博士,研究员。研究方向为分子生物物理,人工智能功能蛋白质设计以及药物分子设计。 E-mail:tpan1039@sjtu.edu.cn洪亮 (1981—),男,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为分子生物物理,人工智能功能蛋白质设计以及药物分子设计。 E-mail:hongl3liang@sjtu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(12104295)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
KANG Liqi, TAN Pan, HONG Liang. Enzyme engineering in the age of artificial intelligence[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(3): 524-534.
康里奇, 谈攀, 洪亮. 人工智能时代下的酶工程[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(3): 524-534.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2023-009
| 蛋白质适应度分类 | 数据集 | ESM-IF1 | ESM-1v | MSA transformer | ProGen2 | Tranception |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 催化活性 | B3VI55_LIPST | 0.291 | 0.272 | 0.316 | 0.239 | 0.290 |
| MTH3_HAEAESTABILIZED | 0.423 | 0.488 | 0.564 | 0.507 | 0.479 | |
| KKA2_KLEPN | 0.204 | 0.198 | 0.153 | 0.191 | 0.077 | |
| MK01_HUMAN | 0.155 | 0.164 | 0.182 | 0.200 | 0.203 | |
| AMIE_PSEAE | 0.295 | 0.537 | 0.523 | 0.526 | 0.517 | |
| RASH_HUMAN | 0.070 | 0.131 | 0.089 | 0.135 | 0.085 | |
| UBC9_HUMAN | 0.485 | 0.518 | 0.425 | 0.484 | 0.476 | |
| BG_STRSQ | 0.665 | 0.670 | 0.727 | 0.749 | 0.656 | |
| TRPC_THEMA | 0.392 | 0.488 | 0.462 | 0.397 | 0.444 | |
| TIM_SULSO | 0.506 | 0.617 | 0.613 | 0.529 | 0.594 | |
| P84126_THETH | 0.519 | 0.564 | 0.656 | 0.558 | 0.548 | |
| BLAT_ECOLX | 0.673 | 0.692 | 0.538 | 0.601 | 0.622 | |
| 稳定性 | PTEN_HUMAN | 0.559 | 0.458 | 0.366 | 0.471 | 0.430 |
| TPMT_HUMAN | 0.560 | 0.531 | 0.530 | 0.458 | 0.478 | |
| 肽段结合能力 | DLG4_RAT | 0.468 | 0.531 | 0.224 | 0.361 | 0.446 |
| WW | 0.415 | 0.399 | 0.441 | 0.309 | 0.563 | |
| 蛋白质结合能力 | IF1_ECOLI | 0.337 | 0.356 | 0.363 | 0.246 | 0.347 |
| SUMO1_HUMAN | 0.543 | 0.548 | 0.565 | 0.482 | 0.423 | |
| RL40B_YEAST | 0.372 | 0.365 | 0.647 | 0.473 | 0.455 | |
| DNA结合能力 | FOSJUN | 0.532 | 0.464 | 0.366 | 0.515 | 0.536 |
| GAL4_YEAST | 0.326 | 0.476 | 0.386 | 0.468 | 0.458 | |
| RNA 结合能力 | RRM | 0.443 | 0.536 | 0.509 | 0.512 | 0.407 |
| TDP43 | 0.158 | 0.026 | 0.117 | 0.013 | 0.125 | |
| Ig-G结合能力 | GB1 | 0.337 | 0.105 | 0.329 | 0.232 | 0.254 |
| 平均值 | 0.413 | 0.453 | 0.438 | 0.376 | 0.374 |
Table 1 Spearman correlation for predicted fitness developed with unsupervised models
| 蛋白质适应度分类 | 数据集 | ESM-IF1 | ESM-1v | MSA transformer | ProGen2 | Tranception |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 催化活性 | B3VI55_LIPST | 0.291 | 0.272 | 0.316 | 0.239 | 0.290 |
| MTH3_HAEAESTABILIZED | 0.423 | 0.488 | 0.564 | 0.507 | 0.479 | |
| KKA2_KLEPN | 0.204 | 0.198 | 0.153 | 0.191 | 0.077 | |
| MK01_HUMAN | 0.155 | 0.164 | 0.182 | 0.200 | 0.203 | |
| AMIE_PSEAE | 0.295 | 0.537 | 0.523 | 0.526 | 0.517 | |
| RASH_HUMAN | 0.070 | 0.131 | 0.089 | 0.135 | 0.085 | |
| UBC9_HUMAN | 0.485 | 0.518 | 0.425 | 0.484 | 0.476 | |
| BG_STRSQ | 0.665 | 0.670 | 0.727 | 0.749 | 0.656 | |
| TRPC_THEMA | 0.392 | 0.488 | 0.462 | 0.397 | 0.444 | |
| TIM_SULSO | 0.506 | 0.617 | 0.613 | 0.529 | 0.594 | |
| P84126_THETH | 0.519 | 0.564 | 0.656 | 0.558 | 0.548 | |
| BLAT_ECOLX | 0.673 | 0.692 | 0.538 | 0.601 | 0.622 | |
| 稳定性 | PTEN_HUMAN | 0.559 | 0.458 | 0.366 | 0.471 | 0.430 |
| TPMT_HUMAN | 0.560 | 0.531 | 0.530 | 0.458 | 0.478 | |
| 肽段结合能力 | DLG4_RAT | 0.468 | 0.531 | 0.224 | 0.361 | 0.446 |
| WW | 0.415 | 0.399 | 0.441 | 0.309 | 0.563 | |
| 蛋白质结合能力 | IF1_ECOLI | 0.337 | 0.356 | 0.363 | 0.246 | 0.347 |
| SUMO1_HUMAN | 0.543 | 0.548 | 0.565 | 0.482 | 0.423 | |
| RL40B_YEAST | 0.372 | 0.365 | 0.647 | 0.473 | 0.455 | |
| DNA结合能力 | FOSJUN | 0.532 | 0.464 | 0.366 | 0.515 | 0.536 |
| GAL4_YEAST | 0.326 | 0.476 | 0.386 | 0.468 | 0.458 | |
| RNA 结合能力 | RRM | 0.443 | 0.536 | 0.509 | 0.512 | 0.407 |
| TDP43 | 0.158 | 0.026 | 0.117 | 0.013 | 0.125 | |
| Ig-G结合能力 | GB1 | 0.337 | 0.105 | 0.329 | 0.232 | 0.254 |
| 平均值 | 0.413 | 0.453 | 0.438 | 0.376 | 0.374 |
| 1 | COBB R E, CHAO R, ZHAO H M. Directed evolution: past, present, and future[J]. AIChE Journal, 2013, 59(5): 1432-1440. |
| 2 | LERNER S A, WU T T, LIN E C. Evolution of a catabolic pathway in bacteria[J]. Science, 1964, 146(3649): 1313-1315. |
| 3 | SARAC I, HOLLENSTEIN M. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase in the synthesis and modification of nucleic acids[J]. ChemBioChem, 2019, 20(7): 860-871. |
| 4 | TOBIN M B, GUSTAFSSON C, HUISMAN G W. Directed evolution: the 'rational' basis for 'irrational' design[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2000, 10(4): 421-427. |
| 5 | CHEN K, ARNOLD F H. Tuning the activity of an enzyme for unusual environments: sequential random mutagenesis of subtilisin E for catalysis in dimethylformamide[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1993, 90(12): 5618-5622. |
| 6 | STEMMER W P C. Rapid evolution of a protein in vitro by DNA shuffling[J]. Nature, 1994, 370(6488): 389-391. |
| 7 | STEMMER W P. DNA shuffling by random fragmentation and reassembly: in vitro recombination for molecular evolution[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1994, 91(22): 10747-10751. |
| 8 | LIEBETON K, ZONTA A, SCHIMOSSEK K, et al. Directed evolution of an enantioselective lipase[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2000, 7(9): 709-718. |
| 9 | REETZ M T, ZONTA A, SCHIMOSSEK K, et al. Creation of enantioselective biocatalysts for organic chemistry by in vitro evolution[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 1997, 36(24): 2830-2832. |
| 10 | POREBSKI B T, BUCKLE A M. Consensus protein design[J]. Protein Engineering, Design and Selection, 2016, 29(7): 245-251. |
| 11 | STERNKE M, TRIPP K W, BARRICK D. Consensus sequence design as a general strategy to create hyperstable, biologically active proteins[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(23): 11275-11284. |
| 12 | PALMER B, ANGUS K, TAYLOR L, et al. Design of stability at extreme alkaline pH in streptococcal protein G[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2008, 134(3/4): 222-230. |
| 13 | MINAKUCHI K, MURATA D, OKUBO Y, et al. Remarkable alkaline stability of an engineered protein A as immunoglobulin affinity ligand: C domain having only one amino acid substitution[J]. Protein Science, 2013, 22(9): 1230-1238. |
| 14 | ROMERO-RIVERA A, GARCIA-BORRÀS M, OSUNA S. Computational tools for the evaluation of laboratory-engineered biocatalysts[J]. Chemical Communications, 2017, 53(2): 284-297. |
| 15 | KHERSONSKY O, LIPSH R, AVIZEMER Z, et al. Automated design of efficient and functionally diverse enzyme repertoires[J]. Molecular Cell, 2018, 72(1): 178-186.e5. |
| 16 | WEINREICH D M, DELANEY N F, DEPRISTO M A, et al. Darwinian evolution can follow only very few mutational paths to fitter proteins[J]. Science, 2006, 312(5770): 111-114. |
| 17 | LI R F, WIJMA H J, SONG L, et al. Computational redesign of enzymes for regio- and enantioselective hydroamination[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2018, 14(7): 664-670. |
| 18 | CUI Y L, WANG Y H, TIAN W Y, et al. Development of a versatile and efficient C-N lyase platform for asymmetric hydroamination via computational enzyme redesign[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2021, 4(5): 364-373. |
| 19 | CAPRIOTTI E, FARISELLI P, CASADIO R. A neural-network-based method for predicting protein stability changes upon single point mutations[J]. Bioinformatics, 2004, 20(S1): i63-i68. |
| 20 | CAPRIOTTI E, FARISELLI P, CASADIO R. I-Mutant2.0: predicting stability changes upon mutation from the protein sequence or structure[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2005, 33(S2): W306-W310. |
| 21 | 曲玉辰, 陆路, 姜世勃. 利用I-Mutant 2.0辅助设计与优化中东呼吸综合征冠状病毒融合抑制多肽[J]. 微生物与感染, 2019, 14(2): 72-81. |
| QU Y C, LU L, JIANG S B. Using I-Mutant2.0 to assist the design and optimization of MERS-CoV fusion inhibitory peptides[J]. Journal of Microbes and Infections, 2019, 14(2): 72-81. | |
| 22 | YANG Y, DING X S, ZHU G C, et al. ProTstab - predictor for cellular protein stability[J]. BMC Genomics, 2019, 20(1): 804. |
| 23 | FARISELLI P, MARTELLI P L, SAVOJARDO C, et al. INPS: predicting the impact of non-synonymous variations on protein stability from sequence[J]. Bioinformatics, 2015, 31(17): 2816-2821. |
| 24 | LAIMER J, HOFER H, FRITZ M, et al. MAESTRO—multi agent stability prediction upon point mutations[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2015, 16: 116. |
| 25 | DEHOUCK Y, KWASIGROCH J M, GILIS D, et al. PoPMuSiC 2.1: a web server for the estimation of protein stability changes upon mutation and sequence optimality[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2011, 12: 151. |
| 26 | PIRES D E V, ASCHER D B, BLUNDELL T L. DUET: a server for predicting effects of mutations on protein stability using an integrated computational approach[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2014, 42(W1): W314-W319. |
| 27 | WORTH C L, PREISSNER R, BLUNDELL T L. SDM—a server for predicting effects of mutations on protein stability and malfunction. Nucleic acids research, 2011, 39(S2): W215-W222. |
| 28 | PIRES D E V, ASCHER D B, BLUNDELL T L. mCSM: predicting the effects of mutations in proteins using graph-based signatures[J]. Bioinformatics, 2014, 30(3): 335-342. |
| 29 | The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: the universal protein knowledgebase in 2023[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2023, 51(D1): D523-D531. |
| 30 | MEIER J, RAO R S, VERKUIL R, et al. Language models enable zero-shot prediction of the effects of mutations on protein function[C/OL]// Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34 (NeurIPS 2021), 2021. 34: 29287-29303 [2023-01-03]. . |
| 31 | RAO R M, LIU J, VERKUIL R, et al. MSA transformer[C/OL]// Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR,2021, 139:8844-8856 [2023-01-03]. . |
| 32 | JUMPER J, EVANS R, PRITZEL A, et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold[J]. Nature, 2021, 596(7873): 583-589. |
| 33 | HSU C, VERKUIL R, LIU J, et al. Learning inverse folding from millions of predicted structures[EB/OL]. bioRxiv, 2022[2023-01-03]. . |
| 34 | JING B, EISMANN S, SURIANA P, et al. Learning from protein structure with geometric vector perceptrons[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2020: 2009.01411[2023-01-03]. . |
| 35 | ZHOU B X, LV O T Y, YI K, et al. Lightweight equivariant graph representation learning for protein engineering[C/OL]//Machine Learning for Structural Biology Workshop - NeurIPS 2022[2023-01-03]. . |
| 36 | RIESSELMAN A J, INGRAHAM J B, MARKS D S. Deep generative models of genetic variation capture the effects of mutations[J]. Nature Methods, 2018, 15(10): 816-822. |
| 37 | NIJKAMP E, RUFFOLO J, WEINSTEIN E N, et al. ProGen2: exploring the boundaries of protein language models[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2022: 2206.13517[2023-01-03]. . |
| 38 | NOTIN P, DIAS M, FRAZER J, et al. Tranception: protein fitness prediction with autoregressive transformers and inference-time retrieval[C/OL]// International Conference on Machine Learning, arXiv, 2022[2023-01-03]. . |
| 39 | LU H Y, DIAZ D J, CZARNECKI N J, et al. Machine learning-aided engineering of hydrolases for PET depolymerization[J]. Nature, 2022, 604(7907): 662-667. |
| 40 | RIVES A, MEIER J, SERCU T, et al. Biological structure and function emerge from scaling unsupervised learning to 250 million protein sequences[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2021, 118(15): e2016239118. |
| 41 | LUO Y N, JIANG G D, YU T H, et al. ECNet is an evolutionary context-integrated deep learning framework for protein engineering[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 5743. |
| 42 | LI M C, KANG L Q, XIONG Y, et al. SESNet: sequence-structure feature-integrated deep learning method for data-efficient protein engineering[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2022: 2301.00004[2023-01-03]. . |
| 43 | CUI Y L, CHEN Y C, LIU X Y, et al. Computational redesign of a PETase for plastic biodegradation under ambient condition by the GRAPE strategy[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2021, 11(3): 1340-1350. |
| 44 | ROCKLIN G J, CHIDYAUSIKU T M, GORESHNIK I, et al. Global analysis of protein folding using massively parallel design, synthesis, and testing[J]. Science, 2017, 357(6347): 168-175. |
| 45 | HUANG B, XU Y, HU X H, et al. A backbone-centred energy function of neural networks for protein design[J]. Nature, 2022, 602(7897): 523-528. |
| 46 | DOU J Y, VOROBIEVA A A, SHEFFLER W, et al. De novo design of a fluorescence-activating β-barrel[J]. Nature, 2018, 561(7724): 485-491. |
| 47 | YEH A H W, NORN C, KIPNIS Y, et al. De novo design of luciferases using deep learning[J]. Nature, 2023, 614(7949): 774-780. |
| 48 | RUSS W P, FIGLIUZZI M, STOCKER C, et al. An evolution-based model for designing chorismate mutase enzymes[J]. Science, 2020, 369(6502): 440-445. |
| 49 | REPECKA D, JAUNISKIS V, KARPUS L, et al. Expanding functional protein sequence spaces using generative adversarial networks[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2021, 3(4): 324-333. |
| 50 | MADANI A, KRAUSE B, GREENE E R, et al. Large language models generate functional protein sequences across diverse families[J/OL]. Nature Biotechnology, 2023[2023-02-01]. . |
| 51 | SINAI S, WANG R, WHATLEY A, et al. AdaLead: a simple and robust adaptive greedy search algorithm for sequence design[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2020: 2010.02141[2023-01-03]. . |
| 52 | BISWAS S, KHIMULYA G, ALLEY E C, et al. Low-N protein engineering with data-efficient deep learning[J]. Nature Methods, 2021, 18(4): 389-396. |
| 53 | HU R Y, FU L H, CHEN Y C, et al. Protein engineering via Bayesian optimization-guided evolutionary algorithm and robotic experiments[J]. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2023, 24(1): bbac570. |
| 54 | CASTRO E, GODAVARTHI A, RUBINFIEN J, et al. Transformer-based protein generation with regularized latent space optimization[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2022, 4(10): 840-851. |
| 55 | LIN Z, AKIN H, RAO R, et al. Evolutionary-scale prediction of atomic-level protein structure with a language model[J]. Science, 2023, 379(6637): 1123-1130. |
| [1] | WEN Yanhua, LIU Hedong, CAO Chunlai, WU Ruibo. Applications of protein engineering in pharmaceutical industry [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 65-86. |
| [2] | FU Yu, ZHONG Fangrui. Recent advances in chemically driven enantioselective photobiocatalysis [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1021-1049. |
| [3] | ZHANG Jun, JIN Shixue, YUN Qian, QU Xudong. Biosynthesis of the unnatural extender units with polyketides and their structural modifications for applications in medicines [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 561-570. |
| [4] | TANG Zhijun, HU Youcai, LIU Wen. Enzymatic (4+2)- and (2+2)-cycloaddition reactions: fundamentals and applications of regio- and stereoselectivity [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 401-407. |
| [5] | XI Mengyu, HU Yiling, GU Yucheng, GE Huiming. Genome mining-directed discovery for natural medicinal products [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 447-473. |
| [6] | LEI Ru, TAO Hui, LIU Tiangang. Deep genome mining boosts the discovery of microbial terpenoids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 507-526. |
| [7] | ZHU Jingyong, LI Junxiang, LI Xuhui, ZHANG Jin, WU Wenjing. Advances in applications of deep learning for predicting sequence-based protein interactions [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(1): 88-106. |
| [8] | SUN Mengchu, LU Liangyu, SHEN Xiaolin, SUN Xinxiao, WANG Jia, YUAN Qipeng. Fluorescence detection-based high-throughput screening systems and devices facilitate cell factories construction [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(5): 947-965. |
| [9] | MING Yang, CHEN Bin, HUANG Xiaoqiang. Recent advances in photoenzymatic synthesis [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(4): 651-675. |
| [10] | WANG Sheng, WANG Zechen, CHEN Weihua, CHEN Ke, PENG Xiangda, OU Fafen, ZHENG Liangzhen, SUN Jinyuan, SHEN Tao, ZHAO Guoping. Design of synthetic biology components based on artificial intelligence and computational biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(3): 422-443. |
| [11] | Qiaozhen MENG, Fei GUO. Applications of foldability in intelligent enzyme engineering and design: take AlphaFold2 for example [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(3): 571-589. |
| [12] | CHEN Zhihang, JI Menglin, QI Yifei. Research progress of artificial intelligence in desiging protein structures [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(3): 464-487. |
| [13] | Qilong LAI, Shuai YAO, Yuguo ZHA, Hong BAI, Kang NING. Microbiome-based biosynthetic gene cluster data mining techniques and application potentials [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(3): 611-627. |
| [14] | Qingyun RUAN, Xin HUANG, Zijun MENG, Shu QUAN. Computational design and directed evolution strategies for optimizing protein stability [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 5-29. |
| [15] | Yanping QI, Jin ZHU, Kai ZHANG, Tong LIU, Yajie WANG. Recent development of directed evolution in protein engineering [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(6): 1081-1108. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||